ACS: Construction Data Auto-Correction System—Taiwan Public Construction Data Example
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Construction Data Management
1.2. Public Construction Cost Estimation System in Taiwan
1.3. Benefits and Challenges of the PCCES
1.4. Research Objectives
- (1)
- Develop an auto-correct function to automatically correct the data from public databases related to the construction field and the unstructured construction project data. Users could use this function to correct data that they obtained from the open data database made by the government.
- (2)
- Develop a recommender function, which can help users to perform their job efficiently without having experience in construction classification systems.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Challenges in Construction Data Management
2.2. Unstructured Data Processing
2.3. Machine-Learning-Based Methods For Construction Data Processing
3. ACS Methodology
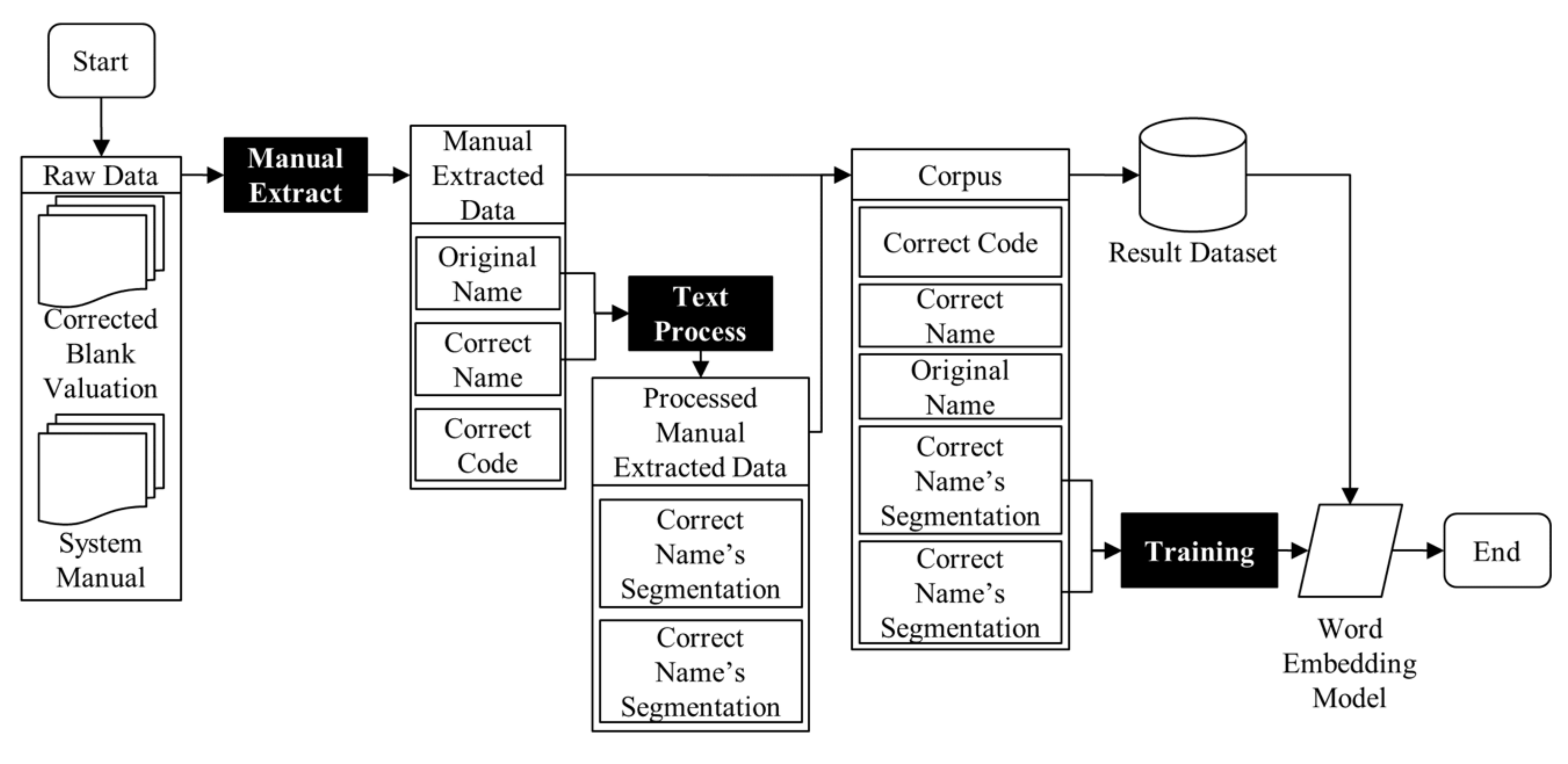
3.1. System Overview
3.2. Data Processing Module
3.2.1. Raw Data Collection
3.2.2. Text Processor
3.3. Search Processing Module
3.3.1. Word Embedding
3.3.2. Similarity Calculation
3.4. Mapping Process Module
4. Implementation
4.1. Training Data
4.1.1. PCCES System Manuals
4.1.2. Blank Valuations
4.2. System Implementation
4.2.1. Text Processing
4.2.2. Database
4.2.3. Model Training
4.2.4. Searching
4.2.5. Mapping
5. Validation
5.1. System Evaluation
5.1.1. Data Source
5.1.2. Classification
5.1.3. Results and Discussion for System Evaluation
5.2. User Test
5.2.1. Background of the Subjects
5.2.2. Testing Scenario
5.2.3. Results and Discussion for the User Test
6. Discussions
6.1. Contributions
6.2. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziz, R.F.; Hafez, S.M. Applying lean thinking in construction and performance improvement. Alex. Eng. J. 2013, 52, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Public Construction Commission. Turnkey Cases That Already Been Awarded between 1 December 2017 and 30 June 2020. Available online: https://pcces2.pcc.gov.tw/PCC_MRP/Announcement/AnnDetail/9dec7761-dc2c-4dad-8cd4-be61fa44e5a7 (accessed on 18 November 2020). (In Chinese)
- Public Construction Commission 2020. Public Construction Cost Estimation System. Available online: https://pcces.pcc.gov.tw/CSInew/Default.aspx?FunID=Fun_12&SearchType=E (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Norman, E.S.; Brotherton, S.A.; Fried, R.T. Breakdown Structures: The Foundation for Project Management Excellence; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M. Study of Current State of Software for Drafting and Estimating in Construction. National Kaohsiung University. 2011. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11296/t7u695 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Yu, S.H. Evaluation of the Public Works Procedure Efficiency of E-Procurement of Government of Kaohsiung. National Sun Yat-sen University. 2004. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11296/w4h5xd (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Davatzikos, C.; Ruparel, K.; Fan, Y.; Shen, D.G.; Acharyya, M.; Loughead, J.W.; Gur, R.C.; Langlebenb, D.D. Classifying Spatial Patterns of Brain Activity with Machine Learning Methods: Application to Lie Detection. NeuroImage 2005, 28, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.C. Study on Budget Rationality and Supervision Practice of Construction Safety and Health. 2014. Available online: https://www.grb.gov.tw/search/planDetail?id=8390698 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Chen, Y.C. Combination of Public Construction Coding System and Building Information Modeling for Budget Estimate. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan. 19 June 2013. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11296/khec2y (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Huang, C.H.; Yang, I.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, M.J. A Study of Introducing Omniclass on BIM-based Building Design Checking, Architecture and Building Research Institute, Ministry of the Interior, ROC (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan. 2017. Available online: https://www.grb.gov.tw/search/planDetail?id=12066805 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Caldas, C.H.; Soibelman, L. Automating hierarchical document classification for construction management information systems. Autom. Constr. 2003, 12, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Construction Specifications Institute. CSI MasterFormat. 2008. Available online: https://www.csiresources.org/home (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Charette, R.P.; Marshall, H.E. UNIFORMAT II Elemental Classification for Building Specifications, Cost Estimating and Cost Analysis; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; NIST Interagency or Internal Reports (NISTIR) 6389.
- Ioannou, P.G.; Liu, L.Y. Advanced Construction Technology System—ACTS. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 1993, 119, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.D.; Chiu, C.Y.; Korde, T. Visual Representation of Construction Management Data. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ahmad, I. Applying Metadata Models to Unstructured Content of Construction Documents: A View-Based Approach. Autom. Constr. 2007, 16, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soibelman, L.; Wu, J.; Caldas, C.; Brilakis, I.; Lin, K.Y. Management and Analysis of Unstructured Construction Data Types. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2008, 22, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sint, R.; Schaffert, S.; Stroka, S.; Ferstl, R. Combining unstructured, fully structured and semi-structured information in Semantic Wikis. In CEUR Workshop Proceedings; Heraklion: Crete, Greece, 2009; pp. 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.M.; Schütz, R.; Kazman, R.; Matthes, F. Amazon in the Air: Innovating with Big Data at Lufthansa. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; pp. 5096–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, O.; Halcu, I.; Grigoriu, O.; Neculoiu, G.; Sandulescu, V.; Marinescu, M.; Marinescu, V. Converting Unstructured and Semi-Structured Data into Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2013 11th RoEduNet International Conference, Sinaia, Romania, 17–19 January 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, H.; Anzaldi, L.J.; Hernandez, L.; Davison, A.; Boyd, C.M.; Leff, B.; Kimura, J.; Weiner, J.P. The Value of Unstructured Electronic Health Record Data in Geriatric Syndrome Case Identification. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Hou, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, L.P. A Hybrid Solution for Extracting Structured Medical Information from Unstructured Data in Medical Records via a Double-Reading/Entry System. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2016, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhadloo, M.; Patterson, R.A.; Rolland, E. Modeling Customer Satisfaction from Unstructured Data Using a Bayesian Approach. Decis. Support Syst. 2016, 90, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubaey, M.; Asadi, A.; Makatsoris, H. A Naïve Bayes Approach for EWS Detection by Text Mining of Unstructured Data: A Construction Project Case. In Proceedings of the IntelliSys 2015—Proceedings of 2015 SAI Intelligent Systems Conference, London, UK, 10–11 November 2015; pp. 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Chi, S. Accident Case Retrieval and analyses: Using natural language processing in the construction industry. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 04019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.J.; Fernandez, C.; Borraz, R.; Alonso, D. A Machine Learning Approach to Pedestrian Detection for Autonomous Vehicles Using High-Definition 3D Range Data. Sensors 2016, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sainath, T.N.; Weiss, R.J.; Senior, A.; Wilson, K.W.; Vinyals, O. Learning the Speech Front-End with Raw Waveform CLDNNs. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, INTERSPEECH, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.isca-speech.org/archive/interspeech_2015/i15_0001.html (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Krasnopolsky, V.M.; Fox-Rabinovitz, M.S. Complex Hybrid Models Combining Deterministic and Machine Learning Components for Numerical Climate Modeling and Weather Prediction. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Bhagavatula, S.; Bauer, L.; Reiter, M.K. Accessorize to a crime: Real and stealthy attacks on state-of-the-art face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A Survey of Image Classification Methods and Techniques for Improving Classification Performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Neural Baby Talk. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7219–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.H.; Yu, A.; Tsai, C.W.; Koh, J.L.; Kuo, C.C.; Chen, A.L.P. Keyword Extraction and Structuralization of Medical Reports. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhakumar, N.; Sherkat, E.; Milios, E.E.; Gu, H.; Butler, M. Clinically Significant Information Extraction from Radiology Reports. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Symposium on Document Engineering—DocEng ’17, Valletta, Malta, 4–7 September 2017; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.L.; Chan, H.Y.; Tsai, M.H. NLP-Based Method for Auto-Correcting Public Constructions Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Civil and Building Engineering Informatics, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan, 6–9 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Hao, L. Automatic Identification of Stop Words in Chinese Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, IEEE, Wuhan, China, 12–14 December 2008; pp. 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Shen, Y. On the Dimensionality of Word Embedding. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2–8 December 2018; pp. 887–898. Available online: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7368-on-the-dimensionality-of-word-embedd (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Hasan, M.; Islam, I.; Hasan, K.M.A. Sentiment Analysis Using Out of Core Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), IEEE, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 7–9 February 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Shivananda, A. Converting Text to Features. In Natural Language Processing Recipes; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Photonics Technology Letters Information for Authors. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2009, 21, C3. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, L.; Guo, K.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y. Build a Tourism-Specific Sentiment Lexicon via Word2vec. Ann. Data Sci. 2018, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebret, R.; Collobert, R. Word Emdeddings through Hellinger PCA. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 26–30 April 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA; pp. 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Goldberg, Y. Neural Word Embedding as Implicit Matrix Factorization. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Mit Press: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014; pp. 2177–2185. Available online: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5477-neural-word-embedding-as (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, X.; Chen, E. Word Embedding Revisited: A New Representation Learning and Explicit Matrix Factorization Perspective. In Proceedings of the IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 25–31 July 2015; pp. 3650–3656. Available online: https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/15/Papers/513.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Globerson, A.; Chechik, G.; Pereira, F.; Tishby, N. Euclidean Embedding of Co-Occurrence Data. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2007, 8, 2265–2295. Available online: https://www.jmlr.org/papers/v8/globerson07a.html (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Qureshi, M.A.; Greene, D. EVE: Explainable Vector Based Embedding Technique Using Wikipedia. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2019, 53, 137–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2013—Workshop Track Proceedings, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013; Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781 (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Hatamian, M.; Hung, D.; Kurmas, Z.; Frenzel, J.; Pinter-Lucke, J.; and Zhao, P. In Praise of Digital Design and Computer Architecture. In Digital Design and Computer Architecture; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016; pp. i–ii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, G.; Gelbukh, A.; Gómez-Adorno, H.; Pinto, D. Soft Similarity and Soft Cosine Measure: Similarity of Features in Vector Space Model. Comput. Sist. 2014, 18, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Murthy, C.D. Effective Text Classification by a Supervised Feature Selection Approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Brussels, Belgium, 10 December 2012; pp. 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chung, B.S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, J. Language Independent Semantic Kernels for Short-Text Classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2019—2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies—Proceedings of the Conference 1 (October), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805 (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models Are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. OpenAI Blog 2020, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, H.; Kim, K.; Cha, K.; Lee, J.Y.; Mun, H.; Cho, S.J.; Chung, J.I.; Pyo, J.H.; Lee, K.C.; Kang, M. Application of Efficient Data Cleaning Using Text Clustering for Semistructured Medical Reports to Large-Scale Stool Examination Reports: Methodology Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, A.J.; Kiros, R.; Kešelj, V.; Milios, E. Exploratory visual analysis and interactive pattern extraction from semi-structured data. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2015, 5, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Chapter No. | Chapter Name | Class (6th) | Compressive Strength (7th) | Cement Type (8th) | Chemical Admixture (9th) | Valuation Unit (10th) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03330 | Building Concrete | (0) | (0) | (0) | (0) | M (1) | |
| Machine-mixed (1) | 80 kgf/cm2 (1) | - | - | M2 (2) | |||
| Ready-mixed (2) | 140 kgf/cm2 (2) | - | - | 3 M (3) | |||
| Machine-mixed underwater (3) | 175 kgf/cm2 (3) | - | - | Lump (4) | |||
| Ready-mixed underwater (4) | 280 kgf/cm2 (4) | - | - | T (5) | |||
| Ready-mixed, under 10F (5) | 315 kgf/cm2 (5) | - | - | Piece (6) | |||
| Ready-mixed, under 20F (6) | 350 kgf/cm2 (6) | - | - | Each (7) | |||
| Ready-mixed, under 30F (7) | 400 kgf/cm2 (7) | - | - | Set (8) | |||
| - | - | - | - | KG (9) | |||
| Wrong Data | Correct Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Work Item/Material | Code | Work Item/Material | Code |
| Technician | L00000520A5 | Senior Worker | L000006200001 |
| Unskilled Laborer | L0000061005 | Junior Worker | L000006100001 |
| Plastic Road Marking | M02898A003 | Product, Road Marking, Glass Ball | M0289801009 |
| Reflective Glass Ball | M02898B003 | Road Marking, Glass Ball | 02898B0009 |
| Adhesive | M02900C000F | Product, Road Marking Adhesive | M0289800019 |
| Equipment Fee | E0512450001 | Not Classified Machinery | E000001000004 |
| Tool Wear | W0127120004 | Tool Wear | W0127120004 |
| Before | Action | |
|---|---|---|
| Stop words | “.” (period) | Remove |
| Symbols | “m2” (square meter) | Replace with “m2” |
| Unnecessary prepositions | “and”, “or”, “included” | Remove |
| Full width character | “(” (left parenthesis), “。” (period) | Remove |
| Unify units | “3000psi” | Replace with “210 kgf/cm2” |
| Field Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Correct_Code | 0331043003 |
| Correct_Desc | Building Concrete and Ready-Mixed Underwater Concrete 140 kgf/cm2m2 |
| Original_Code | N/A |
| Original_Desc | N/A |
| Correct_Desc_Seg | “building concrete,” “ready-mixed,” “underwater,” “concrete,” “140 kgf/cm3,””m3” |
| Original_Desc_Seg | N/A |
| Field Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Correct_Code | 0331023003 |
| Correct_Desc | Building Concrete and Ready-Mixed Concrete 140 kgf/cm2m2 |
| Original_Code | 331000003 |
| Original_Desc | 140 kgf/cm2 premix concrete |
| Correct_Desc_Seg | “building concrete,” “ready-mixed,” “concrete,” “140 kgf/cm3,””m3” |
| Original_Desc_Seg | “140 kgf/cm2,” “ready-mixed” |
| Index | Segmentation List |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0331023003 |
| 2 | “building concrete,” “ready-mixed,” “underwater,” “concrete,” “140 kgf/cm3,””m3” |
| … | … |
| n | “140 kgf/cm2,” “ready-mixed” |
| Total (A) | Rule 1 | Rule 2 | Rule 3 | Rule 4 | Subtotal (B) | Correct Rate (B/Ax100) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18,551 | 7392 | 1532 | 4268 | 1025 | 14,217 | 76.64% |
| Subject | Background | Experience in Using PCCES (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| A | Undergrad student from Civil Engineering Department | 0 |
| B | Graduate students from Civil Engineering Department | 0 |
| C | Graduate students from Civil Engineering Department | 0 |
| D | Graduate students from Civil Engineering Department | 0 |
| E | Graduate students from Civil Engineering Department | 0 |
| F | Civil Engineer | 1 |
| G | Civil Engineer | 4 |
| H | Civil Engineer | 8 |
| Task | Raw Data |
|---|---|
| T1 | Structure concrete, ready-mixed, 210 kgf/cm2 |
| T2 | Structure concrete, including placing and compacting |
| T3 | 210 kg/cm2 ready-mixed concrete |
| T4 | Concrete placing and compacting |
| T5 | Structure concrete, ready-mixed, 210 kgf/cm2, nighttime construction |
| T6 | Structure concrete, ready-mixed, 140 kgf/cm2, nighttime construction |
| T7 | 140 kgf/cm2 ready-mixed concrete |
| T8 | Structure concrete, ready-mixed, 140 kgf/cm2, daytime construction |
| T9 | 175 kg/cm2 ready-mixed concrete |
| T10 | 280 kg/cm2 ready-mixed concrete |
| User | Operation Time (Sec.) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | Total | Avg. | |
| Q1 | 62.80 | 59.40 | 72.60 | 61.60 | 65.20 | 37.70 | 31.30 | 113.11 | 35.90 | 52.50 | 592.11 | 59.21 |
| Q2 | 74.77 | 64.20 | 52.54 | 43.08 | 51.73 | 33.18 | 29.81 | 37.28 | 29.64 | 27.45 | 443.68 | 44.37 |
| Q3 | 102.64 | 50.81 | 68.09 | 33.33 | 59.56 | 44.06 | 31.66 | 33.97 | 32.54 | 36.55 | 493.20 | 49.32 |
| Q4 | 62.75 | 85.04 | 72.15 | 45.26 | 53.25 | 45.78 | 41.16 | 40.51 | 41.15 | 32.60 | 519.65 | 51.97 |
| Q5 | 69.04 | 87.15 | 51.87 | 42.07 | 53.88 | 49.01 | 37.02 | 42.18 | 35.76 | 41.19 | 509.17 | 50.92 |
| Q6 | 83.82 | 71.67 | 49.50 | 56.35 | 51.79 | 47.19 | 45.06 | 39.62 | 33.76 | 29.30 | 518.06 | 51.81 |
| Q7 | 43.23 | 37.09 | 30.50 | 31.44 | 33.35 | 29.57 | 35.95 | 28.88 | 28.82 | 28.92 | 327.75 | 32.78 |
| Q8 | 86.27 | 97.47 | 99.77 | 63.55 | 67.59 | 46.86 | 49.89 | 52.99 | 52.99 | 39.44 | 646.57 | 64.66 |
| Total | 585.32 | 552.83 | 497.01 | 376.68 | 446.35 | 333.35 | 301.85 | 388.54 | 388.54 | 287.95 | - | - |
| Avg. | 73.17 | 69.10 | 62.13 | 47.09 | 55.79 | 41.67 | 37.73 | 48.57 | 48.57 | 35.99 | - | - |
| User | Operation Time (Sec.) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | Total | Avg. | |
| Q1 | 12.15 | 17.90 | 22.11 | 22.72 | 30.81 | 28.11 | 27.25 | 21.60 | 23.02 | 22.30 | 227.97 | 22.80 |
| Q2 | 11.14 | 22.83 | 20.38 | 19.20 | 24.52 | 21.78 | 21.29 | 21.96 | 20.44 | 21.37 | 204.91 | 20.49 |
| Q3 | 18.30 | 15.12 | 29.43 | 30.68 | 28.01 | 24.92 | 22.82 | 27.51 | 25.14 | 21.39 | 243.32 | 24.33 |
| Q4 | 16.76 | 13.09 | 24.14 | 22.76 | 28.61 | 27.13 | 37.92 | 23.62 | 18.42 | 22.33 | 234.78 | 23.48 |
| Q5 | 15.61 | 20.36 | 31.42 | 25.92 | 27.95 | 28.04 | 29.01 | 26.26 | 25.32 | 27.97 | 257.86 | 25.79 |
| Q6 | 21.34 | 16.82 | 38.53 | 38.23 | 32.84 | 31.97 | 28.09 | 28.72 | 26.69 | 25.01 | 288.24 | 28.82 |
| Q7 | 12.01 | 19.42 | 17.52 | 16.43 | 23.14 | 17.75 | 17.57 | 22.18 | 15.68 | 16.66 | 178.36 | 17.84 |
| Q8 | 25.80 | 16.63 | 23.10 | 28.34 | 37.57 | 20.23 | 20.33 | 25.06 | 23.69 | 19.50 | 240.25 | 24.03 |
| Total | 133.11 | 142.17 | 206.63 | 204.28 | 233.45 | 199.93 | 204.28 | 196.91 | 178.40 | 176.53 | - | - |
| Avg. | 16.64 | 17.77 | 25.83 | 25.54 | 29.18 | 24.99 | 25.54 | 24.61 | 22.30 | 22.07 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.-L.; Tsai, M.-H. ACS: Construction Data Auto-Correction System—Taiwan Public Construction Data Example. Sustainability 2021, 13, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010362
Yu M-L, Tsai M-H. ACS: Construction Data Auto-Correction System—Taiwan Public Construction Data Example. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010362
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Meng-Lin, and Meng-Han Tsai. 2021. "ACS: Construction Data Auto-Correction System—Taiwan Public Construction Data Example" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010362
APA StyleYu, M.-L., & Tsai, M.-H. (2021). ACS: Construction Data Auto-Correction System—Taiwan Public Construction Data Example. Sustainability, 13(1), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010362





