Designing a Geo-Strategic Railway Freight Network in Brazil Using GIS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Up-to-Date Concepts on Terminal Requirements
4. Case Study
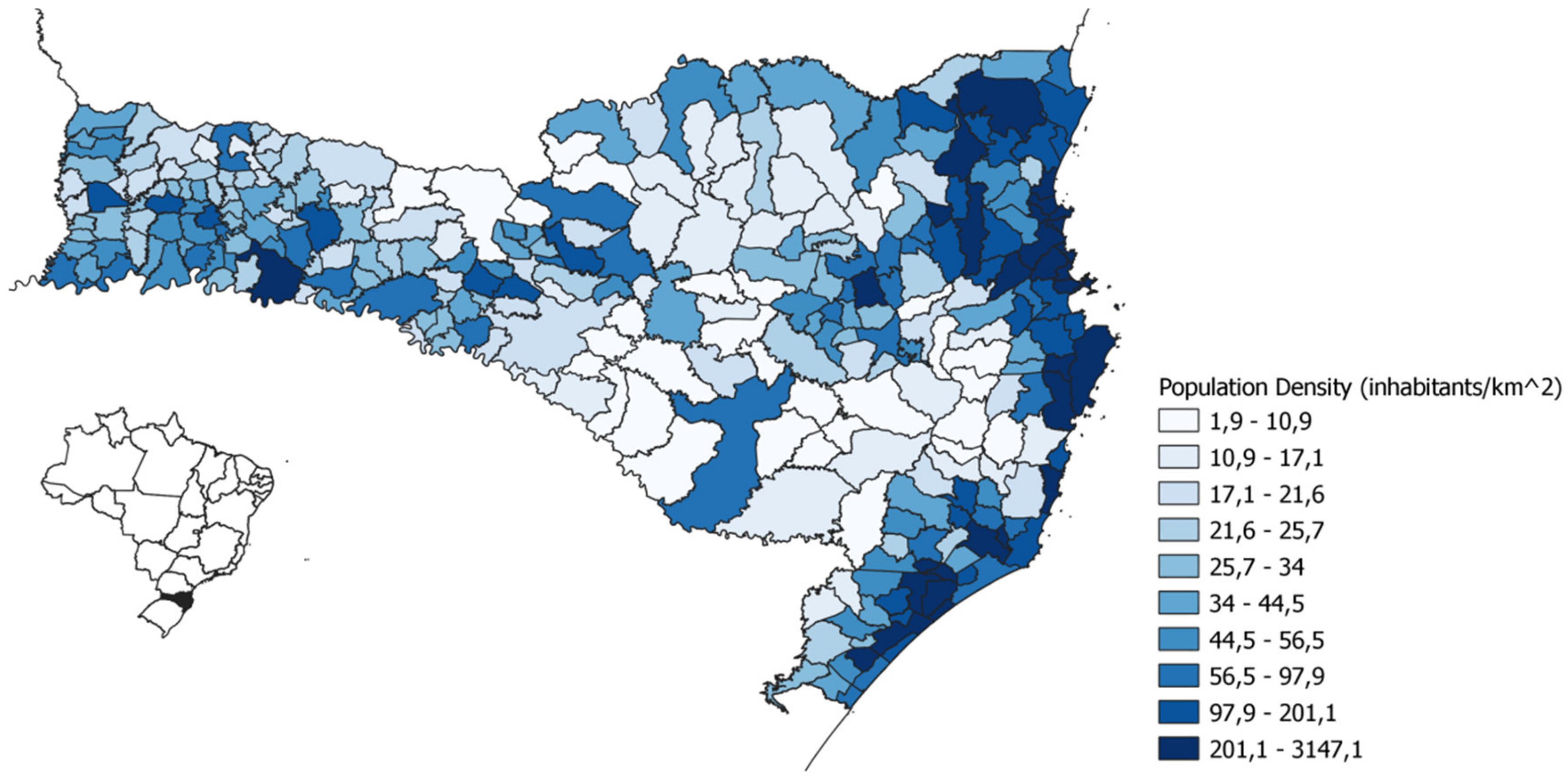
4.1. The State of Santa Catarina
4.2. Freight Flows and Network Development
4.3. Location of Specialized Terminals for Freight Transport
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasconcellos, E.A. Urban transport policies in Brazil: The creation of a discriminatory mobility system. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 67, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontoura, W.B.; Chaves, G.D.L.D.; Ribeiro, G.M. The Brazilian urban mobility policy: The impact in São Paulo transport system using system dynamics. Transp. Policy 2019, 73, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.M.; Perez-Martinez, P.J.; Andrade, M.D.F.; Ribeiro, F.N.D. Relationship between black carbon (BC) and heavy traffic in São Paulo, Brazil. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2019, 68, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, K.M.; Cardoso MR, A.; Zannin PH, T. Exposure to road traffic noise: Annoyance, perception and associated factors among Brazil’s adult population. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.; Losekann, L.; Silveira Filho, G. Demand of automotive fuels in Brazil: Underlying energy demand trend and asymmetric price response. Energy Econ. 2018, 74, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, D.M.Z.; Blinge, M. The future of European rail freight transport and logistics. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, J.E.H.; Bartholomeu, D.B.; Junior, P.N.A.; Caixeta Filho, J.V. Evaluation of the economic and environmental impacts from the addition of new railways to the Brazilian’s transportation network: An application of a network equilibrium model. Transp. Policy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Yau, S. Case studies on transport infrastructure projects in belt and road initiative: An actor network theory perspective. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 71, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.; Şahin, I.; Ricci, S.; Vasic-Franklin, G. Railway operations, time-tabling and control. Res. Transp. Econ. 2013, 41, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Negenborn, R.R.; De Schutter, B. Intermodal freight transport planning—A receding horizon control approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 60, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Febbraro, A.; Sacco, N.; Saeednia, M. An agent-based framework for cooperative planning of intermodal freight transport chains. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 2016, 64, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, J.; Su, M.; Wan, S.; Zhang, Z. The relationship between freight transport and economic development: A case study of China. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, R.J.; De Jong, G.; Larranaga, A.M.; Cybis, H.B.B. Application of MDCEV to infrastructure planning in regional freight transport. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 133, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ramesh, A. Location selection of multimodal freight terminal under STEEP sustainability. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2019, 33, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SteadieSeifi, M.M.; Dellaert, N.N.; Nuijten, W.W.; Van Woensel, T.T.; Raoufi, R.R. Multimodal freight transportation planning: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 233, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, R. Evaluating road–rail intermodal transport services—A heuristic approach. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2008, 11, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protic, S.M.; Geerlings, H.; van Duin, R. Environmental Sustainability of Freight Transportation Terminals. In Sustainable Transportation and Smart Logistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 233–260. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, P.; Peeters, D.; Thomas, I. Modelling a rail/road intermodal transportation system. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2004, 40, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elevli, B. Logistics freight center locations decision by using Fuzzy-PROMETHEE. Transport 2014, 29, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Chauhan, S.S.; Goyal, S.K. A multi-criteria decision making approach for location planning for urban distribution centers under uncertainty. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 53, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.V.; Viegas, J.M. Tactical management of rail freight transportation services: Evaluation of yard performance. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2011, 34, 363–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.; Woroniuk, C.; Zunder, T.H. Recent developments with Single Wagon Load services, policy and practice in Europe. In Proceedings of the 2012 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS 2012), Wroclaw, Poland, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 1097–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Woroniuk, C.; Marinov, M.; Zunder, T.; Mortimer, P.; Zunder, T.H. Time series analysis of rail freight services by the private sector in Europe. Transp. Policy 2013, 25, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fernández, L.E.; De Cea Ch, J.; Giesen, E.R. A strategic model of freight operations for rail transportation systems. Transp. Plan. Tech. 2004, 27, 231–260. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, W.; Topaloglu, H. Fleet Management; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, W.; Carvalho, C.; Simao, H.; Godfrey, G. Dynamic Fleet Management as a Logistics Queuing Network; Statistics and Operations Research, Technical Report SOR-94-18; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, W.; Shapiro, J.; Simao, H. Dynamic Management of Heterogeneous Resources; Statistics and Operations Research, Technical Report SOR-98-06; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Lin, R. Modeling the railway network design problem: A novel approach to considering carbon emissions reduction. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2017, 56, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, F.; Codina, E. A model that assesses proposals for infrastructure improvement and capacity expansion on a mixed railway network. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 47, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortúzar, J.D.; Willumsen, L.G. Modelling Transport; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, P. The dynamics of modal split for freight transport. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 70, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacyna-Gołda, I.; Żak, J.; Gołębiowski, P. Models of traffic flow distribution for various scenarios of the development of proecological transport system. Arch. Transp. 2014, 32, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.G. Service network design in freight transportation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 122, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.G.; Roy, J. OR tools for tactical freight transportation planning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1988, 33, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.G.; Laporte, G. Planning models for freight transportation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 97, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.; Ferland, J.-A.; Rousseau, J.-M. A Tactical Planning Model for Rail Freight Transportation. Transp. Sci. 1984, 18, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T. A Survey of optimization models for long-haul freight transportation. In Handbook of Transportation Science, 2nd ed.; Kluwer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Farvolden, J.M.; Powell, W.B. Subgradient Methods for the Service Network Design Problem. Transp. Sci. 1994, 28, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, M.; Peeters, D.; Thisse, J. Location on Networks. In Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Tavasszy, L.; Peng, Q. Freight network design with heterogeneous values of time. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alumur, S.; Kara, B.Y. Network hub location problems: The state of the art. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 190, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.F.; O’Kelly, M.E. Twenty-Five Years of Hub Location Research. Transp. Sci. 2012, 46, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, H.-J. The multi-class, multi-criteria traffic network equilibrium and systems optimum problem. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2004, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantos-Sánchez, P.; Moner-Colonques, R.; Sempere-Monerris, J.J.; Álvarez-SanJaime, Ó. Viability of new road infrastructure with heterogeneous users. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pr. 2011, 45, 435–450. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Yang, H. The impact of user heterogeneity on road franchising. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2012, 48, 958–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.T.; Ehrgott, M. Modelling Route Choice Behaviour in a Tolled Road Network with a Time Surplus Maximisation Bi-objective User Equilibrium Model. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 80, 266–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kockelman, K.M. On-line marginal-cost pricing across networks: Incorporating heterogeneous users and stochastic equilibria. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2006, 40, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Tavasszy, L.A.; Rezaei, J. Freight service network design with heterogeneous preferences for transport time and reliability. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 124, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Imai, K.; Nakamura, T.; Taniguchi, E. A supply chain-transport supernetwork equilibrium model with the behaviour of freight carriers. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.G.; Liu, X.; Rioult, J.; Angeloudis, P. A cost-based maritime container assignment model. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2013, 58, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffi, Y. Urban Transportation Networks: Equilibrium Analysis with Mathematical Programming Methods; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Marinov, M.; Viegas, J.M. A mesoscopic simulation modelling methodology for analyzing and evaluating freight train operations in a rail network. Simul. Model. Pr. Theory 2011, 19, 516–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuby, M.; Xu, Z.; Xie, X. Railway network design with multiple project stages and time sequencing. J. Geogr. Syst. 2001, 3, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, M.W.; Grubesic, T.H. A GIS-based planning approach to locating urban rail terminals. Transportation 2001, 28, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Lamberti, R. High-Speed Rail Track Design Using GIS And Multi-Criteria Analysis. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 54, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngunyi, J.; Mundia, C.; Gachari, M. Analysis of Standard Gauge Railway Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Am. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2017, 6, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kurwi, S.; Demian, P.; Hassan, T.M. Integrating BIM and GIS in railway projects: A critical review. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ARCOM Conference, Cambridge, UK, 4–6 September 2017; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Marinov, M.; Zunder, T.; Islam, D. Concepts, models and methods for rail freight and logistics performances: An inception paper. In Proceedings of the 12th World Conference on Transport Research, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–15 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.; Mortimer, P.; Greening, P.; Piecyk, M.; Dadhich, P. A cost and CO2 comparison of using trains and higher capacity trucks when UK FMCG companies collaborate. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 58, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordnejad, B. Stakeholder analysis in intermodal urban freight transport. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on City Logistics, Tenerife, Spain, 17–19 June 2015; Volume 12, pp. 750–764. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE. Contagem da População 2007. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 2019. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/downloads-estatisticas.html (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- IBGE. Divisão do Brasil em Mesorregiões e Microrregiões. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 1990. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/monografias/GEBIS%20-%20RJ/DRB/Divisao%20regional_v01.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Cignoni, P.; Montani, C.; Scopigno, R. DeWall: A fast divide and conquer Delaunay triangulation algorithm in Ed. Comput. Des. 1998, 30, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIE Plano Diretor Rodoviário do Estado de Santa Catarina. Secretaria de Estado da Infraestrutura e Mobilidade de Santa Catarina. 2019. Available online: https://www.sie.sc.gov.br (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Kordnejad, B. Intermodal transport cost model and intermodal distribution in urban freight. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 125, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Product | 2005 | 2015 | 2023 | Class * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar–Refined | 157.56 | 176.99 | 192.77 | C |
| Sugar–Raw | 314.45 | 352.44 | 383.17 | C |
| Rice | 951.45 | 1087.35 | 1289.42 | B |
| Beverages–Ingredients | 429.01 | 510.63 | 700.20 | C |
| Beverages–Final product | 1223.27 | 1456.01 | 1996.55 | C |
| Limestone | 618.84 | 702.77 | 817.54 | B |
| Meat | 1982.43 | 2499.81 | 4484.17 | R |
| Pottery | 1467.24 | 1802.63 | 2840.42 | C |
| Clay | 931.40 | 1144.31 | 1803.09 | B |
| Cement | 1949.02 | 2301.45 | 3058.01 | C |
| Mineral Coal | 570.00 | 673.07 | 894.33 | B |
| Clinker | 406.63 | 480.16 | 638.00 | B |
| Fuel–Outbound | 3793.91 | 4280.48 | 4676.47 | L |
| Fuel–Internal Distribution | 1597.86 | 1790.89 | 1947.05 | L |
| Soy Bean | 3359.23 | 3791.93 | 4335.92 | B |
| Petroleum Coke | 504.20 | 595.37 | 791.09 | B |
| Fertilizer | 606.73 | 689.02 | 801.54 | B |
| Cigarettes–Final Product | 198.78 | 233.64 | 305.00 | C |
| Tobacco | 110.86 | 130.30 | 170.10 | C |
| Apple | 213.69 | 238.51 | 264.68 | C |
| Wood | 1615.04 | 1806.57 | 2016.14 | C |
| Furniture | 1080.51 | 1208.65 | 1348.86 | C |
| Mechanical Industry–Final product | 683.16 | 775.82 | 902.51 | C |
| Mechanical Industry–Raw material | 1093.67 | 1242.00 | 1444.83 | C |
| Corn | 2719.30 | 3069.57 | 3509.93 | B |
| Corn–Inbound | 2501.27 | 2823.46 | 3228.51 | B |
| Paper and Cardboard–Final product | 1376.57 | 1596.78 | 1987.35 | C |
| Paper and Cardboard–Raw material | 1895.30 | 2198.49 | 2736.24 | C |
| Plastic–Final product | 540.26 | 644.13 | 889.07 | C |
| Plastic–Raw material | 628.60 | 749.45 | 1034.44 | C |
| Textile–Final product | 221.21 | 256.95 | 321.39 | C |
| Textile–Raw material | 300.65 | 349.23 | 436.81 | C |
| Wheat | 615.50 | 687.00 | 762.37 | B |
| Glass–Final product | 226.00 | 281.49 | 474.03 | C |
| Glass–Raw material | 200.00 | 249.11 | 419.49 | C |
| Total | 37,083.60 | 42,876.45 | 53,901.53 | - |
| Class | 2005 | 2015 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Cargo (B) | 13,784.55 | 15,744.00 | 18,871.75 |
| Container (C) | 15,924.84 | 18,561.27 | 23,922.09 |
| Liquid (L) | 5391.77 | 6071.37 | 6623.52 |
| Refrigerated (R) | 1982.43 | 2499.81 | 4484.17 |
| Total | 37,083.60 | 42,876.45 | 53,901.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isler, C.A.; Asaff, Y.; Marinov, M. Designing a Geo-Strategic Railway Freight Network in Brazil Using GIS. Sustainability 2021, 13, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010085
Isler CA, Asaff Y, Marinov M. Designing a Geo-Strategic Railway Freight Network in Brazil Using GIS. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsler, Cassiano A., Yesid Asaff, and Marin Marinov. 2021. "Designing a Geo-Strategic Railway Freight Network in Brazil Using GIS" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010085
APA StyleIsler, C. A., Asaff, Y., & Marinov, M. (2021). Designing a Geo-Strategic Railway Freight Network in Brazil Using GIS. Sustainability, 13(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010085






