Effects of Amendments on Physicochemical Properties and Respiration Rate of Soil from the Arid Region of Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Soil Amendments
2.3. Experiment Regimes
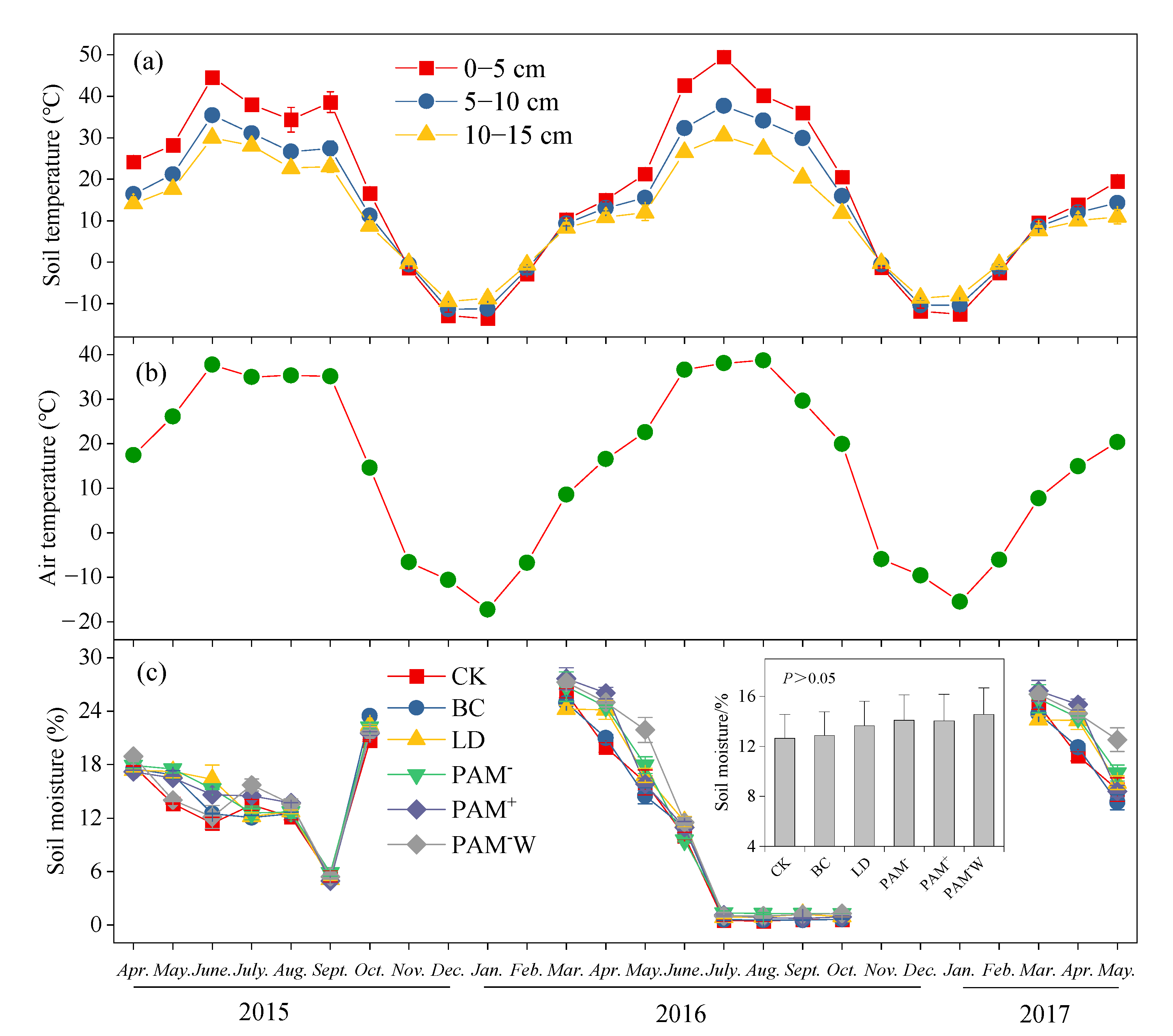
2.4. Soil Temperature, Moisture, and SR Measurements
2.5. Measurement of Soil and Amendment Properties
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Soil Amendments on Soil Properties
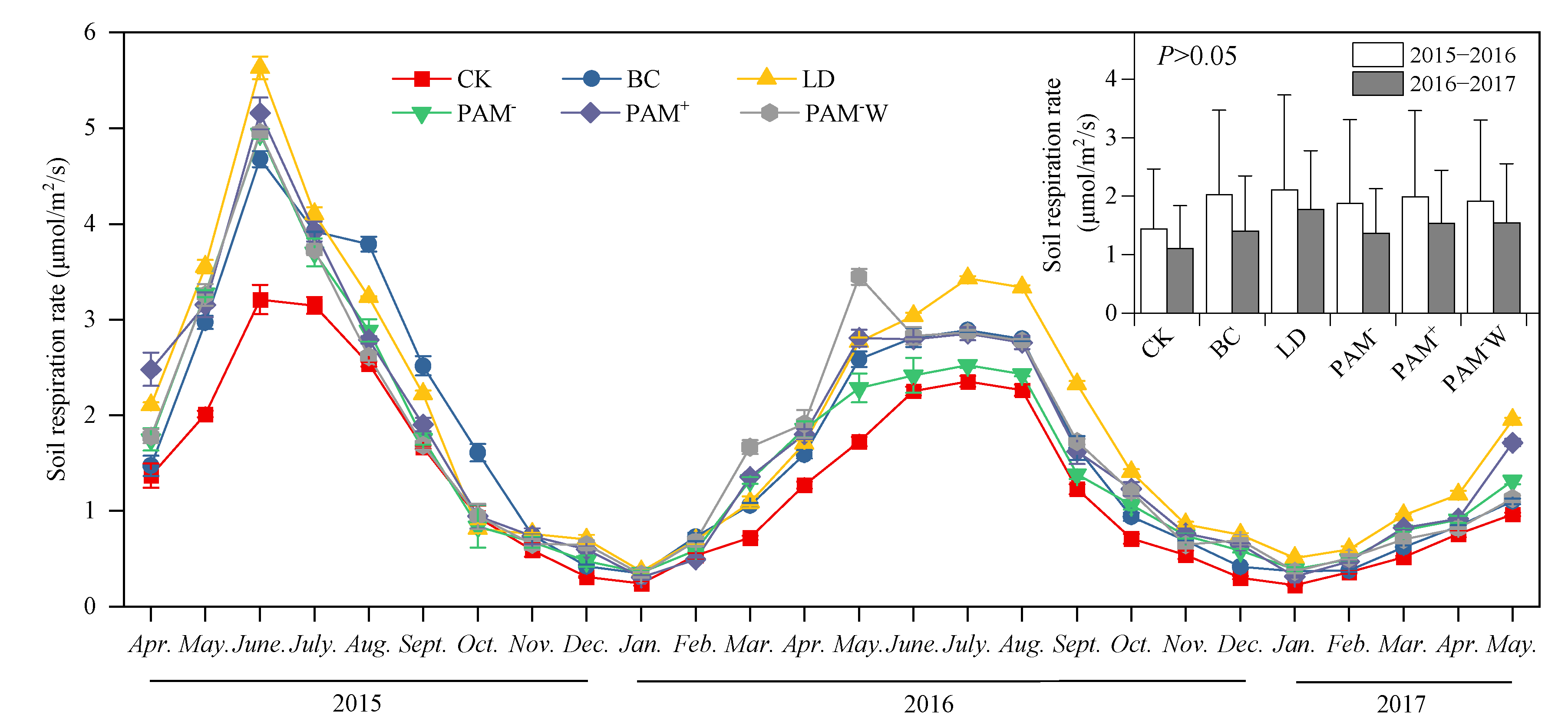
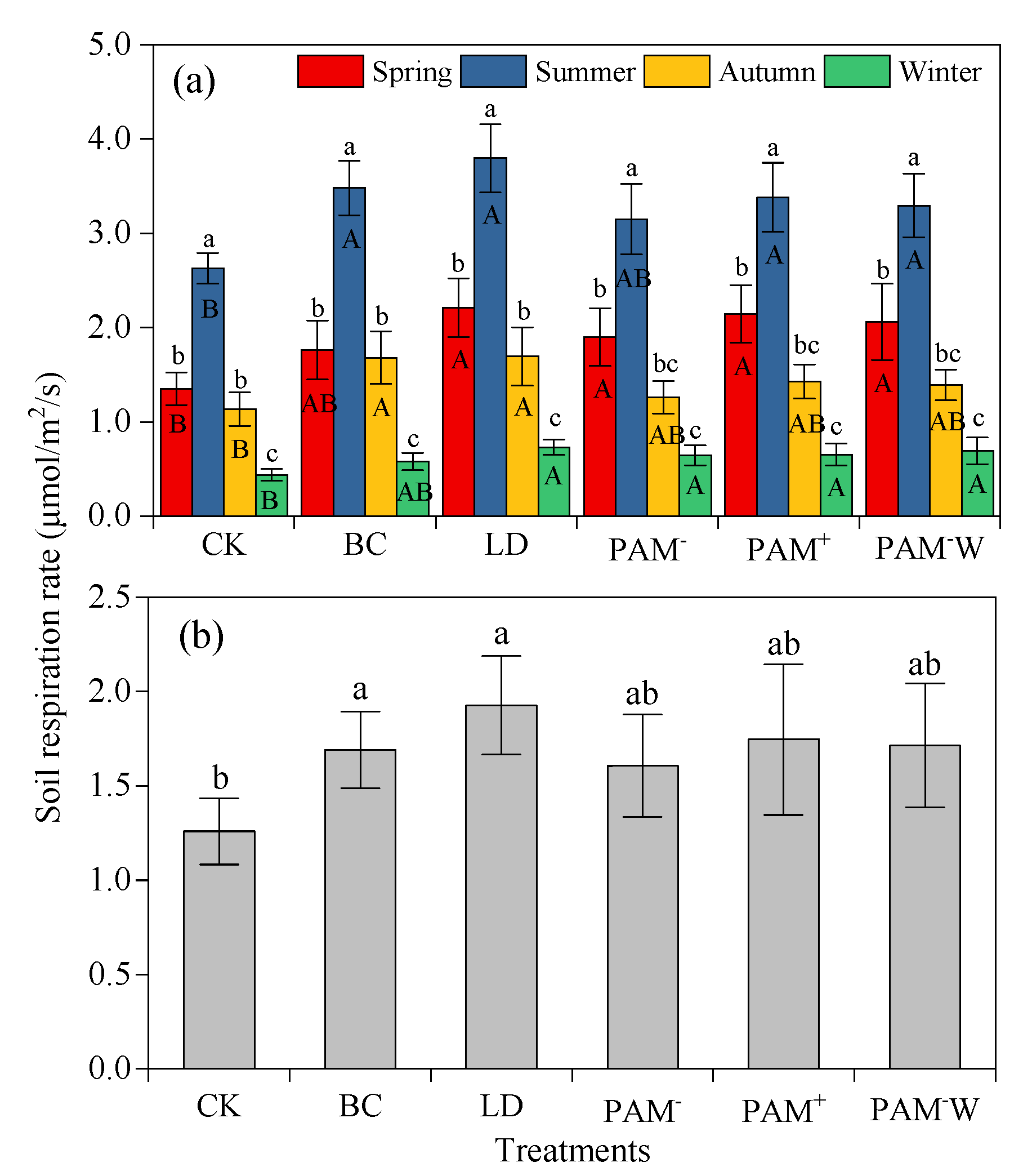
3.2. Dynamics of SR
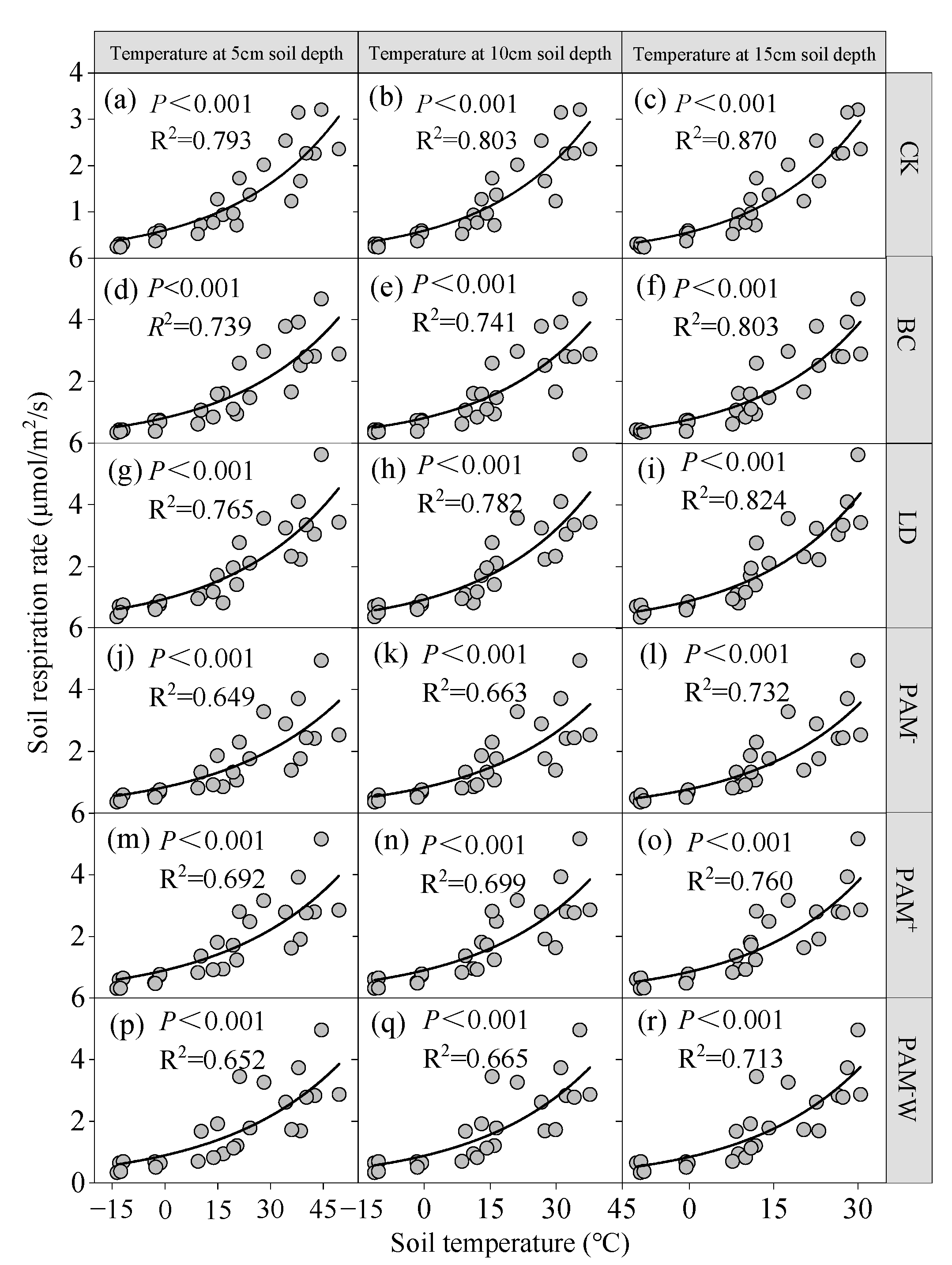
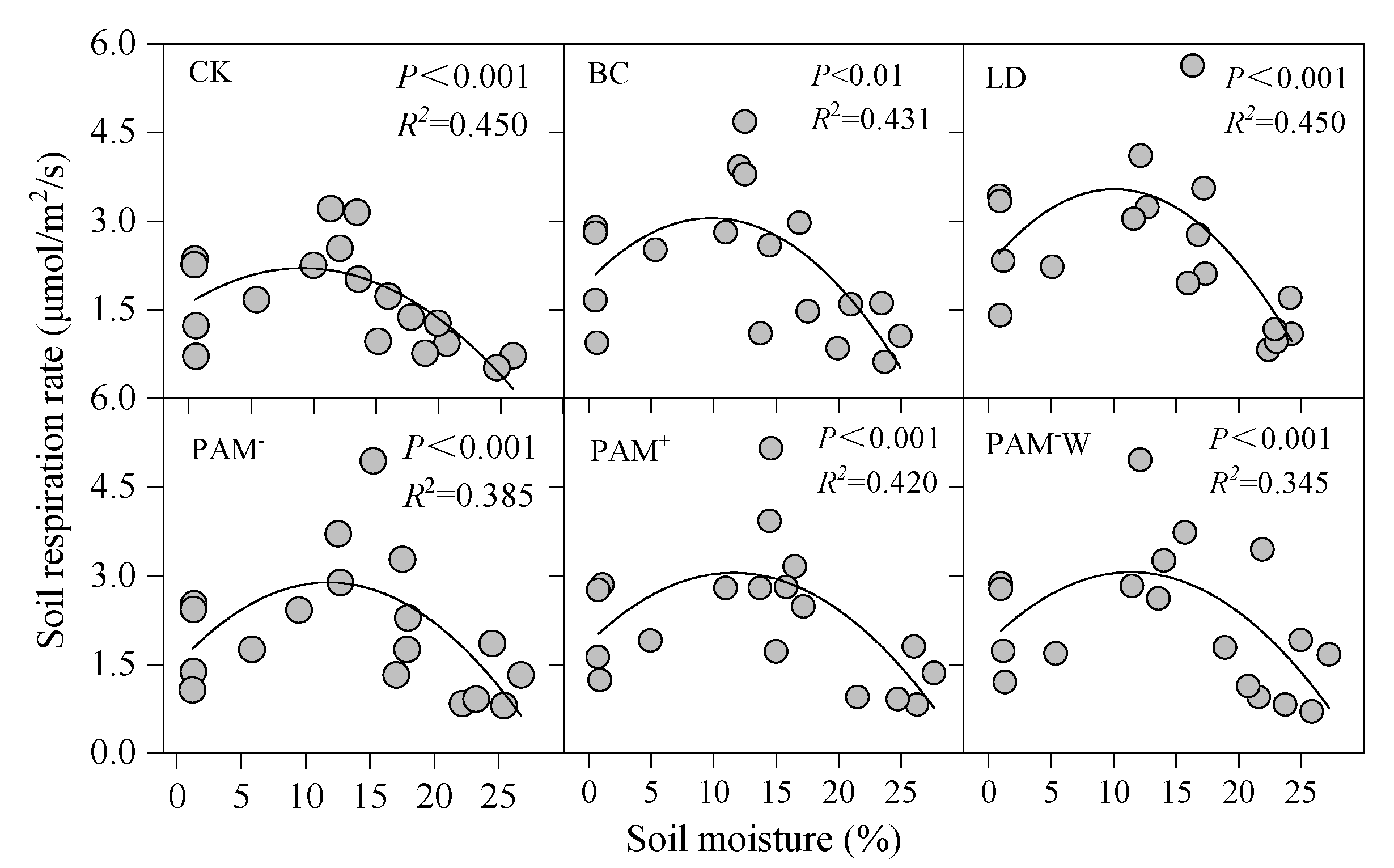
3.3. Driving Factors for SR
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Soil Amendments on SR
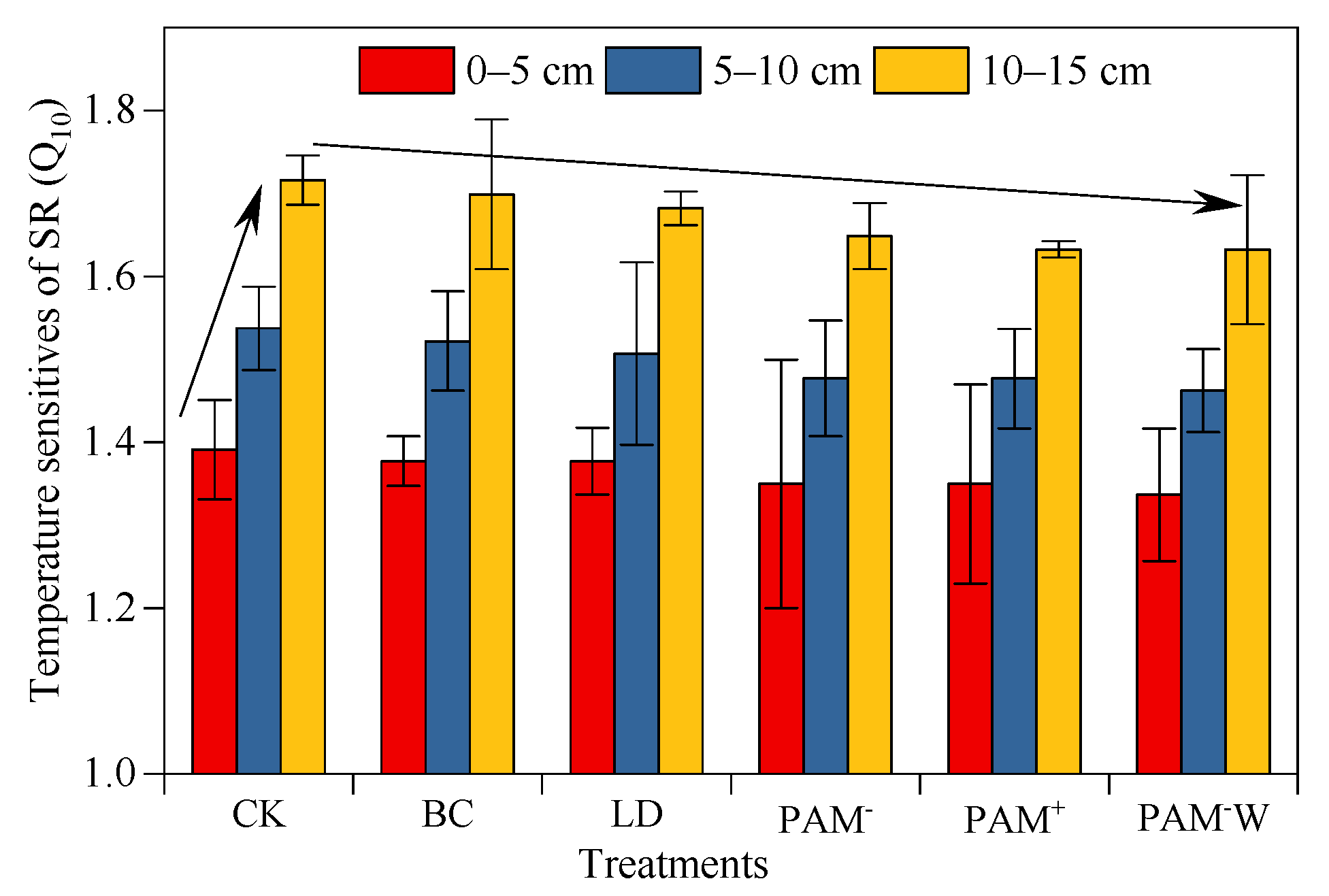
4.2. Amendments Decrease Temperature Sensitivity of SR (Q10)
4.3. Effect of Amendments Addition on Soil Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, M.B.; Wang, X.H.; Liusui, Y.H.; Sun, X.Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, H. Diversity and abundance of soil animals as influenced by long-term fertilization in grey desert soil, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10837–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; He, G.; Liu, W. Long-term cropping effects on agricultural sustainability in alar oasis of Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, S. The Influence of the continuous cotton cropping on the physical properties of cotton field in different cropping systems in south Xinjiang. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 48–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Bian, X. Effects of long-term continuous cropping system of cotton on soil physical-chemical properties and activities of soil enzyme in oasis in Xinjiang. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 725–733. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Sun, Z.X.; Zheng, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Feng, L.; Qian, C.; Yang, N.; Chen, F.; Zhe, Z. The combination of subsoil and the incorporation of corn stover affect physicochemical properties of soil and corn yield in semi-arid China. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 98, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Shen, J.L.; Qu, Z.; Yang, D.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Nie, X.H.; Zhu, L.F. Effects of long-term cotton continuous cropping on soil microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Si, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, P.; Reithmuller, G.; Collins, M. Biochar application to soil. In Biochar for Environmental Management: Science and Technology; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Zou, C.; Du, S.; Ren, Z. Effects of polyacrylamide on water use efficiency and output value of different crops in arid and semi-arid regions. Trans. CSAE 2015, 31, 101–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pan, G.; Ok, Y.S. Biochars and the plant soil interface. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.X.; Wen, Y.P.; Tan, X.M.; Zeng, Y.J.; Shang, Q.Y. Adsorption and leaching characteristics of ammonium and nitrate from paddy soil as affected by biochar amendment. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapáková, B.; Jeřábková, J.; Voříšek, K.; Tejnecký, V.; Drábek, O. The biochar effect on soil respiration and nitrification. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 64, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Li, T.; Hu, S.; Zhao, B. Characterization of pH-fractionated humic acids derived from Chinese weathered coal. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, L.; Bi, D.; Wei, J.; Yuan, G. Processes of leonardite altering cation and anion composition of soil solution in salt-affected soil in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 1367–1376. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Qi, R.; Wang, T.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of weathered coal on soil respiration of reconstructed soils on mining area’s earth disposal sites in Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Monglia adjacent area. Trans. CSAE 2015, 31, 230–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sojka, R.E.; Bjorneberg, D.L.; Entry, J.A.; Lentz, R.D.; Orts, W.J. Polyacrylamide in agriculture and environmental land management. Adv. Agron. 2007, 92, 75–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.P.; Fa-Hu, L.; Yang, S.M. Effect of polyacrylamide application on runoff, erosion, and soil nutrient loss under simulated rainfall. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.D. Polyacrylamide and biopolymer effects on flocculation; aggregate stability; and water seepage in a silt loam. Geoderma 2015, 241, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Singh, Y.; Iqbal, T.; Knoblauch, C.; Simon, P.; Wichern, F. Short-term effects of polyacrylamide and dicyandiamide on c and n mineralization in a sandy loam soil. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, R.; Xie, W. Effects of different amendments application on cotton growth and soil properties in arid areas. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 29, 757–762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.G.; Huang, G.; Lin, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.M. No synergistic effects of water and nitrogen addition on soil microbial communities and soil respiration in a temperate desert. Catena 2016, 142, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Steele, M.K.; Thomas, Q.; Day, S.D.; Hodges, S.C. Constraining estimates of global soil respiration by quantifying sources of variability. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 4143–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Tao, H.; Yao, H.; Zhao, C. Assessment of the effect of plastic mulching on soil respiration in the arid agricultural region of china under future climate scenarios. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Ok, Y.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of polyacrylamide; biopolymer and biochar on the decomposition of 14C-labelled maize residues and their stabilization in soil aggregates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Biochar-induced negative carbon mineralization priming effects in a coastal wetland soil, roles of soil aggregation and microbial modulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zheng, J.F.; Zhang, D.X.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, H.M.; Zhang, A.F.; Li, L.Q.; Joseph, S.; Smith, P.; Crowley, D.; et al. Biochar has no effect on soil respiration across Chinese agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, J.M.; Nieto, M.A.; Lopez-de-Sa, E.G.; Gasco, G.; Mendez, A.; Plaza, C. Carbon dioxide emissions from semi-arid soils amended with biochar alone or combined with mineral and organic fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V.; Khalid, M.; Ahmad, W.; Edwards-Jones, G.; DeLuca, T.H. Short-term biochar-induced increase in soil CO2 release is both biotically and abiotically mediated. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Collins, H.P.; Bailey, V.L. The effect of young biochar on soil respiration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2345–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H.; Ishimura, F.; Takeda, T.; Hikuma, M. Isolation of polyacrylamide-degrading microorganisms from soil. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2002, 7, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y. Biodegradation of polyacrylamide by bacteria isolated from activated sludge and oil-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Shi, P.J.; Hui, D.F.; Luo, Y.Q. Global pattern of temperature sensitivity of soil heterotrophic respiration (Q10) and its implications for carbon-climate feedback. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 2009, 114, G02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, N.; Zhang, Q. Sensitivity of soil respiration to soil temperature decreased under deep biochar amended soils in temperate croplands. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2016, 108, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittl, T.F.; Canisares, L.; Sagrilo, E.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dannenmann, M.; Cerri, C.E.P. Temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition varies with biochar application and soil type. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). World reference base for soils resources. In World Soil Resource Report No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Streubel, J.D.; Collins, H.P.; Garcia-Perez, M.; Tarara, J.; Granatstein, D.; Kruger, C.E. Influence of contrasting biochar types on five soils at increasing rates of application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shao, H.; Li, W.; Bi, R.; Bai, Z. Improving soil enzyme activities and related quality properties of reclaimed soil by applying weathered coal in opencast-mining areas of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; Guo, J.; Zou, S. The dynamic response of soil respiration to land-use changes in subtropical China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry, 1st ed.; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Yan, J.X.; Yue, X.F.; Wang, M.B. Significance of soil temperature and moisture for soil respiration in a Chinese mountain area. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagrilo, E.; Jeffery, S.; Hoffland, E.; Kuyper, T.W. Emission of CO2 from biochar amended soils and implications for soil organic carbon. GCB Bioenergy 2014, 7, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Major, J.; Rondon, M.; Molina, D.; Riha, S.J.; Lehmann, J. Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, G.N.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Gao, B. Catechol and humic acid sorption onto a range of laboratory-produced black carbons biochars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W. Rhizosphere priming effect, its functional relationships with microbial turnover; evapotranspiration, and C-N budgets. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Shu, A.P.; Zhao, B.P.; Lin, Z.A.; Liu, G.R.; Li, Z.Z. The infrared spectrum analysis on compound urea with humic acid extracted from weathered coal. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2014, 31, 393–400. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Caesar-TonThat, T.C.; Busscher, W.J.; Novak, J.M.; Gaskin, J.F.; Kim, Y. Effects of polyacrylamide and organic matter on microbes associated to soil aggregation of Norfolk loamy sand. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Ye, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Wang, K. Effects of tillage on CO2 fluxes in a typical karst calcareous soil. Geoderma 2019, 337, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.; Feng, M.; Lin, S.; Malghani, S.; Ali, I.M. Microbial biomass; and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses, a case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.; Hui, D.F. Soil respiration patterns and controls in limestone cedar glades. Plant Soil 2014, 389, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Chen, L.; Fang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y. Temperature sensitivity of SOM decomposition governed by aggregate protection and microbial communities. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Chao, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, J.; Chang, X.; Su, A.; Luo, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Temperature sensitivity of nutrient release from dung along elevation gradient on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Arafat, Y.; Lin, W.; Jiang, Y.; Weng, B.; Lin, W. Characterizing rhizosphere microbial communities in long-term monoculture tea orchards by fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 81, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomik, M.; Arain, M.; McCaughey, J.H. Temporal and spatial variability of soil respiration in a boreal mixed-wood forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 140, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Shen, Z. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in different ecosystems in china. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, M.; Acosta, M.; Marek, M.V.; Kutsch, W.; Janous, D. Dependence of the Q10 values on the depth of the soil temperature measuring point. Plant Soil 2007, 292, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gershenson, A.; Bader, N.E.; Cheng, W. Effects of substrate availability on the temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, K.; Subramaniayan, P.; Gnasekaran, P.; Chitraputhirapillai, S. Effect of biochar amendment on soil physical; chemical and biological properties and groundnut yield in rainfed Alfisol of semi-arid tropics. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2016, 62, 1293–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Schumacher, T.E.; Kumar, S.; Malo, D.D.; Rice, J.A.; Bleakley, B.; Chilom, G.; Clay, D.E.; Julson, J.L.; Papiernik, S.K.; et al. Molecular characterization of biochars and their influence on microbiological properties of soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, H.; Cao, P. Amelioration of weathered coal on soil physical, chemical properties and enzyme activities with vegetation restoration. J. Agro Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 1855–1861. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sasse, J.; Martinoia, E.; Northen, T. Feed your friends: Do plant exudates shape the root microbiome? Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 23, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Kinyangi, J.; Grossman, J.; O’Neill, B.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Thies, J.; Luizao, F.J.; Petersen, J.; et al. Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikutta, R.; Kleber, M.; Kaiser, K.; John, R. Review: Organic matter removal from soils using hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochloride, and disodium perodisulfate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Sun, B. Temperature and duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: Characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an ultisol in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Gantzer, C.; Thompson, A.; Anderson, S. Polyacrylamide and gypsum amendments for erosion and runoff control on two soil series. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 65, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entry, J.A.; Sojka, R.E.; Watwood, M.; Ross, C. Polyacrylamide preparations for protection of water quality threatened by agricultural runoff contaminants. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Sohi, S.P.; Thies, J.E.; O’Neill, B.; Trujillo, L.; Gaunt, J.; Solomon, D.; Grossman, J.; Neves, E.G. Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Peters, A.; Trinks, S.; Schonsky, H.; Facklam, M.; Wessolek, G. Impact of biochar and hydrochar addition on water retention and water repellency of sandy soil. Geoderma 2013, 202, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil & Amendments | pH | EC (dS/cm) | OC | TN | TP | CEC (cmol+/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/kg) | ||||||
| Soil | 8.62 ± 0.22 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 c | 7.41 ± 0.09 b | 0.78 ± 0.07 d | 0.74 ± 0.04 b | 3.84 ± 0.26 b |
| Biochar | 9.37 ± 0.11 a | 3.70 ± 0.19 a | 417 ± 9 a | 21.8 ± 0.9 a | 10.6 ± 0.3 a | 12.0 ± 0.32 a |
| Leonardite | 4.87 ± 0.26 d | 1.33 ± 0.21 b | 431 ± 11 a | 8.70 ± 0.1 c | 0.24 ± 0.05 c | |
| Anionic PAM | 7.36 ± 0.09 c | 434 ± 15 a | 16.2 ± 0.4 b | |||
| Cationic PAM | 7.06 ± 0.12 c | 421 ± 8 a | 16.2 ± 0.3 b | |||
| Treatment | pH | EC (μS/cm) | SOM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AN (mg/k g) | AP (mg/k) | CEC (cmol+/kg) | BD (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.63 ± 0.04 b | 242 ± 8 c | 12.53 ± 0.03 b | 0.727 ± 0.020 a | 0.695 ± 0.009 a | 29.97 ± 1.86 c | 6.93 ± 0.12 c | 3.88 ± 0.05 c | 1.41 ± 0.01 a |
| BC | 8.89 ± 0.02 a | 253 ± 4 b | 12.66 ± 0.05 a | 0.733 ± 0.005 a | 0.705 ± 0.008 a | 41.93 ± 1.68 a | 9.40 ± 0.16 a | 4.26 ± 0.08 a | 1.42 ± 0.02 a |
| LD | 8.08 ± 0.04 c | 267 ± 3 a | 12.64 ± 0.07 a | 0.735 ± 0.009 a | 0.698 ± 0.017 a | 37.03 ± 0.17 b | 8.41 ± 0.08 b | 4.07 ± 0.07 b | 1.42 ± 0.00 a |
| PAM− | 8.60 ± 0.02 b | 250 ± 3 b | 12.57 ± 0.04 ab | 0.727 ± 0.012 a | 0.720 ± 0.020 a | 32.57 ± 0.53 c | 7.04 ± 0.07 c | 3.85 ± 0.03 c | 1.42 ± 0.02 a |
| PAM+ | 8.58 ± 0.02 b | 248 ± 2 b | 12.61 ± 0.03 ab | 0.725 ± 0.011 a | 0.709 ± 0.011 a | 31.73 ± 1.41 c | 6.91 ± 0.15 c | 3.86 ± 0.03 c | 1.41 ± 0.00 a |
| PAM−W | 8.59 ± 0.03 b | 247 ± 3 b | 12.59 ± 0.06 ab | 0.720 ± 0.008 a | 0.704 ± 0.008 a | 32.43 ± 0.50 c | 7.04 ± 0.08 c | 3.88 ± 0.04 c | 1.41 ± 0.02 a |
| Parameters | Soil Respiration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DF | F | p | |
| Amendment | 5 | 3.017 * | 0.015 |
| Month | 11 | 43.005 ** | <0.001 |
| Amendment × Month | 55 | 0.211 | >0.05 |
| Treatment | Regression Equation | R2 | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | SR = SM × 0.060 + AT × 0.103 − 1.715 | 0.896 | 64.406 | <0.0001 |
| BC | SR = SM × 0.088 + AT × 0.142 − 2.509 | 0.873 | 51.429 | <0.0001 |
| LD | SR = ST15 × 0.129 + 0.212 | 0.722 | 44.204 | <0.0001 |
| PAM− | SR = ST15 × 0.153 + SM × 0.071 − 1.641 | 0.746 | 22.058 | <0.0001 |
| PAM+ | SR = ST15 × 0.142 + SM × 0.050 − 0.956 | 0.694 | 16.976 | <0.0001 |
| PAM−W | SR = ST15 × 0.147 + SM × 0.057 − 1.229 | 0.644 | 13.557 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; An, S.; Jia, H. Effects of Amendments on Physicochemical Properties and Respiration Rate of Soil from the Arid Region of Northwest China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105332
Li D, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Sun T, An S, Jia H. Effects of Amendments on Physicochemical Properties and Respiration Rate of Soil from the Arid Region of Northwest China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(10):5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105332
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dianpeng, Jianqin Zhou, Yuxin Zhang, Tao Sun, Shuqing An, and Hongtao Jia. 2021. "Effects of Amendments on Physicochemical Properties and Respiration Rate of Soil from the Arid Region of Northwest China" Sustainability 13, no. 10: 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105332
APA StyleLi, D., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Sun, T., An, S., & Jia, H. (2021). Effects of Amendments on Physicochemical Properties and Respiration Rate of Soil from the Arid Region of Northwest China. Sustainability, 13(10), 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105332






