Dynamics and Drivers of Grasslands in the Eurasian Steppe during 2000–2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
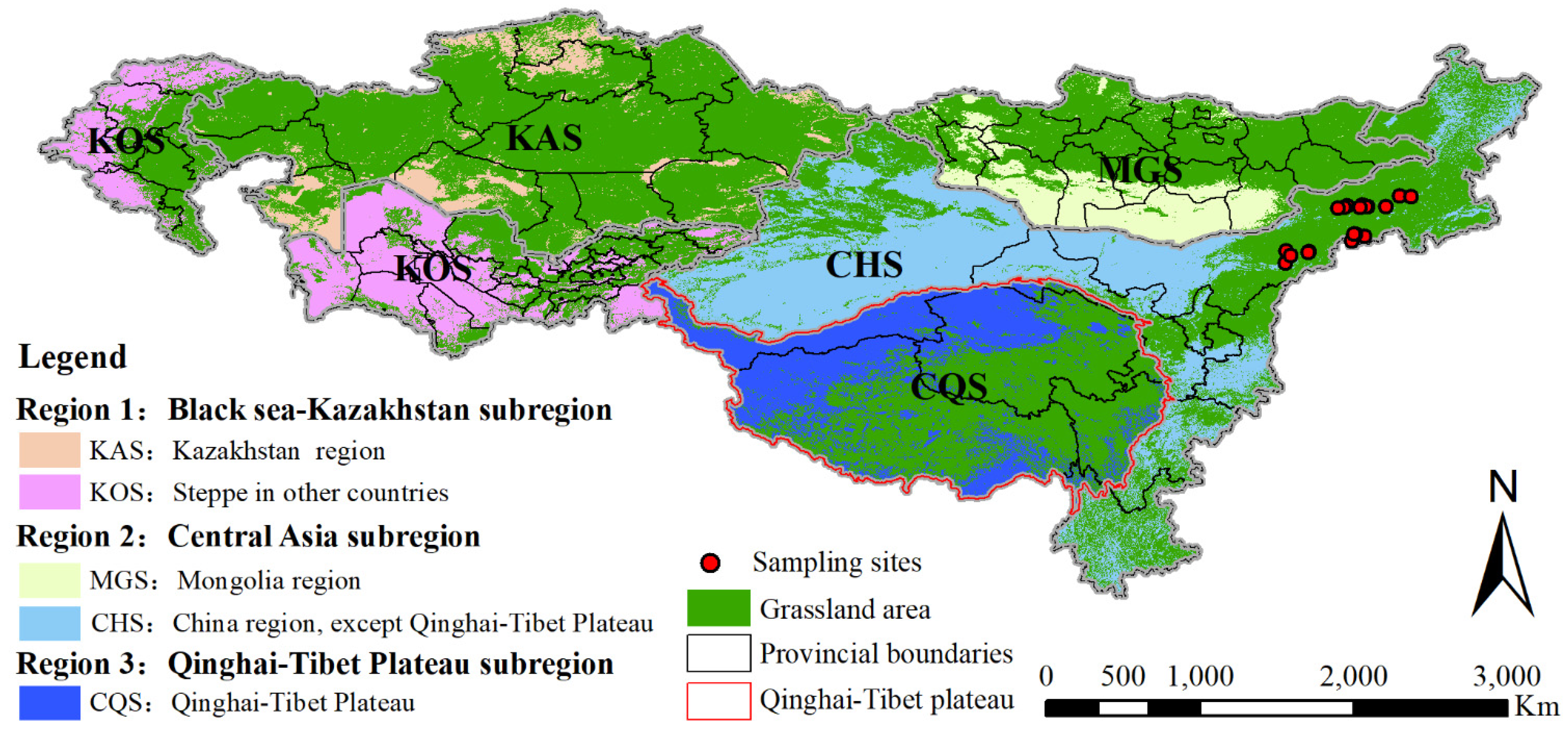
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Calculating Actual NPP (ANPP)
2.4. Calculating Climate NPP (CNPP)
2.5. Estimation of Human-Caused NPP (HNPP)
2.6. Quantitative Assessment Method
3. Results
3.1. Validation of NPP Model
3.2. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of ANPP
3.3. Analysis of Grassland Degradation and Recovery
3.4. Effects of Climate Variation on Grassland NPP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dairaku, K.; Emori, S.; Nozawa, T. Impacts of global warming on hydrological cycles in the Asian monsoon region. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Bastos, A.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S. Interannual variation of terrestrial carbon cycle: Issues and perspectives. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voinov, A.; Seppelt, R.; Reis, S.; Nabel, J.E.M.S.; Shokravi, S. Values in socio-environmental modelling: Persuasion for action or excuse for inaction. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 53, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golosov, N.V.; Gennadiev, A.N.; Olson, K.R.; Markelov, M.V.; Zhidkin, A.P.; Chendev, Y.G.; Kovach, R.G. Spatial and temporal features of soil erosion in the forest-steppe zone of the East-European Plain. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2011, 44, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, G.J.; Stocks, B.J. Eurasian Perspective of Fire: Dimension, Management, Policies, and Scientific Requirements; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Duan, L.; Luo, Y. Trend and extreme occurrence of precipitation in a mid-latitude Eurasian steppe watershed at various time scales. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 28, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, I.; Wigen, E. The importance of the Eurasian steppe to the study of international relations. J. Int. Relat. Dev. 2013, 16, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ju, W.; Ye, J.; Hickler, T.; Liao, C.; Feng, L.; Ruan, H. Great uncertainties in modeling grazing impact on carbon sequestration: A multi-model inter-comparison in temperate Eurasian Steppe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Mu, M. Nonlinearly combined impacts of initial perturbation from human activities and parameter perturbation from climate change on the grassland ecosystem. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2011, 18, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Qi, J.; Odeh, I. Quantitative assessment of the contributions of climate change and human activities on global grassland degradation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4273–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Samanta, A.; Costa, M.H.; Ganguly, S.; Nemani, R.R.; Myneni, R.B. Widespread decline in greenness of Amazonian vegetation due to the 2010 drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Zapata, J.; Carrete, M.; Gravilov, A.; Sklyarenko, S.; Ceballos, O.; Donázar, J.; Hiraldo, F. Land use changes and raptor conservation in steppe habitats of Eastern Kazakhstan. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 111, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, X.; Lu, C.; Gao, Y. Impacts of human economic activities on wind and sand environment in Kerqin sandy land. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, K.; Feng, J. The temporal change of driving factors during the course of land desertification in arid region of North China: The case of Minqin County. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hua, T. Roles of climate changes and human interventions in land degradation: A case study by net primary productivity analysis in China′s Shiyanghe Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, C. Quantitative assessment of the individual contribution of climate and human factors to desertification in northwest China using net primary productivity as an indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Han, B.; Yang, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W. Determining the contributions of climate change and human activities to the vegetation NPP dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China, from 2000 to 2015. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.; Qi, J. Comparative assessment of grassland degradation dynamics in response to climate variation and human activities in China, Mongolia, Pakistan and Uzbekistan from 2000 to 2013. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 135, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; An, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Shangguan, Z. Effect of desertification on productivity in a desert steppe. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ju, W.; Groisman, P.; Li, J.; Propastin, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, W.; Ruan, H. Quantitative assessment of carbon sequestration reduction induced by disturbances in temperate Eurasian steppe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammat, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Myneni, R.B.; Piao, S. Drought and spring cooling induced recent decrease in vegetation growth in Inner Asia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 178–179, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Yu, G.; He, N.; Ma, A.; Ge, J.; Hu, Z. Spatial pattern of grassland aboveground biomass and its environmental controls in the Eurasian steppe. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 27, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.; Randerson, J.; Field, C.; Matson, P.; Klooster, S. Terrestrial Ecosystem Production: A Process Model Based on Global Satellite and Surface Data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B. Global net primary production: Combining ecology and remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potter, C.; Klooster, S.; Genovese, V. Net primary production of terrestrial ecosystems from 2000 to 2009. Clim. Chang. 2012, 115, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J. Estimation of net primary productivity of Chinese terrestrial vegetation based on remote sensing. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 31, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Ju, W.; Odeh, I. Dynamic of grassland vegetation degradation and its quantitative assessment in the northwest China. Acta Oecol. 2014, 55, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horion, S.; Cornet, Y.; Erpicum, M.; Tychon, B. Studying interactions between climate variability and vegetation dynamic using a phenology based approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 20, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Tao, P. Simulating and estimating tempo-spatial patterns in global human appropriation of net primary production (HANPP): A consumption-based approach. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; An, R.; Wang, K.; Odeh, I.; et al. Quantitative assess the driving forces on the grassland degradation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, in China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegerl, G.; Zwiers, F.; Stott, P.; Kharin, V. Detectability of Anthropogenic Changes in Annual Temperature and Precipitation Extremes. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3683–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gang, C.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, J.; Odeh, I.; Groisman, P.Y. Comparative Assessment of Grassland NPP Dynamics in Response to Climate Change in China, North America, Europe and Australia from 1981 to 2010. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, D. Dominant climatic factors driving annual runoff changes at the catchment scale across China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, N.A.; Almeida, A.C.D.; Coelho, C.O.A. Impacts of land use and cover type on runoff and soil erosion in a marginal area of Portugal. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, G.; Peng, D.; Wen, J.; Cai, Z.; Xu, J. Research on trend of warm-humid climate in Central Asia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 74, 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli, A.; Gilad, U.; Ponzet, M.; Svoray, T.; Mirzadinov, R.; Fedorina, O. Assessing land-cover change and degradation in the Central Asian deserts using satellite image processing and geostatistical methods. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megoran, N. Prospects for Pastoralism in Kazakstan and Turkmenistan: From State Farms to Private Flocks-Edited by Carol Kerven. Geogr. J. 2006, 172, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Yan, H.; Du, W.; Hu, Y. The Variations and Causes of Grassland Distribution in Kazakhstan from the Global Land Cover Datasets. J. Geo Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 372–383. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Impact of human activities and climate change on the grassland dynamics under different regime policies in the Mongolian Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, X.; Meng, F.; Bai, H. Mongolia and Inner Mongolia LUCC Regional Differentiation Over the Past 30 Years. J. Geo Inf. Sci. 2013, 15, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kienzler, K.; Martius, C.; Mirzabaev, A.; Ikramov, R. Research Prospectus: A Vision for Sustainable Land Management Research in Central Asia. ICARDA 2009, 1, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabaev, A. Land Degradation and Sustainable Land Management Innovations in Central Asia. In Technological and Institutional Innovations for Marginalized Smallholders in Agricultural Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]




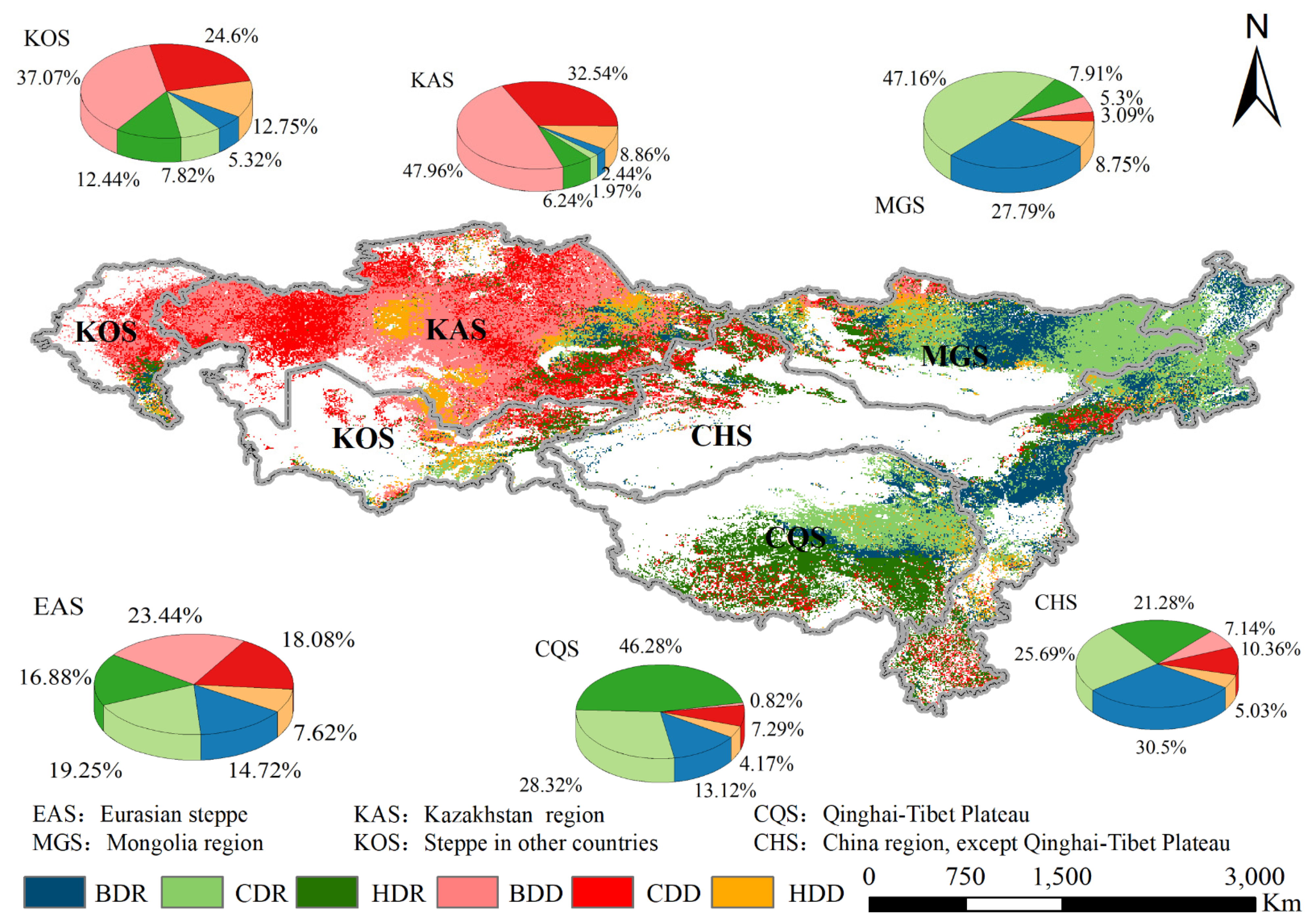


| Scenario | SlopeANPP | SlopeCNPP | SlopeHNPP | Grassland Condition | Roles of Factors about Climate and Human Activities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | + | + | + | Recovery | Climate-caused recovery (CDR) |
| S2 | − | − | Human activities-caused recovery (HDR) | ||
| S3 | + | − | Both two factors caused recovery (BDR) | ||
| S4 | − | − | − | Degradation | Climate-caused degradation (CDD) |
| S5 | + | + | Human activities-caused degradation (HDD) | ||
| S6 | − | + | Both two factors caused degradation (BDD) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Dynamics and Drivers of Grasslands in the Eurasian Steppe during 2000–2014. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13115887
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Wang Z, Li J, Xu Z. Dynamics and Drivers of Grasslands in the Eurasian Steppe during 2000–2014. Sustainability. 2021; 13(11):5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13115887
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanzhen, Qian Wang, Zhaoqi Wang, Jianlong Li, and Zengrang Xu. 2021. "Dynamics and Drivers of Grasslands in the Eurasian Steppe during 2000–2014" Sustainability 13, no. 11: 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13115887
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, Z., Li, J., & Xu, Z. (2021). Dynamics and Drivers of Grasslands in the Eurasian Steppe during 2000–2014. Sustainability, 13(11), 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13115887






