Mathematical Model to Simulate the Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soil to Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- the life of a plant (or of any other biological entity) does not end at harvest or sacrifice; hence it must be studied entirely over generations and the optimal choices can be made only after these studies;
- -
- Newtonian time is a useful parameter for accurately tracking and reporting events in the evolution of biological entities, but there are intrinsic parameters of each entity that indicate in which stages of evolution they are.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The General Mathematical Model
2.2. Model of Zinc Bioaccumulation Process
2.3. The Introduction of Temperature Influence in the Original Model
- the temperature favorable to the development of the lettuce crop is between 15–25 °C;
- harvesting is done at an average weight of 0.9 kg·m−2 or at an average mass of 113 g per lettuce;
- the accumulation of heavy metal in the plant must be monotonous (it does not decrease, because there is no experimental support to reduce the concentration of metal in the plant).
2.4. The Thermal Control Modification of the Model to Simulate the Effects of Heavy Metal Accumulation
3. Results
Accumulation of Zinc in Green Lettuce
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankaite, A. Soil remediation from heavy metals using mathematical modelling. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. 2009, 17, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cortes, V.; Phelps, B.; Van Ryswyk, H.; Srebotnjak, T. Experimental Analysis of Soil and Mandarin Orange Plants Treated with Heavy Metals Found in Oilfield-Produced Wastewater. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, Y.N.; Islam, A.; Akbar, S. Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables and possible health risk assessment. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.Q.Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X. Instances of Soil and Crop Heavy Metal Contamination in China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2001, 10, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buekers, J.; Degryse, F.; Maes, A.; Smolders, E. Modelling the effects of ageing on Cd, Zn, Ni and Cu solubility in soils using an assemblage model. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibuike, G.U.; Obiora, S.C.; Chibuike, G.U. Heavy Metal Polluted Soils: Effect on Plants and Bioremediation Methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 752708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Wei, W.; Li, M.; Huang, R.; Yang, F.; Duan, Y. Heavy metal contamination and potential health risks in rice-producing soils of Hunan Province. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15584–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Modeling and mapping of critical loads for heavy metals in Kunshan soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Kuek, C.; Chaudhry, T.; Khoo, C.; Hayes, W. Role of plants, mycorrhizae and phytochelators in heavy metal contaminated land remediation. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.; Datta, S.; Chhonkar, P.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, L.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, C.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Health Risks of Metals in Contaminated Farmland Soils and Spring Wheat Irrigated with Yellow River Water in Baotou, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Voicu, G. Water Scarcity and Wastewater Reuse in Crop Irrigation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, D. Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R.; Malaviya, D.; Pandiyan, K.; Singh, U.B.; Sahu, A.; Shukla, R.; Singh, B.P.; Rai, J.P.; Sharma, P.K.; Lade, H.; et al. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Soil and Aquatic Environment: An Overview of Principles and Criteria of Fundamental Processes. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2189–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, G.; Deng, O.; Pu, Y. Heavy metals in soils from a typical industrial area in Sichuan, China: Spatial distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16618–16630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, Y. Potential ecological risk and health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid in soil around Xunyang mining areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrino, M.; Abollino, O.; Buoso, S.; Giacomino, A.; La Gioia, C.; Mentasti, E. Accumulation of heavy metals from contaminated soil to plants and evaluation of soil remediation by vermiculite. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmani-Muller, H.; van Oort, F.; Gélie, B.; Balabane, M. Strategies of heavy metal uptake by three plant species growing near a metal smelter. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 109, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghobar, M.A.; Suresha, S. Evaluation of metal accumulation in soil and tomatoes irrigated with sewage water from Mysore city, Karnataka, India. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017, 16, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinos, S.; Zabetakis, I. The uptake of nickel and chromium from irrigation water by potatoes, carrots and onions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinos, S.; Nasopoulou, C.; Tsikrika, C.; Zabetakis, I. The Bioaccumulation and Physiological Effects of Heavy Metals in Carrots, Onions, and Potatoes and Dietary Implications for Cr and Ni: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Chauhan, R.K. Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated soil in Haridwar (Uttarakhand), India. Agric. Sci. Res. J. 2015, 5, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Thakur, R.K. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals via Dietary Intake of Vegetables Grown in Wastewater Irrigated Areas of Jagjeetpur, Haridwar India. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2018, 3, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.; Fletcher, T.D.; McCarthy, D.T. Heavy Metal Contamination of Vegetables Irrigated by Urban Stormwater: A Matter of Time? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Bhattacharyya, A. Heavy metal accumulation in wheat plant grown in soil amended with industrial sludge. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, L.Q. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Bocanegra, J.; Roca, N.; Febrero, A.; Bort, J. Assessment of heavy metal tolerance in two plant species growing in experimental disturbed polluted urban soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2305–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekidan, A.; Weldegebriel, Y.; Hadera, A.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Toxicological assessment of heavy metals accumulated in vegetables and fruits grown in Ginfel river near Sheba Tannery, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradelo, R.; Villada, A.; Barral, M.T. Heavy Metal Uptake of Lettuce and Ryegrass from Urban Waste Composts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; Hussain, M.I.; Ismail, S.; Khan, Q.M. Evaluating heavy metal accumulation and potential health risks in vegetables irrigated with treated wastewater. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silapanuntakul, S.; Intrarasaksit, P.; Vatanasomboon, P.; Tantrakarnapa, K. Uptake of copper and zinc in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) planted in sida soil and lignite bottom ash mixtures. Naresuan Univ. J. Sci. Techol. 2017, 25, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, I.M.; Chaney, R.L.; Williams, F.M. The effects of cadmium and zinc interactions on the accumulation and tissue distribution of zinc and cadmium in lettuce and spinach. Environ. Pollut. 1993, 79, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Baretta, D.; Becegato, V.A.; Almeida, V.D.C.; Paulino, A.T. Copper/Zinc Bioaccumulation and the Effect of Phytotoxicity on the Growth of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in Non-contaminated, Metal-Contaminated and Swine Manure-Enriched Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Negim, O.E. Heavy metals uptake and translocation by lettuce and spinach grown on a metal-contaminated soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2018, 18, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gharbi, F.; Rejeb, S.; Ghorbal, M.H.; Morel, J.-L. Plant Response to Copper Toxicity as Affected by Plant Species and Soil Type. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.K.; Pathak, C. Bioaccumulation and Translocation Efficiency of Heavy Metals in Vegetables Grown on Long-Term Wastewater Irrigated Soil Near Bindal River, Dehradun. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.H. Health risk assessment and multivariate apportionment of trace metals in wild leafy vegetables from Lesser Himalayas, Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lv, F.; Zhou, J.; Song, Y.; Li, F. Health Risk Assessment of Vegetables Grown on the Contaminated Soils in Daye City of Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, S.; Rehman, W.; Menaa, F.; Ullah, A. Heavy Metal Levels in Vegetables Cultivated in Pakistan Soil Irrigated with Untreated Wastewater: Preliminary Results. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Singh, N.; Patel, M.; Tiwari, M.; Rai, U. Metal contamination of soil and translocation in vegetables growing under industrial wastewater irrigated agricultural field of Vadodara, Gujarat, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, antioxidant enzyme activities, and photosynthesis in cuttings and seedlings of Jatropha curcas L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrėnaitė-Gediene, E.; Butkus, D. Modelling of Cu, Ni, Zn, Mn and Pb transport from soil to seedlings of coniferous and leafy trees. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. 2007, 15, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Kiran, B.; Rani, S.; Rani, A.; Kaur, B.; Mittal, N. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.B.V.; Nascimento, C.W.A.D.; Araújo, P.R.M.; da Silva, L.H.V.; da Silva, R.F. Assessing heavy metal sources in sugarcane Brazilian soils: An approach using multivariate analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cârdei, P.; Nedelcu, A.; Ciupercă, R. Mathematical model for the evolution of Chlorella algae. INMATEH Agric. Eng. 2019, 57, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfiru, R.; Cârdei, P.; Vlăduţ, V.; Matache, M. The role of mathematical modeling in research in the field of bioaccumulation of heavy metals. Ann. Fac. Eng. Hunedoara 2018, 16, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cardei, P.; Tudora, C. Theoretical research on evolution of health of plants affected by heavy metal absorption process. In Proceedings of the 17th International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–25 May 2018; pp. 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guala, S.D.; Vega, F.A.; Covelo, E.F. The dynamics of heavy metals in plant–soil interactions. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales-Pastrana, R.R. Phytoremediation Dynamic Model for Environmental Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad del Turabo, Gurabo, Puerto Rico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Prusinkiewicz, P. Simulation modeling of plants and plant ecosystems. Commun. ACM 2000, 43, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangahu, B.V.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.; Anuar, N.; Mukhlisin, M. A Review on Heavy Metals (As, Pb, and Hg) Uptake by Plants through Phytoremediation. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 2011, 939161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, D.N.; Crookes, M.J. Review of Bioaccumulation Models for Use in Environmental Standards; Science Report SC030197/SR1; Environment Agency: London, UK, 2007; 276p.
- Verma, P.; George, K.; Singh, H.; Singh, R. Modeling cadmium in radish, carrot, spinach and cabbage. Appl. Math. Model. 2007, 31, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Le, B.V.; Richter, O. The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; El Afandi, G. Phytoremediation uptake model of heavy metals (Pb, Cd and Zn) in soil using Nerium oleander. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; Galal, T.M.; El-Bebany, A.F. Regression models for monitoring trace metal accumulations by Faba sativa Bernh. plants grown in soils amended with different rates of sewage sludge. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, S.; Molini, A.; Porporato, A. Stochastic modelling of phytoremediation. Proc. R. Soc. A 2011, 467, 3188–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, A.; Cârdei, P.; Ciupercă, R.; Ștefan, V.; Zaica, A. Statistical models proposed for algal growth in open system to optimize the cultivation technology. INMATEH Agric. Eng. 2019, 58, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, G.; Delfuria, L.; Gatto, M. The Interaction between Soil Acidity and Forest Dynamics: A Simple-Model Exhibiting Catastrophic Behavior. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1993, 43, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guala, S.; Vega, F.A.; Covelo, E.F. Modification of a soil–vegetation nonlinear interaction model with acid deposition for simplified experimental applicability. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitu, D. Lettuce Culture in the Garden and Field—Complete Technology. Available online: http://www.horticultorul.ro/legume/cultura-salatei-in-gradina_camp (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Smical, A.-I.; Hotea, V.; Oros, V.; Juhasz, J.; Pop, E. studies on transfer and bioaccumulation of heavy metals from soil into lettuce. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2008, 7, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalu, C.I.O.; Okere, P.C.; Egbufor, U.C.; Nwandikom, G.I.; Obijiaku, J.C.; Asomungha, C.C. Modeling and optimization of phytoremediation kinetics of metals in soil by a plant hyperacumulator. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 196–207. [Google Scholar]
- Pruteanu, A.; Vladut, V.; Cardei, P.; Bordean, D. General Tendencies of the Behaviour of Vegetables Developed in a Soil Contaminated with Heavy Metals. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achakzai, A.K.K.; Bazai, Z.A.; Kayani, S.A. Accumulation of heavy metals by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) irrigated with different levels of wastewater of Quetta city. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Sánchez, D.; Thorne, M.C.; Limer, L.M.C. A mathematical model for the behaviour of Se-79 in soils and plants that takes account of seasonal variations in soil hydrology. J. Radiol. Prot. 2012, 32, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




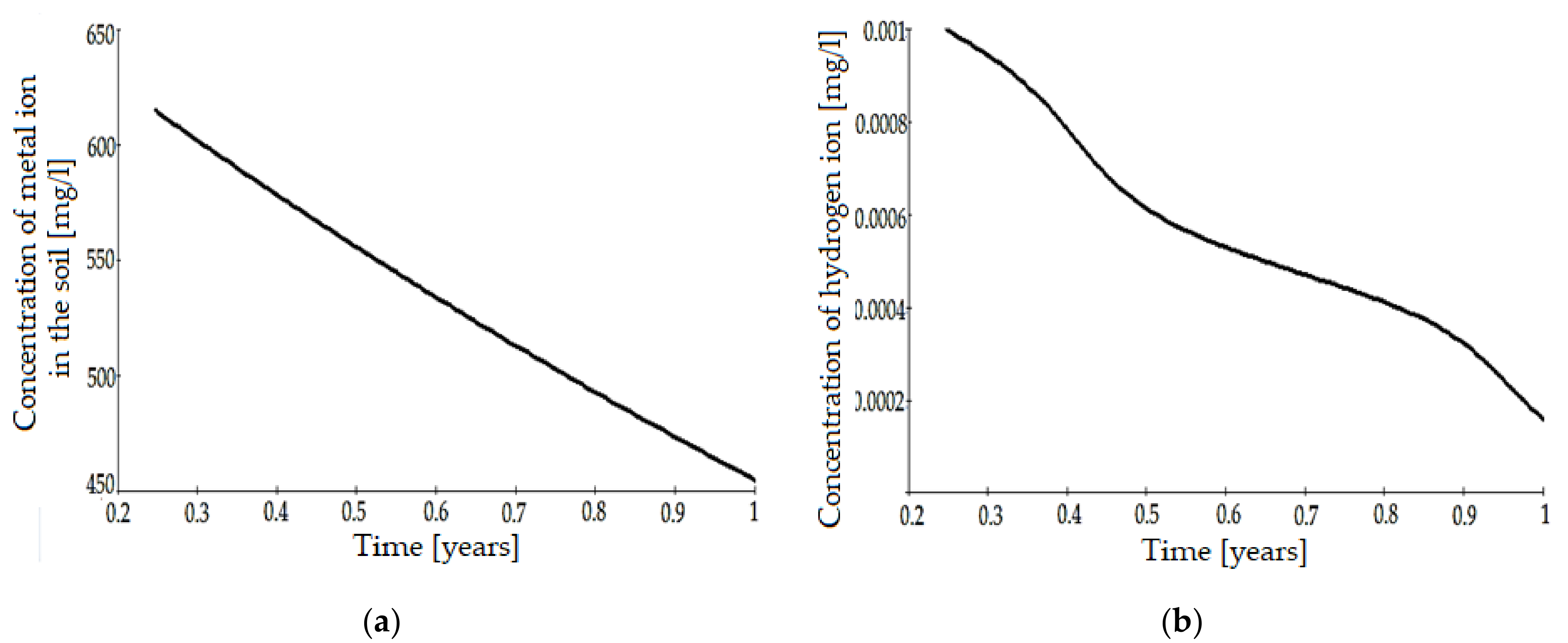

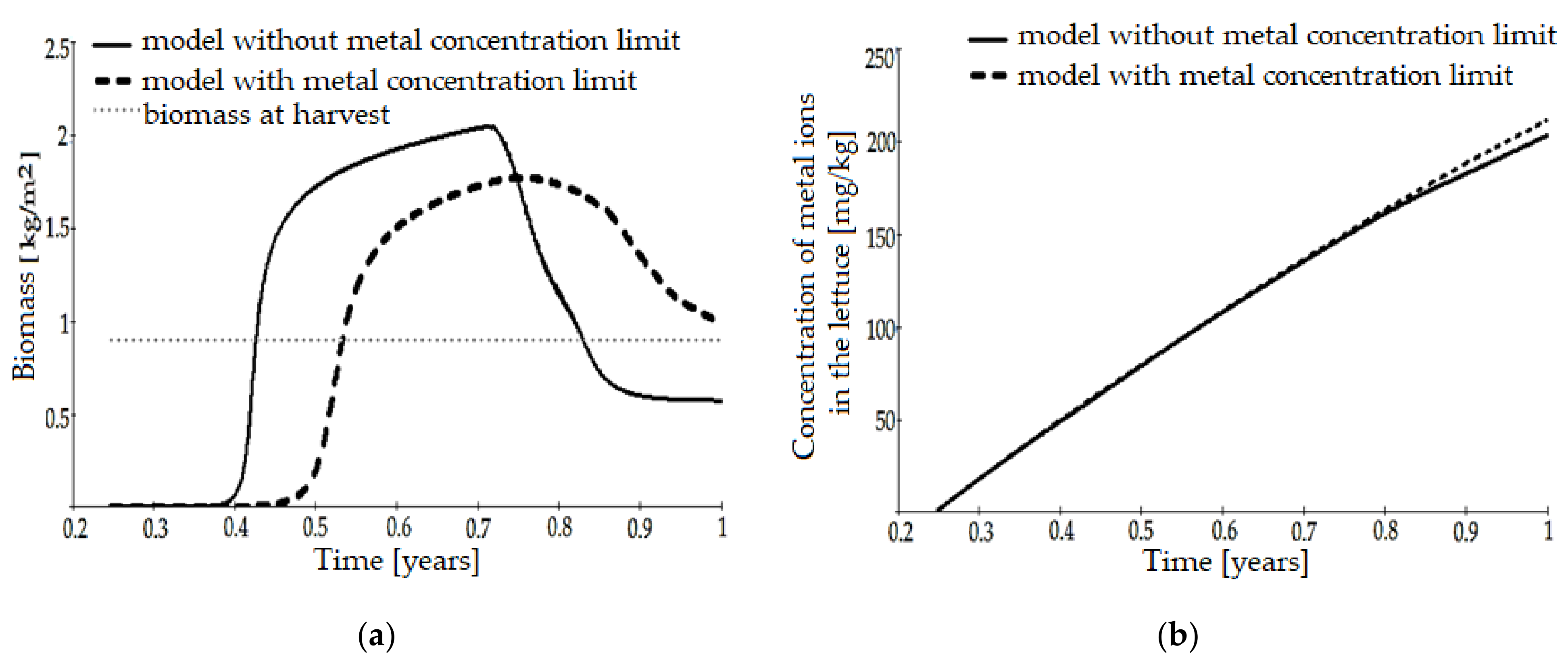
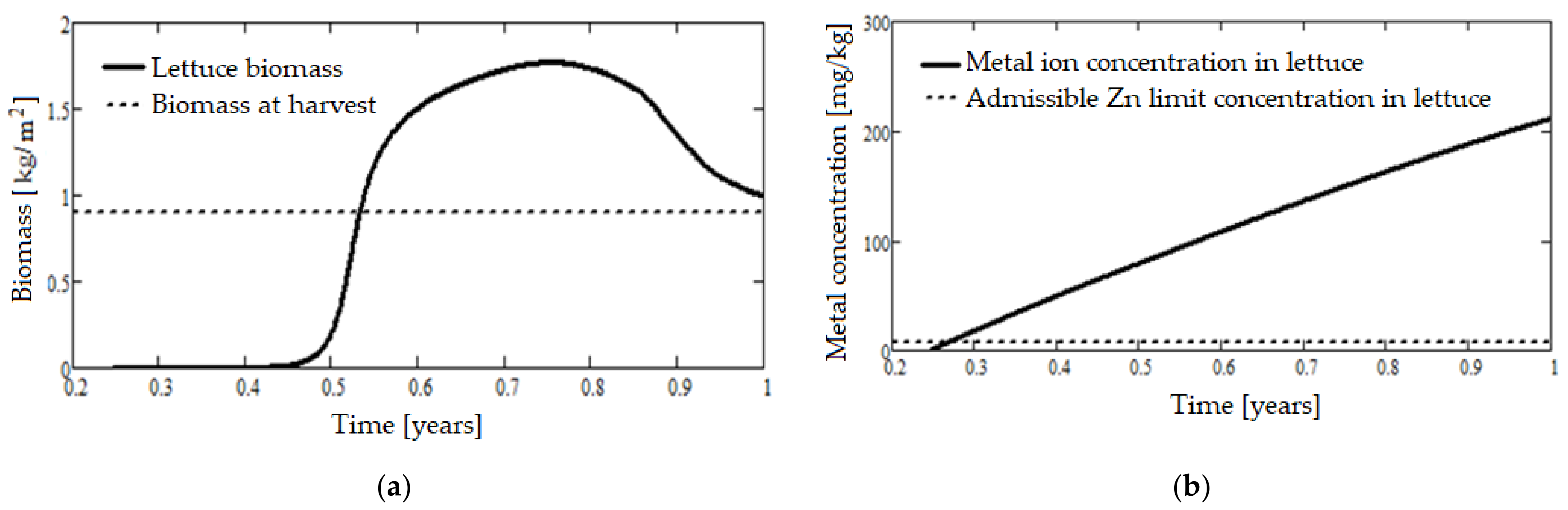

| Parameter | Notation | Measurement Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Plant biomass | PB(t) | kg·m−2 |
| Concentration of metal ions in the plant | Me(t) | mg·kg−1 |
| Concentration of metal ions in the soil | S(t) | mg·L−1 |
| Concentration of hydrogen ions in the soil | H(t) | mg·L−1 |
| Time | t | years |
| Flux of protons to the soil during rainfall | W(t) | mg·m−2·year−1 |
| Available water for roots | p(t) | mm |
| Absorption coefficient | α | L·kg−1·year−1 |
| Leakage coefficient | β | year−1 |
| Reaction coefficient | φ | year−1 |
| Net growth function | h(PB) | year−1 |
| Function of mortality or metabolic inefficiency of trees due to the concentration of metal ions in plant | μ(Me) | year−1 |
| Constant a of the model (positive) | a | year−1 |
| Constant b of the model (positive) | b | kg−1·m2 |
| Constant c of the model (positive) | c | year−1 |
| Constant f of the model (positive) | f | year−1 |
| Constant e of the model (positive) or survival limit value | e | mg·kg−1 |
| Gaussian function | G | - |
| Bump function | B | - |
| Temperature influencing factors | - | |
| Influencing factors that give the concentration of heavy metals in the plant | Ch, Cµ | - |
| Reference Time | Years | Months | Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time planting (initial) measured at the beginning of the year (January 1st) | 0.2 | 3 | 90 | ||
| The end time (end of year) | 1 | 12 | 365 | ||
| Reference Data—the Lettuce Crop | |||||
| Harvest time (estimated) | 0.4 | 5 | 156 | ||
| Production of harvested lettuce (kg·m−2) | 0.91 | ||||
| Average mass—one lettuce plant (kg) | 0.11 | ||||
| Metal concentration at harvesting in the plant (mg·kg−1) | 56.45 | ||||
| Model Constants | |||||
| α = 0.55 | β = 0.44 | a = 10 | b = 1 | ||
| Reference Times | Years | Months | Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time, initial (planting): beginning of the year (January 1) | 0.2 | 3 | 90 | ||
| Time (end of year) | 1 | 12 | 365 | ||
| Reference Data—the Lettuce Crop | |||||
| Harvest time (estimated) | 0.5 | 6 | 195 | ||
| Production of harvested lettuce (kg·m−2) | 0.9 | ||||
| Average mass—one lettuce plant (kg) | 0.11 | ||||
| Metal concentration: in the plant at harvest (mg·kg−1) | 88.77 | ||||
| Model Constants | |||||
| α = 0.55 | β = 0.44 | a = 10 | b = 1 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cârdei, P.; Tudora, C.; Vlăduț, V.; Pruteanu, M.A.; Găgeanu, I.; Cujbescu, D.; Bordean, D.-M.; Ungureanu, N.; Ipate, G.; Cristea, O.D. Mathematical Model to Simulate the Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soil to Plant. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116157
Cârdei P, Tudora C, Vlăduț V, Pruteanu MA, Găgeanu I, Cujbescu D, Bordean D-M, Ungureanu N, Ipate G, Cristea OD. Mathematical Model to Simulate the Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soil to Plant. Sustainability. 2021; 13(11):6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116157
Chicago/Turabian StyleCârdei, Petru, Cătălina Tudora, Valentin Vlăduț, Mirabela Augustina Pruteanu, Iuliana Găgeanu, Dan Cujbescu, Despina-Maria Bordean, Nicoleta Ungureanu, George Ipate, and Oana Diana Cristea. 2021. "Mathematical Model to Simulate the Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soil to Plant" Sustainability 13, no. 11: 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116157
APA StyleCârdei, P., Tudora, C., Vlăduț, V., Pruteanu, M. A., Găgeanu, I., Cujbescu, D., Bordean, D.-M., Ungureanu, N., Ipate, G., & Cristea, O. D. (2021). Mathematical Model to Simulate the Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soil to Plant. Sustainability, 13(11), 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116157








