Abstract
With the development of economy and the improvement of people’s living standard, landfill leachate has been increasing year by year with the increase in municipal solid waste output. How to treat landfill leachate with high efficiency and low consumption has become a major problem, because of its high ammonia nitrogen and organic matter content, low carbon to nitrogen ratio and difficult degradation. In order to provide reference for future engineering application of landfill leachate treatment, this paper mainly reviews the biological treatment methods of landfill leachate, which focuses on the comparison of nitrogen removal processes combined with microorganisms, the biological nitrogen removal methods combined with ecology and the technology of direct application of microorganisms. In addition, the mechanism of biological nitrogen removal of landfill leachate and the factors affecting the microbial activity during the nitrogen removal process are also described. It is concluded that the treatment processes combined with microorganisms have higher nitrogen removal efficiency compared with the direct application of microorganisms. For example, the nitrogen removal efficiency of the combined process based on anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) technology can reach more than 99%. Therefore, the treatment processes combined with microorganisms in the future engineering application of nitrogen removal in landfill leachate should be paid more attention to, and the efficiency of nitrogen removal should be improved from the aspects of microorganisms by considering factors affecting its activity.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, the output of municipal solid waste has been increasing year by year with the acceleration of urbanization, the changes of lifestyle and the growth of population [1,2,3]. According to the statistics of China Statistical Yearbook (2009–2018), the annual output of municipal solid waste reached 22.818 billion tons. Therefore, solid waste treatment has become an important part of urban management. Many cities will face the phenomenon of “garbage siege” if it is not properly handled [4].
There are several ways to treat municipal solid waste, such as thermochemical treatment and biological treatment [5,6]. At present, landfill and incineration are the main treatment technology for municipal solid waste in China [7]. It is reported that there are a total of 1091 municipal solid waste treatment sites in China, including 994 waste incinerators and landfills [8]. However, a secondary pollutant, landfill leachate, is inevitably produced in the process of incineration and landfill disposal [9,10,11]. Landfill leachate is a kind of high-concentration organic wastewater [12], which contains a variety of organic and inorganic pollutants [13,14], such as humus, heavy metals, inorganic salts, ammonia nitrogen and so on [8]. High ammonia nitrogen content is a typical feature of mature landfill leachate, and ammonia nitrogen content generally does not decrease with the increase in landfill age [15]. It is easy for landfill leachate coupled with the high content of organic matter to cause surface water and groundwater pollution. Therefore, improper disposal of landfill leachate leads to a series of serious environmental contamination.
The treatments of landfill leachate are generally divided into physical–chemical method and biological method [16]. However, the physical–chemical method has high cost and is prone to causing secondary pollution [17]. In compost, biological treatment is widely used for nitrogen removal of leachate due to its low cost [18,19], such as the traditional nitrification/denitrification process, the new ANAMMOX nitrogen removal process, the new enhanced biological nitrogen removal process using dominant bacteria [20] and the nitrogen removal in leachate by constructing artificial wetland in ecological engineering [21]. However, it is very important for the landfill leachate treatment to select the reasonable process of nitrogen removal due to the different properties of leachate.
Therefore, this paper reviews the biological treatment of leachate from municipal solid waste. The focus is on nitrogen removal process, mechanism, various other nitrogen removal methods combined with microorganisms and the factors affecting microbial activity during the process. The purpose of this review is to provide necessary information for the rational selection of nitrogen removal treatment process for leachate from municipal solid waste.
2. Methods and Techniques of Biological Nitrogen Removal from Landfill Leachate
2.1. Biological Nitrogen Removal Processes and Reactors of Landfill Leachate
Biological treatment has been considered as one of the most favorable nitrogen removal technologies for mature landfill leachate [19], which involves nitrification in aerobic reactor and denitrification in anoxic reactor. The traditional biological treatment process of landfill leachate usually includes two stages: nitrification and denitrification. However, the traditional approach requires a large amount of oxygen in the nitrification process and a large number of carbon sources in the denitrification process [22]; therefore, the operation cost is relatively high [23]. At present, a new process of nitrogen removal of landfill leachate, which is a traditional process combined with an ANAMMOX process, is commonly used in the reactor [24]. This new process has the advantages of high nitrogen removal capacity [25,26], low energy consumption and low sludge yield, and it does not need additional carbon sources during operation [27,28]. Most of the processes used in the reactor can be divided into the following categories: the combination process of nitrification and denitrification, the combination process of partial nitrification, nitrosation, denitrification and ANAMMOX, biofilm treatment process based on ANAMMOX and membrane bioreactor, etc. Table 1 shows the types of different processes and reactors, the sources and basic characteristics of leachate, the efficiency of nitrogen removal, and the microorganisms and dominant strains involved in the process of nitrogen removal.

Table 1.
The efficiency of nitrogen removal and dominant microbial strains in different processes and reactors.
In general, the efficiency of nitrogen removal is not high in a simple process, and a variety of processes is needed to coordinate to improve the efficiency of nitrogen removal. At the same time, the appropriate process should be selected to improve its efficiency according to the different properties of landfill leachate. When the COD concentration in the leachate reaches above 10,000 mg/L, the leachate is young leachate (landfill time is less than 5 years); when the COD concentration reaches between 4000 and 10,000 mg/L, the leachate is intermediate leachate (landfill time is between 5–10 years); when the COD concentration reaches less than 4000 mg/L, the leachate is old leachate (landfill time is larger than 10 years) [47]. The problem of carbon source should be solved in the process of denitrification due to the low C/N ratio of the aged leachate. According to Table 1, partial nitrification and integrated fermentation–denitrification (PNIFD) system, modified sequencing batch reactor (SBR), the combination process of traditional process and ANAMMOX (PN/A, PD/A, SNAD and PNA) and dynamic membrane bioreactor (DMBR) are the main bioreactors for nitrogen removal of aging leachate at present. These processes can solve the problem of carbon source shortage in the traditional denitrification process well. In addition, the organic matter can be first converted to CO2 or CH4 by an improved SBR reactor or a membrane bioreactor for biological nitrogen removal of leachate since the COD concentration of the intermediate and young leachate can reach about 10,000 mg/L.
Among them, the combined process based on ANAMMOX has a higher efficiency of nitrogen removal in the biological treatment for landfill leachate. It is a biological process in which Anammox microorganisms use nitrite nitrogen as an electron acceptor to react with ammonia nitrogen to generate nitrogen and then remove it under anaerobic or anoxic conditions [27,48]. Many microorganisms will participate in it, mainly taking anaerobic ammoxidation autotrophic bacteria as the core [24]. Therefore, the combined process based on ANAMMOX has great development prospects in the biological treatment for landfill leachate in the future. In addition, more attention should be paid to the dynamic changes of microbial strains to improve the efficiency of nitrogen removal from the perspective of microorganisms.
2.2. Biological Nitrogen Removal Methods Combined with Ecology
2.2.1. Algae-Bacteria Combined System
It is also a promising treatment method to use microalgae to treat landfill leachate [49,50], which has good nutrient recovery capabilities and additional benefits of bio-lipid production [51]. Microalgae are single-celled photosynthetic microorganisms living in marine or freshwater ecosystems. They can convert solar energy, nutrients and carbon dioxide into biomass and biofuels [52]. Various studies have also shown that the cultivation of microalgae may have high potential as a commercial and environment-friendly energy source [53,54,55]. At the same time, microalgae can absorb a large amount of inorganic nitrogen, such as ammonium [54], which can reduce the nitrogen content in pollutants; therefore, it can be used to remove nitrogen from landfill leachate [50,56,57]. Wu et al. introduced anaerobic digestion as the ammonization pretreatment of the leachate from food waste before the subsequent microalgae treatment. The concentrations of COD and TN in this leachate from food waste are about 12,000 and 552 mg/L, respectively, and the pH value is 5.53, meaning it is a kind of young leachate. It significantly improved the performance of the subsequent microalgae treatment compared with the single microalgae treatment. D. tertiolecta could remove 98.99% of total nitrogen and 65% of total phosphorus, while C. aponinum could remove 80% of total nitrogen and more than 65% of total phosphorus [58]. Nguyen et al. also found that leachate can be treated at an appropriate dilution with simultaneous electricity generation in algae cathode MFC [59]. Previous studies have shown that removal of ammonia nitrogen by microalgal assimilation can remove 65–85% of nitrogen from leachate during growth and deposition of organic nitrogen in a stabilizer tank [60]. In addition, compared with the single treatment of microalgae, the coexistence of microalgae and bacteria in the photo-bioreactor can obviously improve the efficiency of nitrogen removal of landfill leachate [55,56,61]. Tighiri and Erkurt et al. evaluated the efficiency of biological treatment of landfill leachate, combined microalgae with bacteria and observed that the symbiotic relationship between microalgae and bacteria in the leachate did not restrict the growth of the culture. In both batches, the concentrations of COD and TN in leachate are about 10,000 and 3800 mg/L, respectively; ammonia nitrogen was completely removed from the leachate; and the second batch removed nitrate over 90% [61]. Zhao et al. also found that the combination of microalgae and bacteria was effective in the treatment of landfill leachate. The removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in landfill leachate was up to 95% and 90% under the culture condition with the total nitrogen concentration of 221.6 mg/L and the peak ratio of leachate of 10% [56]. Chang et al. used a membrane photo-bioreactor (M-PBR) to increase the concentration of microalgae biomass from 0.66 in the traditional photo-bioreactor (T-PBR) to 0.95 g/L. M-PBR was significantly higher than T-PBR in terms of the recovery efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus [51]. Sniffen et al. studied a remediation system for the removal of nitrogen from a young landfill leachate in which COD concentration is more than 10,000 mg/L by a mixed algae–bacteria culture. The results showed that the maximum efficiency of nitrogen removal was 9.18 mg N/(L day), and the maximum biomass density was 480 mg biomass/L. The efficiency of ammonia nitrogen removal increased with the increase in initial ammonia concentration. The maximum nitrogen removal occurred when the ammonia concentration was 80 mg N-NH3/L [55]. Xu et al. used cultures of Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus obliquus, Spirulina platensis, and aerobic activated sludge in raw municipal wastewater, whose results showed that the highest total nitrogen removal efficiency was 2.34 d−1 during summer and autumn with aeration [62]. Sniffen et al. found the accumulation of nitrite and nitrate within the algal–bacterial leachate treatment system was attributed to high relative abundances of ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria [63]. What is more, studies have shown that the high diversity of microalgae has higher nitrogen removal efficiency from landfill leachate compared with single culture [64]. Martins et al. showed that the mixed microalgae strains dominated by chlamydia had a nitrogen removal efficiency of 75–99% in the treatment of landfill leachate [60]. Martins et al. screened five kinds of microalgae mixed with natural algae to treat landfill leachate, and the removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen was 99.9% [65].
In summary, it would be ideal to use algae as the main biological component of the young landfill leachate treatment system, because the natural growth of algae requires nitrogen and phosphorus. Besides, ammonia is the preferred nitrogen source for many types of algae, and the concentration of COD is high in some young landfill leachate. The use of existing waste sources, such as landfill leachate, as the growth medium for algae, not only reduces the current costs of disposing of these wastes in landfills but also facilitates the development of the algal biomass production industries.
2.2.2. Constructed Wetlands
The cost of using physical, chemical and biological methods to treat landfill leachate is high, while land or natural systems are of low price in developing countries. They have certain economic benefits and are another important way to treat landfill leachate, such as waste stabilization ponds and constructed wetlands [66]. Among them, constructed wetlands (CWs) are engineering systems that use wetland vegetation, soil and related microorganisms to treat nitrogen-rich wastewater. The mechanism of nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands includes volatilization, nitrification, denitrification, anaerobic ammonia oxidation, plant absorption, nitrogen fixation and substrate adsorption [67]. Sawaittayothin and Polprasert et al. showed that a constructed wetland unit with a hydraulic retention time of 8 d had the highest efficiency in treating high nitrogen and high bacterial content of sanitary landfill leachate (COD = 1820–4100 mg/L, TKN = 140–1260 mg/L) under tropical conditions (temperature is about 30 °C), and the TN removal efficiency could reach 96%. In addition, 88% of the total nitrogen input was absorbed by plant biomass based on the mass balance analysis of the total nitrogen content, plant biomass, dissolved oxygen and redox potential value [21]. Tanveer Saeed et al. co-treated landfill leachate and municipal by a three parallel two-stage Phragmites- or Vetiver-based constructed wetland mesocosms and found that second-stage wetland mesocosms achieved higher nitrogen removal (85–92%) [68]. Their research identified the factors associated with organics and nutrients removal performance based on four hybrid wetland systems dosed with landfill leachate, whose nitrogen removal percentage ranged between 50% and 93% [69]. The research of Bialowiec showed that the final total nitrogen, nitrate and chemical oxygen demand of reed ponds and willow ponds were significantly lower than those of unplanted ponds on the nitrogen removal of landfill leachate from reed and willow constructed wetlands. These might be achieved through plant absorption and the effects of increased oxygen and organic carbon levels in the rhizosphere soil on nitrification and denitrification [70]. However, Ye et al. reviewed that the nitrogen removal efficiency of the constructed wetland treatment system based on ANAMMOX was lower and more unstable than that of the conventional nitrogen removal process because of its inhibitory effect of organic matter and high-strength nitrogen on Anammox bacteria. Therefore, the constructed wetland treatment system based on ANAMMOX could be used to treat the low-intensity wastewater from the traditional leachate treatment process [71].
2.2.3. Aquatic Plant
Aquatic plants (helophytes), such as bryophytes, can absorb inorganic compounds to meet their own nutritional needs [72,73]; therefore, they can be used in all kinds of wastewater treatment systems. Among them, high-quality DOM is released mainly through the leachate of plant leaf litter [74,75], which enhances the removal of nitrogen and promotes the heterotrophic activity of the microbial combinations [76]. Ribot et al. tested the effects of iris and reed leaf litter leachate on the structure and activity of freshwater biofilm grown in flumes fed by effluent from a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) and found that all DOM sources significantly enhanced the aerobic respiration and denitrification of biofilm, and increased the total abundance of microorganisms, thus improving the absorption of N and C by microorganisms [77]. Therefore, many Helophytes can be included in the bioengineering treatment of landfill leachate system to increase the cooperative nitrogen removal pathway.
2.3. Biological Nitrogen Removal in Conjunction with Other Solid Organic Wastes
According to the reactor processes reviewed above, the combined processes of nitrification, denitrification and ANAMMOX are commonly used to treat mature landfill leachate. However, the low COD/TN ratio (C/N < 3) strongly inhibits the denitrification process due to the severe lack of organic carbon sources as electron donors [78]. Therefore, the addition of external carbon sources is generally considered as a necessary condition for effective nitrogen removal [79]. However, traditional carbon sources, such as methanol [80], glycerol [80,81], peptone [82] and so on [83,84,85,86,87], are too costly, which limits their feasibility [88]. At present, organic solid wastes such as activated sludge [89,90] and food waste [91,92,93] can be regarded as a promising carbon source due to their high organic matter content. Yan et al. fermented the de-oiled food waste and the oily food waste and applied it as an external carbon source in the aerobic/anoxic membrane bioreactor for biological nitrogen removal of old landfill leachate. Finally, the effluent could meet the general emission standards of total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen in China and the stricter emission standards in some special areas [94]. Kaczorek and Ledakowicz et al. used sodium acetate as external carbon source in a double-sludge sequential intermittent reactor system to remove nitrogen from landfill leachate, which the concentrations of COD and TN in leachate are about 2480–4850 mg/L and 1950–2450 mg/L, respectively and the pH value is 7.5–7.86. This reactor system could remove 99% of inorganic nitrogen compounds [95]. Zhang et al. added activated sludge to the old landfill leachate and developed an innovative process (PN-SBR and IFD-SBR) to improve the nitrogen removal capacity of the mature landfill leachate with low carbon/nitrogen (1:1). Finally, it reduced the nitrogen content in the landfill leachate. Moreover, the total nitrogen removal efficiency was 95.0%, and the average nitrogen removal rate (NRR) was 0.63 kg/m3 d in the final operation stage [29]. Xie et al. also found the technical viability of a bioreactor packed with a mixture of slag and aged refuse at a v/v ratio of 2:1 for landfill leachate pollutant removal [96]. In general, it is beneficial for nitrogen removal and can also save costs to add activated sludge, food waste and other solid organic waste as external carbon sources in the old landfill leachate treatment process. However, in order to avoid introducing a large amount of nitrogen into the treatment system to increase its burden, organic solid wastes with high C/N ratio should be selected as far as possible since these organic wastes also contain nitrogen. For example, acid-producing liquid derived from activated sludge [97] or food waste [85] can be used as an external carbon source to accelerate the denitrification process [84,85]. In addition, it is relatively easy to produce high-quality carbon sources for denitrification and the cycle time is short by controlling only the hydrolysis and acidification of anaerobic fermentation [98]. Tang et al. used fermentation liquid of food waste (FLFW) as an external carbon source to treat domestic wastewater with low COD/TN ratio in a pilot-scale anoxic-/oxic-membrane bioreactor (A/O-MBR) system. The results showed that the total nitrogen removal increased from less than 20% to 44–67% over 150 days of operation with the addition of FLFW [99].
2.4. Microbiological Processes for Direct Nitrogen Removal of Leachate
Nitrogen removal of landfill leachate is inseparable from the role of microorganisms including aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria (AnAOB), nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB), heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria and so on. Some processes improve the efficiency of nitrogen removal by inoculation with some strong denitrifying bacteria. Some processes can be used to find and screen out some efficient nitrogen-free bacteria. Other processes use bacteria-loaded materials to improve nitrogen removal performance. Several microbiological processes for direct nitrogen removal of leachate are shown below.
2.4.1. To Find, Screen and Isolate Highly Effective Bacteria from the Process
Generally, nitrification and denitrification are used to remove nitrogen from leachate. However, the nitrogen removal efficiency is limited by their different conditions. The discovery of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification (HN-AD) effectively solved the above problems. Acinetobacter tandoii MZ-5, which is capable of HN-AD, was isolated from the sediment of a polluted river for the first time. It used NH4+-N, NO2−-N and NO3−-N as sole nitrogen sources with maximum removal rates of 2.28, 1.18 and 1.04 mg L−1 h−1, respectively. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification were observed when using mixed N sources, and NH4+-N was preferentially utilized. High nitrogen removal efficiencies (>90%) were achieved under the following conditions: C/N ratio 11–18, pH 6–8, 25–30 °C and dissolved oxygen 7.35–7.66 mg L−1 [20]. Three novel strains capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification were isolated from the landfill leachate treatment system, which were Agrobacterium sp. LAD9, Achromobacter sp. GAD3 and Comamonas sp. GAD4. The maximum aerobic nitrification-denitrification rate was achieved by the strain GAD4 followed by LAD9 and GAD3 [100]. Chen and Ni et al. also newly isolated Agrobacterium sp. LAD9 with heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification capability for nitrogen removal [101]. In addition, other bacteria can be screened to improve the efficiency of nitrogen removal. Yang et al. screened out AOB with efficient and stable ammonia-nitrogen removal capability through various methods [102]. Feng et al. isolated mixed Marine bacterial for ammonia-removal nitrogen from Marine sediments [103]. Wei found that Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria and Firmicutes were the dominant phyla in the Anammox-denitrification biomass [104]. Therefore, efficient bacteria can be screened and isolated from the processes, and their nitrogen removal performance can be enhanced through domestication, which is more conducive to the improvement of nitrogen removal efficiency.
2.4.2. To Cultivate and Inoculate Efficient Bacteria
Cultivation or direct inoculation of bacteria with high nitrogen removal capacity in the reactor is also an approach to improve the system’s nitrogen removal capacity. Isaka et al. cultured nitrifying bacteria with high nitrification rate in a polyethylene glycol PEG gel carrier at 10 °C for more than 1 year, and Nitrosomonas sp. was the dominant ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in the gel carrier at low temperature [105]. Dadrasnia developed a novel resident strain microbe that can survive in high ammonia nitrogen concentrations. Bacillus salmalaya strain 139SI, which removed 78% of ammonia nitrogen when the concentrations of NH4+-N in leachate, are about 2000 mg/L [106]. He et al. nitrified the landfill leachate under the conditions of pH 7.5–8.5 and DO 0.5–2.0 mg/L in a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) by inoculating the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) AHAA-4, and the ammonia removal was over 95% [107].
2.4.3. Microbial and Photocatalytic Processes
The use of photocatalysts to improve the biodegradability and treatability of leachate has attracted much attention in recent years. Hu et al. proposed to use immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium loaded with nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles to treat raw landfill leachate with a very low biodegradability ratio (BOD5/COD) of 0.09. The most superior removal efficiencies of NH4+-N of landfill leachate were over 74% in 72 h at an initial COD concentration of 200 mg L−1 [108]. Hassan et al. used advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) by heterogeneous photocatalysis (TiO2/UV) and persulfate (S2O82−) oxidation to test the effectiveness of anoxic aged refuse-based bioreactor (ARB) for biological leachate pretreatment, which degraded 81% and 92% NH4+-N and TN, respectively [109]. Yasmin et al. found a new landfill leachate pre-treatment by photocatalytic TiO2/Ag nanocomposite prior to fermentation using Candida tropicalis strain, and the degradation rate of NH4+-N achieved 75% when used to treat young leachate with COD and NH4+-N concentrations of about 24,000 and 346 mg/L and pH of 7.3, respectively [110]. However, the efficiency of photocatalytic processes combined with microorganisms is generally not high compared to biological nitrogen removal processes.
2.4.4. Microbial Fuel Cell
Microbial fuel cells are devices that use microorganisms as catalysts to convert chemical energy in compounds into electrical energy. Microbial fuel cells are also a newly developed method for nitrogen removal from leachate in recent years. The high concentration of organic carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in landfill leachate limited its treatment. Therefore, the possibility of converting leachate into a new energy source by microbial fuel cells is still inadequate [111]. Cai et al. studied the supercapacitor microbial fuel cell, whose bioanode was dominated by salt-tolerant denitrifying bacteria (38.5%), and 78.2% of ammonia nitrogen was removed [112]. Hassan et al. utilized different landfill leachate substrate to remove pollutants. In total, 66.0 ± 3.3% NH4+-N and 86.0 ± 0.1% NO2-N were removed [113]. In general, although the nitrogen removal efficiency of microbial fuel cells is not high at present, it still has demonstrated the potential for wastewater treatment along with energy harvesting and provides a new avenue toward sustainable leachate management. In future studies, the focus can be on improving the nitrogen removal performance.
3. Mechanism of Nitrogen Removal and Factors of Microbial Activity on Nitrogen Removal Efficiency
The biological mechanism of nitrogen removal is the joint action of ammoniation, nitrification, denitrification and anammoxidation. (Figure 1) Real-time PCR studies revealed that landfill leachate harbored diverse nitrogen-converting microbial communities that include ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, Anammox bacteria, ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and so on [114]. The activities of these microbial populations had a significant effect on the efficiency of nitrogen removal. Therefore, the efficiency of nitrogen removal can be enhanced by improving the activity of related microorganisms. Several factors influencing microbial activity are listed below, including the concentration of nitrite, free ammonia (FA), free nitrous acid (FNA) in leachate, carbon source in leachate, microbial activity, contact time between microorganism and leachate; temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen (DO), biodegradable carbon and oxygen content, electric potential (EP) and so on.
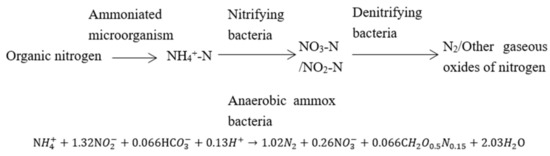
Figure 1.
Biological nitrogen removal mechanism.
3.1. Influences of Content of Nitrite, Free Ammonia (Fa) and Free Nitrous Acid (Fna) in Leachate
Both Anammox bacteria and heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria require the consumption of nitrites. Excessive nitrite content in the inlet water of ANAMMOX would accumulate in the reactor, and a lower nitrite supply could force a loss of specific Anammox bacteria activity due to the nitrite competition with denitrifying bacteria [115]. Spagni et al. thought that the high concentration of free ammonia (FA) in the leachate might inhibit microbial activity [116]. Tian et al. found that AOB (ammonium oxidation bacteria) had a great ability to adapt to abroad FA and FNA concentration, whereas NOB (nitrite-oxidizing bacteria) were inhibited by either FA or FNA concentration to a certain extent [117].
3.2. Influences of Carbon Source in Leachate
The nitrogen removal process in biological denitrification requires carbon sources, but the effect of different types of carbon source on the nitrogen removal performance of landfill leachate is unclear. Glycogen accumulating organisms (GAOs) capable of storing organic compounds as poly-hydroxyalkanoate (PHA) have been used for endogenous denitrification (ED). With acetate, propionate and glucose examined as the carbon sources, their effects on yields and compositions of PHA produced by GAOs were determined and associated with nitrogen removal performance. In addition, Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum. Among the 108 genera detected in this ED system, the genera responsible for denitritation were Thauera, Paracoccus, Ottowia and Comamonadaceae_unclassification, accounting for 46.21% of total bacteria. Especially, Paracoccus and Comamonadaceae_unclassification transformed the carbon source into PHA for denitrification, and carried out endogenous denitrification [83]. A novel system coupling an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (ASBR) and sequencing batch reactor (SBR) was proposed without the addition of external carbon sources. The removal efficiency of total nitrogen (TN) was above 95% [118]. Du et al. studied the sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) with different carbon sources for partial-denitrification: acetate (R1) and ethanol (R2) and found Thauera genera were dominant in both SBRs. Different Anammox species were detected with Candidatus Brocadia and Candidatus Kuenerda in R1 and only Candidatus Kuenenia in R2 [119]. In general, the addition of carbon sources and different carbon sources has a significant impact on the dominant strains of microorganisms in the nitrogen removal process. Therefore, the influence of external carbon sources and their types should be considered in the subsequent process selection.
3.3. Influences of Microbial Activity, Contact Time between Microorganism and Leachate
Recent studies have shown that other processes of anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) also play a role in nitrogen removal of biological systems, the dominant bacteria was Kuenenia stuttgartiensis genome fragment KUST_E and the uncultured Crenarchaeota clone NJYPZT_C1, respectively [120]. The experimental results of Panter showed that the removal efficiency of nitrate and nitrite was highest when the contact time was 16–24 h, and the degradation efficiency was very low when the contact time was below 8 h [121].
3.4. Influences of Salinity, Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Biodegradable Carbon and Oxygen Content, Electric Potential (EP) and So on
Increased salinity might decrease microbial activity, resulting in the increase in N2O production. However, the system would gradually adapt to the environment of high salinity under the impact of high salinity, and high salinity enhanced the effect of high ammonia nitrogen concentration and low DO concentration on N2O yield. The relative proportion of Nitrosomonas europaea increased with the increase in salinity, and thus the efficiency of nitrogen removal was improved [122]. Temperature affected AOB activity during the treatment of landfill leachate with high nitrogen concentration by partial nitration SBR process, which was achieved by inhibition of free ammonia (FA) and free nitrite (FNA) [123]. The ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency was positively correlated with DO concentration, and TN removal efficiency reached over 90% at the optimal DO concentration of 2.7 mg/L in the single-stage nitrogen removal using Anammox and partial nitritation (SNAP) system [124]. The diversity of microbial community in the landfill bioreactor would be significantly affected with the increase in biodegradable carbon and oxygen content, increasing the internal denitrification capacity of the whole system from 50% to 70%. Redundancy analysis (RDA) suggested that only biodegradable carbon content was the determinant of total nitrogen removal efficiency, although both oxygen and biodegradable carbon affected the microbial community structure [125]. Electric potential (EP) could also promote the removal of organic matter in the ANAMMOX process, and the removal efficiency of total nitrogen reached 71.9% at the optimal EP of 0.06 V. High-throughput DNA sequencing revealed that Anammox bacteria in the genus Candidatus Kuenenia were enriched for on electrodes with the applied EP. Heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria had the potential to degrade organic macromolecules, which were more abundant on the electrodes with EP compared with the control reactor [126].
In conclusion, the microbial activity in the nitrogen removal process is affected by various factors. Therefore, factors such as the composition of leachate, the nature of microorganisms and environmental conditions should be taken into account comprehensively to improve the activity of microorganisms so as to achieve efficient nitrogen removal when selecting the technology of nitrogen removal of landfill leachate.
4. Conclusions
At present, if the age of the landfill is more than 5 years, even 10 years, the high-efficiency process of nitrogen removal is mainly combined with ANAMMOX for this intermediate or old leachate with a very low biodegradability ratio (BOD5/COD) of less than 0.3, because it can better solve the problem of carbon source shortage in the process of denitrification. For example, partial nitrification, ANAMMOX, and denitrification (SNAD) process achieved a nitrogen removal efficiency of 98.9–99.9%. Therefore, the combined process based on ANAMMOX has a great prospect in biological treatment of landfill leachate in the future. On the other hand, if the age of the landfill is less than 5 years, for this young leachate with a high biodegradability ratio (BOD5/COD) of more than 0.3 and COD concentration more than 10,000 mg/L, microbial fuel cells or constructed wetlands can be used to remove nitrogen in leachate through microbial transformation and ecological transformation. In addition, in order to improve the nitrogen removal efficiency from the microbial perspective, it is necessary to pay attention to the dynamic changes of the microbial community and create appropriate conditions of salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), biodegradable carbon and oxygen content, electric potential (EP) and so on. At the same time, the technology combined with ecology is also an efficient nitrogen removal method, in which the algal–bacterial combined system has an ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency of 95%. From the point of view of the direct application of microbial for nitrogen removal, the efficiency of nitrogen removal entirely dependent on microbial is not high (about 80%), because there are too many influencing factors. Considering the economic feasibility of microbial treatment, the subsequent research can focus on the screening of efficient bacteria or bacterial modification, and selecting economical and efficient nitrogen removal technology according to the properties of leachate in practical projects.
Author Contributions
Y.L., F.T., and D.X.: investigation, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. B.X.: project administration, work designing, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1901000), Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Biotransformation of Organic Solid Waste (19DZ2254400), State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse Foundation (PCRRF17001), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ouda, O.K.M.; Raza, S.A.; Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Al-Waked, R.; Korres, N.E. Waste to energy potential: A case study of Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, P.L.; Pal, P.; Leong, H.Y.; Juan, J.C.; Ling, T.C. A review on the advanced leachate treatment technologies and their performance comparison: An opportunity to keep the environment safe. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.X.; Mu, Y.J.; Cheng, X.; Sun, D.Z. Treatment of fresh leachate with high-strength organics and calcium from municipal solid waste incineration plant using UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5498–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yan, D.Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, L.H. A review of the challenges and application of public-private partnership model in Chinese garbage disposal industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmans, A.; Vanderreydt, I.; Geysen, D.; Helsen, L. The crucial role of Waste-to-Energy technologies in enhanced landfill mining: A technology review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Z.; Yin, L.J.; Wang, H.; He, P.J. Pyrolysis technologies for municipal solid waste: A review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2466–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Ye, B.; De Costa, Y.G.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Yi, S.; Yang, S.F.; Xia, S.Q. Inorganic characteristics of cake layer in A/O MBR for anaerobically digested leachate from municipal solid waste incineration plant with MAP pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Chen, W.M.; Gu, Z.P.; Li, Q.B. A review of the characteristics of Fenton and ozonation systems in landfill leachate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.M.; Li, Q.B. Elimination of UV-quenching substances from MBR- and SAARB-treated mature landfill leachates in an ozonation process: A comparative study. Chemosphere 2020, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.Z.; Tran, N.H.; Yin, T.R.; He, Y.L.; Gin, K.Y.H. Removal of selected PPCPs, EDCs, and antibiotic resistance genes in landfill leachate by a full-scale constructed wetlands system. Water Res. 2017, 121, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propp, V.R.; De Silva, A.O.; Spencer, C.; Brown, S.J.; Catingan, S.D.; Smith, J.E.; Roy, J.W. Organic contaminants of emerging concern in leachate of historic municipal landfills. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.J.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, C.A.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W. A sequential treatment of intermediate tropical landfill leachate using a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) and coagulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; Miao, L.; Cao, T.H.; Zhang, F.Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Han, J.H. Continuous-flow combined process of nitritation and ANAMMOX for treatment of landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. Efficient step-feed partial nitrification, simultaneous Anammox and denitrification (SPNAD) equipped with real-time control parameters treating raw mature landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yang, G.Q.; Tao, T.; Peng, Y.Z. Recent advances in nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using biological treatments—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthi, T.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T.; Nidheesh, P.V. Stabilized landfill leachate treatment using heterogeneous Fenton and electro-Fenton processes. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, J.P.Y.; Kettunen, R.H.; Sormunen, K.M.; Rintala, J.A. Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate: Low-cost nitrification in biofilters and laboratory scale in-situ denitrification. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4079–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Zhou, S.Q. The biological treatment of landfill leachate using a simultaneous aerobic and anaerobic (SAA) bio-reactor system. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wang, K.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wong, M.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Chen, H.R.; Yang, X.W.; Li, S.F. A study on the nitrogen removal efficacy of bacterium Acinetobacter tandoii MZ-5 from a contaminated river of Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaittayothin, V.; Polprasert, C. Nitrogen mass balance and microbial analysis of constructed wetlands treating municipal landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, S.M.; Brazil, B.; Novak, J.T.; He, Z. Resource recovery from landfill leachate using bioelectrochemical systems: Opportunities, challenges, and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Shi, L.; Gu, Y.Y. Three-stage aged refuse biofilter for the treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Lin, J.G. Co-existence of anammox and denitrification for simultaneous nitrogen and carbon removal-Strategies and issues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Graaf, A.A.; de Bruijn, P.; Robertson, L.A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Kuenen, J.G. Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 1996, 142, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Z.X.; Rhee, S.K.; Zuo, J.E.; Yang, Y.; Bae, J.W.; Park, J.R.; Lee, S.T.; Park, Y.H. Diversity of ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a granular sludge anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) reactor. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamchoi, N.; Nitisoravut, S.; Schmidt, J.E. Inactivation of ANAMMOX communities under concurrent operation of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) and denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3331–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliekers, A.O.; Derwort, N.; Campos-Gomez, J.L.; Strous, M.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. High-efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate and waste activated sludge (WAS) reduction via partial nitrification and integrated fermentation-denitritation process (PNIFD). Water Res. 2019, 160, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Sun, B.; Li, Q.; Deng, X.Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, W.X. Pilot-scale nitrogen removal from leachate by ex situ nitrification and in situ denitrification in a landfill bioreactor. Chemosphere 2014, 101, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, B.K.; Cao, T.H.; Xue, T.L.; Peng, Y.Z. Advanced nitrogen removal via nitrite using stored polymers in a modified sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.W.; Peng, Y.Z.; Shi, X.N. Advanced treatment of landfill leachate using anaerobic-aerobic process: Organic removal by simultaneous denitritation and methanogenesis and nitrogen removal via nitrite. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Miao, L.; Ma, B.; Peng, Y.Z. Biological nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using anaerobic-aerobic process: Denitritation via organics in raw leachate and intracellular storage polymers of microorganisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, S.; Wang, W.; Peng, Y.Z. A continuous-flow combined process based on partial nitrification-Anammox and partial denitrification-Anammox (PN/A plus PD/A) for enhanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; Miao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, B.K. A novel simultaneous partial nitrification Anammox and denitrification (SNAD) with intermittent aeration for cost-effective nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Zhou, S.Q.; Ma, W.H.; Huang, P.F.; Huang, G.T.; Qin, Y.J.; Xu, B.; Ouyang, H. Long-term performance and microbial ecology of a two-stage PN-ANAMMOX process treating mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Zhong, Z.; Deng, C.L.; Chen, Z.G.; Chen, X.K. Biological nitrogen removal via combined processes of denitrification, highly efficient partial nitritation and Anammox from mature landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29408–29421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Lin, Z.Y.; He, L.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.; He, Q. Simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process for nitrogen and refractory organic compounds removal from mature landfill leachate: Performance and metagenome-based microbial ecology. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.F.; Hu, X.L.; Zhang, C.L.; He, Q.L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhan, X. A pilot-scale study on the treatment of landfill leachate by a composite biological system under low dissolved oxygen conditions: Performance and microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Cao, T.H.; Peng, Y.Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.Y. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate via Anammox system based on Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor (SBBR): Effective protection of biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, Y.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, F.Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S. Advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate via partial nitrification-Anammox biofilm reactor (PNABR) driven by high dissolved oxygen (DO): Protection mechanism of aerobic biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmas, N.; Melidis, P.; Zerva, I.; Kristoffersen, J.B.; Nikolaki, S.; Tsiamis, G.; Ntougias, S. Dominance of candidate Saccharibacteria in a membrane bioreactor treating medium age landfill leachate: Effects of organic load on microbial communities, hydrolytic potential and extracellular polymeric substances. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Campanaro, S.; Squartini, A. Dynamic membrane bioreactor (DMBR) for the treatment of landfill leachate; bioreactor’s performance and metagenomic insights into microbial community evolution. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z.; Chen, R.; Huang, L.K.; Ma, H.M.; Mu, D.Y.; Zhao, Q.L. Microbial characteristics of landfill leachate disposed by aerobic moving bed biofilm reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Lv, Z.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.Z.; Li, X.Z. Nitrogen removal through different pathways in an aged refuse bioreactor treating mature landfill leachate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9225–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xie, B.; Han, L.; Xu, X.F. Study of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacterial community in the aged refuse bioreactor with 16S rRNA gene library technique. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Xie, B. Use of aged refuse-based bioreactor/biofilter for landfill leachate treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6543–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘anammox’) process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, W.L.; He, H.J.; Wu, S.H.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, C.P.; Zeng, G.M.; Luo, L.; Lou, W. Responses of microalgae Coelastrella sp to stress of cupric ions in treatment of anaerobically digested swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Garcia, A.; Velasquez-Orta, S.B.; Novelo, E.; Yanez-Noguez, I.; Monje-Ramirez, I.; Ledesma, M.T.O. Wastewater-leachate treatment by microalgae: Biomass, carbohydrate and lipid production. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.X.; Quan, X.J.; Zhong, N.B.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.F.; Li, G.; Cheng, Z.L.; Yang, L. High-efficiency nutrients reclamation from landfill leachate by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris in membrane photobioreactor for bio-lipid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostaric, M.; Klinar, D.; Bricelj, M.; Golob, J.; Berovic, M.; Likozar, B. Growth, lipid extraction and thermal degradation of the microalga Chlorella vulgaris. New Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Schideman, L.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.H. A synergistic combination of algal wastewater treatment and hydrothermal biofuel production maximized by nutrient and carbon recycling. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3765–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniffen, K.D.; Sales, C.M.; Olson, M.S. Nitrogen removal from raw landfill leachate by an algae-bacteria consortium. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Qiu, D.Y.; Schideman, L.; Chai, X.L.; Zhao, Y.C. Characterization of microalgae-bacteria consortium cultured in landfill leachate for carbon fixation and lipid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.E.L.; Goncalves, A.L.; Moreira, F.C.; Silva, T.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Pires, J.C.M. Nitrogen Removal from Landfill Leachate by Microalgae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.C.; Yau, Y.H.; Sze, E.T.P. Application of anaerobic bacterial ammonification pretreatment to microalgal food waste leachate cultivation and biofuel production. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.H.; Kalzarla, R.; Min, B. Algae cathode microbial fuel cells for electricity generation and nutrient removal from landfill leachate wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 29433–29442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.L.; Fernandes, H.; Costa, R.H.R. Landfill leachate treatment as measured by nitrogen transformations in stabilization ponds. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighiri, H.O.; Erkurt, E.A. Biotreatment of landfill leachate by microalgae-bacteria consortium in sequencing batch mode and product utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zou, X.; Xue, Y.; Qu, Y.; Li, Y. The impact of seasonal variations about temperature and photoperiod on the treatment of municipal wastewater by algae-bacteria system in lab-scale. Algal Res. -Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2021, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniffen, K.D.; Price, J.R.; Sales, C.M.; Olson, M.S. Influence of Scale on Biomass Growth and Nutrient Removal in an Algal Bacterial Leachate Treatment System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13344–13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Ling, T.C.; Show, P.L.; Juan, J.C.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, D.J. Cultivation in wastewaters for energy: A microalgae platform. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, E.M.; Phang, S.M.; Chu, W.L. Use of an algal consortium of five algae in the treatment of landfill leachate using the high-rate algal pond system. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshoodeh, R.; Alavi, N.; Oldham, C.; Santos, R.M.; Babaei, A.A.; Vymazal, J.; Paydary, P. Constructed wetlands for landfill leachate treatment: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C. Role of plant uptake on nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands located in the tropics. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Miah, M.J.; Majed, N.; Hasan, M.; Khan, T. Pollutant removal from landfill leachate employing two-stage constructed wetland mesocosms: Co-treatment with municipal sewage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28316–28332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Miah, M.J.; Majed, N.; Alam, M.K.; Khan, T. Effect of effluent recirculation on nutrients and organics removal performance of hybrid constructed wetlands: Landfill leachate treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialowiec, A.; Davies, L.; Albuquerque, A.; Randerson, P.F. Nitrogen removal from landfill leachate in constructed wetlands with reed and willow: Redox potential in the root zone. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 97, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Ye, M.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.Y. Towards advanced nitrogen removal and optimal energy recovery from leachate: A critical review of anammox-based processes. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 612–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peipoch, M.; Gacia, E.; Blesa, A.; Ribot, M.; Riera, J.L.; Marti, E. Contrasts among macrophyte riparian species in their use of stream water nitrate and ammonium: Insights from N-15 natural abundance. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.; Peipoch, M.; Canas, L.; Chappuis, E.; Ribot, M.; Gacia, E.; Riera, J.L.; Marti, E.; Sabater, F. Nitrogen Stable Isotopes in Primary Uptake Compartments Across Streams Differing in Nutrient Availability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10155–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucker, B.; Brauns, M.; Pusch, M.T. Effects of wastewater treatment plant discharge on ecosystem structure and function of lowland streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.G.; Huang, G.C.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.G.; Sun, L. Identifying the sources and fate of anthropogenically impacted dissolved organic matter (DOM) in urbanized rivers. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5027–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, M.D.; Richardson, J.S. Microbial utilization of dissolved organic carbon leached from riparian litterfall. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribot, M.; Cochero, J.; Vaessen, T.N.; Bernal, S.; Bastias, E.; Gacia, E.; Sorolla, A.; Sabater, F.; Marti, E. Leachates from Helophyte Leaf-Litter Enhance Nitrogen Removal from Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7613–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.N.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, T.; Peng, Y.Z.; Zhang, J. Analysis of the impact of reflux ratio on coupled partial nitrification-anammox for co-treatment of mature landfill leachate and domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmas, N.; Melidis, P.; Katsioupi, E.; Ntougias, S. Effects of high organic load on amoA and nirS gene diversity of an intermittently aerated and fed membrane bioreactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Yang, Q.; Peng, Y.Z.; Shi, X.N.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, S.J. Nitrite Accumulation during the Denitrification Process in SBR for the Treatment of Pre-treated Landfill Leachate. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K. Nitritation-denitritation in landfill leachate with glycerine as a carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.E.D.; Moura, R.B.; Damianovic, M.; Foresti, E. Influence of COD/N ratio and carbon source on nitrogen removal in a structured-bed reactor subjected to recirculation and intermittent aeration (SBRRIA). J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, B.K.; Cao, T.H.; Zhang, F.Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.Z. Effect of carbon source type on intracellular stored polymers during endogenous denitritation (ED) treating landfill leachate. Water Res. 2016, 100, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elefsiniotis, P.; Li, D. The effect of temperature and carbon source on denitrification using volatile fatty acids. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 28, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.M.; Welander, T. The effect of different carbon sources on respiratory denitrification in biological wastewater treatment. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1996, 82, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, O.; Fukushi, K.; Yamamoto, K. Denitrification with methane as external carbon source. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2726–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.B.; Wang, D.B.; Li, X.M.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, G.M. Enhancement of post-anoxic denitrification for biological nutrient removal: Effect of different carbon sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5887–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, A.; Khan, S.T. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates for denitrification in water and wastewater treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhou, J.T.; Chen, M.X. Waste activated sludge fermentation liquid as carbon source for biological treatment of sulfide and nitrate in microaerobic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, X.C.C.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, J.L. Effect of fermentation liquid from food waste as a carbon source for enhancing denitrification in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Shin, S.G.; Hwang, S.; Lee, C. Continuous fermentation of food waste leachate for the production of volatile fatty acids and potential as a denitrification carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Jiang, J.G.; Li, M.L.; Yan, F.; Gong, C.X.; Wang, Q. Biological nitrate removal using a food waste-derived carbon source in synthetic wastewater and real sewage. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Choi, D.W.; Lee, W.G.; Kwon, S.; Chang, H.N. Volatile fatty acids production from food wastes and its application to biological nutrient removal. Bioprocess Eng. 2000, 22, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Jiang, J.G.; Zhang, H.W.; Liu, N.; Zou, Q. Biological denitrification from mature landfill leachate using a food-waste-derived carbon source. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorek, K.; Ledakowicz, S. Kinetics of nitrogen removal from sanitary landfill leachate. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 29, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Lv, B.Y.; Hu, C.; Liang, S.B.; Tang, Y.; Lu, J. Landfill leachate pollutant removal performance of a novel biofilter packed with mixture medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7754–7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, M.; Daufin, G.; Gesan-Guiziou, G. Denitrification potential and rates of complex carbon source from dairy effluents in activated sludge system. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.; Buitron, G.; Moreno-Andrade, I.; Chamy, R. Effect of the initial total solids concentration and initial pH on the bio-hydrogen production from cafeteria food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 13288–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.L.; Wang, X.C.C.; Hu, Y.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Applying fermentation liquid of food waste as carbon source to a pilot-scale anoxic/oxic-membrane bioreactor for enhancing nitrogen removal: Microbial communities and membrane fouling behaviour. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 236, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ni, J.R. Heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification by novel isolated bacteria. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ni, J.R. Ammonium removal by Agrobacterium sp LAD9 capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, F. Screening and ammoxidation characteristics of an ammonium oxidizing bacteria group. Weishengwu Xuebao 2015, 55, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.L.; Yi, A.F.; Li, H.R.; Wang, W.D.; Du, Y.L. Ocean bacteria: Performance on CODCr and NH4+-N removal in landfill leachate treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Hassan, M.; Han, L.; Xie, B. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation-denitrification synergistic interaction of mature landfill leachate in aged refuse bioreactor: Variations and effects of microbial community structures. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, K.; Yoshie, S.; Sumino, T.; Inamori, Y.; Tsuneda, S. Nitrification of landfill leachate using immobilized nitrifying bacteria at low temperatures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Azirun, M.S.; Ismail, S.B. Optimal reduction of chemical oxygen demand and NH3-N from landfill leachate using a strongly resistant novel Bacillus salmalaya strain. Bmc Biotechnol. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, N.; Tao, Y.; Li, D.; Li, W.; Ding, Y. Shortcut Nitrification of High Ammonia Concentration Wastewater and Ammonia-oxidizing Bacterial Community. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2013, 19, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, G.Q.; Dong, H.R.; Liu, Y.T.; Wan, J.; Chen, A.W.; Guo, Z.; Yan, M.; Wu, H.P.; et al. Treatment of landfill leachate using immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium loaded with nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Hussain, A.; Xie, B. Coupling ARB-based biological and photochemical (UV/TiO2 and UV/S2O82-) techniques to deal with sanitary landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, C.; Lobna, E.; Mouna, M.; Kais, D.; Mariam, K.; Rached, S.; Abdelwaheb, C.; Ismail, T. New trend of Jebel Chakir landfill leachate pre-treatment by photocatalytic TiO2/Ag nanocomposite prior to fermentation using Candida tropicalis strain. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.H.; Dolfing, J.; Xie, B. Perspective of harnessing energy from landfill leachate via microbial fuel cells: Novel biofuels and electrogenic physiologies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7827–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Jiang, N.; Zhen, G.Y.; Meng, L.J.; Song, J.L.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.B.; Huang, M.H. Simultaneous energy harvest and nitrogen removal using a supercapacitor microbial fuel cell. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Wei, H.; Qiu, H.; Su, Y.; Jaafry, S.W.H.; Zhan, L.; Xie, B. Power generation and pollutants removal from landfill leachate in microbial fuel cell: Variation and influence of anodic microbiomes. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, D.; Yuzer, B.; Yapsakli, K.; Mertoglu, B. Nitrogen Converters in Various Landfill Leachates. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscalleda, M.; Puig, S.; Mora, X.; Lopez, H.; Ganigue, R.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. The effect of urban landfill leachate characteristics on the coexistence of anammox bacteria and heterotrophic denitrifiers. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagni, A.; Psaila, G.; Rizzo, A. Partial nitrification for nitrogen removal from sanitary landfill leachate. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2014, 49, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.D.; An, K.J.; Ma, C.; Han, X.K. Partial nitritation for subsequent Anammox to treat high-ammonium leachate. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhu, R.L.; Miao, L.; Peng, Y.Z. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate without addition of external carbon using a novel system coupling ASBR and modified SBR. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, S.B.; Li, B.K.; Niu, M.; Wang, S.Y.; Peng, Y.Z. Performance and microbial community analysis of a novel DEAMOX based on partial-denitrification and anammox treating ammonia and nitrate wastewaters. Water Res. 2017, 108, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapsakli, K.; Aliyazicioglu, C.; Mertoglu, B. Identification and quantitative evaluation of nitrogen-converting organisms in a full-scale leachate treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panter, Z.; Rosu, G.; Matei, F. The Effect of the Time of Contact on the Microbiological Treatment of Leachate. Sci. Pap. Ser. E-Land Reclam. Earth Obs. Surv. Environ. Eng. 2018, 7, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, T.T.; Peng, Y.Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Xiao, H. Effect of salinity on N2O production during shortcut biological nitrogen removal from landfill leachate. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarro, J.; Ganigue, R.; Gich, F.; Ruscalleda, M.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. Effect of temperature on AOB activity of a partial nitritation SBR treating landfill leachate with extremely high nitrogen concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.L.; Qing, X.X.; He, Q. Effects of dissolved oxygen on microbial community of single-stage autotrophic nitrogen removal system treating simulating mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.H.; Xie, B. Effects of oxygen and carbon content on nitrogen removal capacities in landfill bioreactors and response of microbial dynamics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6427–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, D.Z.; Tian, H.Z.; Yan, L.M.; Dang, Y.; Smith, J.A. Enhancing biotreatment of incineration leachate by applying an electric potential in a partial nitritation-Anammox system. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).