Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Global Moran’s I Statistic
2.2. Spatial Durbin Model
2.3. Spatial Weights Matrix
3. Variable Selection and Data Source
3.1. Coastal Marine Pollution
3.2. Industrial Land Conveyance
3.3. Control Variables
3.4. Data Resource
4. Results
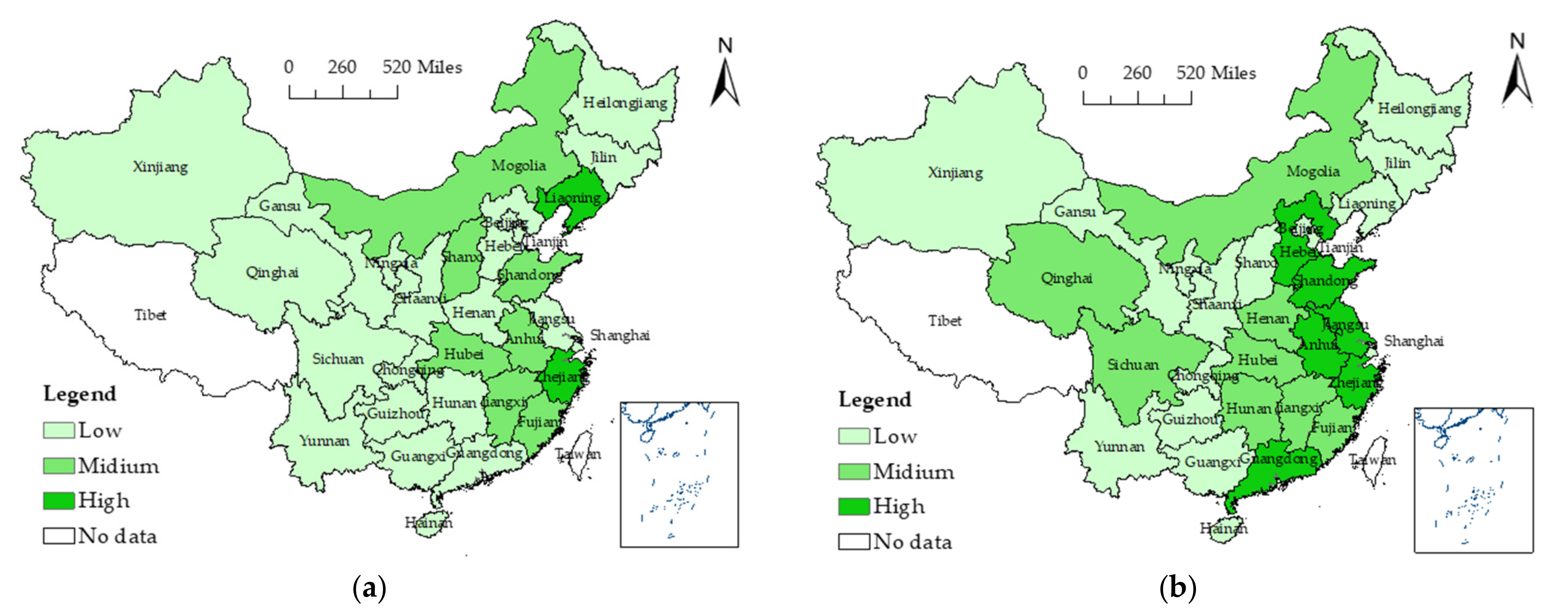
4.1. Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Industrial Land Conveyance and Coastal Marine Pollution
4.2. Spatial Econometric Regression Results
4.3. Robustness Test
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borowski, P. Environmental pollution as a threats to the ecology and development in Guinea Conakry. Ochr. Sr. Zasobów Nat. 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Bulletin of China’s Marine Ecological Environment. 2018. Available online: http://hys.mee.gov.cn/dtxx/201905/P020190529532197736567.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Jiang, S.-S.; Li, J.-M. Do political promotion incentive and fiscal incentive of local governments matter for the marine environmental pollution? Evidence from China’s coastal areas. Mar. Policy 2021, 128, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Hu, Q.; Yu, X.; Imwa, B.T. Does coastal local government competition increase coastal water pollution? Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.G.; Shen, W.T.; Chen, Q. On the institutional roots of marine ecological damage and its countermeasures. Issues Agric. Econ. 2019, 40, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Serious pollution in the coastal waters of Jiaojiang River in Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/zysthjbhdc/dczg/202009/t20200924_20800212.shtml (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Zhao, R. Analyzing the decoupling relationship between marine economic growth and marine pollution in China. Ocean Eng. 2017, 137, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. An empirical correlation mechanism of economic growth and marine pollution: A case study of 11 coastal provinces and cities in China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 2020, 198, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Espinosa Díaz, L.F.; Pereira Cardoso, R.; Costa Muniz, M. The impact of tourism on marine litter pollution on Santa Marta beaches, Colombian Caribbean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Guo, J.; Kang, P. Environmental response to growth in the marine economy and urbanization: A heterogeneity analysis of 11 Chinese coastal regions using a panel vector autoregressive model. Mar. Policy 2021, 124, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhao, J. Distribution and geochemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments from coastal area suffered rapid urbanization, a case study of Shantou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.A.; Corbett, D.R.; Fitzgerald, A.M.; Lemley, D.A.; Quigg, A.; Steppe, C.N. Impacts of urbanization and development on estuarine ecosystems and water quality. Estuar. Coast. 2019, 42, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing ecological risks caused by human activities in rapid urbanization coastal areas: Towards an integrated approach to determining key areas of terrestrial-oceanic ecosystems preservation and restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bu, C.; Li, H.; Wei, W. Seawater environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from seawater quality in China’s coastal waters. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Pan, Y.C.; Kong, F.H.; Yang, Y. A study of China’s land-based marine pollution governance from the perspective of political promotion. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 30, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Su, J. Development and management of land reclamation in China. Ocean. Coast. Manage. 2014, 102, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Niu, Y.; Zhu, J. Characterization and environmental impact analysis of sea land reclamation activities in China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2016, 130, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Lv, J.; Meng, M.; Li, G. Heavy metal pollution and the risk from tidal flat reclamation in coastal areas of Jiangsu, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Lin, G.C.S. Placing China’s land marketization: The state, market, and the changing geography of land use in Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.D.; Xiao, W. Land marketization, fiscal decentralization, and the dynamics of urban land prices in transitional China. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Yang, X. Strategic interaction of industrial land conveyance behaviors in China: Based on an asymmetric two-regime Spatial Durbin Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.J.; Zhuo, P.; Yang, J.D. Industrial land conveyance and bottom competition of investment quality dd the empirical analysis based on the city-level panel data from 2007 to 2011. Manag. World 2014, 36, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, W.; Zhang, A. Can market reforms curb the expansion of industrial land?—Based on the panel data analysis of five national-level urban agglomerations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-H.; Jiang, X.; Gong, M.-Q. How land transfer marketization influence on green total factor productivity from the approach of industrial structure? Evidence from China. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.L.; Ma, X.L.; Shi, X.P.; Zou, X.; Lan, J. Does the supply of industrial land affect industial energy carbon emissions? Chn. Popu. Res. Environ. 2019, 29, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.X.; Yu, L.L.; Chen, S.X. Industrial land conveyance, the investment quality race in the bottom line and environmental pollution. Chn. Popu. Res. Environ. 2017, 27, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Xu, M.; Xu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Shu, X.; Xie, P.; Wu, J. Promotion incentives, infrastructure construction, and industrial landscapes in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Lv, Z. Spillover effects of economic globalization on CO2 emissions: A spatial panel approach. Energ. Econ. 2018, 73, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, G.; Huang, L.; Luo, W. Distribution, source, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in Sanya offshore area, South Hainan Island of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunde, O.L.; Oluwagbenga, A.P. Assessment of heavy metals contamination and sediment quality in Ondo coastal marine area, Nigeria. J. Afr. Earth Sc. 2020, 170, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhaby, D.; Ouddane, B.; Net, S.; Halwani, J. Assessment of persistent organic pollutants in surface sediments along Lebanese coastal zone. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, P.; Neelamani, S.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Philip, L.; Hong, G.-H. Assessment of the levels of coastal marine pollution of Chennai city, Southern India. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1187–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q. Nonlinear effects of marine economic growth and technological innovation on marine pollution: Panel threshold analysis for China’s 11 coastal regions. Mar. Policy 2020, 121, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, B. Study on relationship between marine economy and marine environmental pollution in Bohai sea ring area. Resour. Dev. Market. 2017, 33, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.R.; Zhang, S.M.; Cui, B.H.; Zhang, B.L. EKC framework analysis of relationship between provincial economic development and marine environmental pollution in coastal areas of China. Mar. Econ. 2020, 10, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Yu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Qu, F.; Yang, J. Impacts of inland pollution input on coastal water quality of the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 756, 142691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.; Pace, R.K. Spatial econometric models. In Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 355–376. [Google Scholar]
- LeSage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics, 1st ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Qiu, S.; Sun, Y. Land finance dependence and urban land marketization in China: The perspective of strategic choice of local governments on land transfer. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Xie, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Q. Is urban land development driven by economic development or fiscal revenue stimuli in China? Land Use Policy 2018, 77, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, C.; Li, H. Local government intervention, firm–government connection, and industrial land expansion in China. J. Urban. Aff. 2019, 41, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Fang, Y. Driving factors of the industrial land transfer price based on a geographically weighted regression model: Evidence from a rural land system reform pilot in China. Land 2020, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, L.-A. Political turnover and economic performance: The incentive role of personnel control in China. J. Public Econ. 2005, 89, 1743–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhang, P. Environmental decentralization, local government competition, and regional green development: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Definition | Obs. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnorgncon | Inorganic nitrogen concentration in coastal waters (mg/L) | 495 | 0.292 | 0.296 | 0.120 | 2.271 |
| lnagreearea | Logarithm of the area of industrial land conveyance by agreement | 495 | 5.900 | 0.935 | 4.608 | 8.341 |
| lnbidarea | Logarithm of the area of industrial land conveyance by bidding, auction, and listing | 495 | 2.948 | 1.676 | 0.768 | 7.497 |
| lnbalarea | Logarithm of the area of industrial land conveyance by bidding, auction, and listing | 495 | 5.602 | 1.092 | 4.001 | 8.118 |
| lnpergdp | Logarithm of GDP per capita (104 CNY) | 495 | 10.556 | 0.500 | 9.916 | 12.784 |
| lnpergdp2 | Quadratic term of the logarithm of GDP per capita | 495 | 111.673 | 10.693 | 98.326 | 163.418 |
| lndensity | Logarithm of population density (person/km2) | 495 | 7.744 | 0.588 | 6.980 | 9.908 |
| urbanization | Urbanization rate (%) | 495 | 49.504 | 18.778 | 30.259 | 100.000 |
| SecondGDP | Proportion of secondary industry to GDP (%) | 495 | 49.940 | 7.067 | 41.090 | 76.530 |
| lnMGDP | Logarithm of gross ocean product (108 CNY) | 495 | 8.467 | 0.704 | 7.463 | 9.809 |
| basinpoll | Watershed area proportion of water quality worse than grade V (%) | 495 | 10.436 | 11.092 | 3.000 | 53.100 |
| VARIABLE | Dependent Variable: Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration in Coastal Waters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| l2_lnindarea | 0.0007 | 0.0282 ** | ||||
| (0.0141) | (0.0115) | |||||
| l2_lnagreearea | 0.1654 *** | 0.6055 *** | ||||
| (0.0260) | (0.185) | |||||
| l2_lnbalarea | 0.0682 | 0.0183 ** | ||||
| (0.0742) | (0.0088) | |||||
| lnpgdp | −2.2321 *** | −1.8822 *** | −2.0080 *** | |||
| (0.5814) | (0.5561) | (0.5709) | ||||
| lnpgdp2 | 0.1043 *** | 0.0889 *** | 0.0941 *** | |||
| (0.0268) | (0.0257) | (0.0263) | ||||
| lnpopden | 0.1332 *** | 0.1257 *** | 0.1300 *** | |||
| (0.0222) | (0.0224) | (0.0223) | ||||
| urbanrate | 0.0025 *** | 0.0023 *** | 0.0027 *** | |||
| (0.0008) | (0.0008) | (0.0008) | ||||
| Second_GDP | 0.0072 *** | 0.0065 *** | 0.0068 *** | |||
| (0.0021) | (0.0021) | (0.0021) | ||||
| lnmarGDP | −0.2458 | −0.2072 | −0.2444 | |||
| (0.2076) | (0.2069) | (0.2085) | ||||
| basinwpoll | −0.0061 * | −0.0061 * | −0.0063 * | |||
| (0.0033) | (0.0032) | (0.0033) | ||||
| W*l2_lnindarea | 0.0545 | 0.0910 | ||||
| (0.0392) | (0.0714) | |||||
| W*l2_lnagreearea | 0.2172 ** | 1.0545 ** | ||||
| (0.0854) | (0.481) | |||||
| W*l2_lnbalarea | 0.3749 | 0.0387 | ||||
| (0.2873) | (0.0390) | |||||
| W*lnpgdp | −1.6822 | −1.0135 | −0.4974 | |||
| (2.4787) | (2.4925) | (2.4608) | ||||
| W*lnpgdp2 | 0.0686 | 0.0440 | 0.0157 | |||
| (0.1135) | (0.1143) | (0.1130) | ||||
| W*lnpopden | −0.0667 | −0.0218 | −0.0768 | |||
| (0.0943) | (0.0986) | (0.0951) | ||||
| W*urbanrate | −0.0039 | −0.0041 | −0.0028 | |||
| (0.0029) | (0.0028) | (0.0029) | ||||
| W*Second_GDP | 0.0289 *** | 0.0232 ** | 0.0252 ** | |||
| (0.0107) | (0.0105) | (0.0105) | ||||
| W*lnmarGDP | −0.2757 | −0.4280 | −0.1328 | |||
| (0.4562) | (0.4630) | (0.4508) | ||||
| W*basinwpoll | 0.0133 * | 0.0093 | 0.0139 * | |||
| (0.0073) | (0.0072) | (0.0076) | ||||
| ρ | 0.4473 *** | 0.3025 ** | 0.4566 *** | −0.2927 * | −0.2983 * | −0.2794 * |
| (0.1152) | (0.1290) | (0.1138) | (0.1651) | (0.1656) | (0.1651) | |
| Province Dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 405 | 405 | 405 | 405 | 405 | 405 |
| R2 | 0.0042 | 0.0614 | 0.0022 | 0.4414 | 0.4170 | 0.5476 |
| VARIABLE | Dependent Variable: Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration in Coastal Waters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| l2_lnindarea | 0.0270 ** | 0.0655 | 0.0925 ** | ||||||
| (0.0117) | (0.0424) | (0.0446) | |||||||
| l2_lnagreearea | 0.5951 *** | 0.7065 ** | 1.3016 *** | ||||||
| (0.1896) | (0.3343) | (0.4301) | |||||||
| l2_lnbalarea | 0.0180 ** | 0.0265 | 0.0445 | ||||||
| (0.0089) | (0.0320) | (0.0346) | |||||||
| lnpgdp | −2.2432 *** | −1.8979 *** | −2.0385 *** | −0.8971 | −0.4297 | −0.0179 | −3.1403 | −2.3276 | −2.0564 |
| (0.5584) | (0.5283) | (0.5470) | (2.0678) | (2.0616) | (2.0588) | (2.2076) | (2.1819) | (2.1772) | |
| lnpgdp2 | 0.1051 *** | 0.0898 *** | 0.0958 *** | 0.0335 | 0.0168 | −0.0058 | 0.1386 | 0.1066 | 0.0900 |
| (0.0257) | (0.0244) | (0.0252) | (0.0948) | (0.0947) | (0.0947) | (0.1010) | (0.1002) | (0.1001) | |
| lnpopden | 0.1351 *** | 0.1266 *** | 0.1320 *** | −0.0849 | −0.0462 | −0.0917 | 0.0503 | 0.0804 | 0.0403 |
| (0.0212) | (0.0218) | (0.0213) | (0.0714) | (0.0762) | (0.0729) | (0.0774) | (0.0802) | (0.0787) | |
| urbanrate | 0.0025 *** | 0.0024 *** | 0.0028 *** | −0.0037 | −0.0039 * | −0.0029 | −0.0012 | −0.0015 | −0.0001 |
| (0.0007) | (0.0007) | (0.0007) | (0.0023) | (0.0023) | (0.0023) | (0.0025) | (0.0026) | (0.0026) | |
| Second_GDP | 0.0067 *** | 0.0061 *** | 0.0063 *** | 0.0218 ** | 0.0173 ** | 0.0192 ** | 0.0285 *** | 0.0234 ** | 0.0255 *** |
| (0.0020) | (0.0019) | (0.0020) | (0.0088) | (0.0084) | (0.0086) | (0.0098) | (0.0094) | (0.0096) | |
| lnmarGDP | −0.2432 | −0.2006 | −0.2446 | −0.1715 | −0.3054 | −0.0609 | −0.4147 | −0.5060 * | −0.3056 |
| (0.2238) | (0.2238) | (0.2247) | (0.4294) | (0.4414) | (0.4243) | (0.2709) | (0.2833) | (0.2625) | |
| basinwpoll | −0.0065 ** | −0.0064 * | −0.0067 ** | 0.0121 * | 0.0089 | 0.0126 * | 0.0055 | 0.0025 | 0.0059 |
| (0.0033) | (0.0033) | (0.0033) | (0.0065) | (0.0065) | (0.0068) | (0.0043) | (0.0043) | (0.0046) | |
| VARIABLE | Dependent Variable: Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration in Coastal Waters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| l2_lnindarea | 0.0110 ** | 0.0065 | 0.0176 * | ||||||
| (0.0051) | (0.0196) | (0.0092) | |||||||
| l2_lnagreearea | 0.6117 *** | 0.3980 *** | 1.0097 *** | ||||||
| (0.1384) | (0.1109) | (0.1874) | |||||||
| l2_lnbalarea | 0.0017 * | 0.0041 | 0.0058 | ||||||
| (0.0009) | (0.0141) | (0.0173) | |||||||
| lnpgdp | −2.5025 *** | −2.4224 *** | −2.4061 *** | 5.9227 *** | 5.8575 *** | 6.0684 *** | 3.4202 *** | 3.4351 *** | 3.6623 *** |
| (0.4496) | (0.4156) | (0.4386) | (1.2474) | (1.2140) | (1.2245) | (1.2619) | (1.2095) | (1.2160) | |
| lnpgdp2 | 0.1207 *** | 0.1173 *** | 0.1162 *** | −0.2688 *** | −0.2666 *** | −0.2753 *** | −0.1482 ** | −0.1493 *** | −0.1591 *** |
| (0.0206) | (0.0191) | (0.0201) | (0.0588) | (0.0573) | (0.0578) | (0.0595) | (0.0573) | (0.0575) | |
| lnpopden | 0.1092 *** | 0.0951 *** | 0.1064 *** | 0.1772 *** | 0.2074 *** | 0.1673 *** | 0.2864 *** | 0.3025 *** | 0.2737 *** |
| (0.0155) | (0.0158) | (0.0155) | (0.0441) | (0.0447) | (0.0434) | (0.0528) | (0.0528) | (0.0524) | |
| urbanrate | 0.0019 *** | 0.0017 *** | 0.0019 *** | 0.0014 | 0.0010 | 0.0014 | 0.0032 *** | 0.0027 ** | 0.0033 *** |
| (0.0005) | (0.0005) | (0.0005) | (0.0010) | (0.0010) | (0.0010) | (0.0012) | (0.0012) | (0.0012) | |
| Second_GDP | −0.0011 | −0.0010 | −0.0011 | 0.0029 | 0.0024 | 0.0025 | 0.0018 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 |
| (0.0013) | (0.0012) | (0.0012) | (0.0021) | (0.0020) | (0.0021) | (0.0027) | (0.0025) | (0.0026) | |
| lnmarGDP | −0.2543 * | −0.2895 * | −0.2334 | −0.0179 | −0.0619 | −0.0272 | −0.2723 ** | −0.3514 *** | −0.2605 ** |
| (0.1529) | (0.1486) | (0.1533) | (0.2055) | (0.2049) | (0.2048) | (0.1288) | (0.1328) | (0.1254) | |
| basinwpoll | 0.0040 * | 0.0035 | 0.0039 | −0.0031 | −0.0033 | −0.0030 | 0.0009 | 0.0002 | 0.0008 |
| (0.0024) | (0.0024) | (0.0024) | (0.0037) | (0.0036) | (0.0037) | (0.0026) | (0.0026) | (0.0026) | |
| VARIABLE | Dependent Variable: Active Phosphate | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| l2_lnindarea | 0.0010 ** | −0.0007 | 0.0003 | ||||||
| (0.0004) | (0.0013) | (0.0013) | |||||||
| l2_lnagreearea | 0.0120 * | 0.0031 *** | 0.0151 *** | ||||||
| (0.0068) | (0.0005) | (0.0011) | |||||||
| l2_lnbalarea | 0.0002 | −0.0013 | −0.0011 | ||||||
| (0.0003) | (0.0010) | (0.0010) | |||||||
| lnpgdp | −0.0473 ** | −0.0360 * | −0.0381 * | 0.1200 * | 0.1291 ** | 0.1210 * | 0.0727 | 0.0931 | 0.0829 |
| (0.0198) | (0.0189) | (0.0194) | (0.0631) | (0.0645) | (0.0629) | (0.0668) | (0.0677) | (0.0657) | |
| lnpgdp2 | 0.0022 ** | 0.0017 * | 0.0018 ** | −0.0054 * | −0.0058 * | −0.0054 * | −0.0033 | −0.0041 | −0.0036 |
| (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0029) | (0.0030) | (0.0029) | (0.0031) | (0.0031) | (0.0030) | |
| lnpopden | 0.0033 *** | 0.0029 *** | 0.0032 *** | −0.0040 * | −0.0026 | −0.0044 * | −0.0008 | 0.0003 | −0.0012 |
| (0.0007) | (0.0008) | (0.0008) | (0.0023) | (0.0025) | (0.0023) | (0.0024) | (0.0026) | (0.0024) | |
| urbanrate | 0.0001 *** | 0.0001 *** | 0.0001 *** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0002 ** | −0.0002 ** | −0.0002 ** |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | |
| Second_GDP | 0.0001 ** | 0.0002 ** | 0.0002 ** | 0.0000 | −0.0000 | −0.0000 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0003) | (0.0003) | (0.0002) | (0.0003) | (0.0003) | (0.0003) | |
| lnmarGDP | −0.0114 | −0.0099 | −0.0116 | −0.0054 | −0.0098 | −0.0039 | −0.0169 ** | −0.0197 ** | −0.0155 ** |
| (0.0081) | (0.0082) | (0.0082) | (0.0142) | (0.0148) | (0.0140) | (0.0082) | (0.0087) | (0.0079) | |
| basinwpoll | −0.0003 ** | −0.0003 ** | −0.0003 ** | 0.0004 * | 0.0004 * | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0002) | (0.0002) | (0.0002) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Shen, W. Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137209
Hu Q, Shen W. Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137209
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qiuguang, and Weiteng Shen. 2021. "Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137209
APA StyleHu, Q., & Shen, W. (2021). Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis. Sustainability, 13(13), 7209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137209





