A Critical Analysis of Job Shop Scheduling in Context of Industry 4.0
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Objectives
- What is the existing research status of JSSP?
- How are JSSP models classified?
- What techniques/algorithms have been used for solving various JSSP classifications and what are their limitations?
- How JSSP can be integrated with the technological pillars of Industry 4.0?
3. Review Methodology
4. Research Design
5. Literature Review
- Each job will be assigned to different machines with a specified processing time;
- Each machine can perform only one job at a moment;
- The processing time of the job is fixed, and once the job is started it cannot be interrupted for each machining operation [22].
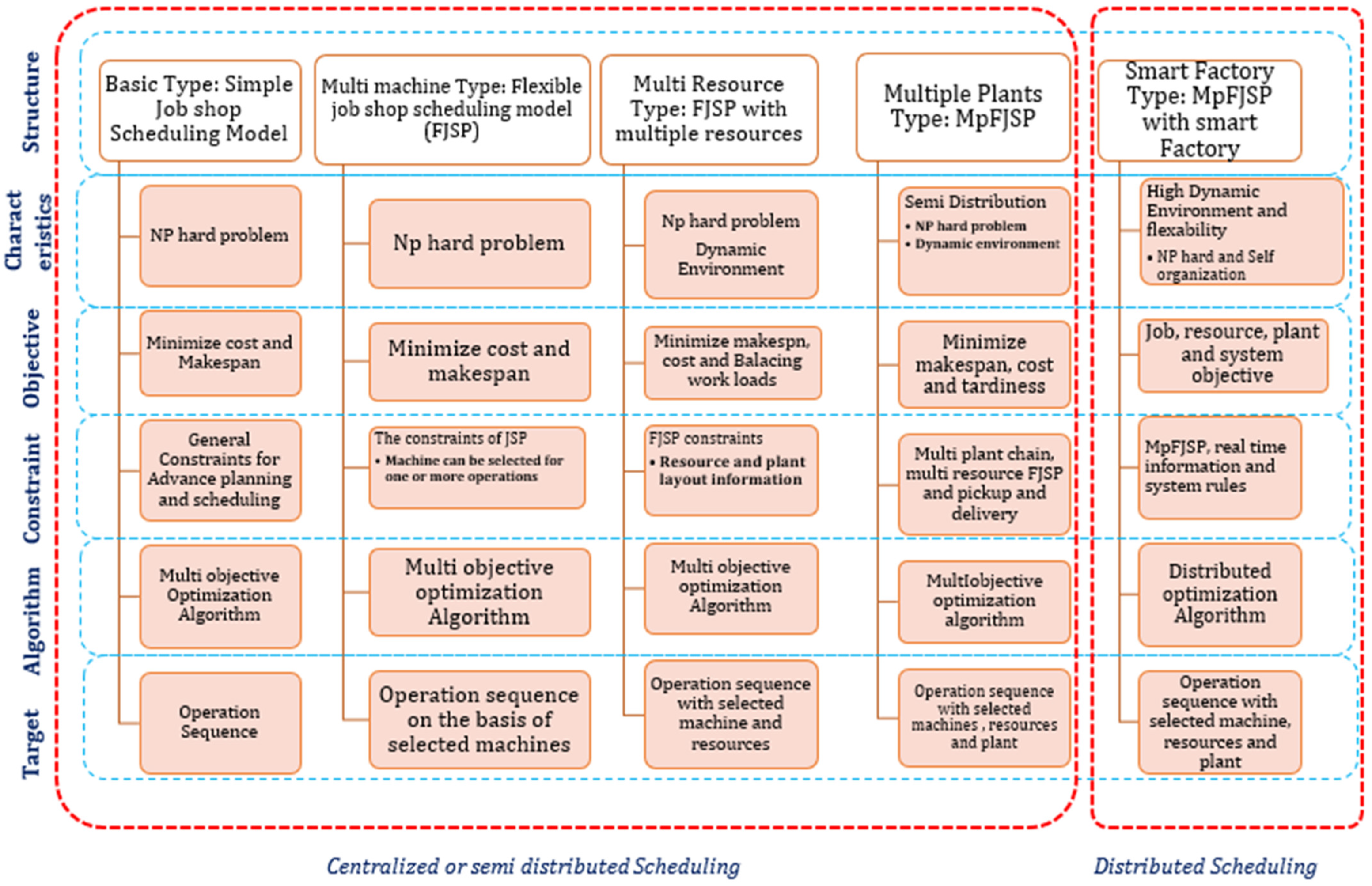
5.1. Scheduling Model Structures
5.2. Classification of Scheduling Algorithm
5.3. Characteristics, Limitations, and Challenges of Exact and Approximate Optimization Methods
6. Decentralization
6.1. Industry 4.0 Mainspring for Smart Distributed Scheduling
6.1.1. Internet of Things (IoT)
6.1.2. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
6.1.3. Smart Factory
6.1.4. Cloud Computing
6.1.5. Deep Learning
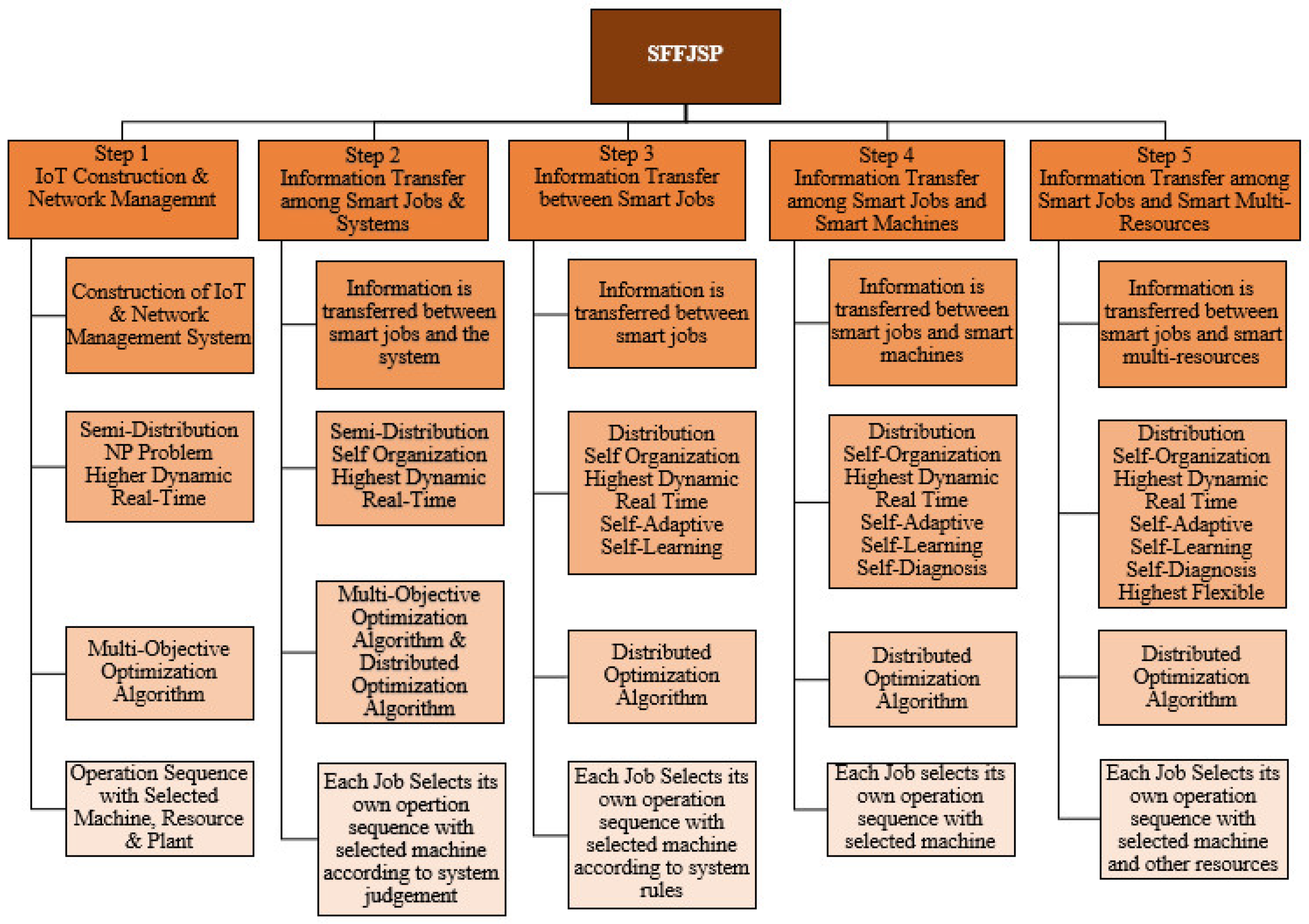
6.2. Implementation Steps of JSSP Structure with SFFJSP
7. Latest Research Trends in SFFJSP
7.1. Use of IoT
7.2. Use of Genetic Algorithm
7.3. Decision Support System
7.4. Decentralization Outperformance
7.5. Use of Semi Hierarchal Configuration
7.6. Use of Heuristic Approaches
7.7. Maximizing Hamiltonian Function
7.8. Use of CBJSP
7.9. Use of RFID Based IoT
7.10. Industry 4.0 in SFFJSP
7.11. Use of Firefly Algorithm
7.12. Use of Lagrange Relaxation Method
7.13. Use of AGVs
7.14. Use of HSTL
7.15. Use of DSS with Big Data
7.16. Development of Standard Dataset
7.17. Use of Q-Learning Algorithm
7.18. Use of RRCF
8. Robustness in Job Shop and Industry 4.0
9. Future Research Agenda
- Incorporation of customized decision-making criteria for machine learning-based decentralized operating systems.
- Industry 4.0 also provides room for human-machine collaboration where smart machines can assist humans to achieve efficient solutions, as discussed in Berti et al. [122]. Moreover, involvement of human input in decision-making for efficient and sustainable decisions directed towards Industry 5.0 framework.
- Development of customized smart sensors for manufacturing performance criteria assurance and assessment.
- Development of specialized sensors and quality assurance procedures for decentralized JSSP for medical-grade manufacturing.
- Implementation of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies in a manufacturing environment for sharing and retrieving data of machines functions between agents.
- Determination of sustainability indices for decentralized JSSP.
- Implementation of sustainability indices and other decision-making criteria for application in decentralized JSSP focused on the concept of Industry 5.0 (fueled by Information Technology and Environmental Sustainability).
10. Conclusions
- Integration of FJSSP with Industry 4.0 provides a conducive solution regarding computational time, makespan, tardiness, lateness, etc.
- The latest research trends indicate that conventional JSSP is no more practical to study.
- Multi machines, multi operations, multi resources with multiple factories and logistics centers should be incorporated in conventional JSSP to evaluate the actual dynamics of the system.
- Currently, the research focus is on approximate algorithms rather than exact algorithms for solving JSSP and FJSSP. The global and local optimum solution is evaluated with the aid of multi-objective optimization techniques.
- The metaheuristics approaches have acquired great popularity for solving the JSSP and FJSSP. Recent studies show that hybrid approaches are vastly used for solving JSSP under the Industry 4.0 environment.
- The use of PID controllers, RFIDs, and barcodes has become a great source of integrating actual plant with its digital part.
- Recent studies indicate the use of smart agents to determine the efficient sequencing of jobs while minimizing the complexity of JSSPs, is a competitive approach adopted by many scholars.
- The merger of AI, CPS, deep learning, cloud computing, etc., in JSSPs has outperformed the conventional approaches of finding optimal solutions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.C.; Bobrowski, P.M. Impact of sequence-dependent setup time on job shop scheduling performance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1994, 32, 1503–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, P.-Y.; Lyne, P.; Meyer, E.; Soler, L.-G. Impact of sugarcane supply scheduling on mill sugar production: A South African case study. Agric. Syst. 2008, 96, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, D.R.; Mesch, D.J. The Impact of Flexible Scheduling on Employee Attendance and Turnover. Adm. Sci. Q. 1990, 35, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażewicz, J.; Ecker, K.H.; Pesch, E.; Schmidt, G.; Weglarz, J. Scheduling Computer and Manufacturing Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Geyik, F.; Cedimoglu, I.H. The strategies and parameters of tabu search for job-shop scheduling. J. Intell. Manuf. 2004, 15, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Croce, F.; Tadei, R.; Volta, G. A genetic algorithm for the job shop problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 1995, 22, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, E.; Smutnicki, C. A Fast Taboo Search Algorithm for the Job Shop Problem. Manag. Sci. 1996, 42, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurink, J.; Jurisch, B.; Thole, M. Tabu search for the job-shop scheduling problem with multi-purpose machines. Oper. Res. Spectr. 1994, 15, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlier, J.; Pinson, E. An Algorithm for Solving the Job-Shop Problem. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazewicz, J.; Domschke, W.; Pesch, E. The job shop scheduling problem: Conventional and new solution techniques. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 93, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrolilli, M.; Gambardella, L.M. Effective neighbourhood functions for the flexible job shop problem. J. Schedul. 2000, 3, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, R.; Yamada, T. Conventional genetic algorithm for job shop problems. ICGA 1991, 91, 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Yan, C. A genetic algorithm for job-shop scheduling. J. Softw. 2010, 5, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, C.S.; Low, M.Y.H.; Sivakumar, A.I.; Gay, K.L. A Bee Colony Optimization Algorithm to Job Shop Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2006 Winter Simulation Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2006; pp. 1954–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Qing-Dao-Er-Ji, R.; Wang, Y. A new hybrid genetic algorithm for job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, I.A.; Khan, A.A. A research survey: Review of flexible job shop scheduling techniques. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2016, 23, 551–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Ullah, H. Review on job-shop and flow-shop scheduling using. J. Mech. Eng. 2011, 41, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, G.; Zou, Y.; Qin, S.; Fu, J. Review of job shop scheduling research and its new perspectives under Industry 4.0. J. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 30, 1809–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M. Optimal two-and three-stage production schedules with setup times included. Naval Res. Log. Q. 1954, 1, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garey, M.R.; Johnson, D.S.; Sethi, R. Complexity of Flowshop and Jobshop Scheduling. Math. Oper. Res. 1976, 1, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, K.-H. Flexible job shop scheduling with parallel machines using Genetic Algorithm and Grouping Genetic Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10016–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leusin, M.E.; Frazzon, E.M.; Maldonado, M.U.; Kück, M.; Freitag, M. Solving the Job-Shop Scheduling Problem in the Industry 4.0 Era. Technologies 2018, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Hao, X.-C.; Gen, M.; Jo, J.-B. Network modeling and evolutionary optimization for scheduling in manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2011, 23, 2237–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.A.; Lin, X. Continuous-time versus discrete-time approaches for scheduling of chemical processes: A review. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2004, 28, 2109–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graves, S.C. A Review of Production Scheduling. Oper. Res. 1981, 29, 646–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.E.; Driss, O.B.; Khaled, G.A. Classification Schema for the Job Shop Scheduling Problem with Transportation Resources: State-of-the-Art Review. Artif. Intell. Perspect. Intell. Syst. 2016, 464, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, I.; Hammadi, S.; Borne, P. Approach by localization and multiobjective evolutionary optimization for flexible job-shop scheduling problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2002, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, O.; Sotskov, Y.N. Solving parallel machines job-shop scheduling problems by an adaptive algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 52, 3888–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, J.; Engelbrecht, A.P.; Kok, S.; Yadavalli, S. Metaheuristics for the multi-objective FJSP with sequence-dependent set-up times, auxiliary resources and machine down time. Ann. Oper. Res. 2009, 180, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.F.; Mirrazavi, S.K.; Tamiz, M. Multi-objective meta-heuristics: An overview of the current state-of-the-art. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Moon, I.; Bae, H.; Kim, J. Flexible job-shop scheduling problems with ‘AND’/‘OR’ precedence constraints. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 1979–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.A.; Lin, X. Mixed Integer Linear Programming in Process Scheduling: Modeling, Algorithms, and Applications. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 139, 131–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaliş, B.; Bulkan, S. A research survey: Review of AI solution strategies of job shop scheduling problem. J. Intell. Manuf. 2013, 26, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.S.; Meeran, S. A State-of-the-Art Review of Job-Shop Scheduling Techniques. 1998. Available online: https://neuro.bstu.by/ai/To-dom/My_research/Papers-0/For-courses/Job-SSP/jain.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Hefetz, N.; Adiri, I. An Efficient Optimal Algorithm for the Two-Machines Unit-Time Jobshop Schedule-Length Problem. Math. Oper. Res. 1982, 7, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.M. An integer linear-programming model for machine scheduling. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 1959, 6, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, A.S. On the Job-Shop Scheduling Problem. Oper. Res. 1960, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomnicki, Z.A. A “Branch-and-Bound” Algorithm for the Exact Solution of the Three-Machine Scheduling Problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1965, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.C.; Ahn, S.; Bishop, A.B. An improved branching scheme for the branch and bound procedure of schedulingnjobs onmparallel machines to minimize total weighted flowtime. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1988, 26, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteyhe, M.; DeBrouwere, F. Application of non-deterministic uncertainty models to improve resource constraint optimal scheduling. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, G.; Florian, M. On Scheduling with Ready Times and Due Dates to Minimize Maximum Lateness. Oper. Res. 1975, 23, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.R.; McMahon, G.B. Scheduling the General Job-Shop. Manag. Sci. 1985, 31, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, D.J.; Stearns, R.E.; Lewis, P.M. An analysis of several heuristics for the traveling salesman problem. Fundam. Prob. Comput. 2009, 6, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Enscore, E.E.; Ham, I. A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega 1983, 11, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Kozan, E. A hybrid shifting bottleneck procedure algorithm for the parallel-machine job-shop scheduling problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2012, 63, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauzere-Peres, S.; Lasserre, J.B. A modified shifting bottleneck procedure for job-shop scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1993, 31, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Balas, E.; Zawack, D. The Shifting Bottleneck Procedure for Job Shop Scheduling. Manag. Sci. 1988, 34, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenqi, H.; Aihua, Y. An improved shifting bottleneck procedure for the job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2004, 31, 2093–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesch, E.; Tetzlaff, U.A.W. Constraint Propagation Based Scheduling of Job Shops. Inf. J. Comput. 1996, 8, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, N.; Fox, M.S. Variable and value ordering heuristics for the job shop scheduling constraint satisfaction problem. Artif. Intell. 1996, 86, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, F.Y.-P.; Takefuji, Y. Stochastic neural networks for solving job-shop scheduling. I. Problem representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 July 1988; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, F.Y.-P.; Takefuji, Y. Stochastic neural networks for solving job-shop scheduling. II. Architecture and simulations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 July 1988; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Akyol, D.E.; Bayhan, G.M. A review on evolution of production scheduling with neural networks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2007, 53, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.-S.; Yih, Y. Selection of dispatching rules on multiple dispatching decision points in real-time scheduling of a semiconductor wafer fabrication system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2003, 41, 3921–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensana, E.; Bel, G.; Dubois, D. OPAL: A multi-knowledge-based system for industrial job-shop scheduling†. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1988, 26, 795–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.S. Genetic algorithm with fuzzy logic controller for preemptive and non-preemptive job-shop scheduling problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2002, 43, 623–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, S.; Liouane, N.; Hammadi, S.; Borne, P. A controlled genetic algorithm by fuzzy logic and belief functions for job-shop scheduling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2000, 30, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacem, I.; Hammadi, S.; Borne, P. Pareto-optimality approach for flexible job-shop scheduling problems: Hybridization of evolutionary algorithms and fuzzy logic. Math. Comput. Simul. 2002, 60, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolonko, M. Some new results on simulated annealing applied to the job shop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1999, 113, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Shahandashti, S.M. Hybrid of genetic algorithm and simulated annealing for multiple project scheduling with multiple resource constraints. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouleimen, K.; Lecocq, H. A new efficient simulated annealing algorithm for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem and its multiple mode version. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 149, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaga, E.M.; Valarmathi, M. Multi-agent based Patient Scheduling Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Procedia Eng. 2012, 30, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorin, D.A.; Kostenko, V.A. Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Job Shop Scheduling on Reliable Real-Time Systems. In Proceedings of the Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 509, pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Meeran, S.; Morshed, M.S. A hybrid genetic tabu search algorithm for solving job shop scheduling problems: A case study. J. Intell. Manuf. 2011, 23, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, A.K.; Aktepe, A.; Inal, A.F.; Ersoz, O.O.; Das, G.S.; Birgoren, B. A Decision Support System for Dynamic Job-Shop Scheduling Using Real-Time Data with Simulation. Mathematics 2019, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X. Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms, 2nd ed.; Luniver Press: Beckington, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781905986286. [Google Scholar]
- Colorni, A.; Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V. Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In Proceedings of the First European Conference on Artificial Life, Paris, France, 11–13 December 1991; Volume 142, pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.C.; Ng, K.M.; Ong, H.L. A modified tabu search algorithm for cost-based job shop problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2010, 61, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocholl, J.; Mönch, L. Decomposition heuristics for parallel-machine multiple orders per job scheduling problems with a common due date. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, O.; Sotskov, Y.N.; Werner, F.; Zatsiupo, A.S. Heuristic Algorithms to Maximize Revenue and the Number of Jobs Processed on Parallel Machines. Autom. Remote Control 2019, 80, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, D.J.; Navaresse, D. Artificial neural networks for job shop simulation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2002, 16, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apt, K.R. Principles of Constraint Programming; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Van Beek, P.; Walsh, T. (Eds.) Handbook of Constraint Programming; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Adibi, M.; Zandieh, M.; Amiri, M. Multi-objective scheduling of dynamic job shop using variable neighborhood search. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, J.B.; Zhu, Y.C.; Hu, Y. Multi-Objective Scheduling Simulation of Flexible Job-Shop Based on Multi-Population Genetic Algorithm. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2017, 16, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, O.; Sotskov, Y.N. A fast heuristic algorithm for solving parallel-machine job-shop scheduling problems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, O.; Sotskov, Y.N.; Werner, F. A Genetic Algorithm for Hybrid Job-Shop Scheduling Problems with Minimizing the Makespan or Mean Flow Time. J. Adv. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 17, 461–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongchairerks, P. A self-tuning PSO for job-shop scheduling problems. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, D.; Hsu, C.-Y. A hybrid particle swarm optimization for job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2006, 51, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thizy, J.-M.; Van Wassenhove, L.N.; Khumawala, B.M. Comparison of exact and approximate methods of solving the uncapacitated plant location problem. J. Oper. Manag. 1985, 6, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlauf, F. Design of Modern Heuristics: Principles and Application; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamura, K.; Sugimura, N. A study on real-time scheduling for autonomous distributed manufacturing systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 October 2010; pp. 1352–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, M.; Pentek, T.; Otto, B. Design principles for industrie 4.0 scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; pp. 3928–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.; Vera, D.; Ahmad, B. Engineering the smart factory. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 29, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N. Multiagent and Bargaining-Game-Based Real-Time Scheduling for Internet of Things-Enabled Flexible Job Shop. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 2518–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzis, D.; Vlachou, E. A cloud-based cyber-physical system for adaptive shop-floor scheduling and condition-based maintenance. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 47, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lödding, H.; Riedel, R.; Thoben, K.-D.; von Cieminski, G.; Kiritsis, D. (Eds.) Advances in Production Management Systems. The Path to Intelligent, Collaborative and Sustainable Manufacturing; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ortíz, M.A.; Betancourt, L.E.; Negrete, K.P.; De Felice, F.; Petrillo, A. Dispatching algorithm for production programming of flexible job-shop systems in the smart factory industry. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 264, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajrizi, E. Smart Solution for Smart Factory. IFAC Pap. 2016, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narman, H.S.; Hossain, S.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Shen, H. Scheduling internet of things applications in cloud computing. Ann. Telecommun. 2016, 72, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Joshi, R.C. A genetic. In Proceedings of the International Conference & Workshop on Emerging Trends in Technology—ICWET ’11, Mumbai, India, 25–26 February 2011; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xie, J.; Hu, J. Independent Tasks Scheduling Based on Genetic Algorithm in Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2009 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Beijing, China, 24–26 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, A.; Mei, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, M. Many-objective genetic programming for job-shop scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; LeCun, Y. Scaling Learning Algorithms towards AI. Large-Scale Kernel Mach. 2007, 34, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y. Deep learning of representations for unsupervised and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the ICML Workshop on Unsupervised and Transfer Learning, Bellevue, WA, USA, 2 July 2011; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oerlemans, A.; Lao, S.; Wu, S.; Lew, M.S. Deep learning for visual understanding: A review. Neurocomputing 2016, 187, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehues, M.; Blum, M.; Teschemacher, U.; Reinhart, G. Adaptive job shop control based on permanent order sequencing. Prod. Eng. 2017, 12, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, A.; Caricato, P.; Gianfreda, D.; Pesce, M.; Rigon, V.; Tregnaghi, L.; Voglino, A. An Industry 4.0 Case Study in Fashion Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrsai, A.; Figueira, G.; Santos, N.; Amorim, P.; Al-mada-Lobo, B. Decentralized vs. Centralized Sequencing in a Complex Job-Shop Scheduling. In Advances in Production Management Systems. The Path to Intelligent, Collaborative and Sustainable Manufacturing; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guizzi, G.; Vespoli, S.; Santini, S. On The Architecture Scheduling Problem Of Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the CEUR Workshop; CEUR-WS.org: London, UK, 2017; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.A.; Varela, M.L.R.; Alves, C.; Machado, J. Job shop schedules analysis in the context of Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), Madeira, Portugal, 27–29 June 2017; pp. 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B.; Werner, F.; Ivanova, M. A dynamic model and an algorithm for short-term supply chain scheduling in the smart factory Industry 4.0. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.Q.; Kozan, E.; Masoud, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, F.T. Job shop scheduling with a combination of four buffering constraints. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 56, 3274–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Jiang, P. RFID-based production data analysis in an IoT-enabled smart job-shop. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2018, 5, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuett-Garza, H.; Kurfess, T. A brief discussion on the trends of habilitating technologies for Industry 4.0 and Smart manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 2018, 15, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, W.T.; Cherri, L.H.; Voos, H. A Mathematical Model and a Firefly Algorithm for an Extended Flexible Job Shop Problem with Availability Constraints. In Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 235–246. ISBN 9783319912530. [Google Scholar]
- Lukasik, S.; Żak, S. Firefly Algorithm for Continuous Constrained Optimization Tasks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Collective Intelligence, Wroclaw, Poland, 5–7 October 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Bragin, M.A.; Luh, P.B. Novel Formulation and Resolution of Job-Shop Scheduling Problems. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3387–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, J.; Voß, T. Dynamic priority based dispatching of AGVs in flexible job shops. Procedia CIRP 2019, 79, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sethi, S.P.; Sokolov, B. Scheduling in production, supply chain and Industry 4.0 systems by optimal control: Fundamentals, state-of-the-art and applications. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.; Tiefenbacher, A.; Gronau, N. Need for Standardization and Systematization of Test Data for Job-Shop Scheduling. Data 2019, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, M. An improved Q-learning based rescheduling method for flexible job-shops with machine failures. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 15th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22–26 August 2019; pp. 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Pannek, J. Development of Operator Theory in the Capacity Adjustment of Job Shop Manufacturing Systems. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salido, M.A.; Escamilla, J.; Barber, F.; Giret, A.; Tang, D.; Dai, M. Energy efficiency, robustness, and makespan optimality in job-shop scheduling problems. Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 2015, 30, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, I.G.; Puente, J.; Varela, R.; Rodriguez-Vela, C. A Study of Schedule Robustness for Job Shop with Uncertainty. In Proceedings of the Advances in Artificial Intelligence—IBERAMIA 2008, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2008; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.-N.; Han, Y.; Fu, J. Robustness measures and robust scheduling for multi-objective stochastic flexible job shop scheduling problems. Soft Comput. 2016, 21, 6531–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamili, A. Robust job shop scheduling problem: Mathematical models, exact and heuristic algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 55, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y. Robust scheduling for multi-objective flexible job-shop problems with flexible workdays. Eng. Optim. 2016, 48, 1973–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, T. A Meta-Model-Based Multi-Objective Evolutionary Approach to Robust Job Shop Scheduling. Mathematics 2019, 7, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berti, N.; Finco, S.; Battaïa, O.; Delorme, X. Ageing workforce effects in Dual-Resource Constrained job-shop scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 237, 108151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Scheduling Algorithm | Study | Objective | Problem Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficient Rule Approach | [19] | Min. Makespan | 2-Machines JSSP problem |
|
| [35] | Min. Makespan | 2-Machines JSSP problem |
| |
| Mathematical Programming Approach | [36] | Min. Makespan | 3-Machines JSSP problem |
|
| [37] | Min. Makespan | 2-Machines JSSP problem |
| |
| Branch & Bound Method | [38,39,40] | Min. Makespan | 3-Machines JSSP problem |
|
| Scheduling Algorithm | Study | Objective | Problem Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constructive Method | Priority Dispatch Rule Method | [42] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | 10-Machines JSSP problem |
|
| Insert Algorithms | [43,44] | Min. Makespan | 5-Machines JSSP problem |
| |
| Bottleneck Based Heuristics Method | [45,46,47,48] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | Multiple machines & jobs |
| |
| Artificial Intelligence 1 | Constraint Satisfaction Technique 2 | [49,50] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | Multiple numbers of machines in JSSP |
|
| Neurons Networks 3 | [51,52] | Min. Earliest Starting time & Makespan | Multiple machines JSSP problem | ||
| Expert System and Knowledge-based Method | [10,55] | Min. Makespan | Multiple Machines in JSSP problem |
| |
| Fuzzy Logic | [56,57] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | Large scale JSSP problem |
| |
| Local Search Method | Simulated Annealing (SA), Genetic Local Search (GLS), Iterative Improvement (IM). | [59,60,61] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | 3-Machines JSSP problem | |
| Meta Heuristics Method 4 | Genetic Algorithm (GA) 5, Tabu Search (TS) 6, Ant colony Optimization (ACO) 7, Fire fly Algorithm (FA) 8, and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) 9 etc. | [6,7,9,29,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] | Min. CPU Time & Makespan | Multiple machines with multiple jobs |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liaqait, R.A.; Hamid, S.; Warsi, S.S.; Khalid, A. A Critical Analysis of Job Shop Scheduling in Context of Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147684
Liaqait RA, Hamid S, Warsi SS, Khalid A. A Critical Analysis of Job Shop Scheduling in Context of Industry 4.0. Sustainability. 2021; 13(14):7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiaqait, Raja Awais, Shermeen Hamid, Salman Sagheer Warsi, and Azfar Khalid. 2021. "A Critical Analysis of Job Shop Scheduling in Context of Industry 4.0" Sustainability 13, no. 14: 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147684
APA StyleLiaqait, R. A., Hamid, S., Warsi, S. S., & Khalid, A. (2021). A Critical Analysis of Job Shop Scheduling in Context of Industry 4.0. Sustainability, 13(14), 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147684








