Abstract
With a view of shedding light on the accumulation capability of the epigeous organs of common reed (Phragmites australis), employed worldwide in metal biomonitoring, an accumulation study of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn was performed, focusing on leaves belonging to different whorls and culms. To this end, in five sampling sites on the littoral zone of the volcanic Lake Averno (Italy), and in one occasion (autumn) before plant senescence, leaves of different ages and culms were collected and analyzed for metal concentrations. In terms of the suitability for biomonitoring, culms demonstrated poor performances in relation to the low metal accumulation and the difficulties in sampling and processing, whereas leaves proved their effectiveness in highlighting whole plant exposure. Since the accumulation degree of Cr, Cu, Fe and Zn is unaffected by leaf age, the pooling of leaves from different whorls is advisable to improve the representativeness of samplings. This strategy becomes mandatory in the case of Ni, the non-monotonic age-dependent variations of which would affect the derivation of contamination gradients otherwise. For Mn, Cd and Pb, the accumulation patterns strictly dependent on age can instead be exploited in selecting the sensitivity of biomonitoring by focusing on the organs where they are preferentially accumulated: old leaves for Mn and young leaves for Cd and Pb.
1. Introduction
The toxic and hazardous nature of metal contamination in freshwater ecosystems has become a global concern because these inorganic pollutants are persistent in the environment and are biomagnified through the food chains [1]. Although metals occur naturally in the environment, anthropogenic activities have contributed to undesirable toxic concentrations in several aquatic ecosystems [1,2,3,4,5]. A prerequisite for the assessment of the impact of these pollutants on the environment and human health, as well as for a sustainable management of the aquatic ecosystems, is their monitoring [6,7]. In this context, macrophytes play a prominent role in detecting the first symptoms of ecological degradation of different aquatic ecosystems worldwide [6,7,8,9].
The leaves of several helophytes effectively serve as good biomonitors of metal concentration gradients in freshwater ecosystems, both in relation to metal absorption (and translocation) from water and sediments [1,2,9,10,11] and atmospheric depositions [3,9]. In this context, particularly useful in metal biomonitoring studies are the epigeous organs of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel [3,12], also known as common reed. It is one of the most common macrophytes living in freshwater ecosystems throughout the world, able to withstand extreme environmental conditions, including high concentrations of toxic contaminants [8,13]. This rooted and emerged aquatic plant can absorb and accumulate metals through both the root-rhizome system and the leaf–culm system, above all in relation to the expanded area of the epigeous apparatus, able to trap particulate matter, sorb metal ions and accumulate and sequester pollutants [14]. Considering the wide distribution of the common reed, the good capability to accumulate metals from water, sediments and atmosphere and the easy collection of its epigeous organs, leaves and culms can be effectively employed in active biomonitoring studies of metal contamination [9,12].
Factors affecting metal accumulation by P. australis [1,2,13] can be biological (e.g., organ, age) and non-biological (e.g., season, temperature, water salinity and pH, sediment texture and organic matter content, metal concentration and speciation). Recent studies [1] have been performed with the view of proposing empirical prediction models based on these factors, but scarce attention has been paid to the age of the leaves when these organs are used in biomonitoring studies. It is possible that P. australis selectively allocates exceeding metals to senescing leaves, as observed in other metal-tolerant plant species, but this metal-dependent mechanism has been little investigated. Windham et al. [15] for Pb and Weis et al. [16] for Cu, Pb and Zn reported that the younger (upper) leaves of P. australis tended to have lower metal concentrations than the older (lower) leaves, concluding that in biomonitoring studies, collecting several leaves and pooling them allow obtaining more accurate data, since individual leaves may not be representative of the plant as a whole. In general, however, since the translocation and accumulation of metals may be element- and age-dependent, the clarification of these processes is crucial for the wise selection of the samples in biomonitoring studies. With the aim to gain insight into the metal accumulation capability of leaves of different age and culms of P. australis, a bioaccumulation study was performed on the littoral zone of Lake Averno (Southern Italy). The study embraced a space-for-time substitution approach by sampling the epigeous organs in a unique seasonal period, that allowed removing the potential confounding effects of season-dependent phenology, and by adopting the progressive whorl number along the culm as a proxy for leaf age.
2. Materials and Methods
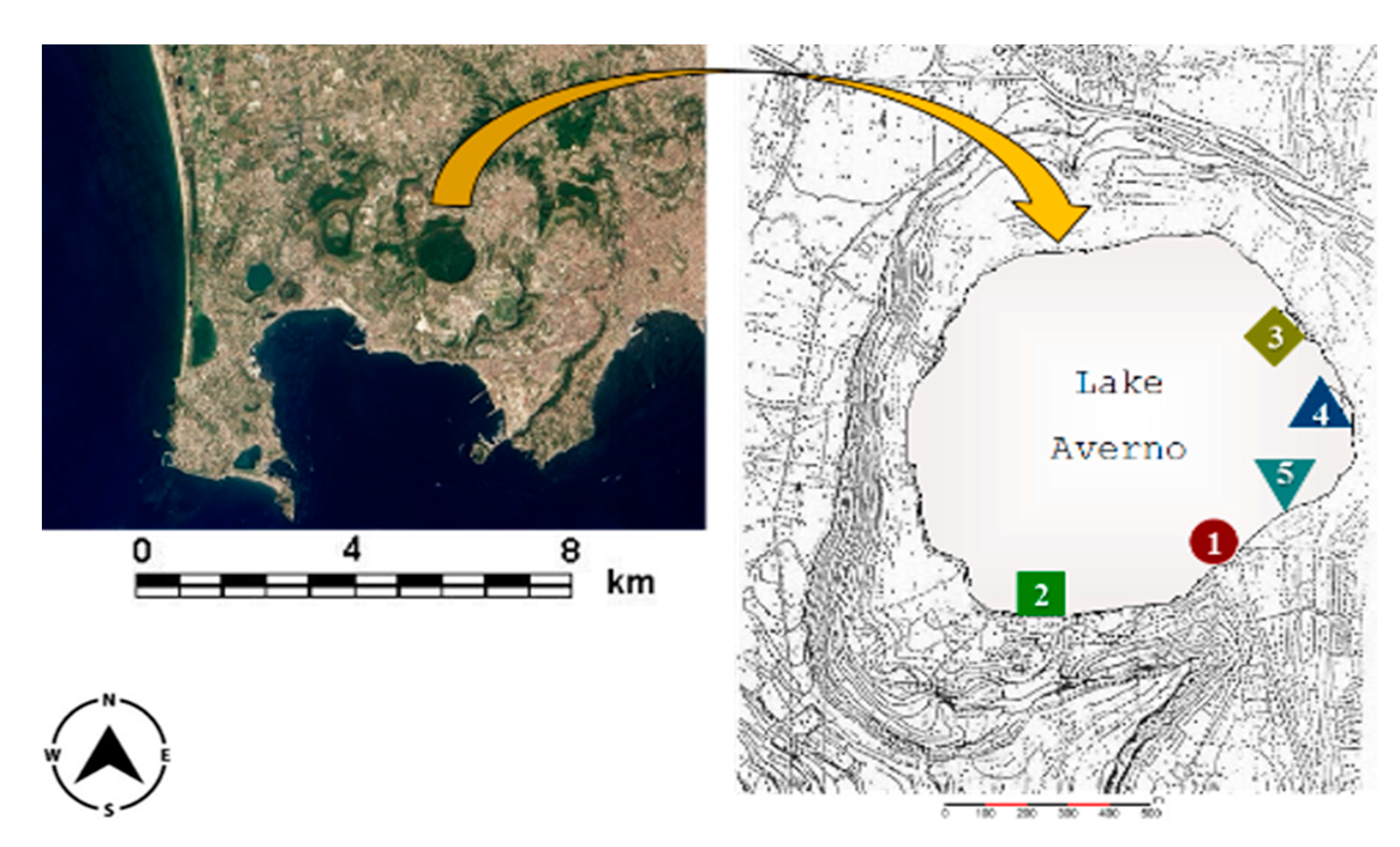
Lake Averno (40°50′20′′ N, 14°04′34′′ E, 3 m a.s.l.; Figure 1) is a volcanic lake in the Campi Flegrei area near Naples (Southern Italy). It is brackish due to the morphological characteristics of the basin (the lake is close to the sea), the high temperature and the salt content [8]. It is round, with a diameter of roughly 800 to 1000 m. The entire area is subjected to considerable human impact, such as construction works, recreation facilities and agriculture. In addition, a channel used as an overflow for a Naples sewage treatment plant flows into the lake when rainfall is abundant [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. All these sources contribute to the metal contamination of the lake [8,17], whose concentrations in water and sediments (as total and available fraction) are reported in Baldantoni et al. [14].
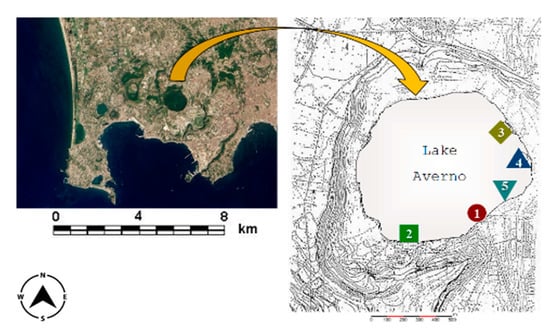
Figure 1.
Map of Lake Averno in the Campi Flegrei area (Southern Italy), showing location of sampling sites (1–5) in the littoral zone.
The dominant plant species of the littoral zone of Lake Averno is Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel, growing in small discontinuous clumps due to human pressure. Common reed is a perennial helophyte, preferentially colonizing eutrophic and stagnating waters across temperate and tropical regions all over the world, where it forms wide stands known as reed beds, which provide habitats for several birds and mammals [3,12]. P. australis belongs to the Poaceae family and is the most common species of the Phragmites genus [9], characterized by a C3 photosynthetic pathway [15]. It is a rhizomatous helophyte, with culms 2–6 m high and lanceolate leaves 20–50 cm long and 2–3 cm wide [3,9,12]. In temperate climates, it usually shows a distinct seasonal cycle, with the flowering time in late summer, followed by the desiccation of the epigeous organs during winter and plant persistence through the perennating underground rhizomes [17].
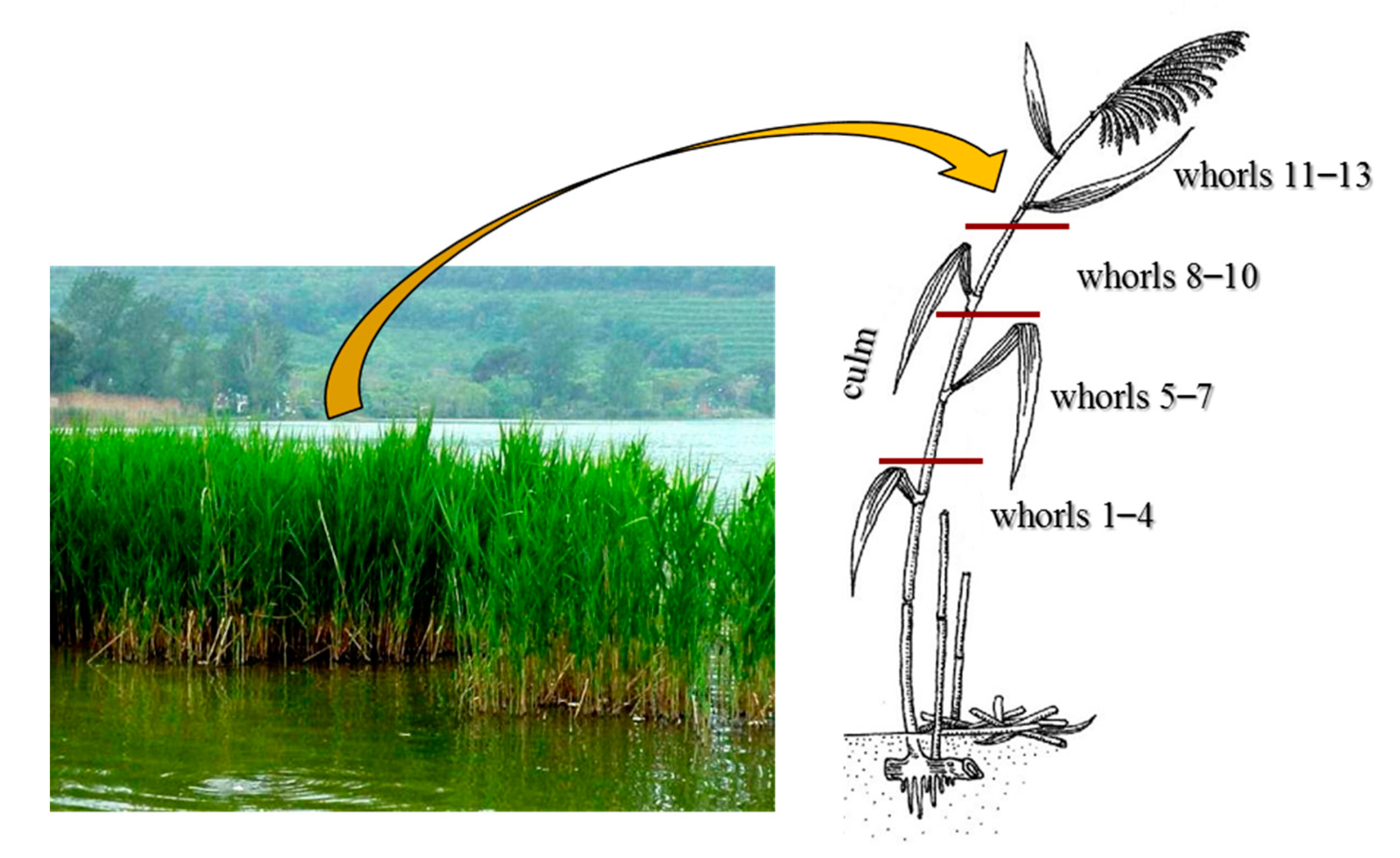
In autumn, before the epigeous organs senescence, ten healthy representative plants of current year were collected, on one occasion, at each of five sampling sites on the littoral zone of Lake Averno (Figure 1). Care was taken in all sampling to avoid the introduction of metal contamination. In the laboratory, leaves belonging to different whorls (1–4, 5–7, 8–10, 11–13, numbered from the lower/older to the upper/younger) and culms of each plant were separated (Figure 2), and for each site, subsamples from each plant were pooled together with the view of obtaining a representative sample. To evaluate total metal concentrations (deriving from water and sediment translocation and from atmospheric deposition), the epigeous organs were not washed.
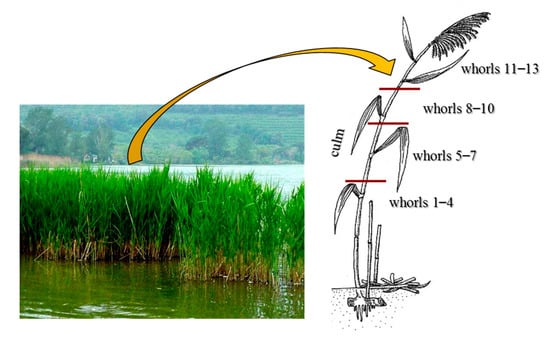
Figure 2.
P. australis clump in the littoral zone of Lake Averno and indication of the different epigeous organs analyzed: whorls 1–4, 5–7, 8–10 and 11–13 (collected from base to apex of the plant) and the culm.
Each sample was oven-dried at 75 °C to a constant weight and ground into a fine powder by a Fritsch pulverisette (00.502) with an agate pocket to prevent metal contamination. Three laboratory replicates of each sample were mineralized with 50% HF and 65% HNO3 at a ratio of 1:2 (v/v) in a Milestone (mls 1200) micro-wave oven [17], and metal concentrations were measured by a Varian (Spectr AA 20) atomic absorption spectrometer, via graphite furnace (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb) or via flame (Fe, Mn, Zn). The evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the entailed protocols was carried out through the concurrent analysis of a certified reference material (Olive leaves, BCR-062), with recoveries in the range of 92 to 103%.
Data analysis aimed at evaluating possible differentiations among the organs (leaves from different whorls and culms) and entailed both multivariate and univariate approaches. In this context, the possible differentiations among the whorls in relation to their metal concentrations was employed as a mean of evaluating age-related variations in metal accumulation. In the multivariate domain, the Euclidean distances among observations, based on metal concentrations, were fitted using one-way permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) with the organ as predictor. The same distances were also projected onto a two-dimensional space using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS), with the superimposition of the confidence ellipses (for α = 0.05) for each organ. In the univariate domain, the concentrations of each metal in the different organs were modelled through linear mixed models (LMMs), using the organ as a fixed effect and the sampling site as a random effect. The significance of the fixed effect was then evaluated through the Satterthwaite’s degrees of freedom method and, upon rejection of the null hypothesis, the pairwise comparisons between the estimated marginal means for each organ were carried out using the Tukey multiplicity adjustment. All the analyses were carried out within the R 4.0.5 programming environment [18], using the functions of the “vegan” [19], “lme4” [20], “lmertest” [21] and “emmeans” [22] packages.
3. Results and Discussion
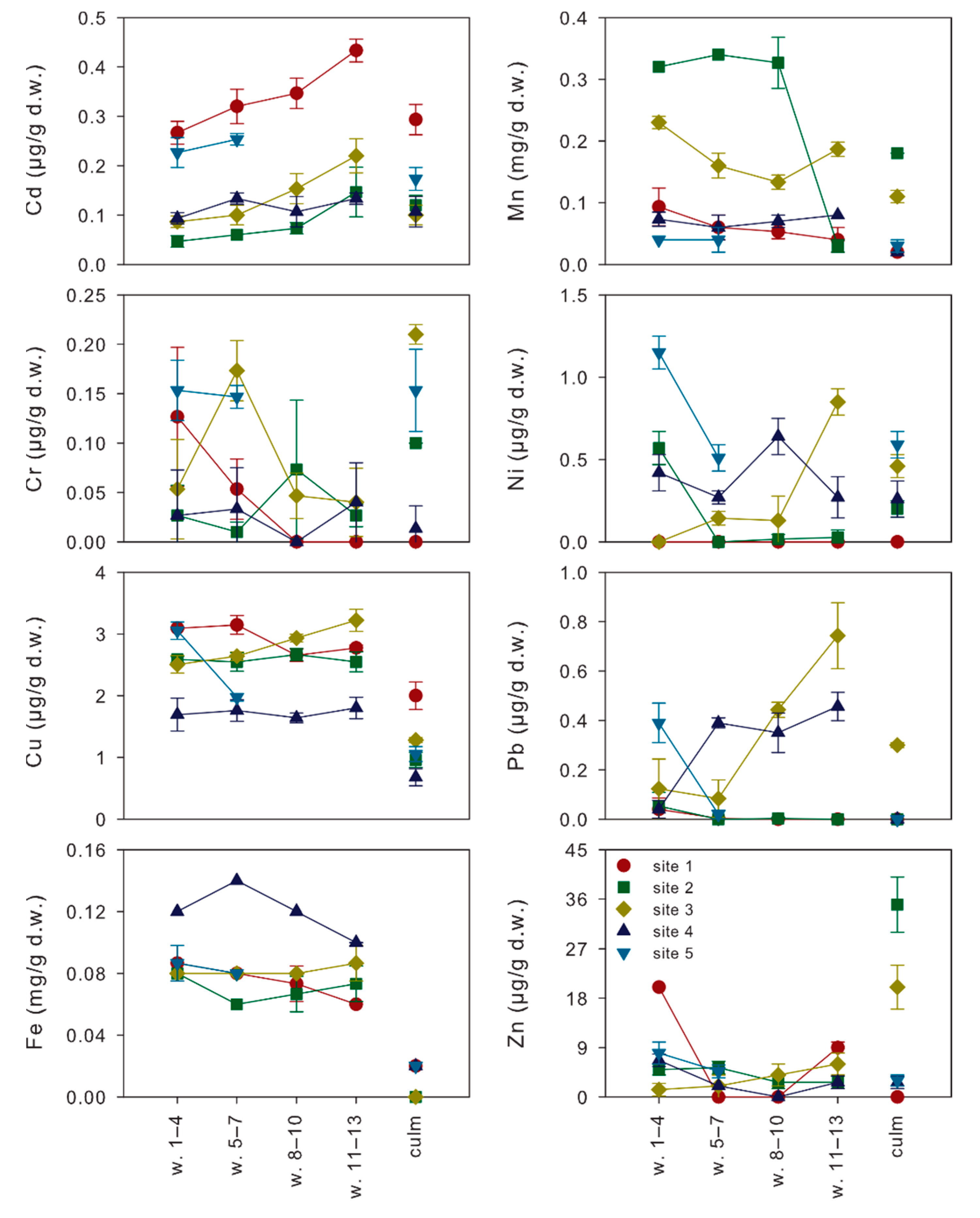
Metal concentrations measured in non-senescing leaves from different whorls and in culms of P. australis collected in the five sampling sites on the littoral zone of Lake Averno (Figure 3) showed values always below phytotoxic concentrations [23,24]. According to their average concentrations in the epigeous organs of P. australis (Figure 3; Table 1), they were sorted as Mn > Fe > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cd = Pb > Cr in leaves and Mn > Zn > Fe > Cu >Ni > Cd > Cr > Pb in culms. With the exception of Cd (always undetectable) and Fe (not investigated), the order observed for leaves was the same reported by Bonanno [2], whereas the one observed for culms showed inversions in the lowest ranks (Mn > Zn > Cu > Pb > Cr > Ni). In spite of the preferential accumulation of metals, Cu and Mn concentrations in both leaves and culms were in the same order of magnitude of those found in the same organs of P. australis growing at the mouth of two rivers, in Southern Italy, flowing in areas affected by urban, agricultural and industrial activities [2,12]. Conversely, Cr, Fe and Pb concentrations in both the organs, and Cd, Ni and Zn concentrations in leaves were at least one order of magnitude lower than those reported in the studies of Bonanno and Lo Giudice [12] and of Bonanno [2,9], indicating relatively low contaminations from these metals in Lake Averno.
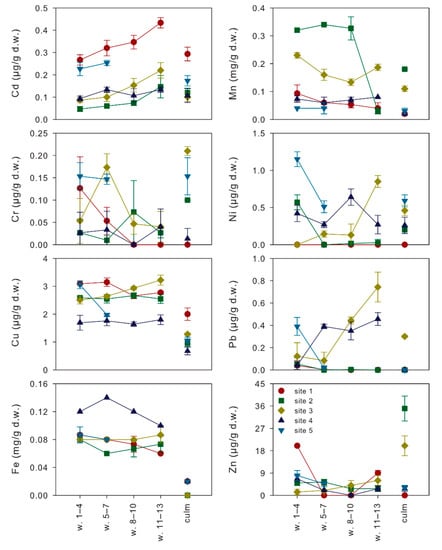
Figure 3.
Mean metal concentrations (± standard deviations) measured in the different epigeous organs (whorls 1–4, 5–7, 8–10, 11–13 and culm) of P. australis plants collected in the five sampling sites of Lake Averno.

Table 1.
F coefficients and p values (*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001) for each metal according to the linear mixed models (LMM). The estimated marginal means (µg/g d.w.) for each metal in each organ (whorls 1–4, 5–7, 8–10, 11–13 and culm) and the significance of the differences among them (different letters highlight significant differences for α = 0.05), according to the Tukey multiplicity adjustment, are also reported.
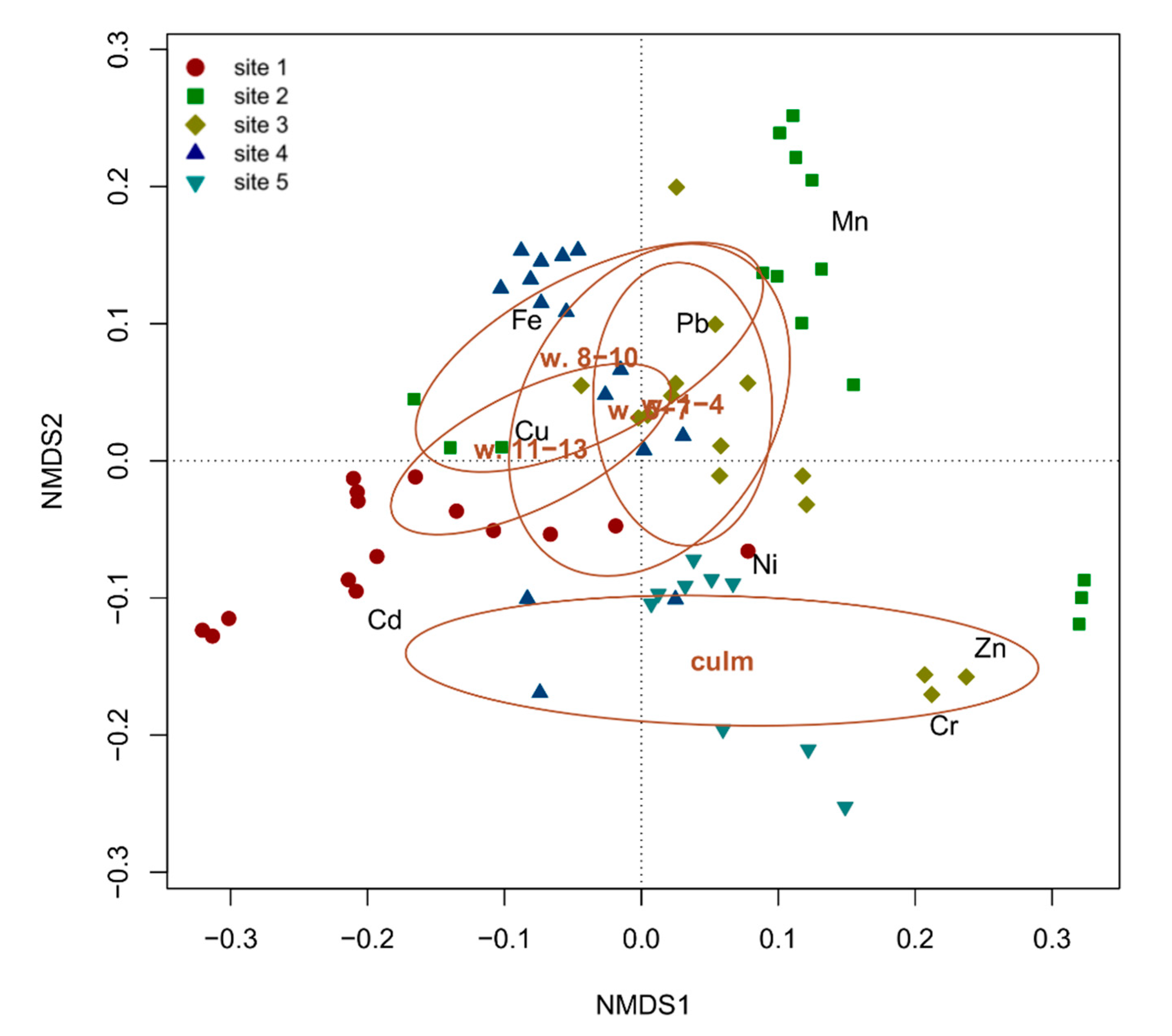
The one-way PERMANOVA highlighted significant (F = 4.5708, p < 0.01) differences among the analyzed organs, attributable to the differentiation of the culms from the leaves, the confidence ellipses of which are clearly separated on the NMDS space (Figure 4). Conversely, leaves belonging to different whorls, and thus of different ages, have largely overlapping confidence ellipses and are thus indistinguishable based on the overall accumulation of the analyzed metals. On average, culms showed the highest concentrations of Cr and Zn, whereas all the other metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni and Pb) were most abundant in leaves (Figure 4). This observation can be explained considering that metals are usually sequestered in leaf cell vacuoles [25], whereas stems (or culms) generally represent supporting and translocation organs that are not involved in metal accumulation [26].
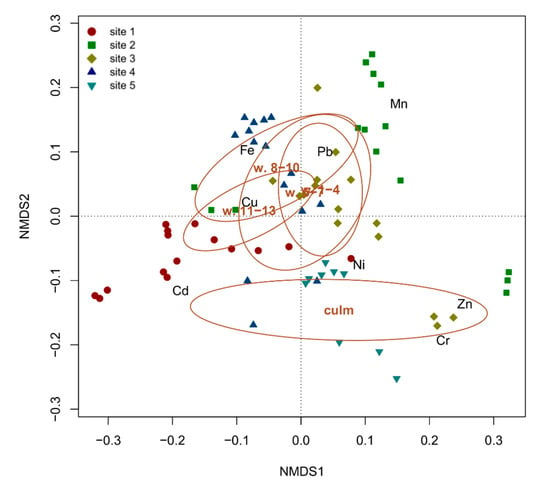
Figure 4.
NMDS biplot with the superimposition of confidence ellipses (for α = 0.05) showing the differentiation among the epigeous organs (whorls 1–4, 5–7, 8–10, 11–13 and culm) of P. australis as a function of metal concentrations in each of the five sampling sites of Lake Averno.
For all the analyzed metals, LMMs highlighted significant differences among organs of common reed from Lake Averno, but the pairwise comparisons between the estimated marginal means for each organ indicated significant differences only in few cases (Table 1). Apart from the differences in metal concentrations between leaves and culms, our findings contribute to clarify the age-related accumulation gradients in leaves (Figure 3; Table 1). In particular, Mn showed increasing concentrations with the increase in leaf age: from 64.6 to 151.3 µg/g d.w, whereas the opposite occurred for Cd and Pb from 0.25 to 0.14 µg/g d.w. and from 0.31 to 0.13 µg/g d.w., respectively. Significant differences among leaves from different whorls were also observed for Ni, but with an unclear age-related pattern: the highest concentrations were found in the oldest (0.43 µg/g d.w.) and youngest (0.39 µg/g d.w.) leaves, decreasing in the leaves of middle age (0.19–0.30 µg/g d.w.). All the other metals (Cr, Cu, Fe and Zn) did not show significant differences among leaves from different whorls.
The expected gradient, with older (lower) leaves accumulating more metals than younger (upper) leaves [16], was thus confirmed only for Mn, a nutrient playing important roles in several processes of a plantifecycle, being involved in photosynthesis, respiration, scavenging of reactive oxygen species, pathogen defense and hormone signaling [27,28]. For this element, increasing concentrations with leaf age in plants growing in submerged soils were previously observed for rice [29,30]. In this species, a member (OsNramp3) of the Nramp transporter family preferentially allocates this nutrient to the young leaves, requiring Mn for active cell division and elongation, at low environmental Mn concentrations [30]. At high Mn concentrations, the OsNramp3 protein is rapidly (within a few hours) degraded, resulting in the redistribution of Mn to older leaves and in the avoidance of Mn toxicity to the younger leaves [30]. In this case, the distribution of Mn follows the transpiration, since older leaves, having larger surface areas, are characterized by a higher transpiration rate [30]. In poorly drained soils, waterlogging causes a reduction of MnOx (most likely by the low O2 concentration), leading to an increase in plant-available Mn2+ in the soil solution up to toxic levels [28]. Since Mn concentrations measured in the epigeous organs of common reed from Lake Averno are on average one order of magnitude higher than the critical range (10–20 µg/g d.w.) reported for Mn deficiency [28], we can assume that in the study area Mn concentrations are far from being limiting. This consideration finds its foundations in the volcanic nature [31] of Lake Averno, characterized by sediments rich in total and available Mn concentrations [14].
Apart from Mn, all the other nutrients (Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Zn) playing important roles in plant nutrition at low concentrations [24] were equally distributed in leaves of different whorls. These findings are supported by the observations of [30], who found a different allocation of Mn in rice leaves of different ages but unclear patterns for the other nutrients (Cu, Fe and Zn) investigated. Such age-independent variations in metal concentrations suggest the adoption of sampling schemes based on the random collection of leaves from different whorls and their pooling to improve the representativeness of samples. Conversely, the accumulation patterns of Mn demand for the standardization of samplings by leaf age, a strategy that can also be effectively exploited to modulate the sensitivity of biomonitoring.
The two non-essential elements analyzed, Cd and Pb, showed an unexpected reduction in their concentrations with the increase in leaf age. A possible explanation for this pattern comes from the physiology of the uptake, detoxification and accumulation of these metals. Indeed, it is known that Cd is a highly toxic element affecting plant metabolism and growth [32] due to its interaction with the uptake of other elements [33] and the production of oxidative stress [34]. P. australis is renowned as a Cd-tolerant helophyte that relies on increased antioxidant enzyme activities as its primary defense strategy [12]. These activities are depressed in older leaves, a process in which the increased Mn concentrations have a direct contribution [35]. It can be thus hypothesized that the common reed preferentially accumulates Cd where cell oxidative stress can be effectively counteracted, that is, in young leaves. Similar considerations apply for Pb, another toxic element for plants, which is rather immobile and scantly translocated and accumulated in the epigeous plant organs [24]. These characteristics, in turn, led several authors to identify the exhaust fumes of the vehicular traffic as the primary source for leaf Pb concentrations, through atmospheric depositions [12]. However, such a hypothesis would imply that older leaves should accumulate higher Pb concentrations than younger leaves, that was not the case. It can be thus concluded that atmospheric depositions did not significantly affect leaf Pb (and Cd) concentrations in Lake Averno, an occurrence that had the upside of allowing highlighting the allocation of Pb to the young leaves. This finding disagrees with the results of Windham et al. [15] and Weis et al. [16] who reported higher Pb concentrations in older leaves of common reed grown under greenhouse conditions, and puts the attention on the need to accurately select leaves according to their age when biomonitoring of non-essential elements is carried out.
4. Conclusions
The bioaccumulation of metals in the epigeous organs of P. australis is element- and organ-specific and, in the case of leaves, it may depend on their age. Leaves are certainly the epigeous organs of common reed most suitable for bioaccumulation studies, but their age must be carefully considered in the biomonitoring of certain metals. In particular, whereas for Cr, Cu, Fe and Zn, leaf age does not affect metal concentrations and the collection and pooling of leaves of different age is recommended, Cd, Mn, Ni and Pb have age-dependent variations in their concentrations, demanding tailored sampling schemes addressing the low representativeness of individual leaves for the plant as a whole. For Ni, with unclear age-related patterns, the collection and pooling of leaves from different whorls represent a viable solution to obtain accurate biomonitoring data. For Mn, Cd and Pb, instead, the clear trends allow selecting specific whorls as the source material, a solution that allows modulating the sensitivity of biomonitoring by choosing leaves able to accumulate metals in higher or lower concentrations. Culms, representing supporting and translocation organs, are generally not involved in metal accumulation and, considering the difficulties in their sampling and processing, should be considered a last resort for the biomonitoring of metal concentration gradients, adoptable when alternative and preferable source materials are unavailable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B.; methodology, D.B. and A.B.; data acquisition, D.B.; data analysis, D.B. and A.B.; data curation, D.B. and A.B.; resources, D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B.; writing—review and editing, D.B. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research received no dedicated external funding, but relied on the facilities provided by University of Naples Federico II (Italy) for its implementation.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in the study are available in the figures and the table accompanying the present article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Anna Alfani (University of Salerno, Italy) for transmitting the passion and expertise needed to approach the biomonitoring of water, air and soil quality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eid, E.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; Al-Sodany, Y.M.; Haroun, S.A.; Galal, T.M.; Ayed, H.; Khedher, K.M.; Jensen, K. Common reed (Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel) as a candidate for predicting heavy metal contamination in Lake Burullus, Egypt: A biomonitoring approach. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 148, 105787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G. Comparative performance of trace element bioaccumulation and biomonitoring in the plant species Typha domingensis, Phragmites australis and Arundo donax. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2013, 97, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, G.; Pavone, P. Leaves of Phragmites australis as potential atmospheric biomonitors of Platinum Group Elements. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldantoni, D.; Alfani, A. Usefulness of different vascular plant species for passive biomonitoring of Mediterranean rivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13907–13917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldantoni, D.; Bellino, A.; Lofrano, G.; Libralato, G.; Pucci, L.; Carotenuto, M. Biomonitoring of nutrient and toxic element concentrations in the Sarno River through aquatic plants. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellino, A.; Alfani, A.; de Riso, L.; Gregorio, R.; Pellegrino, T.; Baldantoni, D. Long-established and new active biomonitors jointly reveal potentially toxic element gradients across spatial scales in freshwater ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellino, A.; Alfani, A.; de Riso, L.; Gregorio, R.; Pellegrino, T.; Baldantoni, D. A promising cosmopolitan biomonitor of potentially toxic elements in freshwater ecosystems: Concentration gradients in sensitive areas. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldantoni, D.; Maisto, G.; Bartoli, G.; Alfani, A. Analyses of three native aquatic plant species to assess spatial gradients of lake trace element contamination. Aquat. Bot. 2005, 83, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G. Trace element accumulation and distribution in the organs of Phragmites australis (common reed) and biomonitoring applications. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, G. Arundo donax as a potential biomonitor of trace element contamination in water and sediment. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favas, P.J.C.; Pratas, J.; Prasad, M.N.V. Accumulation of arsenic by aquatic plants in large-scale field conditions: Opportunities for phytoremediation and bioindication. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Lo Giudice, R. Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the organs of Phragmites australis (common reed) and their potential use as contamination indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Pociecha, A.; Szarek-Gwiazda, E.; Waloszek, A.; Wilk-Woźniak, E. Small effects of a large sediment contamination with heavy metals on aquatic organisms in the vicinity of an abandoned lead and zinc mine. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9825–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldantoni, D.; Alfani, A.; Di Tommasi, P.; Bartoli, G.; Virzo de Santo, A. Assessment of macro and microelement accumulation capability of two aquatic plants. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windham, L.; Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Lead uptake, distribution, and effects in two dominant salt marsh macrophytes, Spartina alterniflora (cordgrass) and Phragmites australis (common reed). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S.; Windham, L.; Weis, P. Patterns of metal accumulation in leaves of the tidal marsh plants Spartina alterniflora Loisel and Phragmites australis Cav. Trin ex Steud. over the growing season. Wetlands 2003, 23, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldantoni, D.; Ligrone, R.; Alfani, A. Macro- and trace-element concentrations in leaves and roots of Phragmites australis in a volcanic lake in Southern Italy. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 101, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.6.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans. (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Allen, S.E. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Material, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, S.; Plamgren, M.G.; Krämer, U. A long way ahead: Understanding and engineering plant metal accumulation. Trends Plant. Sci. 2002, 7, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldantoni, D.; Cicatelli, A.; Bellino, A.; Castiglione, S. Different behaviours in phytoremediation capacity of two heavy metal tolerant poplar clones in relation to iron and other trace elements. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Álvarez, C.; Alonso-Castro, A.J.; Alfaro-de la Torre, M.C.; García-de la Cruz, R.F. Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in Scirpus americanus and Typha latifolia from an artificial lagoon in San Luis Potosí, México. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 188, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, S.; Höller, S.; Meier, B.; Peiter, E. Manganese in plants: From acquisition to subcellular allocation. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlamis, J.; Williams, D.E. Iron and manganese relations in rice and barley. Plant Soil 1964, 20, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, N.; Sasaki, A.; Xia, J.X.; Yokosho, K.; Ma, J.F. A node-based switch for preferential distribution of manganese in rice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Linhares, D.P.; Ventura Garcia, P.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A. Trace elements in volcanic environments and human health effects. In Trace Metals in the Environment—New Approaches and Recent Advances; Murillo-Tovar, M.A., Saldarriaga-Noreña, H., Saeid, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Divan, A.M., Jr.; de Oliveira, P.L.; Perry, C.T.; Atz, V.L.; Azzarini-Rostirola, L.N.; Raya-Rodriguez, M.T. Using wild plant species as indicators for the accumulation of emissions from a thermal power plant, Candiota, South Brazil. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.E.; Lozano, E.; Gárate, A.; Carpena, R. Influence of cadmium on the uptake, tissue accumulation and subcellular distribution of manganese in pea seedlings. Plant. Sci. 1998, 132, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lelandais, M.; Kunert, K.J. Photooxidative stress in plants. Physiol. Plantarum 1994, 92, 696–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandziora-Ciupa, M.; Nadgórska-Socha, A.; Barczyk, G.; Ciepał, R. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and ecophysiological responses to heavy metal stress in selected populations of Vaccinium myrtillus L. and Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).