Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Material and Measures
2.2.1. Heart Rate Variability
2.2.2. Slow-Paced Breathing
2.2.3. Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ruiz, M.; Robazza, C. Feelings in Sport—Theory, Research, and Practical Implications for Performance and Well-Being; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.V. Controlling emotions in sport. Sport Psychol. 2003, 17, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.S. How emotions influence performance in competitive sports. Sport Psychol. 2000, 14, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, A.R.; Polman, R.C. Coping in sport: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, A.R.; Taylor, N.J.; Carroll, S.; Perry, J.L. The Development of a New Sport-Specific Classification of Coping and a Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Different Coping Strategies and Moderators on Sporting Outcomes. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.J.; Shearer, D.A.; Bringer, J.D.; Hall, R.; Cook, C.J.; Kilduff, L.P. Abbreviated Resonant Frequency Training to Augment Heart Rate Variability and Enhance On-Demand Emotional Regulation in Elite Sport Support Staff. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2016, 41, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.J.; Hall, R.; Bringer, J.D.; Cook, C.J.; Kilduff, L.P.; Shearer, D.A. Resonant frequency training in elite sport: A case study example. J. Sport Psychol. Action 2017, 8, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Laborde, S.; Salvotti, C.; Zammit, N.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of a Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session on Cardiac Vagal Activity in Athletes. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Lentes, T.; Hosang, T.J.; Borges, U.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of slow-paced breathing on inhibition after physical exertion. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Vagal Tone in Psychophysiological Research—Recommendations for Experiment Planning, Data Analysis, and Data Reporting. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Hansen, A.L.; Saus-Rose, E.; Johnsen, B.H. Heart rate variability, prefrontal neural function, and cognitive performance: The neurovisceral integration perspective on self-regulation, adaptation, and health. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 37, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Mertgen, A. Vagal Tank Theory: The Three Rs of Cardiac Vagal Control Functioning—Resting, Reactivity, and Recovery. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Heuer, S.; Mosley, E. Effects of a Brief Hypnosis Relaxation Induction on Subjective Psychological States, Cardiac Vagal Activity, and Breathing Frequency. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2018, 66, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E. Commentary: Heart rate variability and self-control–A meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, D.; Wenzel, M.; Kubiak, T. Response: Commentary: Heart rate variability and self-control–A meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, D.; Adams, J.; Krohn, J.; Wenzel, M.; Mann, C.G.; Gomille, L.K.; Jacobi-Scherbening, V.; Kubiak, T. Heart rate variability and self-control—A meta-analysis. Biol. Psychol. 2016, 115, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Santarelli, D.M.; O’Rourke, D. The physiological effects of slow breathing in the healthy human. Breathe 2017, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, L. Fundamentals of Physiology: A Human Perspective, 3rd ed.; Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, G.J.; Derrickson, B.H. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, D.J.; Hochman, S. Hypothesis: Pulmonary afferent activity patterns during slow, deep breathing contribute to the neural induction of physiological relaxation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, R.J.S.; Band, G.P.H. Breath of Life: The Respiratory Vagal Stimulation Model of Contemplative Activity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccaro, A.; Piarulli, A.; Laurino, M.; Garbella, E.; Menicucci, D.; Neri, B.; Gemignani, A. How Breath-Control Can Change Your Life: A Systematic Review on Psycho-Physiological Correlates of Slow Breathing. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.; Thayer, J.F. How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 19, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Gevirtz, R. Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Front. Psychol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Meehan, Z.M. A practical guide to resonance frequency assessment for heart rate variability biofeedback. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Lane, R.D. Claude Bernard and the heart-brain connection: Further elaboration of a model of neurovisceral integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Thayer, J.F.; Khalsa, S.S.; Lane, R.D. The hierarchical basis of neurovisceral integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntson, G.G.; Bigger, J.T.; Eckberg, D.L.; Grossman, P.; Kaufmann, P.G.; Malik, M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Porges, S.W.; Saul, J.P.; Stone, P.H.; et al. Heart rate variability: Origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology 1997, 34, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M. Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromenacker, B.W.; Sanova, A.A.; Marcus, F.I.; Allen, J.J.B.; Lane, R.D. Vagal Mediation of Low-Frequency Heart Rate Variability During Slow Yogic Breathing. Psychosom. Med. 2018, 80, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penttila, J.; Helminen, A.; Jartti, T.; Kuusela, T.; Huikuri, H.V.; Tulppo, M.P.; Coffeng, R.; Scheinin, H. Time domain, geometrical and frequency domain analysis of cardiac vagal outflow: Effects of various respiratory patterns. Clin. Physiol. 2001, 21, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, O.; Schumann, B.; Kluttig, A.; Greiser, K.H.; Haerting, J. Time domain parameters can be estimated with less statistical error than frequency domain parameters in the analysis of heart rate variability. J. Electrocardiol. 2008, 41, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenger, C.R.; Fuller, J.T.; Thomson, R.L.; Davison, K.; Robertson, E.Y.; Buckley, J.D. Monitoring Athletic Training Status Through Autonomic Heart Rate Regulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1461–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M. Monitoring training status with HR measures: Do all roads lead to Rome? Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Peake, J.M.; Buchheit, M. Cardiac parasympathetic reactivation following exercise: Implications for training prescription. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1259–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Raab, M. The tale of hearts and reason: The influence of mood on decision making. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Raab, M.; Kinrade, N.P. Is the ability to keep your mind sharp under pressure reflected in your heart? Evidence for the neurophysiological bases of decision reinvestment. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 100C, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Furley, P.; Schempp, C. The relationship between working memory, reinvestment, and heart rate variability. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, S.; Noel, B.; Musculus, L.; Werner, K.; Laborde, S.; Lopes, M.C.; Greco, P.J.; Memmert, D.; Raab, M. Creative and Intuitive Decision-Making Processes: A Comparison of Brazilian and German Soccer Coaches and Players. Res. Quaterly Exerc. Sport 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, E.; Laborde, S.; Kavanagh, E. Coping related variables, cardiac vagal activity and working memory performance under pressure. Acta Psychol. 2018, 191, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Lautenbach, F.; Allen, M.S. The contribution of coping-related variables and heart rate variability to visual search performance under pressure. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Brüll, A.; Weber, J.; Anders, L.S. Trait emotional intelligence in sports: A protective role against stress through heart rate variability? Personal. Individ. Differ. 2011, 51, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, M.O.; Laborde, S.; Rummel, J.; Giessing, L.; Kasperk, C.; Plessner, H.; Heck, R.-B.; Strahler, J. Heidelberg Risk Sport-Specific Stress Test: A Paradigm to Investigate the Risk Sport-Specific Psycho-Physiological Arousal. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minns, D.; Mosley, E.; Laborde, S.; Wimshurst, Z.L. The contribution of cardiac vagal activity on peripheral perception under pressure. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 240, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, P.; Filaire, E.; Mourot, L.; Nicolas, M. Stress and recovery in sports: Effects on heart rate variability, cortisol, and subjective experience. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 143, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, L.S.; da Costa, B.D.V.; Paes, P.P.; do Nascimento Junior, J.R.A.; Fiorese, L.; Ferreira, M.E.C. Influence of Competitive-Anxiety on Heart Rate Variability in Swimmers. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2017, 16, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mosley, E.; Laborde, S.; Kavanagh, E. The contribution of coping-related variables and cardiac vagal activity on prone rifle shooting performance under pressure. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Wang, C.J.K. Pre-performance Physiological State: Heart Rate Variability as a Predictor of Shooting Performance. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2018, 43, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, E.; Laborde, S.; Kavanagh, E. The contribution of coping related variables and cardiac vagal activity on the performance of a dart throwing task under pressure. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Ueberholz, L. Enhancing cardiac vagal activity: Factors of interest for sport psychology. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 240, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatisson, J.; Oswald, V.; Lalonde, F. Influence diagram of physiological and environmental factors affecting heart rate variability: An extended literature overview. Heart Int. 2016, 11, e32–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Mertgen, A. A unifying conceptual framework of factors associated to cardiac vagal control. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez Morgan, S.; Molina Mora, J.A. Effect of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback on Sport Performance, a Systematic Review. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagaduan, J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Fell, J.W.; Xuan Wu, S.S. Can Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Improve Athletic Performance? A Systematic Review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 73, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Andrasik, F. Biofeedback: A Practitioner’s Guide, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wheat, A.L.; Larkin, K.T. Biofeedback of heart rate variability and related physiology: A critical review. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2010, 35, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Kaur, K.; Sharma, A.; Shah, K.; Huseby, R.; Bhavsar, J.; Zhang, Y. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Improves Emotional and Physical Health and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, W.A.; Kennedy, T.D.; Hughes, P.A.; Calzada, P.J. A Single-Participants Investigation of the Effects of Various Biofeedback-Assisted Breathing Patterns on Heart Rate Variability: A Practitioner's Approach. Biofeedback 2009, 37, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B. Resonant frequency biofeedback training to increase cardiac variability: Rationale and manual for training. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2000, 25, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.; Outhred, T.; Heathers, J.A.; Quintana, D.S.; Kemp, A.H. Matter over mind: A randomised-controlled trial of single-session biofeedback training on performance anxiety and heart rate variability in musicians. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, S.; Jendreizik, L.; Ettinger, U.; Laborde, S. Keeping the pace: The effect of slow-paced breathing on error monitoring. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.; Borges, U.; Hosang, T.; Furley, P.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. The influence of slow-paced breathing on executive function. J. Psychophysiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Hosang, T.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of a 30-day slow paced breathing intervention compared to social media use on subjective sleep quality and cardiac vagal activity. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diest, I.; Verstappen, K.; Aubert, A.E.; Widjaja, D.; Vansteenwegen, D.; Vlemincx, E. Inhalation/Exhalation ratio modulates the effect of slow breathing on heart rate variability and relaxation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss-Blasche, G.; Moser, M.; Voica, M.; McLeod, D.R.; Klammer, N.; Marktl, W. Relative timing of inspiration and expiration affects respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckberg, D.L. Human sinus arrhythmia as an index of vagal cardiac outflow. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 54, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntson, G.G.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Quigley, K.S. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Autonomic origins, physiological mechanisms, and psychophysiological implications. Psychophysiology 1993, 30, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.M.; Tai, L.Y.; Fan, S.Y. Breathing at a rate of 5.5 breaths per minute with equal inhalation-to-exhalation ratio increases heart rate variability. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 91, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.S.; Heathers, J.A. Considerations in the assessment of heart rate variability in biobehavioral research. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.E.B.; Scott, A.B.; Boggero, I.A.; Carlson, C.R. Inclusion of a rest period in diaphragmatic breathing increases high frequency heart rate variability: Implications for behavioral therapy. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, P. Respiration, stress, and cardiovascular function. Psychophysiology 1983, 20, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Niskanen, J.P.; Lipponen, J.A.; Ranta-Aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Kubios HRV--heart rate variability analysis software. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Gohring, N.; Dosseville, F. The effect of slow-paced breathing on stress management in adolescents with intellectual disability. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2017, 61, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.; Friedman, B.H. Positive emotion reduces dyspnea during slow paced breathing. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Myers, C.W.; Halliwill, J.R.; Seidel, H.; Eckberg, D.L. Sympathetic restraint of respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Implications for vagal-cardiac tone assessment in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H2804–H2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckberg, D.L.; Eckberg, M.J. Human sinus node responses to repetitive, ramped carotid baroreceptor stimuli. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 242, H638–H644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskerville, A.L.; Eckberg, D.L.; Thompson, M.A. Arterial pressure and pulse interval responses to repetitive carotid baroreceptor stimuli in man. J. Physiol. 1979, 297, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Gholamrezaei, A.; Franssen, M.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Aziz, Q.; Van den Bergh, O.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Van Diest, I. Can slow deep breathing reduce pain? An experimental study exploring mechanisms. J. Pain 2020, 21, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, A.E.; Seps, B.; Beckers, F. Heart rate variability in athletes. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; Watkins, P.J. Cardiac denervation in diabetes. Br. Med. J. 1973, 4, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, D.J. Cardiovascular reflexes and autonomic neuropathy. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 1978, 55, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, D.J.; Clarke, B.F. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br. Med. J. Clin. Res. Ed. 1982, 285, 916–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaschillo, E.G.; Vaschillo, B.; Lehrer, P.M. Characteristics of resonance in heart rate variability stimulated by biofeedback. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2006, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, H.; Vandoni, M.; Debarbieri, G.; Codrons, E.; Ugargol, V.; Bernardi, L. Cardiovascular and respiratory effect of yogic slow breathing in the yoga beginner: What is the best approach? Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med 2013, 2013, 743504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herakova, N.; Nwobodo, N.H.N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zheng, D. Effect of respiratory pattern on automated clinical blood pressure measurement: An observational study with normotensive subjects. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.S.; Gould, D. Foundations of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 7th ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, S.; Borges, U.; Broker, L.; Laborde, S.; Liepelt, R.; Lobinger, B.H.; Loffler, J.; Musculus, L.; Raab, M. The Psychophysiology of Action: A Multidisciplinary Endeavor for Integrating Action and Cognition. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Strack, N.; Mosley, E. The influence of power posing on cardiac vagal activity. Acta Psychol. 2019, 199, 102899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, U.; Laborde, S.; Raab, M. Influence of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on cardiac vagal activity: Not different from sham stimulation and no effect of stimulation intensity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, U.; Knops, L.; Laborde, S.; Klatt, S.; Raab, M. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation May Enhance Only Specific Aspects of the Core Executive Functions. A Randomized Crossover Trial. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, U.; Pfannenstiel, M.; Tsukahara, J.; Laborde, S.; Klatt, S.; Raab, M. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation via tragus or cymba conchae: Are its psychophysiological effects dependent on the stimulation area? Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Kauschke, D.; Hosang, T.J.; Javelle, F.; Mosley, E. Performance Habits: A Framework Proposal. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
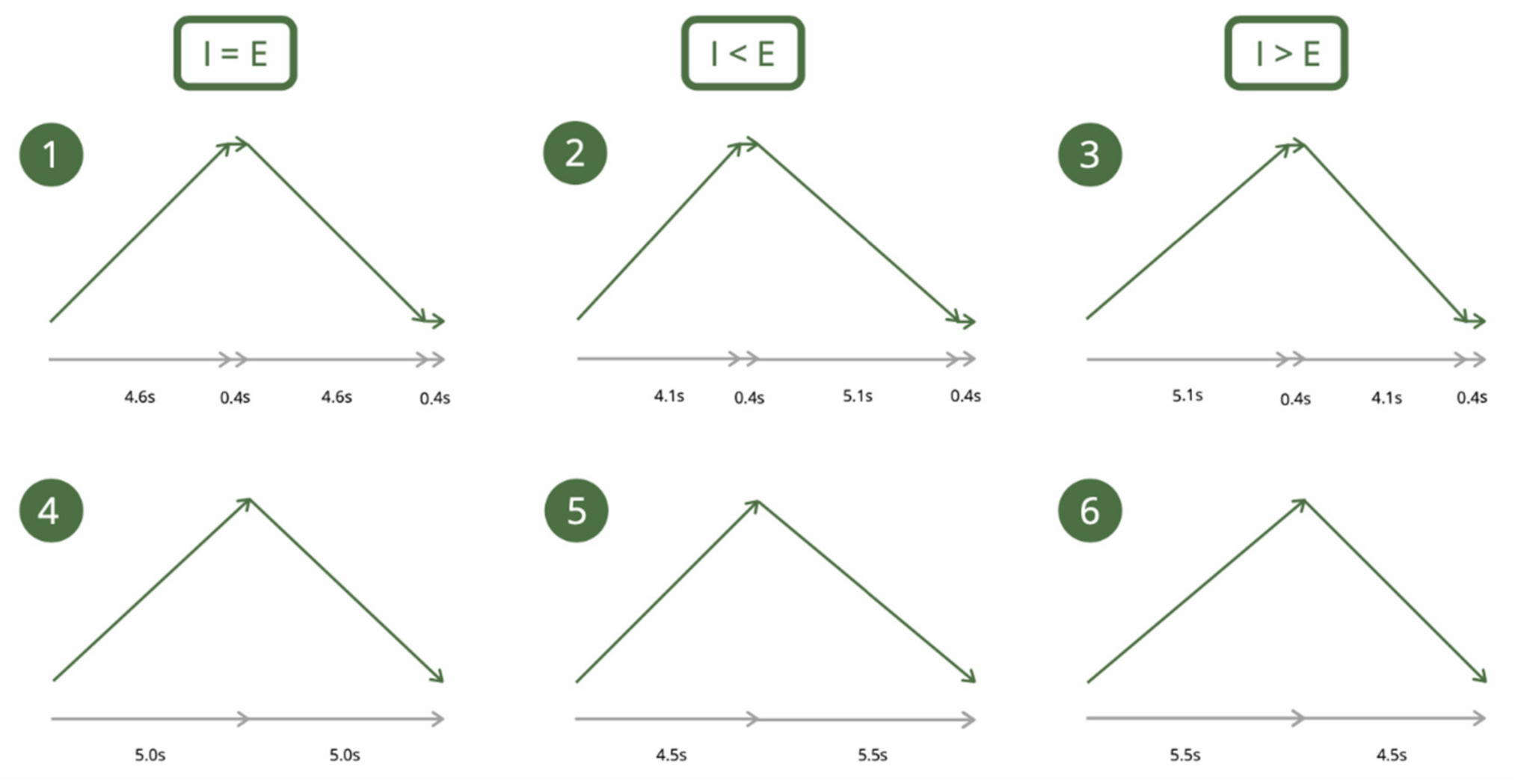

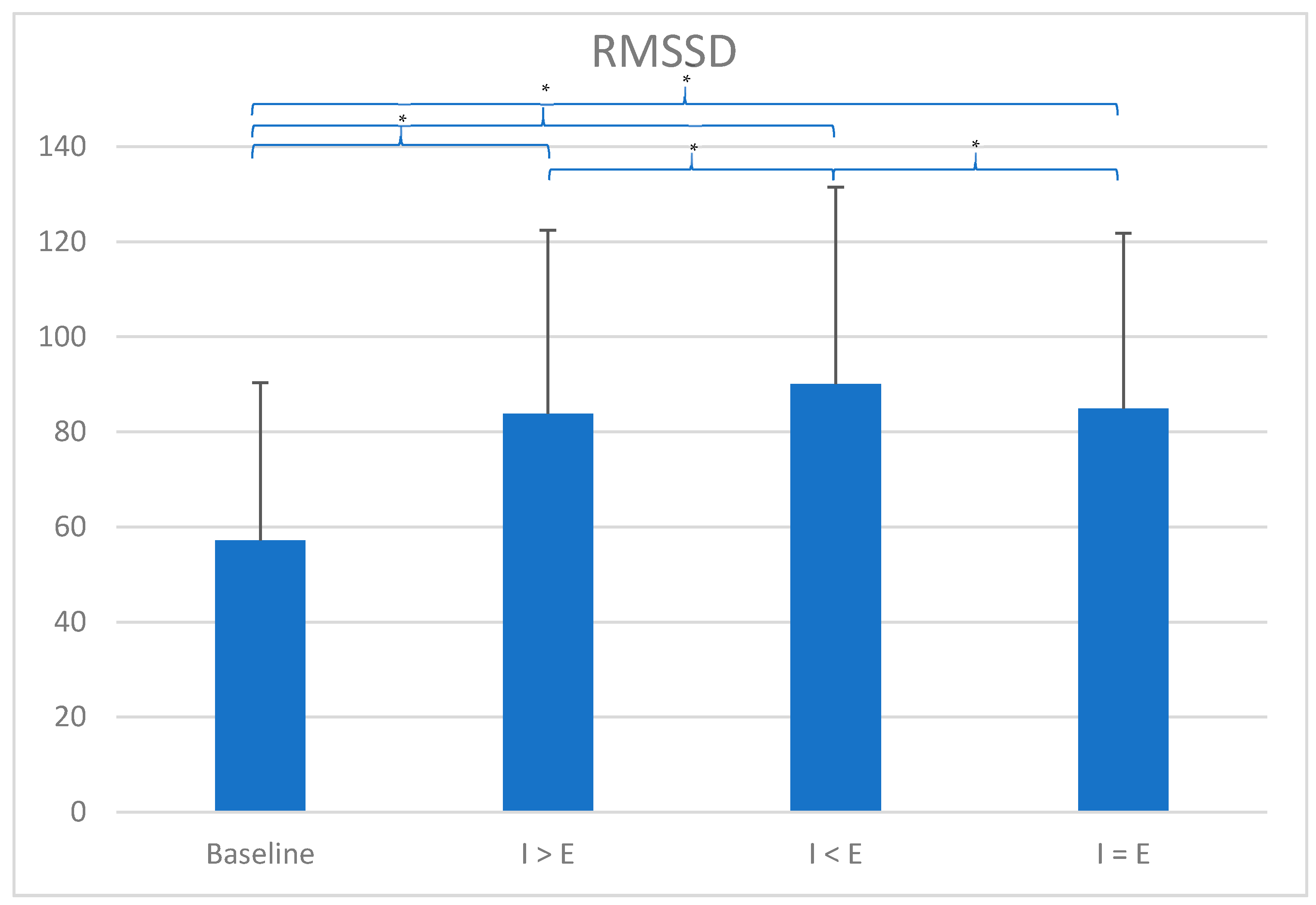
| Conditions | HR | SDNN | RMSSD | Log RMSSD | LF | HF | LF/HF | Breathing Frequency | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | M | SD | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Baseline | 67.18 | 7.97 | 92.22 | 37.37 | 57.14 | 33.17 | 1.70 | 4.09 | 3.91 | 0.22 | 3735.74 | 6586.00 | 1266.25 | 1450.35 | 11.45 | 2.03 |
| I > E RP | 68.23 | 6.68 | 138.11 | 54.94 | 85.29 | 38.95 | 1.89 | 17.52 | 14.53 | 0.20 | 14,031.93 | 10,768.08 | 1427.02 | 1473.48 | 6.55 | 0.26 |
| I < E RP | 68.23 | 6.53 | 133.89 | 45.04 | 90.27 | 41.38 | 1.91 | 14.30 | 12.38 | 0.20 | 14,587.38 | 11,754.30 | 1954.86 | 1918.53 | 6.49 | 0.30 |
| I = E RP | 68.37 | 6.57 | 132.06 | 42.74 | 86.82 | 39.35 | 1.89 | 16.52 | 12.95 | 0.21 | 14,352.57 | 11,242.16 | 1664.05 | 1702.17 | 6.51 | 0.22 |
| I > E no RP | 68.91 | 7.06 | 127.94 | 39.02 | 82.44 | 38.09 | 1.87 | 16.92 | 12.22 | 0.20 | 12,761.97 | 9874.21 | 1415.16 | 1621.83 | 6.52 | 0.23 |
| I < E no RP | 68.59 | 6.86 | 161.10 | 42.80 | 89.93 | 41.39 | 1.91 | 16.13 | 13.15 | 0.20 | 14,580.16 | 11,277.36 | 1602.47 | 1403.40 | 6.54 | 0.32 |
| I = E no RP | 68.78 | 6.30 | 128.27 | 38.72 | 82.94 | 34.54 | 1.88 | 15.91 | 11.81 | 0.18 | 13,597.23 | 9134.12 | 1465.51 | 1506.67 | 6.48 | 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laborde, S.; Iskra, M.; Zammit, N.; Borges, U.; You, M.; Sevoz-Couche, C.; Dosseville, F. Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147775
Laborde S, Iskra M, Zammit N, Borges U, You M, Sevoz-Couche C, Dosseville F. Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity. Sustainability. 2021; 13(14):7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147775
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaborde, Sylvain, Maša Iskra, Nina Zammit, Uirassu Borges, Min You, Caroline Sevoz-Couche, and Fabrice Dosseville. 2021. "Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity" Sustainability 13, no. 14: 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147775
APA StyleLaborde, S., Iskra, M., Zammit, N., Borges, U., You, M., Sevoz-Couche, C., & Dosseville, F. (2021). Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity. Sustainability, 13(14), 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147775






