A P-Hub Location Problem for Determining Park-and-Ride Facility Locations with the Weibit-Based Choice Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Notation
3. Multinomial Logit Model and Multinomial Weibit Model
3.1. Multinomial Logit Model
3.2. Multinomial Weibit Model
4. MNW P-Hub Problem for P&R Facility Location
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Small Network
5.1.1. Comparison between MNL-Based and MNW-Based Models
5.1.2. Effect of the MNW Model Parameters
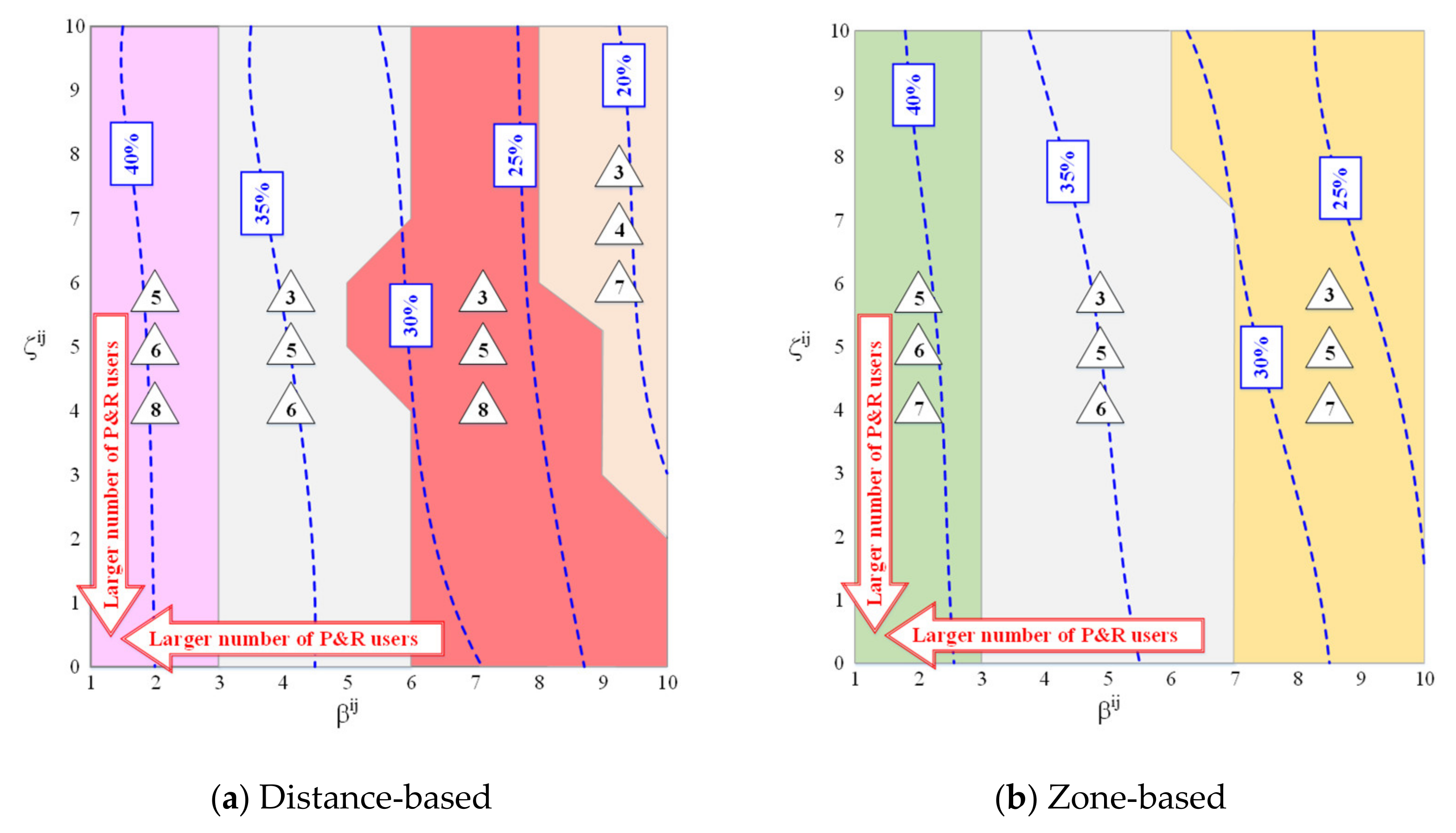
5.2. Chiang Mai Transportation Network
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opasanon, S.; Kitthamkesorn, S. Border crossing design in light of the ASEAN economic community: Simulation based approach. Transp. Policy 2016, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanuri, C.; Venkata, K.; Maitia, C.; Mulukutlaa, P. Leveraging innovation for last-mile connectivity to mass transit. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 41, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, J.; Owen, D.; Waygood, E.; Letarte, L. Modeling the desire for using public transport. Travel Behav. Soc. 2020, 10, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavadas, J.; Antunes, A.P. Optimization-based study of the location of park-and-ride facilities. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2019, 42, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ReVelle, C. The maximum capture or “sphere of influence” location problem: Hotelling revisited on a network. J. Reg. Sci. 1986, 26, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drezner, T.; Eiselt, H. Consumers in competitive location models. In Facility Location: Applications and Theory; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, O.; Drezner, T.; Drezner, Z.; Krass, D. Modeling competitive facility location problems: New approaches and results. In TutORials in Operations Research; INFORMS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, D.L. Defining and estimating a trade area. J. Mark. 1964, 28, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, W. The Law of Retail Gravitation; Knickerbocker Press: New York, NY, USA, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Swait, J. Discrete choice theory and modeling. In The Oxford Handbook of the Economics of Food Consumption and Policy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, F. Decisional processing on parking behavior in entropic settings. Arch. Transp. 2017, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, M. A perceptual-behavioural approach with non-parametric experimental coefficient for urban parking business design. Arch. Transp. 2016, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benati, S.; Hansen, P. The maximum capture problem with random utilities: Problem formulation and algorithms. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, K. Discrete Location Planning; Technical Report WP-09-07; Institute for Transport and Logistics Studies, University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aros-Vera, F.; Marianov, V.; Mitchell, J.E. p-Hub approach for the optimal park-and-ride facility location problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 226, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffi, Y.; Daganzo, C.F. Hypernetworks and supply-demand equilibrium obtained with disaggregate demand models. Transp. Res. Rec. 1978, 673, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Berman, O.; Verter, V. The impact of client choice on preventive healthcare facility network design. OR Spectr. 2012, 34, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, K.; Müller, S. A comparison of linear reformulations for multinomial logit choice probabilities in facility location models. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 232, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Meng, Q. Bus-based park-and-ride system: A stochastic model on multimodal network with congestion pricing schemes. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 45, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Meng, Q.; Kim, I. Remote park-and-ride network equilibrium model and its applications. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2018, 117, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, C.; Cortés, C.E.; Jara-Moroni, P.; Moreno, E. Integrated traffic-transit stochastic equilibrium model with park-and-ride facilities. Transp. Res. Part C 2016, 71, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffi, Y. Urban Transportation Networks: Equilibrium Analysis with Mathematical Programming Methods; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Daganzo, C.F.; Sheffi, Y. On stochastic models of traffic assignment. Transp. Sci. 1977, 11, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekhor, S.; Prashker, J.N. Formulations of extended logit stochastic user equilibrium assignments. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory, Jerusalem, Israel, 20–23 July 1999; pp. 351–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Akiva, M.; Bierlaire, M. Discrete choice methods and their applications to short term travel decisions. In Handbook of Transportation Science; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 5–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.; Chen, A.; Kitthamkesorn, S. A Two-Phase Gradient Projection Algorithm for Solving the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Problem with Nested Logit Function. J. Adv. Transp. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A. Unconstrained weibit stochastic user equilibrium model with extensions. Transp. Res. Part B 2014, 59, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Khani, A. Modeling park-and-ride location choice of heterogeneous commuters. Transportation 2018, 45, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Menéndez, J.M.; Jiménez, P.; Rivas, A. Closed form expressions for choice probabilities in the Weibull case. Transp. Res. Part B 2008, 42, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Akiva, M.; Lerman, S.R. Discrete Choice Analysis: Theory and Application to Travel Demand; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A. A path-size weibit stochastic user equilibrium model. Transp. Res. Part B 2013, 57, 378–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Tóth, J.; Péter, T.; Moslem, S. An Integrated Model of Park-And-Ride Facilities for Sustainable Urban Mobility. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM. IBM ILOG CPLEX. 2019. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/ilog-cplex-optimization-studio (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Office of Transport and Traffic Policy and Planning (OTP) Public Transportation Master Plan in Chiang Mai; Ministry of Transport: Bangkok, Thailand, 2017.
- Wirasanti, P.; Kammuang-Lue, N.; Kitthamkesorn, S. Feasibility study of electric rubber-tire bus potential in Chiang Mai-electrification planning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Bangkok, Thailand, 6–9 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, X.; Ryu, S. Modeling mode and route similarities in network equilibrium problem with go-green modes. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2016, 16, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D. Conditional logit analysis of quantitative choice behaviour. In Frontiers of Econometrics; Zarembka, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A. Alternate weibit-based model for assessing green transport systems with combined mode and route travel choices. Transp. Res. Part B 2017, 103, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, X. Elastic demand with weibit stochastic user equilibrium flows and application in a motorised and non-motorised network. Transp. A 2015, 11, 158–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polycarpou, E.; Lambrinos, L.; Protopapadakis, E. Smart parking solutions for urban areas. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 14th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, R.E.; Giuffrè, T.; Siniscalchi, S.M.; Morgano, M.A.; Tesoriere, G. Architecture for parking management in smart cities. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 8, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jun, H.B. A study on smart parking guidance algorithm. Transp. Res. Part C 2014, 44, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahogianni, E.I.; Kepaptsoglou, K.; Tsetsos, V.; Karlaftis, M.G. A real-time parking prediction system for smart cities. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 20, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Rivano, H.; Le Mouël, F. A survey of smart parking solutions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3229–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelen, G.; Podobnik, V.; Babic, J. Contextual prediction of parking spot availability: A step towards sustainable parking. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Train, K.E. Discrete Choice Methods with Simulation; Cambridge university press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Dios Ortúzar, J. Estimating individual preferences with flexible discrete-choice-models. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzolo, A.; Comi, A. Individual utility-based path suggestions in transit trip planners. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 10, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
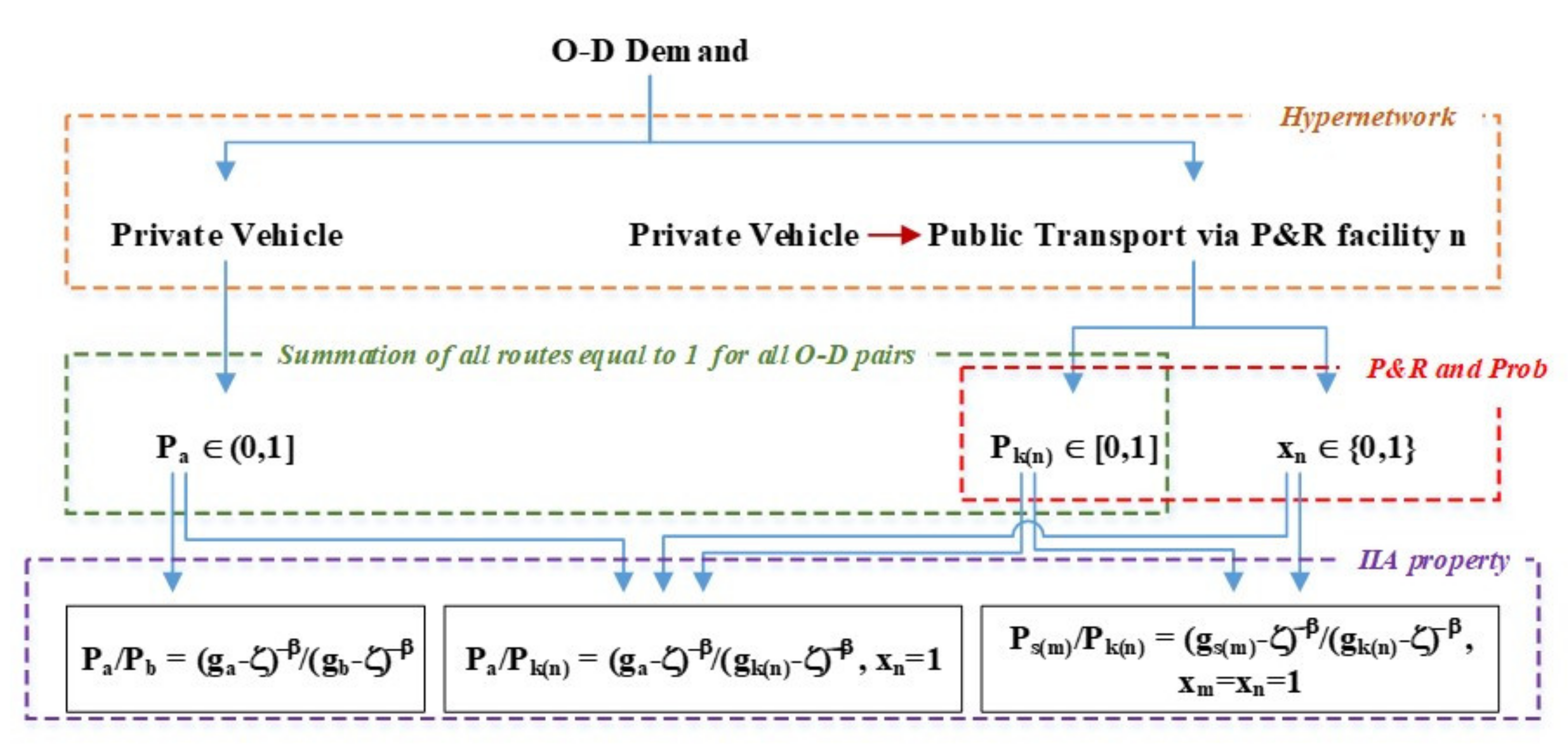

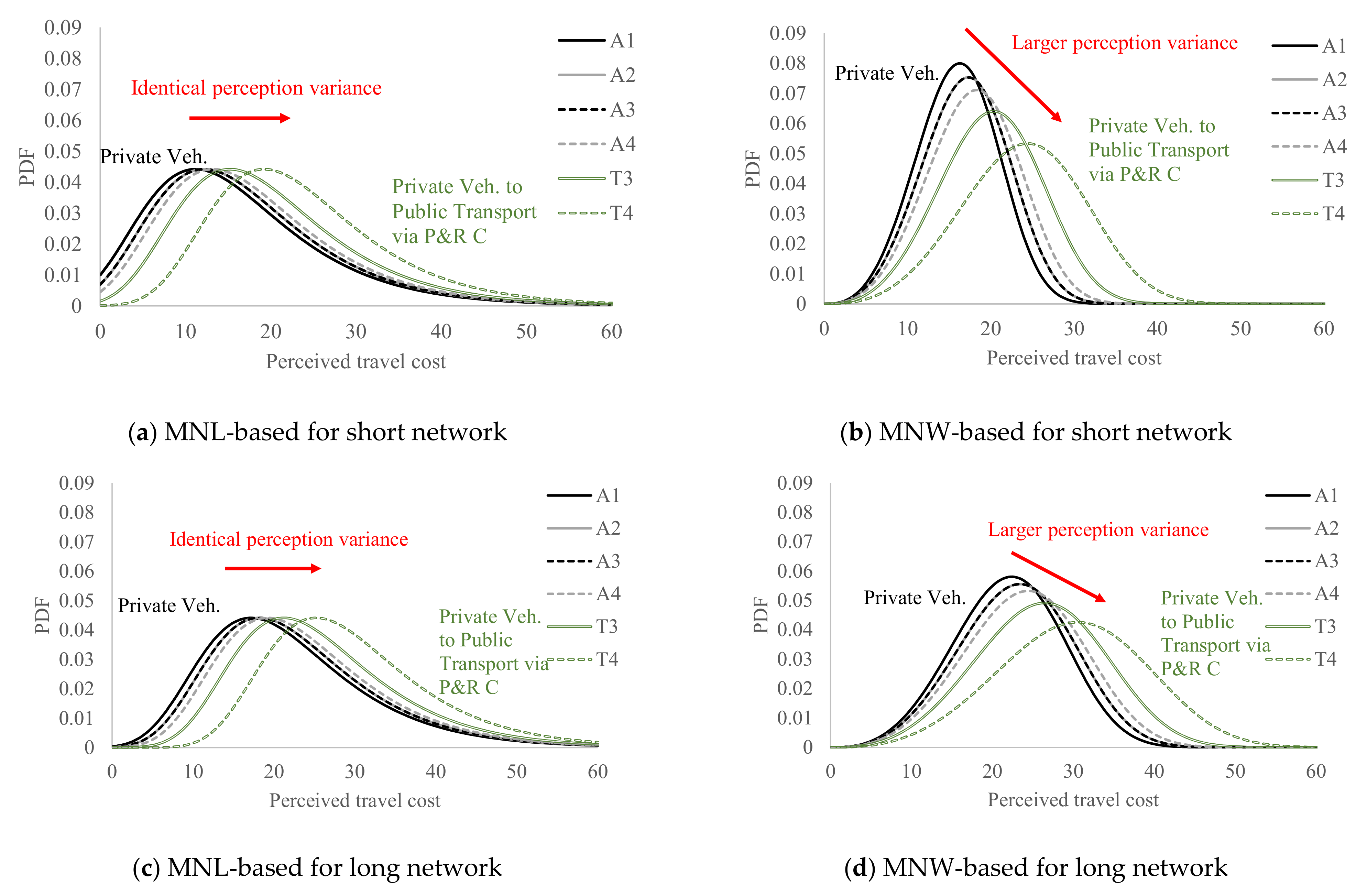




| Type | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Set | IJ | Set of origin-destination (O-D) pairs |
| Set of routes between O-D pair ij∈IJ | ||
| N | Set of potential park and ride (P&R) facility locations | |
| Set of public transport routes via P&R n∈N between O-D pair ij∈IJ () | ||
| Set of auto routes between O-D pair ij∈IJ () | ||
| Variable | Probability of choosing route k∈ passing through P&R n∈N between O-D pair ij∈IJ | |
| Probability of choosing route a∈ between O-D pair ij∈IJ | ||
| Binary variable for P&R facility at location n∈N | ||
| Parameter | θ | Multinomial Logit (MNL) model dispersion parameter |
| Multinomial Weibit (MNW) model shape parameter between O-D pair ij∈IJ | ||
| Multinomial Weibit (MNW) model location parameter between O-D pair ij∈IJ | ||
| Travel cost on route r∈Rij between O-D pair ij∈IJ | ||
| p | Number of P&R facilities |
| CDF () | |
| Mean () | |
| Variance |
| CDF () | |
| Mean () | |
| Variance |
| Choice Model | Short Network | Long Network | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P&R Facility Location | Number of P&R Users | P&R Facility Location | Number of P&R Users | |
| MNL | C | 244.02 | C | 244.02 |
| MNW | C | 210.21 | C | 180.44 |
| From/To | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 25 | 40 |
| 2 | 25 | 10 | 25 |
| 3 | 40 | 25 | 10 |
| p | Fare Structure | Distance-Based | Zone-Based | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choice Model | MNL | MNW | MNL | MNW | |
| 4 | P&R users | 30.05% | 39.53% | 31.56% | 40.44% |
| P&R facility site | 3, 5, 6, 7 | 3, 5, 6, 8 | 3, 4, 5, 7 | 3, 5, 6, 7 | |
| 3 | P&R users | 28.61% | 35.23% | 30.06% | 36.28% |
| P&R facility site | 3, 5, 7 | 3, 5, 6 | 3, 5, 7 | 3, 5, 6 | |
| 2 | P&R users | 24.17% | 27.13% | 26.39% | 28.81% |
| P&R facility site | 3, 5 | 3, 6 | 3, 5 | 3, 5 | |
| 1 | P&R users | 14.84% | 17.66% | 14.17% | 17.58% |
| P&R facility site | 6 | 6 | 3 | 6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A.; Opasanon, S.; Jaita, S. A P-Hub Location Problem for Determining Park-and-Ride Facility Locations with the Weibit-Based Choice Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147928
Kitthamkesorn S, Chen A, Opasanon S, Jaita S. A P-Hub Location Problem for Determining Park-and-Ride Facility Locations with the Weibit-Based Choice Model. Sustainability. 2021; 13(14):7928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147928
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitthamkesorn, Songyot, Anthony Chen, Sathaporn Opasanon, and Suwicha Jaita. 2021. "A P-Hub Location Problem for Determining Park-and-Ride Facility Locations with the Weibit-Based Choice Model" Sustainability 13, no. 14: 7928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147928
APA StyleKitthamkesorn, S., Chen, A., Opasanon, S., & Jaita, S. (2021). A P-Hub Location Problem for Determining Park-and-Ride Facility Locations with the Weibit-Based Choice Model. Sustainability, 13(14), 7928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147928







