The Impact of Financial Hoarding on Economic Growth in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
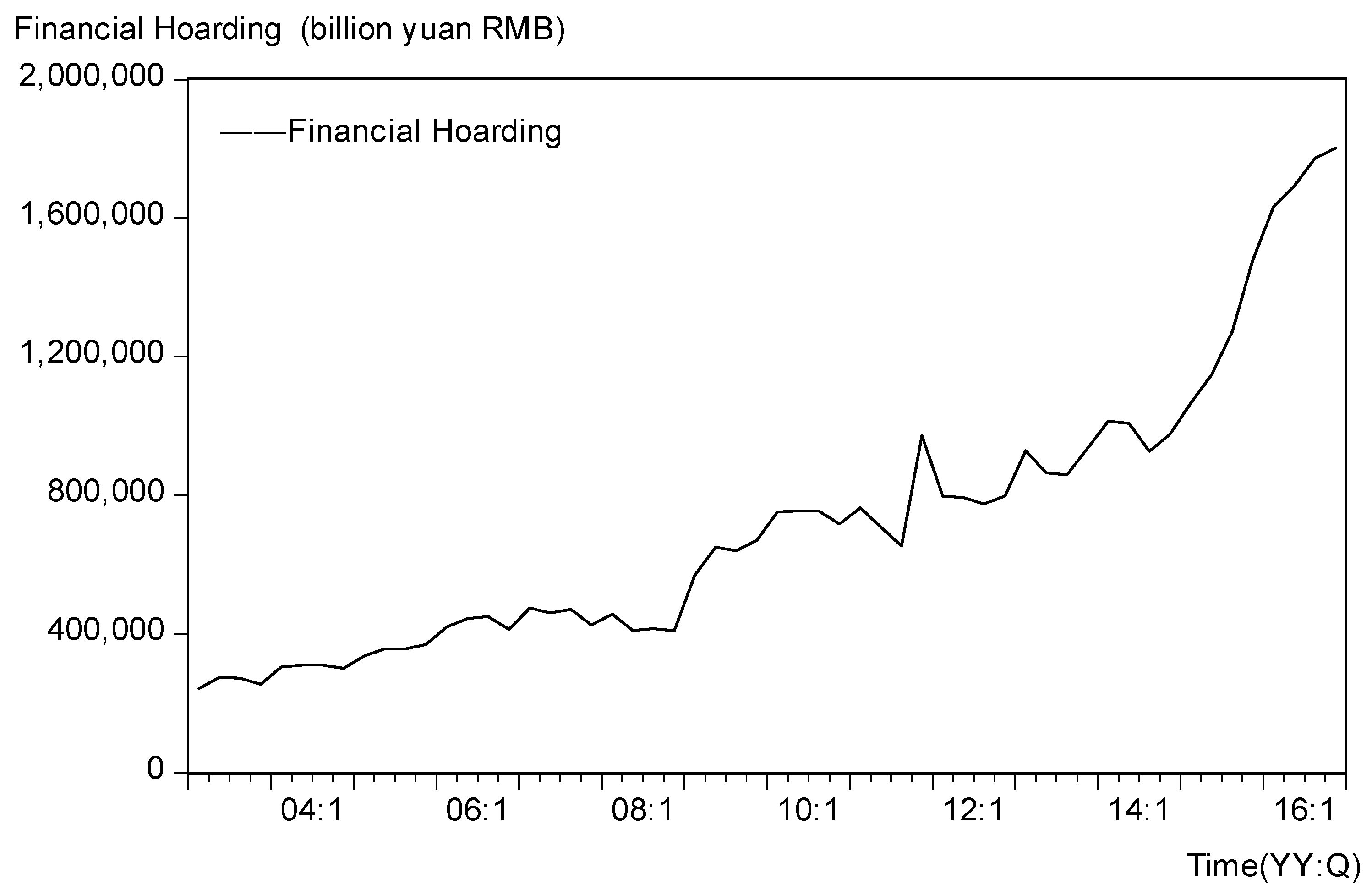
3.1. Financial Hoarding and Economic Growth
3.2. Empirical Framework
3.2.1. Model
3.2.2. Data
4. Results
4.1. The Long-Term Relationship between Financial Hoarding and Economic Growth
4.2. The Relationship between Financial Hoarding and Economic Growth in Different Economic Growth Regimes
4.2.1. Model Setting
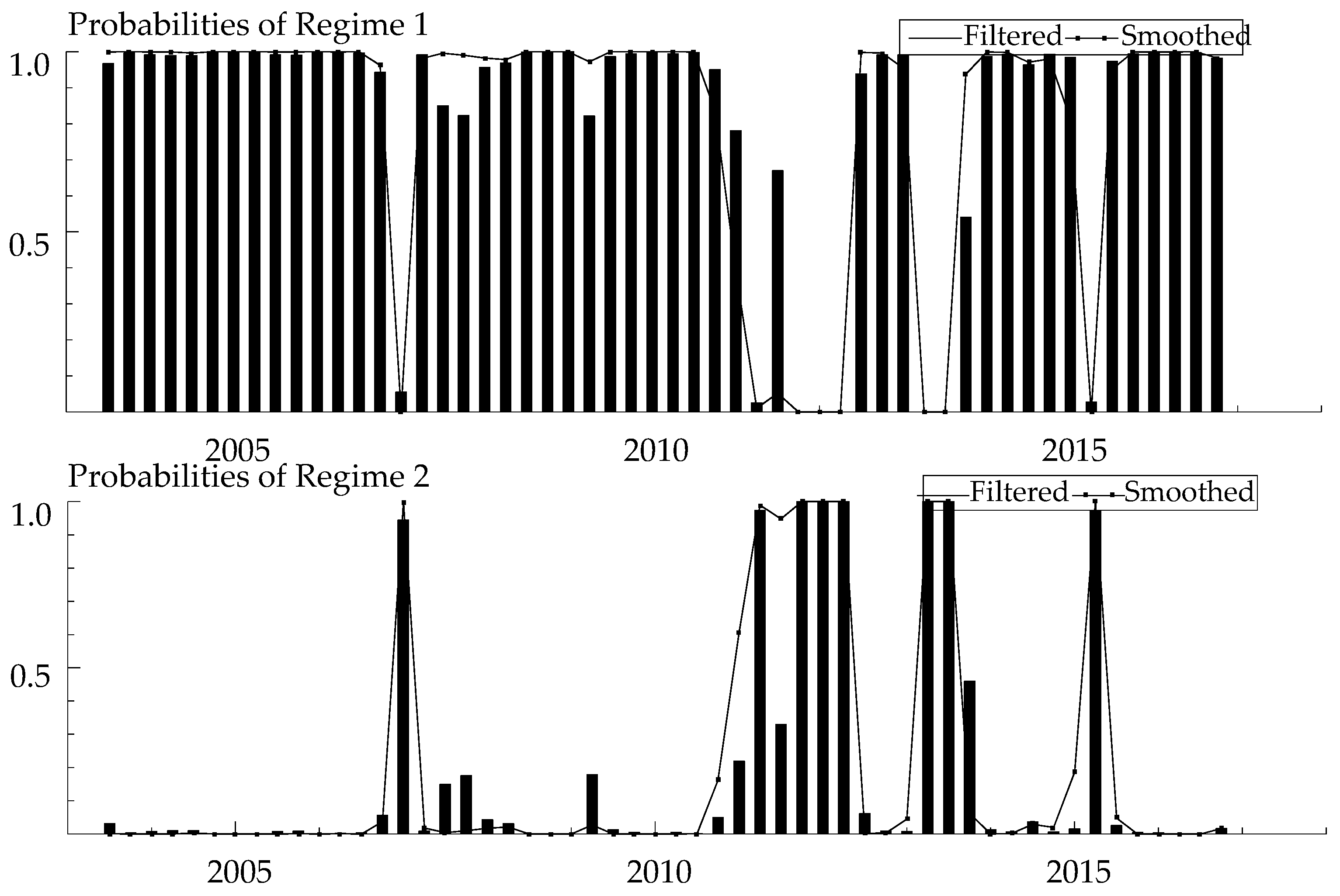
4.2.2. Regime Probabilities Analysis
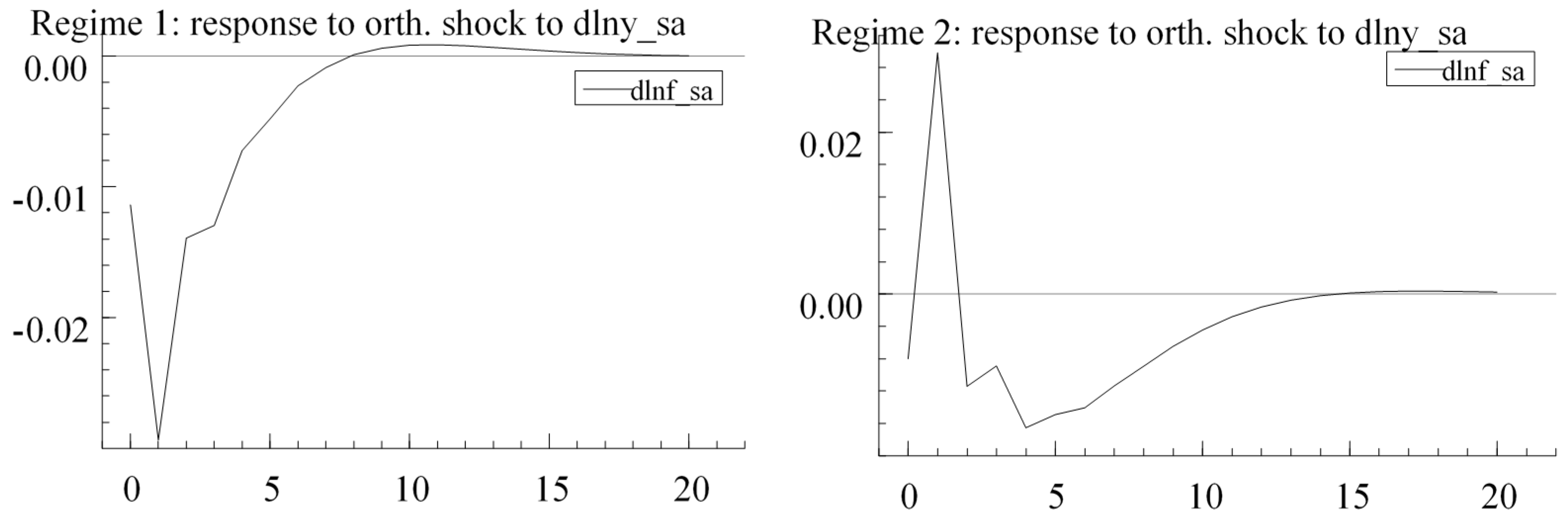
4.2.3. Impulse Response Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wicksell, K. The influence of the rate of interest on prices. Econ. J. 1907, 17, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binswanger, M. The finance process on a macroeconomic level from a flow perspective: A new interpretation of hoarding. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 1997, 6, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, T.A. Critique of a Post Keynesian model of hoarding, and an alternative model. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2006, 60, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, R.; Karim, Z.A.; Rahman, A.A.; Sarmidi, T. Financial inclusiveness and economic growth: New evidence using a threshold regression analysis. Econ. Res. 2020, 33, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabail, A.I.; Muhammad, R.Y.; Rakhshanda, K.; Muhammad, U.; Muhammad, S.A.M. Impact of Trade Openness and Human Capital on Economic Growth: A Comparative Investigation of Asian Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2930. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Aging and economic growth: Is there a role for a two-child policy in China? Econ. Res. 2020, 33, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvonimira, S.G.; Marinela, K.N.; Elena, R. Circular Economy Concept in the Context of Economic Development in EU Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3060. [Google Scholar]
- Iuga, I.C.; Mihalciuc, A. Major Crises of the XXIst Century and Impact on Economic Growth. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyniak, D.; Doryń, W. Does the quality of institutions modify the economic growth-carbon dioxide emissions nexus? Evidence from a group of emerging and developing countries. Econ. Res. 2020, 33, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romualdas, G.; Gitana, D.; Martin, S.; Kęstutis, P. The inter linkages between financial and economic development in the European Union Countries. Econ. Res. 2019, 32, 128–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, E.H.; Low, S.W.; Mohd, A.S.Z. Oil price shocks, global economic policy uncertainty, geopolitical risk, and stock price in Malaysia: Factor augmented VAR approach. Econ. Res. 2019, 32, 3700–3732. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F. Special articles for the 60th establishment anniversary of economic research journal. Econ. Res. J. 2015, 12, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Contention on finance serving the real economy. Econ. Res. J. 2017, 6, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Du, C.; Zeng, F. The scale measurement and countermeasures in China’s financial hoarding. South China Financ. 2016, 11, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z. Financial hoarding and China’s currency mystery. J. Chang. Financ. Coll. 2012, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Song, T. Circular flow of money and asset prices fluctuation. Financ. Econ. 2013, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Y. Shadow banking, money hoarding and macroeconomic effect of monetary policy shock: Analysis based on a DSGE model. Stud. Int. Financ. 2017, 8, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, H. On the relationship between financial development and economic development from the perspective of polarization theory—A response to “financial cellar”. Rev. Econ. Manag. 2018, 34, 114–129. [Google Scholar]
- Berrospide, J.M. Bank Liquidity Hoarding and the Financial Crisis: An Empirical Evaluation. FEDS Working Paper No. 2013-03. 2013. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2207754 (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Aizenman, J.; Lee, J. Financial versus monetary mercantilism: Long-run view of large international reserves hoarding. World Econ. 2008, 31, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Huang, J.; Musshoff, O. Climate threshold, financial hoarding and economic growth. Appl. Econ. 2015, 47, 4535–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard, O.; Saroyan, S. Hoarding and short-squeezing in times of crisis: Evidence from the euro overnight money market. J. Int. Financ. Mark. 2016, 40, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Hwang, I.; Song, S. Cash hoarding: Vice or virtue. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2018, 53, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X. Money supply and the development of small and medium sized enterprises from the perspective of “financial hoard”. Xinjiang Soc. Sci. 2019, 7, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Bo, N. Performance, impact and measurement analysis of China’s financial hoard. East China Econ. Manag. 2020, 34, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.N.; Guedhami, O.; Kim, H.H.; Li, X. Economic policy uncertainty and bank liquidity hoarding. J. Financ. Intermed. 2020, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenman, J.; Cheung, Y.; Ito, H. International reserves before and after the global crisis: Is there no end to hoarding? J. Int. Money Financ. 2015, 52, 102–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, B.N. Policy Uncertainty and Bank Liquidity Hoarding: International Evidence. 2020. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3574193 (accessed on 25 April 2020).

| Variables | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7052 | 0.0099 | 71.0866 | 0.0000 | |
| 6.7683 | 0.3388 | 19.9803 | 0.0000 | |
| 8.1561 | 0.3695 | 22.0720 | 0.0000 | |
| −5.3789 | 1.6211 | −3.3180 | 0.0011 | |
| 0.0212 | 0.0116 | 1.8227 | 0.0697 | |
| 0.1135 | 0.0112 | 10.1019 | 0.0000 |
| Variable | (C,T,K) | t-Statistics | 5% Lever | Prob |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (C,0,0) | −3.0385 | −2.9166 | 0.0376 | |
| (C,0,0) | −9.3039 | −2.9166 | 0.0000 | |
| (C,0,0) | −4.4622 | −2.916 | 0.0007 |
| Lag | AIC | HQ | SC | LogL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI(2)-VAR(1) | 12.5081 | 12.8348 | 13.3553 | −314.7195 |
| MSI(2)-VAR(2) | 12.5806 | 13.0381 | 13.7702 | −301.3862 |
| MSI(2)-VAR(3) | 12.9703 | 13.5601 | 14.5088 | −296.2274 |
| Model Type | AIC | HQ | SC | LogL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI(2)-VAR(1) | 12.5081 | 12.8348 | 13.3553 | −314.7195 |
| MSIH(2)-VAR(1) | 11.9329 | 12.3449 | 13.0011 | −293.1892 |
| MSIA(2)-VAR(1) | 12.1925 | 12.6470 | 13.3711 | −297.1970 |
| MSIAH(2)-VAR(1) | 11.6757 | 12.2155 | 13.0753 | −277.2436 |
| MSM(2)-VAR(1) | 12.4823 | 12.8090 | 13.3294 | −314.0211 |
| MSMH(2)-VAR(1) | 11.8808 | 12.2927 | 12.9490 | −291.7815 |
| MSMA(2)-VAR(1) | 14.8975 | 15.3521 | 16.0762 | −370.2333 |
| MSMAH(2)-VAR(1) | 15.1195 | 15.6595 | 16.5194 | −370.2333 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Su, Z.; Guo, Q. The Impact of Financial Hoarding on Economic Growth in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158434
Fu Y, Su Z, Guo Q. The Impact of Financial Hoarding on Economic Growth in China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158434
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yizheng, Zhifang Su, and Qianqian Guo. 2021. "The Impact of Financial Hoarding on Economic Growth in China" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158434
APA StyleFu, Y., Su, Z., & Guo, Q. (2021). The Impact of Financial Hoarding on Economic Growth in China. Sustainability, 13(15), 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158434





