The Addition of a High Dosage of Rubber to Asphalt Mixtures: The Effects on Rutting and Fatigue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Material
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Tests
2.3.1. Marshall Stability and Flow Test
2.3.2. Fatigue Cracking
2.3.3. Rutting Test
3.Results and Discussion
3.1. Air Void and Density
3.2. Marshall Stability and Flow
3.2.1. Marshall Stability
3.2.2. Marshall Flow
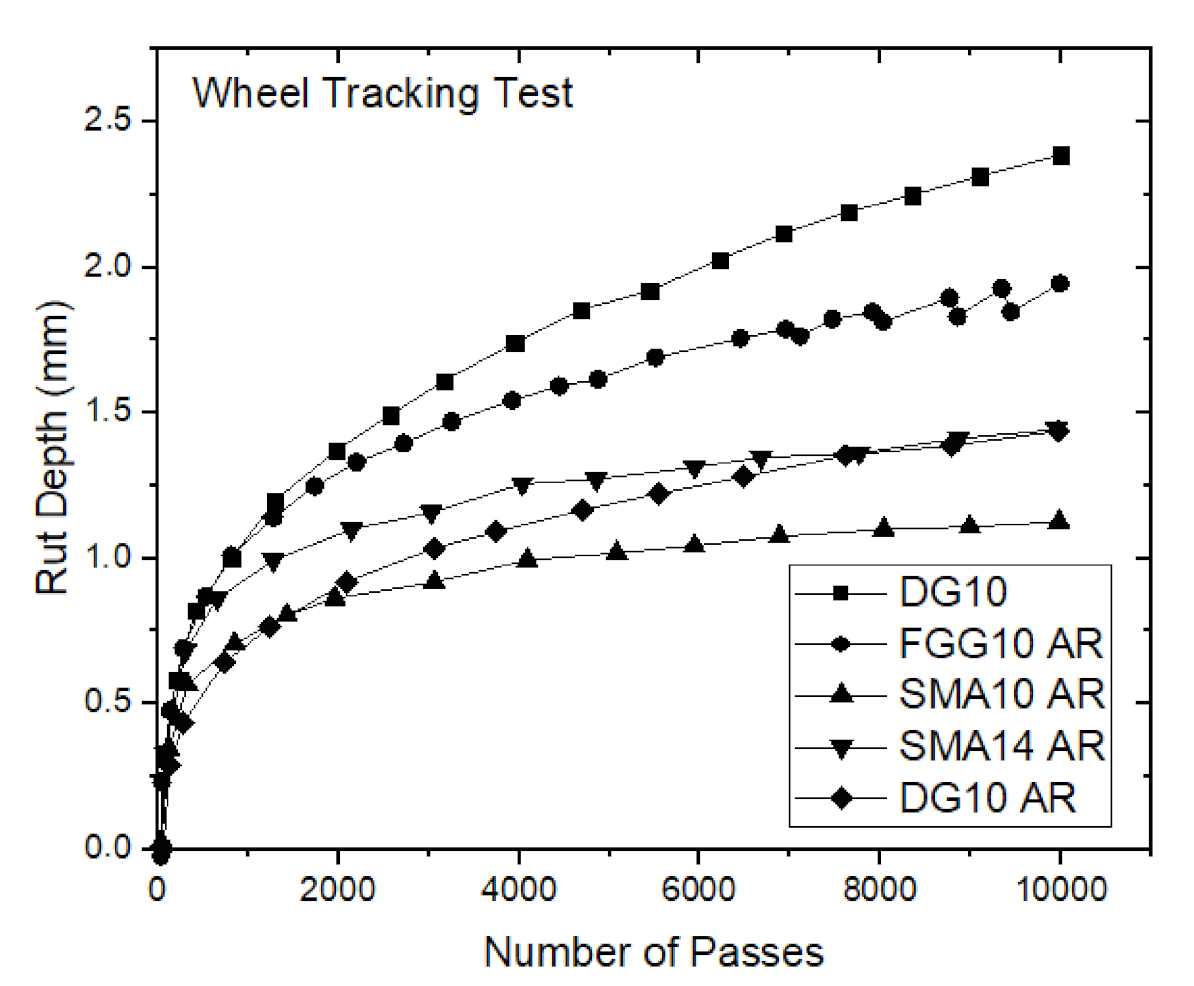
3.3. Rutting Resistance
3.4. Fatigue of Asphalt Rubber
3.4.1. Initial Flexural Stiffness of Asphalt Rubber
3.4.2. Fatigue Cycle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Presti, D.L. Recycled tyre rubber modified bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Mészáros, L.; Bárány, T. Ground tyre rubber (GTR) in thermoplastics, thermosets, and rubbers. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Hoiberg, A. Bituminous Materials: Asphalt Tars and Pitches; sl: Robert Krieger Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, Y. Polymer modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.I.; Foo, K.Y.; Brown, E.R.; Denson, R. Evaluation and characterization of a rubber-modified hot mix asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Rec. 1994, 1436, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, J. Sahuaro concept of asphalt-rubber binders. In Proceedings of the 1st Asphalt Rubber User Producer Workshop, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 1 May 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Brule, B. Polymer-modified asphalt cements used in the road construction industry: Basic principles. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1535, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Jared, D.; Jones, C.; Watson, D. Georgia’s experience with crumb rubber in hot-mix asphalt. Transp. Res. Rec. 1997, 1583, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Ali, A.H.; Koting, S.; Karim, M.R. Performance evaluation of crumb rubber modified stone mastic asphalt pavement in Malaysia. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 304676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, X.; Huang, B. Recycling of waste tire rubber in asphalt and portland cement concrete: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubber Manufacturers Association. U.S Scrap Tire Management Summary 2005–2009; Rubber Manufacturers Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Downes, S. A guide to recycling used car tyres. Available online: https://www.canstarblue.com.au/vehicles/guide-recycling-used-car-tyres/ (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Jamshidi, A.; Kurumisawa, K.; Nawa, T.; Igarashi, T. Performance of pavements incorporating waste glass: The current state of the art, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venudharan, V.; Biligiri, K.P.; Sousa, J.B.; Way, G.B. Asphalt-rubber gap-graded mixture design practices: A state-of-the-art research review and future perspective. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 730–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H.; Rezagholilou, A. Investigating the engineering properties of asphalt binder modified with waste plastic polymer. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; Li, L.; You, Z. Analysis on fatigue crack growth laws for crumb rubber modified (CRM) asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.; Biligiri, K.P. Fracture damage evaluation of asphalt mixtures using Semi-Circular Bending test based on fracture energy approach. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 142, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards, A. Hot Mix Asphalt—A Guide to Good Practice (AS 2150-2005); Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Deformation Resistance of Asphalt Mixtures by the Wheel Tracking Test AGPT-T231-06; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Standards, A. Methods of Sampling and Testing Asphalt—Sampling—Asphalt from Slabs (AS2891.1.3-2008); Australia Standards: Sydney, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Standards, A. Methods of Sampling and Testing Asphalt. Method 5: Compaction of Asphalt by Marshall Method and Determination of Stability and Flow—Marshall Procedure (2891.5: 2015); Australia Standards: Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Standards, A. Methods of Sampling and Testing Asphalt Method 2.1: Sample Preparation—Mixing, Quartering and Conditioning of Asphalt in the Laboratory (As/Nzs 2891.2.1:2014); Sai Global: Haymarket, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Fatigue Life of Compacted Bituminous Mixes Subject to Repeated Flexural Bending Ag:Pt/T233; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Testing Asphalt in Accordance with the Austroads Mix Design Procedures (Ap-T100/08); Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Karim, M.R. Evaluation of permanent deformation of CRM-reinforced SMA and its correlation with dynamic stiffness and dynamic creep. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 981637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouman, M.; Maqbool, Z.; Ali, S.; Saleem, A. Performance Evaluation of Wearing Course Asphalt Mixes Based on Resilient Modulus, Indirect Tensile Strength and Marshall Stability. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, M.Y.; Hilal, M.M.; Flyeh, H.B. Assessment of mechanical stability performance of asphalt mixture using Superpave gyratory compactor. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2019, 145, 04019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhil, T.H.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Fathullah, H.S. The Influence of Curing Methods on Marshall Stability and Flow. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 671, 012132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHI. Superpave Fundamentals, Reference Manual; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 2059. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.R.; Kandhal, P.S.; Roberts, F.L.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kennedy, T.W. Hot Mix Asphalt Materials, Mixture Design, and Construction; NAPA Research and Education Foundation: Lanham, MD, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, O. Design and evaluation of gap-graded asphalt rubber mixtures. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwakaire, C.M.; Yap, S.P.; Yuen, C.W.; Onn, C.C.; Koting, S.; Babalghaith, A.M. Laboratory study on recycled concrete aggregate based asphalt mixtures for sustainable flexible pavement surfacing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegenizadeh, A.; Tokoni, L.; Nikraz, H.; Dadras, E. Effect of ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) on stone mastic asphalt (SMA) behaviour. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piromanski, B.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Mashaan, N.; Nikraz, H. Study on HDPE Effect on Rutting Resistance of Binder. Buildings 2020, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloush, K.E. Asphalt rubber: Performance tests and pavement design issues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, M.; Mamlouk, M.; Kaloush, M.; Kaloush, K.E. Validation of initial and failure stiffness definitions in flexure fatigue test for hot mix asphalt. J. Test. Eval. 2007, 35, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Ali, A.H.; Koting, S.; Karim, M.R. Dynamic properties and fatigue life of stone mastic asphalt mixtures reinforced with waste tyre rubber. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 319259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Guo, N.; You, Z.; Tan, Y. Investigating fatigue life prediction of rubber asphalt mixture based on damage evolution using residual strain analysis approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Combination | DG10 | SMA10 | SMA14-1 | SMA14-2 | FGG10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mm | 12% | 5% | |||
| 10/7 mm | 46% | 30% | |||
| 10 mm | 50% | 35% | |||
| 14 mm (BGC) | 80% | ||||
| 14 MM (Boral) | 75% | ||||
| Dust | 42% | 12% | 12% | 12% | 65% |
| B.Dust | 8% | 8% | 8% |
| Superior Performance | Good Performance | Medium Performance | Low Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| <3.5 | 3.5–8 | 8–13 | >13 |
| Mix Type | Wheel Tracking Test | Fatigue Test | Volumetric and Marshall Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| DG10 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| DG10 AR | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| FGG10 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| FGG10 AR | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| SMA10 | 6 | - | 6 |
| SMA10 AR | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| SMA14 | 6 | - | 6 |
| SMA14 AR | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Asphalt Mixture | Specifications | Results of Volumetric Tests | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitumen Content (%) | Air Voids (%) | VMA (%) | Bitumen Content (%) | Air Voids (%) | VMA (%) | Maximum Density (t/m3) | |||
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | |||||
| DG10 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 3 | 7 | 16 | 4.9 | 5.00 | 16.77 | 2.475 |
| DG10 AR | 4.5 | 6.5 | 3 | 7 | 16 | 6.3 | 6.15 | 20.87 | 2.407 |
| SMA10 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 3 | 6 | 18 | 6.4 | 4.50 | 19.52 | 2.418 |
| SMA10 AR | 6.0 | 7.0 | 3 | 6 | 18 | 7.0 | 5.68 | 22.09 | 2.414 |
| SMA14 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 3 | 6 | 18 | 6.3 | 4.5 | 19.82 | 2.504 |
| SMA14-AR | 5.8 | 6.8 | 3 | 6 | 18 | 6.8 | 4.39 | 20.72 | 2.473 |
| FGG10 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | - | 6.0 | 2.4 | 16.48 | 2.417 |
| FGG10 AR | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | - | 6.5 | 3.68 | 18.43 | 2.338 |
| Asphalt Mixture | Specifications | Results of the Marshall Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitumen Content (%) | Marshall Flow (mm) | Marshall Stability (kN) | Bitumen Content (%) | Marshall Stability (kN) | Marshall Flow (mm) | |||
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | ||||
| DG10 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 2 | 4 | 6.5 | 4.9 | 16 | 2.5 |
| DG10 AR | 4.5 | 6.5 | 2 | 4 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 14.38 | 3.48 |
| SMA10 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 6.4 | 10.30 | 2.8 |
| SMA10 AR | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 7.0 | 10.21 | 3.77 |
| SMA14-2 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 6.3 | 7.1 | 2.39 |
| SMA14-2 AR | 5.8 | 6.8 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 6.8 | 12.89 | 3.55 |
| FGG10 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | 4.5 | 6.0 | 17.85 | 2.76 |
| FGG10 AR | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2 | 5 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 13.29 | 3.52 |
| Ranking | Mix Type | Rut Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SMA10 AR | 1.15 |
| 2 | SMA14 AR | 1.40 |
| 3 | DG10 AR | 1.50 |
| 4 | FGG10 AR | 1.95 |
| 5 | DG10 | 2.40 |
| Mix Type | Air Void (%) | Initial Flexural Stiffness | Number of Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMA10 AR | 4.57 | 5179 | 605,296 |
| FGG10 AR | 3.7 | 4263 | 587,986 |
| SMA14 AR | 2.93 | 4447 | 286,786 |
| DG10 AR | 5.17 | 4691 | 236,363 |
| DG10 | 5.13 | 7928 | 80,843 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chegenizadeh, A.; Jing Shen, P.; Sekar Arumdani, I.; Budihardjo, M.A.; Nikraz, H. The Addition of a High Dosage of Rubber to Asphalt Mixtures: The Effects on Rutting and Fatigue. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9718. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179718
Chegenizadeh A, Jing Shen P, Sekar Arumdani I, Budihardjo MA, Nikraz H. The Addition of a High Dosage of Rubber to Asphalt Mixtures: The Effects on Rutting and Fatigue. Sustainability. 2021; 13(17):9718. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179718
Chicago/Turabian StyleChegenizadeh, Amin, Pak Jing Shen, Indah Sekar Arumdani, Mochamad Arief Budihardjo, and Hamid Nikraz. 2021. "The Addition of a High Dosage of Rubber to Asphalt Mixtures: The Effects on Rutting and Fatigue" Sustainability 13, no. 17: 9718. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179718
APA StyleChegenizadeh, A., Jing Shen, P., Sekar Arumdani, I., Budihardjo, M. A., & Nikraz, H. (2021). The Addition of a High Dosage of Rubber to Asphalt Mixtures: The Effects on Rutting and Fatigue. Sustainability, 13(17), 9718. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179718







