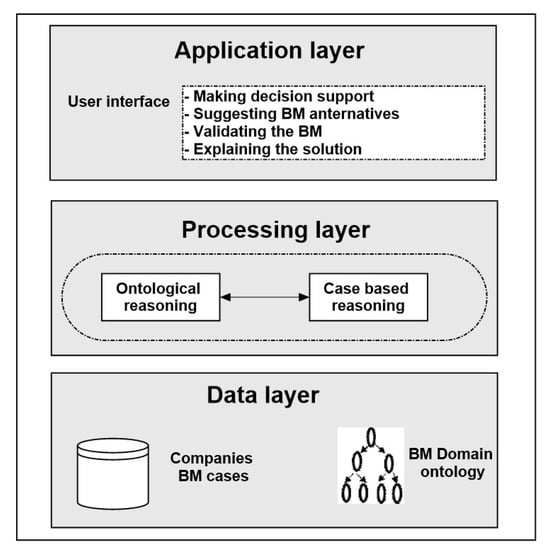
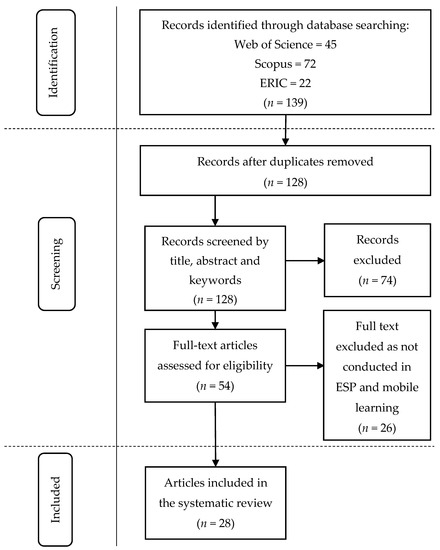
Sustainability 2021, 13(17), 9863; https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179863 - 2 Sep 2021
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 6314
Abstract
Emerging information on the interactions between the COVID-19 pandemic and global food systems have highlighted how the pandemic is accentuating food crises across Africa. Less clear, however, are how the impacts differ between farming systems. Drawing on 50 key informant interviews with farmers,
[...] Read more.
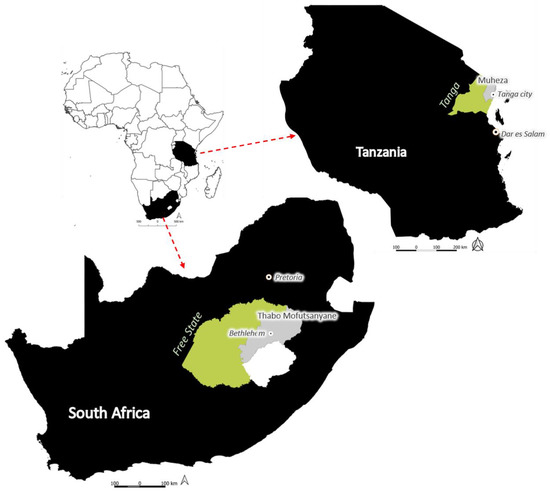
Emerging information on the interactions between the COVID-19 pandemic and global food systems have highlighted how the pandemic is accentuating food crises across Africa. Less clear, however, are how the impacts differ between farming systems. Drawing on 50 key informant interviews with farmers, village leaders and extension officers in South Africa and Tanzania, we identify the effects of COVID-19 and associated measures to curb the spread of the disease on farming production systems, the coping mechanisms adopted by farmers, and explore their longer-term plans for adaptation. We focus on a diverse range of production systems, from small-scale mixed farming systems in Tanzania to large-scale corporate farms in South Africa. Our findings highlight how COVID-19 restrictions have interrupted the supply chains of agricultural inputs and commodities, increasing the storage time for produce, decreasing income and purchasing power, and reducing labour availability. Farmers’ responses were heterogeneous, with highly diverse small-scale farming systems and those less engaged with international markets least affected by the associated COVID-19 measures. Large-scale farmers were most able to access capital to buffer short-term impacts, whereas smaller-scale farms shared labour, diversified to subsistence produce and sold assets. However, compounded shocks, such as recent extreme climate events, limited the available coping options, particularly for smaller-scale and emerging farmers. The study highlights the need to understand the characteristics of farm systems to better equip and support farmers, particularly in contexts of uncertainty. We propose that policy actions should focus on (i) providing temporary relief and social support and protection to financially vulnerable stakeholders, (ii) job assurance for farmworkers and engaging an alternative workforce in farming, (iii) investing in farming infrastructure, such as storage facilities, digital communication tools and extension services, and (iv) supporting diversified agroecological farming systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Post-COVID-19 Agriculture and Food Security)
►
Show Figures