Evaluating the Service Operating Efficiency and Its Determinants in Global Consulting Firms: A Metafrontier Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This study is the first to attempt to measure the efficiencies of global consulting firms. Unlike most previous studies on consulting firms that have examined the quality of consulting services, this study measured the meta-efficiency (ME) of global consulting firms.
- The meta-efficiency (ME), group efficiency (GE), and technology gap ratio (TGR) were analyzed by classifying the global consulting firms into regional groups (USA, Europe, and Asia-Pacific) that reflect their varied operational methods due to geographic specificities. Notably, the USA group showed higher efficiency than the other groups, but many of the firms in the USA group were located in the DRS area, pointing to the necessity to reduce their sizes to improve efficiency.
- The Tobit regression analysis to identify the firms’ internal environmental factors affecting the ME of global consulting firms revealed the negative impact of firms’ leadership on ME. On the other hand, promotion policies were found to have a positive effect on ME. Therefore, global consulting firms need to manage their internal resources strategically to improve their efficiency.
2. Literature Review on Company Efficiency
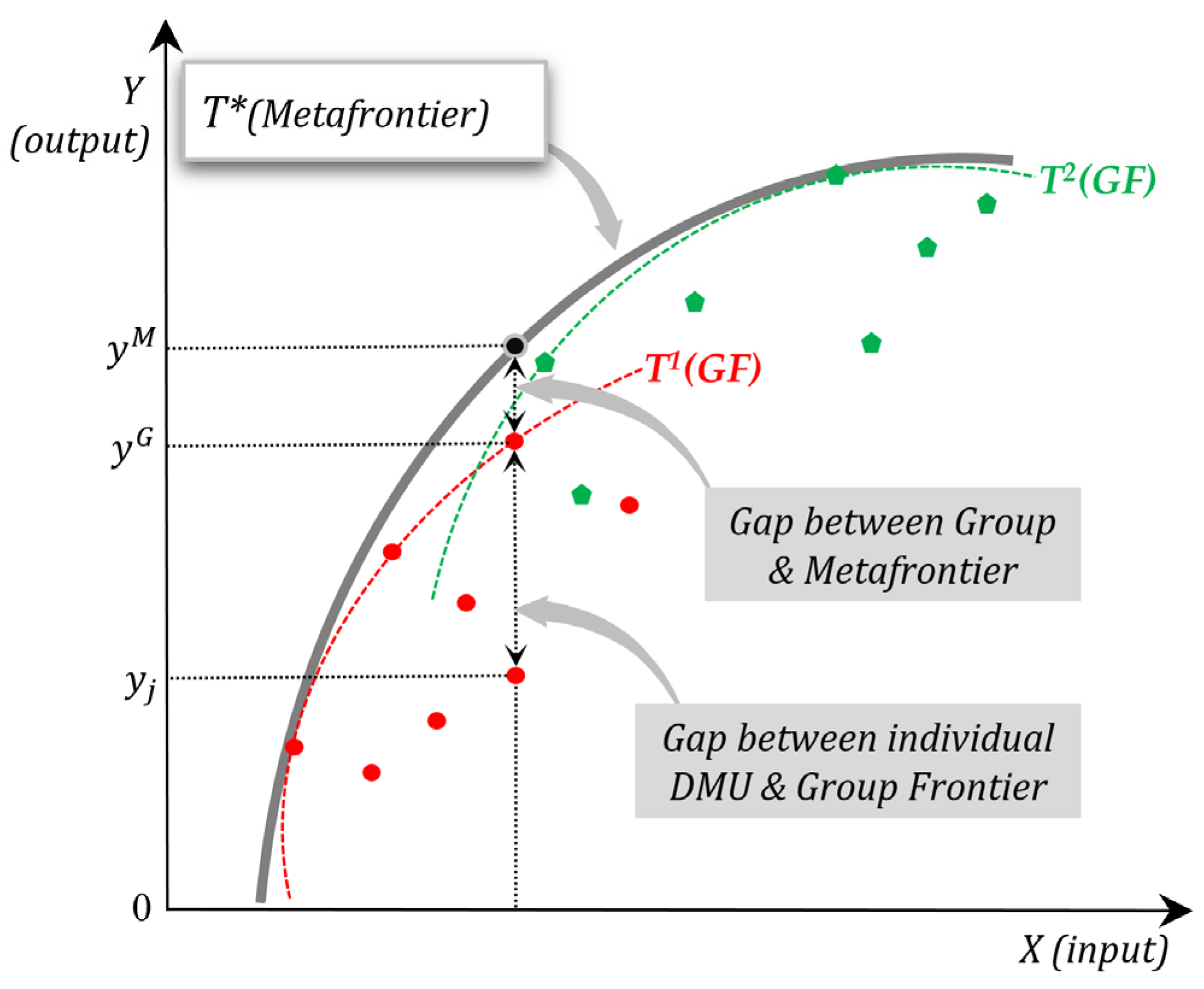
3. Research Methodology: Metafrontier DEA Model
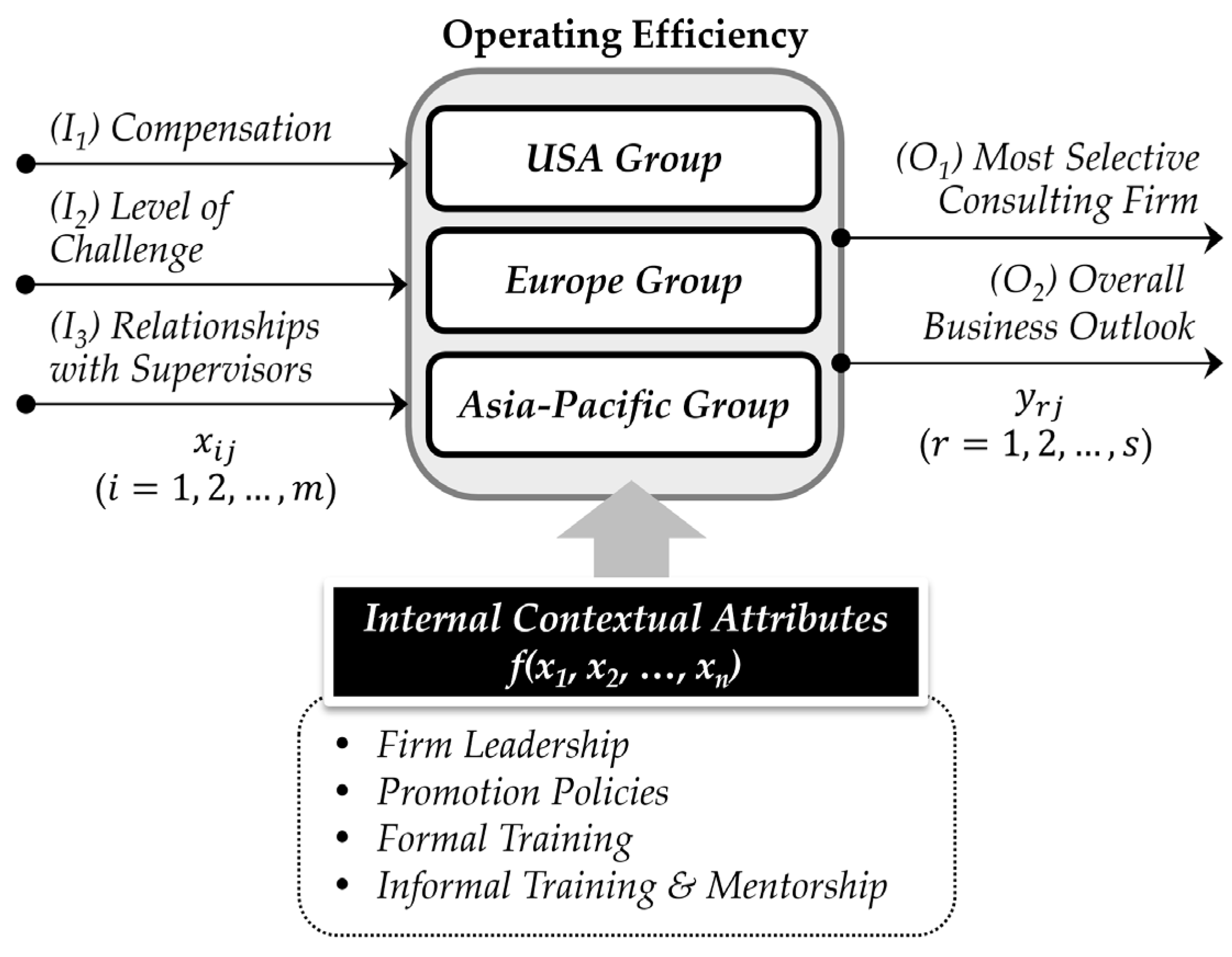
4. Research Model and Data
- (I1) Compensation (COM): Base salary, performance bonuses, housing allowance, relocation package, retirement benefits, special bonuses
- (I2) Level of Challenge (LV): Competition analysis, service differentiation, strategic thinking, new organizational design, knowledge-sharing
- (I3) Relationships with Supervisors (RS): Empathy, teamwork, commitment, communication skills
- (O1) Most Selective Consulting Firms (MC): Number of projects, number of clients, reputation, and market share
- (O2) Overall Business Outlook (OB): Sales revenue, operating profit
5. Empirical Metafrontier Results
5.1. Metafrontier DEA Results
5.2. Comparison among the Typologies of Global Consulting Firms
6. Determinants of Meta-Efficiency (ME)
- = the left-censored ME* score of individual consulting firm
- = firm leadership
- = promotion policies
- = formal training
- = informal training and mentorship
- = the error term (statistical noise)
7. Discussion and Conclusion
7.1. Implications for Theoretical and Operating Practice
- A significant number of consulting firms in the US were located in the DRS area, suggesting the need to improve their efficiency through downsizing. On the other hand, quite a few consulting firms in Europe and the Asia-Pacific were located in the IRS area, making it necessary for them to improve efficiency by expanding their sizes [16,23].
- There were differences in the efficiencies of global consulting firms depending on the characteristics of the region in which they mainly operated. Strategies reflecting differences due to geographical characteristics are necessary to achieve optimal returns to scale. In addition, global consulting firms should allocate and adjust their resources efficiently in relation to internal operating variables that positively or negatively affect ME to realize sustainable growth.
7.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEA | Data Envelopment Analysis |
| GE | Group Efficiency |
| DMU | Decision Making Unit |
| VRS | Variable Returns-to-Scale |
| DRS | decreasing Returns-to-Scale |
| SE | Scale Efficiency |
| ME | Meta-efficiency |
| TGR | Technology Gap Ratio |
| CRS | Constant Returns-to-Scale |
| IRS | Increasing Returns-to-Scale |
| PTE | Pure Technology Efficiency |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology |
References
- McDonald, D. The Firm: The Story of McKinsey and Its Secret Influence on American Business; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Battese, G.E.; Rao, D.S.P. Technology Gap, Efficiency and a Stochastic Metafrontier Function. Int. J. Bus. Econ. 2002, 1, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Momparler, A.; Carmona, P.; Lassala, C. Quality of Consulting Services and Consulting Fees. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Ennew, C.T. Measuring Business-to-Business Professional Service Quality and Its Consequences. J. Bus. Res. 2005, 58, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, S.; Llinares, C.; Garzon, D. Exploring the Relationship between Co-creation and Satisfaction using QCA. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Truex, D. Exploring the Impact of Communication Effectiveness on Service Quality, Trust and Relationship Commitment in IT Services. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2012, 32, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; Martin, M.; Merchant, K.A. The Effect of Measurement Timing on the Information Content of Customer Satisfaction Measures. Manag. Account. Res. 2014, 25, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlin, R. Service Quality in Consulting: What is Engagement Success? Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2000, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Kuo, S.H.; Jiang, M.Y.; Li, Y. Evaluating the Performances of Taiwan’s International Tourist Hotels: Applying the Directional Distance Function and Meta-frontier Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, C.J.; Rao, D.P.; Battese, G.E. Metafrontier Frameworks for the Study of Firm-level Efficiencies and Technology Ratios. Empir. Econ. 2008, 34, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsloo, Y. Establishing a Competitive Intelligence Culture in a Multinational Consulting Engineering Company: A Case Study. Mousaion 2016, 34, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Nordtvedt, L.; Kedia, B.L.; Datta, D.K.; Rasheed, A.A. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Cross-border Knowledge Transfer: An Empirical Examination. J. Manag. Stud. 2008, 45, 714–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, A. Accounting for Size in Efficiency Comparisons of Airports. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2009, 15, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; You, J.; Haiyirete, X.; Zhang, T. Measuring Logistics Efficiency in China Considering Technology Heterogeneity and Carbon Emission through a Meta-Frontier Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, A. Second Stage DEA: Comparison of Approaches for Modelling the DEA Score. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 181, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, M.; Slavtchev, V. How Does Industry Specialization Affect the Efficiency of Regional Innovation Systems? Ann. Reg. Sci. 2010, 45, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, E.G.; Hogan, N.L.; Barton-Bellessa, S.M.; Jiang, S. Examining the Relationship between Supervisor and Management Trust and Job Burnout among Correctional Staff. Crim. Justice Behav. 2012, 39, 938–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lu, C.C.; Shyu, M.K.; Luo, Z. The Technology Gap and Efficiency Measure in WEC Countries: Application of the Hybrid Meta Frontier Model. Energy Policy 2012, 51, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhizer III, G.R.; Turner, L.D.; Shank, M.D. Determinants of Consulting Service Quality for Accounting and Nonaccounting Service Providers. J. Inf. Syst. 2002, 16, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, D.R. Quality in the Consulting Service–evaluation and Impact: A Survey in Spanish Firms. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2001, 11, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttle, F. SERVQUAL: Review, Critique, Research Agenda. Eur. J. Mark. 1996, 30, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, T.P.; Kappelman, L.A.; Prybutok, V.R. Measuring Information Systems Service Quality: Concerns on the Use of the SERVQUAL Questionnaire. MIS Q. 1997, 21, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.O. Knowledge-Based Industry and Regional Growth; IWSG: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, J.M.; Hill, A.V. A Preliminary Investigation of the Relationships between Employee Motivation/Vision, Service Learning, and Perceived Service Quality. J. Oper. Manag. 2001, 19, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Shaw, J.D. Employee Compensation: The Neglected Area of HRM Research. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2014, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samnani, A.K.; Singh, P. Performance-enhancing Compensation Practices and Employee Productivity: The Role of Workplace Bullying. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2014, 24, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Potter, G.; Srinivasan, D. An Empirical Analysis of Continuing Improvements Following the Implementation of a Performance-based Compensation Plan. J. Account. Econ. 2000, 30, 315–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grönroos, C.; Ojasalo, K. Service productivity: Towards a Conceptualization of the Transformation of Inputs into Economic Results in Services. J. Bus. Res. 2004, 57, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambos, T.C.; Schlegelmilch, B.B. Managing Knowledge in International Consulting Firms. J. Knowl. Manag. 2009, 13, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameran, M.; Moizer, P.; Pettinicchio, A. Customer Satisfaction, Corporate Image, and Service Quality in Professional Services. Serv. Ind. J. 2010, 30, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegl, M.; Proserpio, L. Team Member Proximity and Teamwork in Innovative Projects. Res. Policy 2004, 33, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.R.; Huang, C.F.; Wu, K.S. The Association among Project Manager’s Leadership Style, Teamwork and Project Success. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2011, 29, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, F.J.L.; Moreno, A.R.; Morales, V.G. Influence of Support Leadership and Teamwork Cohesion on Organizational Learning, Innovation and Performance: An Empirical Examination. Technovation 2005, 25, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellett, J.B.; Humphrey, R.H.; Sleeth, R.G. Empathy and the Emergence of Task and Relations Leaders. Leadersh. Q. 2006, 17, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, Y.; Bilir, P.; Karademir, T. The Effect of Organizational Commitment on Job Performance: The Case of the Kahramanmaras Provincial Directorate of Youth Services and Sports. Int. J. Acad. Res. 2013, 5, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R. The Management Consulting Industry: Growth of Consulting Services in India: Panel Discussion. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2014, 26, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Krogh, G.; Roos, J. Managing Knowledge: Perspectives on Cooperation and Competition; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.M.; Chen, L.H. A Meta-Frontier Network Data Envelopment Analysis Approach for the Measurement of Technological Bias with Network Production Structure. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battese, G.E.; Rao, D.P.; O’donnell, C.J. A Metafrontier Production Function for Estimation of Technical Efficiencies and Technology Gaps for Firms Operating under Different Technologies. J. Product. Anal. 2004, 21, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.M.; Chen, L.H. Evaluation of Efficiency and Technological Bias of Tourist Hotels by a Meta-Frontier DEA Model. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2020, 71, 718–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Choi, K.; Kang, D.H. Measuring the Meta Efficiency and Its Determinants on Efficiency in the Korean Coffee Shop Franchise. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Satar, N.M. Efficiency of Global Airlines: An Application of the Metafrontier DEA Model. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2019, 20, 1178–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Yao, S.; Chang, Y.C. A Meta-frontier DEA Approach to Efficiency Comparison of Carbon Reduction Technologies on Project Level. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D. Energy Efficiency and Production Technology Heterogeneity in China: A Meta-Frontier DEA Approach. Econ. Model. 2013, 35, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creplet, F.; Dupouet, O.; Kern, F.; Mehmanpazir, B.; Munier, F. Consultants and Experts in Management Consulting Firms. Res. Policy 2001, 30, 1517–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, Y.; Parboteeah, K.P.; Nam, D.I. Innovation in Emerging Markets: The Role of Management Consulting Firms. J. Int. Manag. 2014, 20, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemawat, P. Regional Strategies for Global Leadership. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2005, 83, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W.; Wu, K.S.; Chang, B.G.; Lou, K.R. Measuring Technical Efficiency and Returns to Scale in Taiwan’s Baking Industry―A Case Study of the 85 °C Company. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhidé, A. Building the Professional Firm: McKinsey and Co.: 1939–1968; HBS Working Paper 95-010; Harvard Business School: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Glückler, J.; Armbrüster, T. Bridging Uncertainty in Management Consulting: The Mechanisms of Trust and Networked Reputation. Organ. Stud. 2003, 24, 269–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, P.N.; Reve, T. Transmitting Signals to Consumers for Competitive Advantage. Bus. Horiz. 1990, 33, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargha, A.; Delaney, H.D. The Kruskal-Wallis Test and Stochastic Homogeneity. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1998, 23, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D. An Exploratory Investigation of Multiunit Restaurant Productivity Assessment Using Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2004, 16, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J. Using Least Squares and Tobit in Second Stage DEA Efficiency Analyses. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 197, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Song, W.; Yang, F. Research on the Supply Efficiency of Marine Ecological Products in the Yangtze River Delta Costal Urban Agglomerations Based on DEA-Tobit Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.J.; Cha, B.S.; Kim, B.H.S. Efficient Expenditure Allocation for Sustainable Public Services?—Comparative Cases of Korea and OECD Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xue, X.; Yin, G.; Fang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and Improvement of Technological Innovation Efficiency of New Energy Vehicle Enterprises in China Based on DEA-Tobit Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanov, B.; Dudic, B.; Gregus, M.; Marcikic Horvat, A.; Karovic, V. Using a Two-Stage DEA Model to Measure Tourism Potentials of EU Countries and Western Balkan Countries: An Approach to Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, Y.A. Performance Measurement using Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). In Health Care Benchmarking and Performance Evaluation; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, G.; Nejad, M.H. Strategic Leadership: Short-term Stability and Long-term Viability. Ivey Bus. J. 2009, 73, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Semuel, H.; Siagian, H.; Octavia, S. The Effect of Leadership and Innovation on Differentiation Strategy and Company Performance. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 237, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Sam, M.F.; Tahir, M.N.H.; Abu Bakar, K. Owner-managers of SMEs in IT Sector: Leadership and Company Performance. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2012, 3, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Euwema, M.C.; Wendt, H.; Van Emmerik, H. Leadership Styles and Group Organizational Citizenship Behavior across Cultures. J. Organ. Behav. 2007, 28, 1035–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajagbe, M.A.; Long, C.S.; Solomon, O. The Impact of Sales Promotion and Product Branding on Company Performance: A Case Study of AIICO Insurance Nigerian PLC. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 129, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odunlami, I.B.; Ogunsiji, A. Effect of Sales Promotion as a Tool on Organizational Performance: A Case Study of Sunshine Plastic Company. J. Emerg. Trends Econ. Manag. Sci. 2011, 2, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ahearne, M.; Jelinek, R.; Rapp, A. Moving Beyond the Direct Effect of SFA Adoption on Salesperson Performance: Training and Support as Key Moderating Factors. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2005, 34, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharenou, P.; Saks, A.M.; Moore, C. A Review and Critique of Research on Training and Organizational-level Outcomes. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2007, 17, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.P.; Perrigot, R. Franchised Network Efficiency: A DEA Application to US Networks. In Economics and Management of Networks; Cliquet, G., Tuunanen, M., Hendrikse, G., Windsperger, J., Eds.; Contributions to Management Science; Physica-Verlag HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | Min. | Max. | Ave. | S.D. | Pearson Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COM | LV | RS | MC | OB | ||||||
| Input | COM | 6.71 | 9.65 | 8.44 | 0.71 | 1 | ||||
| LV | 8.07 | 9.79 | 8.97 | 0.44 | 0.864 ** | 1 | ||||
| RS | 8.1 | 9.78 | 9.1 | 0.47 | 0.850 ** | 0.918 ** | 1 | |||
| Output | MC | 7.22 | 9.93 | 9.02 | 0.69 | 0.874 ** | 0.925 ** | 0.911 ** | 1 | |
| OB | 7.63 | 9.93 | 9.02 | 0.59 | 0.795 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.869 ** | 0.828 ** | 1 | |
| Cluster | DUM | CCR (CRS-Based) | BCC (VRS-Based) | SE | RTS | Main Cause of Inefficiency | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME (TE) | GE | TGR | ME (PTE) | GE | TGR | PTE | SE | ||||
| USA | McKinsey & Company_USA | 0.996 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.996 | DRS | ✓ | |
| Bain & Company_USA | 0.996 | 0.996 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.996 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| The Keystone Group | 0.987 | 0.998 | 0.989 | 0.992 | 1 | 0.992 | 0.996 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| The Bridgespan Group | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Boston Consulting Group | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Putnam Associates | 0.977 | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.986 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.990 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| ClearView Healthcare Partners | 0.982 | 1 | 0.982 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.982 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| ghSMART | 0.980 | 0.980 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1 | 0.981 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| Insight Sourcing Group | 0.991 | 1 | 0.991 | 0.992 | 1 | 0.992 | 0.999 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| OC&C Strategy Consultants_USA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Average | 0.991 | 0.997 | 0.994 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.994 | ||||
| Europe | McKinsey & Company_Europe | 0.993 | 1 | 0.993 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.993 | DRS | ✓ | |
| Bain & Company_Europe | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Oliver Wyman_Europe | 0.971 | 0.977 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 1 | 0.978 | 0.993 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Alvarez & Marsal_Europe | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Kearney_Europe | 0.981 | 0.981 | 1 | 0.994 | 1 | 0.994 | 0.987 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Roland Berger_Europe | 0.945 | 0.961 | 0.984 | 0.955 | 0.974 | 0.980 | 0.990 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| OC&C Strategy Consultants_Europe | 0.973 | 0.98 | 0.993 | 0.979 | 0.981 | 0.998 | 0.994 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| Strategy & PwC network_Europe | 0.976 | 0.983 | 0.992 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.976 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Whiteshield Partners EMEA | 0.971 | 0.973 | 0.998 | 0.975 | 0.984 | 0.991 | 0.996 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Average | 0.979 | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.987 | 0.993 | 0.993 | 0.992 | ||||
| Asia-Pacific | McKinsey & Company_Asia-Pacific | 0.981 | 1 | 0.981 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.981 | DRS | ✓ | |
| Bain & Company_Asia | 0.972 | 1 | 0.972 | 0.973 | 1 | 0.973 | 0.998 | DRS | ✓ | ||
| Oliver Wyman_Asia-Pacific | 0.949 | 0.975 | 0.974 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 1 | 0.954 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Alvarez & Marsal_Asia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | CRS | |||
| Kearney_Asia-Pacific | 0.986 | 1 | 0.986 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.986 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Roland Berger_Asia | 0.949 | 0.972 | 0.976 | 0.951 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.998 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| YCP Solidiance | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.995 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.937 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Arthur D. Little_Asia | 0.975 | 0.999 | 0.976 | 0.977 | 0.999 | 0.978 | 0.998 | IRS | ✓ | ||
| Average | 0.969 | 0.986 | 0.982 | 0.987 | 0.996 | 0.991 | 0.982 | ||||
| Division | (I) Group—(J) Group | Test Statistics | Std. Error | Std. Test Statistics | Sig. | Adj. Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metafrontier | Asia_Pacific—Europe | 2.750 | 3.834 | 0.717 | 0.473 | 1.000 |
| Asia_Pacific—USA | 9.000 | 3.472 | 2.405 | 0.160 | 0.049 ** | |
| Europe—USA | 6.205 | 3.625 | 1.724 | 0.085 | 0.254 | |
| Technology gap ratio | Asia_Pacific—Europe | 8.562 | 3.714 | 2.305 | 0.021 | 0.063 * |
| Asia_Pacific—USA | 8.674 | 3.805 | 2.280 | 0.023 | 0.068 * | |
| Europe—USA | −0.111 | 3.598 | −0.031 | 0.975 | 1.000 |
| Environmental Variables | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | p > |t| | [95% Confidence Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Firm Leadership | −0.0558801 *** | 0.0141994 | −3.94 | 0.001 | −0.0857119 | −0.0260484 |
| Promotion Policies | 0.0365931 *** | 0.0120441 | 3.04 | 0.007 | 0.0112895 | 0.0618968 |
| Formal Training | −0.0064659 | 0.0097754 | −0.66 | 0.517 | −0.0270033 | 0.0140715 |
| Informal Training & Mentorship | 0.0080744 | 0.0090839 | 0.89 | 0.386 | −0.0110102 | 0.027159 |
| cons | 0.1892039 *** | 0.0572212 | 3.31 | 0.004 | 0.0689866 | 0.3094211 |
| sigma | 0.0149643 | 0.0025426 | 0.0096225 | 0.0203061 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, G.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, K. Evaluating the Service Operating Efficiency and Its Determinants in Global Consulting Firms: A Metafrontier Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810352
Park G, Lee S-K, Choi K. Evaluating the Service Operating Efficiency and Its Determinants in Global Consulting Firms: A Metafrontier Analysis. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):10352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810352
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Gowangwoo, Seok-Kee Lee, and Kanghwa Choi. 2021. "Evaluating the Service Operating Efficiency and Its Determinants in Global Consulting Firms: A Metafrontier Analysis" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 10352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810352
APA StylePark, G., Lee, S.-K., & Choi, K. (2021). Evaluating the Service Operating Efficiency and Its Determinants in Global Consulting Firms: A Metafrontier Analysis. Sustainability, 13(18), 10352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810352






