Research on the Knowledge-Sharing Incentive of the Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiotic System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
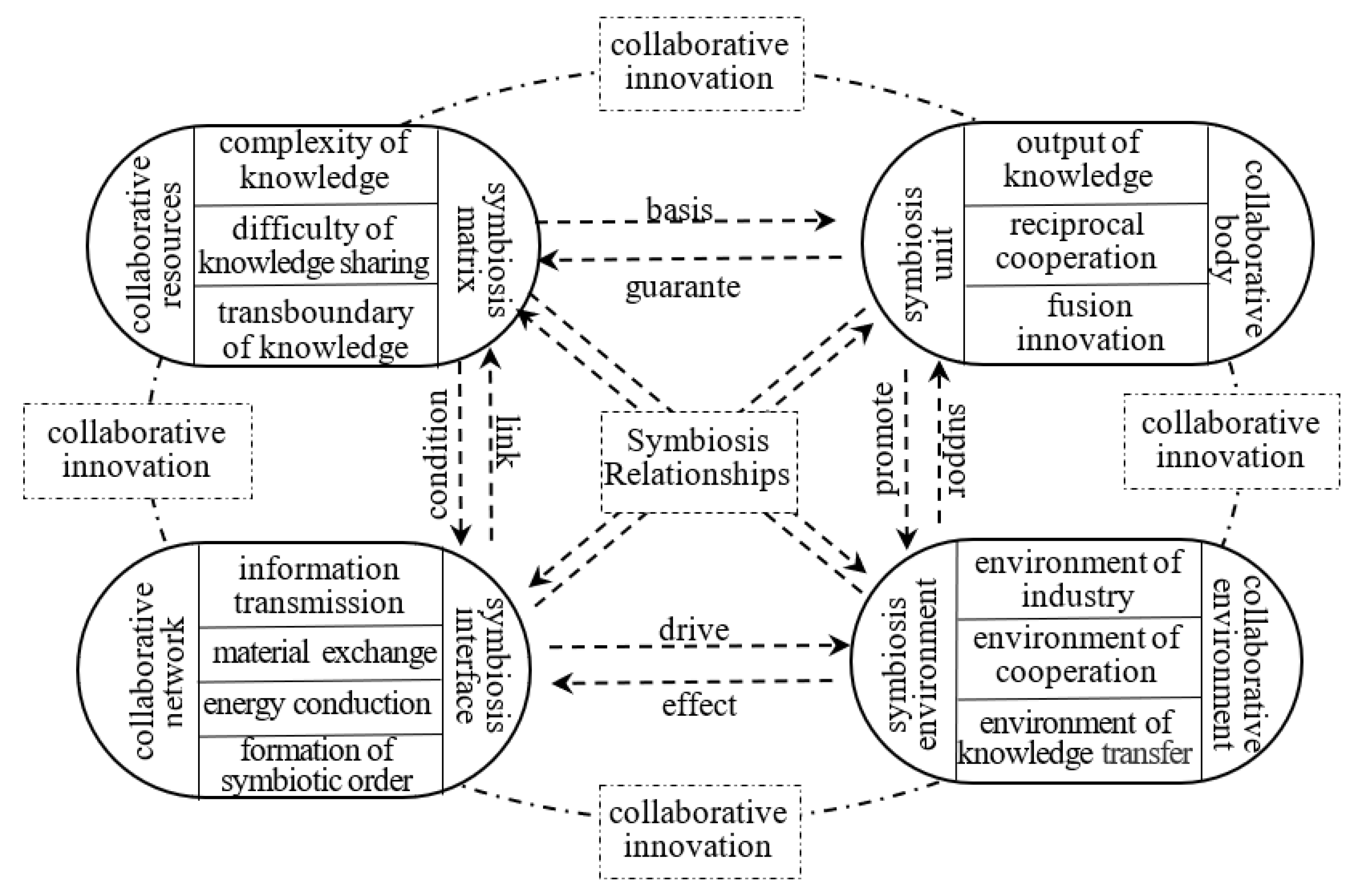
2.1. The Construction of the Symbiotic System Conceptual Model of Cross-Boundary Alliances
2.2. Principal–Agent Relationship of Knowledge-Sharing in Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiosis Systems
3. The Model
3.1. Model Hypothesis
3.2. Model Construction
3.2.1. Expected Income of Knowledge Principal
3.2.2. Expected Income of Knowledge Agent
3.2.3. Knowledge-Sharing Incentive Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Model Output
- Correlation analysis between the internal environment and the external environment of symbiotic systems
- 2.
- Influence analysis of the knowledge potential difference on the knowledge sharing activities
- 3.
- Influence analysis of the symbiotic environment on the knowledge-sharing activities
4.2. Model Simulation
4.2.1. Influence of the Incentive Coefficient of Knowledge-Sharing and Effort Level of the Knowledge-Sharing Unit on the Principal’s Profit
4.2.2. Influence of the Risk Aversion Coefficient of Knowledge-Sharing on the Incentive Coefficient
4.2.3. Influence of the Knowledge Potential Difference on the Incentive Coefficient and Agent’s Effort
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Deck, C.; Erkal, N. An experimental analysis of dynamic incentives to share knowledge. Econ. Inq. 2013, 51, 1622–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobides, M.G.; Billinger, S. Designing the boundaries of the firm: From ‘make, buy, or ally’ to the dynamic benefits of vertical architecture. Organ Sci. 2006, 17, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P. Generative growth with ‘thin’ globalization: Cambridge’s crossover model of innovation. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 26, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, J.A.; Tesluk, P.E.; Carson, J.B. A multilevel investigation of antecedents and consequences of team member boundary-spanning behavior. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lori, R.; Atul, N. Beyond local search: Boundary-spanning, exploration, and impact in the optical disk industry. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 287–306. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, J.; Kriz, A.; Thorpe, M. Industry clusters: An antidote for knowledge sharing and collaborative innovation? J. Knowl. Manag. 2014, 18, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.C. Integrating knowledge activities for team innovation: Effects of transformational leadership. J. Manag. 2018, 44, 1819–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.L.; Bao, Y.T.; Wang, J.K.; Yu, H.; Ma, Z.; Jing, L. Knowledge sharing in R&D teams: An evolutionary game model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6664. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.N.; Lan, Y.F.; Zhao, R.Q. Cooperation royalty contract design in research and development alliances: Help vs. knowledge-sharing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 268, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, S.V.; Reuer, J.J. Knowledge sharing and safeguarding in R&D collaborations: The role of steering committees in biotechnology alliances. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.M.; Jiang, H.; Wu, R.; Li, J. Reconciling the dilemma of knowledge sharing: A network pluralism framework of firms’ R&D alliance network and innovation performance. J. Manag. 2019, 45, 2635–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.S.Y.; Thai, V.V. Knowledge sharing within strategic alliance networks and its influence on firm performance: The liner shipping industry. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2014, 6, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, X.; van der Bij, H.; Dolfsma, W. Knowledge sharing in inter-organisational teams: The role of the advice network and the substitutive role of the formal network in an R&D alliance. Ind. Innov. 2020, 27, 1160–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Vatamanescu, E.M.; Cegarra-Navarro, J.G.; Andrei, A.G.; Dincă, V.-M.; Alexandru, V.-A. SMEs strategic networks and innovative performance: A relational design and methodology for knowledge sharing. J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 24, 1369–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Gupta, S.; Busso, D. Top management knowledge value, knowledge sharing practices, open innovation and organizational performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 128, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassabehji, R.; Mishra, J.L.; Dominguez-Pery, C. Knowledge sharing for innovation performance improvement in micro/SMEs: An insight from the creative sector. Prod. Plan. Control 2019, 30, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P.; Olander, H.; Michailova, S.; Husted, K. Knowledge sharing, knowledge leaking and relative innovation performance: An empirical study. Technovation 2015, 35, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmol, L. Sharing is caring-information and knowledge in industrial symbiosis: A systematic review. In Proceedings of the 21st IEEE Conference on Business Informatics, Moscow, Russia, 15–17 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kwahk, K.; Park, D. The effects of network sharing on knowledge-sharing activities and job performance in enterprise social media environments. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmol, L.; Esswein, W. Capturing the Complexity of Industrial Symbiosis. In Advances and New Trends in Environmental Informatics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, D.; Baas, L.; El-Haggar, S.; Huisingh, D. Critical success and limiting factors for eco-industrial parks: Global trends and Egyptian context. J. Clean Prod. 2011, 19, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golev, A.; Corder, G.D.; Giurco, D.P. Barriers to Industrial Symbiosis: Insights from the Use of a Maturity Grid. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, M.R.; Frayret, J.M.; Robert, J.M. Green social networking: Concept and potential applications to initiate industrial synergies. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 115, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaud, J.P.; Adoue, C.; Sablayrolles, C.; Vialle, C.; Chorro, A. Decision making approach for industrial ecology: Layout and commercialization of an industrial park. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 57, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.M.; Jhang-Li, J.H. Knowledge sharing in communities of practice: A game theoretic analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecelja, F.; Raafat, T.; Trokanas, N.; Innes, S.; Smith, M.; Yang, A.; Zorgios, Y.; Korkofygas, A.; Kokossis, A. E-symbiosis: Technology-enabled support for industrial symbiosis targeting small and medium enterprises and innovation. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 98, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.D.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, T. Dynamic evolution of knowledge sharing behavior among enterprises in the cluster innovation network based on evolutionary game theory. Sustainability 2020, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, A.; Belenzon, S.; Patacconi, A. Knowledge sharing in alliances and alliance portfolios. Manag. Sci. 2021, 67, 1569–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, P.J.; Wu, C.X. How to encourage innovation failure knowledge sharing in virtual research organization: An incentive mechanism based on game theory. Comput. Math. Organ. Theory 2021, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.F.; Jia, J.Y.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Z.J. Incentives and contract design for knowledge sharing in construction joint ventures. Autom. Constr. 2020, 119, 103343. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Guo, P. External incentive mechanism research on knowledge cooperation-sharing in the Chinese creative industry cluster. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2021, 38, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.C.; Xu, Y.M.; Li, J.F. A study of RI clusters based on symbiosis theory. Sustainability 2017, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guido, V.C.; Amrit, C.; Yazan, D.M.; Zijm, H. The influence of knowledge in the design of a recommender system to facilitate industrial symbiosis markets. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2018, 110, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, G.B.; Seager, T.P.; Massard, G.; Nies, L. Information and communication technology for industrial symbiosis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2010, 14, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumate, M.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Oconnor, A. A nonprofit perspective on business–nonprofit partnerships: Extending the symbiotic sustainability model. Bus. Soc. 2018, 57, 1337–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.W.; Hung, C.Z. How to shape the employees’ organization sustainable green knowledge sharing: Cross-level effect of green organizational identity effect on green management behavior and performance of members. Sustainability 2021, 13, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. The symbiotic habit. Bioscience 2015, 61, 326–327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.R. The technological roadmap of cisco’s business ecosystem. Technovation 2009, 29, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.Q. Symbiosis Theory—On Small Economy, 1st ed.; Economic Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Yang, X. Research on interest balance in association standards of high-technology industry and governments’ countermeasures from the perspective of symbiosis. Sci. Sci. Manag. S. T. 2020, 41, 33–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, H.M. Network equilibrium of eco-industrial chain with principal-agency. J. Manag. Sci. 2011, 24, 101–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Z.; Shao, C.Y. Special knowledge sharing incentive mechanism for two clients with complementary knowledge: A principal-agent perspective. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.G.; Xu, T.T.; Gui, M.Z. Incentive mechanism for municipal solid waste disposal PPP projects in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Yu, L.Y. Analysis of enterprise sustainable crowd sourcing incentive mechanism based on principal-agent model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Feng, G. Incentive model of emergency equipment reservation system based on principal-agent theory. J. Syst. Manag. 2020, 29, 833–846. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, P. Incentive strategy about technology innovation based on knowledge ecological coupling in strategic emerging industry. Kybernetes 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Ma, G.H. Study on incentive and supervision mechanisms of technological innovation in megaprojects based on the principal-agent theory. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2021, 28, 1593–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.K.; Shi, Q. The incentive mechanism of knowledge sharing in the industrial construction supply chain based on a supervisory mechanism. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2019, 26, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Cao, X. The influence factors of knowledge potential difference and knowledge transfer in collaborative innovation enterprises. Syst. Eng. 2018, 36, 51–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Enkel, E.; Heil, S. Preparing for distant collaboration: Antecedents to potential absorptive capacity in cross-industry innovation. Technovation 2014, 34, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.; Jonard, N. Network structure and the diffusion of knowledge. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 2004, 28, 1557–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Q.; Guo, R.; Xia, J. The impact of transformational leadership on cross-border team collaborative innovation: An empirical analysis of fintech enterprises in China. Foreign Econ. Manag. 2020, 42, 17–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, I.C. Enhancing employee tendencies to share knowledge-Case studies of nine companies in Taiwan. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2006, 26, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2 | ||
| 0.8 | 4 | ||
| 5 | 5 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.6 | ||
| 2 | 1 | ||
| 4 | 0.5 | ||
| 6 | −5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S. Research on the Knowledge-Sharing Incentive of the Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiotic System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810432
Zhang X, Gao C, Zhang S. Research on the Knowledge-Sharing Incentive of the Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiotic System. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):10432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810432
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoxing, Changyuan Gao, and Shuchen Zhang. 2021. "Research on the Knowledge-Sharing Incentive of the Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiotic System" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 10432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810432
APA StyleZhang, X., Gao, C., & Zhang, S. (2021). Research on the Knowledge-Sharing Incentive of the Cross-Boundary Alliance Symbiotic System. Sustainability, 13(18), 10432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810432






