Effects of Sustainable Strategic Planning Applications in Primary Schools on the Effectiveness of Total Quality Management Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Theoretical Background and Research Hypothesis
- Although education is a production instrument with its expertise, skills, personality development, modernity, and certain technical features, it is also considered a consumption tool because of the learning needs of society.
- Education aims to increase the welfare of society through the development of individuals.
- Educational efficiency varies according to a country’s level of economic and social development.
- Measuring educational efficiency only quantitatively is not sufficient. It should be evaluated as a whole using qualitative measurements.
- Realising performance criteria in line with strategies.
- Comparing performance criteria with goals and objectives.
- Creating the distribution of the strategies prepared in educational institutions according to the fields of the ministries.
- Presenting the evaluation results in a report and sharing them with all stakeholders.
- Determining whether the goals and objectives have been achieved, measuring effectiveness and efficiency, and revealing the reasons if the desired goals have not been achieved.
- Developing alternative strategies and creating solutions or recommendations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Questionnaire Design
2.2. Survey Administration
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Implications of the Study
4.1.1. Theoretical Implications
4.1.2. Practical Implications
4.2. Sustainability Remarks
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luce, I. Sustainable strategic planning principles of colleges. In Proceedings of the Economic Science for Rural Development Conference Proceedings, Riga, Latvia, 28 May 2018; Volume 47, pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, A. Connection of architectural education with the technological world in Northern Cyprus. Int. J. New Trends Soc. Sci. 2020, 4, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabei, E. Innovative, creative VARK learning styles improvement strategies. Glob. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 2018, 8, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, M.N.; Hussin, F. Quality management as a strategic tool to enhance the relationship between leaders’ behavior and lecturers’ job satisfaction. Int. J. Curr. Innov. Interdisip. Sci. Stud. 2019, 3, 1–15. Available online: https://www.un-pub.eu/ojs/index.php/IJ-CISS/article/view/5033 (accessed on 25 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, E.H. Problems and strategy of educational development in Morocco. New Trends Issues Proc. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2019, 6, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlirova, M. Semantic space of elementary teacher attitudes towards computer teaching assistant. Glob. J. Inf. Technol. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkay, A.D.; Mola, S. The status of teachers’ motivation and process of quality education: The case of primary school teachers, Ethiopia. Glob. J. Guid. Couns. Sch. Curr. Perspect. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubieva, V.; Sagiyeva, A.; Sagiyeva, A.; Salimgerey, Z.; Baiseitova, M. Multilingualism is a trend in the development of modern Kazakhstan. Glob. J. Sociol. Curr. Issues 2021, 11, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtabaş, M. Toplam Kalite Yönetimi Uygulamaları ile Öğretmen Performansı Arasındaki İlişkinin Belirlenmesi (Öğretmen Görüşlerine Göre). Determining the Relationship between Total Quality Management Practices and Teacher Performance (According to Teacher Opinions). Master’s Thesis, Yeditepe University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2009. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.; Sharma, P. Teacher education and total quality management (TQM). Int. J. Indian Psychol. 2015, 2, 80–85. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yeztq9az (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Mahmood, H.K.; Hashmi, M.S.; Shoaib, D.M.; Danish, R.; Abbas, J. Impact of TQM practices on motivation of teachers in secondary schools: Empirical evidence from Pakistan. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 1–8. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yhbjn9dx (accessed on 13 February 2021).
- Ereş, F. Eğitim yönetiminde stratejik planlama. Strategic planning in educational administration. Gazi Univ. J. Ind. Arts Educ. Fac. 2004, 15, 21–29. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/296511 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Ergen, H. Planning approaches in education and educational indicators used in Turkey. Mersin Univ. J. Fac. Educ. 2013, 9, 151–167. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/mersinefd/issue/17383/181588 (accessed on 9 January 2021).
- Safaryan, N. Methodological issues of education monitoring and evaluation. Int. J. Learn. Teach. 2020, 12, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatürk, K. Eğitim Planlaması. Education Planning; Pegem Akademi: Ankara, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, S.; Aslan, N. A qualitative study on the opinions of secondary school principals regarding strategic planning. Gaziantep Univ. J. Soc. Sci. 2008, 7, 172–189. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/jss/issue/24257/257122?publisher=gantep (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Abdi, M.; Sharyati, A. Comparing the training effects of problem-solving and coping skills with stress. Glob. J. Psychol. Res. New Trends Issues 2019, 9, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çalık, T. Strategical planning in education and the qualitative evaluation of the schools as regards to strategical planning. Kast. J. Educ. 2003, 11, 251–258. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yjofpob6 (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Memduhoğlu, H.B.; Uçar, İ.H. Developing the Strategic Planning Perception Scale and the Strategic Planning Application Assessment Scale in School. Educ. Adm. Theory Pract. 2012, 18, 545–574. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/kuey/issue/10322/126575 (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Gümüş, E.; Şişman, M. Eğitim Ekonomisi ve Planlaması; Pegem Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 2012; Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yk5ks3hv (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Agha, Z.; EL Daou, B. The role of the special education centers in developing students’ holistic wellbeing. J. Educ. Spec. Educ. Technol. 2018, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, M.A. The Effect of Using Performance-based assessment Strategies to Tenth Grade Students’ Achievement and Self-Efficacy in Jordan. Cypriot J. Educ. Sci. 2018, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, G.; Ardıç, K. Eğitimde toplam kalite yönetimi. Total quality management in educatio. Bilgi J. Soc. Sci. 1999, 1, 73–82. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/301065 (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- Sallis, E. Total Quality Management in Education; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Konst, T.; Kairisto-Mertanen, L. Developing innovation pedagogy. Contemp. Educ. Res. J. 2019, 9, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M. Attitude toward organic foods among Taiwanese as related to health consciousness, environmental attitudes, and the mediating effects of a healthy lifestyle. Br. Food J. 2009, 111, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed, a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, Ş.; Başar, E.E. How does the environmental knowledge of Turkish households affect their environmentally responsible food choices? The mediating effects of environmental concerns. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Food Sci. 2020, 4, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fantauzzi, C.; Colasanti, N.; Fiorani, G.; Frondizi, R. Sustainable strategic planning in Italian higher education institutions: A content analysis. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2021, 22, 1145–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
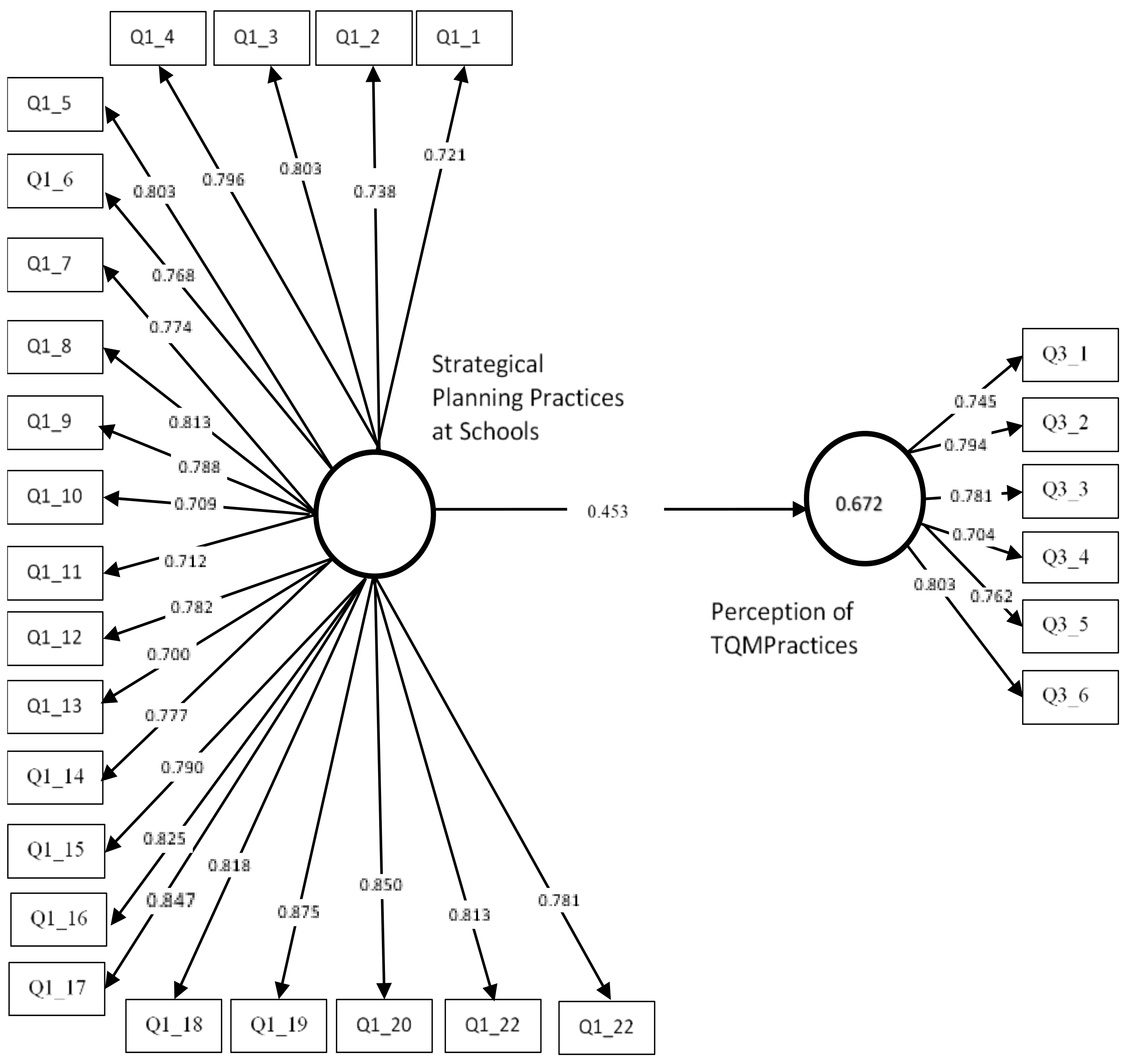
| Latent Constructs | CA | CR | AVE | 01 | 02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategical Planning Practices at Schools | 0.856 | 0.879 | 0.701 | 0.753 | |
| Perception of TQM Practices | 0.791 | 0.809 | 0.728 | 0.711 | 0.732 |
| Items | Strategical Planning Practices at Schools | Perception of TQM Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Q1_1. School administrators have sufficient knowledge about strategic planning. | 0.721 | 0.694 |
| Q1_2. Our school is managed in accordance with strategic planning. | 0.738 | 0.642 |
| Q1_3. The management approach of our school facilitates strategic planning. | 0.803 | 0.709 |
| Q1_4. Our school receives adequate guidance and counselling regarding strategic planning. | 0.796 | 0.638 |
| Q1_5. Our school has a regular strategic planning policy. | 0.803 | 0.687 |
| Q1_6. The strategic plan preparation team is well trained in plan preparation. | 0.774 | 0.691 |
| Q1_7. School staff eagerly participate in strategic planning activities. | 0.774 | 0.596 |
| Q1_8. The strategic plan is prepared by determining realistic goals, principles, resources, and achievements. | 0.813 | 0.613 |
| Q1_9. A comprehensive situation analysis is performed in the strategic planning process. | 0.788 | 0.601 |
| Q1_10. Parents participate in strategic planning activities. | 0.709 | 0.552 |
| Q1_11. Teachers support the strategic planning process. | 0.712 | 0.568 |
| Q1_12. Students are encouraged to participate in the strategic planning process. | 0.782 | 0.596 |
| Q1_13. Adequate preparation is made before strategic planning. | 0.700 | 0.613 |
| Q1_14. The strategic plan is constantly evaluated and revised. | 0.777 | 0.601 |
| Q1_15. The opportunities specified in the strategic plan are evaluated in the best way. | 0.790 | 0.487 |
| Q1_16. School personnel are insensitive to strategic planning studies. (reverse) | 0.825 | 0.512 |
| Q1_17. Not enough time is allocated for the development of the strategic plan. (reverse) | 0.847 | 0.500 |
| Q1_18. School staff do not believe that the prepared strategic plan will be implemented. (reverse) | 0.818 | 0.534 |
| Q1_19. Administrators do not consider strategic planning practices necessary in school. (reverse) | 0.875 | 0.525 |
| Q1_20. Conditions of the environment and the school are ignored when preparing strategic plans. (reverse) | 0.850 | 0.565 |
| Q1_21. Strengths and weaknesses of the school are not determined realistically in the strategic plans. (reverse) | 0.813 | 0.512 |
| Q1_22. The weaknesses and threats to the school determined in the strategic plan are ignored in practice. (reverse) | 0.781 | 0.500 |
| Q2_1. School staff’s ability to communicate well horizontally and vertically contributes to their motivation. | 0.745 | 0.459 |
| Q2_2. A clear knowledge of the roles and responsibilities of all staff in school increases the efficiency of their work. | 0.794 | 0.691 |
| Q2_3. Following new developments in teaching methods and techniques and adapting them to the school contribute to the work performance of staff. | 0.781 | 0.703 |
| Q2_4. Rewarding school staff for their efforts to improve themselves and the institution creates synergy in the institution. | 0.704 | 0.661 |
| Q2_5. All kinds of changes (social, economic) affecting the education process should be closely monitored, and measures should be taken against possible effects. | 0.762 | 0.671 |
| Q2_6. Regular meetings should be held to identify potential obstacles to the educational environment in advance. | 0.803 | 0.602 |
| Causal Hypothesis | β | t | p | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 0.453 | 3.234 | 0.000 | Accepted |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sucuoğlu, E.; Erdem, G. Effects of Sustainable Strategic Planning Applications in Primary Schools on the Effectiveness of Total Quality Management Practices. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13189998
Sucuoğlu E, Erdem G. Effects of Sustainable Strategic Planning Applications in Primary Schools on the Effectiveness of Total Quality Management Practices. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13189998
Chicago/Turabian StyleSucuoğlu, Esen, and Gülümser Erdem. 2021. "Effects of Sustainable Strategic Planning Applications in Primary Schools on the Effectiveness of Total Quality Management Practices" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13189998
APA StyleSucuoğlu, E., & Erdem, G. (2021). Effects of Sustainable Strategic Planning Applications in Primary Schools on the Effectiveness of Total Quality Management Practices. Sustainability, 13(18), 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13189998





