Evaluation of Suitability of Urban Land Using GIS Technology
Abstract
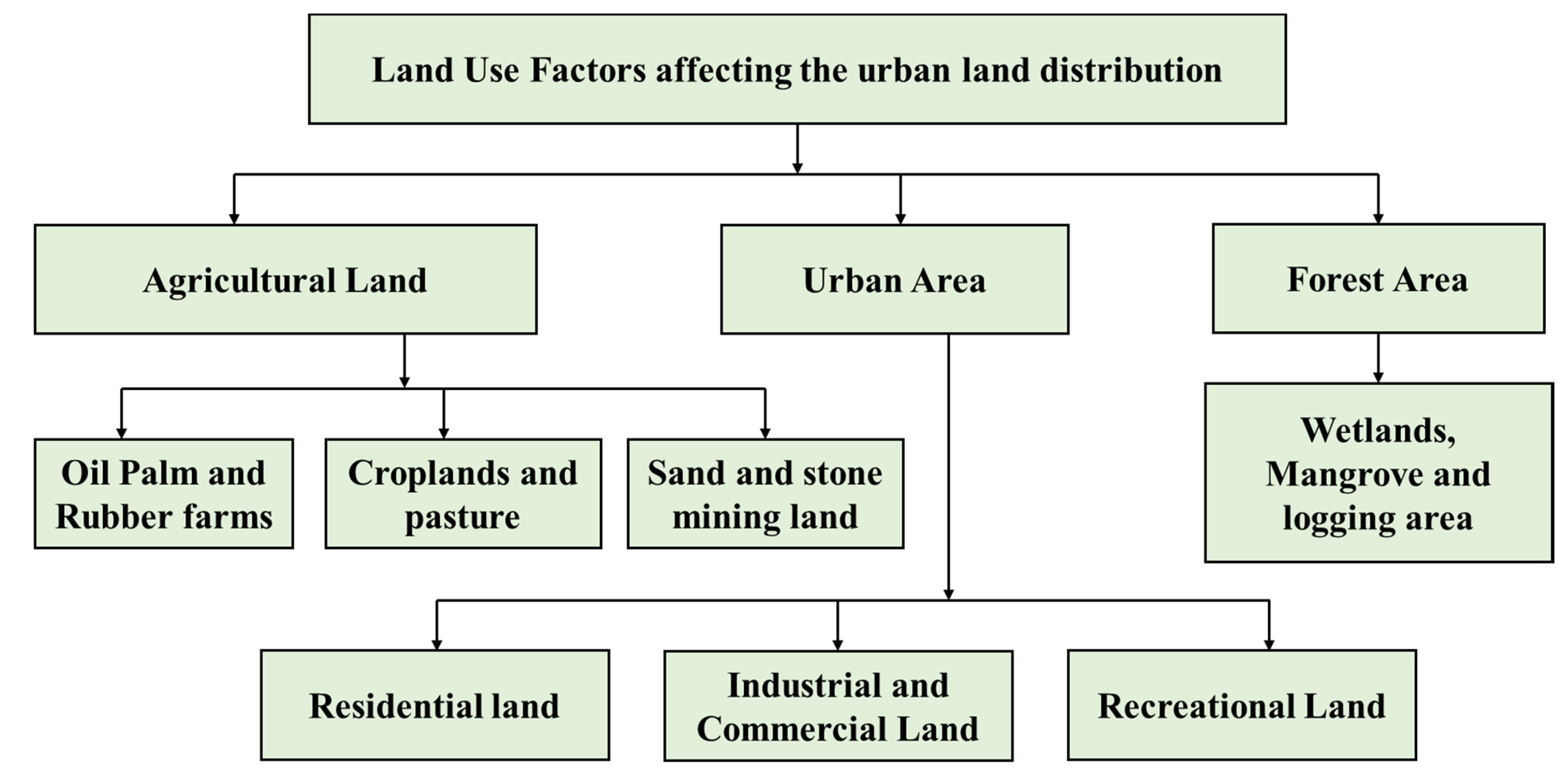
:1. Introduction
- It specifically contributes to the establishment of an evaluation index system for the evaluation of suitability of urban land using Geographic Information System (GIS) technology.
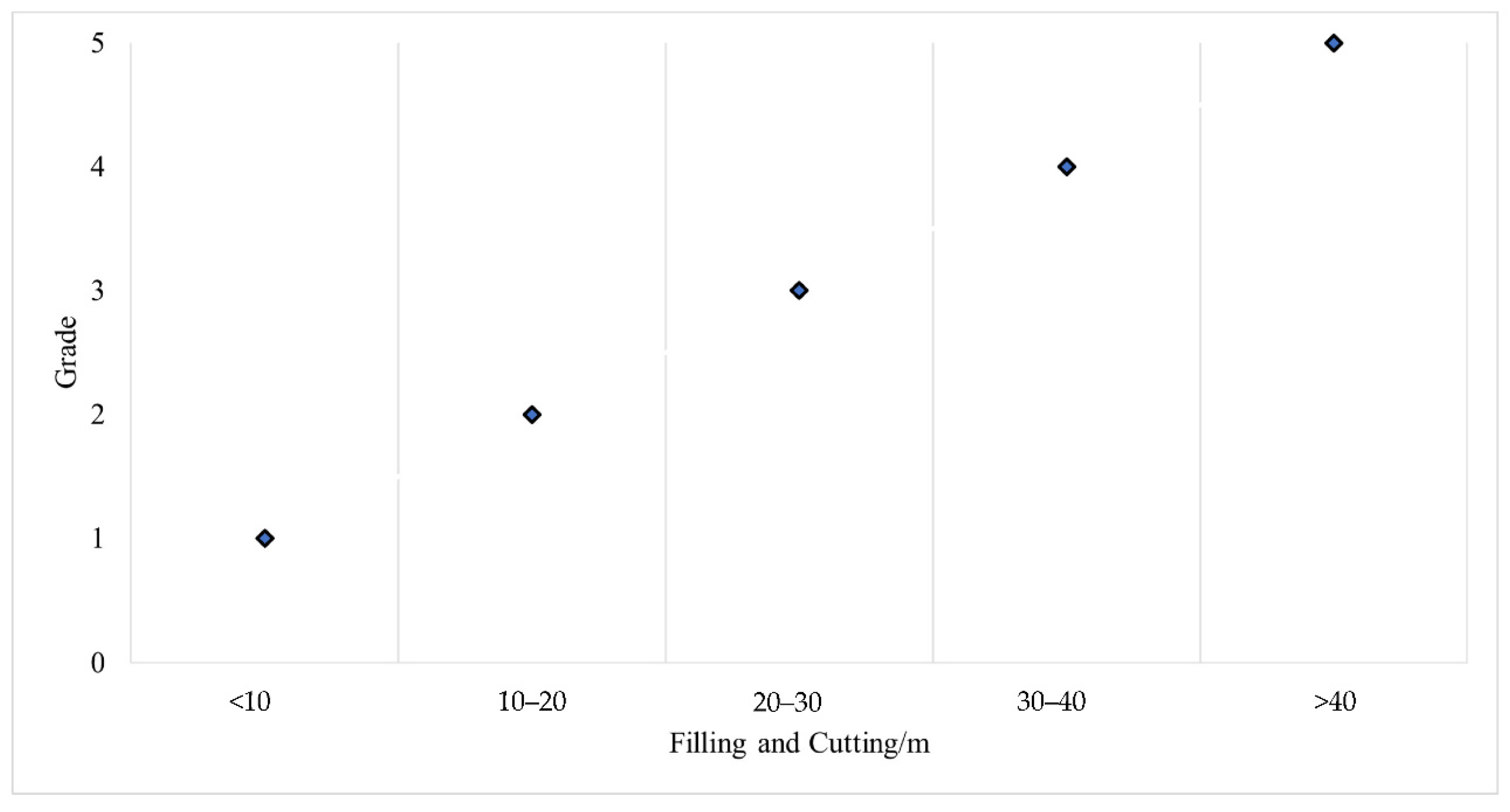
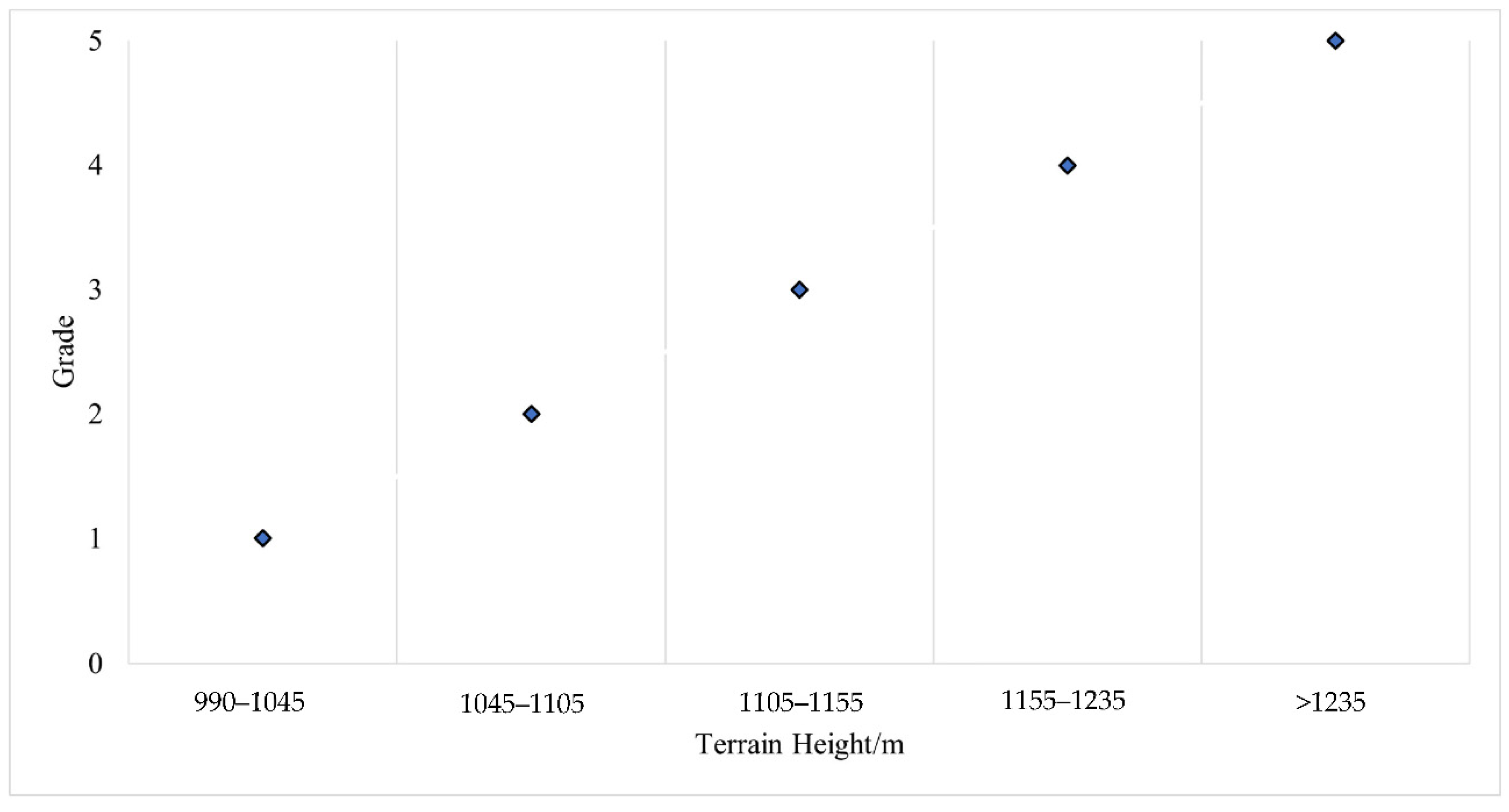
- The topographic aspect of the planning area was determined by the filling and excavation of depth factors and terrain elevation of the planning area.
- Determining the topographic slope of the planning area and evaluation index weight for the analysis of superposition factors.
- The proposed methodology involves GIS data processing methods, document analysis methods, and mathematical models being used to evaluate the suitability of construction land.
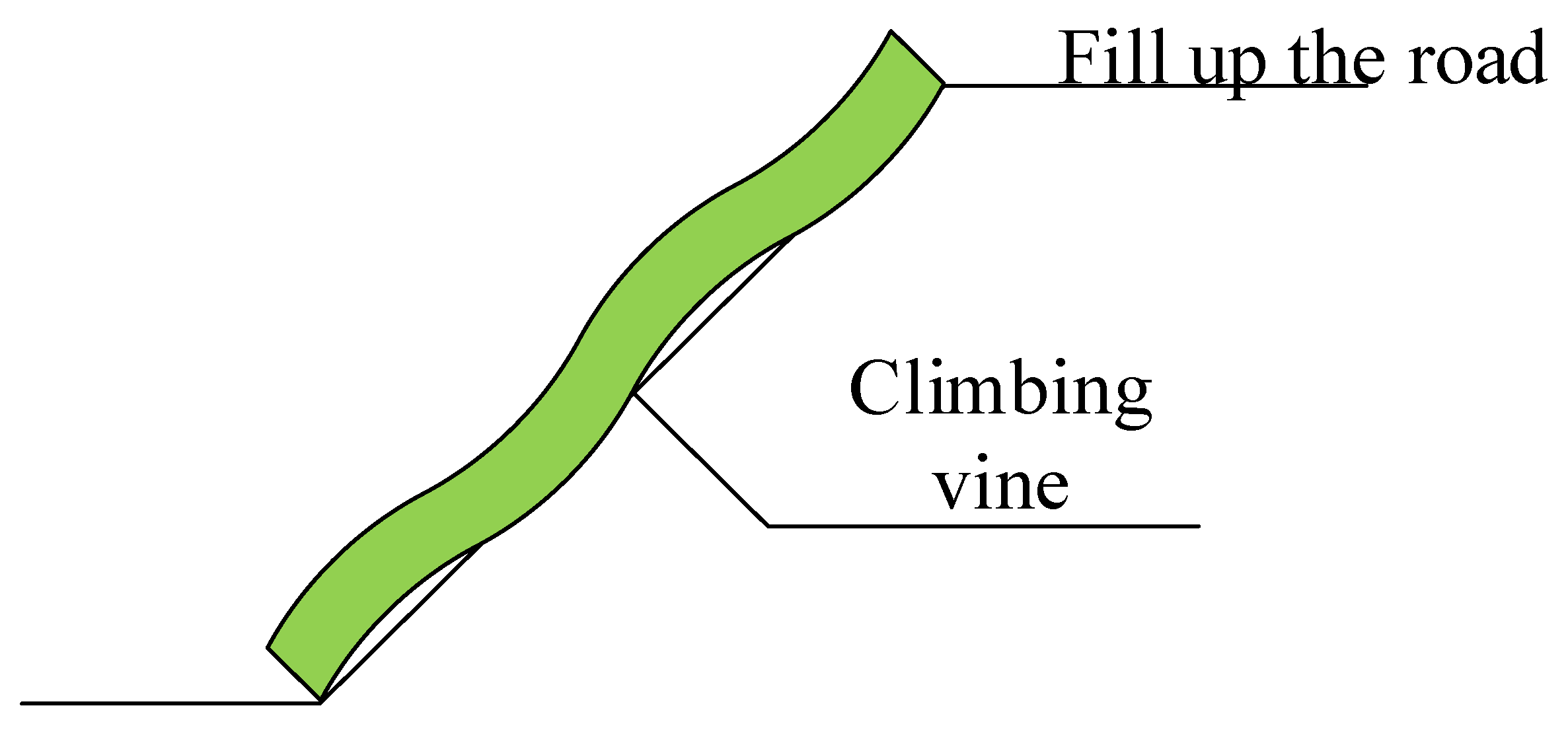
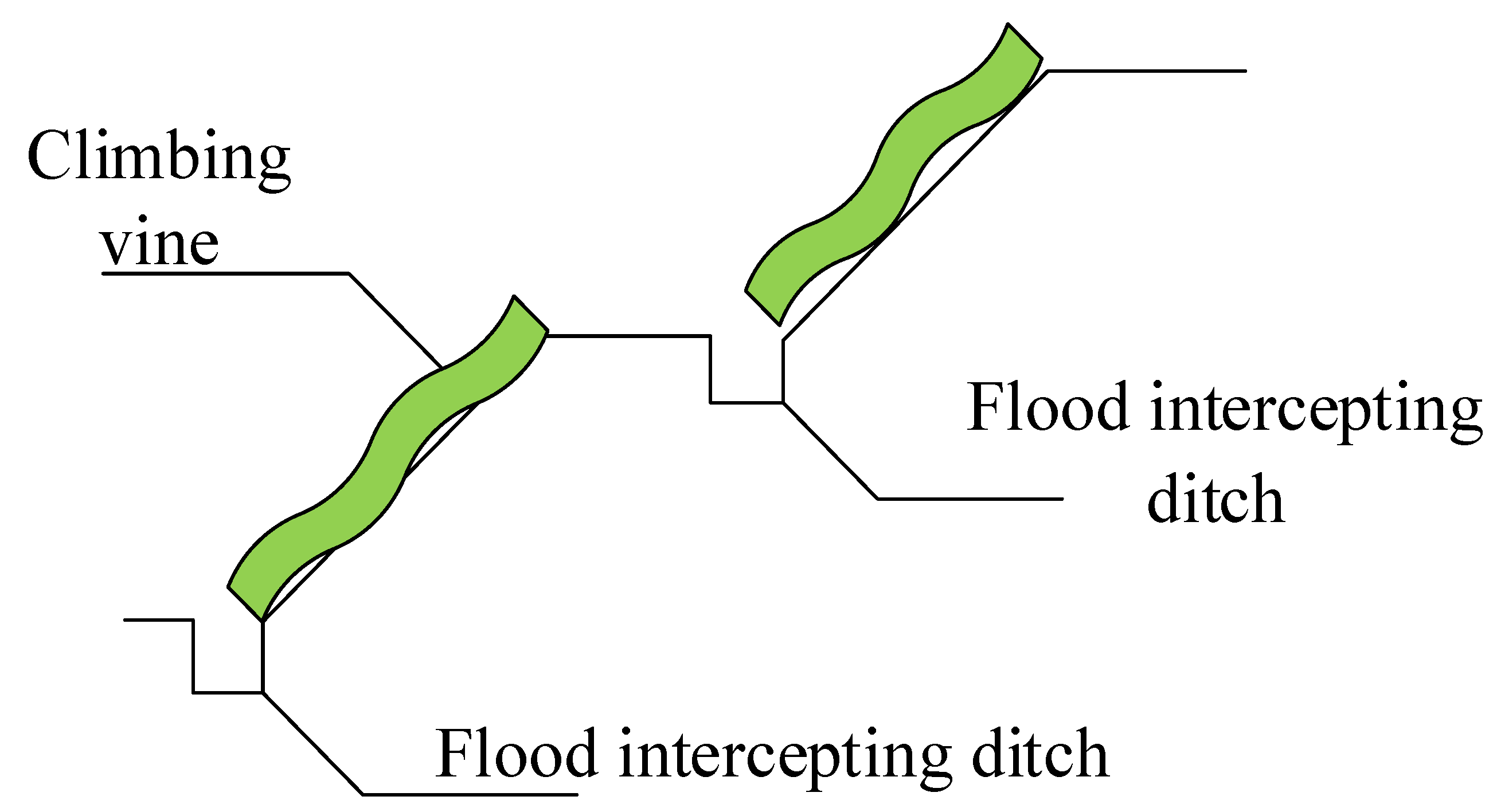
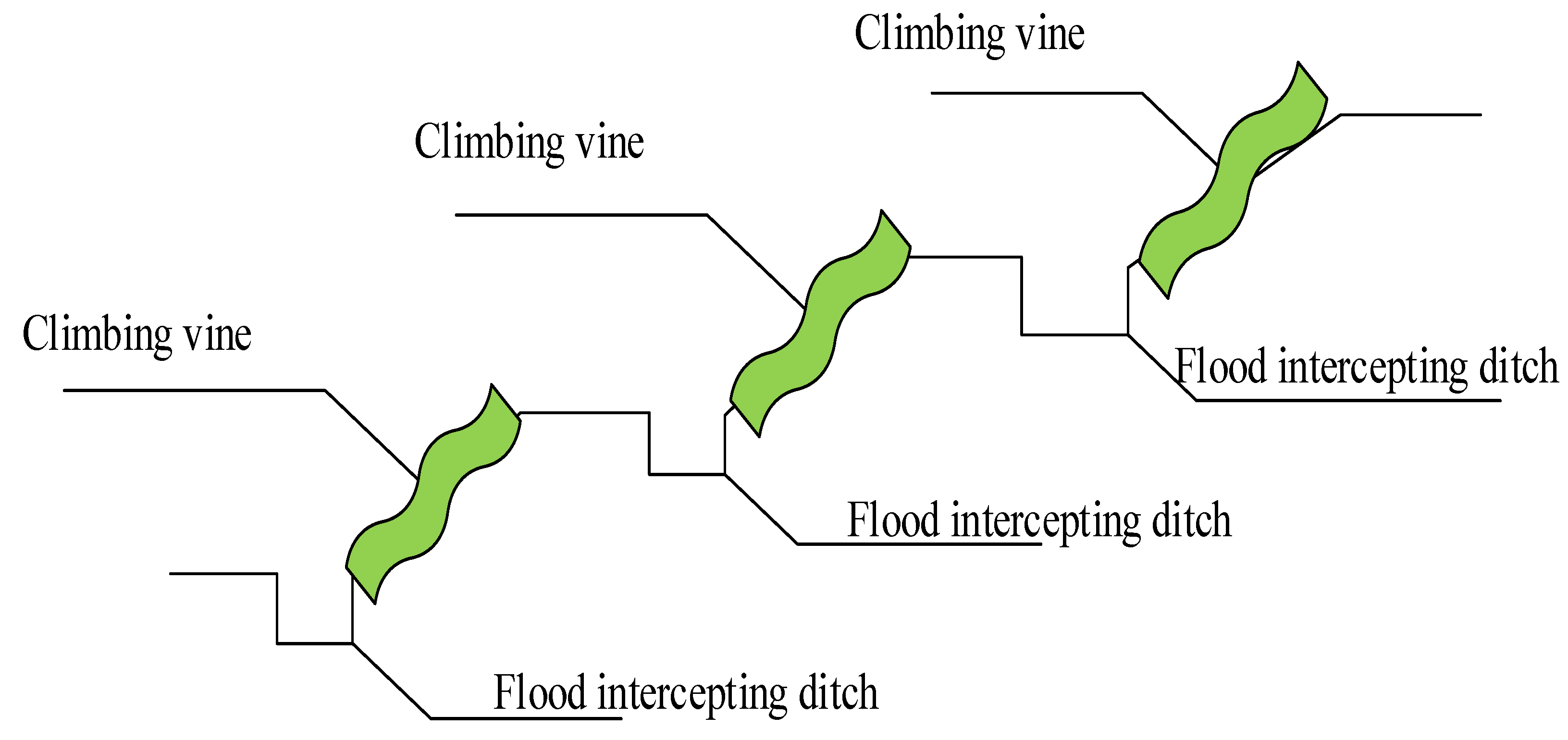
- This method of intercepting flood ditch at the foot of the mountain was designed and adopted, followed by eventual realization of rainwater recycling and safe flood control, making urban land use more reasonable. Therefore, urban land planning is provided with a reasonable reference basis.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
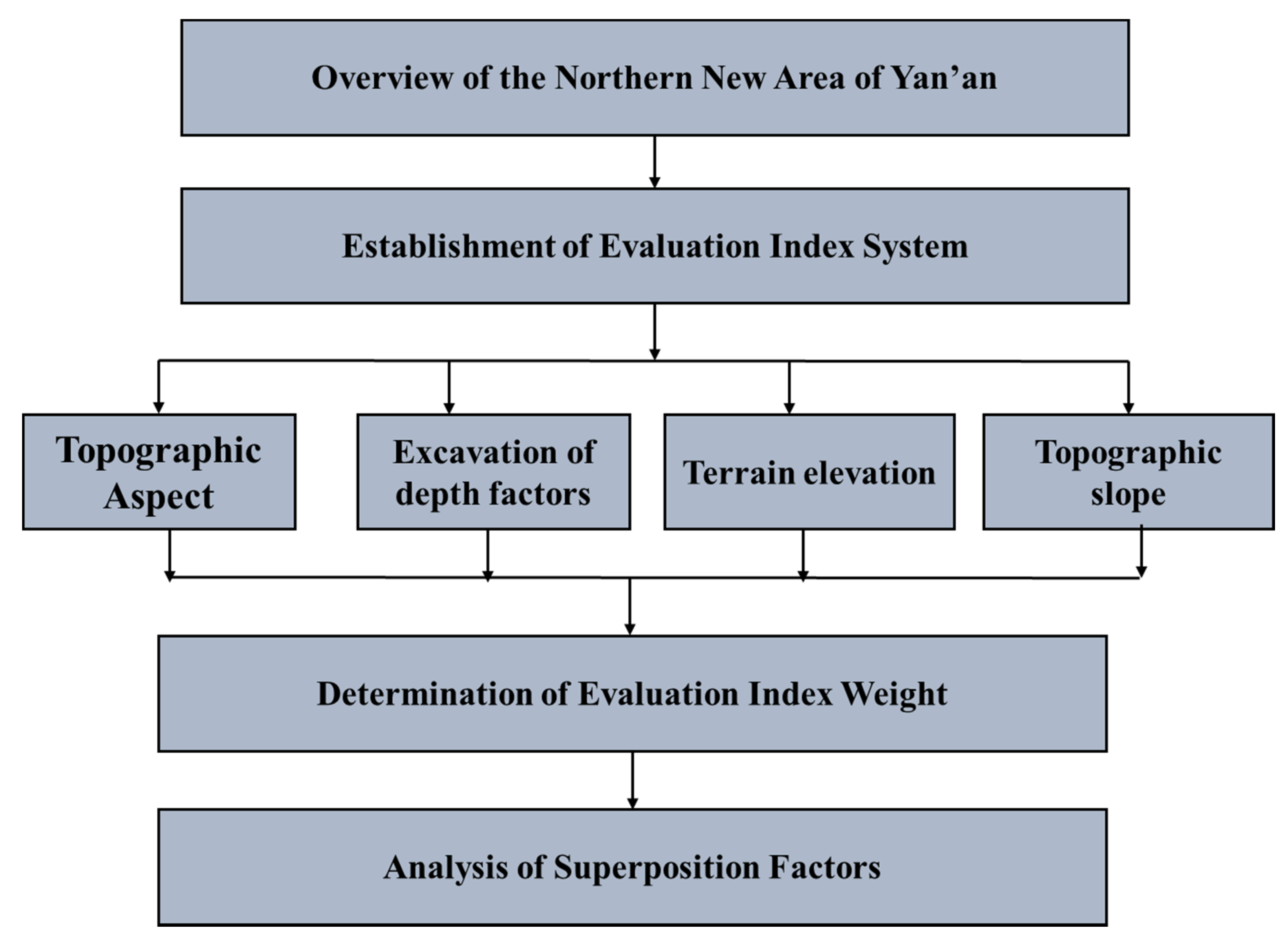
3.1. Overview of the Northern New Area of Yan’an
3.2. Establishment of Evaluation Index System
- (1)
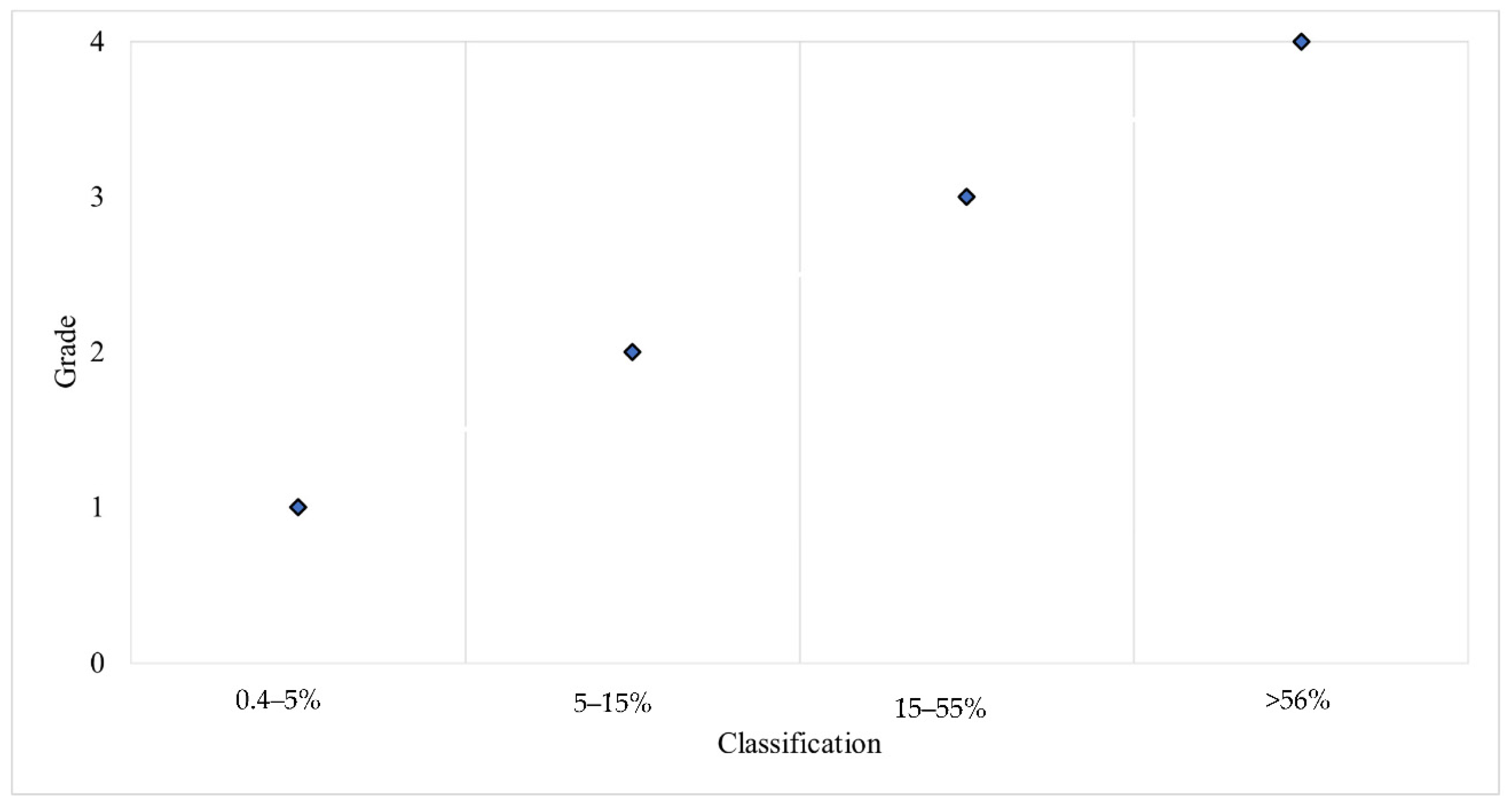
- Topographic aspect of the planning area
- (2)
- Filling and excavation of depth factors
- (3)
- Terrain elevation of the planning area
- (4)
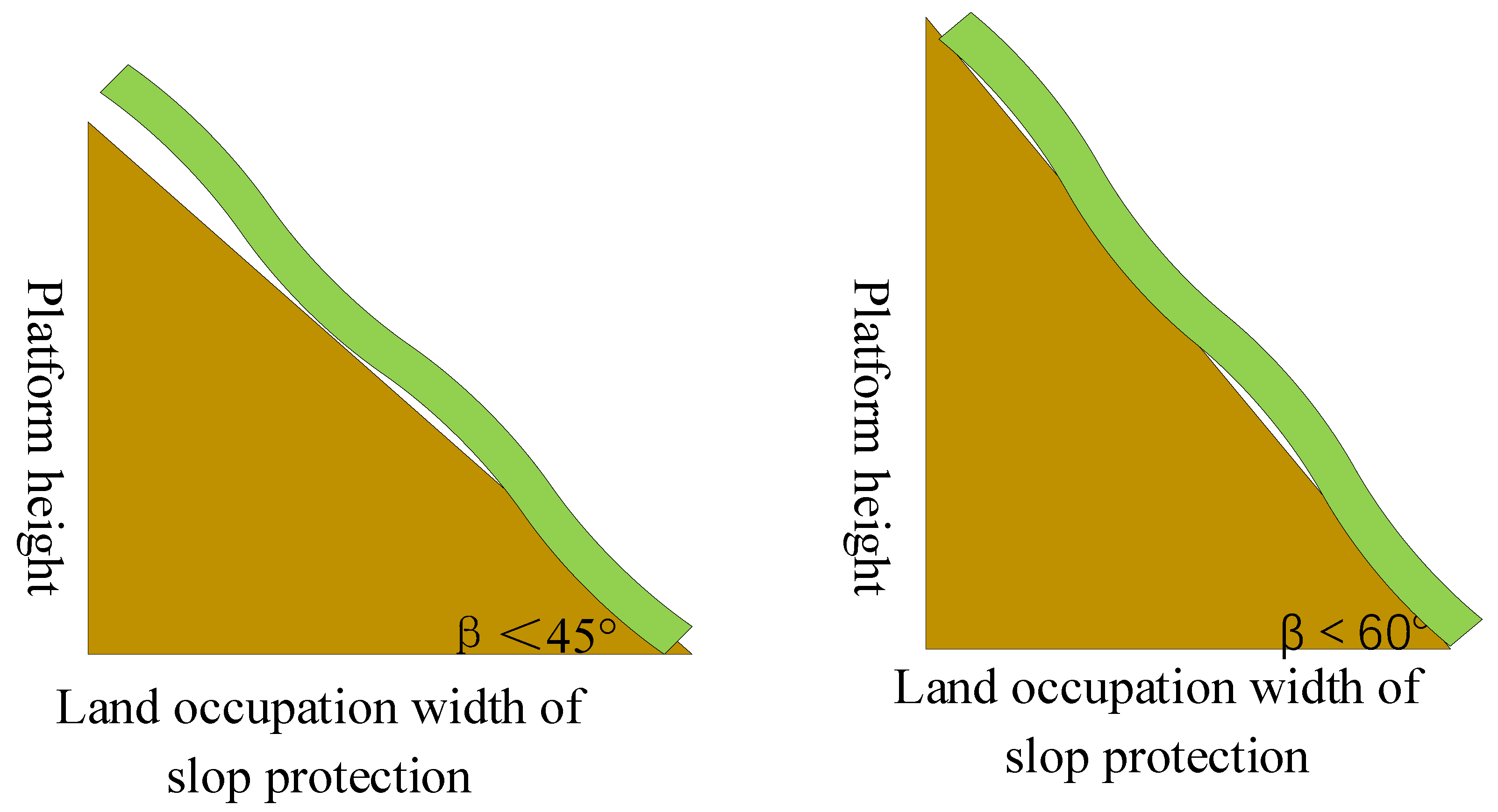
- Topographic slope of the planning area
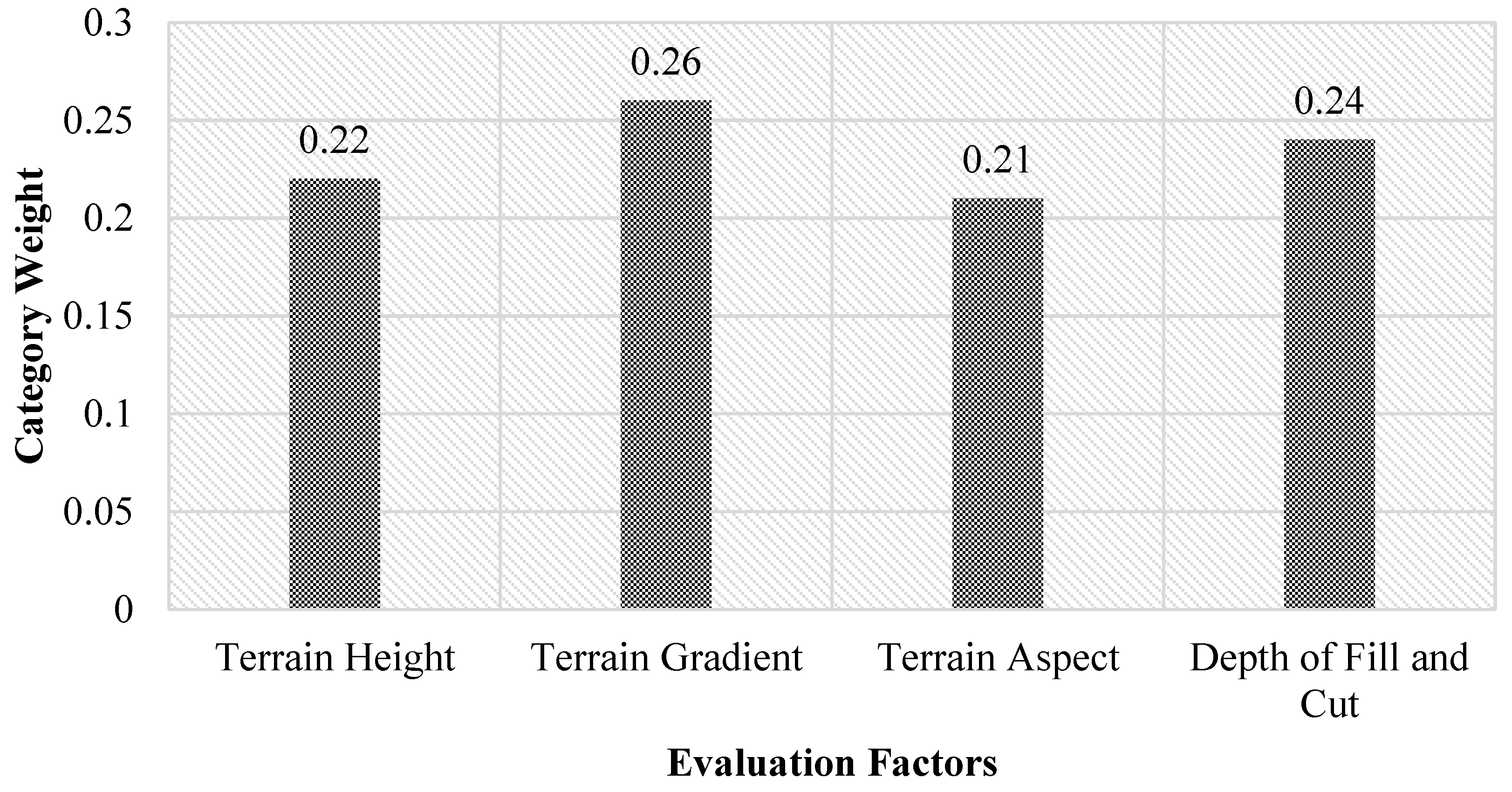
3.3. Determination of Evaluation Index Weight
- (1)
- The product S of the elements in each row is calculated:
- (2)
- The n-th root of S in each row is calculated:
- (3)
- The vector is normalized:
- (4)
- The largest eigenvalue of the matrix is calculated:is a variable, and i represents the ith index. j represents the jth index, and represents the category weight. (BW) is the ith element of the vector BW.
- (5)
- Consistency testThe test equation is:CR is a fuzzy subset of D and the random consistency ratio of the matrix.
3.4. Analysis of Superposition Factors
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis on the Evaluation Results of Land-Use Suitability in the New Planning Area
4.2. Analysis of Safety Planning for Ecological Protection
4.3. Plan the Land Layout According to the Evaluation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondal, B.; Das, D.N. How residential compactness and attractiveness can be shaped by environmental amenities in an industrial city? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, M.L.; Theis, T.L.; Karunanithi, A.T.; Garmestani, A.S.; Cabezas, H. A new framework for urban sus-tainability assessments: Linking complexity, information and policy. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2008, 32, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiong, J.; Andrey, Z. Study on ecological evaluation of urban land based on GIS and RS technology. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Marcella, S.V.; Juan, P.M.D. City Logistics in historic centers: Multi-Criteria Evaluation in GIS for city of Salvador (Bahia–Brazil). Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2019, 7, 772–780. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.F.; Qin, P. Evaluation of the Suitability of Urban Construction Land—A Case Study of Hudai Town. Urban. Land Use 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, Y.; Kamrani, M. Using a fuzzy logic decision system to optimize the land suitability evaluation for a sprinkler irrigation method. Outlook Agric. 2018, 47, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.; Javed, M.A.; Asif, M.; Luqman, M.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ahmad, A.; Akhtar, S.; Hussain, B. Weighted overlay based land suitability analysis of agriculture land in Azad Jammu and Kashmir using GIS and AHP. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 57, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Gallegos, J.J.; Aguirre-Salado, C.A.; Miranda-Aragón, L.; Sánchez-Díaz, G.; Valdez-Lazalde, J.R.; Pedroza-Carneiro, J.W.; Flores-Cano, J.A. Locating potential zones for cultivating Stevia rebaudiana in Mexico: Weighted linear com-bination approach. Sugar Tech 2017, 19, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, A.; Gholizadeh, A. Modeling land suitability evaluation for wheat production by parametric and TOPSIS approaches using GIS, northeast of Iran. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagherzadeh, A.; Ghadiri, E.; Darban, A.R.S.; Gholizadeh, A. Land suitability modeling by parametric-based neural networks and fuzzy methods for soybean production in a semi-arid region. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danvi, A.; Jütten, T.; Giertz, S.; Zwart, S.; Diekkrüger, B. A spatially explicit approach to assess the suitability for rice cultivation in an inland valley in central Benin. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Li, X. GIS-based assessment of land suitability for alfalfa cultivation: A case study in the dry continental steppes of northern China. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, L.D.; Bradley, B.A.; Beukes, H.; Hole, D.G.; Lau, M.; Oppenheimer, M.G.; Schulze, R.; Tadross, M.A.; Turner, W.R. Comparing mechanistic and empirical model projections of crop suitability and productivity: Implications for ecological forecasting. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Blanco, J.; Pérez-Damián, J.L.; Conde-Álvarez, A.C.; Gómez-Díaz, J.D.; Monterroso-Rivas, A.I. Land suitability levels for rainfed maize under current conditions and climate change projections in Mexico. Outlook Agric. 2018, 47, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.M.H.; Mahmood, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Liesenberg, V. Delineation of Potential Sites for Rice Cultivation Through Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2017, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veselov, G.; Tselykh, A.; Sharma, A.; Huang, R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Evolution of Smart Cities and Societies. Informatica 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, L.; Castets, M.; Baron, C.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Bégué, A.; Seen, D.L. Maize yield estimation in West Africa from crop process-induced combinations of multi-domain remote sensing indices. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 108, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.M.; Mansourian, A. Evaluation of Land Suitability for Urban Land-Use Planning: Case Study D haka City. Trans. GIS 2016, 20, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakieh, Y.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Jafarnezhad, J.; Mehri, A.; Kamyab, H.; Galdavi, S. Evaluating the strategy of decentralized urban land-use planning in a developing region. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Borthwick, A.G. Land-use suitability analysis for urban development in Beijing. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terzi, F.; Tezer, A.; Turkay, Z.; Uzun, O.; Köylü, P.; Karacor, E.; Kaya, M. An ecosystem services-based approach for decision-making in urban planning. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.X.; Zeng, C.Q.; Ai, Q. GIS Technology Applied in Urban Plot Ratio Statistics and Land Suitability Evaluation. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 638, pp. 2146–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H. Urban construction land suitability evaluation based on improved multi-criteria evaluation based on GIS (MCE-GIS): Case of New Hefei City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madaminovich, A.B. The use of gis technology to create electronic environmental maps. ACADEMICIA Int. Multidiscip. Res. J. 2020, 10, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. How to Identify Future Priority Areas for Urban Development: An Approach of Urban Construction Land Suitability in Ecological Sensitive Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. Application of urban planning and design in Yan’an new area based on GIS technology. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Andreev, D.V. Possibilities of GIS technologies in the mining industry. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 677, 032090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Du, K. Research on Eco-geological Environment Carrying Capacity Based on GIS Technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 651, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzikulova, O.; Sabitova, N.; Kholdorova, G. The role of GIS technology in determining irrigated geosystems. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 227, 03004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Masud, M. Evaluating software usability of geographic information system. Int. J. Comput. Internet Manag. 2009, 17, 37–54. [Google Scholar]

| Research | Crop | Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Bagherzadeh and Gholizadeh [9] | Alfalfa | Artificial Neural Network (ANN) |
| Bagherzadeh et al. [10] | Soyabean | Fuzzy approach |
| Danvi et al. [11] | Rice | Machine Learning (ML) |
| Deng et al. [12] | Rice | ANN + Genetic Algorithm (GA) |
| Estes et al. [13] | Maize | Machine Learning (ML) |
| Lopez-Blanco et al. [14] | Several Crops | Fuzzy approach + ML |
| Raza et al. [15] | Several Crops | Fuzzy approach |
| Classification of Slope Orientation | Influence Level |
|---|---|
| North | Unsuitable orientation |
| Northeast, northwest | Low orientation |
| East, west | Suitable orientation |
| South, southwest, southeast | Best orientation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sharma, A.; Al-Amri, J.F. Evaluation of Suitability of Urban Land Using GIS Technology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10521. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910521
Yan Y, Zhang Y, Sharma A, Al-Amri JF. Evaluation of Suitability of Urban Land Using GIS Technology. Sustainability. 2021; 13(19):10521. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910521
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yu, Yukun Zhang, Ashutosh Sharma, and Jehad F. Al-Amri. 2021. "Evaluation of Suitability of Urban Land Using GIS Technology" Sustainability 13, no. 19: 10521. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910521
APA StyleYan, Y., Zhang, Y., Sharma, A., & Al-Amri, J. F. (2021). Evaluation of Suitability of Urban Land Using GIS Technology. Sustainability, 13(19), 10521. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910521






