Evaluation of Five Gas Diffusion Models Used in the Gradient Method for Estimating CO2 Flux with Changing Soil Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Gradient Method
2.2. Soil CO2 Concentration, Moisture and Temperature Measurements
2.3. Laboratory Experiment
2.3.1. A General Description of the Laboratory Experiment
2.3.2. Sampling Site
2.3.3. Soil Samples Preparation
2.4. Forest Experiment
2.4.1. Site Description
2.4.2. Field Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Soil Moisture on Applicability of Diffusion Models
3.2. Effect of Soil Bulk Density on Applicability of Diffusion Models
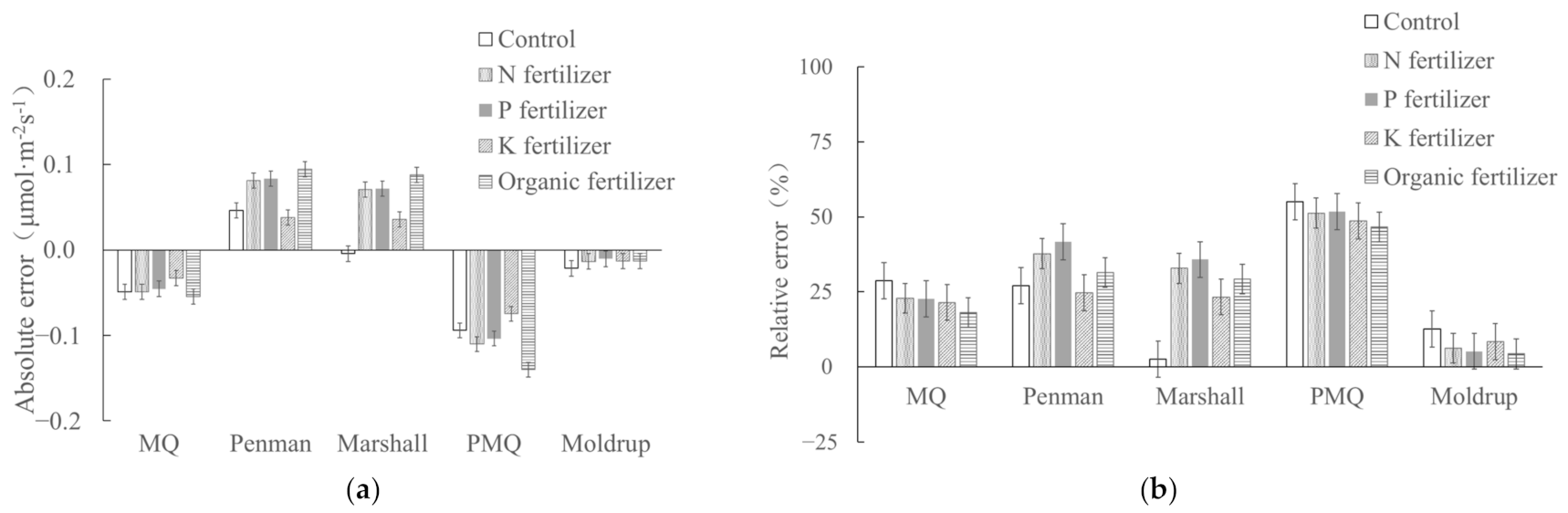
3.3. Effect of Soil Fertility on Applicability of Diffusion Models
3.4. Correlation Analysis between the Five Model Calculations and the Measurements
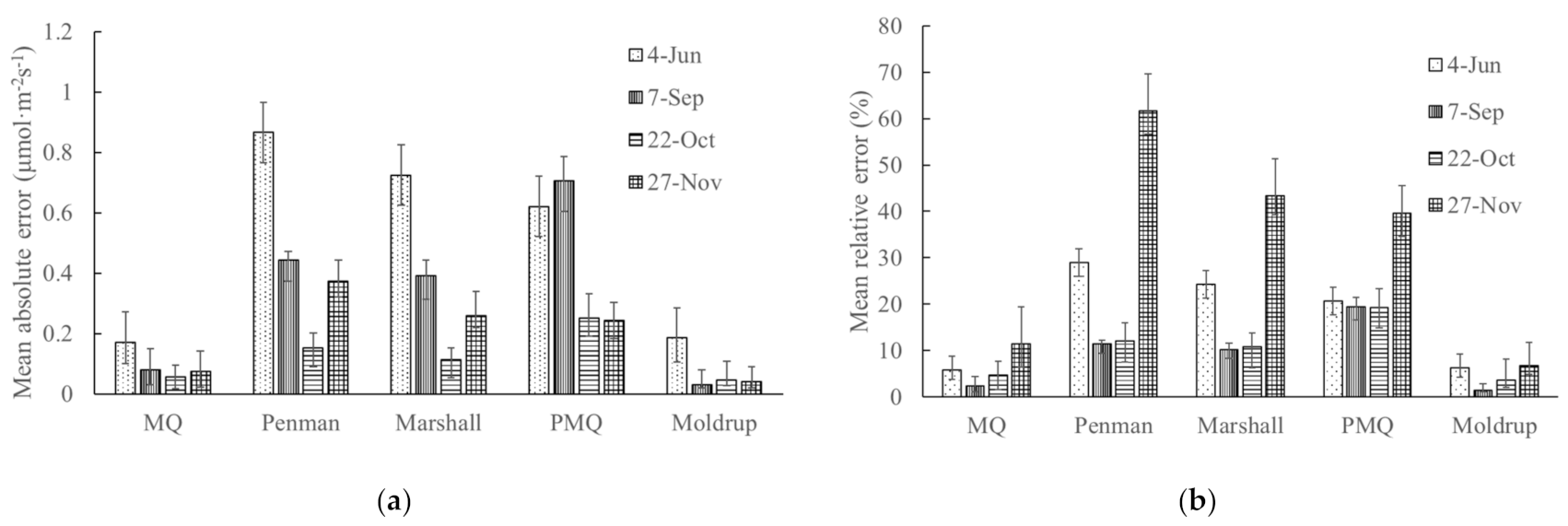
3.5. Measurement of CO2 Flux in Forest Area
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Law, B.E.; Kelliher, F.M.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Anthoni, P.M.; Irvine, J.; Moore, D.; Tuyl, S.V. Spatial and temporal variation in respiration in a young ponderosa pine forest during a summer drought. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 110, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeghiero, M.; Cescatti, A. Main determinants of forest soil respiration along an elevation/temperature gradient in the Italian Alps. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1024–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L. New ideas cultivate high-value permanent forests. Land Green 2017, 9, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Cao, J.H.; Zhu, T.B.; Fan, M.Z.; Ren, M.M. CO2 Transfer characteristics of calcareous humid subtropical forest soils and associated contributions to carbon source and sink in Guilin, Southwest China. Forests 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.D.; Gong, Y.; Francisco, J.E.; Bracho, R.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhao, M. Measuring multi-scale urban forest carbon flux dynamics using an integrated eddy covariance technique. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campioli, M.; Malhi, Y.; Vicca, S.; Luyssaert, S.; Papale, D.; Peñuelas, J.; Reichstein, M.; Migliavacca, M.; Arain, M.A.; Janssens, I.A. Evaluating the convergence between eddy-covariance and biometric methods for assessing carbon budgets of forests. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massman, W.J.; Lee, X. Eddy covariance flux corrections and uncertainties in long-term studies of carbon and energy exchanges. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngao, J.; Epron, D.; Delpierre, N.; Breda, N.; Granier, A.; Longdoz, B. Spatial variability of soil CO2 efflux linked to soil parameters and ecosystem characteristics in a temperate beech forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 154, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumpanen, J.; Kolari, P.; Ilvesniemi, H.; Minkkinen, K.; Vesala, T.; Niinistö, S.; Lohila, A.; Larmola, T.; Morero, M.; Pihlatie, M.; et al. Comparison of different chamber techniques for measuring soil CO2 efflux. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 123, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.; Darenova, E.; Krupková, L.; Pavelka, M. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of soil CO2 efflux in a Norway spruce forest over an eight-year study. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256-257, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Schack-Kirchner, H. Using the gradient method to determine soil gas flux: A review. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 192–193, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myklebust, M.; Hipps, L.; Ryel, R. Comparison of eddy covariance, chamber, and gradient methods of measuring soil CO2 efflux in an annual semi-arid grass, Bromus tectorum. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, B.; Chen, W.; Brüggemann, N.; Zheng, X.; Pumpanen, J.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Applicability of the soil gradient method for estimating soil–atmosphere CO2, CH4, and N2O fluxes for steppe soils in Inner Mongolia. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Gong, Y.S.; Ren, T.S.; Horton, R. Accounting for time-variable soil porosity improves the accuracy of the gradient method for estimating soil carbon dioxide production. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Q.B.; Yang, Z.J. Analysis of vertical profiles of soil CO2 efflux in Chinese fir plantation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.T.; Lin, W.S.; Yang, Y.S. Vertical profile of soil CO2 flux in a young Chinese fir plantation in response to soil warming. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Masakazu, O.; Hiromi, Y. Forest floor CO2 flux estimated from soil CO2 and radon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; Trumbore, S.E. Gas diffusivity and production of CO2 in deep soils of the eastern amazon. Tellus B 1995, 47, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.W.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Ye, Q.; Xu, L. Assessing soil CO2 efflux using continuous measurements of CO2 profiles in soils with small solid-state sensors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 118, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros-Iregui, D.A.; McGlynn, B.L.; Epstein, H.E.; Welsch, D.L. Interpretation and evaluation of combined measurement techniques for soil CO2 efflux: Discrete surface chambers and continuous soil CO2 concentration probes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2008, 113, G4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, B.W.; Dore, S.; Kolb, T.E.; Hart, S.C.; Montes-Helu, M.C. Evaluation of methods for estimating soil carbon dioxide efflux across a gradient of forest disturbance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Allen, M.F. Environmental controls and the influence of vegetation type, fine roots and rhizomorphs on diel and seasonal variation in soil respiration. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pingintha, N.; Leclerc, M.Y.; Beasley, J.P.; Zhang, G.; Senthong, C. Assessment of the soil CO2 gradient method for soil CO2 efflux measurements: Comparison of six models in the calculation of the relative gas diffusion coefficient. Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2010, 62, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrique, P.; Sánchez, C.; Russell, L.S.; Joost, H.; Greg, A.B. Improving the accuracy of the gradient method for determining soil carbon dioxide efflux. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.W.; Luo, W.J.; Zeng, G.N.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, M.F.; Lyu, Y.; Cheng, A.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.L.; Chen, J.; et al. CO2 flux of soil respiration in natural recovering karst abandoned farmland in Southwest China. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G. A quantitative approach to environmental plant physiology. In Plants and Microclimate; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 428. [Google Scholar]
- Millington, R.J.; Quirk, J.P. Permeability of porous solids. Trans Actions Faraday Soc. 1961, 57, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Gas and vapour movements in the soil: I. The diffusion of vapours through porous solids. J. Agric. Sci. 1940, 30, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.J. Gas diffusion in porous media. Science 1959, 130, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Rolston, D.E. Modeling diffusion and reaction in soils: VII. Predicting gas and ion diffusivity in undisturbed and sieved soils. Soil Sci. 1997, 162, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Gamst, J. Predicting the gas diffusion coefficient in repacked soil: Water-induced linear reduction model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Wang, Y.M. Study on the measurement of soil water content based on the principle of standing-wave ratio. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2002, 4, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Xia, W.B.; Wang, F.; Li, X.W.; Chen, Q.; Yang, X.L.; Chen, X.Y. Soil CO2 flux change and its effect factors from 4 different land use types in Huainan city. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2016, 29, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yu, X.X.; Li, H.Z.; Chang, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Tu, Z.H.; Liang, H.R. Simulated erosion using soils from vegetated slopes in the Jiufeng Mountains, China. Catena 2016, 136, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.D.; Perumpral, J.V. Moisture and density effect on cone index. Trans. ASAE 1982, 25, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.F.; Zhao, Y.J.; Cheng, Q.; Zheng, X.L.; Zhao, Y.D. Determining forest duff water content using a low-cost standing wave ratio sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.Z.; Xue, W.L.; Xu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Diurnal and seasonal variations in soil respiration of four plantation forests in an urban park. Forests 2019, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strack, M.; Waddington, J.M.; Tuittila, E.S. Effect of water table drawdown on northern peatland methane dynamics: Implications for climate change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munir, T.M.; Perkins, M.; Kaing, E.; Strack, M. Carbon dioxide flux and net primary production of a boreal treed bog: Responses to warming and water-table-lowering simulations of climate change. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munir, T.M.; Khadka, B.; Xu, B.; Strack, M. Mineral nitrogen and phosphorus pools affected by water table lowering and warming in a boreal forested peatland. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimner, R.A.; Pypker, T.G.; Hribljan, J.A.; Moore, P.A.; Waddington, J.M. Multi-decadal changes in water table levels alter peatland carbon cycling. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 1042–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.R.; Zha, T.G.; Zhang, Z.Q. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil respiration in a poplar plantation in Daxing district, Beijing. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 2308–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Epron, D.; Farque, L.; Lucot, E. Soil CO2 efflux in a beech forest: Dependence on soil temperature and soil water content. Ann. For. Sci. 1999, 56, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Komatsu, T.; SchjØnning, P.; Rolston, D.E. Tortuosity, diffusivity, and permeability in the soil liquid and gaseous phases. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Komatsu, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; SchjØnning, P.; Rolston, D.E. Modeling diffusion and reaction in soils: X. A unifying model for solute and gas diffusivity in unsaturated soil. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




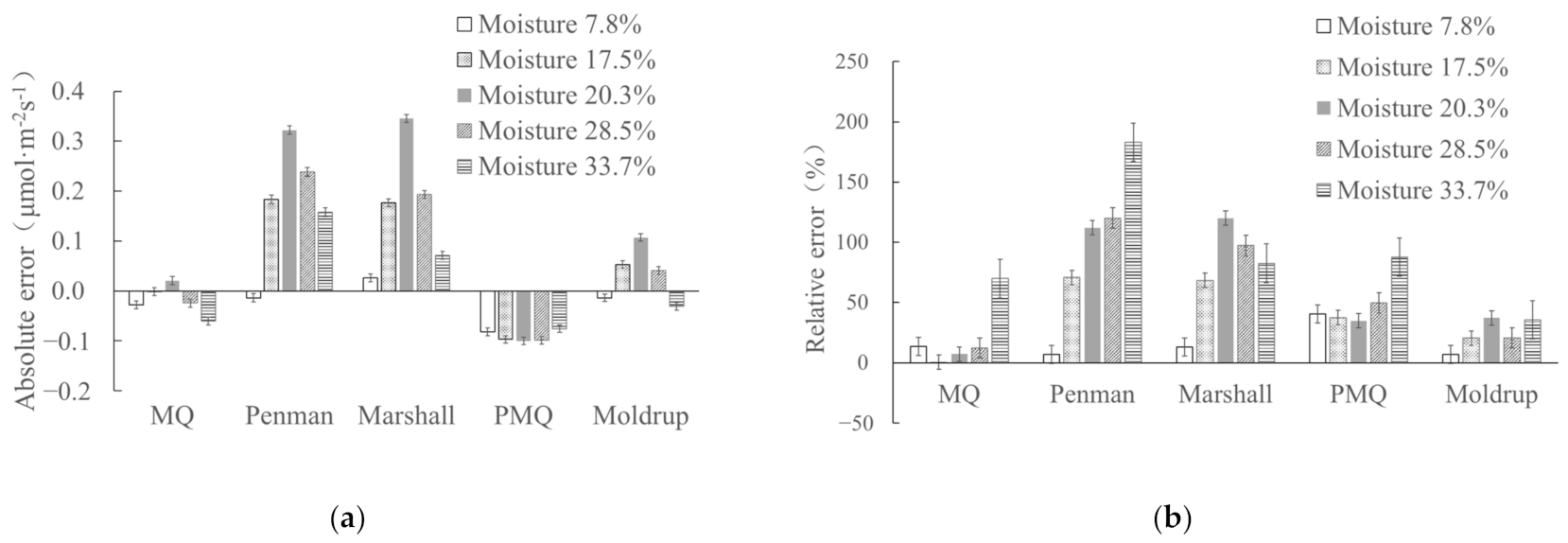



| θv (%) | F (μmol·m−2 s−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali Absorption Method | MQ Model | Penman Model | Marshall Model | PMQ Model | Moldrup Model | |
| 7.8 | 0.202 ± 0.008 | 0.174 ± 0.008 | 0.188 ± 0.009 | 0.228 ± 0.009 | 0.119 ± 0.007 | 0.188 ± 0.008 |
| 17.5 | 0.288 ± 0.009 | 0.258 ± 0.009 | 0.443 ± 0.010 | 0.436 ± 0.010 | 0.162 ± 0.012 | 0.312 ± 0.009 |
| 20.3 | 0.295 ± 0.009 | 0.309 ± 0.009 | 0.610 ± 0.011 | 0.633 ± 0.011 | 0.188 ± 0.008 | 0.395 ± 0.007 |
| 28.5 | 0.199 ± 0.008 | 0.174 ± 0.008 | 0.437 ± 0.010 | 0.392 ± 0.009 | 0.100 ± 0.008 | 0.240 ± 0.008 |
| 33.7 | 0.086 ± 0.008 | 0.026 ± 0.007 | 0.244 ± 0.009 | 0.158 ± 0.008 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.056 ± 0.009 |
| Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | F (μmol·m−2 s−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali Absorption Method | MQ Model | Penman Model | Marshall Model | PMQ Model | Moldrup Model | |
| 1.02 | 0.115 ± 0.007 | 0.119 ± 0.007 | 0.170 ± 0.008 | 0.169 ± 0.008 | 0.082 ± 0.008 | 0.133 ± 0.007 |
| 1.19 | 0.144 ± 0.008 | 0.130 ± 0.007 | 0.193 ± 0.008 | 0.188 ± 0.008 | 0.090 ± 0.008 | 0.145 ± 0.008 |
| 1.34 | 0.173 ± 0.008 | 0.152 ± 0.008 | 0.256 ± 0.009 | 0.157 ± 0.008 | 0.103 ± 0.008 | 0.175 ± 0.008 |
| Fertility Status | F (μmol·m−2 s−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali Absorption Method | MQ Model | Penman Model | Marshall Model | PMQ Model | Moldrup Model | |
| Control | 0.171 ± 0.005 | 0.139 ± 0.007 | 0.224 ± 0.008 | 0.222 ± 0.008 | 0.090 ± 0.008 | 0.163 ± 0.008 |
| N fertilizer | 0.215 ± 0.008 | 0.187 ± 0.008 | 0.305 ± 0.009 | 0.299 ± 0.011 | 0.122 ± 0.009 | 0.220 ± 0.006 |
| P fertilizer | 0.201 ± 0.006 | 0.177 ± 0.008 | 0.293 ± 0.010 | 0.286 ± 0.009 | 0.114 ± 0.007 | 0.209 ± 0.008 |
| K fertilizer | 0.154 ± 0.008 | 0.121 ± 0.007 | 0.192 ± 0.008 | 0.190 ± 0.008 | 0.079 ± 0.008 | 0.141 ± 0.007 |
| Organic fertilizer | 0.301 ± 0.007 | 0.246 ± 0.009 | 0.395 ± 0.009 | 0.389 ± 0.009 | 0.161 ± 0.011 | 0.288 ± 0.009 |
| Method | F (μmol·m−2 s−1) | Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | Slope (a) | R2 | |
| MQ model | 0.309 | 0.026 | 0.170 | 0.884 | 0.986 |
| Penman model | 0.610 | 0.170 | 0.304 | 1.550 | 0.944 |
| Marshall model | 0.633 | 0.157 | 0.288 | 1.504 | 0.947 |
| PMQ model | 0.188 | 0.011 | 0.109 | 0.566 | 0.985 |
| Moldrup model | 0.395 | 0.056 | 0.205 | 1.067 | 0.982 |
| Alkali absorption | 0.301 | 0.086 | 0.196 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, J. Evaluation of Five Gas Diffusion Models Used in the Gradient Method for Estimating CO2 Flux with Changing Soil Properties. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910874
Yan X, Guo Q, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Lin J. Evaluation of Five Gas Diffusion Models Used in the Gradient Method for Estimating CO2 Flux with Changing Soil Properties. Sustainability. 2021; 13(19):10874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910874
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xiaofei, Qinxin Guo, Yajie Zhao, Yandong Zhao, and Jianhui Lin. 2021. "Evaluation of Five Gas Diffusion Models Used in the Gradient Method for Estimating CO2 Flux with Changing Soil Properties" Sustainability 13, no. 19: 10874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910874
APA StyleYan, X., Guo, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhao, Y., & Lin, J. (2021). Evaluation of Five Gas Diffusion Models Used in the Gradient Method for Estimating CO2 Flux with Changing Soil Properties. Sustainability, 13(19), 10874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910874





