Abstract
LiDAR and CALIPSO satellites are effective tools for detecting air pollution, and by employing PM2.5 observation data, ground-based LiDAR measurements, CALIPSO satellite data, meteorological data, and back-trajectory analysis, we analyzed the process of pollution (moderate pollution, heavy pollution, excellent weather, and dust transmission weather) in Hefei, China from 24 to 27 January 2019 and analyzed the meteorological conditions and pollutants causing heavy pollution. Observation data from the ground station showed that the concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 increased significantly on 25 January; the maximum value of PM10 was 175 µg/m3, and the maximum value of PM2.5 was 170 µg/m3. In this study, aerosol transboundary transport was observed using a combination of ground-based LiDAR and CALIPSO satellite observations. This method showed that aerosols were distributed at a height of 3–4 km over Hefei at 12:00 on 26 January, and it was found that the aerosols came from the desert region in northwest China. Moreover, we determined its transport pathway based on the backward trajectory, and the transportation of pollutants from the surrounding important industrial cities in central and eastern China led to severe pollution after aggregating and mixing with local aerosols in Hefei in the winter. Therefore, the method proposed in this paper can effectively monitor the optical properties and transportation process of aerosols, help to explore the causes of pollution under complex conditions, and improve environmental quality.
1. Introduction
Aerosols are fine particles and liquid droplets suspended in the atmosphere. Due to their ability to reflect and scatter light, they affect the radiation and heat balance of the Earth’s atmosphere and thus have direct, semi direct, and indirect effects on the climate [1,2,3], which directly affect air quality. At the same time, aerosols suspended in the air can have a serious impact on human health, especially in causing respiratory diseases [4,5]. In recent years, with the gradual acceleration of China’s urbanization, many aerosols have become increasingly prevalent due to the burning of fossil fuels, emissions from a large number of industries, and so forth [6,7]. As an important economic center in eastern China, the Yangtze River Delta City Group has experienced rapid economic development. Since many government departments in China conducted clean air operations in 2013, which was a series of pollution-reduction measures, emissions of major manmade aerosols in eastern China have been reduced [8]. However, serious pollution incidents still occur frequently in eastern China, especially in winter [9]. As the capital of Anhui Province, Hefei has developed rapidly in recent years and has become one of the important cities in the Yangtze River Delta City Group [8]. Atmospheric emissions are increasing annually, and the regional environment continues to deteriorate, which has aroused the continuous attention of scientists [8]. Therefore, observing the optical properties and temporal and spatial distribution of pollutants in Hefei will help to understand the pollution status and climate impact of large cities in eastern China in recent years [10].
Research on the continuous detection of atmospheric aerosol can analyze aerosol pollution characteristics, optical characteristics, and diffusion mechanisms, which has an important role in pollution prevention and detecting climate impact [11,12,13]. Long-term monitoring of air pollution is essential due to the spatiotemporal variability of aerosols and clouds and their complex, changing processes [14]. LiDAR, as an active remote sensing detection tool, has higher accuracy, resolution, and continuity than traditional atmospheric detection methods and can provide long-term high-precision fixed-point observations [12]. For example, Sun et al. analyzed the vertical structure and spatiotemporal distribution of aerosols using small-scale Scheimpflug LiDAR [15], and Xie et al. analyzed the spatiotemporal distribution of aerosols using scanning LiDAR [10]. However, these experiments could only be applied to a small vertical height of the pollution distribution, and they could not systematically analyze the causes of pollutants. Some scholars have compared ground-based LiDAR and other satellite data. For instance, Tan et al. [16] compared the aerosol extinction coefficient of ground-based LiDAR and CALIPSO, showing that the data have good consistency, thereby verifying the two systems’ stability and reliability. Wu et al. [17] found that the CALIPSO data performed well in classifying aerosol types; the inversion results of CALIPSO and ground-based LiDAR deviated little in the experiment. However, these studies only illustrated the stability of ground-based and satellite data systems from a comparative perspective and could not analyze their temporal and spatial variations combined with contaminants. In terms of pollutant transport, LiDAR has important applications in detecting and tracking dust transport [9,18,19], volcanic ash [20], and forest fires [21,22]; however, such research has only focused on atmospheric model transport processes, with less research on the properties of aerosols and the effects of the environment on said aerosols.
In this study, the causes of complex polluted weather through multisource data were effectively detected. Ground-based LiDAR and satellite data enabled effective remote sensing of aerosol optical properties and transport processes. The data and methods are described in detail in Section 2. Some typical results of the distribution and causes of aerosol particles are presented in Section 3. The conclusions are given in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ground-Based Observations of Meteorological Elements and Ground-Based LiDAR Observations
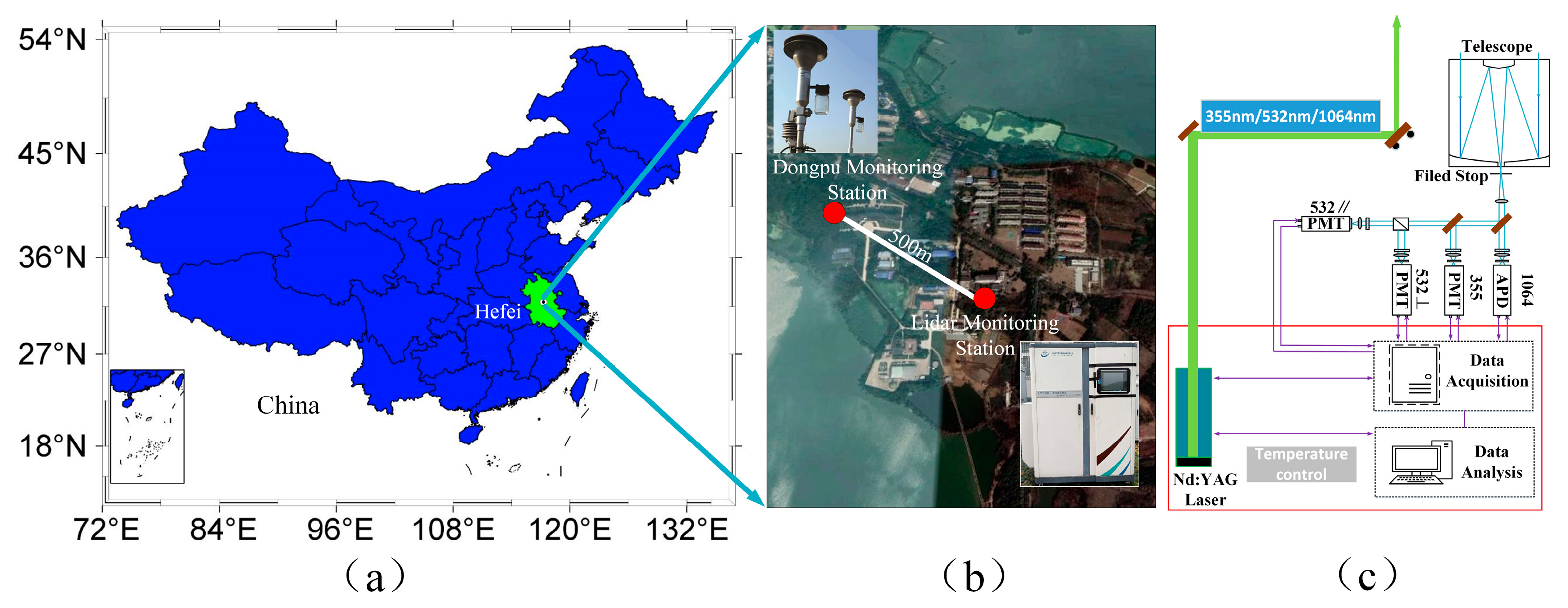
In January 2019, Hefei experienced a relatively typical polluted weather process. In this study, various meteorological observations were selected from 24 to 27 January, and the typical polluted weather in Hefei was studied in detail. The main air pollutants included sulfur dioxide (such as SO2), inhalable particulate matter (such as PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen oxides (such as NO2), and so forth and PM2.5, PM10, SO2, and NO2 were selected for this study. During the study period, the hourly PM2.5 concentrations were obtained from the Dongpu Reservoir, one of the sites operated by the Department of Ecology and Environment of Anhui Province. A β-ray-based particle detector was used for the in situ measurement of particle concentrations (Figure 1b). The relative humidity was also used in this research. All of the data can be found at http://sthjt.ah.gov.cn/index.html. In this paper, the Mie LiDAR was used to detect aerosol, which has three wavelengths and four channels, developed by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. From the beginning of January 2019, the Mie LiDAR has been monitoring the western suburbs of Hefei (31.9 N, 117.16 E) with 24/7 remote sensing. Figure 1a shows the location of Hefei in China; the red positions in Figure 1b are the Dongpu Monitoring Station and the Mie LiDAR monitoring station, respectively, which are only 0.5 km apart horizontally, and a schematic diagram of the Mie LiDAR is given in Figure 1c.
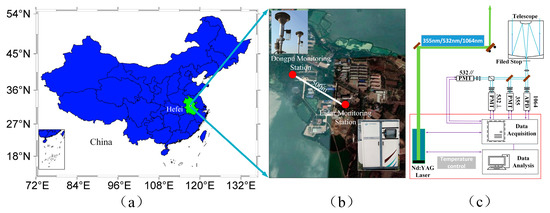
Figure 1.
Geography of the monitoring sites: (a) location of Anhui Province; (b) locations of the Dongpu Monitoring Station and the Mie LiDAR Monitoring Station in Hefei; (c) structural diagram of the Mie LiDAR system.
The three-wavelength and four-channel Mie LiDAR employs an Nd:YAG laser, as the light source generates the third harmonic at 355 nm, the second harmonic at 532 nm, and the fundamental frequency at 1064 nm. The transmitted laser energy is typically 500 mJ at 1064 nm, 480 mJ at 532 nm, and 320 mJ at 355 nm with a repetition rate of 30 Hz. A 406.6 mm diameter Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope with a field of view of 1.5 mrad is used to collect the backscatter light. The receiver has four channels to receive the backscatter light at 355 nm, with parallel and perpendicular polarization components at 532 and 1064 nm. The backscattered signal is received by the respective corresponding photomultiplier tube (PMT) and avalanche diode (APD) through the telescope. It is followed by the optical path through the filter and beam splitter. The backscatter light at 355 and 532 nm is received by the PMT, and the APD receives the backscatter light at 1064 nm. Licel is used as a high-speed collector, which is a powerful data acquisition system designed for the detection of optical signals. The acquirer is a 16-bit digitizer with a sampling rate of 20 MHz and a corresponding vertical resolution of 7.5 m. The specifications of the Mie LiDAR system are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detailed technical parameters of the Mie LiDAR system [14].
The extinction coefficient of atmospheric aerosols can be calculated based on the type of aerosols and the particle size distribution using the Mie scattering theory. The laser of the 355 nm wavelength is sensitive to particles with a radius of less than 0.5 μm. The laser of the 532 nm wavelength has the strongest atmospheric scattering extinction effect on aerosol particles in the range of 0.5–0.7 μm. The 1064 nm laser beam is mainly used to detect aerosol particles in the range of 1–2 μm [15,23,24]. Therefore, this system employs a three-wavelength LiDAR to study the particle properties of aerosols.
The equation of Mie LiDAR in vertical operation is described as follows:
where is the range-corrected signal from atmospheric molecules and particles in the range of , and is the LiDAR system constant, including the laser output energy, LiDAR receiver area, optical efficiency, and so on.
The Fernald [25] method is most commonly used for the Mie LiDAR inversion of tropospheric aerosol extinction coefficients and backscattering coefficients. First, the atmosphere’s backscattering and extinction coefficients are obtained from probe data and atmospheric models; second, the S1 (aerosol extinction backscattering coefficient) is taken as an empirical constant, and the calibration height is assumed in the equation. Then, the aerosol extinction coefficient can be obtained from Equation (1).
In addition to the backscatter ratio and the extinction of particles, the Mie LiDAR can observe their total ratio to demonstrate particles’ nonsphericity [26]. The total depolarization ratio is defined as the perpendicular polarization component ratio to the parallel component of the backscattered signals. The corresponding equation is as follows:
where is the total depolarization ratio, and are the perpendicular and parallel components of the backscattered signals, and is the calibration factor, which can be obtained with a linear polarizer sheet inserted in front of the polarization prism before the experiment [10,15,25].
The aerosol boundary layer (ABL) refers to the troposphere layer influenced by the earth’s surface. The airflow changes caused by the response timescale to the surface include friction, evaporation, transpiration, heat transfer, pollutant emissions, and topography [27]. The ABL determines particles’ space, and it blocks the diffusion and transport of pollutants. Hence, the study of ABL plays an important role in studying pollutants [28,29].
The LiDAR correction signal can directly reflect the change in aerosol particle concentration at different heights, further reflecting the change in the atmospheric boundary layer [30]. According to Equation (1), the LiDAR distance squared correction signal can be obtained as follows:
The gradient method was used to determine the height of the aerosol boundary layer according to the magnitude of the decay rate of with height [19]. The is defined as follows:
This equation reflects the variation of attenuation at different heights of z. The aerosol boundary layer decays fastest at this height, where the function obtains its minimum value.
2.2. CALIPSO Satellite Measurements and Model Product
In 2006, CALIPSO was launched in a sun-synchronous orbit as part of the “A-train” series of satellites, and CALIOP is a dual-wavelength LiDAR (532 and 1064 nm) payload onboard CALIPSO. The vertical structure and optical distribution of aerosols occur within three image types. The 532 nm total attenuated backscatter coefficient (TABC), vertical feature mask (VFM), and aerosol subtype (AS) are the products of CALIPSO, and these data can be obtained from the CALIPSO website (http://www-calipso.larc.nasa.gov/) [31,32].
The 532 nm TABC images from CALIPSO level 1b data are the sum of the 532 nm parallel and vertical return signals. It has been color-coded such that blue corresponds to molecular scattering and weak aerosol scattering, and yellow/red/orange indicate increased aerosol loading. AS images from CALIOP secondary data show vertical and horizontal distributions of different aerosols, such as clean oceans, sand, polluted continents, clean continents, polluted dust, and smog [33].
In this study, the contamination process was analyzed in Hefei in winter using CALIPSO transit data on 25 and 26 January. The profile of both ground-based LiDAR and CALIPSO can accurately reflect the aerosol changes over time and space.
The Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) is a professional model developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for calculating and analyzing the transport and diffusion trajectories of atmospheric pollutants. Stein proved it to be a very useful tool and introduced the backward trajectory systematically [34]. Boming Liu illustrated the potential source contribution function maps of Atmosphere Optical Depth (AOD) for the Wuhan region on seasonal scales based on the 48 h backward trajectory distributions at 500 m [35]. According to the above-generated backward trajectories, the Potential Source Contribution Function (PSCF) model was established using TrajStat software [36]. In this study, the global meteorological data from NOAA’s Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) were used as the initial field to calculate the Hefei air mass trajectory for 24–27 January, corresponding to the 48 h air mass return trajectory based on TrajStat [36].
3. Results
3.1. Ground Station Meteorological Measurements
PM2.5 refers to particles with an equivalent diameter of less than or equal to 2.5 μm in ambient air, and PM10 refers to particles with a particle size less than 10 μm [7]. According to the environmental quality standards set by the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection in 2012 (http://www.mee.gov.cn/), a PM2.5 value of 0–35 µg/m3 is excellent, 75–115 µg/m3 is light pollution, and >150 µg/m3 is heavy pollution. Historical data combined with the above standards indicate that 24 January was lightly polluted, 25 January was heavily polluted, 26 January was excellent weather, and 27 January was lightly polluted. The pollution index was highest at 11:00 on 25 January, and the air quality was excellent at 12:00 on 26 January.
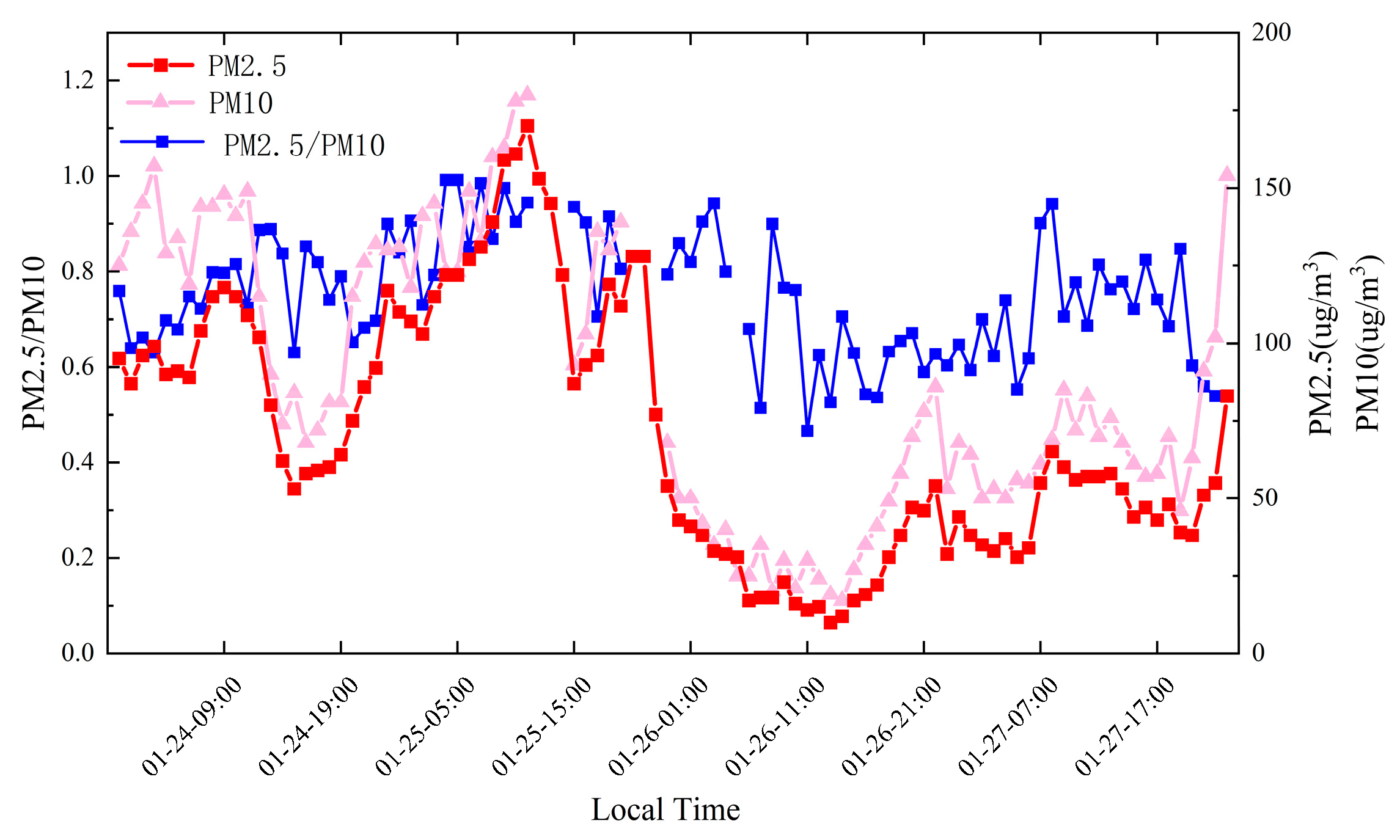
Figure 2 shows the changes in PM2.5, PM10, and PM2.5/PM10. The trends of PM2.5 and PM10 are roughly the same. At 9 o’clock on the 24th, the value of PM was the highest: the concentration of PM2.5 was 118 µg/m3, and the concentration of PM10 was 148 µg/m3. After a period of increase on the 25th, PM2.5 reached its peak at 13 o’clock. The value of PM2.5 was 175 µg/m3, and the value of PM10 was 180 µg/m3. The value of PM2.5 on the 26th was declining. The best air quality time was at 12:00 on the 26th. At this time, the value of PM2.5 was only 14 µg/m3, and the value of PM10 was only 24 µg/m3. Starting on the 27th, the values increased again, and a new round of pollution began to appear. The PM2.5/PM10 change graph mainly shows the size of pollutant particles in the air. As can be seen from Figure 2, overall, the value of PM2.5/PM10 from the 24th to the 25th is slightly higher than the value from the 26th to the 27th, which shows that the concentration of large particulate matter in the air increased from the 26th to the 27th. In response to this pollution phenomenon, we combined other multisource data for further analysis.
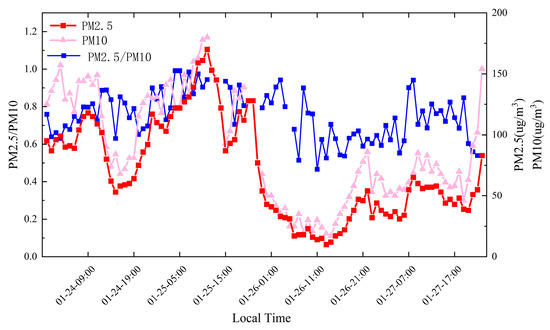
Figure 2.
Changes in PM2.5, PM10, and PM2.5/PM10 at different time periods.
3.2. Ground-Based LiDAR Observations of Tropospheric Aerosols
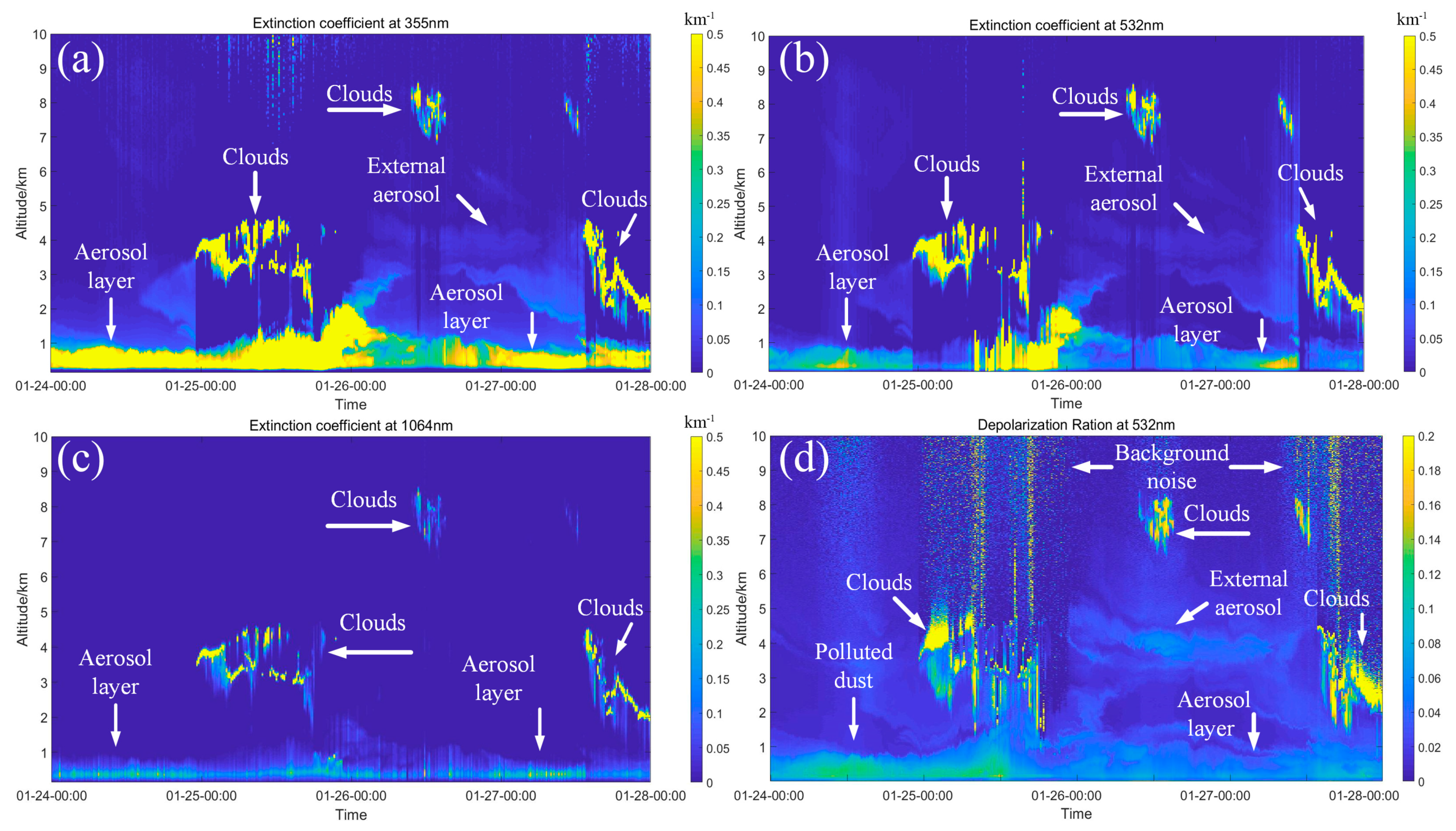
Figure 3 shows maps of the extinction coefficient and depolarization ratio for the three wavelengths observed from the Mie LiDAR. Clouds appeared 8–9 km above the LiDAR site from this observation, so the data were kept uniformly at 10 km. The location of clouds and aerosol layers are marked in Figure 3. Figure 3a shows that the extinction coefficient values at 355 nm were all greater than 0.5 km−1, which means that the aerosol particles were smaller than 0.5 μm. Figure 3b shows that the extinction coefficient values at 532 nm were greater than 0.5 km−1 from 12:00 on 25 January to 00:00 on 26 January, which means that the aerosol particles were mainly 0.5–0.7 μm particles. This was mainly because the particles became larger due to the continuous moisture absorption of the aerosol particles. Moreover, Figure 3d shows that from 24 to 25 January at 12:00, the values of the depolarization ratio ranged from 0.12 to 0.14, indicating that nonspherical particles were heavily concentrated in the air. After 12:00 on 25 January, the depolarization ratio values decreased from 0.12–0.14 to 0.06–0.08. The hygroscopic effect of the aerosols made the nonspherical particles gradually became smaller. On 26 January, it can be seen from the figure that the particles mainly gathered below 2 km. After hygroscopic absorption, the small particles proceeded to settle. The fine transported aerosols appeared at an altitude of approximately 4 km according to Figure 3a–c. From Figure 3d, it can be seen that the size of the depolarization ratio of the particles in the layer was in the range of 0.1–0.12, and the height gradually decreased over time. The pollution trajectory of the aerosol particles in the layer is analyzed in later sections.
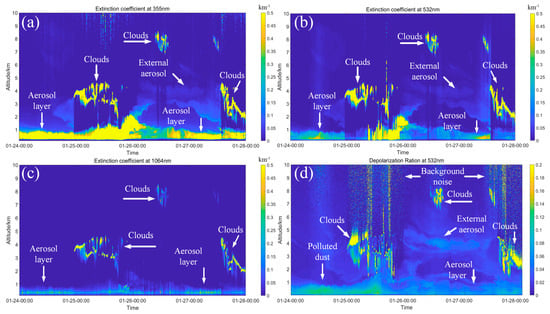
Figure 3.
Maps of the extinction coefficients at three wavelengths and the depolarization ratios: (a) extinction coefficient at 355 nm; (b) extinction coefficient at 532 nm; (c) extinction coefficient at 1064 nm; (d) depolarization ratio at 532 nm.
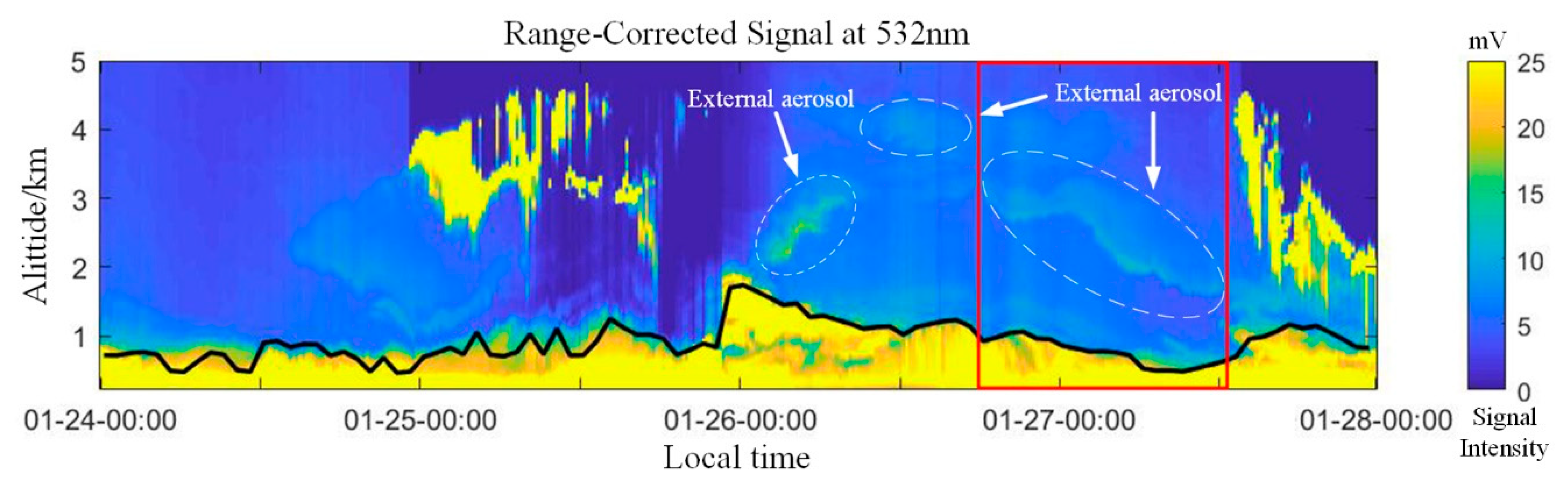
As a result of the aerosol distribution and the lower cloud layer on 24–27 January, the data were selected from the distance correction signal below 5 km, and the aerosol boundary layer (ABL) was obtained using Equations (2)–(4). Figure 4 shows the 0–5 km aerosol backscatter signal and the distance correction signal of the atmospheric boundary layer, and the secondary axis is signal intensity. The boundary layer height was lower from 24 to 25 January; the height was approximately 1 km, the values near the ground were greater than 25 mV, and the pollutants gathered at the bottom of the troposphere. Thus, the nonsphericity of the aerosol particles was greatly reduced by mixing with the local aerosols and accumulating to a certain extent. However, the height of the boundary layer was raised as a result of the rapid diffusion of contaminants on 26 January. The height of the aerosol signal also increased, and the height of the boundary layer was 1.5–2 km. The related particles were also observed over the boundary layer, indicating that there was external aerosol transport. The red box in Figure 4 indicates the area of external aerosol precipitation. It can be seen from the figure that external aerosols began to settle from 18:00 h at an altitude of 3–4 km, and with the passage of time, the height of the transmission aerosol gradually decreased. The distance correction signal for aerosols in this layer is 14–16 mV. The external aerosols had settled to a height of 1.5–2 km at around 12:00 on 27 January, and the boundary layer began to rise on 27 January.
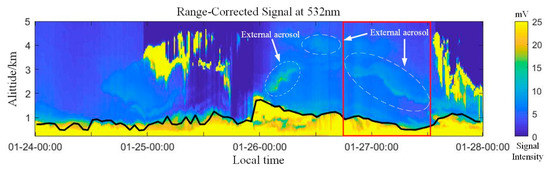
Figure 4.
Backscatter and aerosol boundary layer from the Mie LiDAR.
3.3. Transboundary Aerosol Transport Observed by the CALIPSO Satellite and a Comparison of CALIPSO and Mie LiDAR
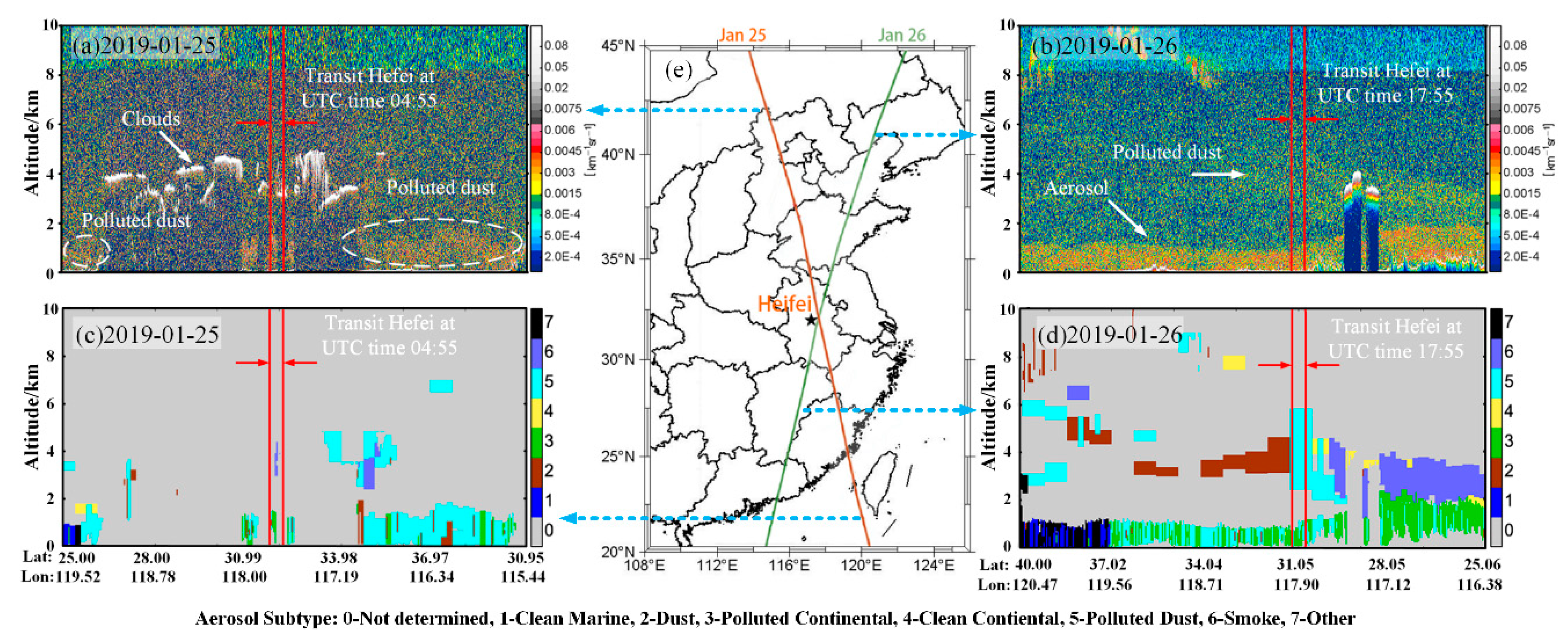
Figure 5 shows the CALIPSO satellite passing over central and eastern China twice on 25 and 26 January 2019. The red line represents the downward orbit track during the day (~13:30), while the green line represents the upward orbit track during the night (~2:30). The altitude–orbit cross-section images of 532 nm TABC (Figure 5a,b) and VFM (Figure 5c,d) along the two orbit tracks are shown in the left and right panels in Figure 5, respectively. The legend for Figure 5c,d is shown at the bottom of Figure 5. The location of the red line represents the location of the transit Hefei area. Figure 5c shows that 25 January was a heavily polluted day, and the pollutants below the boundary layer were mainly of the continental type, with 4 km of soot pollution. The weather on 26 January was clear. Below the boundary layer was continental pollution, with polluted dust around 4 km. From this, it can be seen that the polluted dust was not locally generated but consisted of aerosols transported from outside. Figure 5d shows that the aerosol was a dust aerosol at high latitude, but it was polluted dust at 4 km near Hefei. It was estimated that the nearby dust aerosol was crushed and smoothed by atmospheric dynamics, characterized by nonspherical small particles in the transport process. The aerosol transport into Hefei changed by pressure and wind direction, and the transport path is further analyzed in the following sections. Despite the clear weather on 26 January, aerosol transport trajectories can still be detected from ground-based LiDAR and CALIPSO.
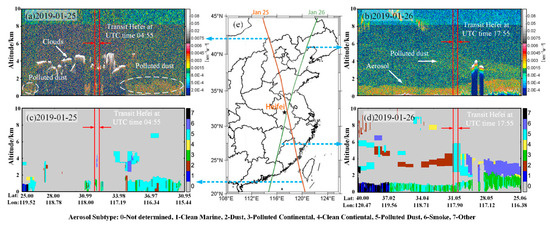
Figure 5.
CALIPSO satellite transit map: (a,b) represent the 532 nm total attenuated backscattering coefficient; (c,d) represent aerosol type; and (e) represents ground track passing through the middle.
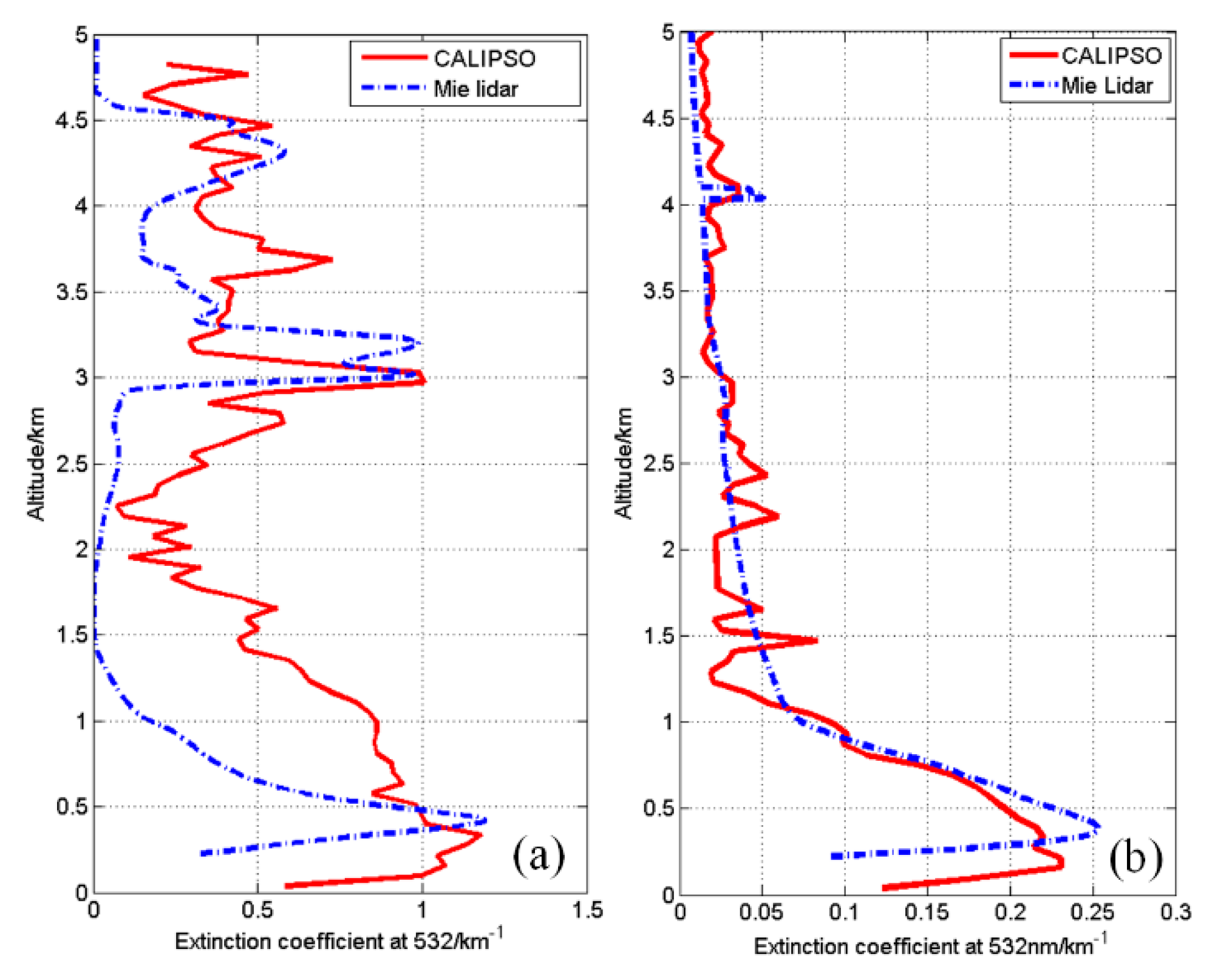
Figure 6 compares the extinction profiles of the CALIPSO satellite and the Mie LiDAR on 25 and 26 January 2019. The 532 extinction coefficients observed by the CALIPSO satellite were averaged and smoothed. In comparison, the 532 nm extinction coefficients observed by the ground-based LiDAR were profile-averaged over a half-hour range around the satellite transit time point. The relative altitudes and the actual ground altitudes of the CALIPSO satellite data were observed by Mie LiDAR. Hefei is located in China’s eastern plain with an average altitude of 20 m, so height matching was neglected in the data processing. After data processing, the extinction curve comparison plot shown in Figure 6 was obtained.
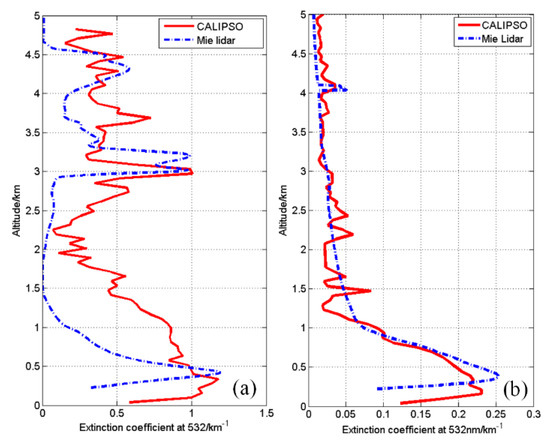
Figure 6.
Comparison of the average 532 nm extinction profiles of CALIPSO and Mie LiDAR: (a) cloudy on 25 January; (b) sunny on 26 January.
Figure 6a shows a comparison of the extinction under cloudy weather on 25 January. From the figure, it can be seen that both CALIPSO and ground-based LiDAR detected the presence of clouds at a 3–4 km altitude, and the extinction coefficient appeared near 3 km, with a peak of 1 km−1. As a result of the presence of clouds, there was a slight observation error, as shown in the figure, and the correlation coefficient between the two observations was 0.49. Figure 6b shows the extinction comparison curve on 26 January, and the trend of the two curves is almost the same, with a correlation coefficient of 0.83. Both CALIPSO and Mie LiDAR observed aerosol distribution at 4 km. The extinction coefficient of ground-based LiDAR was large, while that of CALIPSO was relatively small. These results indicate that smaller aerosol particles were distributed over 4 km.
3.4. HYSPLIT Backward Trajectory and Weather Condition Analysis
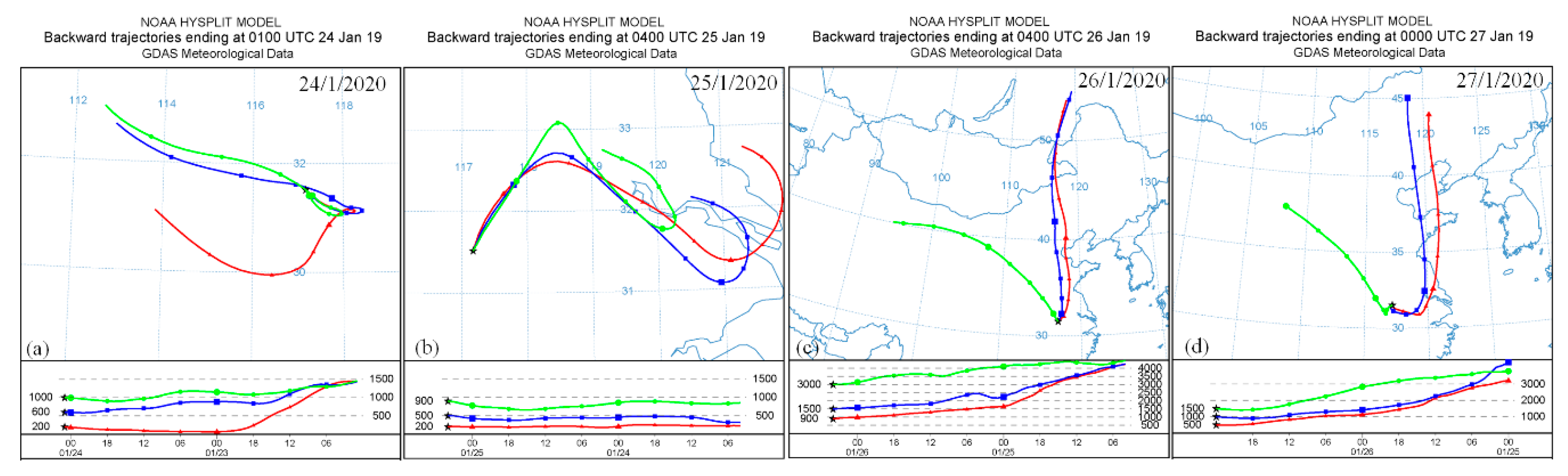
In order to determine the source of aerosol pollutants, the HYSPLIT model provided by NOAA (https://ready.arl.noaa.gov/hypub-bin/trajasrc.pl) was used to perform a backward trajectory analysis of the pollutants from 24 to 27 January at their peak points during the pollution period. The figure’s time is UTC world time, and the local time is 8 h earlier than UTC. According to the aerosol layer structure shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, different heights were selected (Figure 7) for the backward trajectory analysis. The backward trajectories were selected at 9:00 on 24 January from Figure 7a and 12:00 on 25 January from Figure 7b when the PM2.5 content was highest. At 12:00 on 26 January from Figure 7c, the PM2.5 content was relatively low. At 8:00 on 27 January from Figure 7d, the concentration of PM2.5 gradually increased (all were local times).
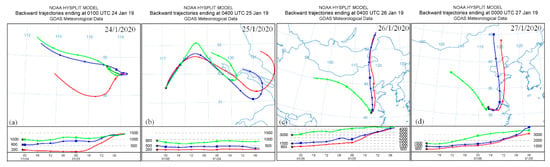
Figure 7.
The 48 h HYSPLIT backward trajectory from 24 to 27 January 2019.
The backward trajectory on 24 January shows that aerosol particles at 1000, 600, and 200 m crossed over Hefei in the northwest direction. As a result of the short and decreasing trajectory lines, it is known that the speed of the wind was low, and pollutant deposits occurred. The backward trajectory on 25 January shows that the aerosol particles mixed and settled with local aerosols and were accumulated locally to form contamination. This phenomenon is consistent with the nonspherical features measured by the Mie LiDAR. The three-track lines on 26 January were all relatively long, indicating the increased wind speed and elevation of the underlying aerosols. The airflow was transported from the north to Hefei, passing through the Bohai Sea. On the one hand, the airflow took away the aerosols that were sustained locally. On the other hand, it brought airflow with higher humidity, in which the humidity increased, but the content of PM2.5 decreased. In particular, the airflow of 3000 m came from the northwest. Thus, it can be seen that the airflow brought particles from the west to Hefei. This phenomenon is consistent with the results observed in Figure 2 and Figure 5. On 27 January, the airflow decreased in Hefei with 1500 m aerosol particles from the west, which was remixed with the aerosols brought in by the north’s airflow. The concentration of PM2.5 rose again, and the number of nonspherical particles in the air increased, consistent with the degenerative ratio signal shown in Figure 3d.
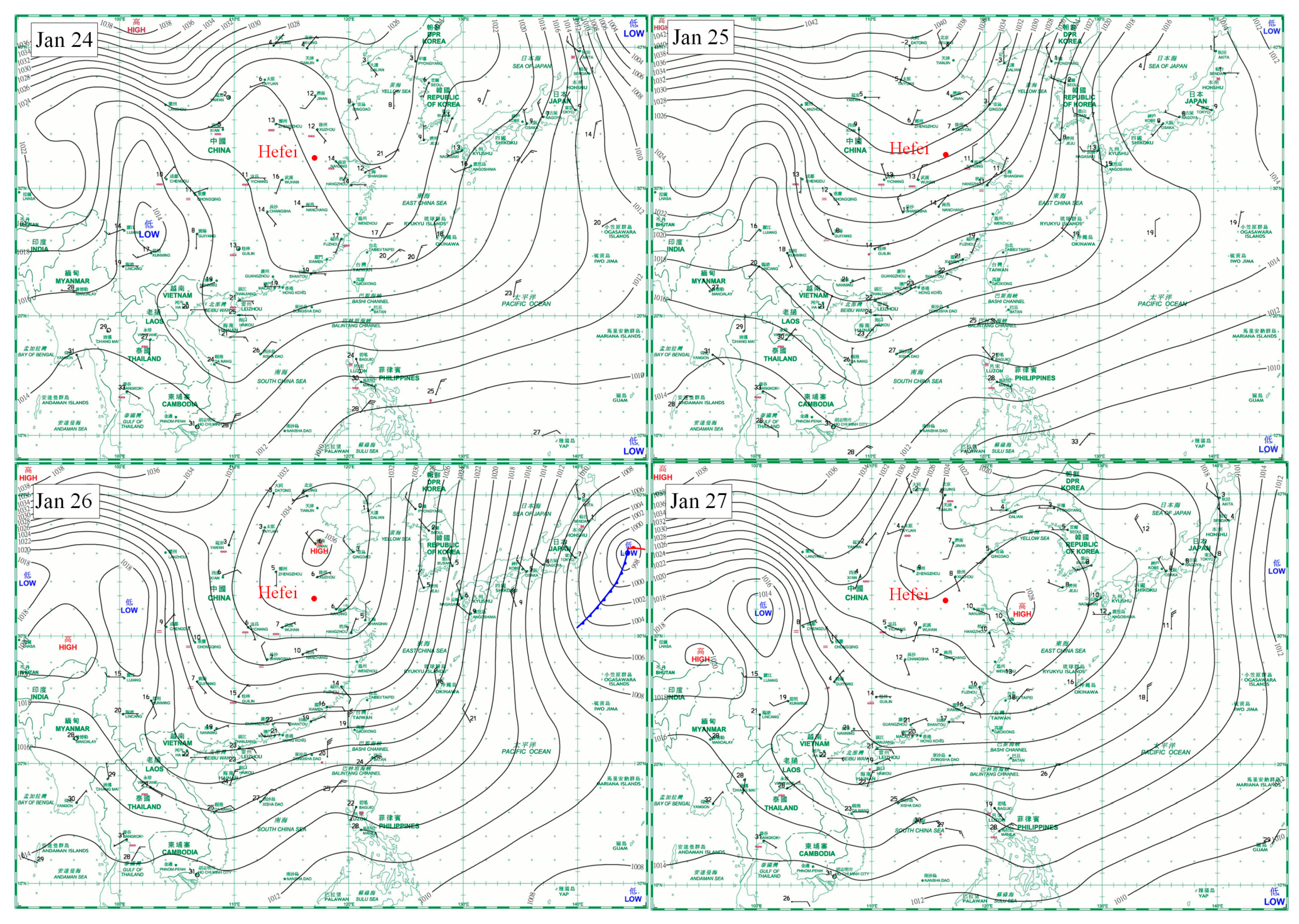
Wind field and pressure are important factors affecting the transport of pollutants [20]. In this study, we used wind field and pressure data from 24 to 26 January to analyze the transport conditions corresponding to this pollution (Figure 8). The wind field and pressure data were provided by the Hong Kong Observatory (https://www.hko.gov.hk/sc/index.html). The high pressure on 24 and 25 January was mainly in northern China, far from the Hefei area, and thus the wind speed was relatively weak. On 26 January, the ridge of high pressure moved toward North China, where radiative and sinking motions often accompanied it. As a result, there was a higher wind speed with denser velocity lines. On 27 January, the high-pressure ridge moved toward Shanghai and the wind speed decreased; thus, the pollutants accumulated again and the air quality became poor.
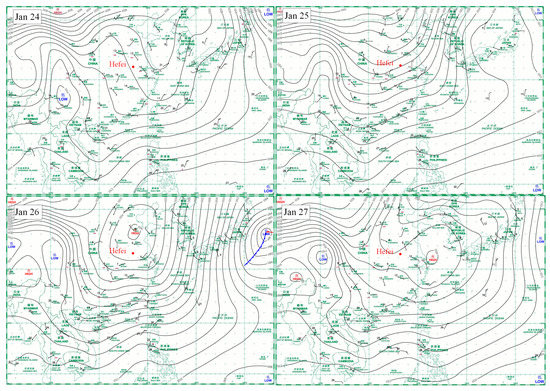
Figure 8.
Wind field and pressure chart.
3.5. Analysis of Pollutant-Related Meteorological Elements
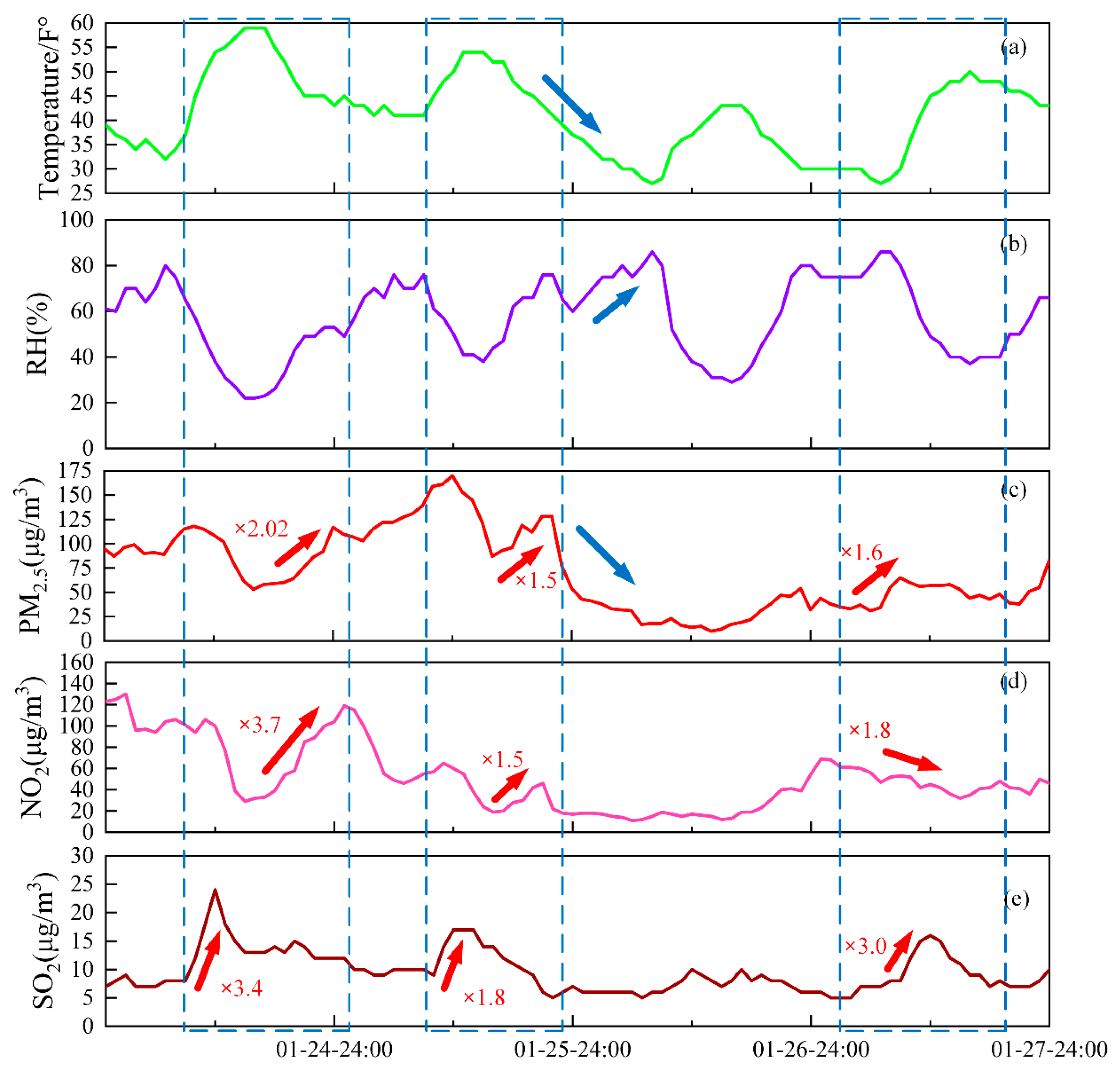
In order to further analyze the relationship between the concentration of particulate matter, pollutant gases, and meteorological conditions, we used a time series diagram, as shown in Figure 9. The graph shows the temperature, relative humidity (RH), PM2.5, NO2, and SO2 changes from the 24th to the 27th.
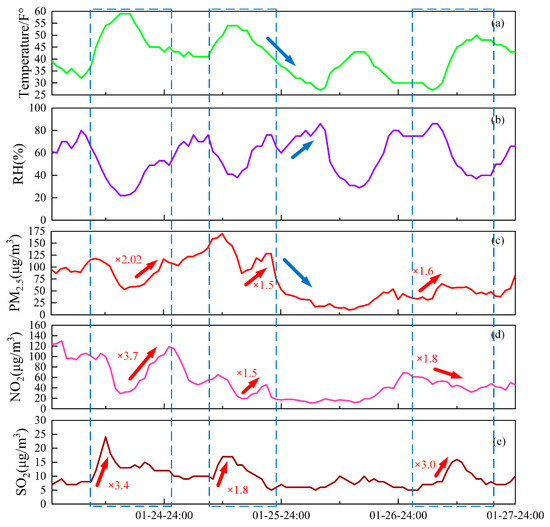
Figure 9.
Comparison of the amplitude of changes between 24 and 27 January 2019: (a) temperature; (b) relative humidity (RH); (c) PM2.5; (d) NO2; (e) SO2.
The three blue boxes in Figure 9 represent the three time periods when pollution was relatively serious. They were from 10:00 on the 24th to 1:00 on the 25th, from 10:00 to 23:00 on the 25th, and from 8:00 to 15:00 on the 27th. PM2.5 increased by 2.02 factors, and NO2 and SO2 increased by 3.7 and 3.4 factors, respectively, during the pollution process on 24 January. This shows that the SO2 in the air at the beginning of this period of time had a greater contribution to air pollution, and as time went by, PM2.5 and NO2 surpassed SO2, making a greater contribution to air pollution. The situation on 25 January was roughly similar to the pollution situation on 24 January, where PM2.5 increased by 1.5 factors, NO2 increased by 1.5 factors, and SO2 increased by 1.8 factors. On 26 January, it can be seen from the blue arrow that the temperature dropped and the humidity rose, indicating that the surrounding humid air merged into Hefei, causing a significant drop in PM2.5. PM2.5 increased by 1.6 factors, NO2 decreased by 1.8 factors, and SO2 increased by 3.0 factors during the pollution process on 27 January, which indicates that the pollution components at this stage were different from those from 24 to 25 January. By fitting the data of PM2.5, NO2, and SO2 during the pollution period, we found that the correlation coefficients of the two are 0.78 and 0.2, respectively, which indicates that NO2 has a greater impact on PM2.5, while SO2 has small relationship with PM2.5. In recent years, with economic development, the population has continued to grow, and urban cars have also increased dramatically, resulting in a rapid increase in NOx emissions, which has a greater impact on aerosol composition and PM2.5 content. The composition of locally produced particulate matter (sulfate and nitrate) and the transmission process have a direct impact on aerosols. The relationship with aerosols is very complicated, and under appropriate conditions, secondary pollution may be formed, thereby increasing pollution. Thus, further research is required.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a pollution process (light pollution, heavy pollution, sunny weather, and dust transmission weather) and transboundary aerosol transport in Hefei from 24 to 27 January 2019 were investigated using ground-based LiDAR, CALIPSO satellite observations, meteorological data, back-trajectory analysis, wind fields, and multisource data. The results are summarized as follows:
First, combined with different observation methods, the pollution process was analyzed in Hefei. The results show that humidity was high in winter, and the transport of aerosols from the surroundings to the area can cause serious pollution. The boundary layer rise will raise with aerosol diffusion in clear weather. However, the air humidity remained high due to the water vapor brought from the Bohai Sea. A small number of aerosols were still present at the bottom of the boundary layer. However, transported aerosols appeared at an altitude of approximately 4 km, giving rise to a peculiar stratification phenomenon. The phenomenon of aerosols transforming from dust to polluted dust was found in this research. Thus, this study provides a basis for further analysis of transboundary aerosol transport and local pollutant mixing in winter haze in Hefei.
Second, ground-based LiDAR with three wavelengths and four channels has advantages in observing aerosols of different particle sizes and degrees of nonsphericity, which play an important role in investigating the optical and chemical properties of pollution. Simultaneously, a combination of the Mie LiDAR and the CALIPSO satellite can be used to study the transport and distribution of aerosols under different weather conditions. This combination provides an efficient way to study the optical properties of aerosol particles.
Third, it is possible to investigate the causes of pollution under different complex conditions. In this case, multisource data observation can help to detect pollutants from near to the ground to a high altitude. In the future, multisource data detection will play an important role in large-scale urban pollution prevention and control by establishing corresponding models to analyze the source and structure of pollutants in an area in detail.
In this case, the cross-border transmission of aerosols was jointly observed by CALIPSO and ground-based LiDAR, which is more advantageous than previous methods. Multisource data observation enables the detection of pollutants from near to the ground to high altitudes in the Yangtze River Delta. In the future, long-term observations of LiDAR and multivariate data will help to develop a deeper understanding of the transmission of aerosols and the changes in the concentration and composition of pollutants. This will play an important role in the study of atmospheric and environmental changes and pollution prevention in the Yangtze River Delta.
Author Contributions
Z.F. analyzed the data and wrote the paper; M.Z. reviewed and edited the paper; Y.C. conceived the LiDAR system and the analytical methods; D.L., and C.X. performed the experiment to obtain the LiDAR data; H.Y. and K.X. obtained the satellite data; all authors participated in developing the LiDAR system. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA17040524) and the Key Program of the 13th Five-Year Plan, CASHIPS (Grant No. KP-2019-05, D040103).
Data Availability Statement
The lidar data presented in this study are available on request from the author, and other data available in a publicly accessible repository.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Optics, the Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, the Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, Atmospheric Science and Data Center (ASDC, https://www.nasa.gov/) and NOAA (https://ready.arl.noaa.gov/hypub-bin/trajasrc.pl) for providing ground-based LiDAR data, backward trajectory data, and meteorological data, respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, I.; Dagan, G.; Altaratz, O. From aerosol-limited to invigoration of warm convective clouds. Science 2014, 344, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Deng, M.; Lee, S.S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhai, P.; Liu, H.; Lv, W.; Yao, W.; Li, X. Delaying precipitation and lightning by air pollution over the Pearl River Delta. Part I: Observational analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6472–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Wei, W.; Ma, Y. Impacts of synoptic condition and planetary boundary layer structure on the trans-boundary aerosol transport from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region to northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Wang, C. Estimating global black carbon emissions using a top-down Kalman Filter approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikawa, E.; Naik, V.; Horowitz, L.W.; Liu, J.; Mauzerall, D.L. Present and potential future contributions of sulfate, black and organic carbon aerosols from China to global air quality, premature mortality and radiative forcing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y. Study of the scanning lidar on the atmospheric detection. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 150, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wu, L.; Wong, M.S.; Letu, H.; Hu, M.; Lang, H.; Sheng, S.; Teng, J.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, L. Trans-boundary aerosol transport during a winter haze episode in China revealed by ground-based Lidar and CALIPSO satellite. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yuan, R.; Wu, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Z. Weather conditions conducive to PM2.5 pollution in western Yangtze River delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Khatri, P.; Zhou, J.; Takamura, T.; Shi, G. Seasonal characteristics of aerosol optical properties at the SKYNET Hefei site (31.90° N, 117.17° E) from 2007 to 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6128–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, D.N. Examination of the traditional raman lidar technique. II. Evaluating the ratios for water vapor and aerosols. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiyu, L.; Ke′e, Y.; Xu, W.; Lihui, L.; Bangxin, W.; Decheng, W.; Shunxing, H.; Jianguo, W.; Zhenfu, M. A mobile lidar system for aerosol and water vapor detection in troposphere with mobile lida. Infrared Laser Eng. 2016, 45, 0330001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Tan, M.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D. Raman lidar for measurement of tropospheric water vapor. Appl. Opt. 2016, 45, 1211003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Qin, L.; Hou, Z.; Jing, X.; He, F.; Tan, F.; Zhang, S. Small-scale Scheimpflug lidar for aerosol extinction coefficient and vertical atmospheric transmittance detection. Optic Express 2018, 26, 7423–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Pan, W.; Zhu, K.; Deng, Z.; Wang, T.; Ma, J. Ground-based Lidar Measurements of Aerosol Vertical Distributions in Golmud, Qinghai. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 35, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Cordero, L.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S.A. Assessment of CALIPSO attenuated backscatter and aerosol retrievals with a combined ground-based multi-wavelength lidar and sunphotometer measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Long-range transport and vertical structure of Asian dust from CALIPSO and surface measurements during PACDEX. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L.; Haywood, J.; Osborne, M.; Chan, C.S.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, J.C. Characteristics of Heavy Particulate Matter Pollution Events Over Hong Kong and Their Relationships with Vertical Wind Profiles Using High-Time-Resolution Doppler Lidar Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9609–9623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revuelta, M.; Sastre, M.; Fernandez, A.; Martín, L.; Garcia, R.M.; Gómez-Moreno, F.; Artíñano, B.; Pujadas, M.; Molero, F. Characterization of the Eyjafjallajökull volcanic plume over the Iberian Peninsula by lidar remote sensing and ground-level data collection. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 48, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cordero, L.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Smoke plume optical properties and transport observed by a multi-wavelength lidar, sunphotometer and satellite. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottle, P.; Strawbridge, K.; McKendry, I. Long-range transport of Siberian wildfire smoke to British Columbia: Lidar observations and air quality impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, G.; Jin, C.; Qi, F.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Gong, Z.; Shi, G.; Nakajima, T.; Takamura, T. Lidar observations of Asian dust over Hefei, China, in spring 2000. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, AAC 5-1–AAC 5-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Guasta, M. Daily cycles in urban aerosols observed in Florence (Italy) by means of an automatic 532~1064 nm LIDAR. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2853–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassen, K. The polarization lidar technique for cloud research: A review and current assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 72, 1848–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.X.; Wu, D.C.; Ma, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.J. Correlation of Boundary Layer Height and Particulate Matter Concentration in Beijing in Winter 2014. Infrared Laser Eng. 2018, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, K.; Giannakaki, E.; Mielonen, T.; Pfüller, A.; Laakso, L.; Vakkari, V.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Beukes, J.P.; Van Zyl, P.G.; et al. Atmospheric boundary layer top height with lidar and radiosonde in South Africa: Atmospheric Reasurements compared to three atmospheric models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4263–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H. Urban boundary layer height area determination from lidar measurements over the Paris. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Behrendt, A.; Wulfmeyer, V. Elastic—backscatter-lidar-based characterization of the convective boundary layer and investigation of related statistics. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 825–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.A.; Ferrare, R.; Vaughan, M.; Omar, A.H.; Rogers, R.R.A.; Hostetler, C.; Hair, J.W. Aerosol classification from airborne HSRL and comparisons with the CALIPSO vertical feature mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.; Vaughan, M.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the hysplit-4 modeling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 195–308. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jin, S.; Jin, Y.; Gong, W. The characteristics and sources of the aerosols within the nocturnal residual layer over Wuhan, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).