Industry 4.0 Technologies and Their Impact in Contemporary Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Existing Literature Review Studies
3. Research Methodology
- RQ1: What is the current impact of Industry 4.0 in contemporary logistics? Which are the most prominent technologies and what can we learn from their application thus far?
- RQ2: What are the major challenges that Industry 4.0 has to overcome in order to grow and prevail in the logistics context?
4. Descriptive Analysis
5. Review
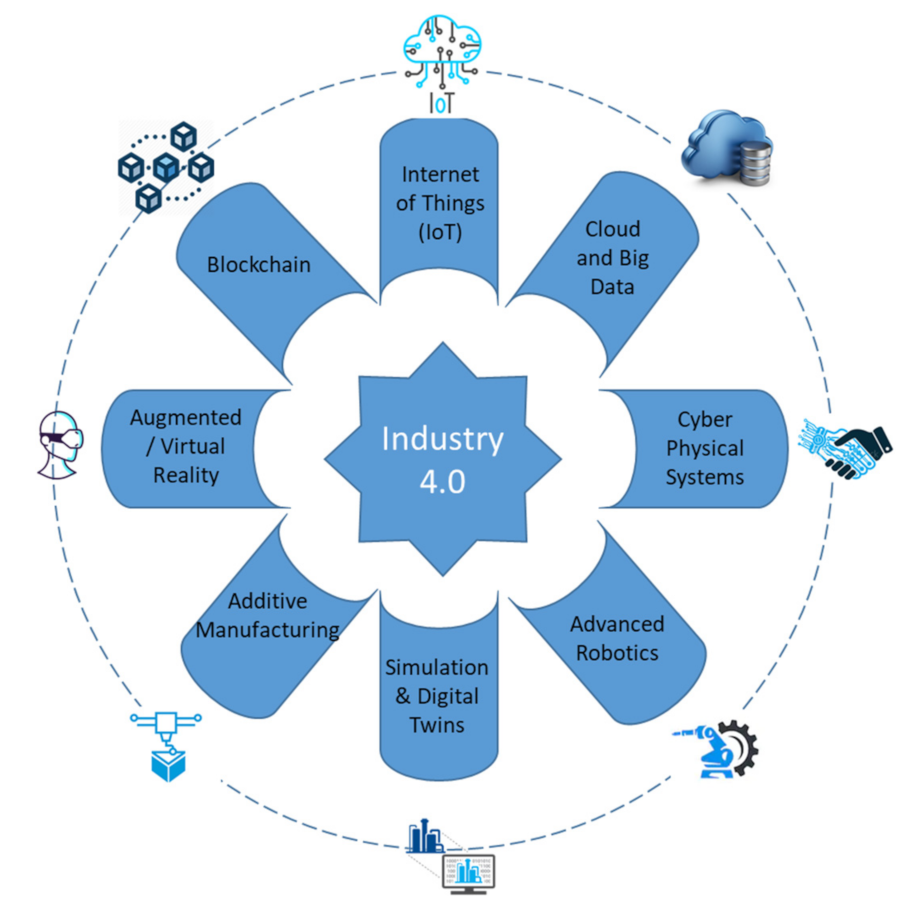
5.1. Industry 4.0 Technologies
5.1.1. Internet of Things
5.1.2. The Cloud and Big Data Analytics
5.1.3. Cyber Physical Systems
5.1.4. Advanced Robotics
5.1.5. Simulation and Digital Twins
5.1.6. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
5.1.7. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
5.1.8. Blockchain
5.2. Impact
6. Challenges
7. Conclusions
7.1. Contributions to Theory and Practice
7.2. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kagermann, V.H.; Lukas, W.-D.; Wahlster, W. Industrie 4 0 Mit Dem Internet Der Dinge Auf Dem Weg Zur Vierten Industriellen Revolution 2; VDI Nachrichten: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Reif, R.; Shirley, A.J.; Liveris, A. Report to the President Accelerating U.S. Advanced Manufacturing; The President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, M. Industry 4.0: Challenges and Opportunities for Chinese Manufacturing Industry. Teh. Vjesn./Tech. Gaz. 2014, 21, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Conseil National de L’industrie. The New Face of Industry in France; French National Industry Council: Paris, France; Available online: https://www.economie.gouv.fr/files/nouvelle_france_industrielle_english.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- European Commission. Factories of the Future PPP: Towards Competitive EU Manufacturing; European Commission: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y. Industry 4.0: A Survey on Technologies, Applications and Open Research Issues. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Sustainable Industry 4.0 Framework: A Systematic Literature Review Identifying the Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiou, O.K.; Ponis, S.T. Current Status of Industry 4.0 in Material Handling Automation and In-House Logistics. Int. J. Ind. Manuf. Eng. 2019, 13, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrin, M.; Othman, F.; Azli, N.; Talib, M. Industry 4.0: A review on industrial automation and robotic. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Wan, J.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Lai, C.-F.; Wang, S. A Review of Industrial Wireless Networks in the Context of Industry 4.0. Wirel. Netw. 2017, 23, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givehchi, O.; Trsek, H.; Jasperneite, J. Cloud Computing for Industrial Automation Systems—A Comprehensive Overview. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 18th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA), Cagliari, Italy, 10–13 September 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lidong, W.; Guanghui, W. Big Data in Cyber-Physical Systems, Digital Manufacturing and Industry 4.0. Int. J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Vilar-Montesinos, M.A. A Review on Industrial Augmented Reality Systems for the Industry 4.0 Shipyard. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13358–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlemann, T.H.-J.; Lehmann, C.; Steinhilper, R. The Digital Twin: Realizing the Cyber-Physical Production System for Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2017, 61, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Möhring, M.; Härting, R.-C.; Reichstein, C.; Neumaier, P.; Jozinović, P. Industry 4.0—Potentials for Creating Smart Products: Empirical Research Results. In International Conference on Business Information Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.G.; Dalenogare, L.S.; Ayala, N.F. Industry 4.0 Technologies: Implementation Patterns in Manufacturing Companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 210, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckute, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, P.; Thelwall, M.; Kousha, K.; Waltman, L.; de Rijcke, S.; Rushforth, A.; Franssen, T. The Metric Tide: Literature Review; HEFCE: Bristol, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhaus, S.; Grosse, E.H. Logistics 4.0: A Systematic Review towards a New Logistics System. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigliardi, B.; Casella, G.; Bottani, E. Industry 4.0 in the Logistics Field: A Bibliometric Analysis. IET Collab. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 3, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdirad, M.; Krishnan, K. Industry 4.0 in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 33, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorio, A.; Zenezini, G.; Mangano, G.; Pinto, R. A Systematic Literature Review of Innovative Technologies Adopted in Logistics Management. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, L.; Amaral, A.; Pereira, T. Industry 4.0 Implications in Logistics: An Overview. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaioui, K.; Fri, M.; Mabroukki, C.; Semma, E.A. The Interaction between Industry 4.0 and Smart Logistics: Concepts and Perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Colloquium on Logistics and Supply Chain Management (LOGISTIQUA), Tangier, Morocco, 26–27 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, V.L.; Kovaleski, J.L.; Pagani, R.N. Technology Transfer in the Supply Chain Oriented to Industry 4.0: A Literature Review. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2018, 31, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Rüsch, M. Industry 4.0 and the Current Status as Well as Future Prospects on Logistics. Comput. Ind. 2017, 89, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, E.; Jayakrishna, K. A Review of Internet of Things (IoT) Embedded Sustainable Supply Chain for Industry 4.0 Requirements. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 127, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrecht, M.; Knez, M.; Szegedi, Z.; Nick, G.; Lisec, A. Review of Industry 4.0 and Forecasting Its Future within Trends in Logistics and Development of Legislation. Acad. J. Széchenyi István Univ. 2017, V, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, C. Doing a Literature Review; Sage Publications: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Q. 2002, 26, xiii–xxiii. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarello, F.; Trivelli, L.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Fantoni, G. Extracting and Mapping Industry 4.0 Technologies Using Wikipedia. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.; Ambad, P.; Bhosle, S. Industry 4.0—A Glimpse. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 20, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikci, Y. Sustainability Impact of Digitization in Logistics. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisuriya, A.; Weerabahu, S.; Wickramarachchi, R. Applicability of Lean and Green Concepts in Logistics 4.0: A Systematic Review of Literature. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Production and Operations Management Society (POMS), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 14–16 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trappey, A.J.C.; Trappey, C.V.; Fan, C.-Y.; Hsu, A.P.T.; Li, X.-K.; Lee, I.J.Y. IoT Patent Roadmap for Smart Logistic Service Provision in the Context of Industry 4.0. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2017, 40, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, K. Internet of Things, Big Data, Industry 4.0—Innovative Solutions in Logistics and Supply Chains Management. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHL|Trend Radar. Available online: https://www.dhl.com/en/about_us/logistics_insights/dhl_trend_research/trendradar.html (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- DHL Brings Internet of Things to Logistics. Available online: https://www.dpdhl.com/en/media-relations/press-releases/2017/dhl-brings-internet-of-things-to-logistics.html (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Industry 4.0 and Cloud Manufacturing: A Comparative Analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, M.; Stoica, I.; Zaharia, M.; Fox, A.; Griffith, R.; Joseph, A.D.; Katz, R.; Konwinski, A.; Lee, G.; Patterson, D.; et al. A View of Cloud Computing. Commun. ACM 2010, 53, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Implementing Smart Factory of Industrie 4.0: An Outlook. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 3159805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ngai, E.W.T.; Papadopoulos, T. Big Data Analytics in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Certain Investigations for Research and Applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 176, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkman, P.; McCormack, K.; de Oliveira, M.P.V.; Ladeira, M.B. The Impact of Business Analytics on Supply Chain Performance. Decis. Support Syst. 2010, 49, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FREIGHTLY. FREIGHTLY|Smart Logistics. Available online: https://www.freightly.com/ (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- ClearMetal. ClearMetal|Continuous Transportation. Available online: https://www.clearmetal.com/ (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, S. CPS-Based Smart Warehouse for Industry 4.0: A Survey of the Underlying Technologies. Computers 2018, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermann, M.; Pentek, T.; Otto, B. Design Principles for Industrie 4.0 Scenarios: A Literature Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307864150_Design_Principles_for_Industrie_40_Scenarios_A_Literature_Reviewh (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Assunta, C.; Guido, G.; Silvestro, V.; Giusy, V. Man-CPS Interaction: An Experimental Assessment of the Human Behavior Evolution. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry (RTSI), Modena, Italy, 11–13 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Geisberger, E.; Broy, M. (Eds.) Agenda CPS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, K.-F.; Nyhuis, P. Cyber-Physical Production Systems Combined with Logistic Models—A Learning Factory Concept for an Improved Production Planning and Control. Procedia CIRP 2015, 32, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabella, R.; Thuelig, A.; Carrozza, M.C.; Ippolito, M. Industrial Automation Enabled by Robotics, Machine Intelligence and 5G. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/ericsson-technology-review/articles/industrial-automation-enabled-by-robotics-machine-intelligence-and-5g (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Strange, R.; Zucchella, A. Industry 4.0, Global Value Chains and International Business. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2017, 25, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotics|SSI SCHAEFER. Available online: https://www.ssi-schaefer.com/en-us/products/order-picking/automated-order-picking/robotics-53898 (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- KNAPP’s Picking Robot. Available online: https://www.knapp.com/en/pick-roboter-von-knapp-ist-bestes-produkt-der-logimat-2017/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- O’Kane, S. UPS Has Been Quietly Delivering Cargo Using Self-Driving Trucks. Available online: Https://Www.Theverge.Com/2019/8/15/20805994/Ups-Self-Driving-Trucks-Autonomous-Delivery-Tusimple (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Rodič, B. Industry 4.0 and the New Simulation Modelling Paradigm. Organizacija 2017, 50, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuniga, E.R.; Moris, M.U.; Syberfeldt, A. Integrating Simulation-Based Optimization, Lean, and the Concepts of Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, R.; Kind, S.; Neumeyer, S. Innovations in Digital Modelling for next Generation Manufacturing System Design. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W.; Ulrich, J.H.; Lang, S.; Reggelin, T.; Tolujew, J. Simulation and Virtual Commissioning of Modules for a Plug-And-Play Conveying System. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Twin|GE. Available online: https://www.ge.com/digital/applications/digital-twin (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- De Jong, J.P.J.; De Bruijn, E. Innovation Lessons from 3-D Printing. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2013, 54, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NextGenAM—Pilot Project for Automated Metallic 3D Printing Proves a Complete Success—Daimler Global Media Site. Available online: https://media.daimler.com/marsMediaSite/en/instance/ko/NextGenAM--pilot-project-for-automated-metallic-3D-printing-proves-a-complete-success.xhtml?oid=43205447 (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Cipresso, P.; Giglioli, I.A.C.; Raya, M.A.; Riva, G. The Past, Present, and Future of Virtual and Augmented Reality Research: A Network and Cluster Analysis of the Literature. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milgram, P.; Kishino, F. A Taxonomy of Mixed Reality Visual Displays. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 1994, E77-D, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B.; Anisetti, M.; Ceravolo, P.; Damiani, E.; Ivkovic, M. Augmented Reality Technologies, Systems and Applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2010, 51, 341–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHL InMotion. DHL Rolls out Global Augmented Reality Program. Available online: https://inmotion.dhl/en/esports/article/dhl-rolls-out-global-augmented-reality-program (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Crosby, M.; Nachiappan; Pattanayak, P.; Verma, S.; Kalyanaraman, V. BlockChain Technology: Beyond Bitcoin. Appl. Innov. Rev. 2016, 2, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Vishnu Rajamanickam. ShipChain and Scanlog Partner over Blockchain-Based Track-and-Trace Platform. Available online: https://www.bita.studio/blockchain-news/2019/2/27/shipchain-and-scanlog-partner-over-blockchain-based-track-and-trace-platform (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Accenture Newsroom|DHL and Accenture Unlock the Power of Blockchain in Logistics. Available online: https://newsroom.accenture.com/news/dhl-and-accenture-unlock-the-power-of-blockchain-in-logistics.htm (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Büyüközkan, G.; Göçer, F. Digital Supply Chain: Literature Review and a Proposed Framework for Future Research. Comput. Ind. 2018, 97, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauf, S.; Berttram, P. Industry 4.0: How Digitization Makes the Supply Chain More Efficient, Agile, and Customer-Focused. Available online: https://www.strategyand.pwc.com/report/digitization-more-efficient (accessed on 9 February 2019).
- Hanifan, G.; Sharma, A.; Newberry, C. The Digital Supply Network a New Paradigm for Supply Chain Management; Accenture Strategy: Dublin, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Strandhagen, J.O.; Vallandingham, L.R.; Fragapane, G.; Strandhagen, J.W.; Stangeland, A.B.H.; Sharma, N. Logistics 4.0 and Emerging Sustainable Business Models. Adv. Manuf. 2017, 5, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Towards Smart Factory for Industry 4.0: A Self-Organized Multi-Agent System with Big Data Based Feedback and Coordination. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tjahjono, B.; Esplugues, C.; Ares, E.; Pelaez, G. What Does Industry 4.0 Mean to Supply Chain? Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, E.; Schumann, C.-A. Smart Interoperable Logistic Environment Innovation Driver for Modern Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), Madeira, Portugal, 27–29 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kagermann, H. Change through Digitization—Value Creation in the Age of Industry 4.0. Manag. Perm. Chang. 2014, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, S.; Albertoni, F.; Piscitello, L.; Fratocchi, L. Returning from Offshore: What Do We Know? AIB Insights 2015, 15, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, J.; Oláh, J.; Erdei, E.; Máté, D.; Popp, J. The Role and Impact of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things on the Business Strategy of the Value Chain—the Case of Hungary. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maslarić, M.; Nikoličić, S.; Mirčetić, D. Logistics Response to the Industry 4.0: The Physical Internet. Open Eng. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel-Lachowska, M.; Polak-Sopinska, A.; Wisniewski, Z. Challenges for Logistics Education in Industry 4.0. In Advances in Human Factors in Training, Education, and Learning Sciences; Nazir, S., Teperi, A.M., Polak-Sopińska, A., Eds.; AHFE 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 785. [Google Scholar]
- Galati, F.; Bigliardi, B. Industry 4.0: Emerging Themes and Future Research Avenues Using a Text Mining Approach. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, S.; Jäger, A.; Hold, P.; Ott, K.; Sihn, W. Tangible Industry 4.0: A Scenario-Based Approach to Learning for the Future of Production. Procedia CIRP 2016, 54, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshal, A.; Natarajarathinam, M.; Johnson, M. Workforce Training and Industry 4.0 Adoption in Warehouses at SMEs. In Proceedings of the 2019 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Tampa, FL, USA, 15–19 June 2019; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.T.R.; Yang, X.; Huang, G.Q.; Luo, H. The Impact of Industrial Wearable System on Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Zhuhai, China, 27–29 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dregger, J.; Niehaus, J.; Ittermann, P.; Hirsch-Kreinsen, H.; ten Hompel, M. Challenges for the Future of Industrial Labor in Manufacturing and Logistics Using the Example of Order Picking Systems. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Industrial Internet Reference Architecture v 1.9|Industrial Internet Consortium. Available online: http://www.iiconsortium.org/IIRA.htm (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Hankel, M.; Rexroth, B. The Reference Architectural Model Industrie 4.0 (Rami 4.0). ZVEI 2015, 2, 4–9. [Google Scholar]

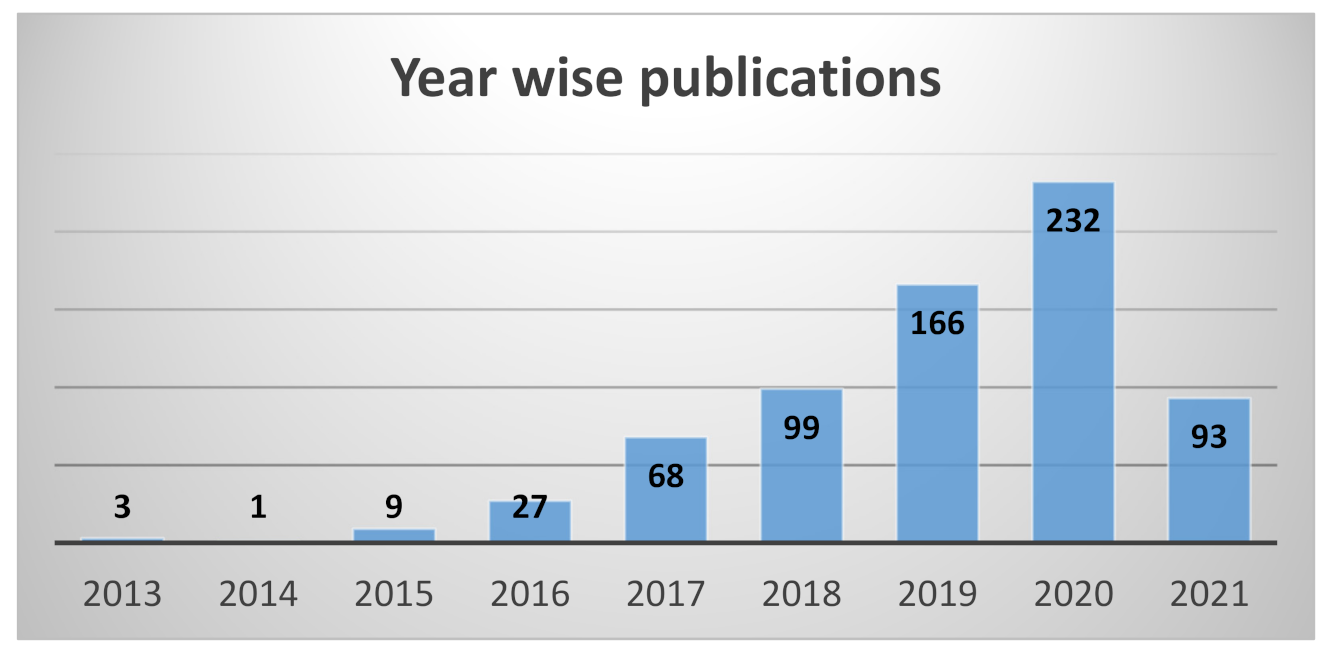

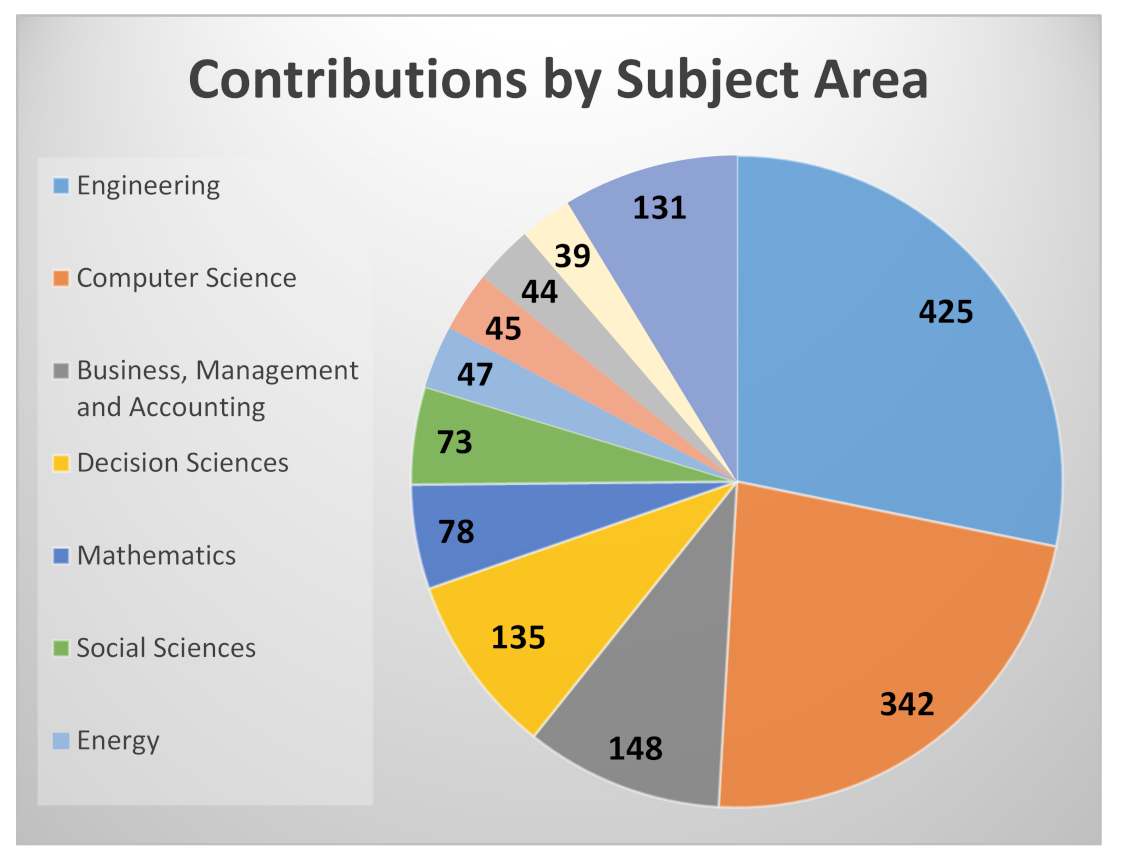



| Authors and Year | Title | Source | Structured Review (Y/N) | Number of Citations * | Focus of the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winkelhaus, S., Grosse, E.H. (2020) | Logistics 4.0: a systematic review towards a new logistics system | Review Paper | Y | 78 | This study performed a systematic literature review in the field of Logistics 4.0. A framework was created that provided a picture of the state of the art of research on Logistics 4.0. |
| Bigliardi et al., (2021) | Industry 4.0 in the logistics field: A bibliometric analysis | Review Paper | Y | 0 | This study examined the state of the art about Logistics 4.0 by analyzing and reviewing the scientific literature relating to Industry 4.0 applied to the logistics field. |
| Abdirad, M. and Krishnan, K. (2020) | Industry 4.0 in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review | Journal Paper | N | 10 | This study provided a description of the current state of research in Industry 4.0 within the supply chain and related future trends in research and practice. |
| Lagorio et al., (2020) | A systematic literature review of innovative technologies adopted in logistics management | Journal Paper | N | 0 | This study was a systematic literature review that explored the adoption of technology in the field of logistics. Several Industry 4.0 technologies were analyzed, and main research trends emerged. |
| Barreto et al., (2017) | Industry 4.0 implications in logistics: an overview | Journal Paper | N | 183 | This study explored the most important dimensions of a Logistics 4.0 implementation and its challenges. |
| Douaioui et al., (2018) | The interaction between industry 4.0 and smart logistics: concepts and perspectives | Conference Proceedings | N | 17 | This study outlined the context and the characteristics of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and discussed the prospects for future research in the field of smart logistics. |
| da Silva et al., (2019) | Technology transfer in the supply chain oriented to industry 4.0: a literature review | Journal Paper | Y | 36 | This study focused on technology transfer (TT) and how it is contextualized in supply chains under the Industry 4.0/Supply Chain 4.0 scenario. |
| Hofmann, E. and Rüsch, M. (2017) | Industry 4.0 and the current status as well as future prospects on logistics | Journal Paper | Y | 520 | This study explored the opportunities of Industry 4.0 in the context of logistics management following a conceptual research approach based on literature review and feedback from experts. |
| Manavalan, E. and Jayakrishna, K. (2019) | A review of Internet of Things (IoT) embedded sustainable supply chain for industry 4.0 requirements | Journal Paper | Y | 143 | This study explored the various aspects of supply chain management (SCM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), IoT, and Industry 4.0 and explored the potential opportunities available in IoT embedded sustainable supply chain for Industry 4.0 transformation. |
| Obrecht et al., (2017) | Review of Industry 4.0 and forecasting its future within trends in logistics and development of legislation | Journal Paper | N | 0 | This study identified several key issues of Industry 4.0 development in the logistics context focusing mostly on the development of legislation relative to environmental protection. |
| Conference Title | Number of Papers | Number of Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Procedia Manufacturing | 30 | 201 |
| 2 | Procedia Computer Science | 25 | 64 |
| 3 | IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering | 17 | 32 |
| 4 | Procedia CIRP | 14 | 144 |
| 5 | Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management | 13 | 20 |
| 6 | Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing | 12 | 43 |
| 7 | IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology | 12 | 105 |
| 8 | IFAC Papersonline | 9 | 0 |
| 9 | Lecture Notes in Computer Science | 8 | 0 |
| 10 | Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering | 8 | 0 |
| Journal Title | Number of Papers | Number of Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sustainability Switzerland | 14 | 205 |
| 2 | Sensors Switzerland | 7 | 17 |
| 3 | International Journal of Production Research | 6 | 239 |
| 4 | IEEE Access | 5 | 48 |
| 5 | Applied Sciences Switzerland | 4 | 24 |
| 6 | Computers in Industry | 4 | 747 |
| 7 | International Journal of Production Economics | 4 | 36 |
| 8 | Procedia Manufacturing | 4 | 110 |
| Author Name | Affiliation | Number of Papers | Number of Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Woschank, M. | Montanuniversität Leoben, Austria | 13 | 38 |
| 2 | Bányai, T. | University of Miskolc, Hungary | 11 | 132 |
| 3 | Illés, B. | Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary | 10 | 86 |
| 4 | Klumpp, M. | Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany | 7 | 31 |
| 5 | Telukdarie, A. | University of Johannesburg, South Africa | 7 | 65 |
| 6 | Ivanov, D. | University of Kassel and Technical University of Kaiserslautern, Germany | 6 | 274 |
| 7 | Thoben, K.-D. | University of Bremen, Germany | 6 | 383 |
| 8 | Zhong, R.Y. | The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong | 6 | 80 |
| Authors and Year | Title | Logistics 4.0 Description |
|---|---|---|
| Winkelhaus, S., Grosse, E.H. (2020) | Logistics 4.0: a systematic review towards a new logistics system | According to the authors, Logistics 4.0 is distinguished and synthesized by a) the changes of logistics processes that are caused by the use of new digital technologies, b) the implications of the changing production model towards mass customization, and c) the importance of sustainability and protecting the environment while satisfying all of the above. |
| Barreto et al., (2017) | Industry 4.0 implications in logistics: an overview | This study summarized Logistics 4.0 as the optimization of logistics processes that are supported by intelligent systems, embedded in software and databases from which relevant information is provided and shared in order to accomplish a significant automation degree. |
| Kamble et al., (2018) | Sustainable Industry 4.0 Framework: A Systematic Literature Review Identifying the Current Trends and Future Perspectives | According to the authors, Industry 4.0 technologies make real time data from several logistics domains available, which can be leveraged to create more efficient logistics decisions. Data acquired from products, logistics activities, and manufacturing machinery become easily accessible, bridging the gap between physical and digital worlds. |
| Tjahjono et al., (2017) | What Does Industry 4.0 Mean to Supply Chain? | The study mentioned that the most affected logistics areas by the introduction of Industry 4.0 technologies are order fulfilment and transport logistics. It was also mentioned that implementation of particular Industry 4.0 technologies can have a significant impact in terms of productivity and work improvement on logistics. |
| Kayikci (2018) | Sustainability Impact of Digitization in Logistics | The study identified digitization of logistics (i.e., Logistics 4.0) as the enabling of integrated planning and execution systems, logistics visibility, autonomous logistics, and smart warehousing through the implementation of a wide range of digital technologies. |
| Strandhagen et al., (2017) | Logistics 4.0 and Emerging Sustainable Business Models | According to the authors [75], Logistics 4.0 was described according to five characteristics: (a) real-time big data analytics, (b) reduced storage requirement due to novel manufacturing techniques, (c) autonomous robots and vehicles within warehouses with tracking and decision systems that lead to improved inventory control, (d) real time exchange of information between various actors, and (e) no information disruption due to smart items and cloud supported network. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Efthymiou, O.K.; Ponis, S.T. Industry 4.0 Technologies and Their Impact in Contemporary Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111643
Efthymiou OK, Ponis ST. Industry 4.0 Technologies and Their Impact in Contemporary Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2021; 13(21):11643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111643
Chicago/Turabian StyleEfthymiou, Orestis K., and Stavros T. Ponis. 2021. "Industry 4.0 Technologies and Their Impact in Contemporary Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 13, no. 21: 11643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111643
APA StyleEfthymiou, O. K., & Ponis, S. T. (2021). Industry 4.0 Technologies and Their Impact in Contemporary Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 13(21), 11643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111643







