Analysis and Prediction of Expansion of Central Cities Based on Nighttime Light Data in Hunan Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
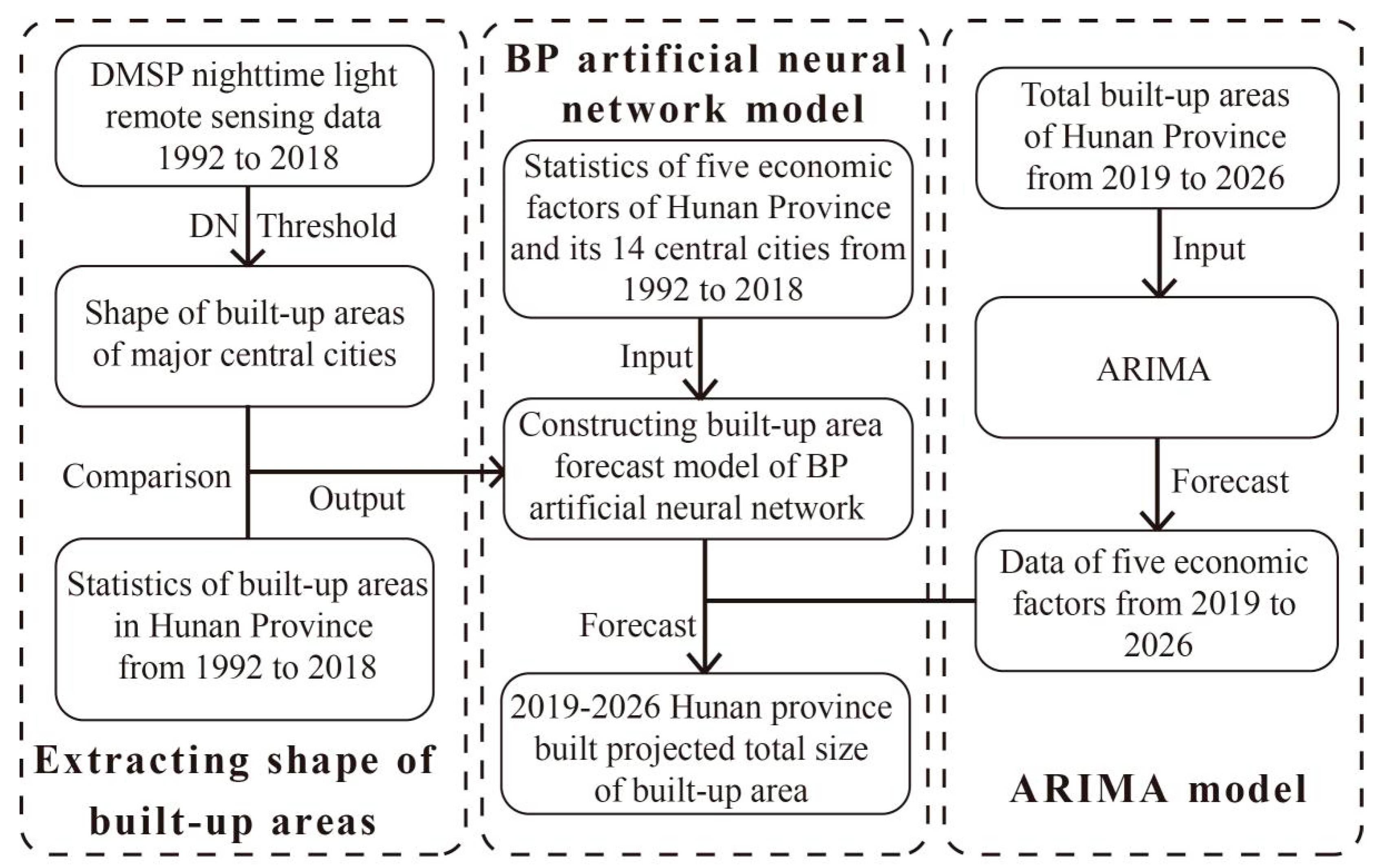
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Extraction of Urban Expansion Feature Data
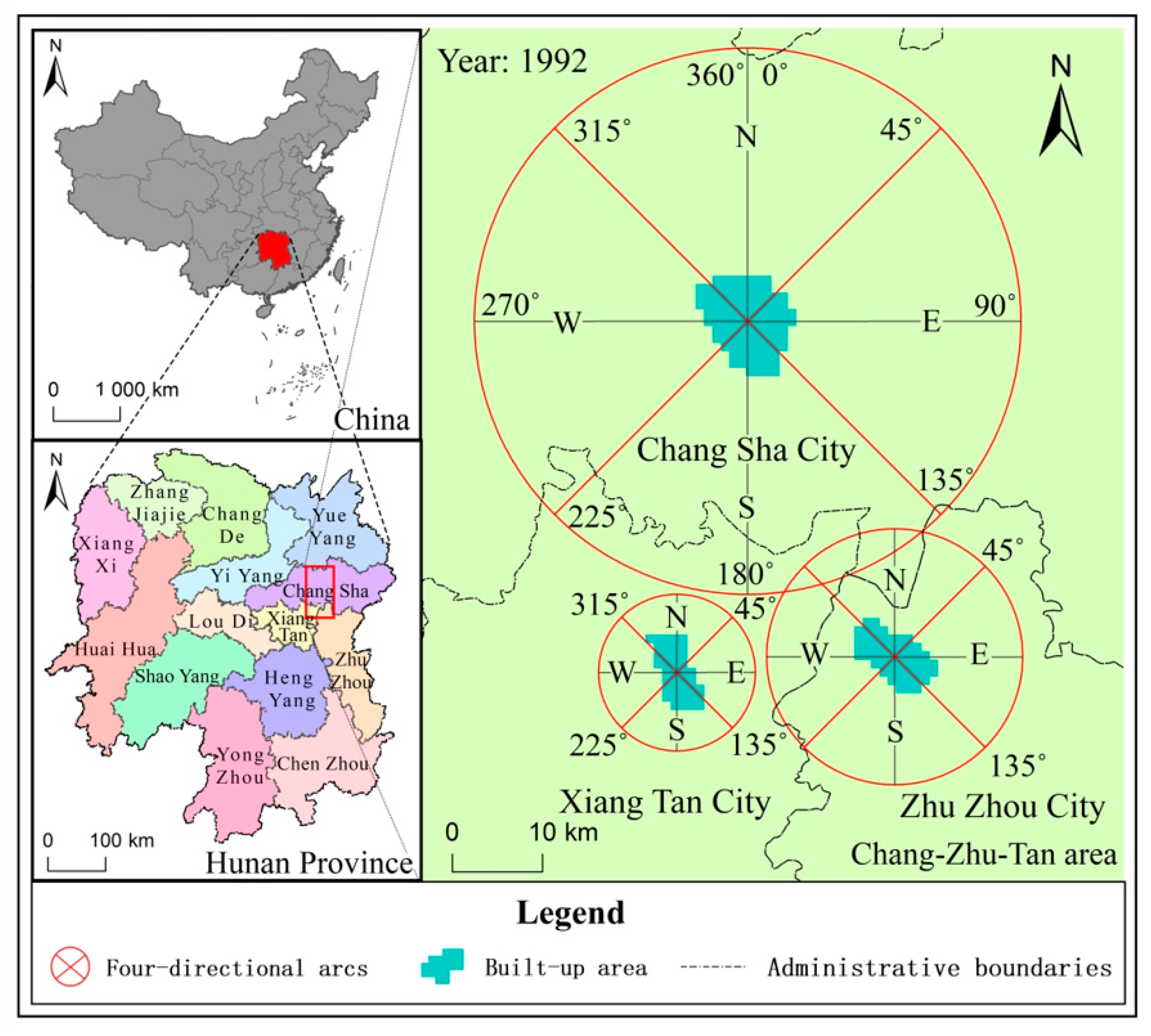
2.2.1. Extraction of Scope and Expansion Directions of Built-Up Area
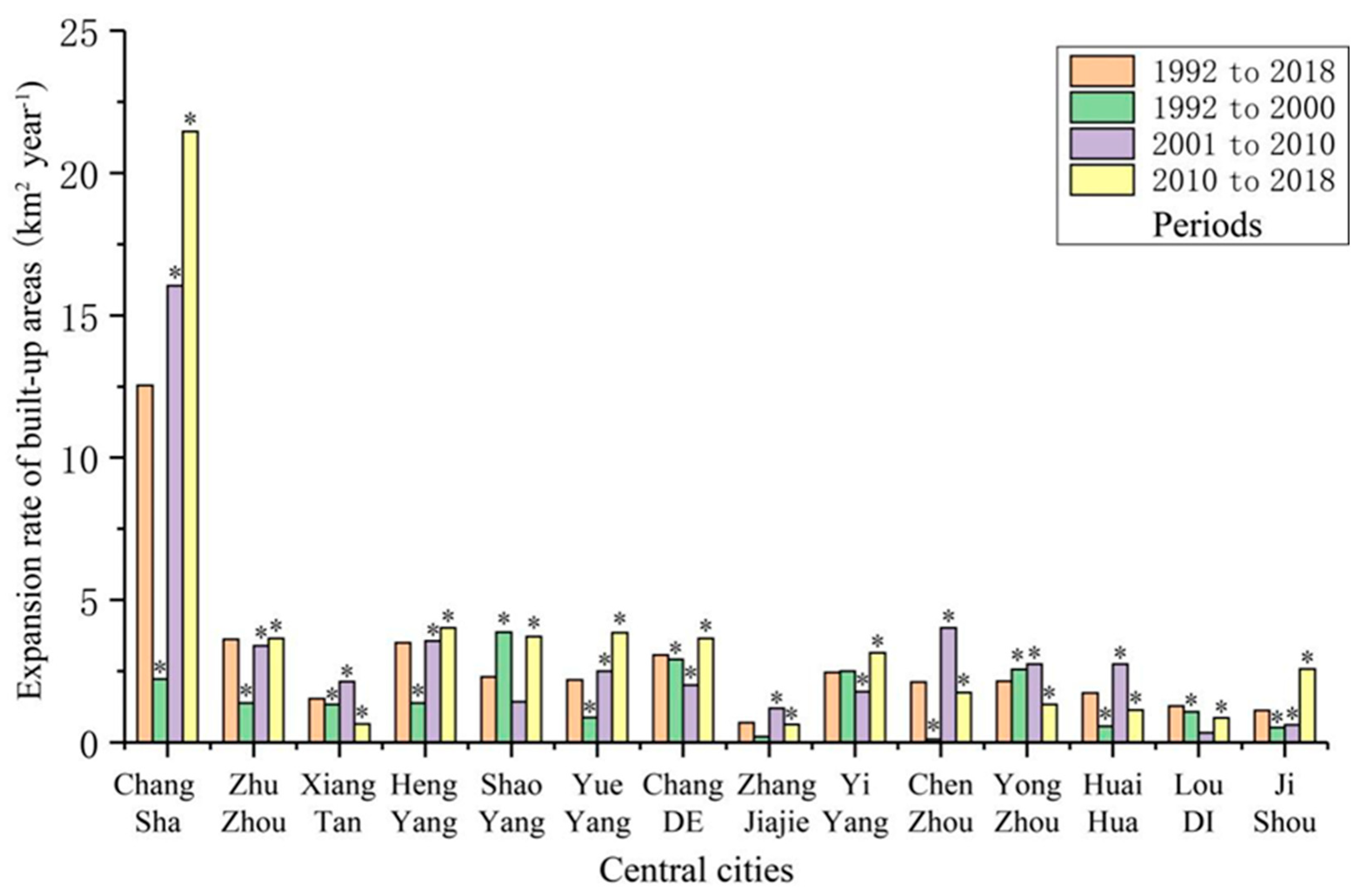
2.2.2. Expansion Speed of Built-Up Areas
2.3. Backpropagation Neural Network Model
2.4. Correlation Analysis and Prediction of Factors
3. Results
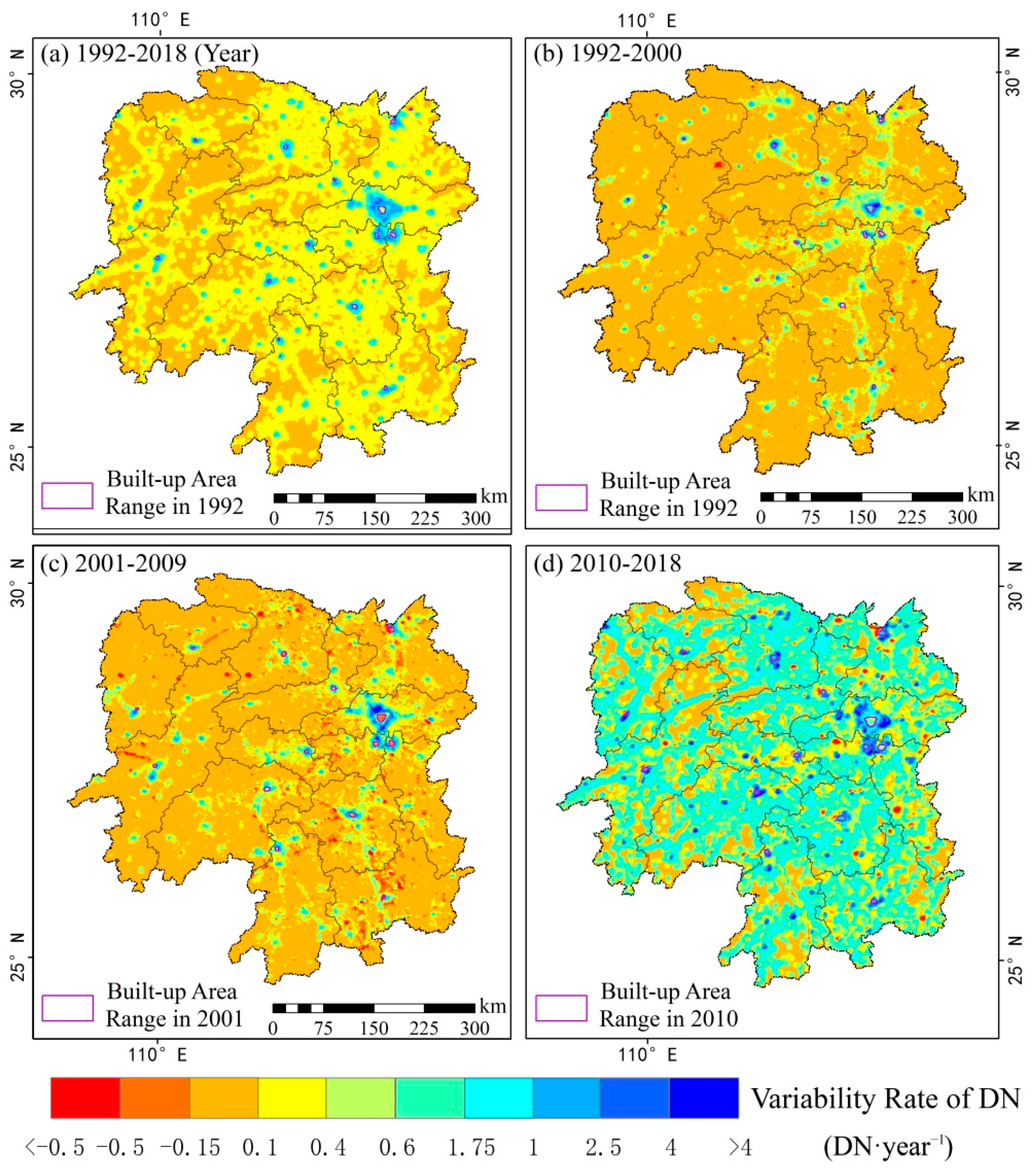
3.1. Urban Built-Up Area Extraction and Spatial Expansion Characteristics
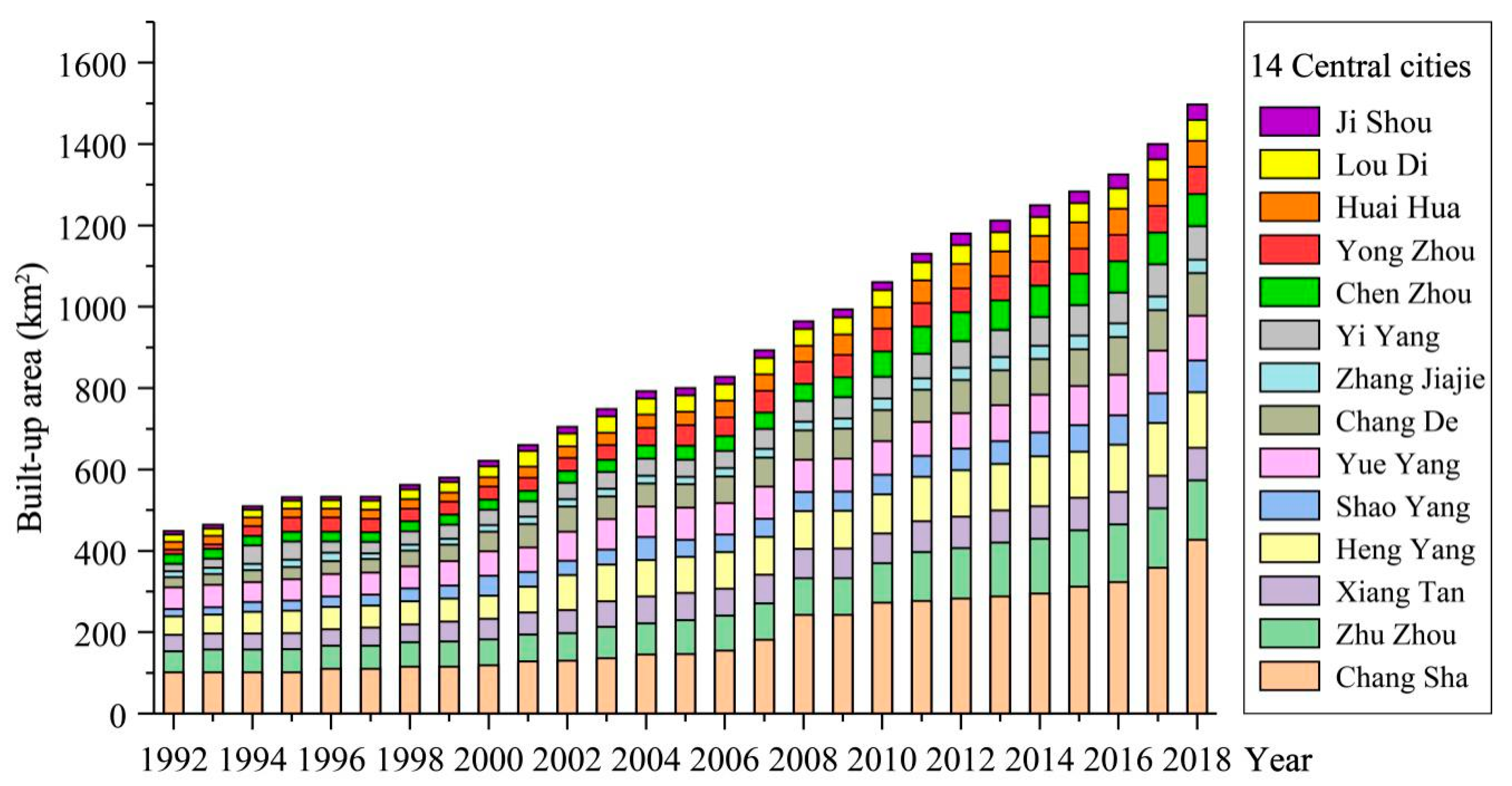
3.1.1. Scale and Expansion Rate of Built-Up Areas
3.1.2. Expansion Direction
3.2. Relationships between Built-Up Areas and Driver Factors
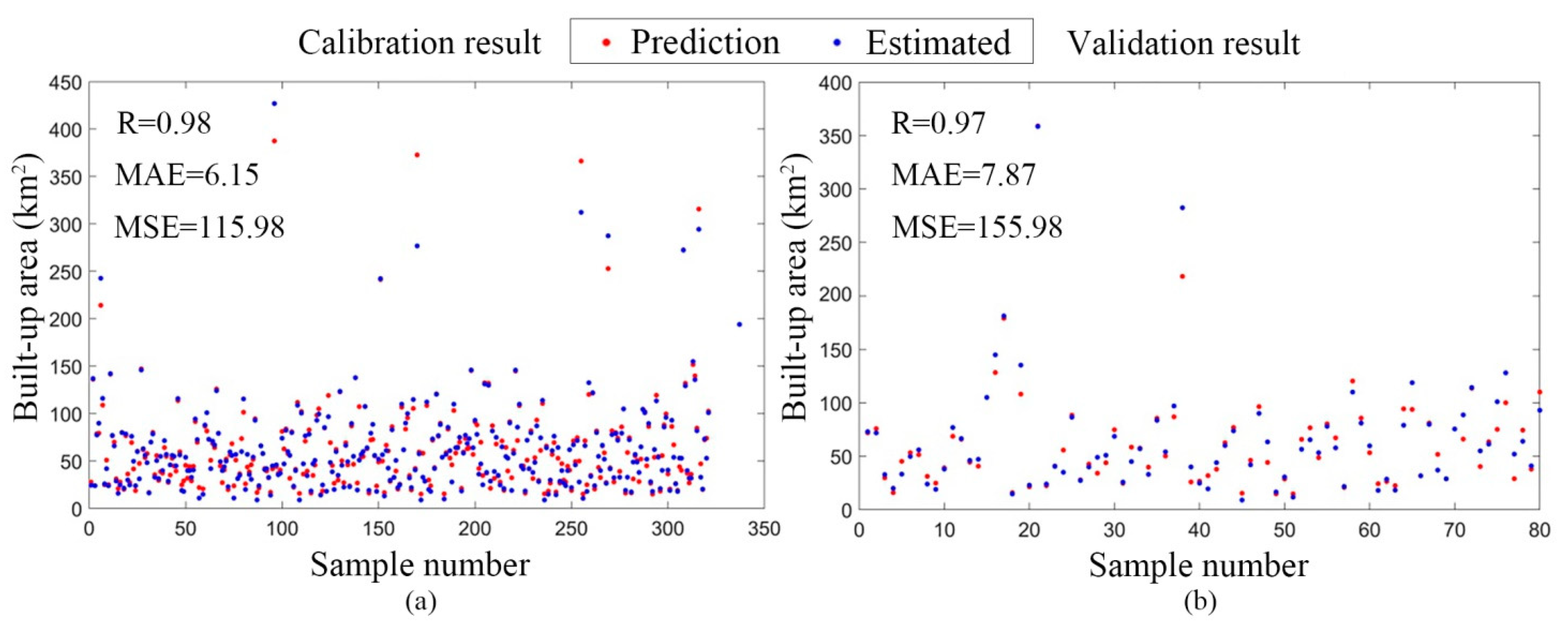
3.3. Precision Inspection of BP Network Model
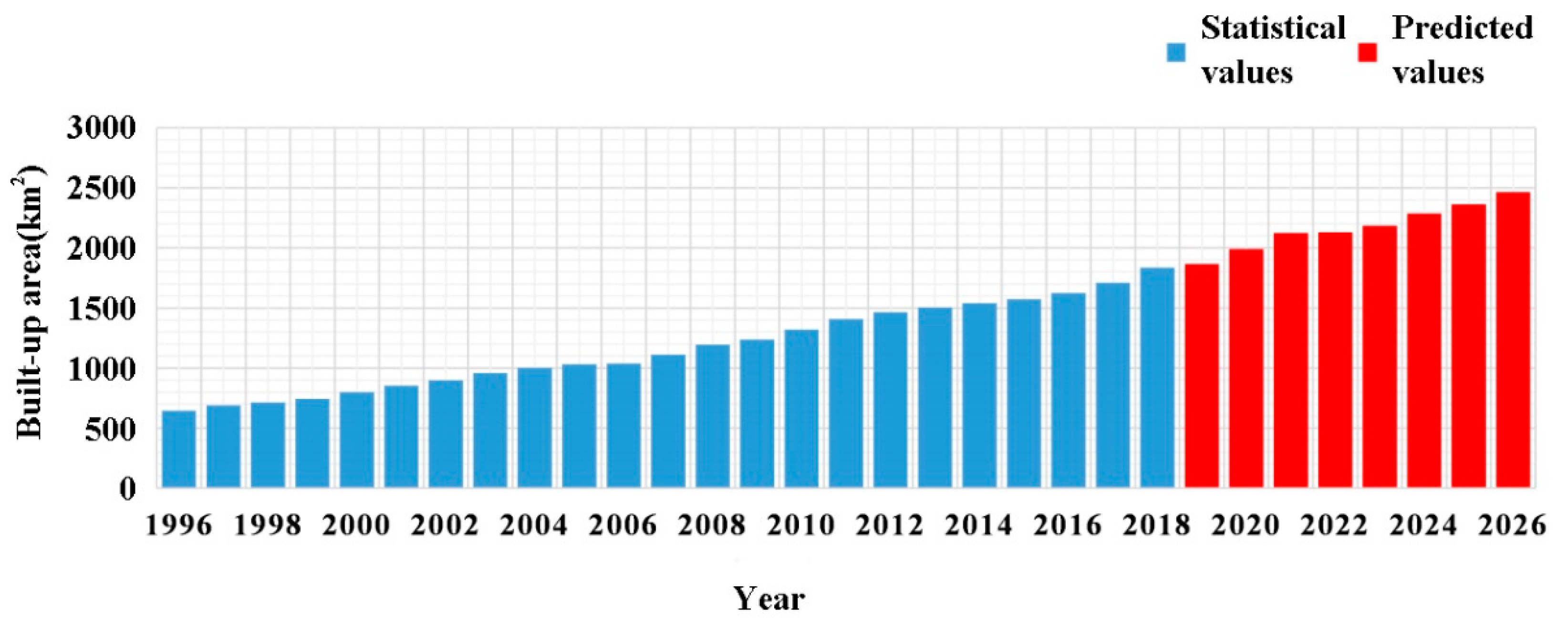
3.4. Forecast of Built-Up Areas in 2019 to 2026
4. Discussion
4.1. The Spatial Expansion Characteristics of Urbanization
4.2. The Influence Factors of Urban Expansion
4.3. The Simulation and Prediction of Urban Expansion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedmann, J. Four theses in the study of China’s urbanization. China City Plan. Rev. 2006, 15, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X. Research progress and scientific issues in the field of urbanization. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Shao, G.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Lin, T.; Yin, K.; Zhao, J. Urban three-dimensional expansion and its driving forces—A case study of Shanghai, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban Land-use Change in Four Cities of China with Time Series Landscape Metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhuang, D.F.; Wang, L.M. Spatial-temporal Changes of Urban Spatial Morphology in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2005, 60, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Sun, C. Spatio-temporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Beijing Central City Since 1932. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Tian, G.J. Study on Spatial Modes and Driving Mechanisms of Tianjin’s Urban Expansion. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, S. Dynamic analysis of urban spatial expansion and its determinants in Xiamen Island. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.F.; Mao, G.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J. Research on Urban Expansion and Land Use Change in Nanjing over the Past 32 Years. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Y.; Peng, W.F.; Mao, H.; Pan, H.J.; Zhou, J.M. Analysis on spatial and temporal change of urban sprawl in Chengdu. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2015, 40, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Wang, Y.D.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J. Urban Expansion and Its Driving Force for Putian City from 1988 to 2014. Remote. Sens. Inf. 2015, 30, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Zhou, Y.K.; Xue, J.F. Study on Urban Land Expansion and Its Driving Mechanism in Jiangsu Province. China Land Sci. 2005, 19, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.Q.; Meng, X.C. Urbanization, Suburbanization and China’s Urban Spatial Expansion. Areal Res. Dev. 2015, 34, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.X.; He, C.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.Y. Understanding Multi-Scale urban expansion driving forces: In the case study of Beijing. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 29, 714–721. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Shi, X. Cellular automata for simulating land use changes based on support vector machines. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Li, X.; Ye, J.A.; He, J.Q.; Tao, J. Using Ant Colony Optimization to Mining the Conversion Rules of Geographical Cellular Automata. Sci. China Press 2007, 37, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.Q. Study on City Growth Spatial from Based on Constrained Logisitic-CA Model. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zeng, Y.N.; Jin, X.B.; Yin, C.L.; Zou, B. Urban Land Expansion Model Based on Multi-agent System and Application. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C. Study of Simulation for Urban Land Expansion Based on GIS and MAS. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, Y.S.; Xie, X.Y. Simulation of Lanzhou urban land expansion based on multi-agent model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 6, 169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Urban expansion simulation under constraint of multiple ecosystem services (MESs) based on cellular automata (CA)-Markov model: Scenario analysis and policy implications. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W. An improved urban cellular automata model by using the trend-adjusted neighborhood. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, X.S. The Fine-Scale Urban Expansion Modeling in the Big Data Era. Urban Dev. Stud. 2017, 24, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Jensen, J.; Weng, Q.; Weaver, R. A Geographically Weighted Regression Analysis of the Underlying Factors Related to the Surface Urban Heat Island Phenomenon. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-W.; Cao, K. Establishment and application of intelligent city building information model based on BP neural network model. Comput. Commun. 2020, 153, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Elvidge, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, C.; Warner, T. Remote sensing of night-time light. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5855–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.J. The Study on Urbanization Process in China Based on DMSP/OLS Data: Development of a Light Index for Urbanization Level Estimation. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Zheng, X.Q.; Yuan, T. Knowledge Mapping of Research Results on DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.Q.; Bai, L.Y. A study of urban expansion feature of China based on DMSP-OLS stable nighttime light data. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.W.; Hu, B.S.; Ju, M. Spatial pattern evolution of urban system in Yangtze River Economic Belt based on DMSP-OLS night light data (1992–2013). Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kohli, D.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, D. Remote sensing modeling of urban density dynamics across 36 major cities in China: Fresh insights from hierarchical urbanized space. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 203, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, Z. Research on the Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Electrical Power Consumption in Three Urban Agglomerations of Yangtze River Economic Belt, China Based on DMSP/OLS Night Light Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Li, J.G. Research on the spatial process reconstruction of China’s mainland urbanization in the 1990s based on DMSP/OLS night light data and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a Series of Consistent Night-Time Light Data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.P.; Yang, Y.C.; Fu, D.X.; Li, H.Y.; Tian, H.Z. Urban spatial expansion based on DMSP_OLS nighttime light data in China in 1992–2010. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.G. The Sprawl Research on Valley City Based on Cellular Automata. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y. An Improved Correction Method of Nighttime Light Data Based on EVI and WorldPop Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H. Machine Learning; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Gong, X.; Liu, H. Prediction of household consumption carbon emission in western cities Based on BP model: Case of Xi′an city. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsanjari, M.M.; Zarandian, A.; Mohammadyari, F.; Visockiene, J.S. Investigation of the impacts of urban vegetation loss on the ecosystem service of air pollution mitigation in Karaj metropolis, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.S.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhou, P.; Jin, J.L. Analysis and prediction of annual precipitation in Huangshan City based on wavelet and ARIMA. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, D.H.; Ding, Y. Application of a combined ARIMA-LSTM model based on SPI for the forecast of drought: A case study in Qinghai Province. Arid Land Geogr. Arid Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, Project team of China Quarterly Macroeconomic Model. Macroeconomic forecasts for China in 2020–2021. J. Xiamen Univ. 2020, 21–29. Available online: https://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XMDS202103008.htm (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Bao, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, K.; Ren, Y. Modeling regional sustainable development scenarios using the Urbanization and Eco-environment Coupler: Case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 689, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.Z.; Chen, S.C.; Liu, T. Changing spatial patterns of internal migration to five major urban agglomerations in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.L. New Structure and New Trend of Formation and Development of Urban Agglomerations in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2011, 31, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. A New Strategy of Hunan Space Development; Hunan Education Press: Hunan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Ran, J.; Jin, R.; Xu, S. Seeking sustainable development policies at the municipal level based on the triad of city, economy and environment: Evidence from Hunan province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.P. Urbanization Spatial Pattern and Affecting Factors Analysis of Hunan Province. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C. Urbanization: Processes and driving forces. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, S. The varying driving forces of urban land expansion in China: Insights from a spatial-temporal analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 766, 142591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, B.; Wen, Q.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Urban expansion in China and its spatial-temporal differences over the past four decades. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1477–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.S.; Wang, M. The allometric growth of urban land use and population and its experiential research. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; De Jong, M.; Jiang, M. City Branding and Industrial Transformation from Manufacturing to Services: Which Pathways do Cities in Central China Follow? Sustainability 2019, 11, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, K.C.; Johnson, J.M. Calibrating SLEUTH with big data: Projecting California’s land use to 2100. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 83, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cities | GDP | The Proportion of Secondary Production | The Proportion of Tertiary Production | Year-End Population | Urban Road Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chang Sha | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.98 | 0.93 |
| Zhu Zhou | 0.99 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| Xiang Tan | 0.84 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
| Heng Yang | 0.92 | 0.65 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 0.88 |
| Shao Yang | 0.91 | 0.60 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| Yue Yang | 0.93 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.98 | 0.93 |
| Yi Yang | 0.95 | 0.72 | 0.46 | 0.83 | 0.93 |
| Chang De | 0.92 | 0.70 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.93 |
| Chen Zhou | 0.98 | 0.84 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.97 |
| Yong Zhou | 0.87 | 0.48 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 0.91 |
| Huai Hua | 0.96 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.96 | 0.90 |
| Zhang Jiajie | 0.96 | −0.50 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.90 |
| Ji Shou | 0.96 | −0.07 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.90 |
| Lou Di | 0.83 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.58 |
| Hunan | 0.97 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| GDP (Billion Yuan) | Proportion of Secondary Industries (%) | Proportion of Tertiary Industries (%) | Year-End Population (Million People) | Urban Road Area(km2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 39,513.39 | 37.86 | 52.10 | 39.46 | 282.04 |
| 2020 | 41,775.50 | 37.82 | 54.32 | 40.39 | 297.56 |
| 2021 | 44,536.86 | 37.70 | 55.92 | 41.41 | 315.14 |
| 2022 | 48,403.38 | 36.77 | 55.72 | 42.57 | 326.33 |
| 2023 | 51,374.60 | 37.92 | 55.67 | 43.81 | 337.63 |
| 2024 | 54,325.03 | 37.88 | 56.55 | 45.07 | 349.62 |
| 2025 | 57,670.55 | 38.12 | 56.60 | 46.25 | 366.31 |
| 2026 | 60,705.07 | 38.81 | 56.85 | 47.36 | 383.98 |
| DW | 1.88 | 1.73 | 1.95 | 1.94 | 1.99 |
| AIC | 398.64 | 244.34 | −124.25 | 290.32 | 408.04 |
| BIC | 407.45 | 266.98 | −107.90 | 300.08 | 425.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Peng, C.; Du, H.; Yuan, S.; Li, P. Analysis and Prediction of Expansion of Central Cities Based on Nighttime Light Data in Hunan Province, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11982. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111982
Liu Y, He T, Wang Y, Peng C, Du H, Yuan S, Li P. Analysis and Prediction of Expansion of Central Cities Based on Nighttime Light Data in Hunan Province, China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(21):11982. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111982
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuxin, Tian He, Yi Wang, Changhui Peng, Hui Du, Shuai Yuan, and Peng Li. 2021. "Analysis and Prediction of Expansion of Central Cities Based on Nighttime Light Data in Hunan Province, China" Sustainability 13, no. 21: 11982. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111982
APA StyleLiu, Y., He, T., Wang, Y., Peng, C., Du, H., Yuan, S., & Li, P. (2021). Analysis and Prediction of Expansion of Central Cities Based on Nighttime Light Data in Hunan Province, China. Sustainability, 13(21), 11982. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111982






