What Is the Customer Value of the Circular Economy? Cross-Industry Exploration of Diverse Values Perceived by Consumers and Business Customers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What is the perceived customer value of CE solutions, specifically economic, symbolic, environmental, and functional value dimensions?
- What are consumers’ and business customers’ major perceived determinants of the customer value of CE solutions?
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Creating Value from CE Innovations and Solutions: The Customer Perspective
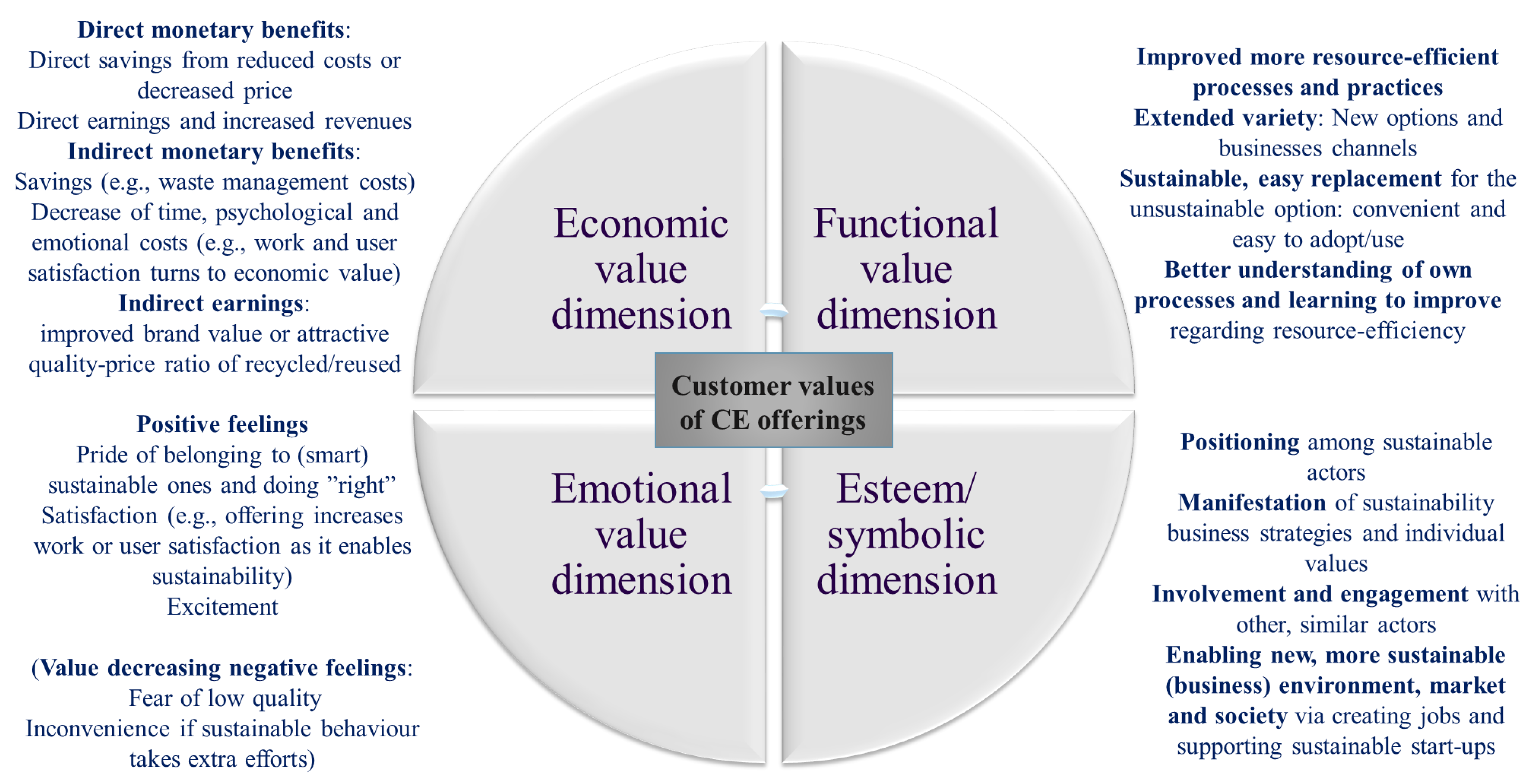
2.2. Toward a Framework for Exploring Customer Value Dimensions of the CE
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design and Data Collection
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Findings: Customer Value of CE Solutions
4.1. Overview of CE Customer Value
4.2. Customer Value of CE Solutions in Business and Consumer Markets
4.2.1. Customer Value of CE Offerings for Consumers
4.2.2. Customer Value of CE Offerings by Business Customers
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Developing a Model for CE Customer Value Dimensions
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Planing, P. Business model innovation in a circular economy reasons for non-acceptance of circular business models. Open J. Bus. Model Innov. 2015, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ranta, V.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Mäkinen, S.J. Creating value in the circular economy: A structured multiple-case analysis of business models. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; A Narus, J. Business marketing: Understand what customers value. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1998, 76, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Lehtimäki, T. Commercializing a radical innovation: Probing the way to the market. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbinati, A.; Chiaroni, D.; Chiesa, V. Towards a new taxonomy of circular economy business models. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, V.; Keränen, J.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L. How B2B suppliers articulate customer value propositions in the circular economy: Four innovation-driven value creation logics. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 87, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Niinimäki, K.; Kujala, S.; Karell, E.; Lang, C. Sustainable product-service systems for clothing: Exploring consumer perceptions of consumption alternatives in Finland. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, B.T.; Boone, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Khor, K.S. Perceived quality of remanufactured products: Construct and measure development. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Otero, J.; Boks, C.; Pettersen, I.N. User acceptance and adoption of circular offerings in the fashion sector: Insights from user-generated online reviews. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuah, A.T.H.; Wang, P. Circular economy and consumer acceptance: An exploratory study in East and Southeast Asia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Honkasalo, A.; Seppälä, J. Circular economy: The concept and its limitations. Ecolog. Econ. 2018, 143, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peronard, J.-P.; Ballantyne, A.G. Broadening the understanding of the role of consumer services in the circular economy: Toward a conceptualization of value creation processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrello, M.; Caracciolo, F.; Lombardi, A.; Pascucci, S.; Cembalo, L. Consumers’ perspective on Circular Economy Strategy for Reducing Food Waste. Sustainability 2017, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antikainen, M.; Lammi, M.; Hakanen, T. Consumer service innovation in a circular economy-the customer value perspective. J. Serv. 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tukker, A. Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Tse, T.; Soufani, K. Introducing a Circular Economy: New Thinking with New Managerial and Policy Implications. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2018, 60, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieder, M.; Asif, F.M.; Rashid, A.; Mihelič, A.; Kotnik, S. A conjoint analysis of circular economy value propositions for consumers: Using “washing machines in Stockholm” as a case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nußholz, J.L.K. A circular business model mapping tool for creating value from prolonged product lifetime and closed material loops. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Rojas Luiz, J.V.; Rojas Luiz, O.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Ndubisi, N.O.; Caldeira de Oliveira, J.H.; Junior, F.H. Circular economy business models and operations management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1525–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdeke-Freund, F.; Gold, S.; Bocken, N.M.P. A Review and Typology of Circular Economy Business Model Patterns. J. Ind. Ecol. 2018, 23, 36–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho-Otero, J.; Boks, C.; Pettersen, I.N. Consumption in the Circular Economy: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wastling, T.; Charnley, F.; Moreno, M. Design for Circular Behaviour: Considering Users in a Circular Economy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Ritala, P.; Thomas, L.D.W. Circular economy ecosystems: A typology, definitions, and implications. In Handbook of Sustainability Agency; Teerikangas, S., Onkila, T., Koistinen, K., Mäkelä, M., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2021; pp. 15–37, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gallaud, D.; Laperche, B. Circular Economy, Industrial Ecology and Short Supply Chain; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Repo, P.; Anttonen, M. Emerging consumer perspectives on circular economy. In Proceedings of the 13th Nordic Environmental Social Science Conference HopefulNESS, Tampere, Finland, 6–8 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Jaakkola, E. Value co-creation in knowledge intensive business services: A dyadic perspective on the joint problem solving process. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2012, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintamäki, T.; Kuusela, H.; Mitronen, L. Identifying competitive customer value propositions in retailing. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2007, 17, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamaria, L.; Escobar-Tello, C.; Ross, T. Switch the channel: Using cultural codes for designing and positioning sustainable products and services for mainstream audiences. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobson, K.; Lynch, N.; Lilley, D.; Smalley, G. Systems of practice and the Circular Economy: Transforming mobile phone product service systems. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2018, 26, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotler, P.; Armstrong, G. Principles of Marketing, 18th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Möhlmann, M. Collaborative consumption: Determinants of satisfaction and the likelihood of using a sharing economy option again. J. Consum. Behav. 2015, 14, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Dabholkar, P.A. Consumer recycling goals and their effect on decisions to recycle: A means-end chain analysis. Psychol. Mark. 1994, 11, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ha, S. Understanding Consumer Recycling Behavior: Combining the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Norm Activation Model. Fam. Consum. Sci. Res. J. 2014, 42, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, D.; Roux, D. A Second-hand Shoppers’ Motivation Scale: Antecedents, Consequences, and Implications for Retailers. J. Retail. 2010, 86, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefers, T. Exploring carsharing usage motives: A hierarchical means-end chain analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2013, 47, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallehn, H.; Seuring, S.; Strähle, J.; Freise, M. Customer experience creation for after-use products: A product–service systems-based review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J. Motivations for Participating in Sharing Economy: Intentions to Use Car Sharing Services. J. Distrib. Sci. 2017, 15, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.A.D.; Almeida, S.O.; Bollick, L.C.; Bragagnolo, G. Second-hand fashion market: Consumer role in circular economy. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 23, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Xia, X. Why are customers loyal in sharing-economy services? A relational benefits perspective. J. Serv. Mark. 2017, 31, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catulli, M.; Cook, M.; Potter, S. Consuming use orientated product service systems: A consumer culture theory perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weelden, E.; Mugge, R.; Bakker, C. Paving the way towards circular consumption: Exploring consumer acceptance of refurbished mobile phones in the Dutch market. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervellon, M.C.; Carey, L.; Harms, T. Something old, something used: Determinants of women’s purchase of vintage fashion vs second-hand fashion. Int. J. Ret. Distrib. Manag. 2012, 40, 956–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.N.; Bae, S.Y.; Xu, H. Second-hand clothing shopping among college students: The role of psychographic characteristics. Young Consum. 2015, 16, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hazen, B. Consumer product knowledge and intention to purchase remanufactured products. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 181, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.; Mattsson, J. Understanding collaborative consumption: Test of a theoretical model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 118, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.; Griffiths, M.A. Share more, drive less: Millennials value perception and behavioral intent in using collaborative consumption services. J. Consum. Mark. 2017, 34, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Evaluation and Research Methods; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission, Directorate-General for Environment. Links between production, the environment and environmental policy. Summary Report. In EU Commission Report; Contract ENV.F.1/FRA/2014/0063; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Flick, U. Semi-structured interviews. In An Introduction to Qualitative Research; SAGE Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 74–95. [Google Scholar]
- Flick, U. Triangulation in qualitative research. In A Companion to Qualitative Research; Flick, U., Von Kardoff, E., Steinke, I., Eds.; SAGE Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Gioia, D.A.; Pitre, E. Multiparadigm perspectives on theory building. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1990, 15, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teece, D.J. Business models, business strategy and innovation. Long Range Plan. 2010, 43, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wiegerinck, V.; Krikke, H.; Zhang, H. Understanding the purchase intention towards remanufactured product in closed-loop supply chains: An empirical study in China. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2013, 43, 866–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, L.; Boks, C. Marketing Approaches for a Circular Economy: Using Design Frameworks to Interpret Online Communications. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codini, A.P.; Bertoli, G.; Frassine, R. Ecodesign strategies and customer value: A conjoint approach. In Customer Satisfaction and Sustainability Initiatives in the Fourth Industrial Revolution; Silvestri, C., Piccarozzi, M., Aquilani, B., Eds.; IGI Global, Busi-ness Science Reference: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 189–211. [Google Scholar]



| CE Business Case, Industry, and BM | Customer Identifier and Type |
|---|---|
| ResQ Club Enables companies to sell surplus food to consumers Industry: Food, grocery, and service Business model: Surplus-selling platforms | Customer 1, Business market customer Donor/seller of used material/products/surplus |
| Customer 2, Business market customer Donor/seller of used material/products/surplus | |
| Customer 3, Consumer market customer Buyer of second-hand/reconditioned/surplus | |
| Customer 4, Consumer market customer Buyer of second-hand/reconditioned/surplus | |
| Customer 5, Consumer market customer Buyer of second-hand/reconditioned/surplus | |
| Netlet Oy Ab Enables companies to sell construction surplus Industry: Construction Business model: Surplus-selling platforms | Customer 6, Business market customer Donor/seller of used material/products/surplus Customer 7, Consumer market customer Buyer of secondhand/reconditioned/surplus |
| Fluid Intelligence Oy Business model: Waste management services Industry: Waste management | Customer 8, Business market customer Waste management service integrator |
| Verso Food Oy Business model: Alternative sustainable solutions Industry: Food | Customer 9, Business market customer Chooser of alternative sustainable solutions (plant-based protein) |
| Gold and Green® Business model: Alternative sustainable solutions Industry: Food | Customer 10, Business market customer Chooser of alternative sustainable solutions (plant-based protein) |
| Customer Value Dimension | Functional Values | Economic Values | Esteem/Symbolic Values | Emotional Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overview of diverse customer value items per value dimension |
|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Welathanthri, M.D.; Ranta, V. What Is the Customer Value of the Circular Economy? Cross-Industry Exploration of Diverse Values Perceived by Consumers and Business Customers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13764. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413764
Aarikka-Stenroos L, Welathanthri MD, Ranta V. What Is the Customer Value of the Circular Economy? Cross-Industry Exploration of Diverse Values Perceived by Consumers and Business Customers. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):13764. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413764
Chicago/Turabian StyleAarikka-Stenroos, Leena, Martina Don Welathanthri, and Valtteri Ranta. 2021. "What Is the Customer Value of the Circular Economy? Cross-Industry Exploration of Diverse Values Perceived by Consumers and Business Customers" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 13764. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413764
APA StyleAarikka-Stenroos, L., Welathanthri, M. D., & Ranta, V. (2021). What Is the Customer Value of the Circular Economy? Cross-Industry Exploration of Diverse Values Perceived by Consumers and Business Customers. Sustainability, 13(24), 13764. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413764






