Numerical Study of Cylindrical Tropical Woods Pyrolysis Using Python Tool
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- a
- Assumptions
- The studied sample is of cylindrical geometry, of infinite length, heated through its surface by convection and radiation;
- Samples are directly exposed to the heat fixed numerically, thus the heating rates are neglected.
- Pyrolysis does not generate any change in the volume of the sample and the latter is considered isotropic;
- For simplicity, heat is assumed to be transmitted inside the solid particle by conduction only;
- The heat and mass transfer of the volatile products and the vapor inside the solid are ignored;
- The volatile products and the vapor leave the solid as soon as they are produced. They are in thermal equilibrium with the solid matrix and therefore the rate of solid mass loss is taken as the mass flux of the volatiles;
- Secondary reactions of the volatile products are not taken into account;
- The chemical reactions of pyrolysis are described by the Arrhenius law of first order.
- b
- Setting in equation of the pyrolysis of wood
- Heat balance
- Mass balance
- Heat balance
- Mass balances of wood, charcoal, gas, liquid and steam:
- Initial and boundary conditions
- -
- At ,
- -
- Due to the cylindrical symmetry, the condition at the center gives:
- -
- At the surface of the sample, in r = R, we have:
- c
- Numerical values of the model constants
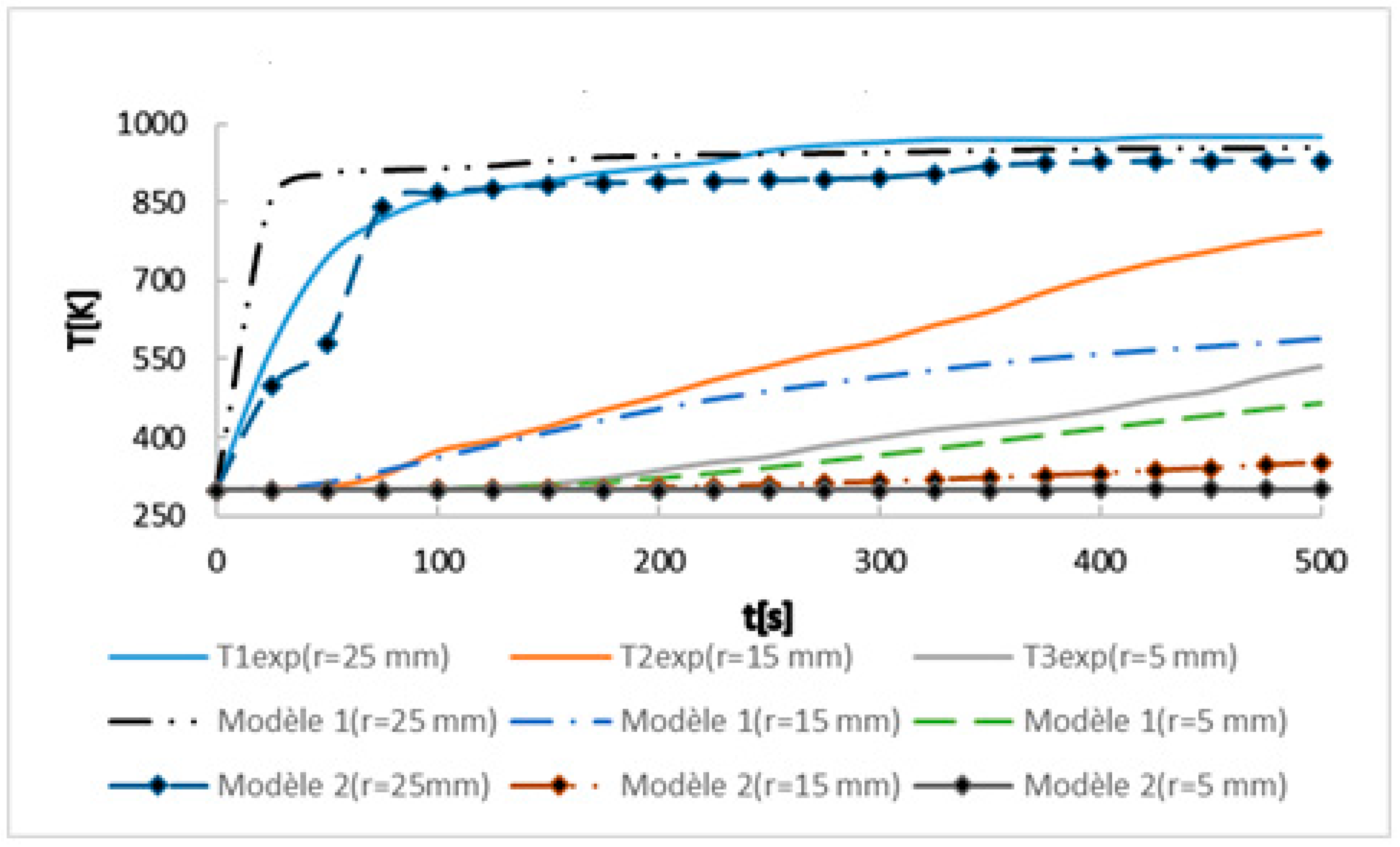
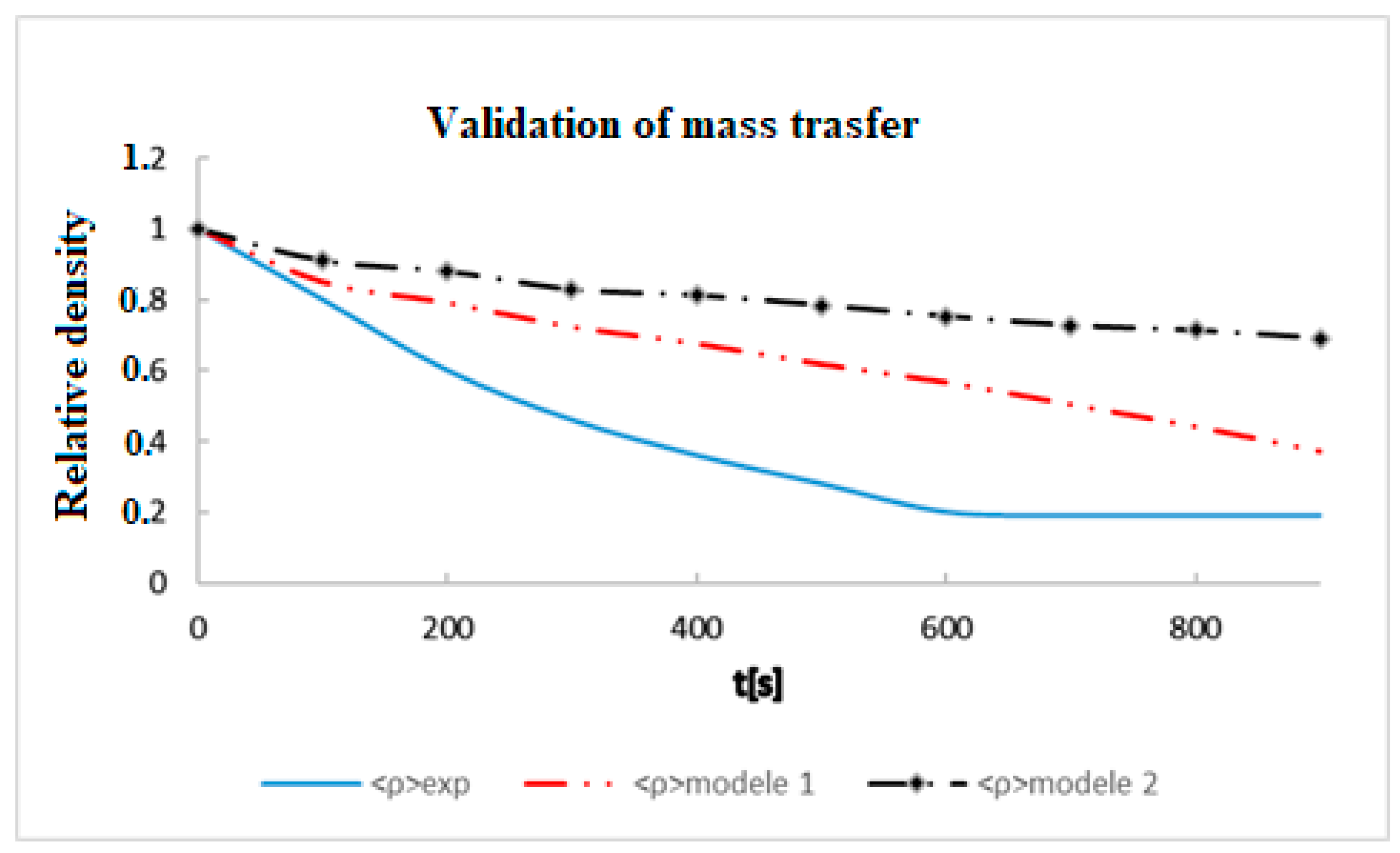
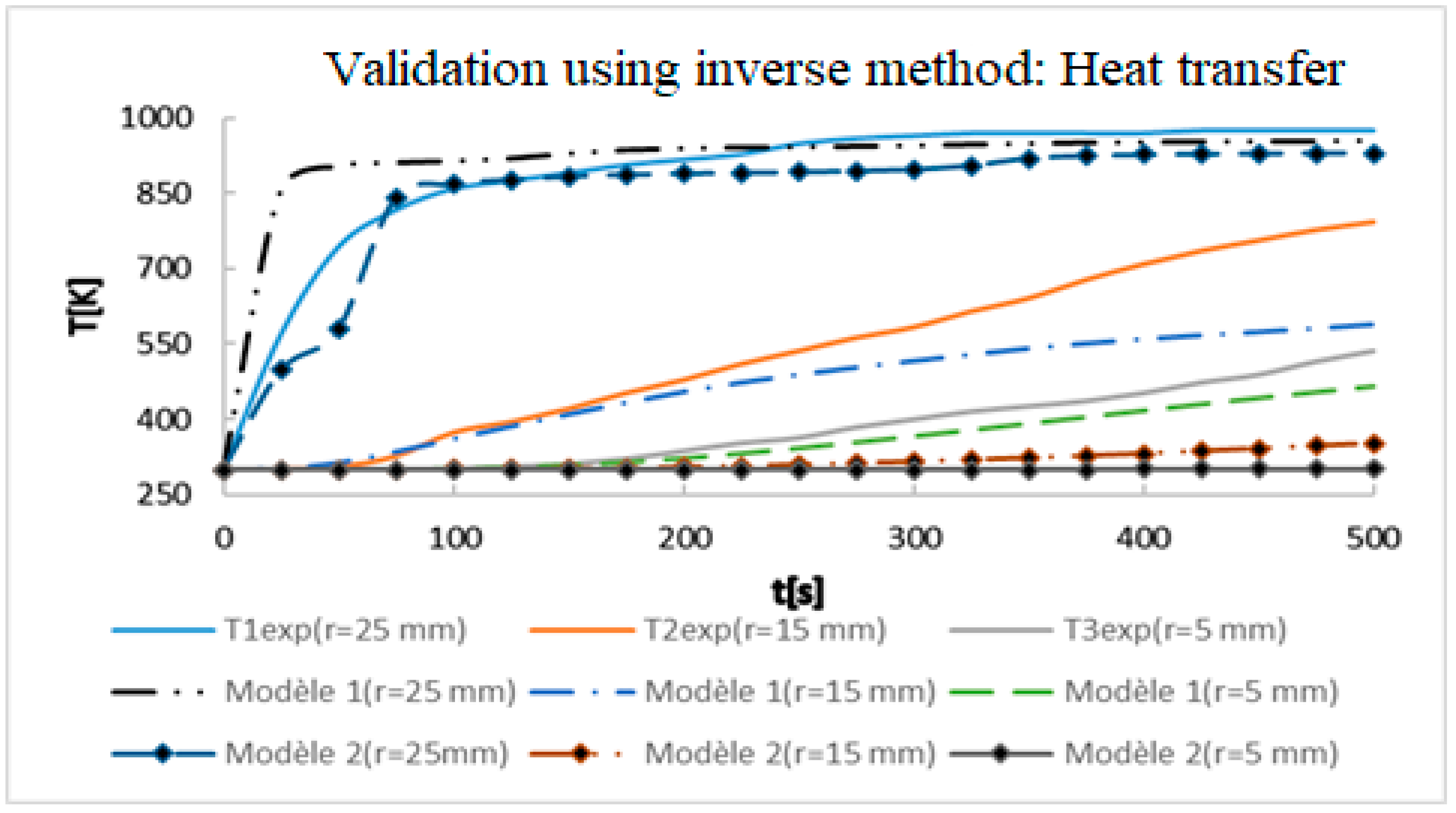
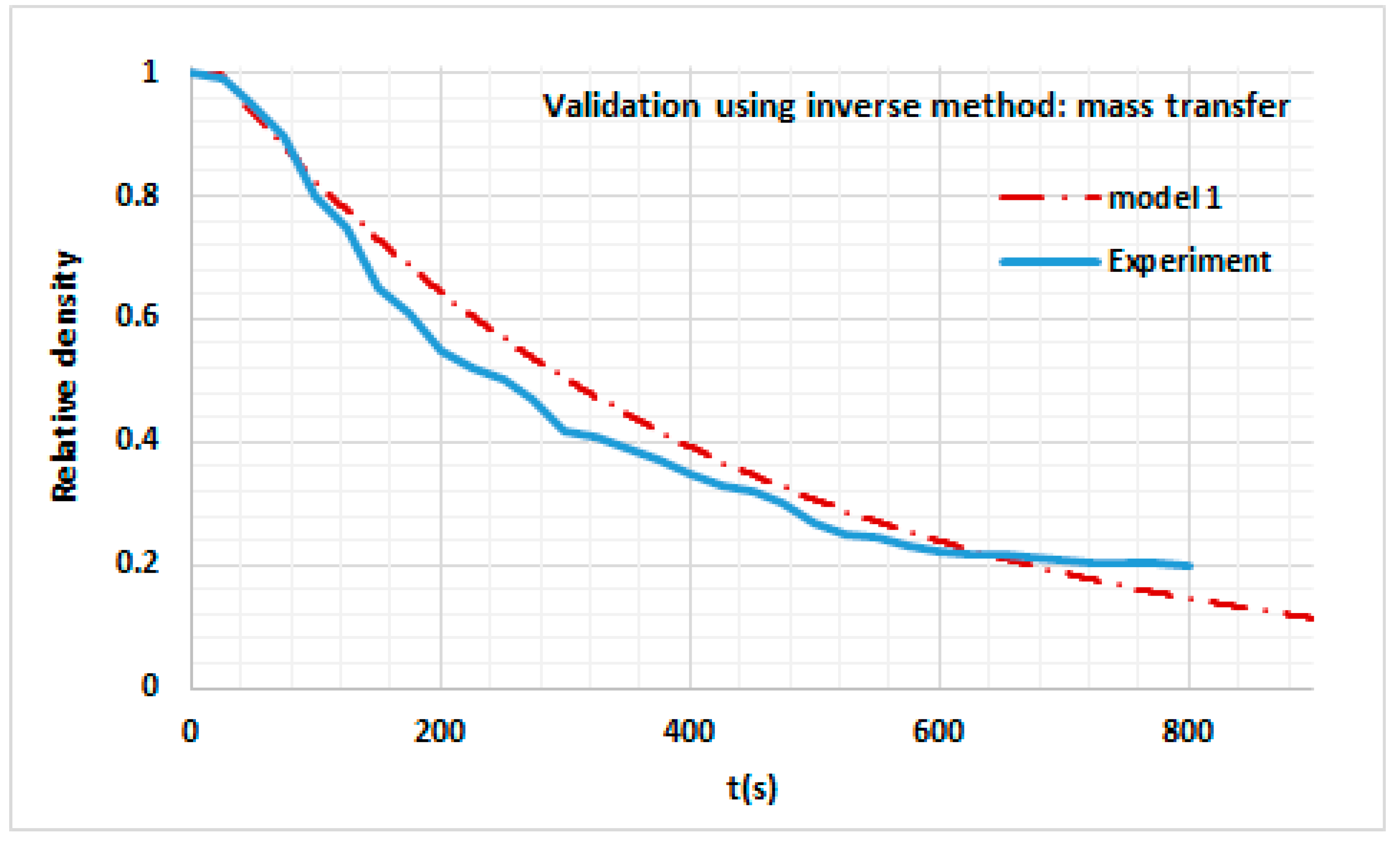
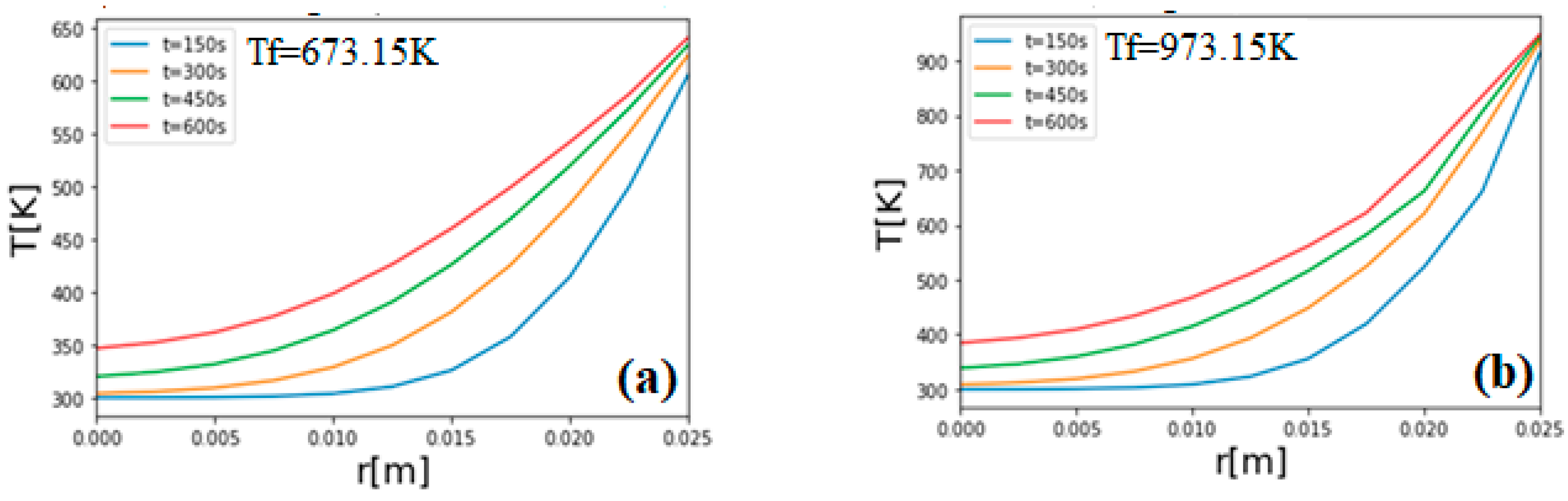
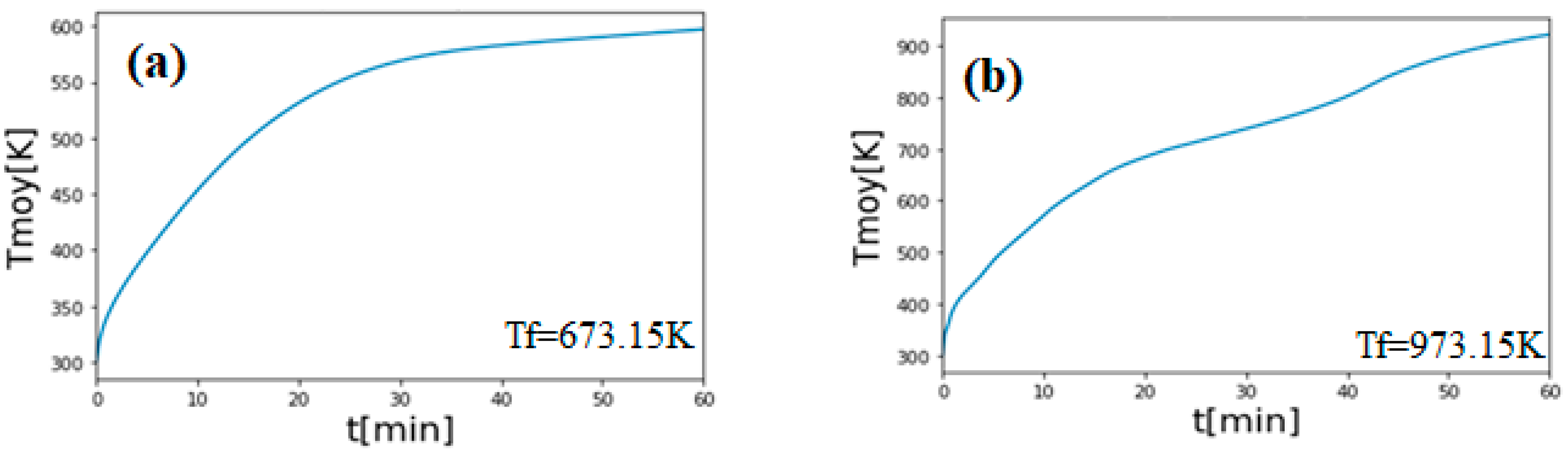
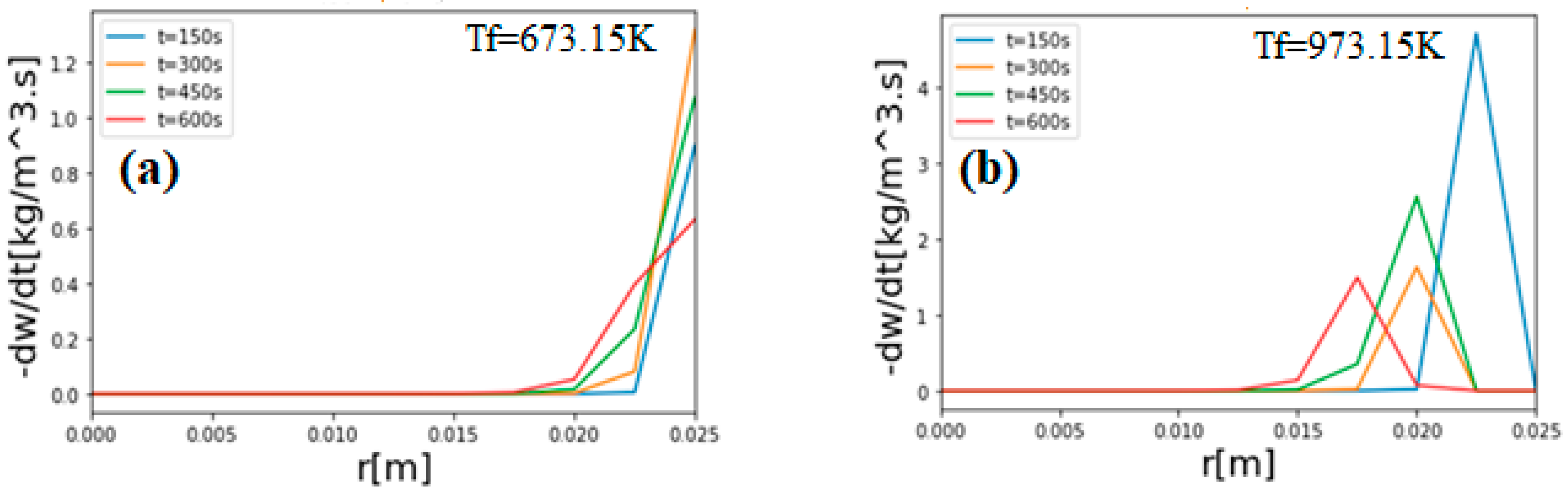
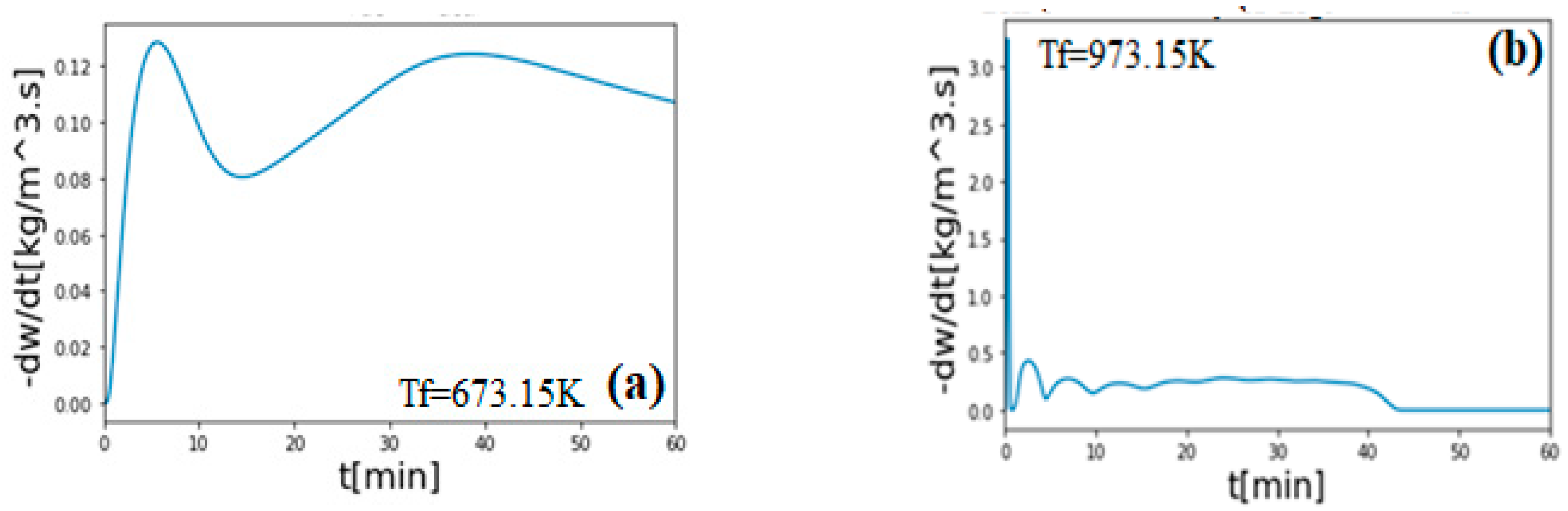
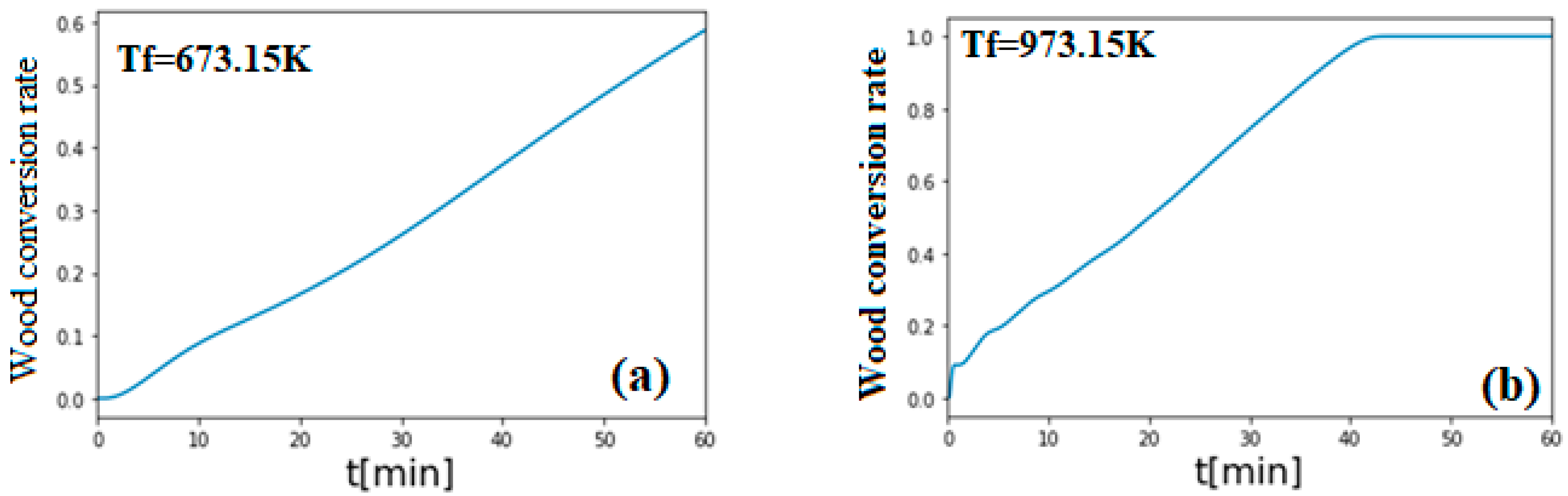
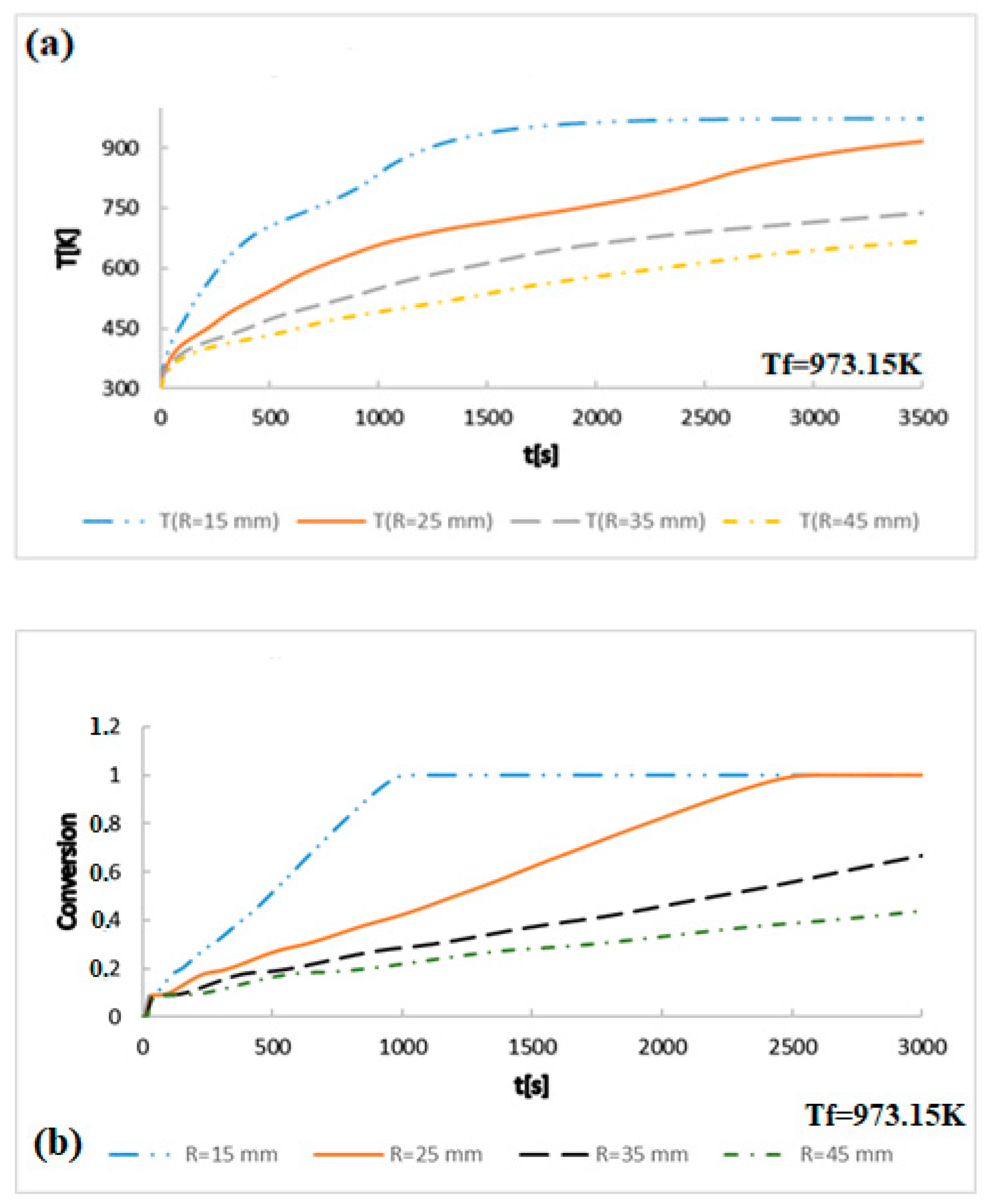
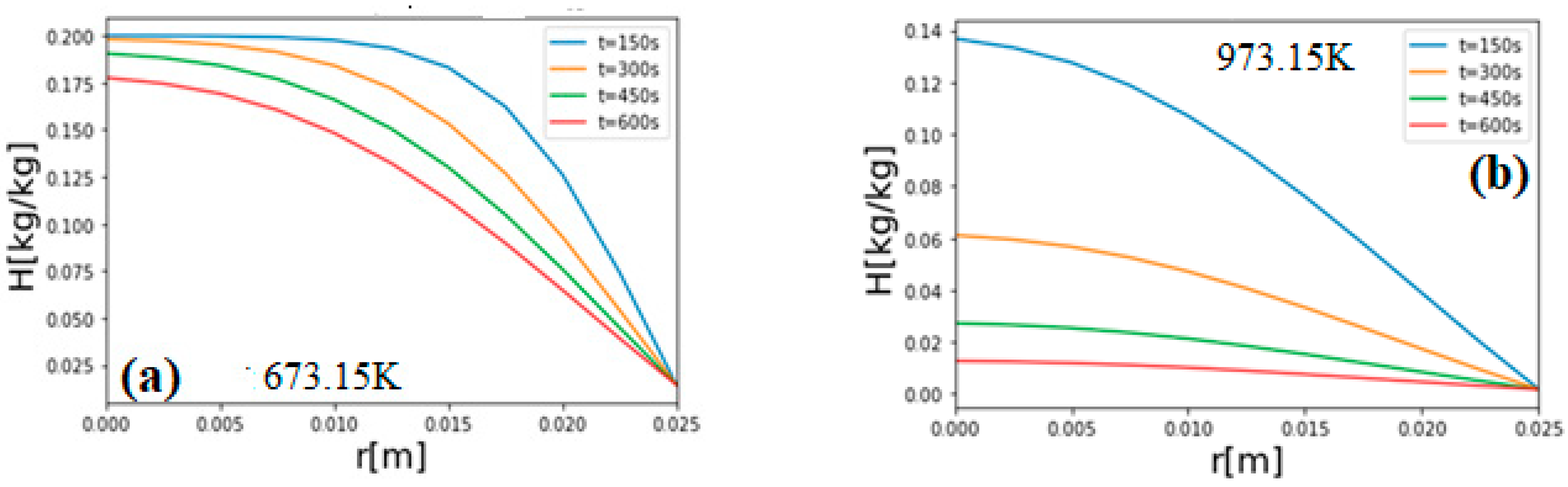
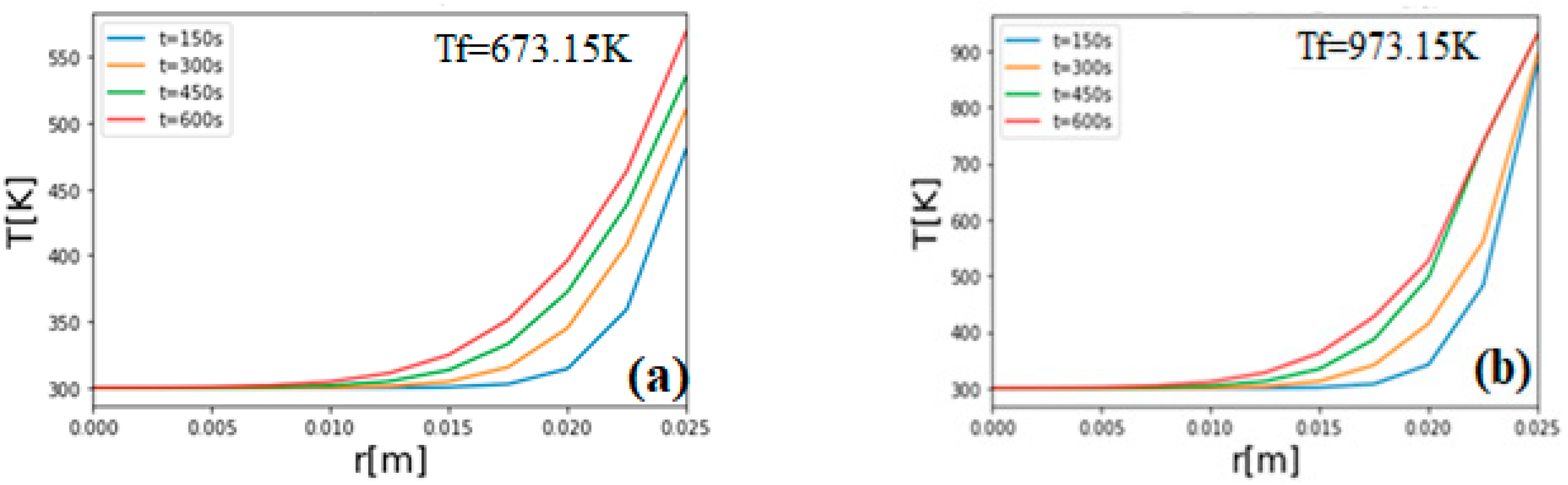
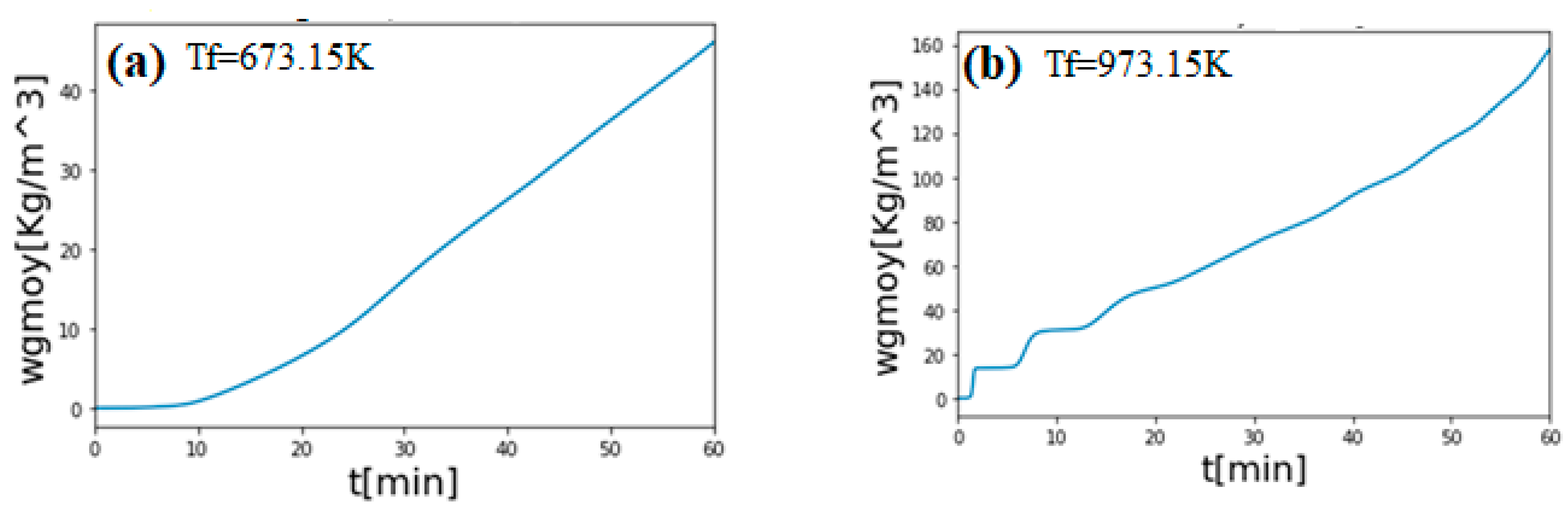
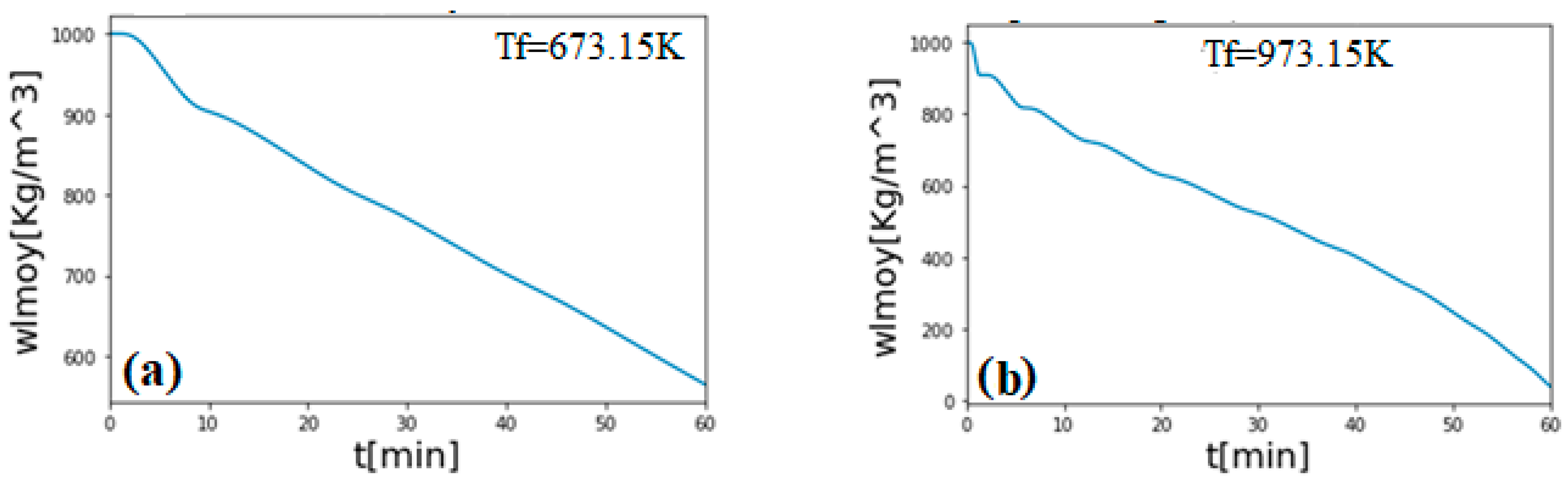
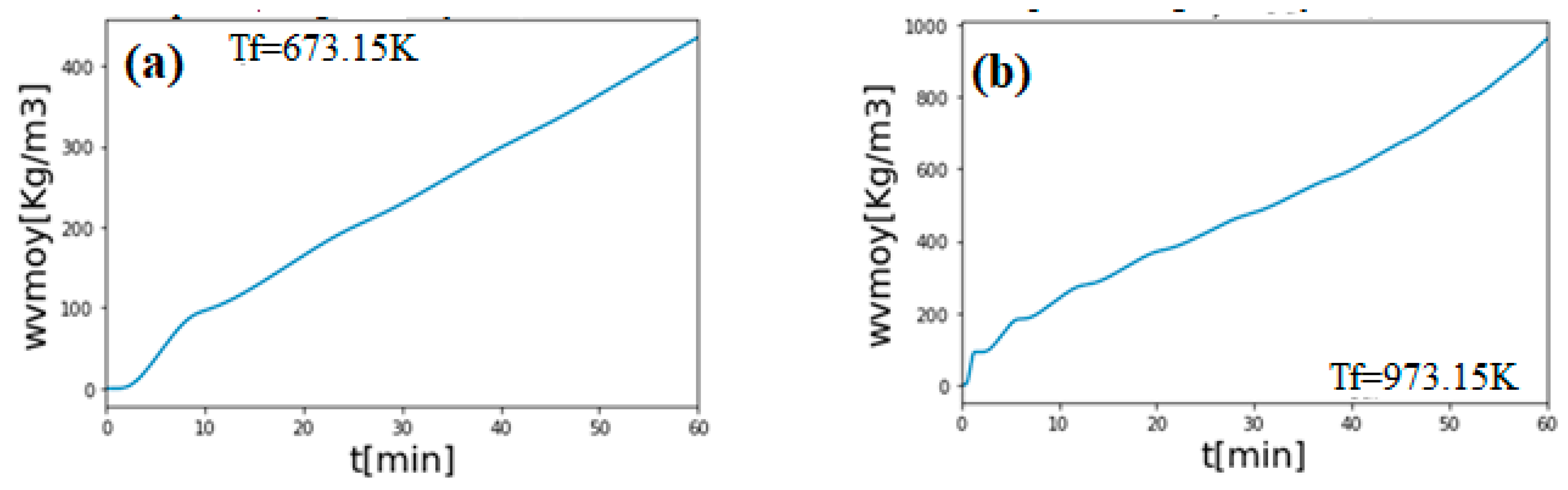
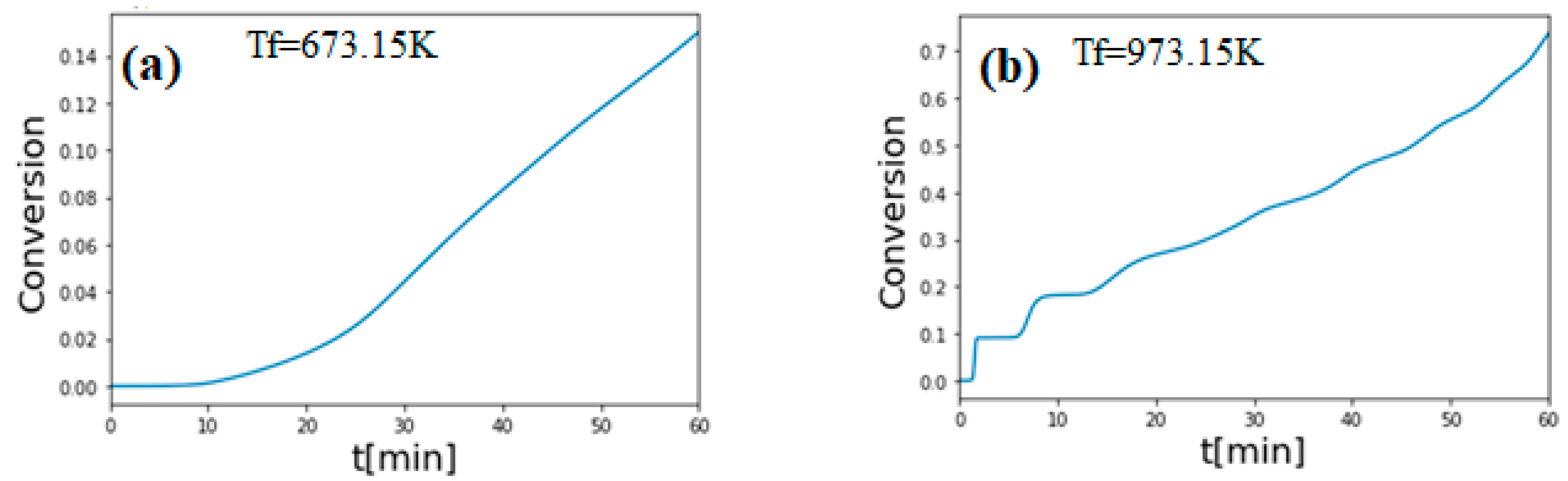
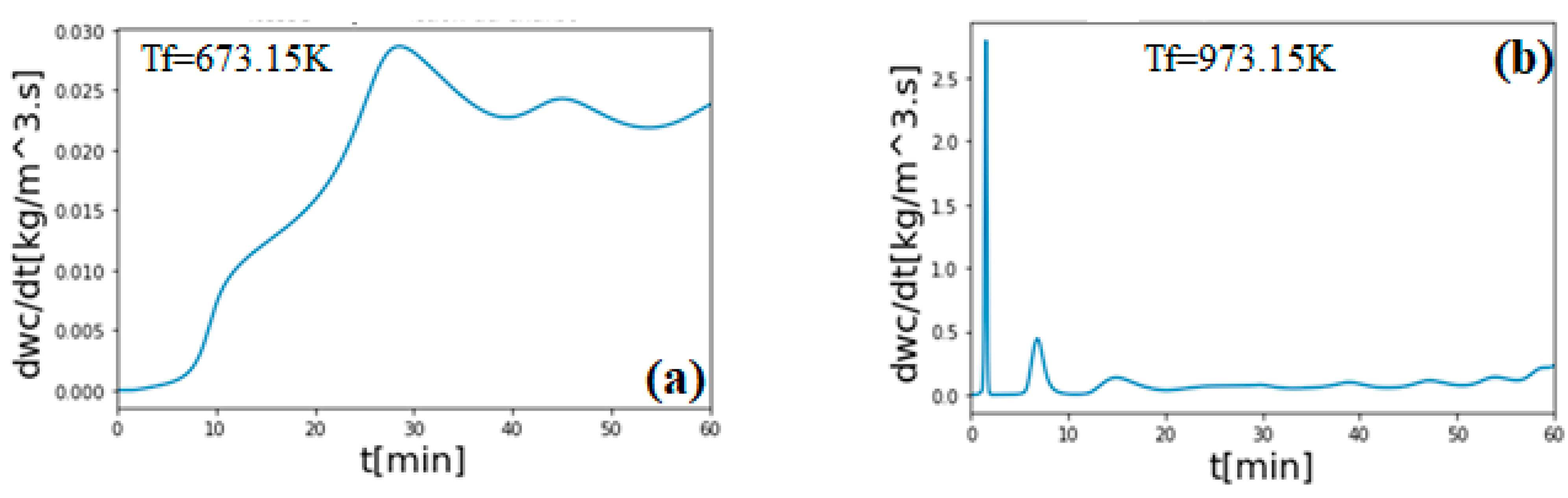
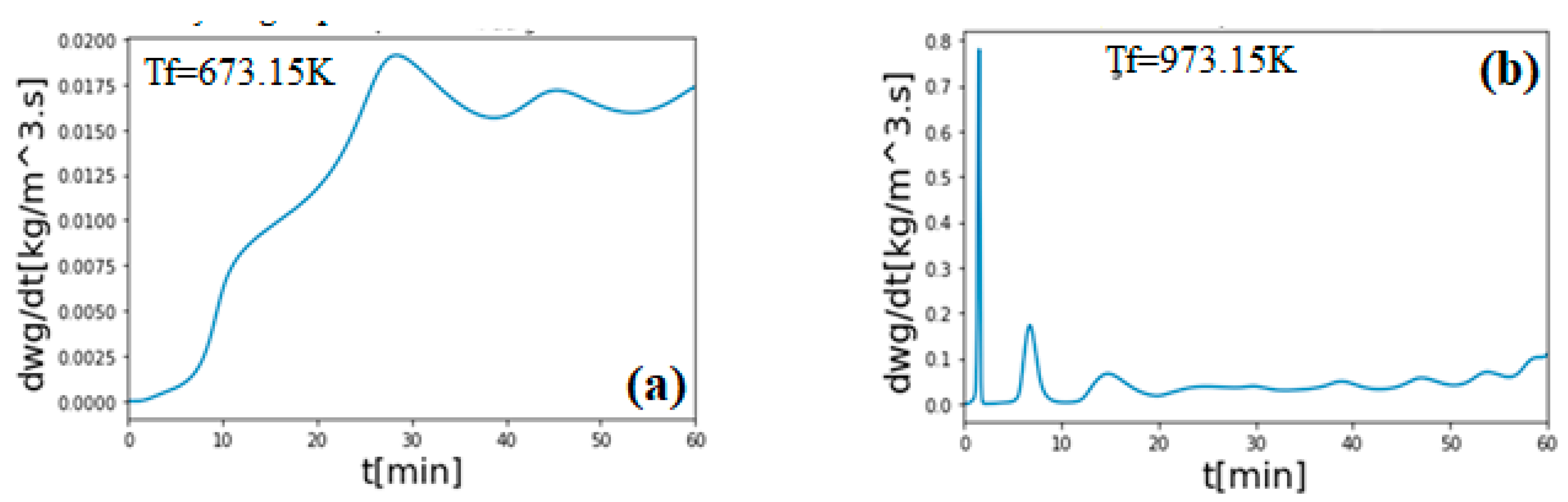
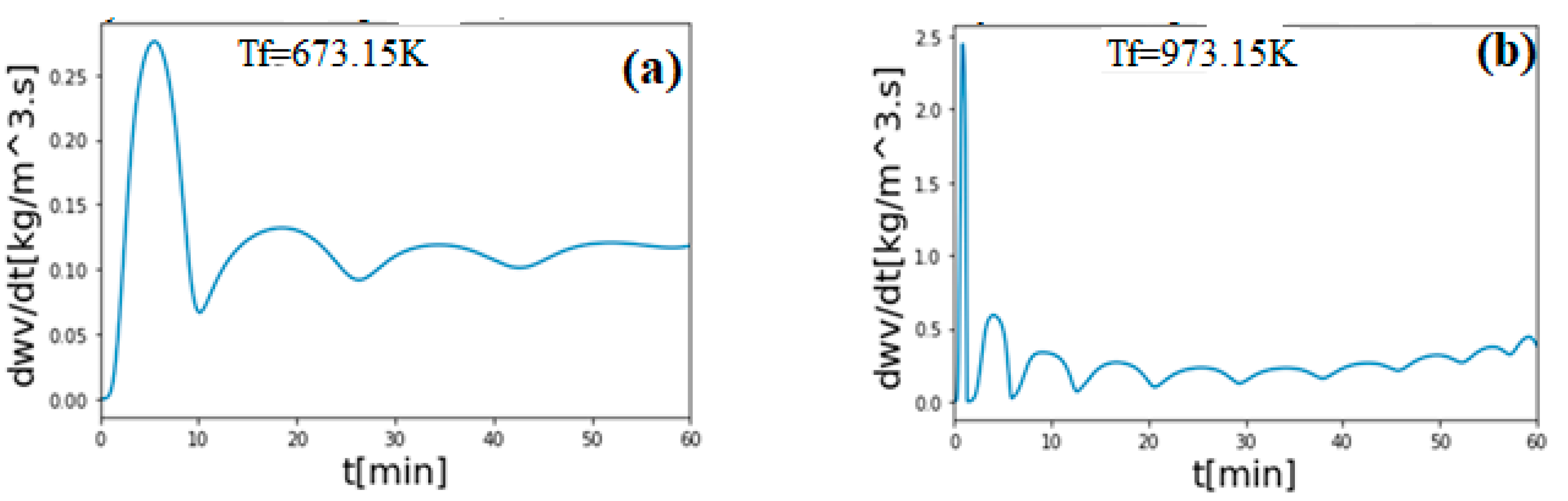
3. Results and Discussion
Validation of the Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Parameters | Units | Descriptions |
| Latin letters | ||
| Frequency factor | ||
| Specific heat | ||
| Mass diffusivity | ||
| Activation energy | ||
| Convective exchange coefficient | ||
| Moisture content | ||
| Enthalpy of the reaction | ||
| Rate constant | ||
| Heat of pyrolysis | ||
| Heat source | ||
| Relative humidity | ||
| Perfect gas constant | ||
| Temperature | ||
| Greek letters | ||
| Emissivity | ||
| Conversion | ||
| Thermal diffusivity | ||
| Thermal conductivity | ||
| Density | ||
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | ||
| Equilibrium moisture content | ||
| Indices | ||
| Initial | ||
| Air | ||
| Wood | ||
| Charcoal | ||
| Gas | ||
| Wet | ||
| Component | ||
| Tar | ||
| moy | average |
References
- Simo-Tagne, M.; Ndukwu, M.C.; Azese, M.N. Experimental modelling of a solar dryer for wood fuel in epinal (France). Modelling 2020, 11, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berahab, R. Energies Renouvelables en Afrique: Enjeux; Défis et Opportunités; Policy Center for the New South: Rabat, Morocco, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Economique des Nations Unies Pour l’Afrique. Développement des Statistiques du Bilan Energétique et d'un Modèle de Système Energétique Pour l'Union des Comores. Available online: https://archive.uneca.org/sites/default/files/images/SROs/EA/French/developpement_des_statistiques_du_bilan_energetique_et_dun_modele_de_systeme_energetique_pour_lunion_des_comores.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Union des Comores, Strategie Nationale et Plan D’action Actualisés Pour la Diversité Biologique. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/km/km-nbsap-v2-fr.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Evaluation des Ressources Forestières Mondiales 2010—Rapport National: Comores. Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/card/fr/c/423807a6-f7a9-5458-80a1-e6e3b437c44d/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Vikram, S.; Rosha, P.; Kumar, S. Recent modeling approaches to biomass pyrolysis: A review. Energy Fuels 2021, 9, 7406–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, C.H.; Crank, J.; Malan, D.H. The combustion of wood, part 1. Camb. Philos. Soc. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1946, 42, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinney, E.R. The combustion of wooden dowels in heated air. Combust. Inst. 1965, 10, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Blasi, C. Modeling and simulation of combustion processes of charring and non-charring solid fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1993, 19, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, K.; Kase, M. Determination of kinetic parameters for pyrolysis of cellulose and cellulose treated with ammonium phosphate by differential thermal analysis and thermal gravimetric analysis. J. Polym. Sci. 1967, 5, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Blasi, C. Analysis of convection and secondary reaction effects within porous solid fuels undergoing pyrolysis. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1993, 90, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Fang, M.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Modeling pyrolysis of wet wood under external heat flux. Fire Saf. J. 2007, 142, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.C.; Atreya, A.; Baum, H.R. Experimental and theoretical investigation of heat and mass transfer processes during wood pyrolysis. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-C.R.; Kelbon, M.; Krieger, B.B. Modelling and experimental verification of physical and chemical processes during pyrolysis of a large biomass particle. Fuel 1985, 64, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J.; Richard, J.-R. Simultaneous drying and pyrolysis of solid fuel particles. Combust. Flame 1996, 1106, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larfeldt, J.; Leckner, B.; Melaaen, M.C. Modelling and measurements of heat transfer in charcoal from pyrolysis of large wood particles. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 118, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo-Tagne, M. Contribution à L’étude du Séchage des Bois Tropicaux au Cameroun: Aspects Caractérisation, Modélisation Multi-Echelle et Simulation. Le cas des bois D’ayous (Triplochiton Scleroxylon) et d’ébène (Diospyros Crassiflora). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Yaoundé 1, Yaounde, Cameroon, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Özisik, M.N.; Orlande, H.R.; Colaço, M.J.; Cotta, R.M. Finite Difference Methods in Heat Transfer. 2017. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.1201/9781315121475/finite-difference-methods-heat-transfer-necati-%C3%B6zi%C5%9Fik-helcio-orlande-marcelo-jos%C3%A9-cola%C3%A7o-renato-machado-cotta (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Di-Blasi, C. Processes of flames spreading over the surface of charring fuels: Effects of the solid thickness. Combust. Flame 1994, 197, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurner, F.; Mann, U. Kinetic investigation of wood pyrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1981, 20, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larfeldt, J.; Leckner, B.; Melaaen, M. Modelling and measurements of the pyrolysis of large wood particles. Fuel 2000, 179, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Blasi, C.; Hernandez, E.G.; Santoro, A. Radiative pyrolysis of single moist wood particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 139, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Blasi, C.; Branca, C.; Masotta, F.; De-Biase, E. Experimental analysis of reaction heat effects during beech wood. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preau, A. Etude de la Pyrolyse de Composés Lignocellulosiques et Modélisation de ce Processus. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Nancy, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Diwan, P. Study of thermal decomposition process and the reaction mechanism of the eucalyptus wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, G.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, P.; Upadhyay, S. Kinetic analysis of the slow pyrolysis of paper wastes. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkoussas, B.; Consalvi, J.-L.; Porterie, B.; Sardoy, N.; Loraud, J.-C. Modelling thermal degradation of woody fuel particles. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, G.; Van de Steene, L.; Martin, E.; Gelix, F.; Salvador, S. Gasification of char from wood pellets and from wood chips: Textural properties and thermochemical conversion along a continuous fixed bed. Fuel 2012, 102, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayhead, G.; Snell, R.; Shelly, J.R. Pyrolysis of Woody Biomass. pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ucanr.edu/sites/woodybiomass/files/78980.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- Commandré, J.-M.; Lahmidi, H.; Salvador, S.; Dupassieux, N. Pyrolysis of wood at high temperature: The influence of experimental parameters on gaseous products. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widiyannita, A.M.; Cahyono, R.B.; Budiman, A.; Sutijan; Akiyama, T. Study of pyrolysis of ulin wood residues. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1755, 050004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charvet, F.; Silva, F.; Ruivo, L.; Tarelho, L.; Matos, A.; Figueiredo da Silva, J.; Neves, D. Pyrolysis characteristics of undervalued wood varieties in the portuguese charcoal sector. Energies 2021, 14, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananias, F.D.J.; Rosi, P.E.; Álison, M.da.-S.; Aécio, D.S.J.; Oliveira, M.P.; Brito, J.O.; Napoli, A.; Magalhães, B.B. Investigating the pyrolysis temperature to define the use of charcoal. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2020, 78, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arous, S.; Koubaa, A.; Bouafif, H.; Bouslimi, B.; Braghiroli, F.L.; Bradai, C. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and wood species on the properties of biochar pellets. Energies 2021, 14, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.U.; Zwawi, M.; Capareda, S.C.; Iqbal, H.; Algarni, M.; Felemban, B.F.; Bahadar, A.; Waqas, A. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on product distribution and characteristics of anaerobic sludge. Energies 2020, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Parameters | Numerical Values | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uni-Reactionary Approach | ||||
| (W.m−1.K−1 ) | [19] | |||
| 0.8 | [12] | |||
| (kg.m−3) | 650 | [19] | ||
| (J.kg−1.K−1) | 1.46 | [19] | ||
| (W.m−2.K−1) | 20 | [13] | ||
| (kJ.kg−1) | −418 | [20] | ||
| (s−1) | [9] | |||
| (kJ.mol−1) | [9] | |||
| Multi-reaction approach | ||||
| Pyrolysis reaction | Drying reaction | |||
| (s−1) | (s−1) | (s−1) | ||
| (s−1) | [12,20] | |||
| (kJ.mol−1) | 106.5 | 88.6 | 88 | [12,20] |
| (kJ.kg−1) | −420 | −420 | −2440 | [12] |
| (J.kg−1.K−1) | [12] | |||
| (m2.s−1) | In this work | |||
| (W.m−1.K−1 ) | 0.105 | |||
| (W.m−1.K−1 ) | ||||
| (m2.s−1) | ||||
| (kg.kg−1) | 0.2 | |||
| (%⁄100) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assoumani, N.; Simo-Tagne, M.; Kifani-Sahban, F.; Tagne Tagne, A.; El Marouani, M.; Obounou Akong, M.B.; Rogaume, Y.; Girods, P.; Zoulalian, A. Numerical Study of Cylindrical Tropical Woods Pyrolysis Using Python Tool. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413892
Assoumani N, Simo-Tagne M, Kifani-Sahban F, Tagne Tagne A, El Marouani M, Obounou Akong MB, Rogaume Y, Girods P, Zoulalian A. Numerical Study of Cylindrical Tropical Woods Pyrolysis Using Python Tool. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):13892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413892
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssoumani, Nidhoim, Merlin Simo-Tagne, Fatima Kifani-Sahban, Ablain Tagne Tagne, Maryam El Marouani, Marcel Brice Obounou Akong, Yann Rogaume, Pierre Girods, and André Zoulalian. 2021. "Numerical Study of Cylindrical Tropical Woods Pyrolysis Using Python Tool" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 13892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413892
APA StyleAssoumani, N., Simo-Tagne, M., Kifani-Sahban, F., Tagne Tagne, A., El Marouani, M., Obounou Akong, M. B., Rogaume, Y., Girods, P., & Zoulalian, A. (2021). Numerical Study of Cylindrical Tropical Woods Pyrolysis Using Python Tool. Sustainability, 13(24), 13892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413892







