Abstract
Comprehensively monitoring indoor environmental quality (IEQ) parameters and their dynamic relations is essential to ensure improved productivity and a healthy environment for building occupants. Although IEQ significantly influences working efficiency, studies addressing this aspect with researchers in institutes as the focal point are limited. Thus, this study employed drill-down analyses, such as floor-by-floor and building-by-building examinations and used an occupant IEQ survey approach to evaluate working conditions in research buildings. This study systematically and objectively assessed IEQ using the Korea building occupant survey system. The results indicate that acoustic qualities affect the work productivity and satisfaction of the building occupants. The floor-by-floor analysis is necessary to identify IEQ factors and the reasons for the satisfaction of occupants. Additionally, it is important to improve the user-friendliness of the system, implement frequent survey distribution systems, and empirically analyze data associations among building, spatial, and demographical characteristics.
1. Introduction
People nowadays spend up to 87 percent of their time indoors, whether in a home or business facility, so they are constantly exposed to the indoor environment [1]. It is critical to completely comprehend the elements impacting indoor environmental quality (IEQ), their interdependence, complexity, and dynamic nature, as well as their influence on people′s health and productivity [2,3]. To this end, many recent studies have focused on IEQ encompassing various factors affecting the satisfaction of occupants with the indoor environment and their health, work efficiency, and productivity [4,5,6].
IEQ surveys are conducted on diverse building typologies such as office, residential, and educational buildings because IEQ factors vary depending on the properties of each building typology [3].
In particular, IEQ assessments for buildings related to the educational environment focus on analyzing the average response of a large group of students regarding educational buildings such as schools and universities [7,8,9,10]. There are few studies on the staff including non-teaching and teaching staff [11,12,13]. In addition, although IEQ has a significant effect on research efficiency and work productivity in a research office [7], few studies have focused on researchers in a research institute [14]. Thus, it is important to conduct IEQ assessments for research buildings to expand the diversity of building typology and occupant.
Furthermore, there are several analyses regarding the average response of a large population in the overall building. However, spatial differences in the IEQ are evident between buildings [15]. In many previous studies that involved empirical investigations, the effect of IEQ on user satisfaction was examined for buildings; however, it was not investigated for the occupants of different floors. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a specific drill-down analysis such as from a building-by-building and floor-by-floor examination for gaining further insights into the IEQ.
Most evaluations of IEQ studies are conducted using paper-based surveys in Korea, with many of these evaluations being one-off surveys and thus fragmentary. Paper-based surveys can take a considerably long time and be very expensive. In the 1990s, online survey tools were introduced in the United States, United Kingdom, and elsewhere to explore measures for significantly reducing the survey time, cost, and effort involved in traditional paper surveys [16]. A web-based survey system equipped with appropriate survey questions and a user interface enables the quick collection of survey response information and helps process and analyze the response results using an accumulated database [17]. Lee and Kim [14] compared and analyzed the online building occupant survey systems in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia and, Lee et al. [18] developed a new prototype of the Korea building occupant survey system (KBOSS).
To date, no studies have been conducted at any research institute buildings for occupants including researchers and administrators to examine IEQ and working productivity. Thus, the study investigates the IEQ parameters and overall satisfaction and productivity of workspace floors depending on the different occupants (researchers and administrators). Further, this study focuses on an occupant IEQ surveying approach with building-by-building and floor-by-floor analyses on research buildings in Korea. The outcome of the current assessment will assist in identifying and evaluating IEQ assessment in research buildings. This study, to the best of our knowledge, is the first systematic study that objectively assesses IEQ using KBOSS to build the Korean IEQ database and describes the IEQ survey criteria and factors, research building, occupants’ information (Section 2), and the statistical results for the groups of researcher and administrator (Section 3). Responses were gathered and quantitatively analyzed using a statistical software package (IBM SPSS 27.0). Further, the paper investigates a building-by-building and floor-by-floor analysis of research buildings (Section 4). Finally, the paper ends with a discussion and a conclusion with recommendations for further research (Section 5 and Section 6).
2. IEQ Survey in Research Institutes
2.1. Characteristics of Occupants
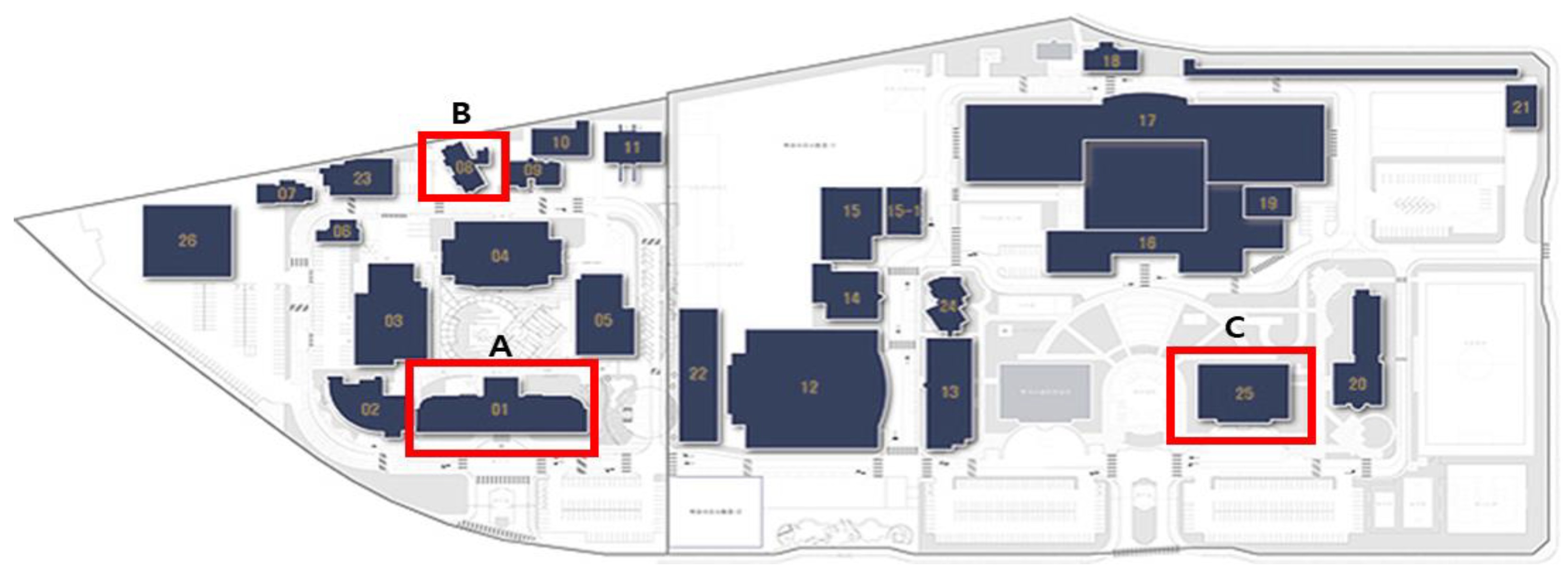
The survey respondents included occupants of three buildings used for research and administration at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT): A_bldg (researcher’s space 70%, administrator’s space 20%, other space 10%), B_bldg (researcher’s space 100%), and C_bldg (researcher’s space 30%, administrator’s space 60%, other space 10%). These three buildings were selected because several researchers and administrators work in these three buildings compared to the other buildings at the KICT, which are mostly used as laboratories and test facilities. The location layout of buildings A–C is shown in Figure 1.
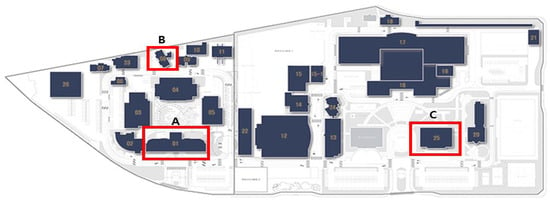
Figure 1.
Location layout of the surveyed buildings (A–C).
In this study, only the web-based survey system, KBOSS, was going to be used; however, as this was a first-time survey, both the online and paper surveys were conducted in parallel to increase the participation rate of occupants and obtain the maximum number of responses on the various improvements of the system. The survey was conducted during a two-week period from 9 September to 20 September 2019.
The survey was given to 200 occupants including the researchers and administrators of the three buildings, who had their own office seats. The final count of the collected responses was 151: 80 from A_bldg (1–5F), 21 from B_bldg (3, 4, 6, 7, and 8F), and 50 from C_bldg (2–5F). The 5th floor of B_bldg used as a laboratory, and the 1st floor of C_bldg used as a community space without occupants were excluded from the survey. Both floors are used for the temporary experiments or meetings, so there are no regular occupants. The subjects were divided into two groups based on gender (male and female), and into two groups based on age: junior group (respondents between 20–40 years) and senior group (respondents between 40–65 years).
Occupants were further divided based on their job function. The job functions at a Korean government-funded research institute include researchers, administrators, technicians, and others (such as students and interns). In this study, post-doctoral researchers and student interns were included in the researcher group, and technicians who deal with experiment supports were included in the administrator group, given their low response rate for the analysis. In addition, the questionnaire included questions on the working hours and duration of employment of the respondents in the three buildings for determining the reliability of the response in terms of whether the IEQ of the workspace of an occupant was represented accurately. The results of the survey responses are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the sample.
2.2. IEQ Factors and Survey Questionnaires
Various criteria and parameters of the IEQ have been proposed in previous studies based on the survey building type, country, and place [19,20]. Although previous survey-based studies were consulted in this study, questions were amended to improve their suitability for an occupant satisfaction survey in a research institute that utilizes the web-based occupant IEQ survey of the UC Berkeley Center for the Built Environment (CBE) published in the ASHRAE [21] guidebook. In addition to its long history, the occupant IEQ survey of CBE is used worldwide and is recommended by several protocols such as EcoSmart and ASHRAE’s performance measurement protocols (PMP) [19]. Seven IEQ criteria were established in this study including the four principal criteria of IEQ including thermal comfort, air quality, lighting, and acoustic quality [22], with three additional criteria including personal workspace, office layout, and overall building layout. Further, a questionnaire comprised five satisfaction domains: four principal criteria of IEQ and the office layout, which significantly affects productivity [23].
In addition, the satisfaction level for each factor was designed based on the 7-point Likert scale (with 1 being highly dissatisfied and 7 being highly satisfied). Respondents are asked to provide reasons for dissatisfaction or additional relevant information if points 1, 2, or 3 were selected, which are lower than the expected satisfaction level (4 points). The IEQ and productivity criteria of the respondents and the survey questions are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Respondent’s IEQ and productivity criteria and survey questions.
2.3. Survey Implementation
KBOSS was used initially to build the large amount of data. The method of using the building occupant survey system involves the following steps:
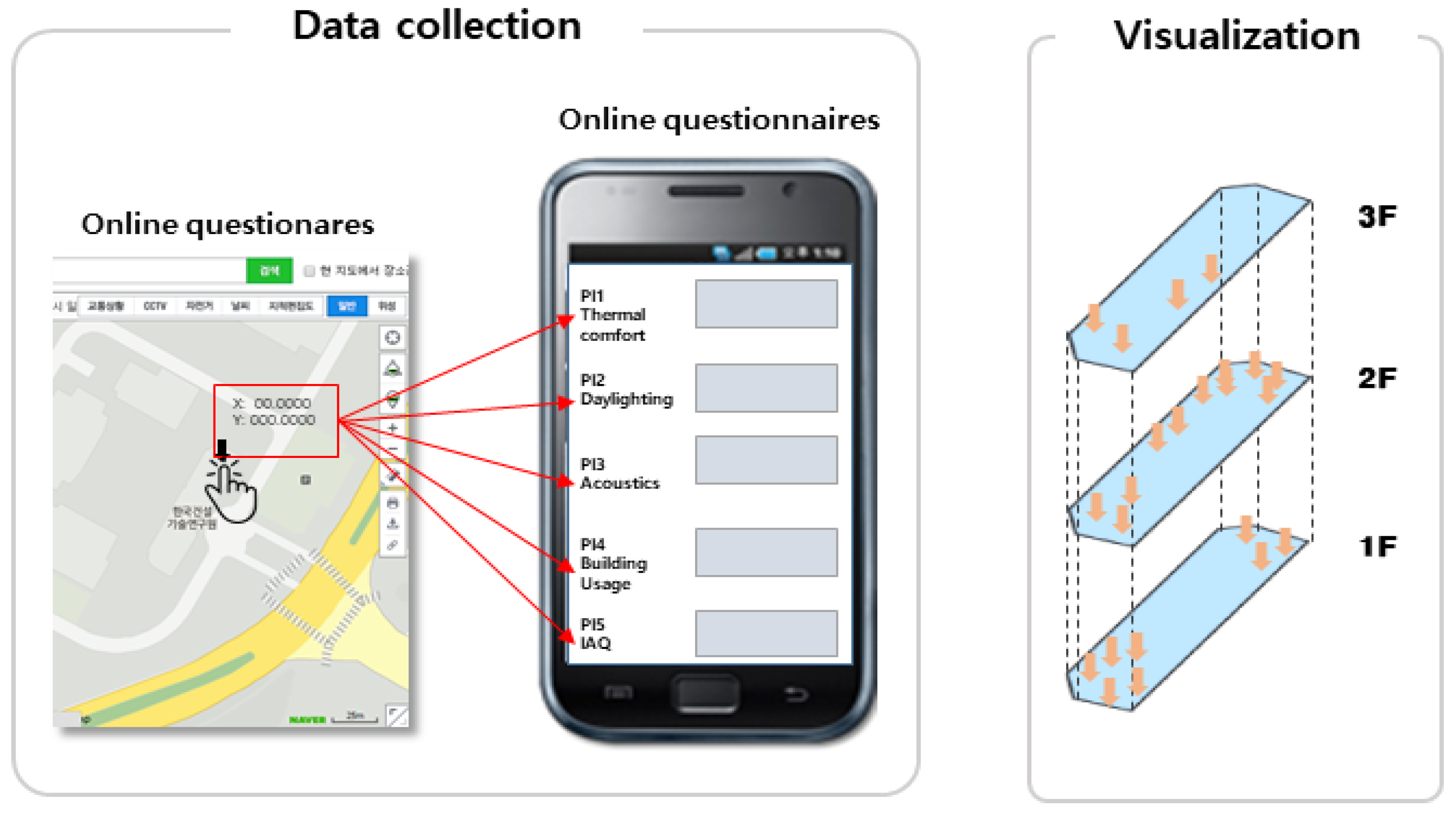
- The office building address of the user is entered, searched, and selected to complete the online survey as shown in Figure 2.
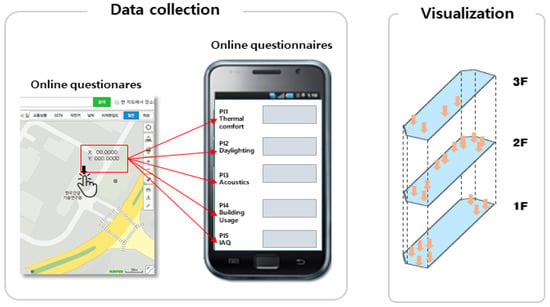 Figure 2. Conceptual model: Data collection of latitude (x), longitude (y), and height (z) with online questionnaire [S] (left). Visualization of floor-based information (right).
Figure 2. Conceptual model: Data collection of latitude (x), longitude (y), and height (z) with online questionnaire [S] (left). Visualization of floor-based information (right). - The office location of the user is selected on the interior map of his or her office building. That is, from the pop-up window on the right-hand side, as shown in Figure 2, the user can directly click the latitude and longitude points [x, y] on the right map and select the height [z] in the left selection box.
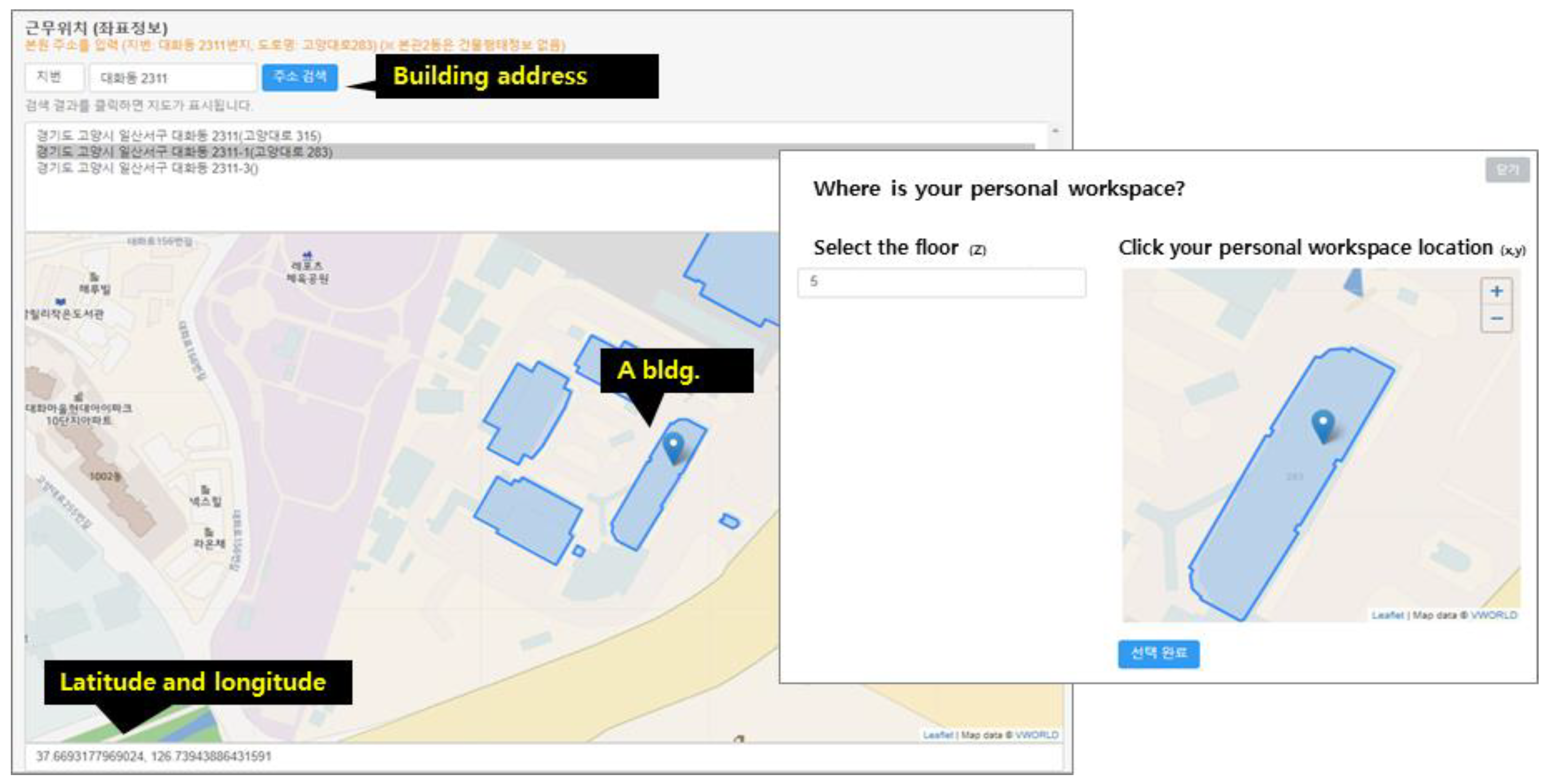
The z-coordinate floor information is automatically linked to the floor numbers at each building address using the building information open database provided by the Korean government. Figure 3 illustrates the concept of vertical visualization of the response results as well as horizontal floors [14,18]. However, in this study, KBOSS was used only for the survey implementation, but not for the floor analysis.
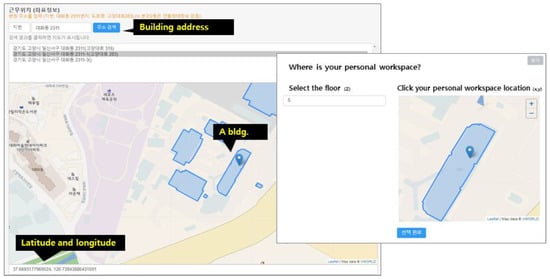
Figure 3.
Example of GIS-based survey interface of the address of A_bldg and floor (latitude, longitude, floor number) of occupants in the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis Results of Individual Measurement Variables
The means and standard deviations of each examined feature are provided on the appropriate scale. The model considered in this study comprises seven latent variables: office layout satisfaction, thermal comfort satisfaction, air quality satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, noise satisfaction, overall satisfaction, and productivity. A descriptive statistical analysis was performed to determine the mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis of the variables to be used in the regression analysis. Further, there was no variable with a standard deviation of 3 or more, and all variables had |skewness| < 2 and |kurtosis| < 2, which indicates a normal distribution. Table 3 lists the descriptive statistical analysis results of the individual measurement variables.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of individual measurement variables (n = 151).
3.2. Exploratory Factor and Reliability Analyses of Independent Variables
Exploratory factor analysis was performed to examine whether the measurement items of the independent variable used in this study were grouped into the same factor. Principal component analysis was used for factor extraction, and the orthogonal Varimax rotation was used as the rotation method. The analysis was conducted on office layout satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, and noise satisfaction, which comprise multiple measurement items besides independent variables that consist of single items such as thermal comfort satisfaction and air quality satisfaction. No measurement items were removed during the analysis process. The analysis results indicate that the KMO value was 0.691; Bartlett′s sphericity test results indicate that the significance probability was less than 0.05, which confirms that the model was suitable. Further, the cumulative variance was 77.120%, which implies the explanatory power of the three factors was satisfactory. For the constituent items of each factor, the first factor contained three items, and the second and third contained two items each. According to the content of the constituent items, the first factor was called office layout satisfaction; the second, lighting satisfaction; and the third, noise satisfaction. All factor loading values were above 0.5, which indicates that the validity was satisfied. Further, a reliability analysis was conducted to examine the internal consistency of each factor. Cronbach’s α was used to determine the internal consistency, and the Cronbach’s α value for each variable was 0.733–0.873, which is a satisfactory level (Cronbach’s α > 0.7). Table 4 summarizes the analysis results.

Table 4.
Results of exploratory factor analysis and reliability analysis for independent variables.
3.3. Exploratory Factor and Reliability Analyses for Dependent Variables
Productivity 1 was removed from the analysis because of a lack of validity. The final analysis results indicate that the KMO value was 0.713, and the significance probability of Bartlett′s sphericity test was less than 0.05, which confirm the model was suitable. The cumulative variance was 69.438%, which suggests that the explanatory power of the two factors was satisfactory. For the constituent items of each factor, the first factor contained four items; the second contained two. Based on the contents of the composed items, the first factor was named productivity, and the second, overall satisfaction. All factor loading values were above 0.5, which indicates that the validity was satisfied. Further, a reliability analysis was performed to examine the internal consistency of each factor. Cronbach’s alpha was used to determine the internal consistency, and Cronbach’s α value for each variable was 0.756–0.889, which was found to be a satisfactory level (Cronbach’s α > 0.7). Table 5 summarizes the analysis results.

Table 5.
Results of exploratory factor analysis and reliability analysis for dependent variables.
3.4. Effect of Office Layout Satisfaction, Thermal Comfort Satisfaction, Air Quality Satisfaction, Lighting Satisfaction, and Noise Satisfaction on Overall Satisfaction
Multiple regression analysis was performed to examine the effects of office layout satisfaction, thermal comfort satisfaction, air quality satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, and noise satisfaction on overall satisfaction. The variables were calculated for office layout satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, noise satisfaction, and overall satisfaction while excluding thermal comfort satisfaction and air quality satisfaction, which comprised a single item. Then, the average value was used for analysis. The analysis results indicate that the regression model was statistically significant (F = 77.273, p < 0.001), and the explanatory power of the regression model was approximately 72.7% (the adjusted R-squared was approximately 71.8%; R² = 0.727, adj R² = 0.718). The Durbin–Watson statistic showed a value close to 2, which implies there was no problem in the assumption of the independence of the residuals. The variance inflation index (VIF) was less than 10, implying that there was no multicollinearity problem. Table 6 summarizes the analysis results. The results indicate office layout satisfaction, thermal comfort satisfaction, air quality satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, and noise satisfaction have significant positive (+) effects on overall satisfaction; the overall satisfaction increased with an increase in these factors.

Table 6.
Effect of independent variables on overall satisfaction.
3.5. Effect of Overall Satisfaction on Productivity
A linear regression analysis was performed to examine the effect of overall satisfaction on productivity. The mean value was used for analysis after calculating the variables for overall satisfaction and productivity. The analysis results indicate that the regression model was statistically significant (F = 38.452, p < 0.001), and the explanatory power of the regression model was about 20.5% (adjusted R-squared about 20.0%; R² = 0.205, adj R² = 0.200). The Durbin–Watson statistic showed a value close to 2, indicating that there was no problem in assuming the independence of the residuals. Table 7 summarizes the analysis results. The results of examining the significance of the regression coefficient indicate that the overall satisfaction (β = 0.453, p < 0.001) had a significant positive (+) effect on productivity, which implies productivity increased with an increase in overall satisfaction.

Table 7.
Effect of overall satisfaction on productivity.
3.6. Critical Ratio Tests of Path Differences by Occupation
A multi-group path analysis was performed to examine the path coefficient and significance of the research model by occupation and to test the path difference. Table 8 summarizes the analysis results.

Table 8.
Multi-group path analysis results.
A significant effect on overall satisfaction was observed in all variables because the researchers tended to gather in specific buildings and on specific floors. However, for the administrators, the effect on overall satisfaction was not significant in all variables because of various workplace variables, given that there were many subgroups such as a small number of people seated with the researchers on a single floor, a small number of people working on each floor, and a large group gathered on a single floor. Accordingly, in the future, it will be necessary to study the effect on the satisfaction of each group and the overall satisfaction based on the location of each floor and room of the administrator.
3.7. Differences in Overall Satisfaction According to Demographic Characteristics
One-way ANOVA was performed to determine whether the mean of overall satisfaction showed a significant difference according to demographic characteristics. Floors 1–14 indicate each of the 14 floors of the 3 buildings. Table 9 summarizes the analysis results. The analysis results indicate that was a significant difference in the overall satisfaction based on the floor (F = 2.634, p < 0.01). Further, there was no significant difference in overall satisfaction caused by the working period at the building, working period at the workplace, working hours per week, age, and gender. The variable, floor, seemed to play an important role in overall satisfaction.

Table 9.
Differences in overall satisfaction according to demographic characteristics.
4. Building-by-Building and Floor-by-Floor Analyses
As mentioned in the statistical analysis, it is necessary to specifically analyze the items and reasons for low satisfaction not only by building but also by floor. In this study, productivity was analyzed only to identify the relationship with overall satisfaction. However, the comparison results for the five productivity items (P1–P5) did not show any statistical significance, and thus, they were excluded from the analysis. The mean value for each floor of A_bldg, which has the highest number of responses and a very low satisfaction for specific items as a result of the comparison of buildings A, B, and C by item, was analyzed. Thus, this study used floor-by-floor analysis to investigate the reasons for dissatisfaction and find a solution for A_bldg. Finally, the reasons for a very low level of satisfaction on a certain floor were analyzed by classifying the results for the researchers and administrators.
The summary characteristics of the survey respondents including gender, age, job function, and the duration of employment in a given building are presented in Table 10. In this study, the respondents with an employment period of less than one year were excluded from the analysis as they were deemed unable to reliably answer the questions designed in the study.

Table 10.
Summary of the respondent characteristics.
In this study, personal workspace descriptions (Table 2), which were not expressed in terms of satisfaction level, were excluded from the analysis, while the responses to 11 questions under thesix types of IEQ criteria were analyzed. The average values of the satisfaction level for each of the questions in the buildings A–C are presented in Table 11. Assuming an average satisfaction level of between 3.5 and 4.5 as “normal,” questionnaire responses with an average satisfaction level <3.5 points were shaded red, and those with an average satisfaction level >4.5 were shaded green. The overall averages for the survey were found to be 4.5, 4.6, and 4.2 for buildings A, B, and C, respectively, i.e., all three buildings showed “normal” satisfaction levels. The average values of all questions showed a correlation with the subjective answers to questions G1 and G2 (overall satisfaction with the personal workspace and overall satisfaction with the building). With respect to the average value for each questionnaire response, all three buildings scored 4.2 or higher for questions G1 and G2. However, a detailed response to question F2 (satisfaction with noise levels) revealed low satisfaction in all three buildings. Further, the satisfaction level for question F1 (satisfaction with the sound privacy) was relatively low in A_bldg, and that of question B1 (satisfaction with the amount of space available) was also low in C_bldg (Table 11).

Table 11.
Average values of the survey results by building (rounded to two decimal places; red for cells with a satisfaction level below 3.5, and green for cells with a satisfaction level above 4.5).
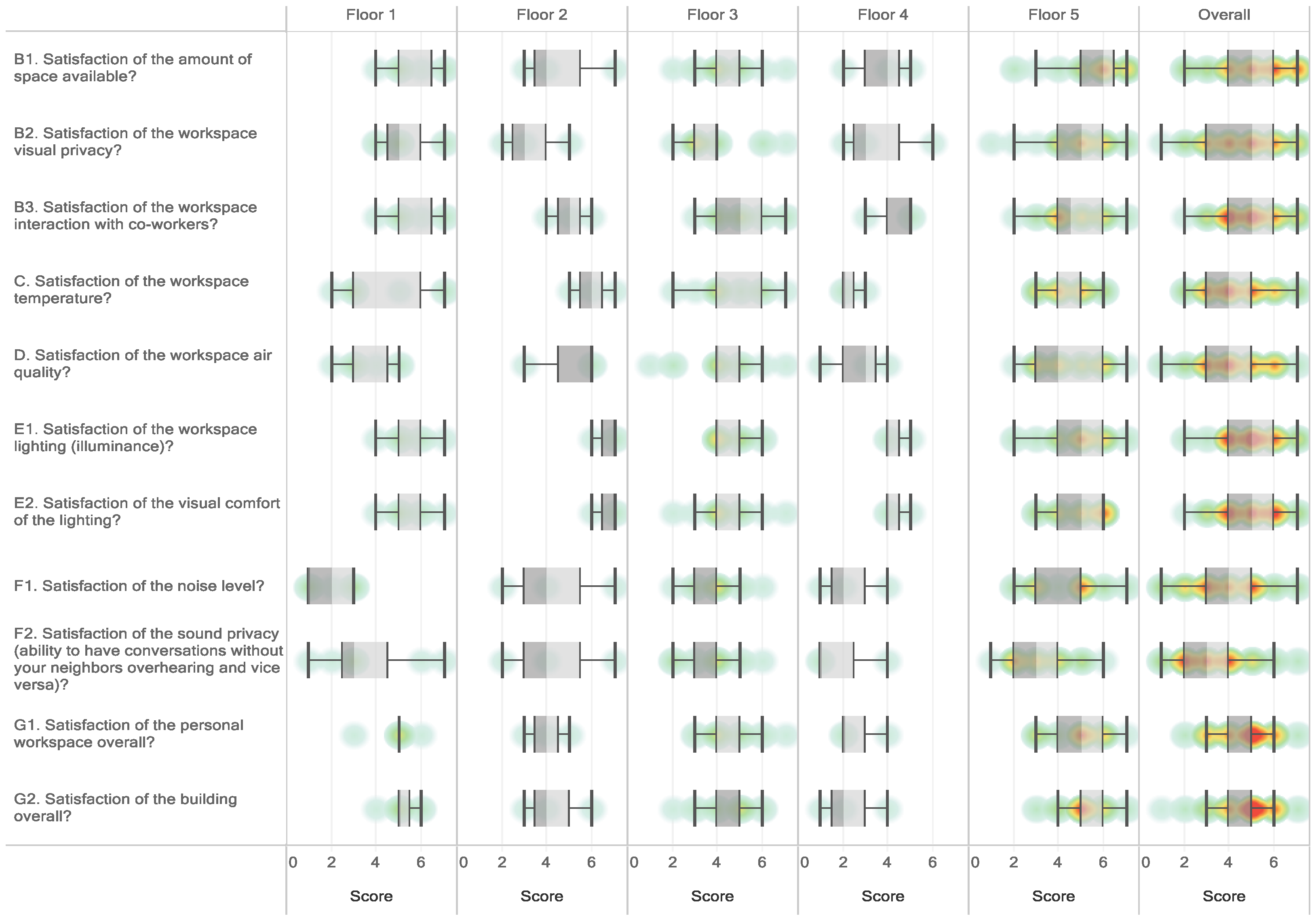
The average value of each questionnaire for A_bldg was compared and analyzed by floor to understand the details from a noise perspective because the responses to question F2 on acoustic quality showed the lowest satisfaction levels in all buildings; the average values of satisfaction levels for F1 were also low (Table 12 and Figure 4). The averages for F1 were low on the first and fourth floors, and the averages for F2 were low on the first, fourth, and fifth floors of building A. As shown in the boxplot in Figure 4, the distributions for the first and fourth floors were skewed lower compared to the overall averages (gray dotted lines). In other words, satisfaction with the acoustic quality was particularly low on the first and fourth floors. The fourth floor scored low on questions C, D, G1, and G2, as well as on question F2.

Table 12.
Survey results for A_bldg by floor (rounded to two decimal places; red for cells with a satisfaction level below 3.5, and green for cells with a satisfaction level above 4.5).
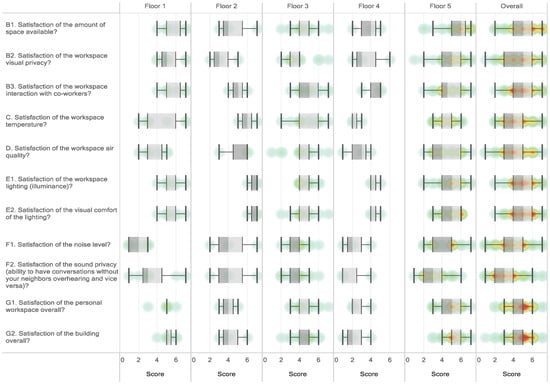
Figure 4.
Boxplot of satisfaction score on each floor of A_bldg. Red indicates overlapping (dense) responses.
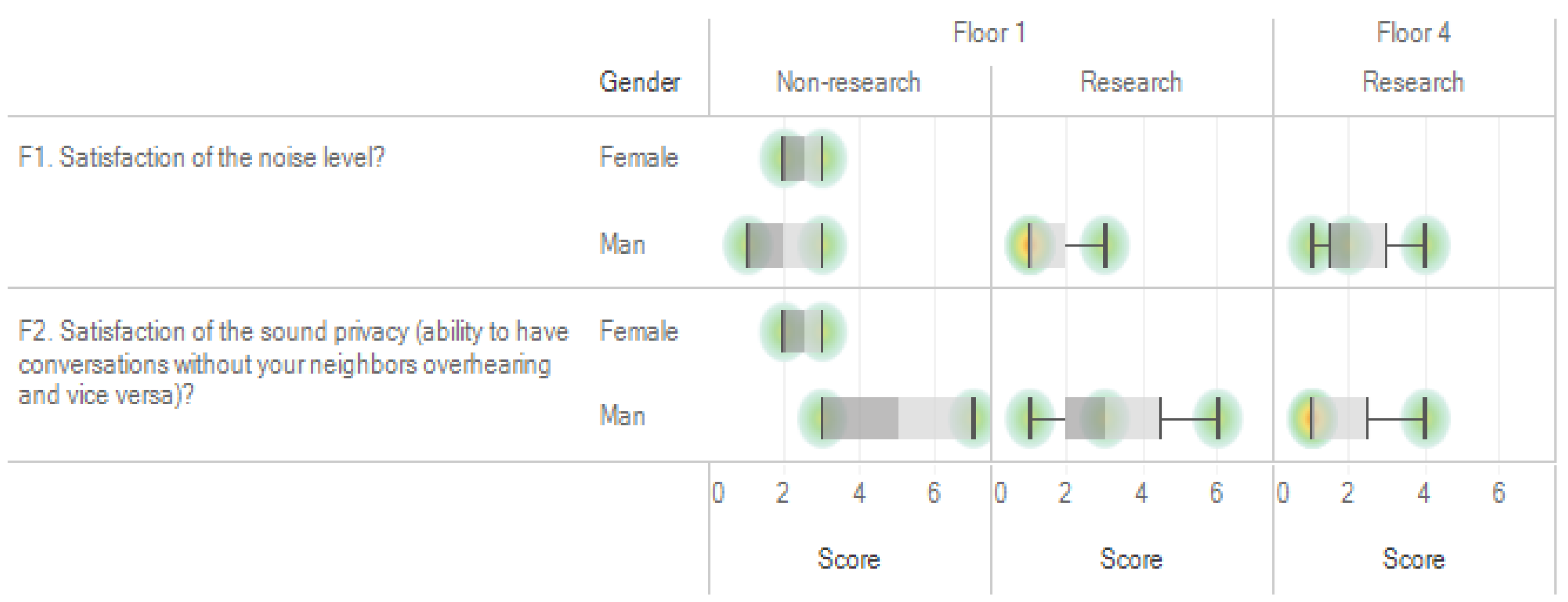
We investigated the reasons for the low satisfaction averages for question F1 for the first and fourth floors. The satisfaction level for F1 was low regardless of the position and gender of the respondent on the first floor and was especially low within the male researcher group. For F2, the female administrator group on the first floor and the male researcher group on the fourth floor showed low satisfaction. The reasons for such low satisfaction levels for F1 and F2 (lower than 3 points) are presented in Table 13 and Figure 5.

Table 13.
Main reasons for the dissatisfaction with the noise level on the 1st and 4th floors.
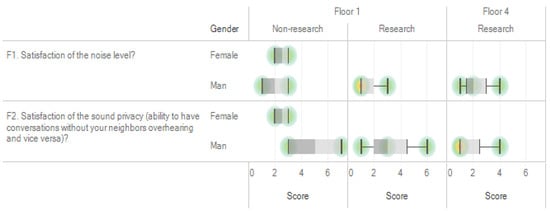
Figure 5.
Satisfaction comparison for questions F1 and F2 on the 1st and 4th floors of A_bldg. Red circles indicate overlapping (dense) responses.
5. Discussion
5.1. Floor-by-Floor Analysis
The satisfaction score of the occupants for questions G1 and G2 for the buildings A–C were identified to be above average at 4.6, 5.0, 4.2 and 4.7, 5.1, 4.6, respectively. The three buildings were regarded as workspaces or buildings where, on average, no abnormalities were observed. However, the result from analyzing the response data of building A through a drill-down and floor-by-floor visualization by survey question, floor, position, and gender revealed the lowest satisfaction scores for noise-related survey questions. This indicates that the floor-by-floor analysis is necessary to identify IEQ factors and the reasons for the satisfaction of occupants.
Further, the result of the analysis for the responses from all the three research institute buildings at KICT showed that the satisfaction level with the noise was low in all buildings. The negative effects of noise and poor acoustics on job productivity and discontent among office workers have been extensively established [22,24]. Noise from machinery (such as printers, phones, and fax machines) can also expose research building occupants to unwanted noises, and a lack of capacity to control those sounds can reduce productivity [25]. This study also showed that acoustic qualities affect the work productivity and satisfaction of the building occupants.
The results indicate that the lowest scores were given by the first and fourth floor occupants. On the first floor, a biased response was observed because of a temporary event (restaurant construction and department furniture rearrangement). F2 (sound privacy) was the item with the highest dissatisfaction level. The analysis of the survey responses by floor indicated that the satisfaction level with noise was particularly low on the first floor regardless of the position and gender of the occupant. Results from the supplementary individual interviews confirmed that the restaurant on the basement floor was being renovated during the survey period in September 2019, and the noise from rearranging the furniture on the first floor was found to be a major factor affecting satisfaction. Thus, the scores of responses to certain questions were biased on some floors because of temporary events; this is an inherent characteristic of the survey method, and measures must be implemented to minimize such bias by conducting surveys regularly (e.g., at least quarterly) or before and after a particular (predictable) event [26].
On the fourth floor, low satisfaction caused by telephone noise was observed. Cost-effective measures such as sound masking or improving the acoustical characteristics of cubicles’ surfaces on the fourth floor were implemented to improve the satisfaction of the occupants, which helped enhance work productivity [27].
The satisfaction level for question B2 (visual privacy) of A_bldg was ranked 6th out of 11 items (normal level), as listed in Table 13; however, it is at a rather low level of 3.3 points on the second floor of the same building. It is believed that visual privacy is less satisfactory here because most administrators use cubicles with low partitions (approximately 1.5 m or less) or share the space with others. Bae, Martin, and Asojo [17] mentioned that when unsatisfied with acoustic characteristics or privacy, workers who work in shared and open workspaces may be more likely to be dissatisfied or experience a negative influence on their job productivity compared to employees who work in private and enclosed offices. Therefore, the presence and height of cubicles that divide the desk layout and areas are important factors for visual privacy, especially for administrators.
5.2. Limitations
There are some limitations to this study, which raises significant issues for future research.
- Our research sample was small and unrepresentative of the floor population in each building, and the uneven sample size across floors could be a potential weakness. Other researchers should attempt to overcome this barrier by devising a survey technique plan that considers the wide range of research institute buildings.
- Our analysis considered only three research institute buildings, despite there being a total of 26 research buildings in the area. Thus, our findings cannot be applied to other research institutes. Future research should confirm our findings in a variety of building environments. In particular, this study focused on the floor-by-floor analysis of A_bldg, so B_bldg and C_bldg should be analyzed in future research.
- Furthermore, no additional information on the principal workplace has been investigated. More studies on spatial aspects such as rooms and zones are required because geographical and zoning variables influence IEQ components [28,29,30].
6. Conclusions
This paper presented the results of a satisfaction survey on IEQ administered to 151 occupants of three research buildings in Korea. The occupants were asked to rate their satisfaction level in terms of personal workspace, office layout, thermal comfort, air quality, lighting, acoustic quality, the building overall, and level of productivity. The main findings indicate that there is a significantly positive (+) effect on layout satisfaction, lighting satisfaction, noise satisfaction, and overall satisfaction, excluding thermal comfort satisfaction and air quality satisfaction, which consist of single items. Further, overall satisfaction has shown a significant positive (+) effect on productivity.
There is a significant difference in the overall satisfaction according to the floor, and the difference in the floor based on the occupation was also found to be statistically significant. Therefore, as a variable, building floor appears to play a significant role in overall satisfaction and differences in occupant satisfaction. This indicates that it is necessary not only to compare the mean values for the buildings but also to analyze each floor in detail in analyzing satisfaction with IEQ.
Further, this research demonstrated that both occupant groups in research institutes are dissatisfied with the acoustic qualities. Administrators who have an open-plan workplace are not satisfied with the visual privacy. This study found that both IEQ factors affect work productivity and satisfaction in research institute. There is a genuine need to minimize dissatisfaction with the build environment to improve productivity because the researchers and administrators in research institute spend a considerable amount of time in these environments. Thus, it is critical to understand how IEQ elements impact occupant satisfaction and perceptions.
In addition, this study analyzes questionnaire items using descriptive exploratory analysis, principal component analysis, linear regression (correlation effect), and path dependence analysis (causal effect). For future research, it is important to consider various new growing methodologies such as partially ordered sets (POSets) in the empirical literature [31,32]. For new methodology, it is again essential to compile large amounts of data in the system.
Finally, a web-based survey system such as KBOSS can be considered a valuable database tool in the accumulation of a large amount of IEQ factors and satisfaction data for a future benchmark study. The comparative benchmarks are significant because they indicate a trend or standard from the dataset under consideration [17,33,34]. The outcomes of this study reinforce the importance of upgrading KBOSS and providing user-centric services of survey systems such as those given below.
- A future study needs to develop KBOSS as a user-friendly system so that more occupants can conduct a survey easily and frequently to solve the limitation of the number of small samples.
- A frequent survey distribution system such as one enacted on a seasonal or monthly basis is required further to minimize biased samples.
- Further research needs to analyze the empirical data associations among building characteristics, spatial characteristics, and demographical characteristics accumulated through KBOSS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, J.-W.L.; project administration, funding acquisition, S.-E.L.; conceptualization, writing—review and editing, D.-W.K.; writing—review and editing, supervision, J.-W.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Major Project of the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) (grant number 20210204-001) and (grant number 20200287-001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study. This study was funded by KICT and conducted for employers in KICT with the information and consent. It was clearly stated that it should have the guarantee of confidentiality and only researchpurposes (publication), not be used for other purposes according to Article 6, 33, 34 of the Korean National Statistical Act.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical reasons.
Acknowledgments
The paper has been substantially updated with fruitful discussions and used analysis from the conference paper, Indoor Environmental Quality Survey in Research Institute: A Floor-by-Floor Analysis, (2021) Building Simulation 2021 Conference, Proceedings.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Klepeis, N.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Ott, W.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Tsang, A.M.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.V.; Hern, S.C.; Engelmann, W.H. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, J.M.; Postolache, T.Τ. The impact of work environment on mood disorders and suicide: Evidence and implications. Int. J. Disabil. Hum. Dev. 2008, 7, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mujan, I.; Anđelković, A.S.; Munćan, V.; Kljajić, M.; Ružić, D. Influence of indoor environmental quality on human health and productivity-A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, R.; Sheau-Ting, L. Criteria for occupant well-being: A qualitative study of Malaysian office buildings. Build. Environ. 2020, 186, 107364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellaris, I.A.; Saraga, D.E.; Mandin, C.; Roda, C.; Fossati, S.; De Kluizenaar, Y.; Carrer, P.; Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Mihucz, V.G.; Szigeti, T.; et al. Perceived indoor environment and occupants’ comfort in European “modern” office buildings: The OFFICAIR study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Pisello, A.L.; De Simone, M.; Kim, A.; Hong, T.; Bandurski, K.; Bavaresco, M.V.; Liu, P.L.; Zhu, Y. The impacts of building characteristics, social psychological and cultural factors on indoor environment quality productivity belief. Build. Environ. 2020, 185, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Ou, D.; Mak, C.M. The impact of indoor environmental quality on work productivity in university open-plan research offices. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allab, Y.; Pellegrino, M.; Guo, X.; Nefzaoui, E.; Kindinis, A. Energy and comfort assessment in educational building: Case study in a French university campus. Energy Build. 2017, 143, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.N.A.M.; Ding, H.H. Indoor environment quality (IEQ): Temperature and indoor air quality (IAQ) factors toward occupants satisfaction. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 864, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verso, V.L.; Giuliani, F.; Caffaro, F.; Basile, F.; Peron, F.; Dalla Mora, T.; Bellia, L.; Fragliasso, F.; Beccali, M.; Bonomolo, M.; et al. Questionnaires and simulations to assess daylighting in Italian university classrooms for IEQ and energy issues. Energy Build. 2021, 252, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Mui, K.W.; Wong, L.T.; Chan, W.Y.; Lee, E.W.M.; Cheung, C.T. Student learning performance and indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in air-conditioned university teaching rooms. Build. Environ. 2012, 49, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivac, N.; Nižetić, S.; Zanki, V. Occupant behavior and thermal comfort field analysis in typical educational research institution: A case study. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhaib, S.; Manton, R.; Griffin, C.; Hajdukiewicz, M.; Keane, M.M.; Goggins, J. An indoor environmental quality (IEQ) assessment of a partially-retrofitted university building. Build. Environ. 2018, 139, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.W. Design of online platform and visualization system based on three-dimensional spatial information for occupant satisfaction with indoor environment quality. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 609, 042037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkinson, T.; Parkinson, A.; de Dear, R. Continuous IEQ monitoring system: Context and development. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huizenga, C.; Laeser, K.; Arens, E. A web-based occupant satisfaction survey for benchmarking building quality. Proc. Indoor Air 2002. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt0hs9x6gm/qt0hs9x6gm_noSplash_0791d6530775f748eb56f95744e7e4ab.pdf?t=mzuucm (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Bae, S.; Martin, C.S.; Asojo, A.O. Indoor environmental quality factors that matter to workplace occupants: An 11-year-benchmark study. Build. Res. Inf. 2021, 49, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S.E.; Jeong, J.W. Development of a Building Occupant Survey System with 3D Spatial Information. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Froese, T.M.; Brager, G. Post-occupancy evaluation: State-of-the-art analysis and state-of-the-practice review. Build. Environ. 2018, 133, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweiker, M.; Ampatzi, E.; Andargie, M.S.; Andersen, R.K.; Azar, E.; Barthelmes, V.M.; Berger, C.; Bourikas, L.; Carlucci, S.; Chinazzo, G.; et al. Review of multi-domain approaches to indoor environmental perception and behaviour. Build. Environ. 2020, 176, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. Performance Measurement Protocols for Commercial Buildings: Best Practices Guide; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Frontczak, M.; Schiavon, S.; Goins, J.; Arens, E.; Zhang, H.; Wargocki, P. Quantitative relationships between occupant satisfaction and satisfaction aspects of indoor environmental quality and building design. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runeson, R.; Norbäck, D.; Stattin, H. Symptoms and sense of coherence—A follow-up study of personnel from workplace buildings with indoor air problems. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2003, 76, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazova, I.; Clausen, G.; Rindel, J.H.; Poulsen, T.; Wyon, D.P. Open-plan office environments: A laboratory experiment to examine the effect of office noise and temperature on human perception, comfort and office work performance. Proc. Indoor Air 2008. Available online: https://www.nickel.odeon.dk/pdf/C101-Indoor_Air_2008_Balazova.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Al Horr, Y.; Arif, M.; Kaushik, A.; Mazroei, A.; Katafygiotou, M.; Elsarrag, E. Occupant productivity and office indoor environment quality: A review of the literature. Build. Environ. 2016, 105, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallio, J.; Vildjiounaite, E.; Koivusaari, J.; Räsänen, P.; Similä, H.; Kyllönen, V.; Muuraiskangas, S.; Ronkainen, J.; Rehu, J.; Vehmas, K. Assessment of perceived indoor environmental quality, stress and productivity based on environmental sensor data and personality categorization. Build. Environ. 2020, 175, 106787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Edward, A. Acoustical Quality in Office Workstations, as Assessed by Occupant Surveys. Proceedings, Indoor Air, 4–9 September 2005, Beijing, China. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0zm2z3jg (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Freihoefer, K.; Guerin, D.; Martin, C.; Kim, H.Y.; Brigham, J.K. Occupants’ satisfaction with, and physical readings of, thermal, acoustic, and lighting conditions of sustainable office workspaces. Indoor Build. Environ. 2015, 24, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Kang, J. Effects of typical dining styles on conversation behaviours and acoustic perception in restaurants in China. Build. Environ. 2017, 121, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetzel, A.; DeKay, M.; Nakai Kidd, A.; Klas, A.; Sadick, A.M.; Whittem, V.; Zinkiewicz, L. Architectural, indoor environmental, personal and cultural influences on students’ selection of a preferred place to study. Arch. Sci. Rev. 2020, 63, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattore, M.; Arcagni, A. A Reduced Posetic Approach to the Measurement of Multidimensional Ordinal Deprivation. Soc. Indic. Res. 2018, 136, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranzano, P.; Ascari, R.; Chiodini, P.M.; Manzi, G. Analysis of Sustainability Propensity of Bike-Sharing Customers Using Partially Ordered Sets Methodology. Soc. Indic. Res. 2021, 157, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, C.; Baird, G. A review of questionnaire-based methods used for assessing and benchmarking indoor environmental quality. Intell. Build. Int. 2013, 5, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, C.; Baird, G. Performance benchmarks for non-domestic buildings: Towards user perception benchmarks. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).