Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
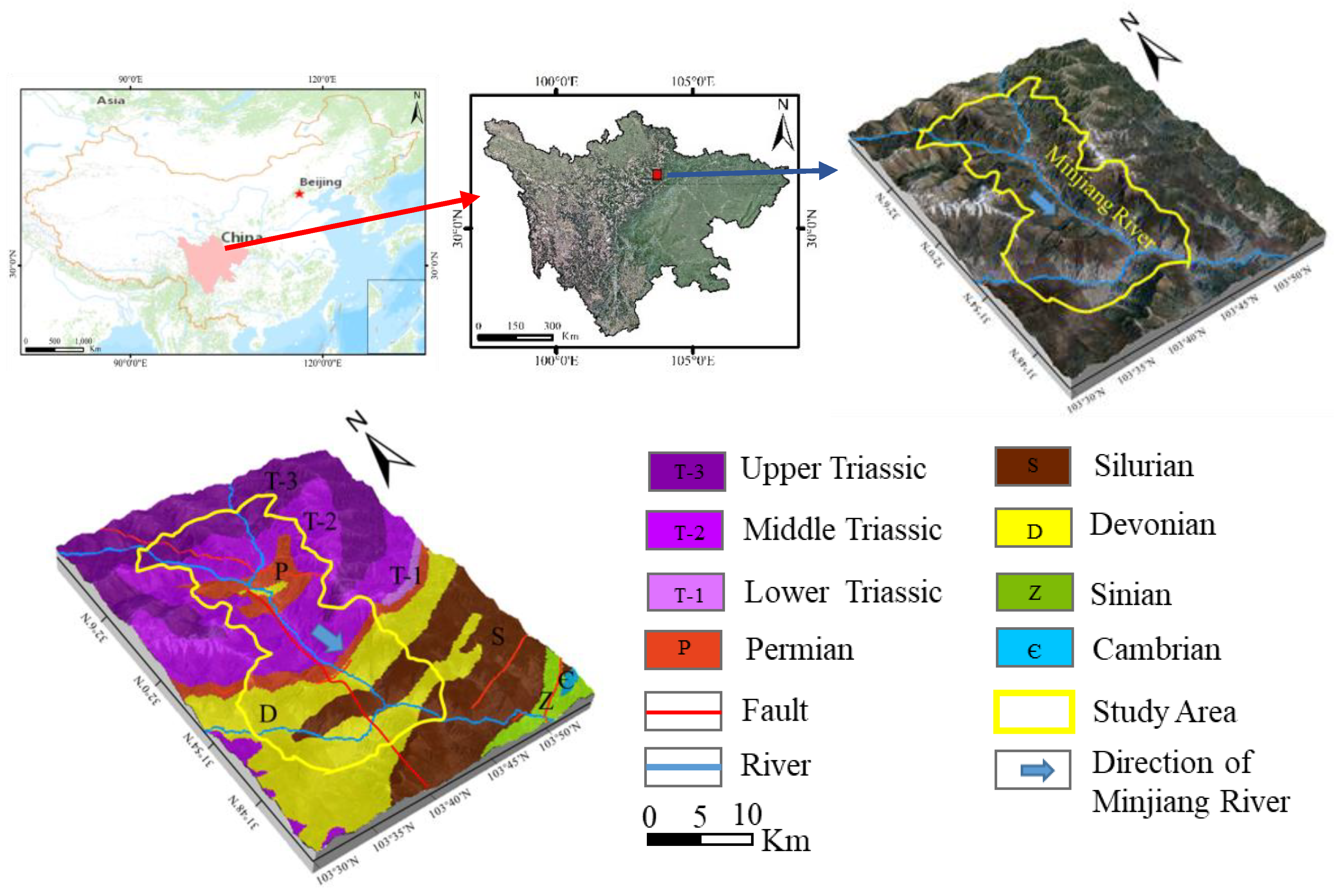
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Time Series InSAR Analysis with SBAS
3.2.2. Visibility Analysis
3.2.3. Spatial Statistical Analysis
Hot Spot Analysis
Kernel Density Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
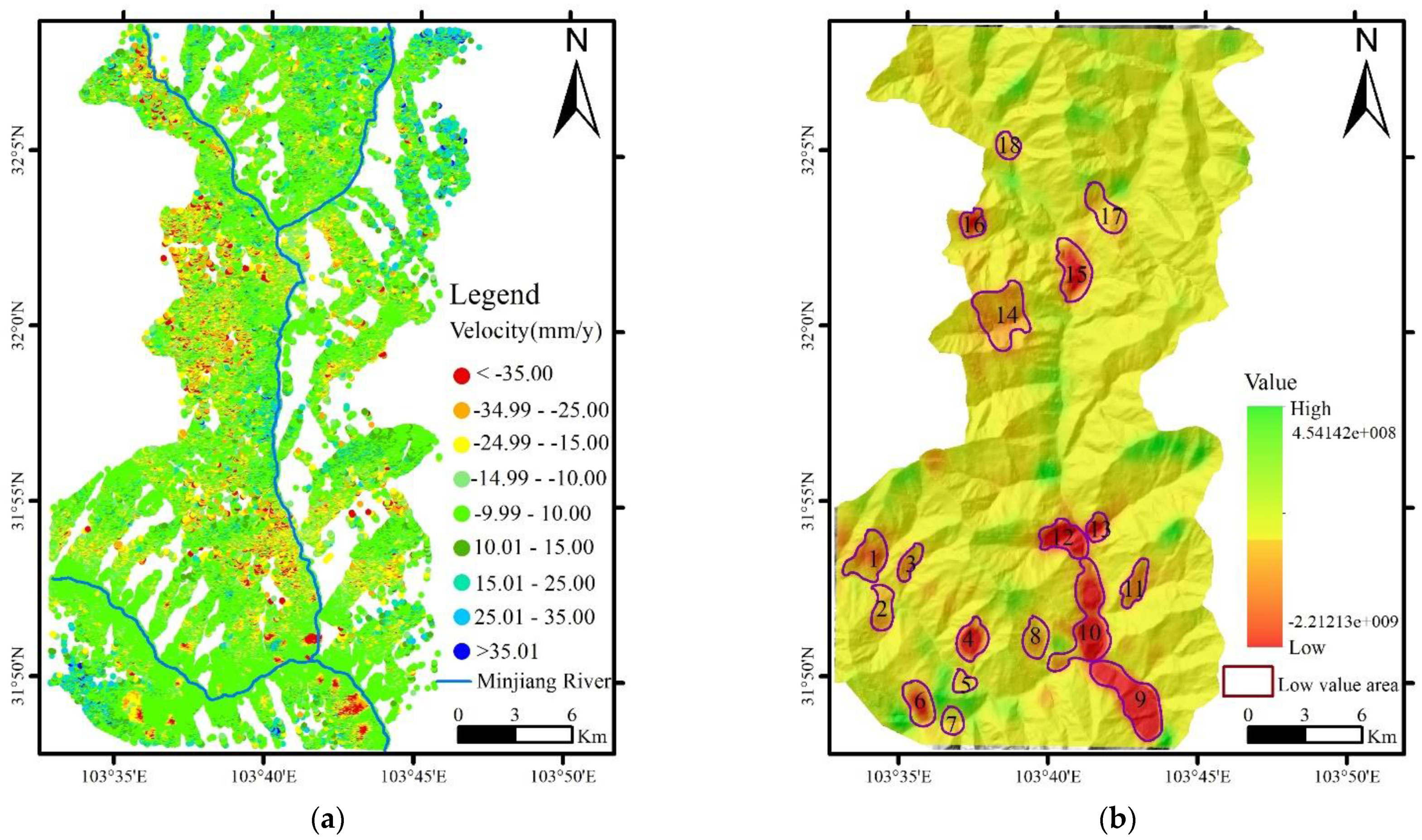
4.1. Ground Deformation and Spatial Distribution
4.2. Discussion
4.2.1. Landslides
4.2.2. Collapse
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, P.; Hu, J. Application of artificial neural network model based on GIS in geological hazard zoning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, E.; Ye, P. Coupling analysis of the heat-water dynamics and frozen depth in a seasonally frozen zone. J. Hydrol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Peng, L.; Pan, H. Linking the Random Forests Model and GIS to Assess Geo-Hazards Risk: A Case Study in Shifang County, China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28033–28042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingran, L.; Hailing, S.; Jian, G. Geologic hazard susceptibility and disaster risk mapping based on information value model for the MianChi county, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Tang, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Geng, Y. Distribution Characteristics of Geo-hazards in a Reservoir Area, South Gansu Province, China. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2020, 49, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-N.; Lei, Y.; Cui, P.; Chen, R.; Yin, P.-H. Chinese public participation monitoring and warning system for geological hazards. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Liao, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Mapping and characterizing displacements of active loess slopes along the upstream Yellow River with multi-temporal InSAR datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Wei, Y. Characteristics and numerical runout modeling analysis of the Xinmo landslide in Sichuan, China. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2020, 24, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.F.; Chen, N.S.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhong, Z.; Rahman, M. New insights into the occurrence of the Baige landslide along the Jinsha River in Tibet. Landslides 2020, 17, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, L. Geological Disaster Recognition on Optical Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 91, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, J.D.; Chung, J.-W. Applying Terzaghi’s method of slope characterization to the recognition of Holocene land slippage. Geomorphology 2016, 265, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nie, D.; Tuo, X.; Zhong, Y. Research on crack monitoring at the trailing edge of landslides based on image processing. Landslides 2020, 17, 985–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Gagliardi, V.; Ferrante, C.; Calvi, A.; D’Amico, F.; Tosti, F. Displacement Monitoring in Airport Runways by Persistent Scatterers SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, B. Landslide Identification and Monitoring along the Jinsha River Catchment (Wudongde Reservoir Area), China, Using the InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahzad, N.; Ding, X.; Wu, S.; Liang, H. Ground Deformation and Its Causes in Abbottabad City, Pakistan from Sentinel-1A Data and MT-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Lu, L.; Yao, Y. Method Combining Probability Integration Model and a Small Baseline Subset for Time Series Monitoring of Mining Subsidence. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.C.; Kim, S.-W.; Jung, H.-S.; Min, K.D.; Won, J.-S. Satellite observation of coal mining subsidence by persistent scatterer analysis. Eng. Geol. 2007, 92, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, Y.; Yin, K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Catani, F.; Ahmed, B. Landslide Characterization Applying Sentinel-1 Images and InSAR Technique: The Muyubao Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Du, S. Monitoring and Analysis of Surface Deformation in Mining Area Based on InSAR and GRACE. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; Wang, Z.; Ni, P.; Li, H. Resolving and Analyzing Landfast Ice Deformation by InSAR Technology Combined with Sentinel-1A Ascending and Descending Orbits Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, V.; Tesauro, M. SAR interferometry and field data of Randazzo landslide (Eastern Sicily, Italy). Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Berardino, P.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E.; Fornaro, G.; Franceschetti, G. Urban subsidence inside the city of Napoli (Italy) observed by satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.; Jung, H.-S.; Feng, G.; Lee, C.-W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Potential of geosynchronous SAR interferometric measurements in estimating three-dimensional surface displacements. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goorabi, A.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Perissin, D. Monitoring of the ground displacement in the Isfahan, Iran, metropolitan area using persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar technique. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Lv, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Multi-Scale Analysis of the Relationship between Land Subsidence and Buildings: A Case Study in an Eastern Beijing Urban Area Using the PS-InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Balz, T.; Zhang, L.; Perissin, D.; Liao, M. Using TSX/TDX Pursuit Monostatic SAR Stacks for PS-InSAR Analysis in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casu, F.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E.; Solaro, G.; Tizzani, P.; Poland, M.; Miklius, A. SBAS-InSAR analysis of surface deformation at Mauna Loa and Kilauea volcanoes in Hawaii. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xing, X.; Wen, D.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, B.; Tan, J. Mining-Induced Time-Series Deformation Investigation Based on SBAS-InSAR Technique: A Case Study of Drilling Water Solution Rock Salt Mine. Sensors 2019, 19, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y. Urban subsidence monitoring by SBAS-InSAR technique with multi-platform SAR images: A case study of Beijing Plain, China. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Jia, C.; Chen, S.; Li, H. SBAS-InSAR Based Deformation Detection of Urban Land, Created from Mega-Scale Mountain Excavating and Valley Filling in the Loess Plateau: The Case Study of Yan’an City. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Montalti, R.; Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Thuegaz, P.; Bertolo, D.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. A Sentinel-1 based hot-spot analysis: Landslide mapping in north-western Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7898–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; Micallef, A.; Spatola, D.; Wang, X. The Tsunami Inundation Hazard of the Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean Sea): A Submarine Landslide and Earthquake Tsunami Scenario Study. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 177, 1617–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Bianchini, S.; Franceschini, R.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Thuegaz, P.; Bertolo, D.; Crosetto, M.; Catani, F. Satellite interferometric data for landslide intensity evaluation in mountainous regions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Ricart Casadevall, S. Analysis of landslide-induced fatalities and injuries in Bangladesh: 2000–2018. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Mondal, P. A Rapidly Assessed Wetland Stress Index (RAWSI) Using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1 Radar Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calligaris, C.; Devoto, S.; Galve, J.; Zini, L.; Pérez-Peña, J. Integration of multi-criteria and nearest neighbour analysis with kernel density functions for improving sinkhole susceptibility models: The case study of Enemonzo (NE Italy). Int. J. Speleol. 2017, 46, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; George, D.L.; Kim, J.; Lu, Z.; Riley, M.; Griffin, T.; de la Fuente, J. Landslide monitoring and runout hazard assessment by integrating multi-source remote sensing and numerical models: An application to the Gold Basin landslide complex, northern Washington. Landslides 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley Caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Su, X.; Yue, D. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping of Karakorum Highway Combined with the Application of SBAS-InSAR Technology. Sensors 2019, 19, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fustos, I.; Abarca-del-Rio, R.; Mardones, M.; Gonzalez, L.; Araya, L.R. Rainfall-induced landslide identification using numerical modelling: A southern Chile case. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, X.; Yuan, L. Identification and monitoring landslides in Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region with InSAR fusion integrated visibility analysis. Landslides 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ge, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, J. Identification of geomorphological hazards in an underground coal mining area based on an improved region merging watershed algorithm. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, P.; Ge, Y.; Yi, Z. Paleosols identified by rock magnetic properties indicate dam-outburst events of the Min River, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 508, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Ji, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, S. Deformation Time Series and Driving-Force Analysis of Glaciers in the Eastern Tienshan Mountains Using the SBAS InSAR Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Yang, T.; Song, S.; Yao, M.; Zhou, K.; Huang, X. Ground Deformation of the Chongming East Shoal Reclamation Area in Shanghai Based on SBAS-InSAR and Laboratory Tests. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, C.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, X.; Du, Y. Characteristics of the Residual Surface Deformation of Multiple Abandoned Mined-Out Areas Based on a Field Investigation and SBAS-InSAR: A Case Study in Jilin, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Casagli, N. How to assess landslide activity and intensity with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI): The PSI-based matrix approach. Landslides 2012, 10, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhao, B.; Xu, Q.; Yang, F.; Fu, H.; Dai, C.; Wu, X. Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of a reactivated landslide in Leidashi, Sichuan, China, on August 6, 2019: An emergency investigation report. Landslides 2020, 17, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, R.K.; Hasegawa, S.; Nonomura, A.; Yamanaka, M.; Masuda, T.; Nishino, K. Failure characteristics of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in granitic terrains of Shikoku Island of Japan. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolesini, T.; Frodella, W.; Bianchini, S.; Casagli, N. Detecting Slope and Urban Potential Unstable Areas by Means of Multi-Platform Remote Sensing Techniques: The Volterra (Italy) Case Study. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dille, A.; Kervyn, F.; Bibentyo, T.M.; Delvaux, D.; Ganza, G.B.; Mawe, G.I.; Buzera, C.K.; Nakito, E.S.; Moeyersons, J.; Monsieurs, E.; et al. Causes and triggers of deep-seated hillslope instability in the tropics—Insights from a 60-year record of Ikoma landslide (DR Congo). Geomorphology 2019, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisseha, S.; Mewa, G. Road failure caused by landslide in north Ethiopia: A case study from Dedebit—Adi-Remets road segment. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 118, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to Determine Mining-Related Deformations Using Sentinel-1 Data: The Case Study of Rydułtowy Mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmons, J.; Elsworth, D.; Voight, B. Classification and idealized limit-equilibrium analyses of dome collapses at Soufrière Hills volcano, Montserrat, during growth of the first lava dome: November 1995–March 1998. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2005, 139, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.-P.; Shi, S.; Cheng, S.; Hu, H.; Wen, T. Dynamic Risk Assessment Method of Collapse in Mountain Tunnels and Application. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Temporal coverage | 2014.10.14~2019.08.13 |
| Imaging mode | IW |
| Orbital direction | Ascending |
| Band | C-band |
| Azimuth resolution | 20 m |
| Range resolution | 5 m |
| Wavelength | 5.6 cm |
| Resolution | 5 × 20 m |
| Polarization | VV |
| Average angle of incidence | 39.3° |
| Relative orbit number | T128 |
| The Number of Disasters | Type | The Number of Disasters | Type | The Number of Disasters | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | landslide | 10 | landslide | 19 | landslide |
| 2 | landslide | 11 | landslide | 20 | landslide |
| 3 | landslide | 12 | landslide | 21 | collapse |
| 4 | landslide | 13 | landslide | 22 | collapse |
| 5 | landslide | 14 | collapse | 23 | landslide |
| 6 | landslide | 15 | collapse | 24 | landslide |
| 7 | landslide | 16 | collapse | 25 | collapse |
| 8 | landslide | 17 | landslide | 26 | landslide |
| 9 | landslide | 18 | landslide |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, K.; Xu, P.; Cao, C.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, X. Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031017
Zhu K, Xu P, Cao C, Zheng L, Liu Y, Dong X. Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031017
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Kuanxing, Peihua Xu, Chen Cao, Lianjing Zheng, Yue Liu, and Xiujun Dong. 2021. "Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031017
APA StyleZhu, K., Xu, P., Cao, C., Zheng, L., Liu, Y., & Dong, X. (2021). Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods. Sustainability, 13(3), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031017






