A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Approaches to Engagement and Management
2.1. The New Form of Community: Online Community
2.2. Digital Tools to Promote Community Collaboration
2.3. The Role of Social Media in Sustainable Cultural Heritage Management
3. Methodology
3.1. Publication Collection
3.2. Publication Selection
3.3. Quantitative Analyzing Method
4. Findings
4.1. Outcome 1
4.2. Outcome 2
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Pereira Roders, A.; van Wesemael, P. Community participation in cultural heritage management: A systematic literature review comparing Chinese and international practices. Cities 2020, 96, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokilehto, J. Definition of Cultural Heritage: References to Documents in History; ICCROM Working Group Heritage and Society: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Roders, P.; Bandarin, F. Reshaping Urban Conservation: The Historic Urban Landscape Approach in Action; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Court, S.; Wijesuriya, G. People-centred approaches to the conservation of cultural heritage: Living heritage. In Heritage, Conservation and Communities: Engagement, Participation and Capacity Building; Chitty, G., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Poulios, I. Discussing strategy in heritage conservation: Living heritage approach as an example of strategic innovation. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 4, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bideau, F.G.; Yan, H. Historic urban landscape in Beijing: The gulou project and its contested memories. In Chinese Heritage in the Making; Maags, C., Svensson, M., Eds.; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 93–118. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K. The Historic Urban Landscape paradigm and cities as cultural landscapes. Challenging orthodoxy in urban conservation. Landsc. Res. 2016, 41, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarin, F.; van Oers, R. Reconnecting the City: The Historic Urban Landscape Approach and the Future of Urban Heritage; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Borona, G.; Ndiema, E. Merging research, conservation and community engagement. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 4, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitty, G. Heritage, Conservation and Communities: Engagement, Participation and Capacity Building; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bandarin, F.; van Oers, R. The Historic Urban Landscape: Managing Heritage in an Urban Century; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Settis, S. We the Citizens, English Translation of chapter 7 of Paesaggio, Costituzione, Cemento: La Battaglia per L’ambiente Contro il Degrado Civile (Einaudi, 2010). Calif. Ital. Stud. 2011, 2. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt7c90g6dp/qt7c90g6dp.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Affleck, J.; Kvan, T. A Virtual community as the context for discursive interpretation: A role in cultural heritage engagement. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2008, 14, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Pereira Roders, A.; van Wesemael, P. State-of-the-practice: Assessing community participation within Chinese cultural World heritage properties. Habitat Int. 2020, 96, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.C. Bridging planned conservation and community empowerment: Portuguese case studies. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2018. Available online: https://repositorio-aberto.up.pt/bitstream/10216/119597/2/330445.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- MacRae, G. Universal heritage meets local livelihoods: “awkward engagements” at the world cultural heritage listing in Bali. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2017, 23, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdini, G.; Frassoldati, F.; Nolf, C. Reframing China’s heritage conservation discourse. Learning by testing civic engagement tools in a historic rural village. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2017, 23, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzarly, A.; Roders, P.; Teller, J. Mapping historic urban landscape values through social media. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Andreu, M. Introduction to the themed section “digital heritage and the public”. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2017, 23. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/13527258.2017.1286780?needAccess=true (accessed on 25 December 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchin, R.; Dodge, M. Code/Space: Software and Everyday Life; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Corallo, A.; Trono, A.; Fortunato, L.; Pettinato, F.; Schina, L. Cultural event management and urban e-planning through bottom-up user participation. Int. J. E Plan. Res. 2018, 7, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Kim, K. Sustainable and ICT-enabled development in developing areas: An e-heritage e-commerce service for handicraft marketing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Development and Green Technology (SDGT 2017), Chiayi, Taiwan, 24–26 November 2017; Volume 989. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/989/1/012009/pdf (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Garduño Freeman, C. Photosharing on Flickr: Intangible heritage and emergent publics. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2010, 16, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giaccardi, E. Heritage and Social Media: Understanding Heritage in a Participatory Culture; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Psomadaki, I.; Dimoulas, C.A.; Kalliris, G.M.; Paschalidis, G. Digital storytelling and audience engagement in cultural heritage management: A collaborative model based on the Digital City of Thessaloniki. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhonju, H.K.; Xiao, W.; Mills, J.P.; Sarhosis, V. Share our cultural heritage (SOCH): Worldwide 3D heritage reconstruction and visualization via web and mobile GIS. ISPRS. Int. J. Geo. Inf. 2018, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafreniere, D.; Weidner, L.; Trepal, D.; Scarlett, S.F.; Arnold, J.; Pastel, R. Public participatory historical GIS. Hist. Methods J. Quant. Interdiscip. Hist. 2019, 52, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummi, P. Crowdsourcing local knowledge with PPGIS and social media for urban planning to reveal intangible cultural heritage. Urban. Plan. 2018, 3, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.J.; Draux, H.; Martín, M.G.; Martin, J.; Bieling, C. Contributions of citizen science to landscape democracy: Potentials and challenges of current approaches. Landsc. Res. 2017, 42, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claisse, C.; Ciolfi, L.; Petrelli, D. Containers of stories: Using co-design and digital augmentation to empower the museum community and create novel experiences of heritage at a house museum. Des. J. 2017, 20, S2906–S2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, E.B.-N.; Stappers, P.J. Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign 2008, 4, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champion, E.; Rahaman, H. 3D digital heritage models as sustainable scholarly resources. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S. Collaborative planning in the new media age: The Dafo temple controversy, China. Cities 2015, 45, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, C.; Reid, P. Social media as a vehicle for user engagement with local history: A case study in the North East of Scotland. J. Doc. 2018, 74. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JD-12-2017-0167/full/pdf?title=social-media-as-a-vehicle-for-user-engagement-with-local-history-a-case-study-in-the-north-east-of-scotland (accessed on 26 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- de Filippi, F.; Coscia, C.; Guido, R. MiraMap: A collective awareness platform to support open policy-making and the integration of the citizens’ perspective in urban planning and governance. In Technologies for Development; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinhans, R.; Ham, M.V.; Evans-Cowley, J. Using social media and mobile technologies to foster engagement and self-organization in participatory urban planning and neighbourhood governance. Plan. Pract. Res. 2015, 30, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroczynska, J. Role of ICT Technologies in the Conservation of Building Monuments; DWE: Wroclaw, Poland, 2012; pp. 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill, S.; Hudson, M.; Lloyd, K.; Outterside, J.; Peterson, J.; Coburn, J.; Thomas, U.; Tiplady, L.; Robinson, P.; Heslop, P. Co-curate: Working with schools and communities to add value to open collections. J. Interact. Media Educ. 2016, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeates, R.; Guy, D. Collaborative working for large digitisation projects. Program. Electron. Libr. Inf. Syst. 2006, 40, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, A. Heritage-making “from below”: The politics of exhibiting architectural heritage on the Internet—A case study. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2016, 22, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beel, D.E.; Wallace, C.D.; Webster, G.; Nguyen, H.; Tait, E.; MacLeod, M.; Mellish, C. Cultural resilience: The production of rural community heritage, digital archives and the role of volunteers. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prictor, S.; Huebner, H.J.; Teare, A.; Burchill, L.; Kaye, J. Australian aboriginal and torres strait Islander collections of genetic heritage: The legal, ethical and practical considerations of a dynamic consent approach to decision making. J. Law. Med. Ethics 2020, 48, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prastyawan, A.; Isbandono, P. The Efforts of Joyoboyo Citizens in Preserving Traditional Children’s Games through Dolanan Village. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Social Sciences (ICSS 2018), Bali, Indonesia, 18–19 October 2018; pp. 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, I.; Barberis, C.; Xhembulla, J.; Malnati, G. Integrating a location-based mobile game in the museum visit: Evaluating visitors’ behaviour and learning. JOCCH 2015, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, T. Revitalization of historical heritage using pop culture in Japan: Shiroishi city and the game/anime Sengoku Basara. Tour. Anal. 2015, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, G.; Schofield, T.; Pisanty, D.T. Framing collaborative processes of digital transformation in cultural organisations: From literary archives to augmented reality. Mus. Manag. Curatorship 2019, 35, 424–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spacca, S.; Dellapiana, E.; Sanna, A. Promoting industrial cultural heritage by augmented reality: Application and assessment. Open Cybern. Syst. J. 2018, 12, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.; Jones, S.; Maxwell, M.; Hale, A.; Jones, C. 3D visualisation, communities and the production of significance. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2020, 3, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Statham, N. Scientific rigour of online platforms for 3d visualisation of heritage. Virtual Archaeol. Rev. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.; Tammi, K.; Joutsiniemi, A. Extending the life of virtual heritage: Reuse of Tls point clouds in synthetic stereoscopic spherical images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurley, A. Chasing the frontiers of digital technology public history meets the digital divide. Publ. Hist. 2016, 38, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loren-Mendez, M.; Pinzon-Ayala, D.; Ruiz, R.; Alonso-Jimenez, R. Mapping heritage: Geospatial online databases of historic roads. The case of the N-340 roadway corridor on the Spanish Mediterranean. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2018, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.B.; Yen, Y.N. A planning by using digital technology in the reconstruction of cultural heritage sites—A case study of qiong-lin settlement in Kinmen area. In ICOMOS/ISPRS International Scientific Committee on Heritage Documentation (CIPA), Proceedings of the 26th International CIPA Symposium—Digital Workflows for Heritage Conservation, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 28 August–1 September 2017; Hayes, J., Ouimet, C., Quintero, M.S., Fai, S., Smith, L., Eds.; ISPRS: Hannover, Germany, 2017; Volume 42-2, pp. 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Hoeven, A. Historic urban landscapes on social media: The contributions of online narrative practices to urban heritage conservation. City Cult. Soc. 2019, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Desha, C. Engaging in design activism and communicating cultural significance through contemporary heritage storytelling A case study in Brisbane, Australia. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 6, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spruce, L.; Leaf, K. Social media for social justice. J. Mus. Educ. 2017, 42, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, J. A review of social media use in e.-government. Adm. Sci. 2012, 2, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouganatou, A. Can heritage bots thrive? Toward future engagement in cultural heritage. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2018, 6, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, M.; Maags, C. Mapping the Chinese heritage regime: Ruptures, governmentality, and agency. In Chinese Heritage in the Making: Experiences, Negotiations and Contestations; Svensson, M., Maags, C., Eds.; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, J.B.; Andersen, H.J.; Rodil, K. Hybrid cemetery culture: Making death matter in cultural heritage using smart mobile technologies. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Culture and Computing (Culture Computing), Kyoto, Japan, 17–19 October 2015; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.B.; Frandsen, T.F. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: A systematic review. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2018, 106, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methley, M.; Campbell, S.; Chew-Graham, C.; McNally, R.; Cheraghi-Sohi, S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: A comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, H.C.; Wilsont, A.T.; Labrosse, F.; Tiddeman, B.P. Alternative representations of 3D-reconstructed heritage data. ACM J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popple, S. The new Reithians: Pararchive and citizen animateurs in the BBC digital archive. Converg. Int. J. Res. New Media Technol. 2015, 21, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falco, E.; Kleinhans, R. Digital participatory platforms for co-production in urban development: A systematic review. In Crowdsourcing: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 663–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concepts | Content | Keywords/Synonyms | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original criteria setting | P | Population | Communities engaged in the cultural heritage management process | (Public or communit* or civic or audience*) Near/3 (participat* or engage* or collaborat*) |
| I | Intervention | Social media | ((social Near/3 (media or network*) or digital or online)) | |
| C | Comparison | Offline community engagement | We excluded this part because this did not add value to the search | |
| O | Outcomes | Outcomes of participatory governance | We excluded this part because this did not add value to the search | |
| S | Study design | Statistical analysis of participatory methods in case studies | We excluded this part because this did not add value to the search | |
| Additional criteria setting | S | Setting | Urban cultural heritage | (culture* or urban*) Near/3 (historic* Near/2 (Cit* or district* or settlement* or area* or plan*)) |
| T | Timing | Duration or date of publication | 1985–present | |
| Step | Number of Publications Retrained | Selection Progress |
|---|---|---|
| 248 | Publications that were retrieved from Wos | |
| 1 | 240 | Publications retained after 8 duplicate publications were excluded |
| 2 | 238 | Publications retained after 2 publication that has the same case as another publication was excluded |
| 3 | 234 | Publications retained after 4 non-English publications were excluded |
| 4 | 195 | Publications retained after 39 inaccessible publications were excluded |
| 5 | 14 | Publications retained after 181 irrelevant-topic publications were excluded |
| 6 | 19 | Publications retained after 5 relevant-topic articles that involve linked case studies were supplemented |
| No. | Publication Time | Location (Nation) | Cultural Heritage Object | Applied Social Media | Interactive Method | Object | Impact on Sustainable Cultural Heritage Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2019 | Greece | Thessaloniki | Website, APP | Storytelling; Mapping; Exhibition; Crowdsourcing | Collective memory | Shared heritage and collective memory |
| 2 | 2019 | Nether-lands | 19 Dutch heritage projects and organizations (eg. Amsterdam Museum, Museum Rotterdam, etc) | Twitter Facebook Flickr YouTube Pinterest blogs Instagram Linkedin TripAdvisor Website Interactive map | Storytelling; Mapping | Collective memory | Shared heritage and collective memory |
| 3 | 2019 | Lebanon | Tripoli and El-Mina municipal boundaries | Flickr | Mapping | Heritage interpretation | People-centered approach |
| 4 | 2018 | Finland | Nikkilä | Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, Interactive map | Communication; Crowdsourcing | Enhance communication | People-centered approach |
| 5 | 2018 | Italy | Puglia | Facebook, Twitter | Communication; Crowdsourcing | Enhance communication | People-centered approach |
| 6 | 2018 | Nepal | Kathmandu Valley | Website | Mapping | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| UK | Newcastle University Quadrangle Gateway | ||||||
| 7 | 2018 | New Zealand | A Museum | Website | Photo sharing; Crowdsourcing | Maintain community archives | Shared heritage and collective memory |
| 8 | 2018 | United Kingdom | the North East of Scotland | Photo sharing; Storytelling | Collective memory | People-centered approach | |
| 9 | 2017 | United Kingdom | UCL’s Grant Museum | Website, Twitter, APP | Exhibition; Crowdsourcing | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| 10 | 2017 | Netherlands | Anne Frank House | Facebook (Messen-ger) | Communication | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| Italy | The House Museums of Milan | ||||||
| Italy | The National Museum of the 21st Century Arts | ||||||
| 11 | 2017 | United Kingdom | Prehistoric Rock Carvings in Northumberland | Facebook; Website | Exhibition; Storytelling | Enhance communication | People-centered approach |
| 12 | 2017 | United State | Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture | Exhibition; Storytelling | Increase access for visitors of color | People-centered approach | |
| 13 | 2017 | Jordan | Amman | Crowdsourcing; Official announcement | Enhance communication | People-centered approach | |
| 14 | 2016 | Australia | Brisbane’s built heritage | Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, Twitter | Storytelling; Crowdsourcing | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| 15 | 2016 | Vienna | The Vienna Werkbund estate | Website, Facebook, Pinterest, Flickr | Photo sharing | Equity of the discourse | People-centered approach |
| 16 | 2015 | China | Dafo Temple | Photo sharing; Communication; Crowdsourcing | Equity of the discourse | People-centered approach | |
| 17 | 2015 | Denmark | Contemporary Danish Urban Cemetery | Interactive map | Mapping | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| 18 | 2010 | Australia | Sydney Opera House | Flickr | Photo sharing | Collective identity representation | Cultural expression |
| 19 | 2006 | UK | South-east of England | Website | Communication; Crowdsourcing; Official announcement | Heritage interpretation | Cultural expression |
| No. | Location | Cultural Heritage Object | Applied Social Media | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| App | Blg | FB | FK | Ins | Lin | Map | Pin | TA | Twi | WB | Web | YT | |||
| 1 | Greece | Thessaloniki | ● | ||||||||||||
| 2 | Lebanon | TripoliandEl-Minamunicipalboundaries | ● | ||||||||||||
| 3 | Finland | Nikkilä | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 4 | Italy | Puglia | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 5 | NewZealand | amuseum | ● | ||||||||||||
| 6 | UK | theNorthEastofScotland | ● | ||||||||||||
| 7 | UK | UCL’sGrantMuseum | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 8 | UK | PrehistoricRockCarvingsinNorthumberland | ● | ||||||||||||
| 9 | US | NationalMuseumofAfricanAmericanHistoryandCulture | ● | ||||||||||||
| 10 | Jordan | Amman | ● | ||||||||||||
| 11 | Australia | Brisbane’sbuiltheritage | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 12 | Vienna | theViennaWerkbundestate | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 13 | China | DafoTemple | ● | ||||||||||||
| 14 | Danmark | ContemporaryDanishUrbanCemetery | ● | ||||||||||||
| 15 | Australia | SydneyOperaHouse | ● | ||||||||||||
| 16 | Netherlands | AmsterdamMuseum | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 17 | Netherlands | MuseumhetSchip | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 18 | Netherlands | BelvédèreRotterdam | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 19 | Netherlands | BijlmerMuseum | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 20 | Netherlands | FinancieelErfgoedopdeKaart | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 21 | Netherlands | GeheugenvanOost | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 22 | Netherlands | TheHistoricalMuseumofThe | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 23 | Netherlands | HagueImagineIC | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 24 | Netherlands | MuseumRotterdamMuseumZonder | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 25 | Netherlands | MurenTransvaal | ● | ||||||||||||
| 26 | Netherlands | OngekendBijzonder | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 27 | Netherlands | OudAmsterdam | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 28 | Netherlands | RotterdaminKaart | ● | ||||||||||||
| 29 | Netherlands | RotterdamVertelt | ● | ||||||||||||
| 30 | Netherlands | StadsarchiefRotterdam | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 31 | Netherlands | WederopbouwRotterdam | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 32 | Netherlands | ZichtopMaastricht | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 33 | Netherlands | HaagseHerinneringen | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 34 | Netherlands | Mappingslavery | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 35 | Nepal | KathmanduValley | ● | ||||||||||||
| 36 | UK | NewcastleUniversityQuadrangleGateway | ● | ||||||||||||
| 37 | Netherlands | AnneFrankHouse | ● | ||||||||||||
| 38 | Italy | TheHouseMuseumsofMilan | ● | ||||||||||||
| 39 | Italy | TheNationalMuseumofThe21stCenturyArts | ● | ||||||||||||
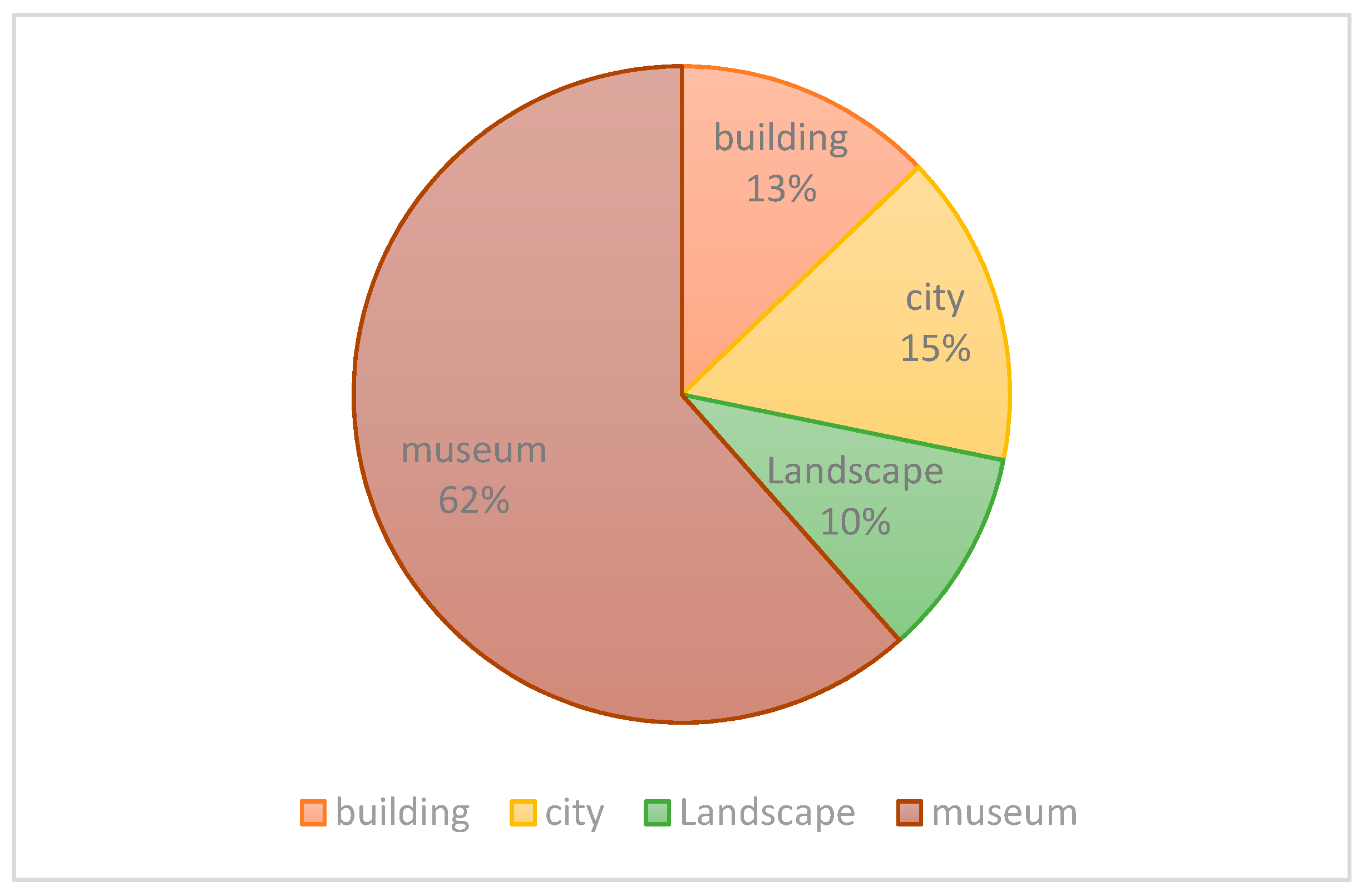
| Categories | No. | Cultural Heritage Object |
|---|---|---|
| Museum | 1 | A museum |
| 2 | Amsterdam Museum | |
| 3 | Belvédère Rotterdam | |
| 4 | Bijlmer Museum | |
| 5 | Financieel Erfgoed op de Kaart | |
| 6 | Geheugen van Oost | |
| 7 | Haagse Herinneringen | |
| 8 | Hague Imagine IC | |
| 9 | Mapping slavery | |
| 10 | Muren Transvaal | |
| 11 | Museum het Schip | |
| 12 | Museum Rotterdam Museum Zonder | |
| 13 | Ongekend Bijzonder | |
| 14 | Oud Amsterdam | |
| 15 | Rotterdam in Kaart | |
| 16 | Rotterdam Vertelt | |
| 17 | Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture | |
| 18 | Stadsarchief Rotterdam | |
| 19 | The Historical Museum of The | |
| 20 | The House Museums of Milan | |
| 21 | The National Museum of The 21st Century Arts | |
| 22 | UCL’s Grant Museum | |
| 23 | Wederopbouw Rotterdam | |
| 24 | Zicht op Maastricht | |
| City | 1 | Thessaloniki |
| 2 | Amman | |
| 3 | Nikkilä | |
| 4 | Puglia | |
| 5 | the North East of Scotland | |
| 6 | Tripoli and El-Mina municipal boundaries | |
| Building | 1 | Anne Frank House |
| 2 | Brisbane’s built heritage | |
| 3 | Dafo Temple | |
| 4 | Sydney Opera House | |
| 5 | the Vienna Werkbund estate | |
| Landscape | 1 | Contemporary Danish Urban Cemetery |
| 2 | Kathmandu Valley | |
| 3 | Newcastle University Quadrangle Gateway | |
| 4 | Prehistoric Rock Carvings in Northumberland |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, X.; Lu, Y.; Martin, J. A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031055
Liang X, Lu Y, Martin J. A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031055
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Xiaoxu, Yanjun Lu, and John Martin. 2021. "A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031055
APA StyleLiang, X., Lu, Y., & Martin, J. (2021). A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability. Sustainability, 13(3), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031055








