Cross-Validation of the MEDEAS Energy-Economy-Environment Model with the Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) and the Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning System (LEAP)
Abstract
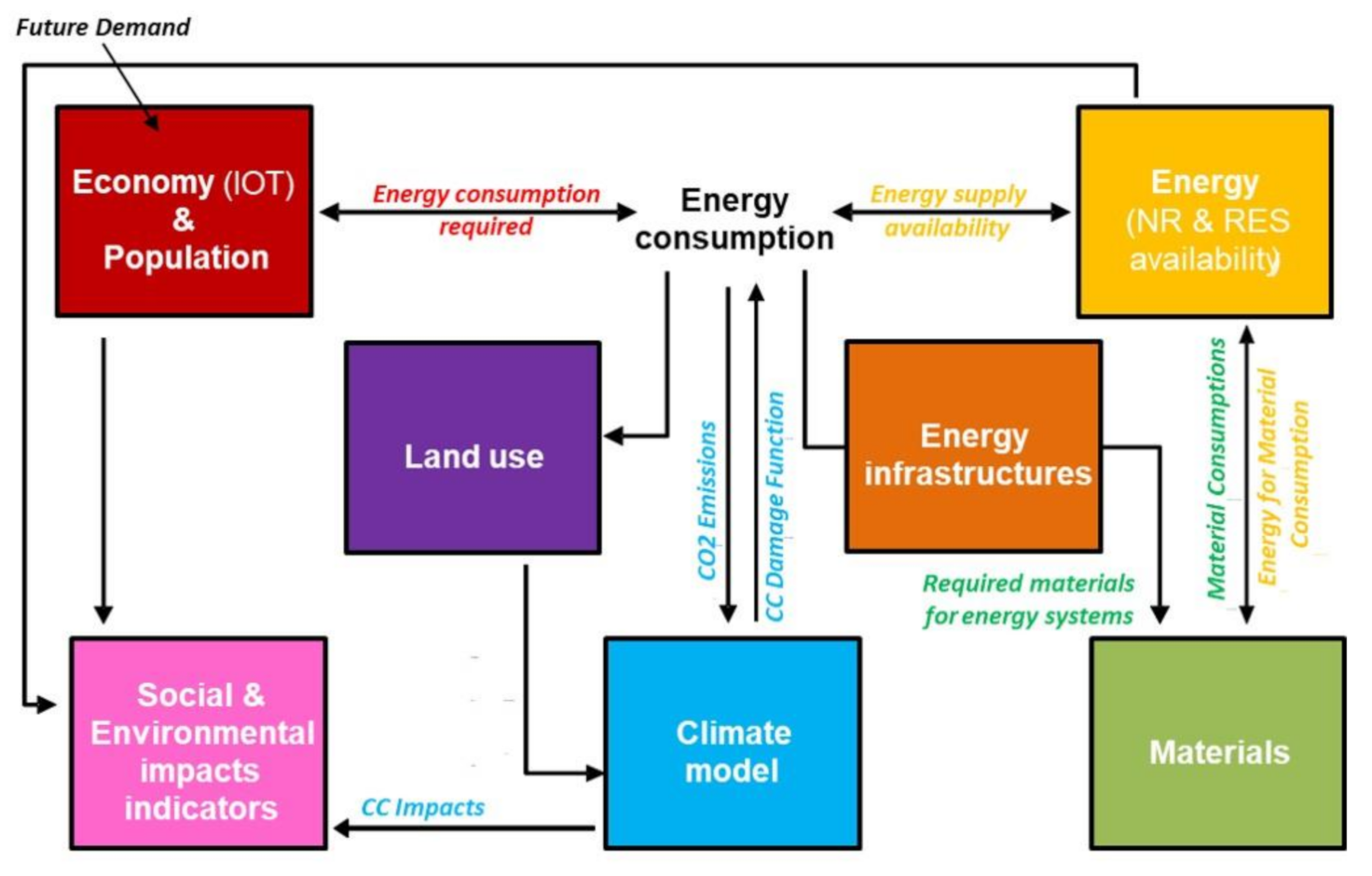
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Standard (or absolute) RMSDs:
- Normalized RMSDs:
3. Results
3.1. Results for Austria
3.2. Results for Bulgaria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Evaluation of National Carbon Budget for Austria and Bulgaria


Appendix B
Appendix B.1. MATLAB CODE Austria Normalized RMSD
Appendix B.2. MATLAB CODE Bulgaria Normalized RMSD
References
- Rotmans, J.; van Asselt, M.B.A. Uncertainty in Integrated Assessment Modelling: A Labyrinthic Path. Uncertain. Integr. Assess. Model. Labyrinthic Path 2001, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, S.; De Carolis, J.; Hirth, L.; Quoilin, S.; Staffell, I. The importance of open data and software: Is energy research lagging behind? Energy Policy 2017, 101, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.H.M. The Limits to Growth. Club Rome 1972, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, S.; Anger-Kraavi, A.; Monasterolo, I.; Jones, A. Emergence of New Economics Energy Transition Models: A Review. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 177, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellán-Pérez, I.; de Blas, I.; Nieto, J.; de Castro, C.; Miguel, L.J.; Carpintero, Ó.; Mediavilla, M.; Lobejón, L.F.; Ferreras-Alonso, N.; Rodrigo, P.; et al. MEDEAS: A new modeling framework integrating global biophysical and socioeconomic constraints. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 986–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrieciu, S.; Rezai, A.; Mechler, R. On the economic foundations of green growth discourses: The case of climate change mitigation and macroeconomic dynamics in economic modeling: Economic foundations of green growth discourses. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2013, 2, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, D.; Moore, F. Quantifying the economic risks of climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, S.; Stern, N. Endogenous Growth, Convexity of Damage and Climate Risk: How Nordhaus’ Framework Supports Deep Cuts in Carbon Emissions. Econ. J. 2015, 125, 574–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ringkjøb, H.-K.; Haugan, P.M.; Solbrekke, I.M. A review of modelling tools for energy and electricity systems with large shares of variable renewables. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 96, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, J.; Samsó, R.; García-Ladona, E.; García-Olivares, A.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Madurell, T.; Turiel, A.; Osychenko, O.; Álvarez, D.; Bardi, U.; et al. Modelling the renewable transition: Scenarios and pathways for a decarbonized future using pymedeas, a new open-source energy systems model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellán-Pérez, I.; de Castro, C.; Miguel González, L.J. Dynamic Energy Return on Energy Investment (EROI) and material requirements in scenarios of global transition to renewable energies. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelloni, G.; Falsini, S.; Di Patti, F.; Bardi, U. MEDEAS-World Model Calibration for the Study of the Energy Transition. PuntOorg Int. J. 2020, 4, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Blas, I.; Miguel, L.J.; Capellán-Pérez, I. Modelling of sectoral energy demand through energy intensities in MEDEAS integrated assessment model. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEDEAS. MEDEAS Project. Modelling the Energy Development under Environmental And Socioeconomic Constraints. 2019. Available online: www.medeas.eu (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Solé, J.; García-Olivares, A.; Turiel, A.; Ballabrera-Poy, J. Renewable transitions and the net energy from oil liquids: A scenarios study. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellán-Pérez, I.; De Blas, I.; Nieto, J.; De Castro, C.; Miguel, L.J.; Mediavilla, M.; Carpintero, O.; Rodrigo, P.; Frechoso, F.; Cáceres, S. Modelling Sustainable Energy System Development under Environmental and Socioeconomic Constraints; MEDEAS scenarios Deliverable D4.1; MEDEAS: Pleasanton, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Decoupling Natural Resource Use and Environmental Impacts from Economic Growth; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Loulou, R. Documentation for the MARKAL Family of Models. Energy Technol. Syst. Anal. Programme 2004, 389, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Loulou, R.; Remne, U.; Kanudia, A.; Lehtila, A.; Goldstein, G. Documentation for the TIMES Model—PART 1. IEA Energy Technol. Syst. Anal. Programme 2005, 1, 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Heaps, Charles Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning (LEAP) System. [software version: 2020.1.20]. Stockholm Environment Institute: Somerville, MA, USA. Available online: https://leap.sei.org (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Connolly, D.; Lund, H.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Leahy, M. A review of computer tools for analysing the integration of renewable energy into various energy systems. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1059–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beeck, N.M.J.P. Classification of Energy Models; FEW Research Memorandum; Operations research: Tilburg, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 777. [Google Scholar]
- «MEDEAS Models Cross Validation», MEDEAS. 2019. Available online: https://www.medeas.eu/model/medeas-vs-times-leap (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Nieto, J.; Carpintero, Ó.; Miguel, L.J.; de Blas, I. Macroeconomic modelling under energy constraints: Global low carbon transition scenarios. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samsó, R.; de Blas, I.; Perissi, I.; Martelloni, G.; Solé, J. Scenario analysis and sensitivity exploration of the MEDEAS Europe energy-economy-environment model. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Paris Agreement. 2015. Available online: http://unfccc.int/paris_agreement/items/9485.php (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Perissi, I.; Falsini, S.; Bardi, U.; Natalini, D.; Green, M.; Jones, A.; Sol, J. Potential European Emissions Trajectories within the Global Carbon Budget. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myung, I.J. The Importance of Complexity in Model Selection. J. Math. Psychol. 2000, 44, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVicar, T. Estimating one-time-of-day meteorological data from standard daily data as inputs to thermal remote sensing based energy balance models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 96, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrensky, L. A Verification Study of the Global WAM Model; technical report no. 63 1987; ECMWF: Shinfield Park, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Siegenfeld, A.F.; Bar-Yam, Y. An Introduction to Complex Systems Science and Its Applications. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, U.; Falsini, S.; Perissi, I. Toward a General Theory of Societal Collapse. A Biophysical Examination of Tainter’s Model of the Diminishing Returns of Complexity. Biophys. Econ. Resour. Qual. 2018, arXiv:1810.07056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabási, A.-L. Scale-Free Networks: A Decade and Beyond. Science 2009, 325, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto, J.; Carpintero, Ó.; Lobejón, L.F.; Miguel, L.J. An ecological macroeconomics model: The energy transition in the EU. Energy Policy 2020, 145, 111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.; Carpintero, Ó.; Miguel, L.J. Less than 2 °C? An Economic-Environmental Evaluation of the Paris Agreement. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Valero, A.; Calvo, G.; Ortego, A. Material bottlenecks in the future development of green technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| SECTORS | MEDEAS_at | TIMES_at | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel AUT [scenarios, final sources! Electricity Gas and Water Supply] | Export-Ver brauch Sektor Energie |
| 2 | Transport sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel AUT [scenarios, final sources! TRANSPORT SECTORS!] | Export-EEV by Sector-en [transport] |
| 3 | Industry | Real final energy by sector and fuel AUT [scenarios, final sources! INDUSTRY SECTORS!] | Export-EEV by Sector-en [industry] |
| 4 | Agriculture | Real final energy by sector and fuel AUT [scenarios, final sources! agriculture hunting forestry and fishing] | Export-EEV by Sector-en [agriculture] |
| 5 | Natural gas | PES fossil fuel extraction [scenarios, gases] | Export-BIV-en [gas] |
| 6 | Coal | PES fossil fuel extraction [scenarios, solids] | Export-BIV-en [coal] |
| 7 | Oil | PES fossil fuel extraction [scenarios, liquids] | Export-BIV-en [oil] |
| 8 | Solar PV | PE solar PV for Elec generation EJ [scenarios] | Export-BIV-en [solar PV] |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | PE hydro for Elec generation EJ [scenarios] | Export-BIV-en [hydro] |
| 10 | Biomass | PE bioE for Elec generation EJ [scenarios] | Export-BIV-en [biomass] |
| 11 | Heat | real FE consumption by fuel [scenarios, heat] | Export-EEV-total-agg-en [heat] |
| 12 | Electricity | real FE consumption by fuel [scenarios, electricity] | Export-EEV-total-agg-en [Elec] |
| 13 | Solar PV | installed capacity RES elec TW [solar PV, scenarios] | Export-ELC-Cap-Ty [solar PV] |
| 14 | Wind (inshore) | installed capacity RES elec TW [wind onshore, scenarios] | Export-ELC-Cap-Ty [windOn] |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | installed capacity RES elec TW [hydro, scenarios] | Export-ELC-Cap-Ty [hydro] |
| 16 | Biomass | installed capacity RES elec TW [“solid bioE-elec”, scenarios] | Export-ELC-Cap-Ty [solid Bio-e] |
| 17 | Electricity sector | GHG emissions by FE Electricity sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTH GSektor-en [elecricity] |
| 18 | Transport sector | GHG emissions by FE Transport sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTH GSektor-en [transport] |
| 19 | Industry sector | GHG emissions by FE Industry sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTH GSektor-en [industry] |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | GHG emissions by FE Agriculture sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTH GSektor-en [agriculture] |
| 21 | Services sector | GHG emissions by FE Services sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTH GSektor-en [services] |
| 22 | Household sector | GHG emissions by FE Households sector [scenarios, final sources] | Export-GHG-perTHG-en [households] |
| 23 | Share of electrification of transport sector | Share demand electricity in transport [scenarios] | Export-Transport-EEV-total-en [transport] |
| SECTORS | MEDEAS_bg | LEAP_bg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel BGR [BAU, transport] | Energy demand final units: Transport |
| 2 | Industry sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel BGR [BAU, industry] | Energy demand final units: Industry |
| 3 | Agriculture sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel BGR [BAU, agriculture] | Energy demand final units: Agriculture |
| 4 | Services sector | Real final energy by sector and fuel BGR [BAU, services] | Energy demand final units: Services |
| 5 | Coal | PES fossil fuel extraction [BAU, solids] | Primary requirements/Coal Antracite + Coal Lignite + Coke |
| 6 | Oil | PES fossil fuel extraction [BAU, liquids] | Primary requirements/Gasoline + Diesel + Jet Kerosine + Residual Fuel oil + LPG |
| 7 | PE solar PV for Elec generation EJ [BAU] | Primary requirements/Solar (PV share) | |
| 8 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | PE onshore wind for Elec generation EJ [BAU] | Primary requirements/wind |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | PE hydro for Elec generation EJ [BAU] | Primary requirements/Hydro |
| 10 | Biomass | PE bioE for Elec generation EJ [BAU] | Primary requirements/biomass + biogas + biodiesel + ethanol + MSW + charcoal |
| 11 | Electricity | real FE consumption by fuel [BAU, electricity] | FEC/electricity |
| 12 | District heat | real FE consumption by fuel [BAU, heat] | FEC/heat |
| 13 | Solar PV | installed capacity RES elec TW [solar PV] | Capacity: PV |
| 14 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | installed capacity RES elec TW [wind onshore] | Capacity: Wind |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | installed capacity RES elec TW [hydro, scenarios] | Capacity: Hydro (excl. PSP) |
| 16 | Biomass (electric) | installed capacity RES elec TW [“solid bioE-elec”, scenarios] | Capacity: Biomass |
| 17 | Electricity sector | GHG Electricity sector [scenarios] | total = direct + indirect (heat and electricity emissions allocated to demand). |
| 18 | Transport sector | GHG Transport sector [scenarios] | |
| 19 | Industry sector | GHG Industry sector [scenarios] | |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | GHG Agriculture sector [scenarios] | |
| 21 | Services sector | GHG Services sector [scenarios] | |
| 22 | Household sector | GHG Households sector [scenarios] | |
| 23 | Cumulative GHG emissions (million metric ton CO2 eq.) | Cumulative CO2e GHG emissions [scenarios] | Direct plus Indirect emissions (CO2e). |
| 24 | Cumulative GHG Transport sector | GHG emissions by FE Transport sector [scenarios, final sources] | Emissions allocated to demands: Transport |
| 25 | Cumulative GHG Industry sector | GHG emissions by FE Industry sector [scenarios, final sources] | Emissions allocated to demands: Industry |
| 26 | Cumulative GHG Agriculture sector | GHG emissions by FE Agriculture sector [scenarios, final sources] | Emissions allocated to demands: Agriculture |
| 27 | Cumulative GHG Services sector | GHG emissions by FE Services sector [scenarios, final sources] | Emissions allocated to demands: Services |
| 28 | Cumulative GHG Household sector | GHG emissions by FE Households sector [scenarios, final sources] | Emissions allocated to demands: Residential |
| 29 | Share of electrification of transport sector | Share demand electricity in transport [scenarios] | Share of electricity vs. Total |
| 30 | Share of RES in transportation | share RES elect in transport [scenarios] + share RES liquids in transport [scenarios] | Includes RES share in transport and RES share of the electricity in transport |
| Austria SECTORS BAU_at Abs | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity sector | 5.87 × 10−2 | 5.67 × 10−2 | 5.52 × 10−2 |
| 2 | Transport sector | 2.36 × 10−1 | 2.26 × 10−1 | 2.16 × 10−1 |
| 3 | Industry | 7.92 × 10−2 | 7.85 × 10−2 | 7.15 × 10−2 |
| 4 | Agriculture | 1.27 × 10−3 | 2.46 × 10−3 | 3.66 × 10−3 |
| 5 | Natural gas | 8.86 × 10−2 | 1.32 × 10−1 | 1.74 × 10−1 |
| 6 | Coal | 1.46 × 10−1 | 2.03 × 10−1 | 2.51 × 10−1 |
| 7 | Oil | 6.24 × 10−2 | 1.06 × 10−1 | 1.50 × 10−1 |
| 8 | Solar PV | 4.07 × 10−3 | 8.51 × 10−3 | 1.47 × 10−2 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 9.91 × 10−3 | 8.33 × 10−3 | 8.51 × 10−3 |
| 10 | Biomass | 1.93 × 10−1 | 1.93 × 10−1 | 1.90 × 10−1 |
| 11 | Heat | 3.10 × 10−1 | 3.35 × 10−1 | 3.64 × 10−1 |
| 12 | Electricity | 8.43 × 10−2 | 1.17 × 10−1 | 1.51 × 10−1 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 8.37 × 10−4 | 1.90 × 10−3 | 3.39 × 10−3 |
| 14 | Wind (inshore) | 8.47 × 10−4 | 1.95 × 10−3 | 2.96 × 10−3 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 1.18 × 10−3 | 1.01 × 10−3 | 9.47 × 10−4 |
| 16 | Biomass | 1.21 × 10−3 | 1.16 × 10−3 | 1.16 × 10−3 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 3.36 × 10−3 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 2.99 × 10−3 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 1.36 × 10−2 | 1.23 × 10−2 | 1.11 × 10−2 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 8.44 × 10−3 | 1.26 × 10−2 | 1.71 × 10−2 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 2.08 × 10−3 | 2.38 × 10−3 | 2.67 × 10−3 |
| 21 | Services sector | 6.41 × 10−3 | 7.65 × 10−3 | 8.80 × 10−3 |
| 22 | Household sector | 2.63 × 10−2 | 3.07 × 10−2 | 3.50 × 10−2 |
| 23 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 2.57 × 10−3 | 7.43 × 10−3 | 1.65 × 10−2 |
| Austria SECTORS OLT_at Abs | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity sector | 5.31 × 10−2 | 4.55 × 10−2 | 4.12 × 10−2 |
| 2 | Transport sector | 2.02 × 10−1 | 1.67 × 10−1 | 1.45 × 10−1 |
| 3 | Industry | 8.06 × 10−2 | 1.17 × 10−1 | 1.49 × 10−1 |
| 4 | Agriculture | 4.71 × 10−3 | 7.04 × 10−3 | 8.09 × 10−3 |
| 5 | Natural gas | 4.02 × 10−2 | 3.57 × 10−2 | 3.29 × 10−2 |
| 6 | Coal | 4.12 × 10−2 | 4.06 × 10−2 | 3.78 × 10−2 |
| 7 | Oil | 1.38 × 10−1 | 2.27 × 10−1 | 2.68 × 10−1 |
| 8 | Solar PV | 9.17 × 10−3 | 2.43 × 10−2 | 4.24 × 10−2 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 1.14 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−2 | 1.21 × 10−2 |
| 10 | Biomass | 1.85 × 10−1 | 2.01 × 10−1 | 1.88 × 10−1 |
| 11 | Heat | 2.70 × 10−1 | 2.51 × 10−1 | 2.44 × 10−1 |
| 12 | Electricity | 4.56 × 10−2 | 6.20 × 10−2 | 1.00 × 10−1 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 2.21 × 10−3 | 6.28 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 10−2 |
| 14 | Wind (inshore) | 8.58 × 10−4 | 2.03 × 10−3 | 3.24 × 10−3 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 1.17 × 10−3 | 9.88 × 10−4 | 8.84 × 10−4 |
| 16 | Biomass | 1.13 × 10−3 | 9.77 × 10−4 | 9.34 × 10−4 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 3.14 × 10−3 | 2.58 × 10−3 | 2.25 × 10−3 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 1.18 × 10−2 | 1.00 × 10−2 | 9.16 × 10−3 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 2.87 × 10−3 | 3.68 × 10−3 | 3.45 × 10−3 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 1.25 × 10−3 | 1.03 × 10−3 | 9.10 × 10−4 |
| 21 | Services sector | 4.96 × 10−3 | 4.64 × 10−3 | 4.36 × 10−3 |
| 22 | Household sector | 2.24 × 10−2 | 2.22 × 10−2 | 2.24 × 10−2 |
| 23 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 4.14 × 10−2 | 1.37 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−1 |
| Austria SECTORS BAU_at Norm | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity sector | 1.44 | 1.36 | 1.29 |
| 2 | Transport sector | 1.84 | 1.73 | 1.65 |
| 3 | Industry | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| 4 | Agriculture | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| 5 | Natural gas | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.38 |
| 6 | Coal | 0.61 | 0.70 | 0.75 |
| 7 | Oil | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.27 |
| 8 | Solar PV | 1.15 | 2.12 | 3.33 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 10 | Biomass | 4.19 | 4.30 | 4.32 |
| 11 | Heat | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| 12 | Electricity | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.37 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 0.75 | 1.50 | 2.45 |
| 14 | Wind (inshore) | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.54 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 16 | Biomass | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.70 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 1.15 | 0.98 | 0.86 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 1.36 | 1.16 | 0.99 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.77 |
| 21 | Services sector | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.92 |
| 22 | Household sector | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.93 |
| 23 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.20 |
| Austria SECTORS OLT_at Norm | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity sector | 1.44 | 1.35 | 1.30 |
| 2 | Transport sector | 1.72 | 1.41 | 1.21 |
| 3 | Industry | 0.24 | 0.39 | 0.54 |
| 4 | Agriculture | 0.23 | 0.39 | 0.49 |
| 5 | Natural gas | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| 6 | Coal | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.46 |
| 7 | Oil | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.62 |
| 8 | Solar PV | 2.60 | 6.02 | 9.53 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 10 | Biomass | 4.05 | 4.59 | 4.46 |
| 11 | Heat | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 12 | Electricity | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.38 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 1.99 | 4.96 | 8.04 |
| 14 | Wind (inshore) | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.55 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| 16 | Biomass | 0.66 | 0.58 | 0.56 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 1.52 | 1.58 | 1.68 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 1.34 | 1.15 | 1.06 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.23 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.68 |
| 21 | Services sector | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| 22 | Household sector | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.90 |
| 23 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 0.77 | 1.89 | 2.04 |
| Bulgaria SECTORS BAU_bg Abs | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport sector | 5.86 × 10−2 | 4.86 × 10−2 | 4.23 × 10−2 |
| 2 | Industry sector | 3.37 × 10−2 | 4.18 × 10−2 | 4.58 × 10−2 |
| 3 | Agriculture sector | 3.18 × 10−3 | 2.65 × 10−3 | 2.37 × 10−3 |
| 4 | Services sector | 3.82 × 10−2 | 3.82 × 10−2 | 3.76 × 10−2 |
| 5 | Coal | 3.42 × 10−2 | 3.87 × 10−2 | 3.38 × 10−2 |
| 6 | Oil | 2.99 × 10−2 | 4.08 × 10−2 | 4.04 × 10−2 |
| 7 | Solar PV requirements | 1.55 × 10−1 | 1.69 × 10−1 | 1.76 × 10−1 |
| 8 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 4.34 × 10−3 | 7.57 × 10−3 | 9.64 × 10−3 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 2.05 × 10−3 | 5.37 × 10−3 | 6.94 × 10−3 |
| 10 | Biomass | 6.35 × 10−3 | 8.41 × 10−3 | 7.87 × 10−3 |
| 11 | Electricity | 2.42 × 10−3 | 4.06 × 10−3 | 5.16 × 10−3 |
| 12 | District heat | 2.06 × 10−2 | 3.09 × 10−2 | 4.27 × 10−2 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 5.46 × 10−2 | 4.75 × 10−2 | 4.16 × 10−2 |
| 14 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 4.08 × 10−4 | 9.75 × 10−4 | 1.49 × 10−3 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 6.97 × 10−4 | 8.14 × 10−4 | 8.03 × 10−4 |
| 16 | Biomass (electric) | 1.82 × 10−4 | 3.33 × 10−4 | 4.41 × 10−4 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 1.38 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−2 | 9.95 × 10−3 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 2.64 × 10−3 | 2.25 × 10−3 | 2.07 × 10−3 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 6.27 × 10−3 | 6.38 × 10−3 | 6.15 × 10−3 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 2.43 × 10−4 | 2.11 × 10−4 | 1.87 × 10−4 |
| 21 | Services sector | 1.13 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 10−3 |
| 22 | Household sector | 8.28 × 10−4 | 7.61 × 10−4 | 8.96 × 10−4 |
| 23 | Cumulative GHG emissions (million metric ton CO2 eq.) | 1.44 × 10−1 | 2.24 × 10−1 | 2.81 × 10−1 |
| 24 | Cumulative GHG Transport sector | 2.21 × 10−2 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 1.63 × 10−2 |
| 25 | Cumulative GHG Industry sector | 1.27 × 10−2 | 1.06 × 10−2 | 9.48 × 10−3 |
| 26 | Cumulative GHG Agriculture sector | 1.16 × 10−3 | 9.61 × 10−4 | 8.54 × 10−4 |
| 27 | Cumulative GHG Services sector | 5.17 × 10−3 | 4.34 × 10−3 | 3.77 × 10−3 |
| 28 | Cumulative GHG Household sector | 5.78 × 10−2 | 5.57 × 10−2 | 5.12 × 10−2 |
| 29 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 4.75 × 10−2 | 1.12 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−1 |
| 30 | Share of RES in transportation | 6.73 × 10−2 | 8.22 × 10−2 | 8.43 × 10−2 |
| Bulgaria SECTORS OLT_bg Abs | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport sector | 5.86 × 10−2 | 4.86 × 10−2 | 4.23 × 10−2 |
| 2 | Industry sector | 3.37 × 10−2 | 4.18 × 10−2 | 4.58 × 10−2 |
| 3 | Agriculture sector | 3.18 × 10−3 | 2.65 × 10−3 | 2.37 × 10−3 |
| 4 | Services sector | 3.82 × 10−2 | 3.82 × 10−2 | 3.76 × 10−2 |
| 5 | Coal | 3.42 × 10−2 | 3.87 × 10−2 | 3.38 × 10−2 |
| 6 | Oil | 2.99 × 10−2 | 4.08 × 10−2 | 4.04 × 10−2 |
| 7 | Solar PV requirements | 1.55 × 10−1 | 1.69 × 10−1 | 1.76 × 10−1 |
| 8 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 4.34 × 10−3 | 7.57 × 10−3 | 9.64 × 10−3 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 2.05 × 10−3 | 5.37 × 10−3 | 6.94 × 10−3 |
| 10 | Biomass | 6.35 × 10−3 | 8.41 × 10−3 | 7.87 × 10−3 |
| 11 | Electricity | 2.42 × 10−3 | 4.06 × 10−3 | 5.16 × 10−3 |
| 12 | District heat | 2.06 × 10−2 | 3.09 × 10−2 | 4.27 × 10−2 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 5.46 × 10−2 | 4.75 × 10−2 | 4.16 × 10−2 |
| 14 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 4.08 × 10−4 | 9.75 × 10−4 | 1.49 × 10−3 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 6.97 × 10−4 | 8.14 × 10−4 | 8.03 × 10−4 |
| 16 | Biomass (electric) | 1.82 × 10−4 | 3.33 × 10−4 | 4.41 × 10−4 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 1.38 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−2 | 9.95 × 10−3 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 2.64 × 10−3 | 2.25 × 10−3 | 2.07 × 10−3 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 6.27 × 10−3 | 6.38 × 10−3 | 6.15 × 10−3 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 2.43 × 10−4 | 2.11 × 10−4 | 1.87 × 10−4 |
| 21 | Services sector | 1.13 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 10−3 |
| 22 | Household sector | 8.28 × 10−4 | 7.61 × 10−4 | 8.96 × 10−4 |
| 23 | Cumulative GHG emissions (million metric ton CO2 eq.) | 1.44 × 10−1 | 2.24 × 10−1 | 2.81 × 10−1 |
| 24 | Cumulative GHG Transport sector | 2.21 × 10−2 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 1.63 × 10−2 |
| 25 | Cumulative GHG Industry sector | 1.27 × 10−2 | 1.06 × 10−2 | 9.48 × 10−3 |
| 26 | Cumulative GHG Agriculture sector | 1.16 × 10−3 | 9.61 × 10−4 | 8.54 × 10−4 |
| 27 | Cumulative GHG Services sector | 5.17 × 10−3 | 4.34 × 10−3 | 3.77 × 10−3 |
| 28 | Cumulative GHG Household sector | 5.78 × 10−2 | 5.57 × 10−2 | 5.12 × 10−2 |
| 29 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 4.75 × 10−2 | 1.12 × 10−1 | 1.78 × 10−1 |
| 30 | Share of RES in transportation | 6.73 × 10−2 | 8.22 × 10−2 | 8.43 × 10−2 |
| Bulgaria SECTORS BAU_bg Norm | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport sector | 1.09 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| 2 | Industry sector | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 3 | Agriculture sector | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.43 |
| 4 | Services sector | 7.49 | 7.85 | 8.11 |
| 5 | Coal | 1.37 | 1.34 | 1.29 |
| 6 | Oil | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.30 |
| 7 | Solar PV requirements | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| 8 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.49 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.28 |
| 10 | Biomass | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| 11 | Electricity | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| 12 | District heat | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.68 |
| 14 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.22 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.32 |
| 16 | Biomass (electric) | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 4.32 | 4.15 | 4.06 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.50 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.29 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 0.36 | 0.41 | 0.45 |
| 21 | Services sector | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| 22 | Household sector | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| 23 | Cumulative GHG emissions (million metric ton CO2 eq.) | 0.44 | 0.59 | 0.69 |
| 24 | Cumulative GHG Transport sector | 5.08 | 4.89 | 4.78 |
| 25 | Cumulative GHG Industry sector | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.61 |
| 26 | Cumulative GHG Agriculture sector | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.58 |
| 27 | Cumulative GHG Services sector | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| 28 | Cumulative GHG Household sector | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 29 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 30 | Share of RES in transportation | 35.94 | 20.59 | 13.10 |
| Bulgaria SECTORS OLT_bg Norm | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport sector | 0.91 | 0.74 | 0.67 |
| 2 | Industry sector | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.83 |
| 3 | Agriculture sector | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.34 |
| 4 | Services sector | 9.06 | 11.06 | 13.04 |
| 5 | Coal | 1.66 | 1.73 | 1.81 |
| 6 | Oil | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.28 |
| 7 | Solar PV requirements | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.35 |
| 8 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 1.21 | 1.97 | 2.28 |
| 9 | Hydroelectric | 0.46 | 1.13 | 1.29 |
| 10 | Biomass | 0.45 | 0.58 | 0.53 |
| 11 | Electricity | 0.94 | 1.62 | 2.12 |
| 12 | District heat | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.54 |
| 13 | Solar PV | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.62 |
| 14 | Wind (onshore and offshore) | 0.44 | 0.98 | 1.36 |
| 15 | Hydroelectric excl. Pumped storage | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 16 | Biomass (electric) | 3.39 | 6.34 | 8.49 |
| 17 | Electricity sector | 6.58 | 7.14 | 7.99 |
| 18 | Transport sector | 0.51 | 0.42 | 0.41 |
| 19 | Industry sector | 0.69 | 0.92 | 1.14 |
| 20 | Agriculture sector | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.33 |
| 21 | Services sector | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.29 |
| 22 | Household sector | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| 23 | Cumulative GHG emissions (million metric ton CO2 eq.) | 0.44 | 0.60 | 0.70 |
| 24 | Cumulative GHG Transport sector | 4.27 | 3.51 | 3.22 |
| 25 | Cumulative GHG Industry sector | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.90 |
| 26 | Cumulative GHG Agriculture sector | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.68 |
| 27 | Cumulative GHG Services sector | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.98 |
| 28 | Cumulative GHG Household sector | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| 29 | Share of electrification of transport sector | 3.05 | 5.67 | 7.12 |
| 30 | Share of RES in transportation | 35.61 | 14.26 | 6.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perissi, I.; Martelloni, G.; Bardi, U.; Natalini, D.; Jones, A.; Nikolaev, A.; Eggler, L.; Baumann, M.; Samsó, R.; Solé, J. Cross-Validation of the MEDEAS Energy-Economy-Environment Model with the Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) and the Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning System (LEAP). Sustainability 2021, 13, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041967
Perissi I, Martelloni G, Bardi U, Natalini D, Jones A, Nikolaev A, Eggler L, Baumann M, Samsó R, Solé J. Cross-Validation of the MEDEAS Energy-Economy-Environment Model with the Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) and the Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning System (LEAP). Sustainability. 2021; 13(4):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041967
Chicago/Turabian StylePerissi, Ilaria, Gianluca Martelloni, Ugo Bardi, Davide Natalini, Aled Jones, Angel Nikolaev, Lukas Eggler, Martin Baumann, Roger Samsó, and Jordi Solé. 2021. "Cross-Validation of the MEDEAS Energy-Economy-Environment Model with the Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) and the Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning System (LEAP)" Sustainability 13, no. 4: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041967
APA StylePerissi, I., Martelloni, G., Bardi, U., Natalini, D., Jones, A., Nikolaev, A., Eggler, L., Baumann, M., Samsó, R., & Solé, J. (2021). Cross-Validation of the MEDEAS Energy-Economy-Environment Model with the Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) and the Long-Range Energy Alternatives Planning System (LEAP). Sustainability, 13(4), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041967









