Spatial Econometric Analysis of Road Traffic Crashes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
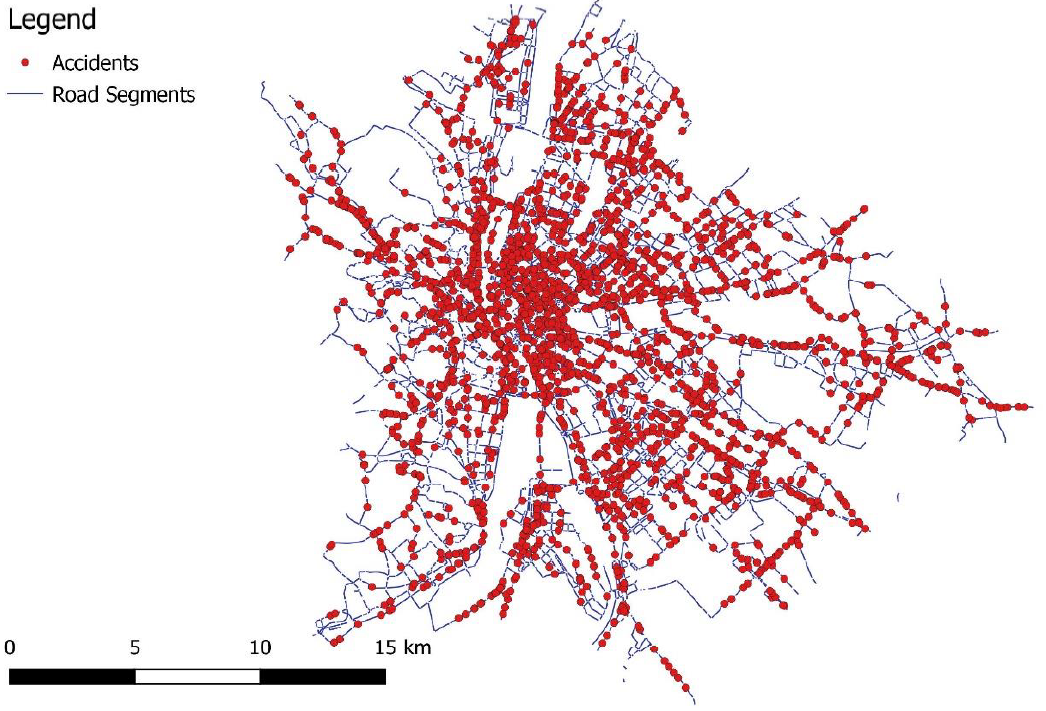
2. Data
Data Collection
- 1.
- Residential streets (free-flow speed is less than or equal with 20 kph);
- 2.
- Urban roads (free-flow speed is between 20 kph and 50 kph);
- 3.
- Main roads (free-flow speed is between 50 kph and 90 kph);
- 4.
- High-speed roads (free-flow speed is above 90 kph).
3. Methodology
- y: dependent variable;
- α: constant term;
- βi: estimated coefficients of the linear regression model (∀j = 1..m);
- xi: explanatory variables (∀j = 1..m);
- ε: error term (Eεi = 0, V(εi) = σ2);
- N: number of observations.
- N: number of investigated points;
- xi, xj: the observed value of two points of interest;
- μ: the expected value of x;
- wij: the elements of the spatial weight matrix;
- S0: normalizer—S0 = ∑i,jwi,j
- y: vector of the dependent variables;
- ρ: autoregressive parameter;
- W: weight matrix;
- β: coefficient vector;
- X: matrix of the independent variables;
- ε: vector of errors (E(εi) = 0, V(εi) = σ2);
- N: number of points of interest;
- K: number of independent variables.
- ζ: vector of spatial dependent errors;
- λ: autoregressive error parameter.
- L1: likelihood value of the inferior model;
- L2: likelihood value of the superior model;
- df: degree of freedom for the chi-square distribution, equal to the number of the surplus estimated variables.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Diagnosis of Spatial Dependence
4.2. Model Outputs
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, S.; Lidbe, A.; Hainen, A. What can open access data from India tell us about road safety and sustainable development? J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 80, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, R.; Cowie, J.; Maher, M. Active Road Studs as an Alternative to Lighting on Rural Roads: Driver Safety Perception. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoufas, A.; Basbas, S.; Salanova Grau, J.M.; Aifadopoulou, G. Analysis of In-Vehicle Warning System for Rail-Road Level Crossings: Case Study in the City of Thessaloniki, Greece. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2020, 49, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Tettamanti, T.; Hörcher, D.; Varga, I. The impact of autonomous vehicles on urban traffic network capacity: An experimental analysis by microscopic traffic simulation. Transp. Lett. 2020, 12, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astarita, V.; Caliendo, C.; Giofrè, V.P.; Russo, I. Surrogate Safety Measures from Traffic Simulation: Validation of Safety Indicators with Intersection Traffic Crash Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, N.; Lu, Y. Macrolevel Traffic Crash Analysis: A Spatial Econometric Model Approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, J. Application of Spatial Econometrics Analysis for Traffic Accident Prediction Models in Urban Areas. In Proceedings of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, Taipei, Taiwan, 9–12 September 2013; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, K.-A.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, Y.; Ulfarsson, G.F. Spatial regression analysis of traffic crashes in Seoul. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 91, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, D. Spatial Autocorrelation: A Primer; Association of American Geographers: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, V.; Mannering, F.; Barfield, W. Effect of roadway geometrics and environmental factors on rural freeway accident frequencies. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1995, 27, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briz-Redón, Á.; Martínez-Ruiz, F.; Montes, F. Spatial analysis of traffic accidents near and between road intersections in a directed linear network. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 132, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.; Hung, W.; Wong, W. An algorithm for assessing the risk of traffic accident. J. Saf. Res. 2002, 33, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, R.B.; Quddus, M.A. Congestion, and safety: A spatial analysis of London. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2005, 39, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.J.; Xing, Y.; Wang, C.; Cai, X. Risk factors affecting the severity of traffic accidents at Shanghai river-crossing tunnel. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado-Sanz, N.; Guirao, B.; Attard, M. Analysis of the Risk Factors Affecting the Severity of Traffic Accidents on Spanish Crosstown Roads: The Driver's Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantillo, V.; Garcés, P.; Márquez, L. Factors influencing the occurrence of traffic accidents in urban roads: A combined GIS-Empirical Bayesian approach. DYNA 2016, 83, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quddus, M.A. Modelling area-wide count outcomes with spatial correlation and heterogeneity: An analysis of London crash data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2008, 40, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Quddus, M.A.; Ison, S.G. Impact of traffic congestion on road accidents: A spatial analysis of the M25 motorway in England. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.; Paleti, R.; Bhat, C.R. A spatial generalized ordered response model to examine highway crash injury severity. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 52, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, K.; Ozbay, K.; Yang, H. Spatial analysis of highway incident durations in the context of Hurricane Sandy. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 74, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Khadka, A.; Kim, I. Traffic crash analysis with point-of-interest spatial clustering. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 121, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pljakić, M.; Jovanović, D.; Matović, B.; Mićić, S. Macro-level accident modeling in Novi Sad: A spatial regression approach. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 132, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soro, W.L.; Zhou, Y.; Wayoro, D. Crash rates analysis in China using a spatial panel model. IATSS Res. 2017, 41, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.; Paleti, R.; Bhat, C.R. A latent variable representation of count data models to accommodate spatial and temporal dependence: Application to predicting crash frequency at intersections. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2012, 46, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, H.-H.; Thill, J.-C. Analysis of traffic hazard intensity: A spatial epidemiology case study of urban pedestrians. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2011, 35, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, B.; Dahlinger, A.; Gahr, B.; Zundritsch, P.; Wortmann, F.; Fleisch, E. Spatial prediction of traffic accidents with critical driving events—Insights from a nationwide field study. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 124, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gim, T.-H.T. A spatial econometrics perspective on the characteristics of urban traffic accidents: Focusing on elderly drivers' accidents in Seoul, South Korea. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2020, 27, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, S.; Wong, S.C.; Xu, P.; Huang, H.; Pei, X. Severity of pedestrian injuries due to traffic crashes at signalized intersections in Hong Kong: A Bayesian spatial logit model. J. Adv. Transp. 2016, 50, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hasani, G.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Soliman, A.-H. Comparison of Spatial Regression Models with Road Traffic Accidents Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Statistics: Theory and Applications (ICSTA'19), Lisbon, Portugal, 13–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, T.U.; Nateghi, R.; Hall, T.; Waldorf, B.S. Statistical Analysis of Area-wide Alcohol-related Driving Crashes: A Spatial Econometric Approach. Geogr. Anal. 2020, 52, 394–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Qu, W. Geographical Detection of Traffic Accidents Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity and Influence Factors. IJERPH 2020, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Guldmann, J.-M.; von Rabenau, B. Interactions between the built and socio-economic environment and driver demographics: Spatial econometric models of car crashes in the Columbus Metropolitan Area. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2018, 22, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Factors influencing traffic accident frequencies on urban roads: A spatial panel time-fixed effects error model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, Y.-C.; Fu, C.; Chih-Wei, H. Incorporating spatial dependence in simultaneously modeling crash frequency and severity. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2014, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sharma, A. Exploring spatio-temporal effects in traffic crash trend analysis. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2017, 16, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões, P.; Shrubsall, S.; Natário, I. A spatial econometrics analysis for road accidents in Lisbon. Int. J. Bus. Intell. Data Min. 2015, 10, 152–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.R. Highway Accidents: A Spatial and Temporal Analysis. Transp. Res. Rec. 1991, 1318, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Karaganis, A.N.; Mimis, A. A Spatial Point Process for Estimating the Probability of Occurrence of a Traffic Accident. In Proceedings of the 46th Congress of the European Regional Science Association: “Enlargement, Southern Europe and the Mediterranean”, Volos, Greece, 30 August–3 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Azimian, A.; Pyrialakou, D. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis in Traffic Safety. Int. J. Geospat. Environ. Res. 2020, 7, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Moons, E.; Brijs, T.; Wets, G. Hot Spot Analysis: Improving a Local Indicator of Spatial Association for Application in Traffic Safety. In Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2008; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Laganà, A., Taniar, D., Mun, Y., Gavrilova, M.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5072, pp. 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korter, G.O. A Spatial Analytical Framework for Examining Road Traffic Crashes. J. Mod. App. Stat. Meth. 2016, 15, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenberghen, T.; Dufays, T.; Thomas, I.; Flahaut, B. Intra-urban location and clustering of road accidents using GIS: A Belgian example. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 18, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dadashova, B.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Z. Rethinking Highway Safety Analysis by Leveraging Crowdsourced Waze Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besag, J. Spatial Interaction and the Statistical Analysis of Lattice Systems. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1974, 36, 192–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, Y.M. Applied Spatial Statistics in R, Section 6. Geostatistics 2010. Available online: http://www.people.fas.harvard.edu/~zhukov/Spatial6.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Besag, J.; York, J.; Mollié, A. Bayesian image restoration, with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1991, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ágoston, G.; Madleňák, R. Road Safety Macro Assessment Model: Case Study for Hungary. Period. Polytech Transp. Eng. 2020, 49, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, Á.O.; Sesztakov, V.; Török, Á. Road Safety Analysis in Győr. Period. Polytech Transp. Eng. 2013, 41, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudolph, F.; Mátrai, T. Congestion from a Multimodal Perspective. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2018, 46, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Lord, D.; Peng, Y. Examining Network Segmentation for Traffic Safety Analysis with Data-Driven Spectral Analysis. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120744–120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziakopoulos, A.; Yannis, G. A review of spatial approaches in road safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 135, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, A. Térökonometria. Stat. Szle. 2002, 80, 354–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento-Barbieri, I. An Introduction to Spatial Econometrics in R. 2016. Available online: http://www.econ.uiuc.edu/~lab/workshop/Spatial_in_R.html (accessed on 11 July 2018).
- Szabó, Z.; Török, Á. Spatial Econometrics—Usage in Transportation Sciences: A Review Article. Period. Polytech Transp. Eng. 2019, 48, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A. Spatial interaction and spatial autocorrelation: A cross-product approach. Environ. Plan. A 1991, 23, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. Some Theorems on Time Series: II the Significance of the Serial Correlation Coefficient. Biometrika 1948, 35, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K.; Florax, R.; Yoon, M.J. Simple diagnostic tests for spatial dependence. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1996, 26, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Microeconometrics: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Wien, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bivand, R.S.; Lewin-Koh, N. Maptools: Tools for Reading and Handling Spatial Objects; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Wien, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bivand, R.S.; Pebesma, E.J.; Gómez-Rubio, V. Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pebesma, E.J.; Bivand, R.S. Classes and methods for spatial data in R. R News 2005, 5, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bivand, R.S.; Wong, D.W.S. Comparing implementations of global and local indicators of spatial association. TEST 2018, 27, 716–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R.S.; Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Computing the Jacobian in Gaussian spatial autoregressive models an illustrated comparison of available methods. Geogr. Anal. 2013, 45, 150–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bivand, R.S.; Piras, G. Comparing Implementations of Estimation Methods for Spatial Econometrics. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddala, G.S. Introduction to Econometrics, 3rd ed; John Wiley&Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chang, S.K.J.; de Backer, H.; Lauwers, D.; de Maeyer, P. Integrating Spatial and Temporal Approaches for Explaining Bicycle Crashes in High-Risk Areas in Antwerp (Belgium). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Articles | Handling of Spatial Interactions | Analyzed Units | Speed (KPH/MPH) | AADT (veh/day) | Infrastructure Design Attributes | SAR | SEM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shankar et al. 2015 | (i) the delimitation of spatial units appears, but the modeling of the interactions between them is omitted | (a) | - | - | × | - | - | [10] |
| Briz-Redón et al. 2019 | (a) | - | LN | × | - | - | [11] | |
| Ng et al. 2002 | (b) | - | - | - | - | - | [12] | |
| Noland and Quddus 2005 | (b) | - | - | × | - | - | [13] | |
| Lu et al. 2016 | (b) | × | - | × | - | - | [14] | |
| Casando-Sanz et al. 2010 | (b) | - | × | × | - | - | [15] | |
| Cantillo et al. 2015 | (b) | - | × | × | - | - | [16] | |
| Quddus 2008 | (ii) comparing models that handle spatial interaction with models that do not take spatial interaction into account | (b) | × | LN | × | NS | × | [17] |
| Wang et al. 2009 | (a) | - | LN | × | - | - | [18] | |
| Castro et al. 2013 | (a) | - | - | × | × | - | [19] | |
| Xie et al. 2014 | (a) | - | - | - | × | × | [20] | |
| Rhee et al. 2016 | (b) | - | × | × | × | × | [8] | |
| Jia et al. 2018 | (b) | - | - | - | × | × | [21] | |
| Pljakić et al. 2019 | (b) | - | × | × | × | × | [22] | |
| Soro et al. 2017 | (b) | - | × | × | × | × | [23] | |
| Castro et al. 2012b | (a) | - | LN | × | × | - | [24] | |
| Ha & Thill 2011 | (b) | - | - | - | × | - | [25] | |
| Ryder et al. 2019 | (b) | - | × | × | - | - | [26] | |
| Lee & Gim 2020 | (b) | - | - | × | × | × | [27] | |
| Wang et al. 2019a | (b) | - | - | × | × | × | [6] | |
| Xu et al. 2016 | (a) | - | - | × | - | - | [28] | |
| Al-Hasani et al. 2019 | (b) | - | - | - | × | × | [29] | |
| Saeed et al. 2020 | (b) | - | - | - | - | - | [30] | |
| Zhang et al. 2020 | (b) | - | - | × | - | - | [31] | |
| Lee et al. 2018 | (b) | - | - | - | × | × | [32] | |
| Wang et al. 2019b | (b) | - | - | × | × | × | [33] | |
| Chiou et al. 2014 | (iii) only models that handle spatial interactions are set up | (a) | - | × | × | - | × | [34] |
| Liu and Sharma 2017 | (b) | - | × | - | - | - | [35] | |
| Simoes et al. 2015 | (b) | - | - | - | - | - | [36] | |
| Black 1991 | (a) | - | - | - | - | - | [37] | |
| Karaganis and Mimis 2006 | (a) | - | - | - | - | × | [38] | |
| Azimian and Pyrialakou 2020 | (b) | - | - | - | - | - | [39] | |
| Moons et al. 2008 | (a) | - | - | - | - | - | [40] | |
| Korter 2016 | (b) | - | - | - | × | - | [41] | |
| Steenberghen et al. 2004 | (b) | - | - | - | - | - | [42] | |
| Li et. al. 2020 | (a) | - | - | - | - | - | [43] |
| (a) Elements of Line Road Network | (b) Spatial Units | |
|---|---|---|
| (i) no spatial interactions considered | [10,11] | [12,13,14,15,16] |
| (ii) compare models with and without spatial parameters | [18,19,20,24,28] | [6,8,17,21,22,23,25,26,27,29,30,31,32,33] |
| (iii) models considering spatial interactions | [34,37,38,40,43] | [35,36,39,41,42] |
| No. | Symbol | Variable Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | CAT_XY | Merged category variable of the free-flow speed, and the number of lanes |
| 1 | BUS_LANE | Dummy variable for the bus lane existence |
| 2 | BUS_VOL | Average daily bus and trolleybus traffic |
| 3 | HGV_12_D | Dummy variable whether the HGVs above 12 tons are allowed or not |
| 4 | BIKE_VOL | Average daily bicycle traffic |
| 5 | AADT | Annual average daily traffic of the passenger cars and LGVs (HGVs below 3.5 tons) |
| 6 | Ratio_HGV | Ratio of the HGVs above 3.5 tons compared to the motorized traffic |
| 7 | LENGTH | Length of the given road segment |
| No. of Accidents | No. of Road Links | % | No. of Accidents | No. of Road Links | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3115 | 66.3 | 9 | 3 | 0.1 |
| 1 | 909 | 19.3 | 10 | 3 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 350 | 7.4 | 11 | 2 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 141 | 3.0 | 12 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 4 | 75 | 1.6 | 15 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 49 | 1.0 | 16 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 6 | 19 | 0.4 | 17 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 7 | 19 | 0.4 | 18 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 8 | 10 | 0.2 | 28 | 1 | 0.0 |
| Total | 4701 | 100.0 |
| Type | Moran I | E(I) | V(I) | z-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (km) | 1 | 3.66 × 10−2 | −2.12811 × 10−4 | 6.67 × 10−5 | 10.0090 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| 0.75 | 3.66 × 10−2 | −7.77000 × 10−4 | 2.41 × 10−5 | 7.6060 | 2.828 × 10−14 | |
| 0.5 | 4.95 × 10−2 | −9.75400 × 10−4 | 5.04 × 10−5 | 7.1088 | 1.17 × 10−12 | |
| 0.25 | 5.05 × 10−2 | −1.30000 × 10−3 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 3.9444 | 8.00 × 10−5 | |
| k nearest neighbor | 1 | 8.71 × 10−2 | −1.17000 × 10−3 | 3.09 × 10−4 | 5.0199 | 5.17 × 10−7 |
| 10 | 5.30 × 10−2 | −7.35700 × 10−4 | 3.62 × 10−5 | 8.9820 | <2.2 × 10−16 | |
| 25 | 3.59 × 10−2 | −2.12766 × 10−4 | 1.45 × 10−5 | 9.6163 | <2.2 × 10−16 | |
| 40 | 2.93 × 10−2 | −6.35600 × 10−4 | 9.01 × 10−6 | 9.9616 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| LM Test | Statistic | p-Value | Significance Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMerr | 59.64 | 1.14 × 10−14 | *** |
| LMlag | 55.02 | 1.19 × 10−13 | *** |
| RLMerr | 4.91 | 0.02664 | * |
| RLMlag | 0.29 | 0.58851 | |
| SARMA | 59.93 | 9.68 × 10−14 | *** |
| Parameter | OLS | SAR | SEM | SAC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | t-Value | Estimate | z-Value | Estimate | z-Value | Estimate | z-Value | ||
| (Intercept) | −4.33 × 10−1 | (−0.956) | −4.67 × 10−1 | (−3.8636) *** | −4.71 × 10−1 | (−1.0454) | −4.72 × 10−1 | (−1.0462) | |
| CAT_12 | 9.77 × 10−1 | (2.368) * | 9.67 × 10−1 | (10.8092) *** | 1.02 × 100 | (2.5033) * | 1.02 × 100 | (2.4917) * | |
| CAT_21 | 1.26 × 100 | (3.07) ** | 1.25 × 100 | (13.7577) *** | 1.30 × 100 | (3.1897) ** | 1.29 × 100 | (3.1796) ** | |
| CAT_22 | 1.01 × 100 | (2.501) * | 1.00 × 100 | (11.6113) *** | 1.06 × 100 | (2.6346) ** | 1.05 × 100 | (2.624) ** | |
| CAT_23 | 1.47 × 100 | (3.217) ** | 1.46 × 100 | (6.4268) *** | 1.51 × 100 | (3.3261) *** | 1.51 × 100 | (3.3161) *** | |
| CAT_24 | 1.02 × 100 | (2.429) * | 1.01 × 100 | (7.3039) *** | 1.05 × 100 | (2.533) * | 1.05 × 100 | (2.5264) * | |
| CAT_25 | 9.04 × 10−1 | (1.769). | 9.01 × 10−1 | (2.826) ** | 9.40 × 10−1 | (1.852). | 9.38 × 10−1 | (1.8466). | |
| CAT_26 | 1.54 × 100 | (3.188) ** | 1.51 × 100 | (5.3031) *** | 1.51 × 100 | (3.1471) ** | 1.51 × 100 | (3.1491) ** | |
| CAT_28 | 8.57 × 10−1 | (0.643) | 8.37 × 10−1 | (0.6308) | 9.89 × 10−1 | (0.7529) | 9.78 × 10−1 | (0.7436) | |
| CAT_31 | 8.51 × 10−2 | (0.101) | 7.42 × 10−2 | NA | 1.42 × 10−1 | (0.1683) | 1.37 × 10−1 | (0.162) | |
| CAT_32 | 7.73 × 10−1 | (1.847). | 7.63 × 10−1 | (5.0947) *** | 8.14 × 10−1 | (1.9556). | 8.10 × 10−1 | (1.9459). | |
| CAT_33 | 1.14 × 100 | (2.571) * | 1.12 × 100 | (5.5661) *** | 1.17 × 100 | (2.6534) ** | 1.16 × 100 | (2.6448) ** | |
| CAT_34 | 8.47 × 10−1 | (2.079) * | 8.38 × 10−1 | (7.0821) *** | 8.82 × 10−1 | (2.1846) * | 8.79 × 10−1 | (2.1758) * | |
| CAT_35 | 8.18 × 10−1 | (1.647). | 8.24 × 10−1 | (2.803) ** | 8.78 × 10−1 | (1.7773). | 8.74 × 10−1 | (1.7692). | |
| CAT_36 | 4.62 × 10−1 | (1.087) | 4.60 × 10−1 | (2.6302) ** | 4.79 × 10−1 | (1.1386) | 4.78 × 10−1 | (1.1353) | |
| BUS_LANE | 5.30 × 10−1 | (5.344) *** | 5.27 × 10−1 | (5.4219) *** | 5.30 × 10−1 | (5.3421) *** | 5.30 × 10−1 | (5.3438) *** | |
| BUS_VOL | 5.16 × 10−4 | (6.556) *** | 5.20 × 10−4 | (6.662) *** | 5.46 × 10−4 | (6.8316) *** | 5.44 × 10−4 | (6.8093) *** | |
| HGV_12_D | 2.22 × 10−3 | (0.047) | 4.95 × 10−3 | NA | 1.55 × 10−2 | (0.3211) | 1.46 × 10−2 | (0.3041) | |
| BIKE_VOL | 9.10 × 10−5 | (5.283) *** | 8.86 × 10−5 | (5.1538) *** | 8.61 × 10−5 | (4.9792) *** | 8.63 × 10−5 | (4.9947) *** | |
| LN_AADT | 1.44 × 10−1 | (7.437) *** | 1.43 × 10−1 | (8.0805) *** | 1.43 × 10−1 | (7.305) *** | 1.43 × 10−1 | (7.3103) *** | |
| Ratio_HGV | −5.77 × 10−1 | (−2.318) * | −5.41 × 10−1 | (−2.2386) * | −5.22 × 10−1 | (−2.0826) * | −5.24 × 10−1 | (−2.0897) * | |
| LN_LENGTH | 9.48 × 10−1 | (24.499) *** | 9.34 × 10−1 | (24.3398) *** | 9.51 × 10−1 | (24.3371) *** | 9.50 × 10−1 | (23.9841) *** | |
| ρ | - | - | 0.0638 | (5.1107) *** | - | - | 0.0058 | (0.15) | |
| λ | - | - | - | - | 0.071 | (5.3861) *** | 0.0654 | (1.6359) | |
| AIC | 15,601 | 15,576 | 15,574 | 15,576 | |||||
| BIC | 15,750 | 15,732 | 15,729 | 15,738 | |||||
| Log-Likelihood | −7777.686 | −7764.688 | −7763.103 | −7763.089 | |||||
| Inferior Model | Superior Model | LR | df | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lc | AIC | BIC | Lc | AIC | BIC | |||||
| OLS | −7777.686 | 15,601 | 15,750 | SAR | −7764.688 | 15,576 | 15,732 | 25.996 | 1 | *** |
| OLS | −7777.686 | 15,601 | 15,750 | SEM | −7763.103 | 15,574 | 15,729 | 29.166 | 1 | *** |
| OLS | −7777.686 | 15,601 | 15,750 | SAC | −7763.089 | 15,576 | 15,738 | 29.194 | 2 | *** |
| SAR | −7764.688 | 15,576 | 15,732 | SAC | −7763.089 | 15,576 | 15,738 | 3.198 | 1 | |
| SEM | −7763.103 | 15,574 | 15,729 | SAC | −7763.089 | 15,576 | 15,738 | 0.028 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sipos, T.; Afework Mekonnen, A.; Szabó, Z. Spatial Econometric Analysis of Road Traffic Crashes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052492
Sipos T, Afework Mekonnen A, Szabó Z. Spatial Econometric Analysis of Road Traffic Crashes. Sustainability. 2021; 13(5):2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSipos, Tibor, Anteneh Afework Mekonnen, and Zsombor Szabó. 2021. "Spatial Econometric Analysis of Road Traffic Crashes" Sustainability 13, no. 5: 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052492
APA StyleSipos, T., Afework Mekonnen, A., & Szabó, Z. (2021). Spatial Econometric Analysis of Road Traffic Crashes. Sustainability, 13(5), 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052492






