Life Cycle Assessment of Households in Santiago, Chile: Environmental Hotspots and Policy Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goal and Scope
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory
2.3. Environmental Impact Assessment
2.4. Environmental Management Scenarios
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Life Cycle Inventory
3.2. Influence of Household Income Level on Environmental Impacts
3.3. Environmental Hotspot Analysis
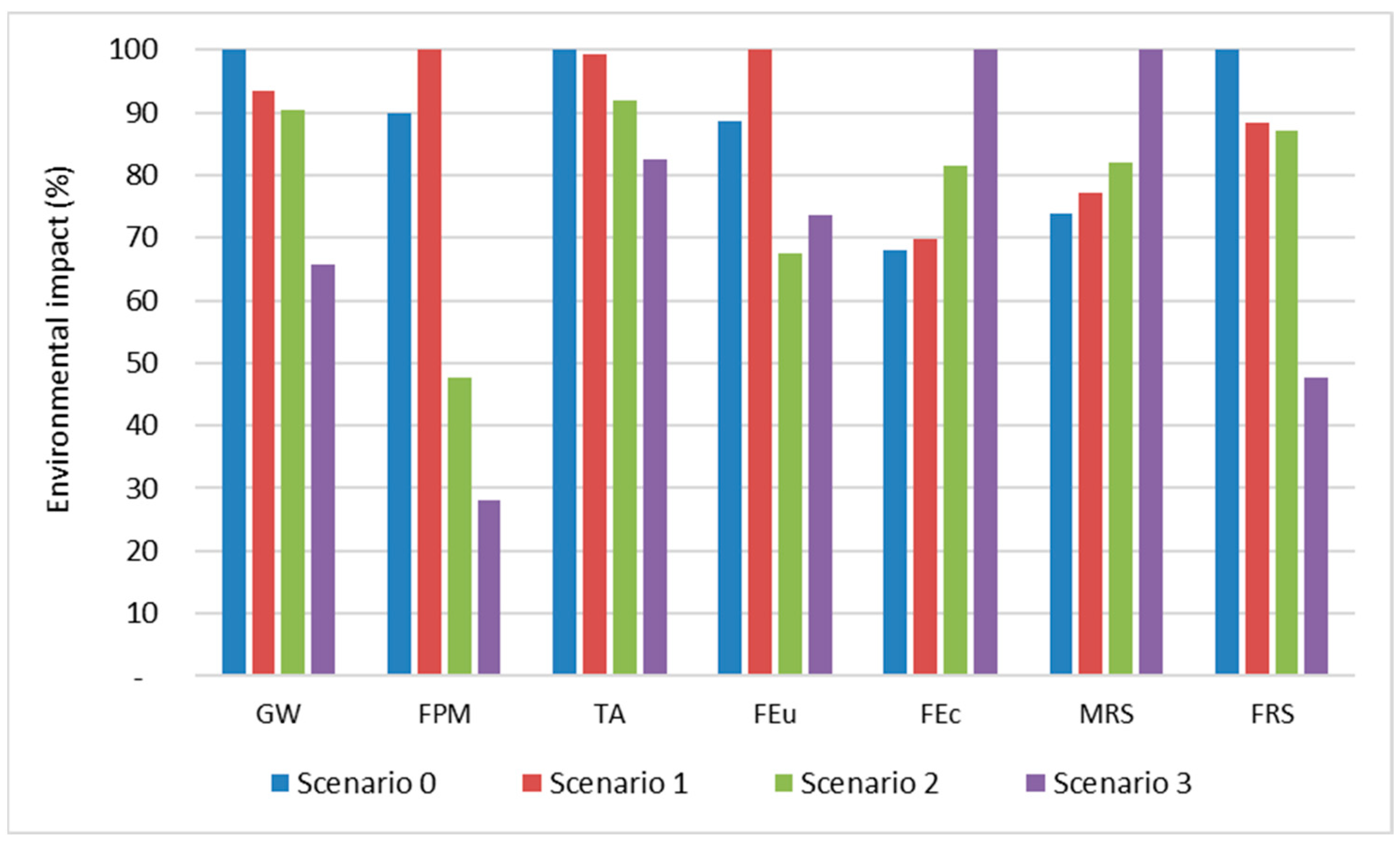
3.4. Scenarios Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, E.; Navia, R. Circular economy in urban systems: How to measure the impact? Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Lankao, P.; Gnatz, D.M. Conceptualizing urban water security in an urbanizing world. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 21, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinatizadeh, S.; Monavari, S.M.; Azmi, A.; Sobhanardakani, S. Evaluation and prediction of sustainability of urban areas: A case study for Kermanshah city, Iran. Cities 2017, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nations, U. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hertwich, E.G. Life cycle approaches to sustainable consumption: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. The System of National Accounts 2018; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Di Donato, M.; Lomas, P.L.; Carpintero, Ó. Metabolism and environmental impacts of household consumption: A review on the assessment, methodology, and drivers. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A. Identifying priorities for environmental product policy. J. Ind. Ecol. 2006, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeiro, S.; Ramos, T.B.; Huisingh, D. Procedures and criteria to develop and evaluate household sustainable consumption indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 27, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froemelt, A.; Dürrenmatt, D.J.; Hellweg, S. Using Data Mining to Assess Environmental Impacts of Household Consumption Behaviors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8467–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuštík, J.; Kočí, V. Environmental impact of personal consumption from life cycle perspective—A Czech Republic case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.; Meyer, D. The determinants of urban resource consumption. Environ. Behav. 2012, 44, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbar, P.P.; Birkved, M.; Hauschild, M.; Kabins, S.; Nygaard, S.E. Environmental impact of urban consumption patterns: Drivers and focus points. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, V.; Beylot, A.; Sala, S. Environmental impacts of household consumption in Europe: Comparing process-based LCA and environmentally extended input-output analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E.G.; Peters, G.P. Carbon footprint of nations: A global, trade-linked analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.J.; Caldeira, K. Consumption-based accounting of CO 2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5687–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. The water footprint of humanity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, M.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S.; Giljum, S. Measuring telecouplings in the global land system: A review and comparative evaluation of land footprint accounting methods. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 114, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausselet, C.; Ellingsen, L.A.W.; Strømman, A.H.; Brattebø, H. A life-cycle assessment model for zero emission neighborhoods. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Parajuli, R.; Thoma, G.J. Life cycle assessment of dietary patterns in the United States: A full food supply chain perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.S.; To, L.S. A systems thinking approach to stimulating and enhancing resource efficiency and circularity in households. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuštík, J.; Kočí, V. A comparative life cycle assessment of electronic retail of household products. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Guaiti, F.; González-García, S.; Villanueva-Rey, P.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Integrating Urban Metabolism, Material Flow Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment in the environmental evaluation of Santiago de Compostela. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, S.; Castellani, V. The consumer footprint: Monitoring sustainable development goal 12 with process-based life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, A.N.; Dente, S.M.R.; Hashimoto, S. Social life-cycle assessment of householdwaste management system in Kabul city. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.P.; Schaubroeck, T.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Ha, V.H.; Huynh, T.H.; Dewulf, J. Material flow analysis for management of waste TVs from households in urban areas of Vietnam. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, L.; Sahakian, M.; Erkman, S. Understanding household food metabolism: Relating micro-level material flow analysis to consumption practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 125, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- SII Cartografía Digital SII Mapas. Available online: https://www4.sii.cl/mapasui/internet/#/contenido/index.html (accessed on 14 August 2018).
- INE. Informe de Principales Resultados VIII Encuesta de Presupuestos Familiares (EPF); INE: Santiago, Chile, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, E.; Curaqueo, G.; Cea, M.; Vera, L.; Navia, R. Environmental hotspots in the life cycle of a biochar-soil system. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 158, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNE. Anuario Estadístico de Energía 2019; CNE: Santiago, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Transportes y Telecomunicaciones, Informe de Evaluación Externa al Sistema de Transporte Público Remunerado de Pasajeros de la Provincia de Santiago y de las Comunas de San Bernardo y Puente Alto. Available online: http://biblioteca.digital.gob.cl/handle/123456789/972 (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- DTP. Mejoramiento y Actualización del Modelo de Asignación de viajes del Sistema Transantiago; DTP: Santiago, Chile, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abello-Passteni, V.; Muñoz Alvear, E.; Lira, S.; Garrido-Ramírez, E. Evaluación de Eco-Eficiencia de Tecnologías de Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales Domésticas en Chile. Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua 2020, 11, 190–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaete-Morales, C.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Stamford, L.; Azapagic, A. Assessing the environmental sustainability of electricity generation in Chile. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalba, R.; Vieli, L.; Spirito, F.; Muñoz, E. Environmental and productive performance of different blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) production regimes: Conventional, organic, and agroecological. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 2019, 256, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; Navia, R.; Zaror, C.; Alfaro, M. Ammonia emissions from livestock production in chile: An inventory and uncertainty analysis. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 16, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herrera, J.; Muñoz, E.; Montalba, R. Evaluation of two production methods of Chilean wheat by life cycle assessment (LCA). IDESIA 2012, 30, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bezama, A.; Douglas, C.; Méndez, J.; Szarka, N.; Muñoz, E.; Navia, R.; Schock, S.; Konrad, O.; Ulloa, C. Life cycle comparison of waste-to-energy alternatives for municipal waste treatment in Chilean Patagonia. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo, S. Pobreza y distribución del ingreso en la Región Metropolitana de Santiago: Resultados Encuesta CASEN 2015. Available online: https://www.desarrollosocialyfamilia.gob.cl/storage/docs/DOCUMENTO_POBREZA_Y_DISTR_ING_RMS_CASEN_2017.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Ministerio de Energía—Gobierno de Chile. Estrategia Nacional de Electromovilidad; Santiago, Chile. 2017. Available online: https://energia.gob.cl/sites/default/files/estrategia_electromovilidad-8dic-web.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Ministerio de Energía—Gobierno de Chile. Energía 2050—Política Energética de Chile; Santiago, Chile. 2015. Available online: https://observatoriop10.cepal.org/es/instrumentos/politica-energetica-chile-energia-2050 (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Superintendencia de Servicios Sanitarios (SISS)—Gobierno de Chile. Informe de Gestión del Sector Sanitario; Santiago, Chile. 2019. Available online: https://www.coursehero.com/file/75668465/Informe-de-gestion-sector-sanitario-SISS-2019pdf/ (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Gonzalez-Garcia, S.; Manteiga, R.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Assessing the sustainability of Spanish cities considering environmental and socio-economic indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUBDERE—Gobierno de Chile. In Diagnostico de la Situación por Comuna y por Región en Materia de Residuos Sólidos Domiciliarios y Asimilables; Santiago, Chile; 2018. Available online: http://www.subdere.gov.cl/sites/default/files/4.1_diagnostico_introduccion_agosto_2018.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Gobierno de Chile. Contribución Determinada a Nivel Nacional (NDC) de Chile; Santiago, Chile. 2020. Available online: https://mma.gob.cl/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Propuesta_actualizacion_NDC_Chile_2019.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Ivanova, D.; Stadler, K.; Steen-Olsen, K.; Wood, R.; Vita, G.; Tukker, A.; Hertwich, E.G. Environmental Impact Assessment of Household Consumption. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, A.; Heiskanen, E.; Perrels, A.; Berghäll, E.; Liesimaa, V.; Mattinen, M.K. Combinations of policy instruments to decrease the climate impacts of housing, passenger transport and food in Finland. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Hofer, J.; Althaus, H.J.; Del Duce, A.; Simons, A. The environmental performance of current and future passenger vehicles: Life Cycle Assessment based on a novel scenario analysis framework. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Quintile | From (USD) | To (USD) | Households Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0 | 120 | 5.8 |
| II | 120 | 210 | 10.1 |
| III | 210 | 315 | 14.2 |
| IV | 315 | 560 | 20.3 |
| V | 560 | -- | 49.6 |
| Subsystem | Unit | Household Income Quintile | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | ||
| Water | m3/inh/year | 55.4 | 68.9 | 66.0 | 83.4 | 90.5 |
| Fruits | kg/inh/year | 28.4 | 52.1 | 57.9 | 52.8 | 54.1 |
| Vegetables | kg/inh/year | 86.0 | 140.1 | 142.0 | 140.4 | 119.4 |
| Legumes | kg/inh/year | 8.3 | 17.0 | 18.2 | 19.2 | 14.2 |
| Processed products | kg/inh/year | 100.4 | 140.7 | 139.8 | 122.4 | 101.2 |
| Dairy products | kg/inh/year | 21.9 | 40.6 | 40.9 | 41.9 | 50.6 |
| Pork | kg/inh/year | 2.1 | 6.6 | 10.1 | 6.9 | 4.6 |
| Chicken | kg/inh/year | 9.6 | 13.8 | 14.8 | 20.1 | 15.8 |
| Beef | kg/inh/year | 7.2 | 10.3 | 12.8 | 15.8 | 15.7 |
| Municipal solid waste | kg/inh/year | 153.7 | 295.7 | 218.8 | 369.9 | 637.2 |
| Electricity | kWh/inh/year | 569.7 | 778.0 | 753.2 | 861.7 | 1204.5 |
| Liquefied petroleum gas | kWh/inh/year | 7500 | 11,389 | 10,278 | 16,667 | 7222 |
| Kerosene | kWh/inh/year | 277.8 | 527.8 | 305.6 | 611.1 | 555.6 |
| Natural gas | kWh/inh/year | 55.6 | 277.8 | 1944.4 | 1388.9 | 3333.3 |
| Gasoline | kWh/inh/year | 6111 | 6389 | 4722 | 10,556 | 21,389 |
| Diesel fuel | kWh/inh/year | 0 | 1944.4 | 2222.2 | 3333.3 | 5277.8 |
| Wastewater | m3/inh/year | 44.3 | 55.1 | 52.8 | 66.7 | 72.4 |
| Impact Category | Unit | Household Income Quintile | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | ||
| Global warming | kg CO2 eq | 1980 | 2616 | 2726 | 3363 | 4038 |
| Fine particulate matter formation | kg PM2.5 eq | 7.9 | 9.9 | 9.6 | 10.9 | 12.7 |
| Terrestrial acidification | kg SO2 eq | 13.3 | 18.6 | 21.8 | 23.6 | 24.1 |
| Freshwater eutrophication | kg P eq | 0.65 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 1.20 |
| Freshwater ecotoxicity | kg 1,4-DCB | 47.5 | 61.7 | 54.8 | 80.0 | 120.7 |
| Mineral resource scarcity | kg Cu eq | 4.0 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 9.5 |
| Fossil resource scarcity | kg oil eq | 431 | 553 | 515 | 719 | 828 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Eccher, C.; Garrido-Ramírez, E.; Franchi-Arzola, I.; Muñoz, E. Life Cycle Assessment of Households in Santiago, Chile: Environmental Hotspots and Policy Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052525
López-Eccher C, Garrido-Ramírez E, Franchi-Arzola I, Muñoz E. Life Cycle Assessment of Households in Santiago, Chile: Environmental Hotspots and Policy Analysis. Sustainability. 2021; 13(5):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052525
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Eccher, Camila, Elizabeth Garrido-Ramírez, Iván Franchi-Arzola, and Edmundo Muñoz. 2021. "Life Cycle Assessment of Households in Santiago, Chile: Environmental Hotspots and Policy Analysis" Sustainability 13, no. 5: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052525
APA StyleLópez-Eccher, C., Garrido-Ramírez, E., Franchi-Arzola, I., & Muñoz, E. (2021). Life Cycle Assessment of Households in Santiago, Chile: Environmental Hotspots and Policy Analysis. Sustainability, 13(5), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052525






