Pacing in Time-Limited Ultramarathons from 6 to 24 Hours—The Aspects of Age, Sex and Performance Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Subjects
2.4. The Races
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
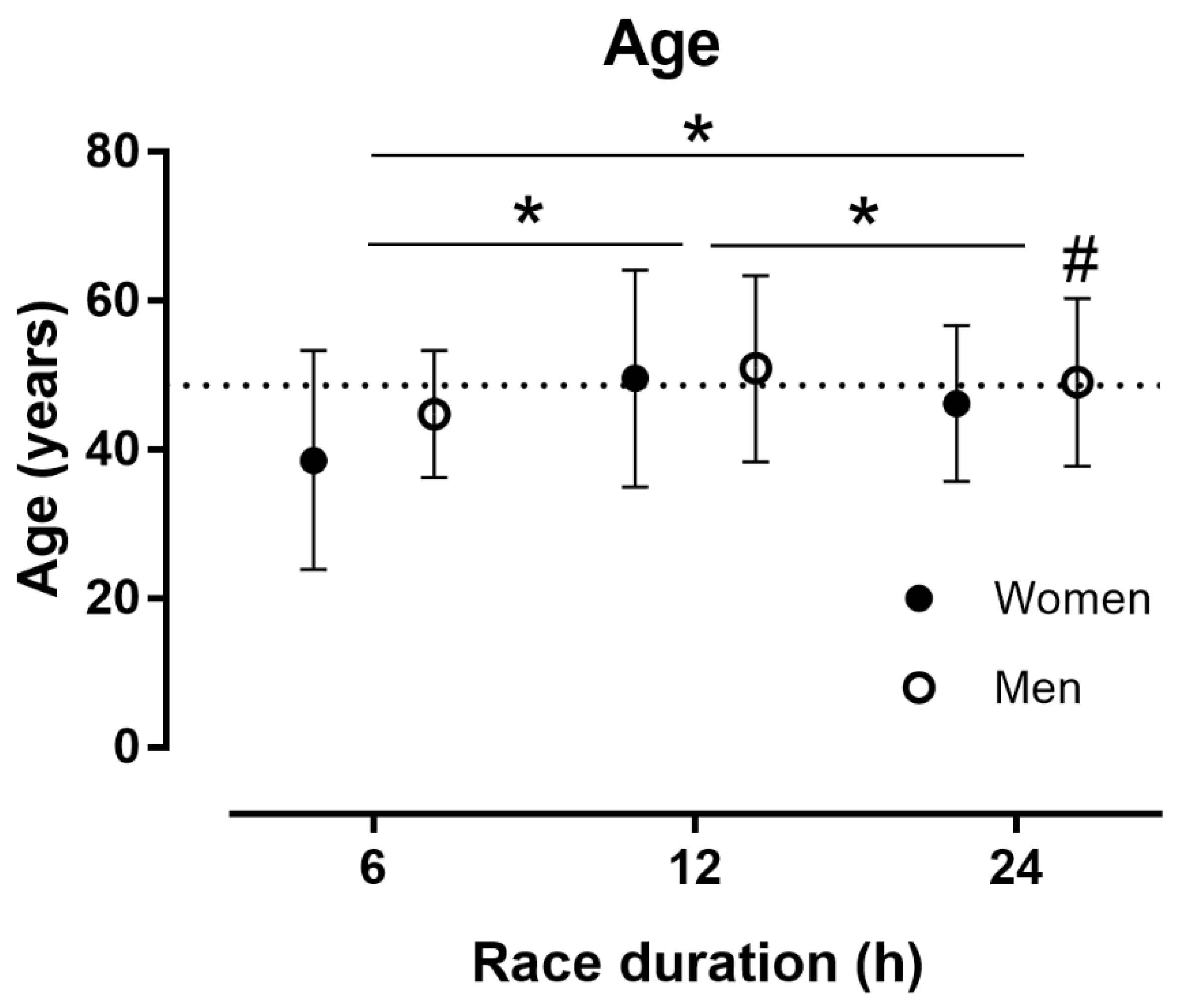
3.1. Participation, Age and Performance by Sex and Race Duration
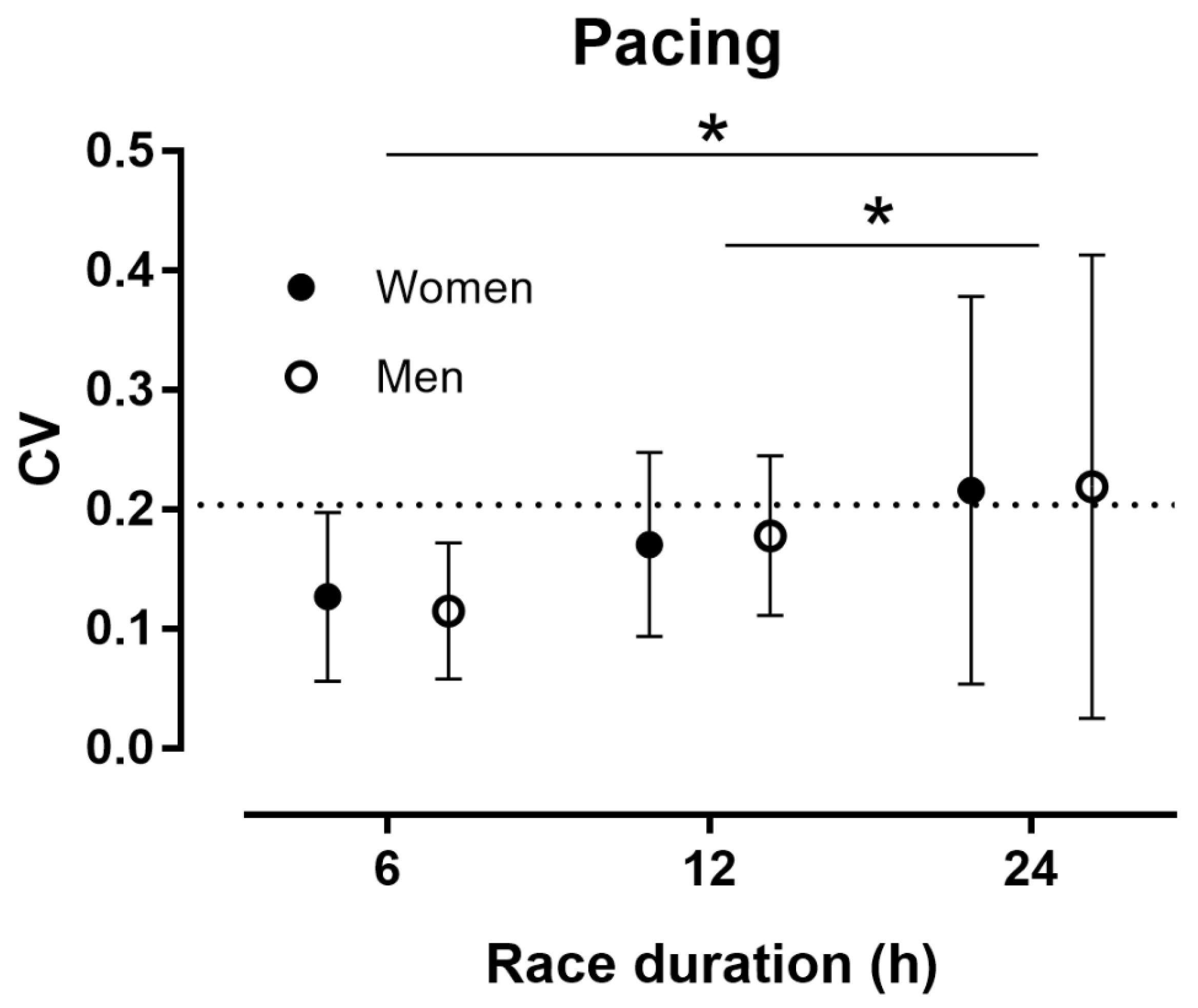
3.2. Pacing by Sex, Race Duration and Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbiss, C.R.; Laursen, P.B. Describing and understanding pacing strategies during athletic competition. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklewright, D.; Parry, D.; Robinson, T.; Deacon, G.; Renfree, A.; Gibson, A.S.C.; Matthews, W.J. Risk perception influences athletic pacing strategy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haney, T.A., Jr.; Mercer, J.A. A description of variability of pacing in marathon distance running. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 4, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Angus, S.D. Did recent world record marathon runners employ optimal pacing strategies? J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Pacing in age group marathoners in the “New York City Marathon”. Res. Sports Med. 2018, 26, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Ozcorta, E.J.; Santos-Concejero, J. The influence of pacing strategy on marathon world records AU—Díaz, José Joaquín. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüst, C.A.; Knechtle, B.; Rosemann, T.; Lepers, R. Analysis of performance and age of the fastest 100-mile ultra-marathoners worldwide. Clinics (Sao Paulo Braz.) 2013, 68, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, M.; Rüst, C.A.; Lepers, R.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Master runners dominate 24-h ultramarathons worldwide-a retrospective data analysis from 1998 to 2011. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2013, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Effect of age and performance on pacing of marathon runners. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2017, 8, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- March, D.S.; Vanderburgh, P.M.; Titlebaum, P.J.; Hoops, M.L. Age, sex, and finish time as determinants of pacing in the marathon. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trubee, N.W.; Vanderburgh, P.M.; Diestelkamp, W.S.; Jackson, K.J. Effects of heat stress and sex on pacing in marathon runners. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lozano, A.; Collado, P.S.; Foster, C.; Lucia, A.; Garatachea, N. Influence of sex and level on marathon pacing strategy. Insights from the New York City Race. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfree, A.; Crivoi do Carmo, E.; Martin, L. The influence of performance level, age and gender on pacing strategy during a 100-km ultramarathon. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.L.S.; Tan, F.H.Y.; Bosch, A.N. Similarities and differences in pacing patterns in a 161-km and 101-km ultra-distance road race. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, D.; Norris, M.; Healy, R.; Anderson, R. Marathon pace control in mastersathletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Do fast older runners pace differently from fast younger runners in the ‘New York City Marathon’? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Age of peak performance in 50-km ultramarathoners—Is it older than in marathoners? Open Access J. Sports Med. 2018, 9, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joyner, M.J. Physiological limits to endurance exercise performance: Influence of sex. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cribari, M.; Rüst, C.A.; Rosemann, T.; Onywera, V.; Lepers, R.; Knechtle, B. Participation and performance trends of East-African runners in Swiss half-marathons and marathons held between 2000 and 2010. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Carter, R.; DeRuisseau, K.C.; Moffatt, R.J. Running performance differences between men and women. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldvogel, K.J.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Di Gangi, S.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Women reduce the performance difference to men with increasing age in ultra-marathon running. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, C.V.; da Silva Aguiar, S.; Rosemann, T.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. American Masters road running records—The performance gap between female and male age group runners from 5 km to 6 days running. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Cesari, M.; Di Bari, M.; Cherubini, A.; Broccatelli, M.; Savera, G.; D’Elia, M.; Pahor, M.; et al. Physical activity and exercise as countermeasures to physical frailty and sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepers, R.; Stapley, P.J. Master athletes are extending the limits of human endurance. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Onywera, V.O.; Knechtle, B. Running performance, nationality, sex, and age in the 10-km, half-marathon, marathon, and the 100-km ultramarathon IAAF 1999–2015. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2189–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Pacing strategies in the ‘Athens Classic Marathon’: Physiological and psychological aspects. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coso, J.; Fernández de Velasco, D.; Abián-Vicen, J.; Salinero, J.J.; González-Millán, C.; Areces, F.; Ruiz, D.; Gallo, C.; Calleja-González, J.; Pérez-González, B. Running pace decrease during a marathon is positively related to blood markers of muscle damage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Helou, N.; Tafflet, M.; Berthelot, G.; Tolaini, J.; Marc, A.; Guillaume, M.; Hausswirth, C.; Toussaint, J.F. Impact of environmental parameters on marathon running performance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Di Gangi, S.; Chtourou, H.; Rüst, C.A.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. The role of environmental conditions on marathon running performance in men competing in Boston Marathon from 1897 to 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Finishers | Race Duration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h | 12 h | 24 h | |
| Women (n) | 17 | 77 | 166 |
| Men (n) | 23 | 155 | 499 |
| Total (n) | 40 | 232 | 665 |
| MWR | 1.35 | 2.01 | 3.01 |
| Race | Race Duration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h (w/m) | 12 h (w/m) | 24 h (w/m) | |
| 2009 (Switzerland) | -/- | 3/10 | 4/34 |
| 2010 (Switzerland) | -/- | 5/8 | 5/33 |
| 2011 (Switzerland) | -/- | 7/14 | 6/25 |
| 2012 (Switzerland) | 3/3 | 4/7 | 4/24 |
| 2013 (Switzerland) | 1/7 | 5/5 | 5/26 |
| 2014 (Switzerland) | 6/5 | 6/13 | 2/20 |
| 2015 (Switzerland) | 2/4 | 1/9 | 6/25 |
| 2016 (Switzerland) | 4/5 | 15/33 | 38/118 |
| 2017 (Switzerland) | -/- | 19/25 | 11/41 |
| 2018 (Switzerland) | -/- | 12/31 | 10/39 |
| 2018 (Rumania) | -/- | -/- | 72/100 |
| 2018 (Greece) | -/- | -/- | 5/18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deusch, H.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Pacing in Time-Limited Ultramarathons from 6 to 24 Hours—The Aspects of Age, Sex and Performance Level. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052705
Deusch H, Nikolaidis PT, Alvero-Cruz JR, Rosemann T, Knechtle B. Pacing in Time-Limited Ultramarathons from 6 to 24 Hours—The Aspects of Age, Sex and Performance Level. Sustainability. 2021; 13(5):2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052705
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeusch, Hagen, Pantelis T. Nikolaidis, José Ramón Alvero-Cruz, Thomas Rosemann, and Beat Knechtle. 2021. "Pacing in Time-Limited Ultramarathons from 6 to 24 Hours—The Aspects of Age, Sex and Performance Level" Sustainability 13, no. 5: 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052705
APA StyleDeusch, H., Nikolaidis, P. T., Alvero-Cruz, J. R., Rosemann, T., & Knechtle, B. (2021). Pacing in Time-Limited Ultramarathons from 6 to 24 Hours—The Aspects of Age, Sex and Performance Level. Sustainability, 13(5), 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052705










