Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts of Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts
2.1. Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in the Process of Wind Erosion Desertification
2.2. Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in the Process of Different Wind Erosion Desertification Controls
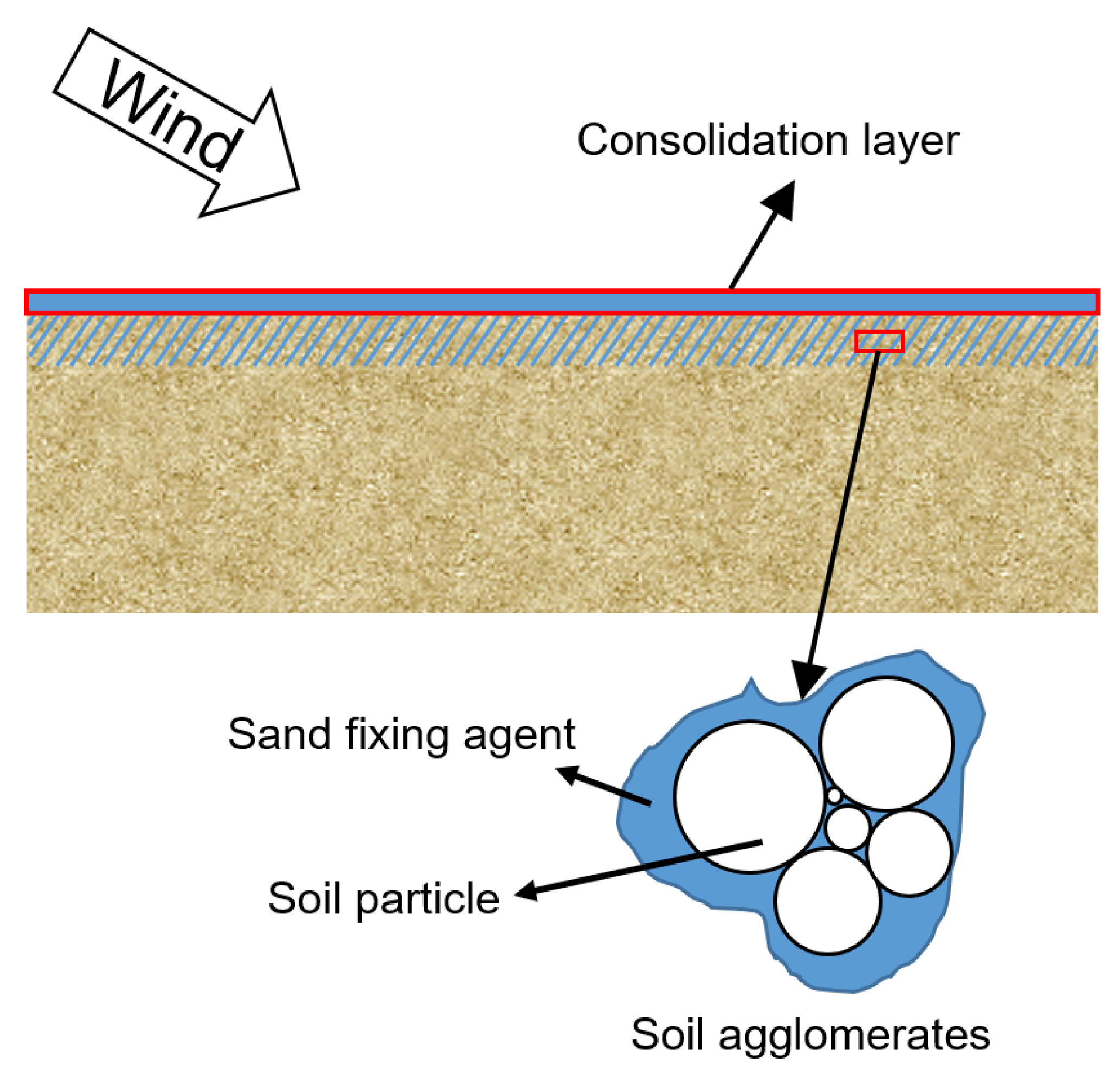
2.2.1. Mechanical Sand Fixation Measures
2.2.2. Chemical Sand Fixation Measures
2.2.3. Biological Sand Fixation Measures
3. Mechanisms of Variation in Silt–Clay Content in Wind-Eroded Deserts
3.1. Mechanisms of Silt–Clay Content in the Process of Wind Erosion Desertification
3.2. Mechanisms of Silt–Clay Content in the Process of Different Wind Erosion Desertification Controls
3.2.1. Mechanical Sand Fixation Measures
3.2.2. Chemical Sand Fixation Measures
3.2.3. Biological Sand Fixation Measures
4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Wind-Erosion Deserts Based on Silt–Clay Content
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gou, F.; Liang, W.; Sun, S.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J. Analysis of the desertification dynamics of sandy lands in Northern China over the period 2000–2017. Geocarto Int. 2019, 10, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bulletin of Status Quo of Desertification and Sandification in China. State Forestry Administration: Beijing, China, 2014; p. 22.
- Zhang, J.G.; Xu, X.W.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, J.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, Y.D. Effect of shifting sand burial on soil evaporation and moisture–salt distribution in a hyper-arid desert. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, N.; Dong, Z.; Van Pelt, R.S.; Zobeck, T.M. Wind erosion induced soil degradation in Northern China: Status, measures and perspective. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8951–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, W. Aeolian desertification and its control in Northern China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, K.T.; Sanders, R.L.; Washton, N.M. Clay minerals. eMagRes 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kussainova, M.; Funakawa, S. Soil properties that determine the mortality and growth of Haloxylon aphyllum in the Aral region, Kazakhstan. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2019, 33, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lü, S.; Wang, T.; Yan, R.; Wei, Z. Large herbivore-induced changes in phytogenic hillocks: Links to soil and windblown sediment on the desert steppe in China. Ecol. Res. 2018, 33, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Zhou, R.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y. Effects of desertification on soil and crop growth properties in Horqin sandy cropland of Inner Mongolia, north China. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Mu, G.; Jin, Z.; Lei, J. The effects of oasis on aeolian deposition under different weather conditions: A case study at the southern margin of the Taklimakan desert. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J. Variability in condensation water and its determinants in arid regions of north-western China. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huisingh, D. Combating desertification in China: Monitoring, control, management and revegetation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zhao, L.Z.; Wang, A.Q.; Chen, T.H.; He, H.P. Current fundamental and applied research into clay minerals in China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Dong, H.; Jiang, H.; Lv, G.; Eberl, D.; Li, S.; Kim, J. The role of clay minerals in the preservation of organic matter in sediments of qinghai lake, NW China. Clays Clay Miner. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, T.; Shukla, M.K.; Chang, Q. Using soil minerals to investigate desert expansion in northern Shaanxi Province, China. Aeolian Res. 2020, 43, 100577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Ji, J. Geochemical characterization of major elements in desert sediments and implications for the Chinese loess source. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.H.; Melo, V.F.; Gilkes, R. Scanning and transmission analytical electron microscopy (STEM-EDX) identifies minor minerals and the location of minor elements in the clay fraction of soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Duan, Z.; Tan, M. Restoration Affect Soil Organic Carbon and Nutrients in Different Particle-size Fractions. L. Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qu, J.; Tan, L.; Fan, Q.; Niu, Q. Fractal features of sandy soil particle-size distributions during the rangeland desertification process on the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, T.; Pu, J.; Yang, F.; Shukla, M.K.; Chang, Q. Response of soil physical, chemical and microbial biomass properties to land use changes in fixed desertified land. Catena 2018, 160, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Lou, J.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Jiao, L. Heterogeneity and loss of soil nutrient elements under aeolian processes in the Otindag Desert, China. Aeolian Res. 2018, 30, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xue, X.; You, Q.; Huang, C.; Dong, S.; Liao, J.; Duan, H.; Tsunekawa, A.; Wang, T. Changes of soil properties regulate the soil organic carbon loss with grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chun, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, X. Particle size characteristics of surface sediments and their environmental significance: A comparative study of deserts in arid western Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Buyantuev, A.; Niu, J.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal patterns of desertification dynamics and desertification effects on ecosystem services in the Mu Us Desert in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Tong, X.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wu, F.; Ha, S.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; He, C. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities along a chronosequence of desertified land revegetation. Ecol. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Lei, Y.; Han, H.; He, J. Biological soil crust distribution in Artemisia ordosica communities along a grazing pressure gradient in Mu Us Sandy Land, Northern China. J. Arid Land 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N.K.; Ge, Y.; Wills, S.; Libohova, Z. Predicting Physical and Chemical Properties of US Soils with a Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectral Library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meihuan, Y.; Mingming, C.; Zhu, Z. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in the Process of Desertification on the Southeastern Edge of Mu Us Sandy Land. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, M.; Ding, J.; Cheng, L.; Bao, F.; Wu, B. Network analysis reveals the strengthening of microbial interaction in biological soil crust development in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Qiu, K.; Xu, D.; Shi, X.; Qi, T.; Pott, R. Spatial heterogeneity of soil and vegetation characteristics and soil-vegetation relationships along an ecotone in Southern Mu Us Sandy Land, China. J. Soils Sediments 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Jia, W.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Sediment grain–size characteristics and relevant correlations to the aeolian environment in China’s eastern desert region. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Origin and morphology of barchan and linear clay dunes in the Shuhongtu Basin, Alashan Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2019, 339, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, G.; Huang, C.; Li, H. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Surface Characteristics in the Badain Jaran, Tengger, and Ulan Buh Deserts of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Li, D.; Jiao, L.; Ma, W.; Cai, D. The potential effects of aeolian processes on the vegetation in a semiarid area: Geochemical evidence from plants and soils. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Caquineau, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Gaudichet, A.; Gomes, L. Mineralogical characteristics of soil dust from source regions in northern China. Particuology 2009, 7, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Zhang, K.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Influence of life form, taxonomy, climate, and soil properties on shoot and root concentrations of 11 elements in herbaceous plants in a temperate desert. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Yang, R.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, X.F. Evolution of soil structure and fertility after conversion of native sandy desert soil to irrigated cropland in arid region, China. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y. Soil properties following cultivation and non-grazing of a semi-arid sandy grassland in northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 75, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhao, W.Z.; Zhang, T.H. Fractal features of soil particle size distribution and the implication for indicating desertification. Geoderma 2004, 122, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J. Effects of land-use changes on organic carbon in bulk soil and associated physical fractions in China’s Horqin Sandy Grassland. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2015, 7, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, F.; Gui, D.; Lei, J. Characteristics of soil environment variation in oasis-desert ecotone in the process of oasis growth. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture, Beijing, China, 29–31 October 2011; Volume 344, pp. 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Grace, M.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. Surface sediments in the marsh-sandy land transitional area: Sandification in the western Songnen Plain, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Akbarzadeh, A. Soil physico-chemical, mineralogical, and micromorphological changes due to desertification processes in Yazd region, Iran. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Raja, P.; Ali, M.; Upreti, N.; Kumar, N.; Tripathi, J.K.; Srivastava, P. Micromorphology, clay mineralogy, and geochemistry of calcic-soils from western Thar Desert: Implications for origin of palygorskite and southwestern monsoonal fluctuations over the last 30 ka. Catena 2018, 163, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Gu, P.F.; Li, L.Y.; Zong, L.Y.; Zhao, W.J. Changes of soil particle size fraction along a chronosequence in sandy desertified land: A fundamental process for ecosystem succession and ecological restoration. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2651–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, X.; Lv, P.; Lian, J.; Yue, X. Long-term grazing effects on vegetation characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid grassland, northern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, J.; Deng, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, R. Fractal scaling of particle-size distribution and associations with soil properties of Mongolian pine plantations in the Mu Us Desert, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Duan, Z.; Luo, T. Changes in soil quality in the critical area of desertification surrounding the Ejina Oasis, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2643–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; An, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Shangguan, Z. Effect of desertification on productivity in a desert steppe. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, P. Soil quality change during reversal of desertification in agro-pastoral transition zone of northern China. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 599, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Jiang, D.; Teng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, W.; Cui, Z. Soil chemical and microbiological properties along a chronosequence of Caragana microphylla Lam. plantations in the Horqin sandy land of Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Kang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F. Spatial variation of topsoil features in soil wind erosion areas of northern China. Catena 2018, 167, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, G.M.; Qu, Z.Q.; Tang, Y.; Lei, J.; Wen, H.M.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Wang, J.P.; et al. Morphology, spatial pattern and sediment of Nitraria tangutorum nebkhas in barchans interdune areas at the southeast margin of the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Geomorphology 2015, 232, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Ding, G.; Yu, M.; Gao, G.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Straw Checkerboards on Wind Proofing, Sand Fixation, and Ecological Restoration in Shifting Sandy Land. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2018, 123, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, J. Geomorphology Effects of checkerboard barriers on the distribution of aeolian sandy soil particles and soil organic carbon. Geomorphology 2019, 338, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R. The physical and chemical properties of soil crust in straw checkerboards with different ages in the Mu Us Sandland, Northern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.T.; Dong, Z.; Li, H.L.; Shao, S.X.; Wang, L.Q. Distribution of soil particle size and soil organic carbon in dunes of checkerboard barriers with different setting years. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, D. Sand fixation function response to climate change and land use in northern China from 1981 to 2015. Aeolian Res. 2019, 40, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Xia, X.; Ding, T. Numerical simulation of wind sand movement in straw checkerboard barriers. Eur. Phys. J. E 2013, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Ding, G. Concave surface features and grain-size characteristics in polylactic acid sand barrier. Arid Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of Biodegradable Poly Lactic Acid Sand Barriers on Surface Sediment Grairrsize Characteristics at Sand Dunes. J. Desert Res. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongju, M.; Ren, X.; Yong, G. Effects of PLA Sand Barriers on Soil Fractal Dimension. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 45, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Hai, C. Soil grain-size characteristics of nitraria tangutorum nebkhas with different degrees of vegetation coverage in a desert-oasis ecotone. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3703–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chang, Q.R.; Qi, Y.B. Fractal characteristics of soil under ecological restoration in the agro-pastoral transition zone of northern China. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 52, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.L.; Ding, G.D.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qin, S.G.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Bao, Y.F.; Liu, Y.D.; Wan, L.; Deng, J.F. Fractal scaling of particle size distribution and relationships with topsoil properties affected by biological soil crusts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.L.; Ding, G.D.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qin, S.G.; Bao, Y.F.; Yu, M.H.; Liu, Y.D. Fractal approach to estimating changes in soil properties following the establishment of Caragana korshinskii shelterbelts in Ningxia, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ma, C.; Yu, H. Different soil particle-size classification systems for calculating volume fractal dimension-a case study of Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Yu, X. Populus simonii Carr. Reduces wind erosion and improves soil properties in Northern China. Forests 2019, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Xu, Z.W.; Jiang, D.M.; Jiang, Y. Soil exchangeable base cations along a chronosequence of Caragana microphylla plantation in a semi-arid sandy land, China. J. Arid Land 2013, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. Long-Term effects of xerophytic shrub haloxylon ammodendron plantations on soil properties and vegetation dynamics in northwest China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, F.; Jia, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Lei, J. Soil aggregation formation in relation to planting time, water salinity, and species in the Taklimakan Desert Highway shelterbelt. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Jia, Y.; Tian, S. Impacts of Artificially Planted Vegetation on the Ecological Restoration of Movable Sand Dunes in the Mugetan Desert, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 32, ISBN 1827487658. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.P.; Li, X.R.; Xiao, H.L.; Pan, Y.X. Evolutionary characteristics of the artificially revegetated shrub ecosystem in the Tengger Desert, northern China. Ecol. Res. 2006, 21, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Lu, J.; Li, J. Spatial variability of vegetation characteristics, soil properties and their relationships in and around China’s Badain Jaran Desert. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6847–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenghu, D.; Honglang, X.; Zhibao, D.; Gang, W.; Drake, S. Morphological, physical and chemical properties of aeolian sandy soils in northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin, W.; Liu, K.; Qu, J. Effects of Sand Barriers on Vegetation and Soil Nutrient in Sand Dunes. J. Desert Res. 2019, 39, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baoying, N.; Jianxia, M.; Zhide, J.; Chun, C.; Xinli, Z.; Jingliang, L. Evolution Characteristics and Development Trends of Sand Barriers. J. Resour. Ecol. 2017, 8, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Ye, C.; Luo, L.; Pei, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Liao, B. Sand fixation property and erosion control through new cellulose-based curing agent on sandy slopes under rainfall. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 4051–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. A new strain of Bacillus tequilensis CGMCC 17603 isolated from biological soil crusts: A promising sand-fixation agent for desertification control. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Zheng, J.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y. Application of sodium alginate in induced biological soil crusts: Enhancing the sand stabilization in the early stage. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, S.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Liu, Z. Study on the stabilization mechanisms of clayey slope surfaces treated by spraying with a new soil additive. Appl. Sci. 2019, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Ge, X.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Liu, Z. Effects of aqua-dispersing nano-binder on clay conductivity at different temperatures. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, Y.; Gong, W.; Xie, H.; Du, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, H. Evaluation and mechanism of anionic waterborne polyurethane dispersion for chemical sand stabilisation. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2016, 45, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, B.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, G.; Kamai, T. Effectiveness of a new organic polymer sand-fixing agent on sand fixation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyejekwe, S.; Ghataora, G.S. Soil stabilization using proprietary liquid chemical stabilizers: Sulphonated oil and a polymer. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Feng, E.; Ran, F.; Dong, Z.; Lei, Z. Preparation and Sand-Fixing Property of a Novel and Eco-friendly Organic-Inorganic Composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, B.; Jiang, H.; Bae, S.; Huang, H. Improvement of water-stability of clay aggregates admixed with aqueous polymer soil stabilizers. Catena 2009, 77, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajalloeian, R.; Matinmanesh, H.; Abtahi, S.M.; Rowshanzamir, M. Effect of polyvinyl acetate grout injection on geotechnical properties of fine sand. Geomech. Geoengin. 2013, 8, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xie, J.; Han, J. A sand control and development model in sandy land based on mixed experiments of arsenic sandstone and sand: A case study in mu us sandy land in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S. Effects of soft rock and biochar applications on millet (Setaria italica L.) crop performance in sandy soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiedi, N.; Besalatpour, A.A.; Shirani, H.; Abbaszadeh Dehaji, P.; Esfandiarpour, I.; Faramarzi, M. Aggregation and fractal dimension of aggregates formed in sand dunes stabilized by PistachioPAM and PistachioPVAc mulches. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, B.; Jiang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, G.; Kamai, T. Research on the stabilization treatment of clay slope topsoil by organic polymer soil stabilizer. Eng. Geol. 2011, 117, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezin, A.B.; Mikheikin, S.V.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zansokhova, M.F.; Sybachin, A.V.; Yaroslavov, A.A. Polymeric stabilizers for protection of soil and ground against wind and water erosion. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 226, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Improvement of physical and hydraulic properties of desert soil with amendment of different biochars. J. Soils Sediments 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Li, X.R.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, R.L.; Hur, J.S. Rapid development of cyanobacterial crust in the field for combating desertification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Li, H.; Lv, G.; Tian, J.; Xu, Y. Effects of ecological restoration on soil properties of the aeolian sandy land around Lhasa, southern Tibetan Plateau. Ecosphere 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.H.; Su, Y.Z.; Cui, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chang, X.X. A leguminous shrub (Caragana microphylla) in semiarid sandy soils of north China. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, L.; He, L. Effects of different plantation types on soil properties after vegetation restoration in an alpine sandy land on the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.L.; Guo, Y.R.; Zhou, R.L.; Drake, S. Biological soil crust and surface soil properties in different vegetation types of Horqin Sand Land, China. Catena 2010, 82, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue mei, W.; Lijun, C. Analysis of Soil Particle Size of Typical Plant Communities in Desert Ecotone on Northern Margin of Tarim Basin. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 32, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Z. The design and application of non-pressure infiltrating irrigation in desertification control. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chepil, W.S. Factors that influence clod structure and erodibility of soil by wind: IV. Sand, silt, and clay. Soil Sci. 1955, 80, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Gao, S.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Ta, W.Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, B.L. Wind erodibility of major soils in the farming-pastoral ecotone of China. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.V. Wind erosion in agricultural soils: An example of limited supply of particles available for erosion. Catena 1998, 33, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.R.; Yue, L.P.; Li, Z.P. The influence of dry lakebeds, degraded sandy grasslands and abandoned farmland in the arid inlands of northern China on the grain size distribution of East Asian aeolian dust. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, S.; Zining, Z. Research Progress on Soil Erodibility. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Horizontal wind erosion flux and potential dust emission in arid and semiarid regions of China: A major source area for East Asia dust storms. Catena 2015, 133, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnappan, B.G.; Burrell, B.C. Using mosand to mitigate the desertification of minqin oasis, Gansu province, China. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Du, L.; Zhan, X. Advances in Study on Soil Erodibility for Wind Erosion. Soils 2014, 46, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Mausbach, M.J.; Doran, J.W.; Cline, R.G.; Harris, R.F.; Schuman, G.E. Soil Quality: A Concept, Definition, and Framework for Evaluation (A Guest Editorial). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laishram, J.; Saxena, K.G.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Rao, K.S. Soil Quality and Soil Health: A Review. Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 38, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of agricultural management practices on soil quality: A review of long-term experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, G.; Ren, Z.P. Changes in soil nutrient and enzyme activities under different vegetations in the Loess Plateau area, Northwest China. Catena 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bowker, M.A.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Tuo, D.; Zhao, Y. Biological soil crusts decrease erodibility by modifying inherent soil properties on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Ding, G.; Gao, G. Effects of straw checkerboard barrier in different setting years on ecological restoration. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 16, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, N.; Gong, K.; Liu, Y. Characteristics of Turbulent Aeolian Sand Movement Over Straw Checkerboard Barriers and Formation Mechanisms of Their Internal Erosion Form. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6907–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, K.; Robillard, A.; Grégoire, J.; Duclos, V.; Kramer, D.L. Functional connectivity from a reef fish perspective: Behavioral tactics for moving in a fragmented landscape. Ecology 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.D.; Dang, X.H.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, Y.M.; Qi, S.; Zhao, C. Alternated desorption-absorption accelerated aging of Salix psammophila sand barrier. BioResources 2020, 15, 6696–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.K.; Cui, M.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.G.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhou, J.X. Effects of vegetation restoration on the aggregate stability and distribution of aggregate-associated organic carbon in a typical karst gorge region. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X. Enhancement of soil ecological self-repair using a polymer composite material. Catena 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Li, X.; Jia, R.L.; Hur, J.S. Effects of Superabsorbent Polymer on Cyanobacterial Biological Soil Crust Formation in Laboratory. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gilhooly, W.P.; Okin, G.S.; Blackwell, J. Abiotic processes are insufficient for fertile island development: A 10-year artificial shrub experiment in a desert grassland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, H.; Li, Q.L.; Yan, X.; Wu, X.Z.; Liu, R.T.; Fang, Y. Desertification control on soil inorganic and organic carbon accumulation in the topsoil of desert grassland in Ningxia, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Qian, G. Nebkha development and its significance to wind erosion and land degradation in semi-arid northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 65, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Vogeler, I.; Schwendenmann, L. Soil aggregation and soil fraction associated carbon under different vegetation types in a complex landscape. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cui, Q.; Vest, M. Effects of biological soil crusts on water infiltration and evaporation Yanchi Ningxia, Maowusu Desert, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Wang, X.; Guan, W.; Zhong, J.; Yi, X.; Wen, Y. Soil physico-chemical properties and their effects on populus euphratica growth in desertification areas. Acta Scietific Agric. 2018, 2, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L. Assessment of the coordination ability of sustainable social-ecological systems development based on a set pair analysis: A case study in Yanchi County, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhan, H.X.; Xu, H. Fractal features of soil particles under different plant communities in the yimeng mountain of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 15731–15743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.; Wei, N. Fractal features of soil particle size distribution in layered sediments behind two check dams: Implications for the Loess Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2016, 266, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, C. Fractal features of soil profiles under different land use patterns on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Desert (Abbreviation) | Sites of Desert | Coordinates | Number of Samples | Type of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hulunbuir Sands (HB) | Northeastern | 115°31′ E-126°04′ E, 47°05′ N-53°20′ N | 135 | Aeolian sandy soil and chestnut soil |
| Horqin Sands (HQ1) | Southern | 42°55′ N,120°41′ E | 90 | Aeolian sandy soil and chestnut soil |
| Southern | 42°55′ N, 120°42′ E | 72 | ||
| Western | 43°80′ N, 119°83′ E | 80 | ||
| Southwestern | 42°15′ N, 120°42′ E | 96 | ||
| Southern | 43°02′ N, 119°39′ E | 48 | ||
| Horqin Sands (HQ2) | Eastern | 101°59′ E-104°12′ E, 38°08′ N-39°26′ N | 80 | Aeolian sandy soil and grey brown desert soil |
| Hunsandak Sands (HD) | Southern | 40°57′ N-41°34′ N, 114°10′ E-115°27′ E | 36 | Aeolian sandy soil |
| Mu Us Sands (MU1) | Southern | 37°42′ N, 107°42′ E | 60 | Aeolian sandy soil and Sierozem |
| Southeastern | 110°04′ E, 39°30′ N | 27 | ||
| Southeastern | 110°04′ E, 39°30′ N | 54 | ||
| Mu Us Sands (MU2) | Southwestern | 37°04′ N-38°10′ N, 106°30′ E-107°41′ E | 175 | Aeolian sandy soil and arenosols of quartisamment |
| Western | 37°55′ N,106°30′ E | 30 | ||
| Southern | 37°04′ N-38°10′ N, 106°30′ E-107°47′ E | 54 | ||
| Southern | 37°04′ N-38°10′ N, 106°30′ E-107°47′ E | 270 | ||
| Kubuqi Desert (KQ) | North | 107°00′ E-111°30′ E, 39°30′ N-40°41′ N | 144 | Aeolian sandy soil and grey desert soils |
| UlanBuh Desert (UB) | Eastern | 106°33′ E-106°51′ E, 39°40′ N-40°13′ N | 121 | Aeolian sandy soil and grey desert soils |
| Eastern | 40°09′ N, 106°50′ E | 90 | ||
| Tengger Desert (TG) | Southeastern | 37°30′ N, 105°03′ E | 96 | Aeolian sandy soil and brown desert soils |
| Southeastern | 37°32′ N, 105°02′ E | 100 | ||
| Southeastern | 38°43′ N, 105°31′ E | 70 | ||
| Badain Jaran Desert (BJ) | Southeastern | 42°41′ N, 102°08′ E | 72 | Aeolian sandy soil, grey desert soils and grey-brown desert soils |
| Southeastern | 40°20′ N, 97°36′ E | 180 | ||
| Qaidam Basin Desert (QB) | Southeastern | 100°24′ E-101°22′ E, 35°27′ N-35°47′ N | 45 | Aeolian sandy soil |
| Kumutag Desert (KT) | Southeastern | 38°20′ N, 94°17′ E | 80 | Aeolian sandy soil |
| Gurbantunggut Desert (GG) | Southern | 44°40′ N-45°56′ N, 84°54′ E-88°48′ E | 60 | Aeolian sandy soil |
| Taklimakan Desert (TK) | Southern | 35°17′ N-39°30′ N, 80°03′ E-82°10′ E | 45 | Aeolian sandy soil |
| Southern | 36°55′ N-37°33′ N, 82°36′ E-83°12′ E | 60 | ||
| Northern | 40°86′ N, 84°10′ E | 45 |
| Desert | Soil Mineral Composition (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MnO | TiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | |
| HB | 72.4 | 2.63 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 11.93 | 2.32 | 0.89 | 2.93 | 2.49 | 0.05 |
| HQ1 | 69.85 | 4.66 | 0.08 | 0.77 | 15.39 | 4.07 | 1.76 | 2.96 | 2.35 | 0.1 |
| HQ2 | 71.15 | 2.81 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 12.21 | 2.32 | 1.05 | 2.87 | 2.5 | 0.1 |
| HD | 72.5 | 2.62 | 0.06 | 0.57 | 11.86 | 2.18 | 0.9 | 2.96 | 3.05 | 0.09 |
| MU1 | 61.8 | 4.02 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 11.83 | 6.42 | 2.15 | 2.12 | 1.99 | 0.2 |
| MU2 | 62.73 | 4.09 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 11.14 | 6.85 | 2.11 | 2.08 | 1.91 | 0.18 |
| KQ | 63.71 | 2.72 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 11.12 | 2.3 | 1 | 2.7 | 2.01 | 0.03 |
| UB | 61.56 | 4.11 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 11.94 | 6.8 | 2.2 | 2.11 | 1.97 | 0.16 |
| TG | 63.03 | 4.22 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 11.16 | 5.92 | 2.33 | 2.41 | 1.57 | 0.15 |
| BJ | 72.5 | 2.62 | 0.06 | 0.57 | 11.86 | 2.18 | 0.9 | 2.96 | 3.05 | 0.09 |
| QB | 59.49 | 3.69 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 10.67 | 8.99 | 2.87 | 2.4 | 2.41 | 0.17 |
| KT | 70.33 | 3.41 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 10.35 | 3.92 | 1.56 | 2.3 | 1.63 | 0.11 |
| GG | 58.63 | 4.14 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 10.5 | 4.46 | 2.61 | 2.48 | 1.86 | 0.19 |
| TK | 59.69 | 3.53 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 8.56 | 6.23 | 4.12 | 1.38 | 1.49 | 0.13 |
| Study Area | Sand Barrier Material | Silt–Clay Content |
|---|---|---|
| Mu Us Sandland [54] | Bare sandy land | 0.139 |
| Salix psammophila | 2.87 | |
| PLA | 1.837 | |
| Tengger Desert [59] | Bare sandy land | 0.11 |
| Straw | 3.44 | |
| PLA | 2.48 | |
| Straw-PLA mix | 3.04 | |
| Badain Jaran Desert [76] | Bare sandy land | 1.15 |
| Dead Salix psammophila | 3.45 | |
| Straw | 2.44 | |
| Live Salix psammophila | 6.68 | |
| Sabina vulgaris | 5.58 |
| Study Area | Vegetation Type | Silt–Clay Content | Study Area | Vegetation Type | Silt–Clay Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonghe Desert [98] | Bare | 1.5 | Horqin Sand Land [99] | Bare | 1.64 |
| A. ordosica | 10.02 | Sabina vulgaris | 18.1 | ||
| C. korshinskii | 10.22 | Ulmus pumila l. | 18.18 | ||
| C. intermedia | 12.47 | Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica | 18.4 | ||
| Otindag Desert [34] | Bare | 1.74 | Taklamakan Desert [100] | Bare | 1.32 |
| Stipa capillata | 22.3 | Caragana korshinskii | 28.9 | ||
| Fir | 18.2 | Artemisia ordosica | 32.9 | ||
| Caragana korshinskii | 11.7 | Haloxylon ammodendron | 28.1 | ||
| Littleleaf peashrub herb | 8.5 | Salix cheilophila | 37 |
| Climate Type | Area | Critical Fractal Dimension | Silt–Clay Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-arid | Southern rim area of the Mu Us Desert [67] | 2.527 | 19.74% silt 3.33% clay |
| Mu Us Desert [64] | 2.505 | 22.59% silt 6.25% clay | |
| South-west end of the Horqin Sandy Land [132] | 2.532 | 21.09% silt 5.93% clay | |
| Arid | Alxa Desert [52] | 2.445 | 19.79% silt 2.7% clay |
| Southeast edge of Qaidam Basin Desert [66] | 2.4160 | 21% silt 4% clay | |
| Hyperarid | Taklimakan Desert [19] | 2.412 | 29.12% silt 1.10% clay |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Lin, K.; Zhou, C.; Huang, W. Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts of Northwest China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052998
Liu Z, Sun H, Lin K, Zhou C, Huang W. Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts of Northwest China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(5):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052998
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhen, Hao Sun, Ke Lin, Cuiying Zhou, and Wei Huang. 2021. "Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts of Northwest China" Sustainability 13, no. 5: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052998
APA StyleLiu, Z., Sun, H., Lin, K., Zhou, C., & Huang, W. (2021). Occurrence Regularity of Silt–Clay Minerals in Wind Eroded Deserts of Northwest China. Sustainability, 13(5), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052998