Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Related Literature
2.1. Supply Chain Management (SCM) Integration
2.2. Innovation System
2.3. Supply Chain Flexibility
2.4. Supply Chain Resilience
2.5. Business Performance
2.6. Concepts Relationship
2.6.1. Supply Chain Integration and Innovation System
2.6.2. Supply Chain Management Integration and the Supply chain flexibility
2.6.3. Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Resilience
2.6.4. Innovation system and Supply Chain Resilience
2.6.5. Supply Chain Flexibility and Supply Chain Resilience
2.6.6. Innovation System and Business Performance
2.6.7. Supply Chain Flexibility and Business Performance
2.6.8. Supply Chain Resilience and the Business Performance
2.6.9. Indirect Relationship between Constructs
3. Methodology
4. Result and Analysis
5. Discussion and Managerial Implication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraus, S.; Clauss, T.; Breier, M.; Gast, J.; Zardini, A.; Tiberius, V. The economics of COVID-19: Initial empirical evidence on how family firms in five European countries cope with the corona crisis. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2020, 26, 1067–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nchanji, E.B.; Lutomia, C.K.; Chirwa, R.; Templer, N.; Rubyogo, J.C.; Onyango, P. Immediate impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on bean value chain in selected countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Syst. 2021, 188, 103034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hyari, K. Initial empirical evidence on how Jordanian manufacturing SMEs cope with the covid-19 pandemic. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, R. COVID-19 Global Pandemic: Impact on Management of Supply Chain. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2020, 10, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chou, M.; Tsai, C. Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Pandemic Exposing the Shortcomings of Current Supply Chain Operations: A Long-Term Prescriptive Offering. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalante, R.; Lassa, J.; Setiamarga, D.; Sudjatma, A.; Indrawan, M.; Haryanto, B.; Mahfud, C.; Sinapoy, M.S.; Djalante, S.; Rafliana, I.; et al. Review and analysis of current responses to COVID-19 in Indonesia: Period of January to March 2020. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 6, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Chowdhury, P. A production recovery plan in manufacturing supply chains for a high-demand item during COVID-19. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2020, 51, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.E.C.; Razon, L.F.; Tan, R.R. Can global pharmaceutical supply chains scale up sustainably for the COVID-19 crisis? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Luo, B.N.; Feng, X.; Liu, J. Supply chain information integration, flexibility, and operational performance: An archival search and content analysis. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 340–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.H.; Quaddus, M. Supply chain resilience: Conceptualization and scale development using dynamic capability theory. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 188, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, P.; Kuo, F.-I. Innovation-oriented supply chain integration for combined competitiveness and firm performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 174, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Azfar, R.; Salah, B.; Saleem, W.; Abas, M.; Khan, R.; Pruncu, C. Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Use of Construction Materials for Supply Chain Integration and Construction Industry Performance through Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Sustainability 2021, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamout, M.D. The nexus between supply chain analytic, innovation and robustness capability: Does firm age matter? VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2020, 51, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, K.; Wang, L.; Ding, L. Pricing Decisions for a Sustainable Supply Chain in the Presence of Potential Strategic Customers. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H. The impact of organizational commitment to the process and product innovation in improving operational performance. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 19, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S. Impact of supplier innovativeness, top management support and strategic sourcing on supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Perform. Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Boer, H.; Taran, Y. Supply chain integration, risk management and manufacturing flexibility. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 690–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Huo, B.; Sun, L. Relationships between intra-organizational resources, supply chain integration and business performance: An extended resource-based view. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2014, 114, 1186–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lai, K.K.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y. The impact of supplier integration on customer integration and new product performance: The mediating role of manufacturing flexibility under trust theory. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Jajja, M.S.S.; Chatha, K.A.; Farooq, S. Supply chain risk management and operational performance: The enabling role of supply chain integration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 227, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H. Influence of Information Quality on Retailer Satisfaction through Supply Chain Flexibility and Supplier Relationship Management in the Retail Industry. J. Tek. Ind. 2020, 22, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, M.A.; El Mokadem, M.Y. The relationship between internal integration and manufacturing flexibility in the Egyptian industry. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2019, 11, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukor, A.A.A.; Newaz, S.; Rahman, M.K.; Taha, A.Z. Supply chain integration and its impact on supply chain agility and organizational flexibility in manufacturing firms. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.; Park, S. Evidence-Based Resilience Management for Supply Chain Sustainability: An Interpretive Structural Modelling Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hohenstein, N.-O.; Feisel, E.; Hartmann, E.; Giunipero, L. Research on the phenomenon of supply chain resilience a systematic review and paths for further investigation. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2015, 45, 90–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-W.; Seo, Y.-J.; Mason, R. Investigating the relationship between supply chain innovation, risk management capabilities and competitive advantage in global supply chains. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huo, B.; Sun, L.; Zhao, X. The impact of supply chain risk on supply chain integration and company performance: A global investigation. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2013, 18, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B. The impact of supply chain integration on company performance: An organizational capability perspective. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2012, 17, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Mochtar, J.; Basana, S.R.; Siagian, H. The effect of competency management on organizational performance through supply chain integration and quality. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 9, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.P.; Sinnandavar, C.M.; Soh, K.-L. The relationship between supply environment, supply chain integration and operational performance: The role of business process in curbing opportunistic behaviour. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 232, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaoa, X.; Wangb, P.; Palb, R. The effects of agro-food supply chain integration on product quality and financial performance: Evidence from Chinese agro-food processing business. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H. The effects of strategic planning, purchasing strategy and strategic partnership on operational performance. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 9, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Otchere, S.; Coffie, C.; Mensah, I.; Baku, R. Supply Chain Integration, Interfirm Value Co-Creation and Firm Performance Nexus in Ghanaian SMEs: Mediating Roles of Stakeholder Pressure and Innovation Capability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S. Supply chain integration and Industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 990–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianto, I.; Tarigan, Z.J.H. The impact TQM System on Supply Chain Performance through Supply Chain Integration and Employee Satisfaction. Petra Int. J. Bus. Stud. 2019, 2, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Hu, Q.; Chin, T.; Chen, C.; Shi, Y. How Supply Chain Integration Affects Innovation in a Digital Age: Moderating Effects of Sustainable Policy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Asian, S.; Wood, L.C.; Wang, B. Logistics innovation capability and its impacts on the supply chain risks in the Industry 4.0 era. Mod. Supply Chain Res. Appl. 2020, 2, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, R.; Ferreira, L.M.D.; Moreira, A.C. The influence of supply chain on the innovation process: A systematic literature review. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2016, 21, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, N.; Wang, H.; Kuruppuarachchi, D. Effect of supply-chain resilience on firm performance and competitive advantage: A study of the Sri Lankan apparel industry. Bus. Process. Manag. J. 2019, 25, 1673–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R. Flexible business strategies to enhance resilience in manufacturing supply chains: An empirical study. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, C.; Schoenherr, T.; Rexhausen, D. Antecedents and enablers of supply chain agility and its effect on performance: A dynamic capabilities perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 1295–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M.; Esmark, C.L.; Holcomb, M.C. Performance outcomes of supply chain agility: When should you be agile? J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33–34, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniszczuk-Jastrząbek, A.; Czermański, E.; Cirella, G.T. Sustainable Supply Chain of Enterprises: Value Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettit, T.J.; Croxton, K.L.; Fiksel, J. Ensuring Supply Chain Resilience: Development and Implementation of an Assessment Tool. J. Bus. Logist. 2013, 34, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Torstensson, H.; Mattila, H. Antecedents of organizational resilience in economic crises—An empirical study of Swedish textile and clothing SMEs. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 410–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambulkar, S.; Blackhurst, J.; Grawe, S.J. Firm’s resilience to supply chain disruptions: Scale development and empirical examination. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33–34, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L.; Shang, K.-C.; Lirn, T.-C.; Lai, K.-H.; Lun, Y.V. Supply chain resilience, firm performance, and management policies in the liner shipping industry. Transp. Res. Part A: Policy Pr. 2018, 110, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunsheng, L.; Wong, C.W.; Yang, C.-C.; Shang, K.-C.; Lirn, T.-C. Value of supply chain resilience: Roles of culture, flexibility, and integration. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2019, 50, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, A.Y.; Chan, F.T.; Ooi, K.; Sim, J. Can Malaysian firms improve organizational/innovation performance via SCM? Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2011, 111, 410–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Kwon, I.G.; Severance, D. Relationship between supply chain performance and degree of linkage among supplier, internal integration, and customer. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2007, 12, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, H.; Imamoglu, S.Z.; Keskin, H.; Akgun, A.; Efe, M.N. The Impact of ERP Systems and Supply Chain Management Practices on Firm Performance: Case of Turkish Companies. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 99, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shboul, M.A.R.; Barber, K.D.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Kumar, V.; Abdi, M.R. The effect of supply chain management practices on supply chain and manufacturing firms’ performance. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2017, 28, 577–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Gandhi, M.A. Exploring correlations in components of green supply chain practices and green supply chain performance. Compet. Rev. 2016, 26, 332–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.Q.; Sameiro, M.; Fernandes, A.C.; Sampaio, P.; Duong, B.A.T.; Duong, H.H.; Vilhenac, E. Supply chain management practices and firms’ operational performance. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2017, 34, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H.; Jie, F. The Role of Top Management Commitment to Enhancing the Competitive Advantage Through ERP Integration and Purchasing Strategy. Int. J. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 16, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, I.C.; De Campos, E.A.R.; Pagani, R.N.; Guarnieri, P.; Kaviani, M.A. Are collaboration and trust sources for innovation in the reverse logistics? Insights from a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 25, 176–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H.; Bua, R.R. The Impact of Information System Implementation to the Integrated System for Increasing the Supply Chain Performance of Manufacturing Companies. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 473, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siagian, H.; Jade, K.; Tarigan, Z.J.H. The role of affective leadership in improving firm performance through the integrated internal system and external integration FMCG Industry. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2020, 4, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfalla-Luque, R.; Marin-Garcia, J.A.; Medina-Lopez, C. An analysis of the direct and mediated effects of employee commitment and supply chain integration on organisational performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-L.; Lee, M.-Y. Integration, supply chain resilience, and service performance in third-party logistics providers. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltantawy, R.A. The role of supply management resilience in attaining ambidexterity: A dynamic capabilities approach. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2016, 31, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgün, A.E.; Keskin, H. Organisational resilience capacity and firm product innovativeness and performance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 6918–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Vonderembse, M.; Ragu-Nathan, T.; Smith, J.T. Exploring relationships among IT-enabled sharing capability, supply chain flexibility, and competitive performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 153, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, U.; Bougie, R. Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 235–260. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, G.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Shiau, W.-L.; Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Fritze, M.P. Methodological research on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Internet Res. 2019, 29, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Description | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 246 | 52.34% |
| Male | 224 | 47.66% | |
| Department | Production Department | 145 | 30.85% |
| Marketing Department | 109 | 23.19% | |
| Finance and Accounting Department | 69 | 14.68% | |
| Warehouse Department | 17 | 3.62% | |
| Human Resources Department | 11 | 2.34% | |
| Planning Production Department | 60 | 12.77% | |
| Purchasing and Supply department | 21 | 4.47% | |
| Information Department | 8 | 1.70% | |
| Others | 30 | 6.38% | |
| Length of work | 1–3 years | 183 | 38.94% |
| 3 to 5 years | 93 | 19.78% | |
| 5–10 years | 60 | 12.77% | |
| More than ten years | 134 | 28.51% | |
| Total manpower | Below 20 | 204 | 43.40% |
| 20–100 | 134 | 28.51% | |
| Above 100 | 132 | 28.09% | |
| Average Hours of | Less than 4 h | 4 | 0.85% |
| Work during COVID | 4–7 h per day | 51 | 10.85% |
| Era | 8 h per day or more | 415 | 88.30% |
| Indicators | SCM Integration | Innovation System | Supply Chain Flexibility | SCM Resilience | Business Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCMI1 | 0.814 | 0.621 | 0.571 | 0.598 | 0.511 |
| SCMI2 | 0.742 | 0.389 | 0.540 | 0.481 | 0.569 |
| SCMI3 | 0.636 | 0.215 | 0.358 | 0.344 | 0.443 |
| SCMI4 | 0.859 | 0.600 | 0.588 | 0.581 | 0.577 |
| SCMI5 | 0.809 | 0.558 | 0.569 | 0.499 | 0.547 |
| In.Sy1 | 0.563 | 0.848 | 0.539 | 0.594 | 0.473 |
| In.Sy2 | 0.484 | 0.815 | 0.510 | 0.596 | 0.391 |
| In.Sy3 | 0.485 | 0.759 | 0.510 | 0.567 | 0.383 |
| In.Sy4 | 0.573 | 0.802 | 0.518 | 0.665 | 0.458 |
| In.Sy5 | 0.521 | 0.853 | 0.537 | 0.652 | 0.492 |
| Fl.Sy1 | 0.437 | 0.531 | 0.794 | 0.459 | 0.439 |
| Fl.Sy2 | 0.329 | 0.391 | 0.583 | 0.390 | 0.397 |
| Fl.Sy3 | 0.516 | 0.398 | 0.796 | 0.463 | 0.595 |
| Fl.Sy4 | 0.653 | 0.563 | 0.641 | 0.496 | 0.478 |
| Fl.Sy5 | 0.557 | 0.485 | 0.867 | 0.527 | 0.606 |
| SCMR1 | 0.562 | 0.637 | 0.541 | 0.786 | 0.554 |
| SCMR2 | 0.511 | 0.557 | 0.489 | 0.784 | 0.540 |
| SCMR3 | 0.394 | 0.498 | 0.427 | 0.686 | 0.368 |
| SCMR4 | 0.491 | 0.591 | 0.436 | 0.687 | 0.392 |
| SCMR5 | 0.453 | 0.491 | 0.435 | 0.733 | 0.553 |
| Bus.P1 | 0.332 | 0.364 | 0.424 | 0.543 | 0.675 |
| Bus.P2 | 0.427 | 0.295 | 0.363 | 0.389 | 0.643 |
| Bus.P3 | 0.437 | 0.361 | 0.501 | 0.461 | 0.637 |
| Bus.P4 | 0.599 | 0.486 | 0.594 | 0.483 | 0.809 |
| Bus.P5 | 0.607 | 0.394 | 0.532 | 0.464 | 0.775 |
| Variable of Research | Cronbach Alpha | Composite Reliability | AVE | R2 | Q2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply chain management integration | 0.834 | 0.882 | 0.602 | - | - |
| Innovation system | 0.874 | 0.909 | 0.666 | 0.417 | 0.274 |
| Supply chain flexibility | 0.791 | 0.858 | 0.553 | 0.474 | 0.246 |
| Supply chain resilience | 0.789 | 0.855 | 0.543 | 0.632 | 0.337 |
| Business performance | 0.753 | 0.835 | 0.506 | 0.560 | 0.276 |
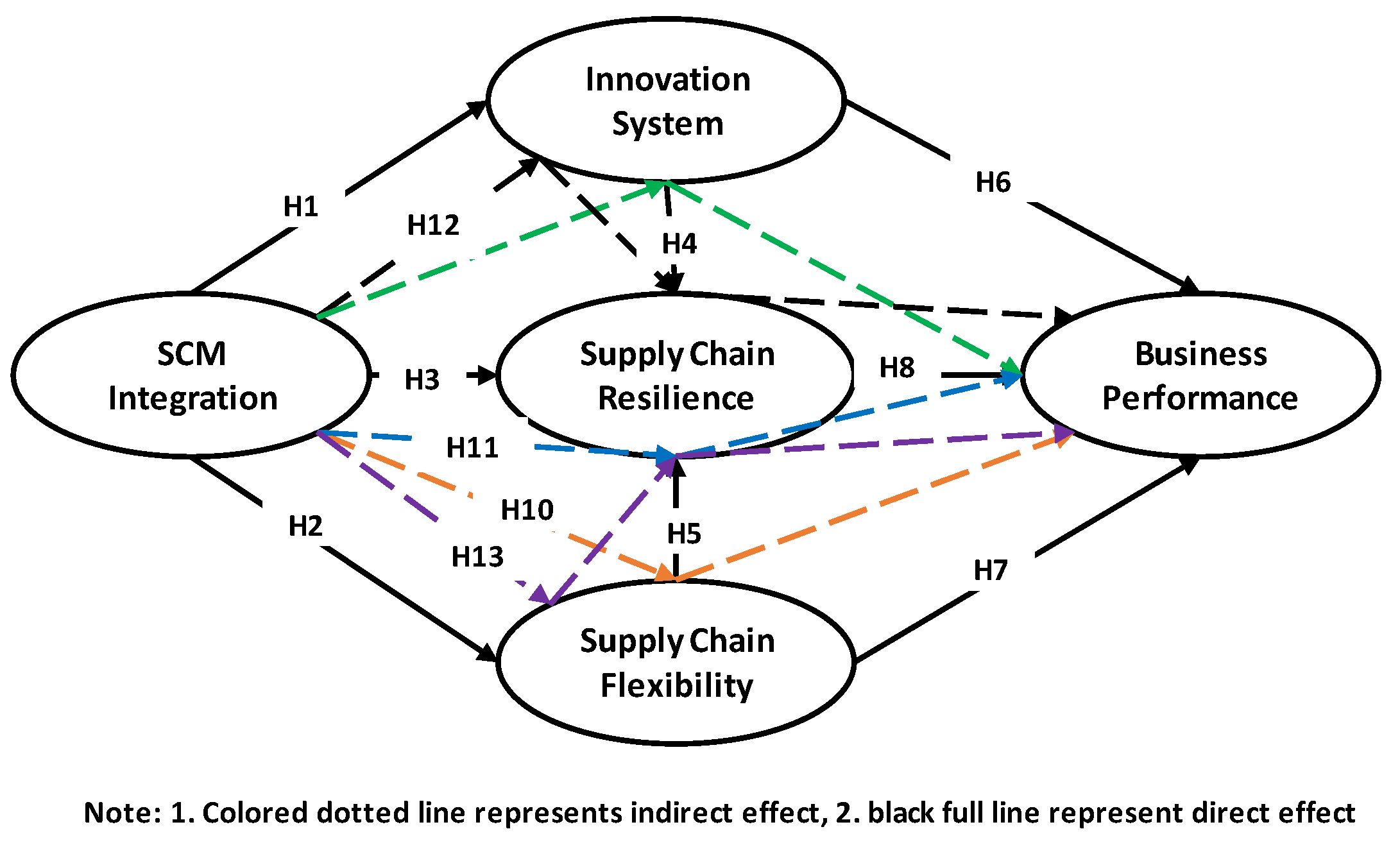
| Hypothesis | Path Coefficient | t-Value | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCM Integration → Innovation system (H1) | 0.646 | 18.365 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → Supply chain flexibility (H2) | 0.688 | 20.248 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → SC Resilience (H3) | 0.222 | 4.842 | 0.000 |
| Innovation system → SC Resilience (H4) | 0.514 | 10.914 | 0.000 |
| SC Flexibility → SC Resilience (H5) | 0.153 | 3.164 | 0.002 |
| Innovation system → Business Performance (H6) | −0.079 | 1.119 | 0.264 |
| SC Flexibility → Business Performance (H7) | 0.471 | 9.439 | 0.000 |
| SC Resilience → Business Performance (H8) | 0.421 | 7.226 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → Innovation system → Business Performance (H9) | −0.051 | 1.122 | 0.262 |
| SCM Integration → SC Flexibility → Business Performance (H10) | 0.325 | 7.758 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → SC Resilience → Business Performance (H11) | 0.093 | 3.568 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → Innovation system → SC Resilience → Business Performance (H12) | 0.140 | 6.539 | 0.000 |
| SCM Integration → SC Flexibility → SC Resilience → Business Performance (H13) | 0.044 | 2.898 | 0.004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siagian, H.; Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Jie, F. Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094669
Siagian H, Tarigan ZJH, Jie F. Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094669
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiagian, Hotlan, Zeplin Jiwa Husada Tarigan, and Ferry Jie. 2021. "Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094669
APA StyleSiagian, H., Tarigan, Z. J. H., & Jie, F. (2021). Supply Chain Integration Enables Resilience, Flexibility, and Innovation to Improve Business Performance in COVID-19 Era. Sustainability, 13(9), 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094669







