Characteristics of Smoldering on Moist Rice Husk for Silica Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
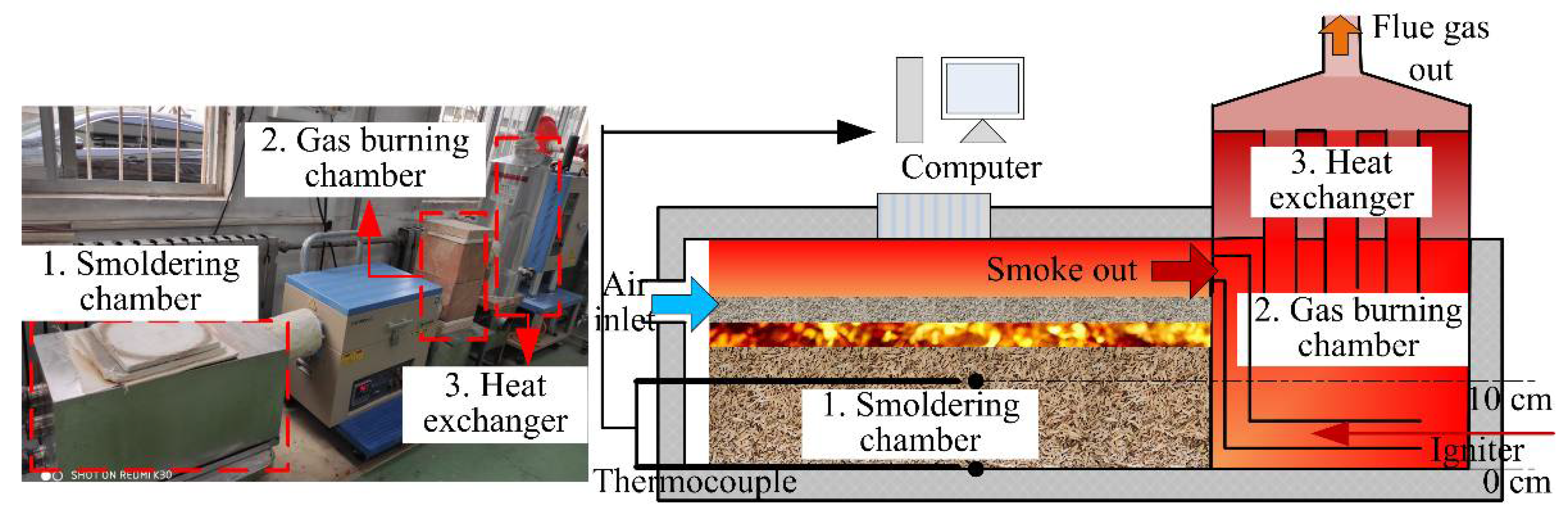
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Ash Preparation and Treatment
2.3.1. Ash Preparation from Rice Husk
2.3.2. Grinding and Drying of Ash
2.4. Thermal and Physical Characterization of Ash
3. Results and Discussion
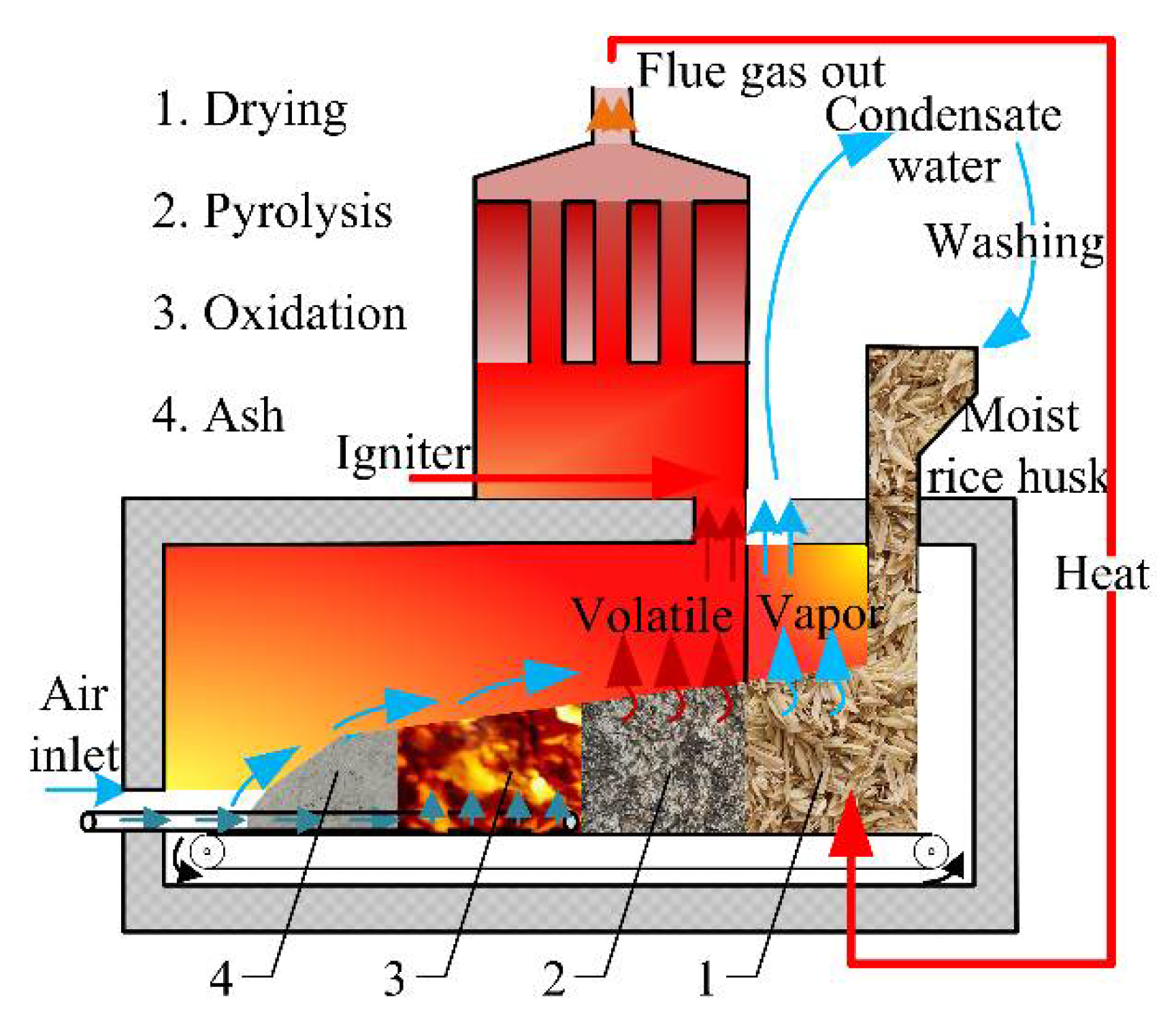
3.1. Characteristics of Smoldering Process
3.1.1. Temperature inside Fuel Bed
3.1.2. Absorption of Volatiles by the Upper Ash
3.2. Physical Properties and Mass Loss Characteristic of Rice Husk Ash
3.2.1. Physical Properties of Ash
3.2.2. Mass Loss Characteristic of Rice Husk Ash
3.3. Silica Content in Rice Husk Ash
3.3.1. Reproducibility and Reliability of XRF Measurement
3.3.2. Content of Silica and Other Main Compositions in Rice Husk Ash
3.3.3. Effect of Production Method on Silica Content
3.4. BET Specific Surface Area
3.4.1. Specific Surface Area of the Four Types of Rice Husk Ash
3.4.2. Factors of Specific Surface Area
3.4.3. Comparison of Specific Surface Area in This Study with Those of Silica Prepared Using Methods in Literature
3.5. Supplementary Experiment of Smoldering Air-Dried Rice Husk after Washing
4. Potential of Mass Product of Silica from Smoldering of Rice Husk
4.1. Measures to Increase Silica Content and Specific Surface Area
4.1.1. Lateral Continuously Smoldering Involving a Dry Stage of Rice Husk
4.1.2. The Supply of Air at the Oxidation Stage
4.2. Feasibility of Mass Product of Silica from Smoldering of Rice Husk
5. Conclusions
- Smoldering is a novel method for producing silica from rice husk. In our experimental set-up with a smoldering chamber, a gas burning chamber and a heat exchanger, the smoldering was self-sustained for naturally-piled rice husk with moisture content of 51.0%. Incomplete-combustion smoldering gas can be burned out in a gas burning chamber, and the heat generated during smoldering can be used for heating.
- The highest temperature inside the fuel bed is around 560 °C, which was lower than those in many combustors. In the piled smoldering process of rice husk, part of the volatiles will be absorbed by the upper ash, which can decrease the silica content and specific surface area of ash. It should be avoided in the future.
- Specific surface area of ash prepared from washed (moist) rice husk by smoldering was lower than those prepared in the laboratory, but it is higher than those produced from most industrial methods. It was greatly improved by air drying of moist rice husk before smoldering.
- In future, a lateral continuously smoldering scheme involving a drying stage and small amount of air supply can be used for silica production. Smoldering of rice husk shows great potential for the industrial production of high-quality silica.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torero, J.L.; Gerhard, J.I.; Martins, M.F.; Zanoni, M.A.B.; Rashwan, T.L.; Brown, J.K. Processes defining smouldering combustion: Integrated review and synthesis. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 81, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chow, T.H.; Huang, X. Smoldering propagation and blow-off on consolidated fuel under external airflow. Combust. Flame 2021, 234, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Gan, Z.; Nie, M. Method of smoldering combustion for refinery oil sludge treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashwan, T.L.; Fournie, T.; Torero, J.L.; Grant, G.P.; Gerhard, J.I. Scaling up self-sustained smouldering of sewage sludge for waste-to-energy. Waste Manag. 2021, 135, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, T.L.; Torero, J.L.; Gerhard, J.I. The improved energy efficiency of applied smouldering systems with increasing scale. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 177, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Qualharini, E.; Vazquez, E.; Haddad, A. Smoldering fire propagation in corn grain: An experimental study. Results Eng. 2020, 7, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyn, H.K.; Konarova, M.; Beltramini, J.; Perkins, G.; Yermán, L. Self-sustaining smouldering combustion of waste: A review on applications, key parameters and potential resource recovery. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 205, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.J.S.; Gudka, B.; Whittaker, C.; Shield, I.; Price-Allison, A.; Maxwell, D.; Jones, J.M.; Williams, A. The use of agricultural residues, wood briquettes and logs for small-scale domestic heating. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 210, 106552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stávková, J.; Maroušek, J. Novel sorbent shows promising financial results on P recovery from sludge water. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Gao, X.; Qiao, Y. Smouldering combustion of sewage sludge: Volumetric scale-up, product characterization, and economic analysis. Fuel 2021, 305, 121485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.; Santos, I.F.S.d.; Machado, G.d.O.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Barros, R.M. Rice husk energy production in Brazil: An economic and energy extensive analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, I.; Navia, R.; Kahhat, R. Energy potential from rice husk through direct combustion and fast pyrolysis: A review. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana Costa, J.A.; Paranhos, C.M. Systematic evaluation of amorphous silica production from rice husk ashes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azat, S.; Korobeinyk, A.V.; Moustakas, K.; Inglezakis, V.J. Sustainable production of pure silica from rice husk waste in Kazakhstan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X. A new method of utilizing rice husk: Consecutively preparing D-xylose, organosolv lignin, ethanol and amorphous superfine silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 291, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, L.Q.; Halog, A. Rice Husk Based Bioelectricity vs. Coal-fired Electricity: Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Case Study in Vietnam. Procedia CIRP 2016, 40, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Téllez, J.F.; Silva, M.P.; Simister, R.; Gomez, L.D.; Fuertes, V.C.; De Paoli, J.M.; Moyano, E.L. Fast pyrolysis of rice husk under vacuum conditions to produce levoglucosan. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 156, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Alyousef, R.; Mohammadhosseini, H. State-of-the-art-review on rice husk ash: A supplementary cementitious material in concrete. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 33, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Appaturi, J.N.; Iqbal, A. The utilization of rice husk silica as a catalyst: Review and recent progress. Catal. Today 2012, 190, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, H.; Xiong, Y.; Dong, F. Rational design, synthesis, and application of silica/graphene-based nanocomposite: A review. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Guo, J.; Noureddine, A.; Wang, A.; Wuttke, S.; Brinker, C.J.; Zhu, W. Sol-Gel-Based Advanced Porous Silica Materials for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Bahrami, A.; Pech-Canul, M.I.; González, L.A. Review on the physicochemical treatments of rice husk for production of advanced materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 899–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.A. Utilization of waste straw and husks from rice production: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidaghy Dizaji, H.; Zeng, T.; Hartmann, I.; Enke, D.; Schliermann, T.; Lenz, V.; Bidabadi, M. Generation of High Quality Biogenic Silica by Combustion of Rice Husk and Rice Straw Combined with Pre- and Post-Treatment Strategies—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kong, S.; Ranjbar, N. Synthesis of sodium waterglass from white rice husk ash as an activator to produce metakaolin-based geopolymer cements. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 6, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Enke, D.; Roth, R.; Roggendorf, H. Hydrothermal Dissolution of Opal in Sodium Hydroxide Lyes for the Synthesis of Water Glass. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 7, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, D.; Wassersleben, S.; Weiß, M.; Denecke, R.; Stark, A.; Enke, D. A Generalized Procedure for the Production of High-Grade, Porous Biogenic Silica. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidaghy Dizaji, H.; Zeng, T.; Hölzig, H.; Bauer, J.; Klöß, G.; Enke, D. Ash transformation mechanism during combustion of rice husk and rice straw. Fuel 2022, 307, 121768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, R.A.; Yahya, R.; Gan, S.N. Production of High Purity Amorphous Silica from Rice Husk. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, S.R.; Elicker, C.; Vieira, B.M.; Cabral, T.H.; Silva, A.F.; Sanches Filho, P.J.; Raubach, C.W.; Hartwig, C.A.; Mesko, M.F.; Moreira, M.L.; et al. Black SiO2 nanoparticles obtained by pyrolysis of rice husk. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 164, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliermann, T.; Hartmann, I.; Dizaji, H.B.; Zeng, T.; Schneider, D.; Wassersleben, S.; Enke, D.; Jobst, T.; Lange, A.; Roelofs, F.; et al. High quality biogenic silica from combined energetic and material utilization of agricultural residues. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium of Energy from Biomass and Waste, Venice, Italy, 15–18 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, I.J.; Calheiro, D.; Kieling, A.G.; Moraes, C.A.M.; Rocha, T.L.A.C.; Brehm, F.A.; Modolo, R.C.E. Characterization of rice husk ash produced using different biomass combustion techniques for energy. Fuel 2016, 165, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprianti, E.; Shafigh, P.; Bahri, S.; Farahani, J.N. Supplementary cementitious materials origin from agricultural wastes—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.J.; Calheiro, D.; Sánchez, F.A.L.; Camacho, A.L.D.; Rocha, T.L.A.d.C.; Moraes, C.A.M.; Sousa, V.C.d. Characterization of Silica Produced from Rice Husk Ash: Comparison of Purification and Processing Methods. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pa, F.C.; Kein, W.K. Removal of iron in rice husk via oxalic acid leaching process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 701, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprianov, V.I.; Kaewklum, R.; Sirisomboon, K.; Arromdee, P.; Chakritthakul, S. Combustion and emission characteristics of a swirling fluidized-bed combustor burning moisturized rice husk. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Saenger, M.; Hartge, E.-U.; Ogada, T.; Siagi, Z. Combustion of agricultural residues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2000, 26, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, F.; Behrendt, F.; Gao, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, C. Inhibition of K2SO4 on evaporation of KCl in combustion of herbaceous biomass. Fuel 2021, 289, 119754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfelice, G.; Della Zassa, M.; Biasin, A.; Canu, P. Onset and propagation of smouldering in pine bark controlled by addition of inert solids. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yi, W.; Li, Y.; Zha, J.; Luo, B. Effects of fuel properties on the natural downward smoldering of piled biomass powder: Experimental investigation. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 67, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faé Gomes, G.M.; Philipssen, C.; Bard, E.K.; Zen, L.D.; de Souza, G. Rice husk bubbling fluidized bed combustion for amorphous silica synthesis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modolo, R.C.E.; Silva, T.; Senff, L.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M.; Silva, L. Bottom ash from biomass combustion in BFB and its use in adhesive-mortars. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Magdziarz, A.; Gajek, M.; Nowińska, K.; Nowak, W. Alkali metals association in biomass and their impact on ash melting behaviour. Fuel 2020, 261, 116421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zhou, J.; Yu, C.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Z. A novel two-staged thermal synthesis method of generating nanosilica from rice husk via pre-pyrolysis combined with calcination. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnarao, R.V.; Subrahmanyam, J.; Kumar, T.J. Studies on the formation of black particles in rice husk silica ash. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, Y.W.; Gamage, P.; Gunarathne, D.S. Hot water washing of rice husk for ash removal: The effect of washing temperature, washing time and particle size. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, X.; Behrendt, F.; Schliermann, T.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y. Critical changes of inorganics during combustion of herbaceous biomass displayed in its water soluble fractions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 198, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cao, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Ke, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, L. Preparation of SiO2 nanowires from rice husks by hydrothermal method and the RNA purification performance. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 662, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohamadsadeghi, S.; Karimi, K. Recovery of silica from rice straw and husk. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasara-A, J.; Gheewala, S.H. Sustainable utilization of rice husk ash from power plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Chang, J.H.; Sang, B.-I. Preparation of high purity silica originated from rice husks by chemically removing metallic impurities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 50, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.; Sommerville, R.; Rowson, N.; Jones, J.; Laughlin, B. Valorisation of rice husks using a TORBED® combustion process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 159, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Proximate Analysis (Arrival Basis, wt.%) | Elemental Analysis (Dry Basis, wt.%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Volatile | Ash | Fixed Carbon | C | H | O | N | S | |
| Washed | 51.0 ± 0.2 | 32.0 ± 1.5 | 9.3 ± 0.3 | 7.7 ± 0.8 | 40.2 ± 0.3 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 35.0 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | <0.1 |
| Unwashed | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 59.0 ± 1.4 | 18.4 ± 0.1 | 14.5 ± 0.7 | 38.7 ± 0.3 | 5.4 ± 0.1 | 35.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | <0.1 |
| Drying | Oxidation | Combustion of Resdiual Carbon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Washed smoldering | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| Unwashed smoldering | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 |
| Washed burning | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Unwashed burning | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| NO. | SiO2 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | P2O5 | MgO | Cl | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 86.6 | 4.16 | 2.61 | 1.25 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.72 |
| 2 | 86.4 | 4.20 | 2.70 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 1.14 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| 3 | 86.2 | 4.20 | 2.76 | 1.26 | 1.22 | 1.15 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.69 |
| Ave | 86.4 ± 0.20 | 4.19 ± 0.03 | 2.69 ± 0.08 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 1.20 ± 0.05 | 1.12 ± 0.04 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 0.71 ± 0.02 | 0.70 ± 0.02 |
| Types | SiO2 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | P2O5 | MgO | Cl | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washed smoldering | 86.4 | 4.19 | 2.69 | 1.26 | 1.20 | 1.12 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| Unwashed smoldering | 89.0 | 4.46 | 1.34 | 0.75 | 1.17 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.49 | 0.41 |
| Washed burning | 93.4 | 1.07 | 2.08 | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.21 |
| Unwashed burning | 90.2 | 4.12 | 1.22 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Yin, D.; He, F.; Cai, J.; Schliermann, T.; Behrendt, F. Characteristics of Smoldering on Moist Rice Husk for Silica Production. Sustainability 2022, 14, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010317
Yan S, Yin D, He F, Cai J, Schliermann T, Behrendt F. Characteristics of Smoldering on Moist Rice Husk for Silica Production. Sustainability. 2022; 14(1):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010317
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shengtai, Dezheng Yin, Fang He, Junmeng Cai, Thomas Schliermann, and Frank Behrendt. 2022. "Characteristics of Smoldering on Moist Rice Husk for Silica Production" Sustainability 14, no. 1: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010317
APA StyleYan, S., Yin, D., He, F., Cai, J., Schliermann, T., & Behrendt, F. (2022). Characteristics of Smoldering on Moist Rice Husk for Silica Production. Sustainability, 14(1), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010317





