How Do Stakeholder Pressures Affect Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises in Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
2.1. The Effects of CSR Practices
2.2. The Relation between Factors of Stakeholders Pressure and CSR
2.2.1. Employees
2.2.2. Customers
2.2.3. Community
2.2.4. Government
2.2.5. Media
2.3. The Mediating Effects of Business Culture on Stakeholders and CSR
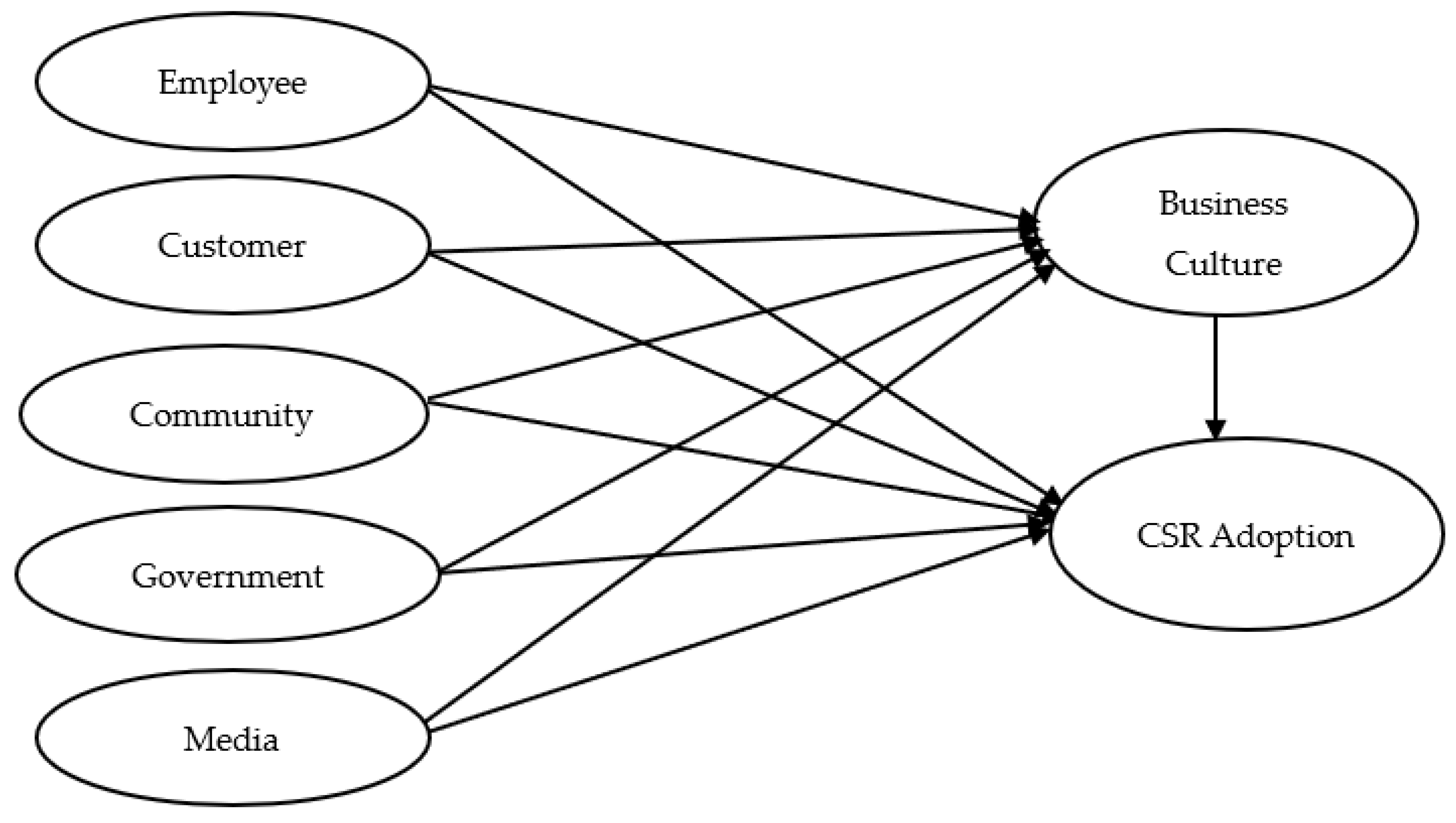
2.4. Conceptual Research Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Sample Selection and Sampling Techniques
3.3. Methods of Data Analysis
3.4. Measurement Items
3.4.1. Corporate Social Responsibility Practices
3.4.2. Independent Variables
3.4.3. Measurements of Mediator Variable
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Demographic Data
4.2. Reliability and Validity Test
4.3. Correlation Matrix and Discriminant Validity
4.4. Weighted Multiple Regression Analysis
4.5. Mediation Effects of Business Culture
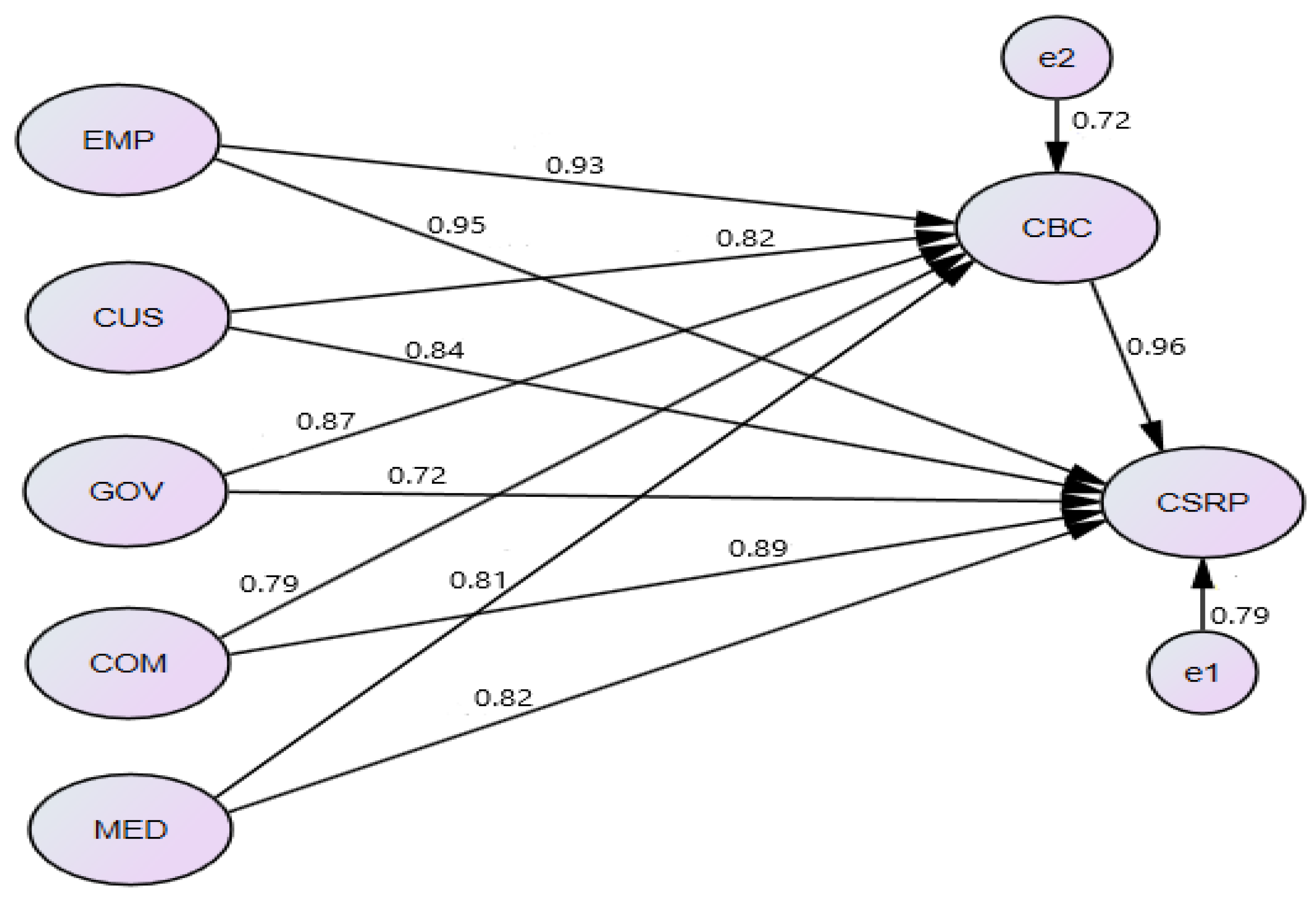
4.6. The Structural Equation Model and Growth Path Modeling Result Analysis
4.6.1. Structural Equation Model Goodness-of-Fit Indices
4.6.2. Growth Path Modeling Goodness-of-Fit Inferences
4.7. The Level of Stakeholder Pressures and Enterprises CSR Trust
4.8. Test of Hypothesis and Decisions
5. Conclusions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Theoretical Implications
5.3. Practical Implications
5.4. Limitations and Directions for Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Originality Statement
Appendix A
| Variables | Items | Source |
|---|---|---|
| CSR Practices | (1) Our company implements special programs to minimize its negative impact on the natural environment; (2) The management of our enterprise is primarily concerned employees’ needs and wants. (3) Our company contributes to campaigns and projects that promote the safety of society. (4) Our company targets sustainable growth that considers future generations. | [92] |
| Employee | (1) Our managers and employees perceive CSR as an important mechanism potentially contributing to the creation of corporate value. (2) Our managers and employees perceive that CSR enhances competitive advantage, and eventually improves the economic value of the firm. (3) Our managers and employees believe enterprises need to contribute to national and local levels, societies and markets. (4) Our managers and employees believe being ethical and socially responsible is the most important thing a firm should do. | [21,47] |
| Customer | (1) Respects customer rights beyond the legal requirements. (2) Customer satisfaction is highly important for our company. (3) Treats customers’ complaints or suggestions seriously. (4) Provides full and accurate information about its products to its customers. | [83] |
| Government | (1) The government has stricter regulations to protect the consumers. (2) The government has effective regulations to encourage firms to improve their product and services quality. (3) There are complete laws and regulations to ensure fair competition. | [67] |
| Community | (1) Communities expect companies to contribute to society development by volunteering time and effort to local activities. (2) Local communities expect companies to contribute to society development by getting involved in community event in non-financial ways. (3) Local communities expect companies to contribute to society development by providing jobs and treating their employees well. | [21] |
| Media | (1) Media plays a pivotal role in maintaining and improving public relations between firms and consumers in the local market. (2) Mass media has a strong power in shaping enterprise image in the local market. (3) Compared with other countries, mass media in Ethiopia pays more attention to the societal role of enterprises in the local market. | [21] |
| CSR-oriented Business Culture | (1) The employees have a strong degree of awareness on the CSR (2) Our leader believes and values the adoption of CSR (3) Our organization develops strategy on the CSR activities (4) Our organization has the CSR-training program for the employees (5) Our organization keeps a special department for CSR management | [2] |
References
- Carroll, A.B.; Shabana, K.M. The Business Case for Corporate Social Responsibility: A Review of Concepts, Research and Practice. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2010, 12, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Choi, Y. Stakeholder pressure and CSR adoption: The mediating role of organizational culture for Chinese companies. Soc. Sci. J. 2014, 53, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.; Rand, J.; Tarp, F.; Trifkovic, N. Corporate Social Responsibility in a Competitive Business Environment. J. Dev. Stud. 2020, 56, 1455–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, R.; Kucharska, W. Corporate social responsibility practices incomes and outcomes: Stakeholders’ pressure, culture, employee commitment, corporate reputation, and brand performance. A Polish–German cross-country study. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 27, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsu, S. Deceptive Advertising: A Corporate Social Responsibility Perspective. Int. J. Health Econ. Dev. 2020, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gulavani, S.; Nayak, N.; Nayak, M. Corporate Social Responsibility Issues and Challenges in India. Int. J. Commer. IT Soc. Sci. 2016, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Morsing, M.; Schultz, M. Corporate social responsibility communication: Stakeholder information, response and involvement strategies. Bus. Ethics A Eur. Rev. 2006, 15, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Olanipekun, A.; Chen, Q.; Xie, L.; Liu, Y. Conceptualising the state of the art of corporate social responsibility (CSR) in the construction industry and its nexus to sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 18, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.L.; Shu, P.G. How does foreign pressure affect a firm’s corporate social performance? Evidence from listed firms in Taiwan. J. Multinatl. Financ. Manag. 2019, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Marshall, R.; Afzali, H. Stakeholder influence, institutional duality, and CSR involvement of MNC subsidiaries. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 91, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.L.; Wicks, A.C.; Kotha, S.; Jones, T.M. Does stakeholder orientation matter? The relationship between stakeholder management models and firm financial performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1999, 42, 488–506. [Google Scholar]
- Marquis, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. Regulatory Uncertainty and Corporate Responses to Environmental Protection in China. Pestic. Outlook 2014, 54, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toit, E.d.; Lekoloane, K. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: Evidence from the Johannesburg Stock Exchange, South Africa. Comp. Econ. Res. 2018, 21, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Khuong, M.N.; Truong an, N.K.; Thanh Hang, T.T. Stakeholders and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programme as key sustainable development strategies to promote corporate reputation—Evidence from vietnam. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2021, 8, 1917333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E.; Velamuri, S.R. A New Approach to CSR: Company Stakeholder Responsibility. Corp. Soc. Responsib. 2006, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Soobaroyen, T.; Sheik-Ellahi, A. A case study on the influence of corporate governance beyond the boardroom: Perceptions from business unit managers. Corp. Gov. 2008, 8, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.; Chung, Y. The effects of corporate social responsibility on firm performance: A stakeholder approach. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2018, 37, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.; Murillo, D.; Mellen, T. CSR and battered women: Stakeholder engagement beyond salience? Bus. Res. Q. 2021, 24, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husillos, J. A Stakeholder-Theory Approach to Environmental Disclousures by Small and Medium Enterprises (SMES). Rev. Contab. 2008, 11, 125–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda-Manzanares, A.; Aragón-Correa, J.A.; Sharma, S. The influence of stakeholders on the environmental strategy of service firms: The moderating effects of complexity, uncertainty and munificence. Br. J. Manag. 2008, 19, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Ghauri, P.N. Determinants influencing CSR practices in small and medium sized MNE subsidiaries: A stakeholder perspective. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.C. Corporate social responsibility and different stages of economic development: Singapore, Turkey, and Ethiopia. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 88, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, A. Determinants of Corporate Social Responsibility Practice of Manufacturing Firms in Dire Dawa Administration. Dev. Ctry. Stud. 2020, 10, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Deyassa, K. CSR From Ethiopian Perspective. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 5, 299–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias Nigatu Bimir Corporate Social Responsibility Learning in the Ethiopian Leather and Footwear Industry. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 7, 1–14.
- Chakrabarty, M. Ethiopia—China Economic Relations: A Classic Win-Win Situation ? Pluto J. 2016, 7, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, F. Chinese Investors in Ethiopia: The Perfect Match? Ifri Center for Aisian Studies: Ifri, France, 2017; pp. 4–42. Available online: https://www.ifri.org/sites/default/files/atoms/files/nicolas_chinese_investors_ethiopia_2017.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Mohammadi, D. Corporate Social Responsibility along the Chinese Financed Railway Mega-Project in East Africa. Res. Brief 2020, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Al-Maimani, K.; Al-Yafi, W. Exploring Corporate Social Responsibility in Saudi Arabia: The Challenges Ahead. J. Leadersh. Account. Ethics 2013, 10, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Perrini, F.; Russo, A.; Tencati, A. CSR Strategies of SMEs and Large Firms. Evidence from Italy. J. Bus. Ethics 2007, 74, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEC. A Renewed EU Strategy 2011-14 for Corporate Social Responsibility; European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kakabadse, N.K.; Rozuel, É.; Lee-Davies, L. Corporate social responsibility and stakeholder approach: A conceptual review. Int. J. Bus. Gov. Ethics 2005, 4, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena Martínez, J.; López Fernández, M.; Romero Fernández, P.M. Corporate social responsibility: Evolution through institutional and stakeholder perspectives. Eur. J. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2016, 25, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Benamraoui, A.; Shah, N.; Mathew, S. Dynamic Capability and Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchenciuc, E.-G.; Rus, M.; Tasente, T. Organizational communication and corporate social responsibility. Case study: Romanian vs. International CSR. Tech. Soc. Sci. J. 2020, 3, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chouaibi, Y.; Rossi, M. The Effect of Corporate Social Responsibility and the Executive Compensation on Implicit Cost of Equity: Evidence from French ESG Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, T.; Le, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xia, B.; Skitmore, M. Understanding the CSR Awareness of Large Construction Enterprises in China. Hindawi Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8866511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.I.; Chidlow, A.; Choi, J. Corporate social responsibility: Stakeholders influence on MNEs’ activities. Int. Bus. Rev. 2014, 23, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, P.M.; Dowden, P.E. Maximizing stakeholder trust as a tool for controlling corruption. Crime Law Soc. Chang. 2018, 71, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, A.; Moisello, A.M. Stakeholders’ Pressure and CSR Engagement. A Case in the Apparel Sector. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2019, 9, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, Y.P.; Park, C.; Petersen, B. The Effect of Local Stakeholder Pressures on Responsive and Strategic CSR Activities. Bus. Soc. 2018, 60, 582–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, W.F.; Xiao, A.; Hilton, E. A Critical Analysis of Corporate Social Responsibility in Ghana’s Telecommunications Industry. S. Afr. J. Commun. Theory Res. 2019, 45, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žukauskas, P.; Vveinhardt, J.; Andriukaitienė, R. Philosophy and Paradigm of Scientific Research. Manag. Cult. Corp. Soc. Responsib. 2018, 8, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, D.E.; Ganapathi, J.; Aguilera, R.V.; Williams, C.A. Employee reactions to corporate social responsibility: An organizational justice framework. J. Organ. Behav. 2006, 27, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Chernatony, L.; Harris, F. Developing Corporate Brands Through Considering Internal and External Stakeholders. Corp. Reput. Rev. 2000, 3, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, D. Measuring corporate social responsibility: A scale development study. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Qun, W.; Abdullah, M.I.; Alvi, A.T. Employees’ Perception of Corporate Social Responsibility Impact on Employee Outcomes: Mediating Role of Organizational Justice for (SMEs). Sustainability 2018, 10, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.; Doyduk, B. Corporte Social Responsibility from Employees ’ Perspective. Turk. Stud.-Soc. Sci. 2020, 15, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Gyamfi, M.; He, Z.; Nyame, G.; Boahen, S.; Frempong, M.F. Effects of Internal CSR Activities on Social Performance: The employee perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Moore, J.H.; Wang, Z. Corporate social responsibility and employee outcomes: A moderated mediation model of organizational identification and moral identity. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Kim, D.O. Good Neighbors but Bad Employers: Two Faces of Corporate Social Responsibility Programs. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 138, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieger, S.A.; Anderer, S.; Fröhlich, A.; Bäro, A.; Meynhardt, T. Too Much of a Good Thing? On the Relationship Between CSR and Employee Work Addiction. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 166, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ahmad, S. Analysis of Corporate Social Responsibility Execution Effects on Purchase Intention with the Moderating Role of Customer Awareness. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Pedrero, A.; Cortés-García, F.J.; Jiménez-Castillo, D. The Relationship between Social Responsibility and Business Performance: An Analysis of the Agri-Food Sector of Southeast Spain. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Saeed, A.; Iqbal, M.K.; Saeed, U.; Sadiq, I.; Faraz, N.A. Linking Corporate Social Responsibility to Customer Loyalty through Co-Creation and Customer Company Identification: Exploring Sequential Mediation Mechanism. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubushar, M.; Rasool, S.; Haider, M.I.; Cerchione, R. The impact of corporate social responsibility activities on stakeholders’ value co-creation behaviour Muhammad. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Gao, Y.; Sadaqat, S.; Shah, H. CSR and Customer Outcomes: The Mediating Role of Customer Engagement. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavana, G.; Gottardo, P.; Moisello, A.M. Do Customers Value CSR Disclosure? Evidence from Italian Family and Non-Family Firms. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatmawati, I.; Fauzan, N. Building Customer Trust through Corporate Social Responsibility: The Effects of Corporate Reputation and Word of Mouth. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 793–805. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, B.A.; Bell, S.J.; Mengüç, B. Corporate reputation, stakeholders and the social performance-financial performance relationship. Int. J. Res. Dev. 2005, 39, 1184–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rela, I.Z.; Awang, A.H.; Ramli, Z.; Taufik, Y.; Sum, S.; Muhammad, M. Effect of corporate social responsibility on community resilience: Empirical evidence in the nickel mining industry in Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffler, S.; Bloom, P.N.; Keller, K.L. Understanding Stakeholder Responses to Corporate Citizenship Initiatives: Managerial Guidelines and Research Directions. J. Public Policy Mark. 2010, 29, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, G.; Tsai, F.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, C.H. The Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Service Innovation Performance: The Role of Dynamic Capability for Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jung, J.Y. Changes in the Influence of Social Responsibility Activities on Corporate Value over 10 Years in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebeck, K. Exploring the responsiveness of companies: Corporate social responsibility to stakeholders. Soc. Responsib. J. 2008, 4, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.G.; Smith, N.C.; John, A. Why we boycott: Consumer motivations for boycott participation. J. Mark. 2004, 68, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R. Corporate social responsibility in China: Impact of regulations, market orientation and ownership structure. Chin. Manag. Stud. 2016, 1, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, D.A. Can Industry Self-Regulation Work? Calif. Manag. Rev. 1983, 25, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, Z. The influence of political connection on corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Listed private companies in China. Int. J. Corp. Soc. Responsib. 2016, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E. Promoting corporate social responsibility: Is market-based regulation sufficient? New Econ. 2002, 9, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloza, J.; Falkenberg, L. The role of collaboration in achieving corporate social responsibility objectives. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2015, 51, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kwon, J. CSR in China: Does being close to the central or local government matter? Sustainability 2021, 13, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock-Fraser, J. TheRoleofthe News MediainInfluencing Corporate Environmental Sustainable Development: An Alternative Methodology to Assess Stakeholder Engagement. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2012, 19, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deephouse, D.L.; Heugens, P.P.M.A.R. Linking Social Issues to Organizational Impact: The Role of Infomediaries and the Infomediary Process. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 86, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.A.; Potter, P.B.K. The Relationships Between Mass Media, Public Opinion, and Foreign Policy: Toward a Theoretical Synthesis. Annu. Rev. Polit. Sci. 2008, 11, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.; Appiah, D.; Okafor, S. The Influence of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Social Media on the Strategy Formulation Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortado, F.J.; Chalmeta, R. Use of social networks as a CSR communication tool. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2016, 3, 1187783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Han, Y. The impact of ownership structure on corporate social responsibility. SSRN Electron. J. 2013, 35, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bushee, B.J. The influence of institutional investors on myopic R&D investment behavior. Account. Rev. 1998, 73, 305–333. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, M.; Abbott, J.A.; Shoemaker, S. The Hospitality Culture Scale: A measure organizational culture and personal attributes. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2011, 30, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverthorne, C. The impact of organizational culture and person-organization fit on organizational commitment and job satisfaction in Taiwan. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2004, 25, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, N.B.D.V.; Shukri, D.S.; Khatibi, P.D.A.; Azam, D.S.M.F. The Impact of Entrepreneurial Orientation on Business Performance in Star Class Hotels of Sri Lanka. Eur. J. Manag. Mark. Stud. 2020, 5, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.A.; Gao, J.H. Exploring the direct and indirect effects of CSR on organizational commitment. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 26, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidu, A.A.; Haron, M.H.; Amran, A. Critical Factors Towards Philanthropic Dimension Of CSR in The Nigerian Financial Sector: The Mediating Effects Of Cultural Influence. Int. J. Bus. Innov. 2018, 4, 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Thanetsunthorn, N. The impact of national culture on corporate social responsibility: Evidence from cross-regional comparison. Asian J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 4, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, H. Exploring the Organizational Culture’s Moderating Role of Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) on Firm Performance: Focused on Corporate Contributions in Korea. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietz, B. Changing Organizational Culture to Establish Sustainability. Control Manag. Rev. 2021, 3, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, K.; Teresa, M. Green Organizational Culture, Corporate Social Responsibility Implementation, and Food Safety. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 585435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.W.; Creswell, J.D. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches, 5th ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H. Sampling Methods in Research Methodology; How to Choose a Sampling Technique for Research. Int. J. Acad. Res. Manag. 2016, 5, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejcie, R.V.; Morgan, D. Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educ. Psychol. Asp. 1970, 30, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J. The effects of external stakeholder pressure and ethical leadership on corporate social responsibility in China. J. Manag. Organ. 2015, 21, 388–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.E. Doing Research in the Real World, 1st ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brusset, X. Does supply chain visibility enhance agility? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 171, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Bollen, K.A. Interpreting the Results from Multiple Regression and Structural Equation Models. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2005, 86, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yay, M. The Mediation Analysis With The Sobel Test And The Percentile Bootstrap. Int. J. Manag. Appl. Sci. 2017, 3, 2394–7926. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, N.U.; Abdullah, N. Making sense of mediating analysis: A marketing perspective. Rev. Integr. Bus. Econ. Res. 2016, 5, 62–76. [Google Scholar]
- Dastgeer, G.; Rehman, A.u.; Asghar, M.A. Selection and use of mediation testing methods: Application in management sciences. Bus. Econ. Rev. 2020, 12, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Ahn, J.W. Model Setting and Interpretation of Results in Research Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Checklist with Guiding Questions for Reporting. Asian Nurs. Res. 2021, 15, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Lee, T.; Maydeu-Olivares, A. Understanding the Model Size Effect on SEM Fit Indices. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2018, 79, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Hubona, G.; Ray, P.A. Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: Updated guidelines. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2015, 116, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepacka, A.; Bagińska, M. The Use of CSR Measurement Matrix in the Aspect of Sustainable Development. Sci. J. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Constructs | Items | Factor Loading | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability (CR) | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR Adoption | CSRP1 | 0.816 | 0.974 | 0.925 | 0.757 |
| CSRP2 | 0.913 | ||||
| CSRP3 | 0.928 | ||||
| CSRP4 | 0.816 | ||||
| Employee | EMP1 | 0.959 | 0.984 | 0.978 | 0.921 |
| EMP2 | 0.950 | ||||
| EMP3 | 0.961 | ||||
| EMP4 | 0.968 | ||||
| Customer | CUS1 | 0.922 | 0.869 | 0.924 | 0.804 |
| CUS2 | 0.816 | ||||
| CUS3 | 0.946 | ||||
| Government | GOV1 | 0.959 | 0.964 | 0.975 | 0.928 |
| GOV2 | 0.961 | ||||
| GOV3 | 0.971 | ||||
| Community | COM1 | 0.930 | 0.914 | 0.934 | 0.836 |
| COM2 | 0.887 | ||||
| COM3 | 0.925 | ||||
| Media | MED1 | 0.783 | 0.877 | 0.910 | 0.773 |
| MED2 | 0.925 | ||||
| MED3 | 0.922 | ||||
| CSR-oriented Business Culture | CBC1 | 0.960 | 0.953 | 0.980 | 0.909 |
| CBC2 | 0.957 | ||||
| CBC3 | 0.946 | ||||
| CBC4 | 0.952 | ||||
| CBC5 | 0.953 |
| CSRP | EMP | CUS | GOV | COM | MED | CBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSRP | 0.869 | ||||||
| EMP | 0.410 | 0.960 | |||||
| CUS | 0.360 | 0.252 | 0.896 | ||||
| GOV | 0.351 | 0.264 | 0.213 | 0.963 | |||
| COM | 0.310 | 0.330 | 0.184 | 0.268 | 0.914 | ||
| MED | 0.279 | 0.286 | 0.140 | 0.309 | 0.286 | 0.879 | |
| CBC | 0.426 | 0.318 | 0.390 | 0.337 | 0.413 | 0.257 | 0.954 |
| Latent Variables | Path | Measurement Variables | Standardized Estimate (β) | S.E. | C.R. | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSRP | <--- | Employee | 0.952 | 0.139 | 6.837 | 0.000 *** |
| CSRP | <--- | Customer | 0.841 | 0.116 | 7.243 | 0.000 *** |
| CSRP | <--- | Government | 0.702 | 0.135 | 5.181 | 0.000 *** |
| CSRP | <--- | Community | 0.894 | 0.137 | 6.505 | 0.000 *** |
| CSRP | <--- | Media | 0.802 | 0.108 | 7.449 | 0.000 *** |
| CSRP | <--- | Business Culture | 0.964 | 0.141 | 6.841 | 0.000 *** |
| CBC | <--- | Employee | 0.931 | 0.466 | 1.999 | 0.000 *** |
| CBC | <--- | Customer | 0.815 | 0.258 | 3.153 | 0.000 *** |
| CBC | <--- | Government | 0.869 | 0.072 | 12.042 | 0.000 *** |
| CBC | <--- | Community | 0.791 | 0.078 | 10.105 | 0.000 *** |
| CBC | <--- | Media | 0.806 | 0.071 | 11.307 | 0.000 *** |
| Mediation Effects | Coefficient | Standard Error | Sobel Test (z-Score) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMP → CBC → CSRP | 0.931 | 0.446 | 1.99646103 | 0.046 |
| 0.964 | 0.141 | |||
| CUS → CBC → CSRP | 0.815 | 0.258 | 2.86761833 | 0.004 |
| 0.964 | 0.141 | |||
| GOV → CBC → CSRP | 0.869 | 0.072 | 5.94785941 | 0.000 |
| 0.964 | 0.141 | |||
| COM → CBC → CSRP | 0.791 | 0.078 | 5.66889243 | 0.000 |
| 0.964 | 0.141 | |||
| MED → CBC → CSRP | 0.806 | 0.071 | 5.85673819 | 0.000 |
| 0.964 | 0.141 |
| Model Fit Indices | Recommended Value | Standard Measured Model |
|---|---|---|
| Chi-square (ꭕ2) | Low | 321.8 |
| Degree of Freedom | >0.0 | 190 |
| ꭕ2/df | <3.0 | 1.794 |
| Goodness-of-Fit Index (GFI) | ≥0.90 | 0.958 |
| Adjusted Goodness of Fit (AGFI) | ≥0.90 | 0.957 |
| Normed Fit Index (NFI) | >0.90 | 0.946 |
| Incremental Fit Index (IFI) | >0.90 | 0.974 |
| Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI) | ≥0.90 | 0.958 |
| Comparative Fit Index (CFI) | ≥0.90 | 0.984 |
| Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) | <0.08 | 0.044 |
| CSR’s Trust | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stakeholder Pressure | Kombolcha | Addis Ababa | Bahir Dar | Debre Birhan | Hawassa |
| Employee | high ⤑ | high ⤑ | ⤌ low | high ⤑ | high ⤑ |
| Customer | ⤌ low | high ⤑ | ⤌ low | high ⤑ | high ⤑ |
| Government | ⤌ low | high ⤑ | ⤌ low | high ⤑ | ⤌ low |
| Community | high ⤑ | ⤌ low | ⤌ low | ⤌ low | high ⤑ |
| Media | ⤌ low | ⤌ low | ⦰ null | ⤌ low | ⤌ low |
| List of Hypothesis | Stated Hypothesis | Direction and Structural Path | p-Value | Decisions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis 1 | H1 (+) | EMP | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| Hypothesis 2 | H2 (+) | CUS | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| Hypothesis 3 | H3 (+) | GOV | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| Hypothesis 4 | H4 (+) | COM | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| Hypothesis 5 | H5 (+) | MED | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| Hypothesis 6 | H6 (+) | CBC | → | CSRP | 0.000 *** | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, M.; Shan, H.; Tikuye, G.A. How Do Stakeholder Pressures Affect Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises in Ethiopia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010443
Ying M, Shan H, Tikuye GA. How Do Stakeholder Pressures Affect Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises in Ethiopia. Sustainability. 2022; 14(1):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010443
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Ma, He Shan, and Gashaw Awoke Tikuye. 2022. "How Do Stakeholder Pressures Affect Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises in Ethiopia" Sustainability 14, no. 1: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010443
APA StyleYing, M., Shan, H., & Tikuye, G. A. (2022). How Do Stakeholder Pressures Affect Corporate Social Responsibility Adoption? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises in Ethiopia. Sustainability, 14(1), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010443





