A Real-Time Comparison of Four Particulate Matter Size Fractions in the Personal Breathing Zone of Paris Subway Workers: A Six-Week Prospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Management
2.3. Statistical Analysis
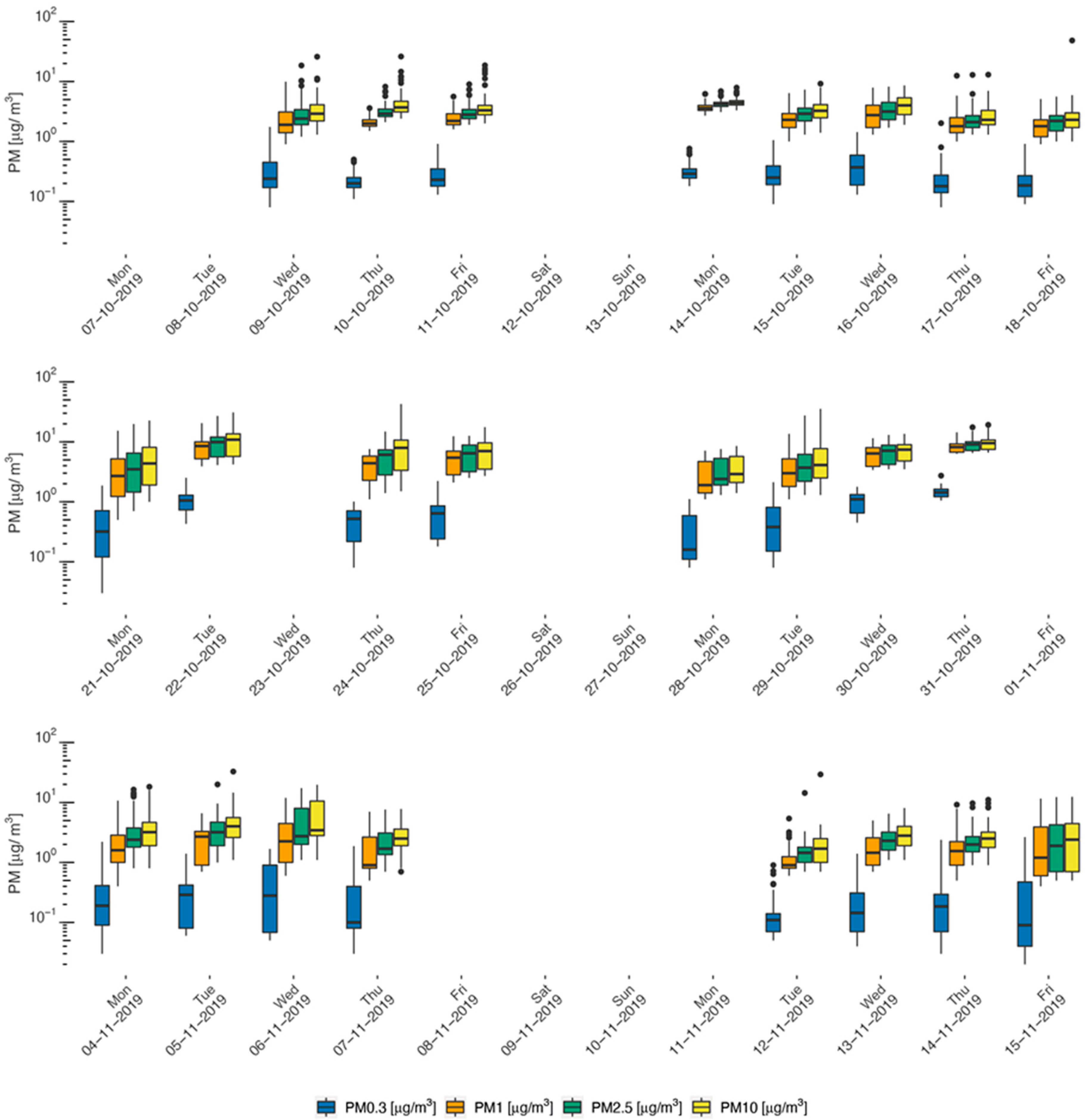
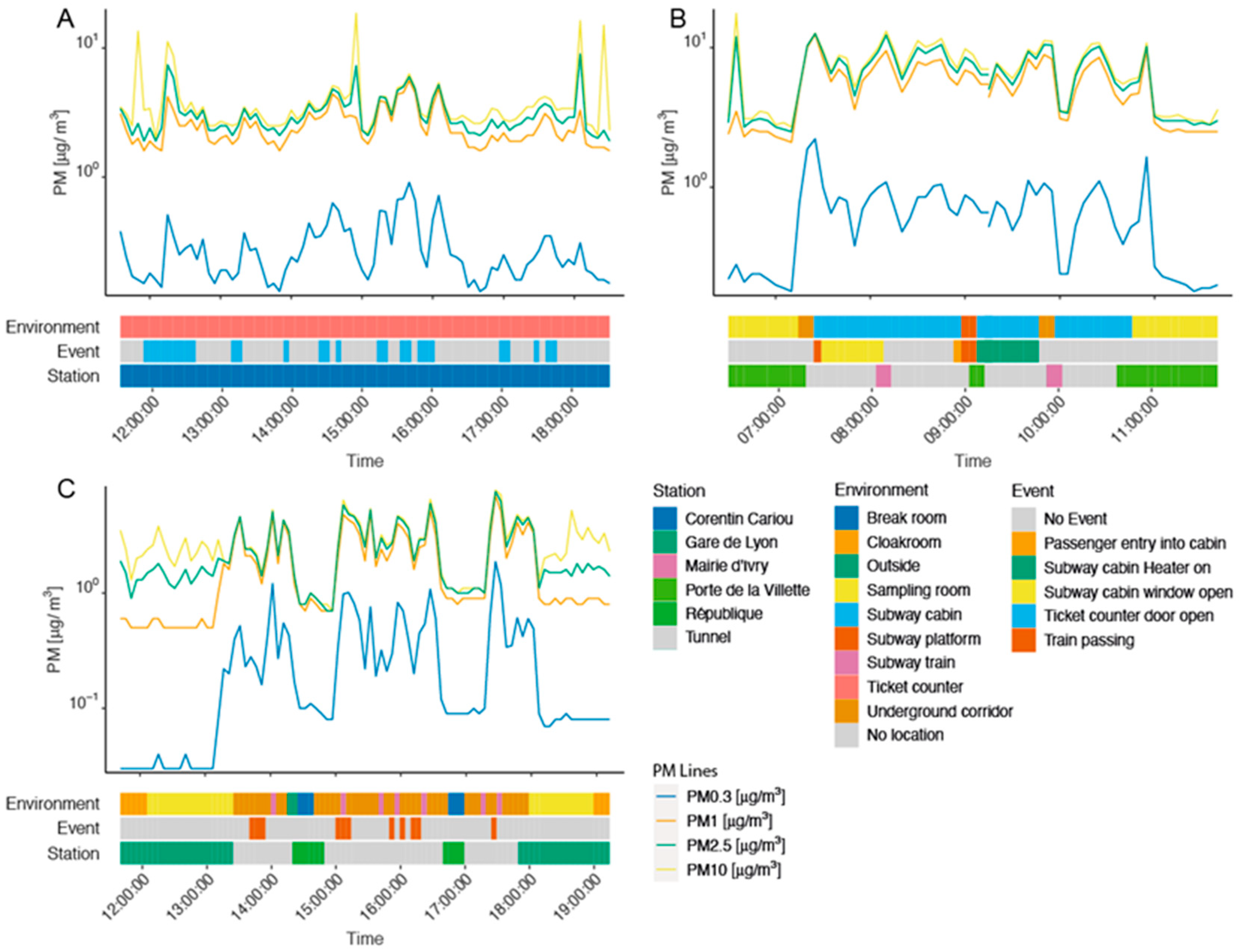
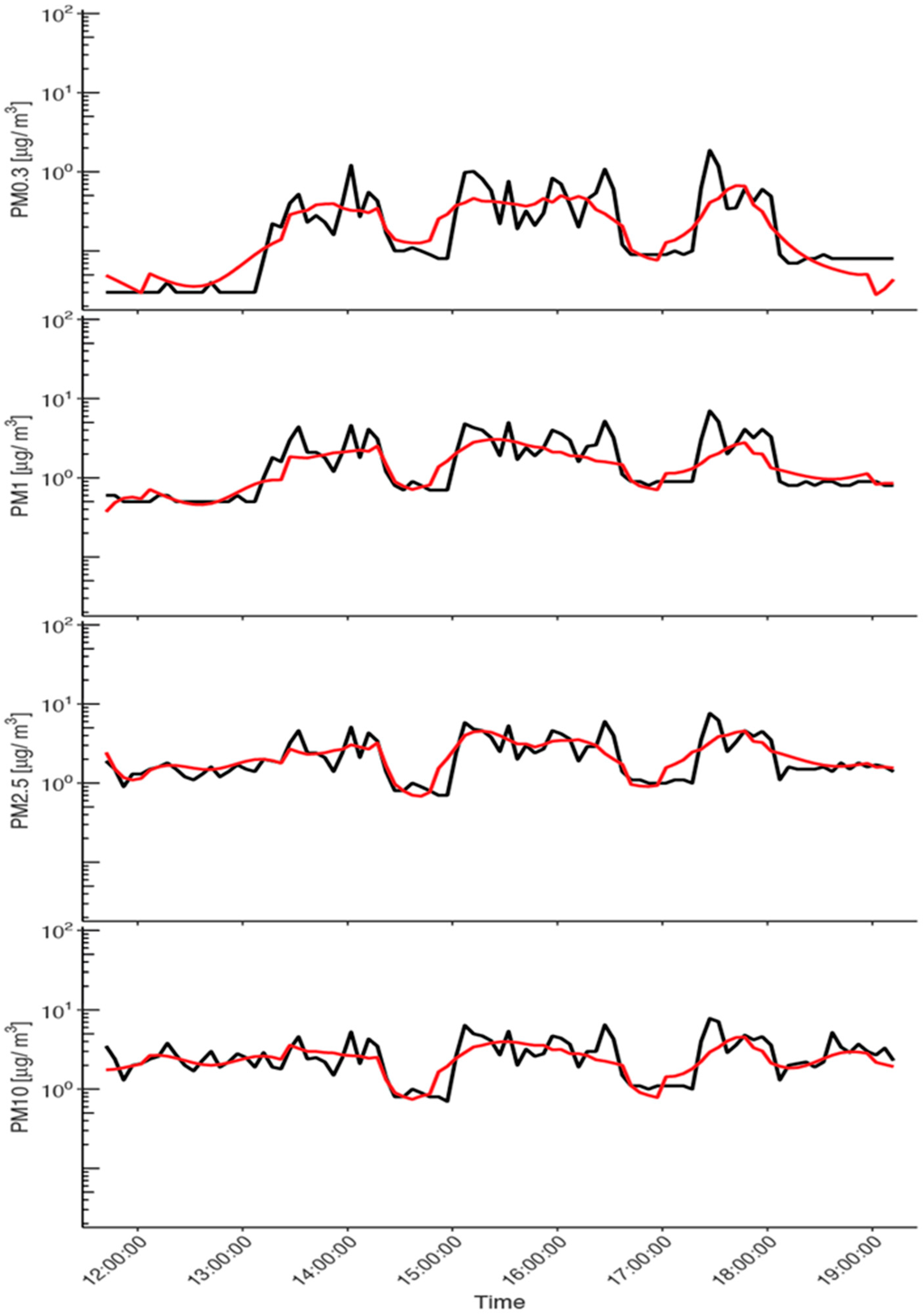
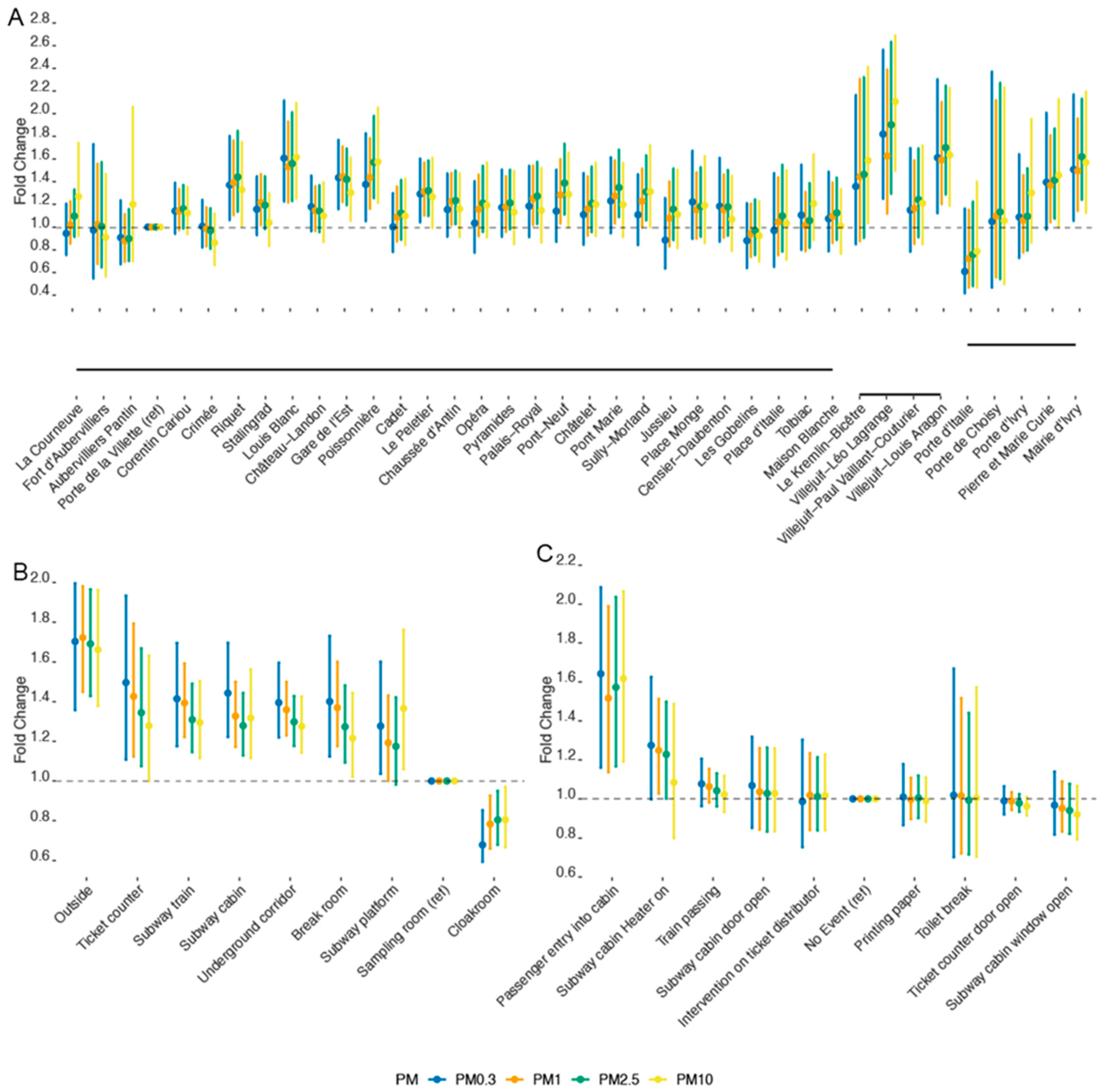
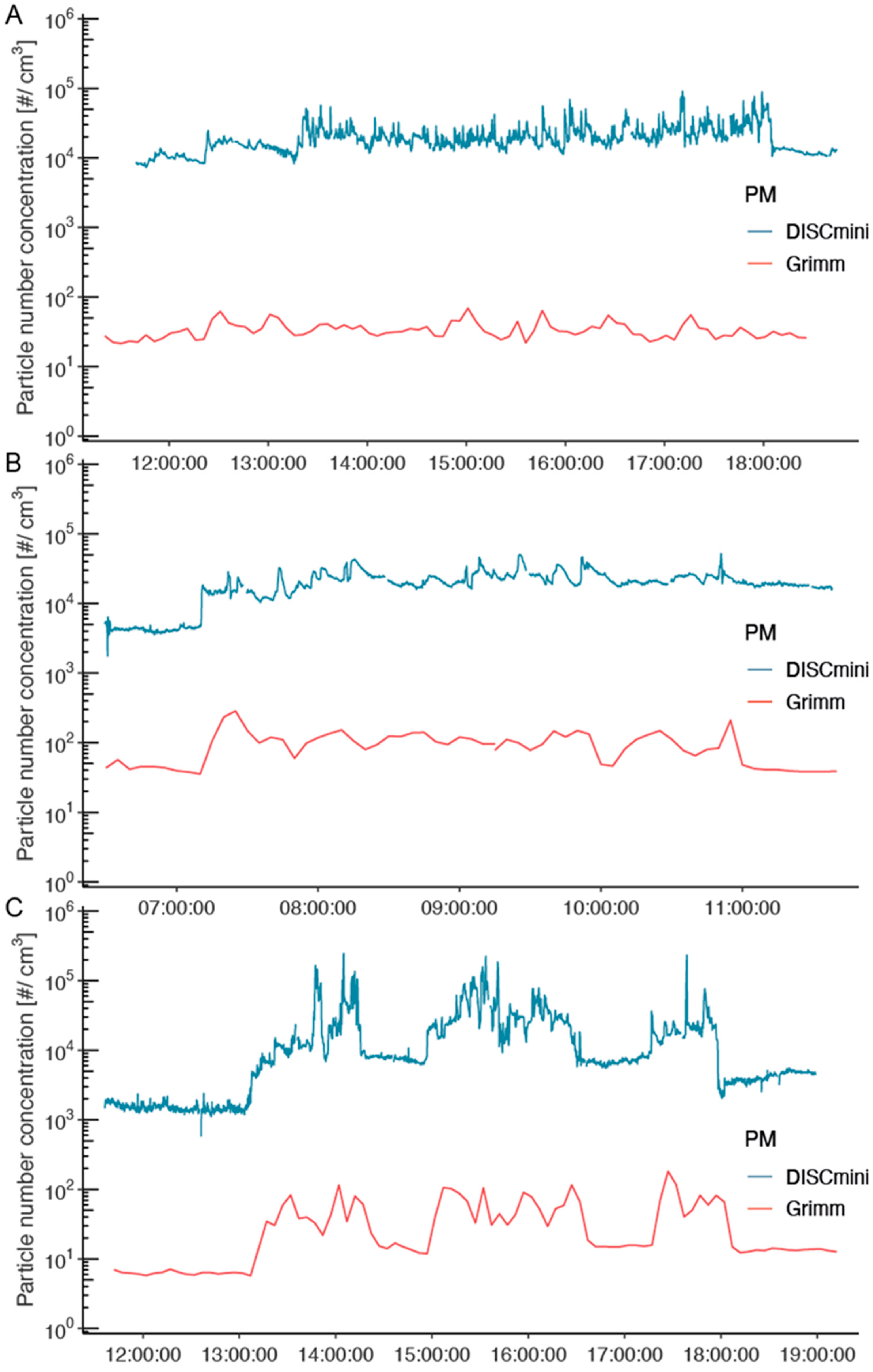
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
3.2. Bayesian Modeling Results
3.3. Comparison of GRIMM and DiSCmini Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Detection Physical Principles
4.2. Qualitative Reliability of Measurements and Inter-Device Comparison Issues
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Quality and Health. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hoek, G. Long-term exposure to PM and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide. Global Update 2005. Summary of Risk Assessment; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global Air Quality Guidelines. Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bencsik, A.; Lestaevel, P.; Guseva Canu, I. Nano- and neurotoxicology: An emerging discipline. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 160, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Biomarkers for the adverse effects on respiratory system health associated with atmospheric particulate matter exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, H. Relationship between particulate matter exposure and female breast cancer incidence and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2021, 94, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Toxicity of airborne particles-established evidence, knowledge gaps and emerging areas of importance. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Sun, M.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, T.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Short-term PM(2.5) exposure and circulating von Willebrand factor level: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, J.; Ning, R.; Du, Z.; Liu, J.; Batibawa, J.W.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. The critical role of endothelial function in fine particulate matter-induced atherosclerosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, T.; Sun, M.; Liang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Effect of particulate matter exposure on the prevalence of allergic rhinitis in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milici, A.; Talavera, K. TRP Channels as Cellular Targets of Particulate Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Hu, W.; Li, L.; Pang, Y.; Ma, S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, R. Association between ambient particulate matter exposure and metabolic syndrome risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Liang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Lin, L.; Li, T.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Particulate matter exposure and biomarkers associated with blood coagulation: A meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ahat, X.; Liang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Sun, M.; Lin, L.; Li, T.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. The relationship between exposure to PM2.5 and atrial fibrillation in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Kuang, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Qian, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Chu, H.; Gong, W.; et al. Effect of PM(2.5) exposure on circulating fibrinogen and IL-6 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxham, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Health effects of particulate matter air pollution in underground railway systems—A critical review of the evidence. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, V.; Moreno, T.; Minguillón, M.C.; Amato, F.; de Miguel, E.; Capdevila, M.; Querol, X. Exposure to airborne particulate matter in the subway system. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.; Barratt, B.; Fuller, G.; Kelly, F.; Loxham, M.; Nicolosi, E.; Priestman, M.; Tremper, A.; Green, D. PM2.5 on the London Underground. Environ. Int. 2019, 134, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Leng, J.; Shen, X.; Han, G.; Sun, L.; Yu, F. Environmental and Health Effects of Ventilation in Subway Stations: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pétremand, R.; Wild, P.; Crézé, C.; Suarez, G.; Besançon, S.; Jouannique, V.; Debatisse, A.; Canu, I.G. Application of the Bayesian spline method to analyze real-time measurements of ultrafine particle concentration in the Parisian subway. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Xiu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z. Preliminary investigation of PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and its metal elemental composition in tunnels at a subway station in Shanghai, China. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2015, 41, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxham, M.; Cooper, M.J.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Cassee, F.R.; Davies, D.; Palmer, M.R.; Teagle, D.A.H. Physicochemical Characterization of Airborne Particulate Matter at a Mainline Underground Railway Station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loxham, M.; Woo, J.; Singhania, A.; Smithers, N.P.; Yeomans, A.; Packham, G.; Crainic, A.M.; Cook, R.B.; Cassee, F.R.; Woelk, C.H.; et al. Upregulation of epithelial metallothioneins by metal-rich ultrafine particulate matter from an underground railway. Met. Int. Biomet. Sci. 2020, 12, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luglio, D.G.; Katsigeorgis, M.; Hess, J.; Kim, R.; Adragna, J.; Raja, A.; Gordon, C.; Fine, J.; Thurston, G.; Gordon, T.; et al. PM2.5 Concentration and Composition in Subway Systems in the Northeastern United States. Environ. Health Persp. 2021, 129, 27001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ryswyk, K.; Kulka, R.; Marro, L.; Yang, D.; Toma, E.; Mehta, L.; McNeil-Taboika, L.; Evans, G.J. Impacts of Subway System Modifications on Air Quality in Subway Platforms and Trains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11133–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canu, I.G.; Hemmendinger, M.; Sauvain, J.J.; Suarez, G.; Hopf, N.B.; Pralong, J.A.; Ben Rayana, T.; Besançon, S.; Sakthithasan, K.; Jouannique, V.; et al. Respiratory Disease Occupational Biomonitoring Collaborative Project (ROBoCoP): A longitudinal pilot study and implementation research in the Parisian transport company. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Canu, I.G.; Crézé, C.; Hemmendinger, M.; Ben Rayana, T.; Besançon, S.; Jouannique, V.; Debatisse, A.; Wild, P.; Sauvain, J.; Suárez, G.; et al. Particle and metal exposure in Parisian subway: Relationship between exposure biomarkers in air, exhaled breath condensate, and urine. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 237, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.R.; Malings, C.; Pandis, S.N.; Presto, A.A.; McNeill, V.; Westervelt, D.M.; Beekmann, M.; Subramanian, R. From low-cost sensors to high-quality data: A summary of challenges and best practices for effectively calibrating low-cost particulate matter mass sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 158, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, A.; Bibic, D.; Pikula, B.; Blazevic, A.; Huremovic, J.; Zero, S. Evaluation of optical particulate matter sensors under realistic conditions of strong and mild urban pollution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6427–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuula, J.; Mäkelä, T.; Aurela, M.; Teinilä, K.; Varjonen, S.; González, Ó.; Timonen, H. Laboratory evaluation of particle-size selectivity of optical low-cost particulate matter sensors. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRIMM Aerosol Technik. Portable Laser Aerosolspectrometer and Dust Monitor Model 1.108/1.109. Users Manual; GRIMM Aerosol Technik: Ainring, Germany, 2010; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-L. Measurement of Particle Mass Concentrations and Size Distributions in an Underground Station. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; Moreno, T.; Martins, V.; Minguillón, M.C.; Jones, T.; De Miguel, E.; Capdevila, M.; Centelles, S.; Querol, X. Factors controlling particle number concentration and size at metro stations. Atmosph. Environ. 2017, 156, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Schoot, R.; Depaoli, S.; King, R.; Kramer, B.; Märtens, K.; Tadesse, M.G.; Vannucci, M.; Gelman, A.; Veen, D.; Willemsen, J.; et al. Bayesian statistics and modelling. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbach, C.; Alexander, C.; Clavaguera, S.; Dahmann, D.; Dozol, H.; Faure, B.; Fierz, M.; Fontana, L.; Iavicoli, I.; Kaminski, H.; et al. Review of measurement techniques and methods for assessing personal exposure to airborne nanomaterials in workplaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H. Comparison of the TSI Model 8520 and Grimm Series 1.108 portable aerosol instruments used to monitor particulate matter in an iron foundry. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2008, 5, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuidema, C.; Stebounova, L.V.; Sousan, S.; Gray, A.; Stroh, O.; Thomas, G.; Peters, T.; Koehler, K. Estimating personal exposures from a multi-hazard sensor network. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuidema, C.; Stebounova, L.V.; Sousan, S.; Thomas, G.; Koehler, K.; Peters, T.M. Sources of error and variability in particulate matter sensor network measurements. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2019, 16, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkart, J.; Steiner, G.; Reischl, G.; Moshammer, H.; Neuberger, M.; Hitzenberger, R. Characterizing the performance of two optical particle counters (Grimm OPC1.108 and OPC1.109) under urban aerosol conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todea, A.M.; Beckmann, S.; Kaminski, H.; Bard, D.; Bau, S.; Clavaguera, S.; Dahmann, D.; Dozol, H.; Dziurowitz, N.; Elihn, K.; et al. Inter-comparison of personal monitors for nanoparticles exposure at workplaces and in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 929–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.B.; Park, J.H.; Peters, T.M. Comparison of the DiSCmini aerosol monitor to a handheld condensation particle counter and a scanning mobility particle sizer for submicrometer sodium chloride and metal aerosols. J Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2013, 10, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pétremand, R.; Suárez, G.; Besançon, S.; Dil, J.H.; Guseva Canu, I. A Real-Time Comparison of Four Particulate Matter Size Fractions in the Personal Breathing Zone of Paris Subway Workers: A Six-Week Prospective Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105999
Pétremand R, Suárez G, Besançon S, Dil JH, Guseva Canu I. A Real-Time Comparison of Four Particulate Matter Size Fractions in the Personal Breathing Zone of Paris Subway Workers: A Six-Week Prospective Study. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105999
Chicago/Turabian StylePétremand, Rémy, Guillaume Suárez, Sophie Besançon, J. Hugo Dil, and Irina Guseva Canu. 2022. "A Real-Time Comparison of Four Particulate Matter Size Fractions in the Personal Breathing Zone of Paris Subway Workers: A Six-Week Prospective Study" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105999
APA StylePétremand, R., Suárez, G., Besançon, S., Dil, J. H., & Guseva Canu, I. (2022). A Real-Time Comparison of Four Particulate Matter Size Fractions in the Personal Breathing Zone of Paris Subway Workers: A Six-Week Prospective Study. Sustainability, 14(10), 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105999





