The Impact of Green Finance on Industrial Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from 279 Cities in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Mechanism and Research Hypothesis
2.1. The Impact of Green Finance on UILUE
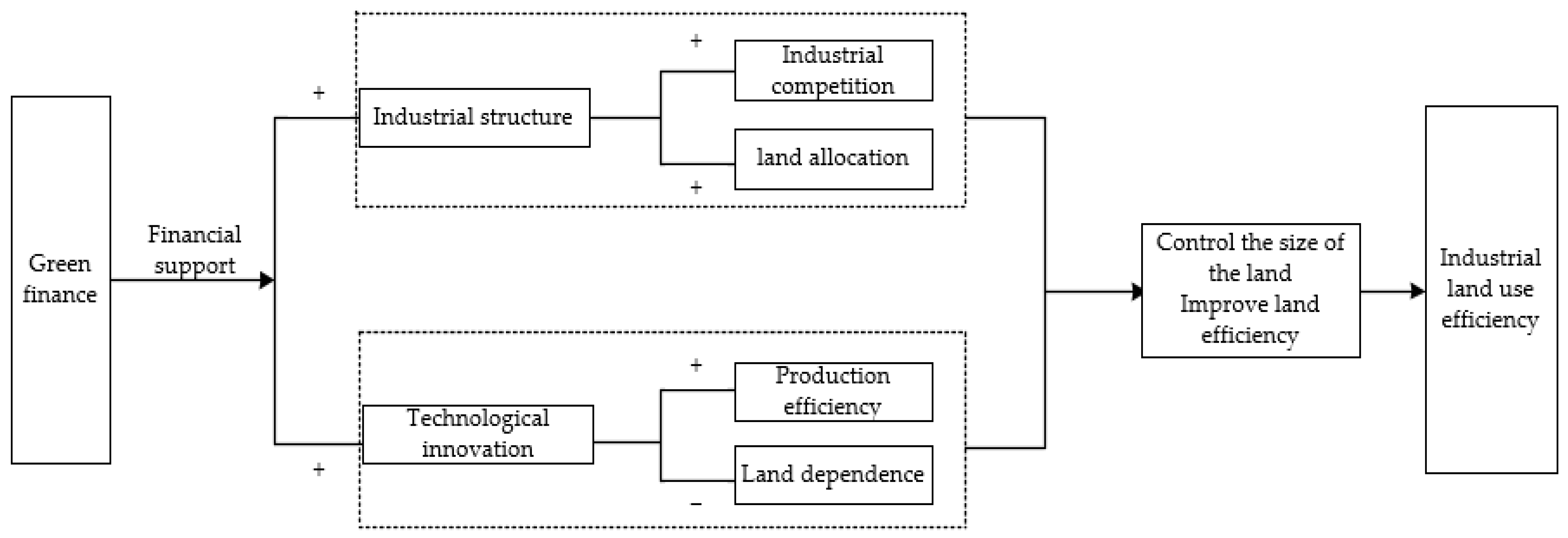
2.2. The Impact Mechanism of Green Finance on UILUE
2.3. The Influence of Local Government Land Finance
3. Research Design
3.1. Model
3.2. Variables
3.2.1. Explained Variable: Urban Industrial Land Use Efficiency (UILUE)
3.2.2. Explanatory Variables: Green Finance (gf)
3.2.3. Mediating Variables
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Data
4. Empirical Results
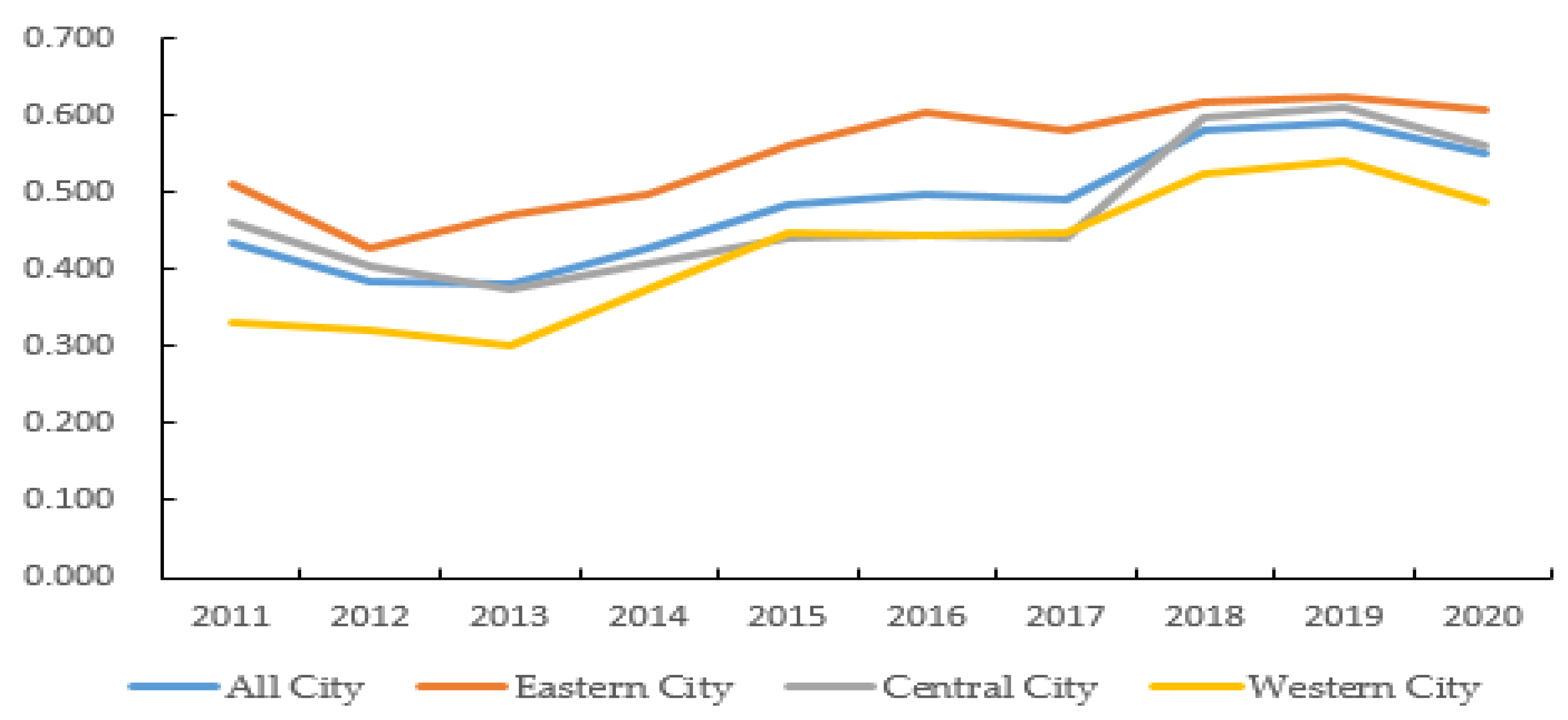
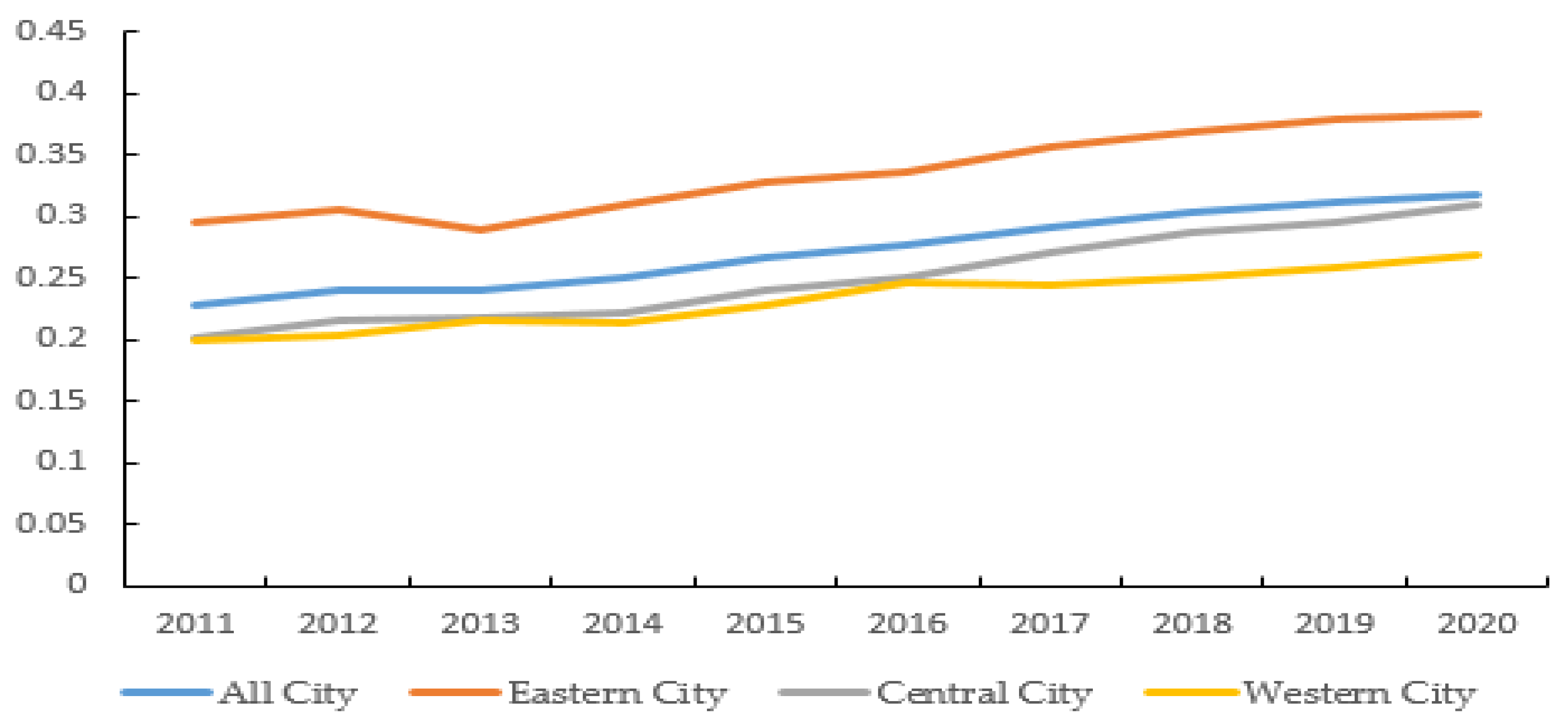
4.1. The Impact of Green Finance on the UILUE
4.2. Robustness Test
4.3. Mechanism Test
4.4. The Role of Land Finance
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Needham, B.; Louw, E.; Metzemakers, P. An economic theory for industrial land policy. Land Use Policy 2013, 33, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, C.; Wehrden, H.; Krausmann, F.; Bruckner, M.; Feng, K.; Klaus, H.; Erb, K.-H.; Abson, D.J. The effect of industrialization and globalization on domestic land-use: A global resource footprint perspective. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2021, 69, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.; Lengoiboni, M.; Zevenbergen, J. Urbanization and urban land use efficiency: Evidence from regional and Addis Ababa satellite cities, Ethiopia. Habit. Int. 2021, 117, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J. Does industrial land sprawl matter in land productivity? A case study of industrial parks of South Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, K.; Krabben, E. Rapid urbanization, land pooling policies & the concentration of wealth. Land Use Policy 2022, 116, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Song, Z.; Xia, Y. Government-enterprise collusion and land supply structure in Chinese cities. Cities 2020, 105, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferm, J.; Jones, E. Beyond the post-industrial city: Valuing and planning for industry in London. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 3380–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, J. Impact of industrial agglomeration on new-type urbanization: Evidence from Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration of China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2022, 77, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H. Can price regulation increase land-use intensity? Evidence from China’s industrial land market. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2020, 81, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, Z.; Rui, W. Land use change and economic growth in urban china: A structural equation analysis. Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 2880–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Huang, X. Change in urban land use efficiency in China: Does the high-speed rail make a mifference? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, O.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; He, R.; Wan, Q. Spatial differentiation and driving factor analysis of urban construction land change in county-level city of Guangxi, China. Land 2021, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. Study the effect of industrial structure optimization on urban land-use efficiency in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.J.; Liu, X. Urban land use efficiency under resource-based economic transformation—A case study of Shanxi Province. Land 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A. Land redevelopment and the built environment in third-wave cities: Review and synthesis. J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.A.; Faria, J.A.; Moglen, G.E. A multiobjective optimization approach to smart growth in land development. Socio-Econ. Plann. Sci. 2006, 40, 212–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Ning, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatial-temporal characteristics of industrial land green efficiency in China: Evidence from prefecture-level cities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Majumdar, D. Transboundary pollution, land use and abatement policy. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 72, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, R. Impact of green finance on economic development and environmental quality: A study based on provincial panel data from china. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19915–19932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liang, J.; Fang, J.; He, H.; Chen, F. How do industrial land price and environmental regulations affect spatiotemporal variations of pollution-intensive industries? Regional analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaleno, M.; Dogan, E.; Taskin, D. A step forward on sustainability: The nexus of environmental responsibility, green technology, clean energy and green finance. Energy Econ. 2022, 109, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, A.; Vu, H.; Cong, M.; Wei, L. Natural resources commodity prices volatility and economic performance: Evaluating the role of green finance. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, C. How does green finance affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D. Do credit constraints favor dirty production? Theory and plant-level evidence. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 84, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Xia, Y. Can green financial development promote renewable energy investment efficiency? A consideration of bank credit. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhu, J.; Luo, S. The impact of fintech innovation on green growth in China: Mediating effect of green finance. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 193, 107308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Hesary, F.T.; Panthamit, N.; Anwar, S.; Abbas, Q.; Vo, X.V. Developing low carbon finance index: Evidence from developed and developing economies. Financ. Res. Lett. 2021, 43, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Shahzad, U.; Zhao, X. How environmental regulations affect the development of green finance: Recent evidence from polluting firms in China. Renew. Energy 2022, 189, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, M.S.; Karim, M.Z.A. The role of green finance in reducing CO2 emissions: An empirical analysis. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 2022, 22, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekoya, O.B.; Oliyide, J.A.; Asl, M.G.; Jalalifar, S. Financing the green projects: Market efficiency and volatility persistence of green versus conventional bonds, and the comparative effects of health and financial crises. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 78, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J. Demand for green finance: Resolving financing constraints on green innovation in china. Energy Policy 2021, 153, 112255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kuo, T.; Wei, S.; Vinh, T. Role of green finance, volatility and risk in promoting the investments in Renewable Energy Resources in the post-COVID-19. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.A.; Boubaker, S.; Nguyen, D.K. Green finance and decarbonization: Evidence from around the world. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 46, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Ji, X.; Mirza, N.; Naqvi, B. Carbon neutrality, bank lending, and credit risk: Evidence from the eurozone. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Ali, S. How land finance affects green economic growth in Chinese cities. Land 2021, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, M.; Chiarini, B.; Marzano, E. Land use and decentralized government: A strategic approach for playing a short-sighted equilibrium. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, J. The Government Land sales programme and developers’ willingness to pay for accessibility in Singapore, 1990–2015. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Peng, L.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, X. Green technology progress and total factor productivity of resource-based enterprises: A perspective of technical compensation of environmental regulation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, M. The impact of land resource mismatch and land marketization on pollution emissions of industrial enterprises in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA–A third pole of technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Spatial–temporal differences of industrial land use efficiency and its influencing factors for China’s central region: Analyzed by SBM model. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojoianu, T.F.; Clark, G.L.; Hoepner, A.G.F.; Veneri, P. Entrepreneurs for a low carbon world: How environmental knowledge and policy shape the creation and financing of green start-ups. Res. Policy 2020, 49, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obobisa, E.S.; Chen, H.; Mensah, I.A. The impact of green technological innovation and institutional quality on CO2 emissions in African countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 180, 121670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Nakagawa, D.; Matsunaka, R.; Oba, T. Study on the factors to transform underused land focusing on the influence of railway stations in central areas of Japanese local cities. Land Use Policy 2014, 41, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Fernandes, C.; Ferreira, F. Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: A comparison of European countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 150, 119770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbahey, J.; Siddig, K.; Grethe, H. Economy-wide effects of cross-border labor mobility: The case of Palestinian employment in Israel. J. Policy Model. 2021, 43, 964–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, G. Research on the impact of green finance on China’s regional ecological development based on system GMM model. Resour. Policy 2022, 75, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements | Indicator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| input | land | Industrial land area |
| capital | Investment in fixed assets per unit of land | |
| energy | Energy consumption per unit of land | |
| labor | Number of industrial employees per unit of land | |
| environment | Investment in industrial pollution control per unit of land | |
| expected output | economy profit | Industrial economic output value per unit of land |
| undesired output | environmental pollution | Amount of industrial wastewater discharged per unit of land |
| Amount of SO2 emitted per unit of land | ||
| Amount of smoke and dust emitted per unit of land |
| Variables | Unit | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UILUE | 1 | 2790 | 0.482 | 0.107 | 0.216 | 0.641 |
| gf | 1 | 2790 | 0.273 | 0.082 | 0.104 | 0.619 |
| is | 1 | 2790 | 1.253 | 0.635 | 0.163 | 3.742 |
| ino | 1 | 2790 | 2.438 | 1.832 | 0.012 | 10.159 |
| lf | 1 | 2790 | 0.479 | 0.275 | 0.093 | 1.783 |
| regdp | yuan | 2790 | 55,694 | 27,190.76 | 4994 | 164,889 |
| Infrastructure | Kilometer | 2790 | 13,226.98 | 10,237.22 | 614 | 174,284 |
| Urbanization | 1 | 2790 | 0.566 | 0.124 | 0.368 | 0.893 |
| Openness | billion-yuan | 2790 | 113.295 | 161.115 | 1.865 | 638.792 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | FE | SYS-GMM | |
| UILUEt-1 | 1.007 ** | ||
| (2.26) | |||
| gf | 0.263 ** | 0.309 *** | 0.321 *** |
| (2.01) | (2.71) | (3.10) | |
| regdp | −0.016 | −0.021 * | −0.023 ** |
| (−1.33) | (−1.71) | (−1.98) | |
| Urbanization | 0.024 * | 0.032 * | 0.038 * |
| (1.74) | (1.69) | (1.81) | |
| Openness | −0.104 * | −0.008 ** | −0.012 ** |
| (−1.83) | (−2.09) | (−2.03) | |
| Infrastructure | 0.160 * | 0.240 ** | 0.198 ** |
| (1.82) | (2.35) | (2.10) | |
| _cons | −0.038 *** | −0.042 *** | −0.043 *** |
| (−2.64) | (−2.70) | (−2.71) | |
| YEAR | YES | YES | YES |
| CITY | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2790 | 2790 | 2790 |
| R2/AR(2) | 0.4571 | 0.6283 | 0.3105 |
| Sargan-test | 0.6252 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYS-GMM | East | Central | West | |
| UILUEt-1 | 0.996 ** | 1.217 *** | 0.964 ** | 0.853 * |
| (2.22) | (3.18) | (2.18) | (1.77) | |
| gf1 | 0.275 ** | |||
| (2.00) | ||||
| gf | 0.380 *** | 0.290 *** | 0.242 * | |
| (4.02) | (2.93) | (1.88) | ||
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YEAR | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| CITY | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2790 | 2790 | 2790 | 2790 |
| AR(2) | 0.276 | 0.361 | 0.305 | 0.298 |
| Sargan-test | 0.583 | 0.680 | 0.649 | 0.602 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| is | ULIUE | ino | UILUE | |
| gf | 0.297 ** | 0.257 ** | 1.033 *** | 0.233 *** |
| (2.30) | (2.24) | (2.93) | (3.19) | |
| is | 0.215 ** | |||
| (2.41) | ||||
| ino | 0.085 ** | |||
| (2.28) | ||||
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YEAR | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| CITY | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2790 | 2790 | 2790 | 2790 |
| R2/AR(2) | 0.597 | 0.261 | 0.503 | 0.270 |
| Sargan-test | 0.627 | 0.633 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | East | Central | West | |
| ULIUEt-1 | 1.062 ** | 1.195 *** | 0.924 ** | 0.818 * |
| (2.17) | (3.11) | (2.14) | (1.75) | |
| gf | 0.299 ** | 0.347 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.220 * |
| (2.01) | (2.47) | (2.31) | (1.80) | |
| gf × lf | −0.064 ** | −0.012 ** | −0.080 ** | −0.116 ** |
| (−2.13) | (−2.07) | (−2.35) | (−2.26) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| YEAR | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| CITY | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| AR(2) | 0.281 | 0.359 | 0.303 | 0.294 |
| Sargan-test | 0.579 | 0.663 | 0.630 | 0.594 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, F.; Hou, S. The Impact of Green Finance on Industrial Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from 279 Cities in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106184
Tian F, Hou S. The Impact of Green Finance on Industrial Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from 279 Cities in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):6184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106184
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Fa, and Shiying Hou. 2022. "The Impact of Green Finance on Industrial Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from 279 Cities in China" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 6184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106184
APA StyleTian, F., & Hou, S. (2022). The Impact of Green Finance on Industrial Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from 279 Cities in China. Sustainability, 14(10), 6184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106184






