Optimal Waste-to-Energy Strategy Assisted by Fuzzy MCDM Model for Sustainable Solid Waste Management
Abstract
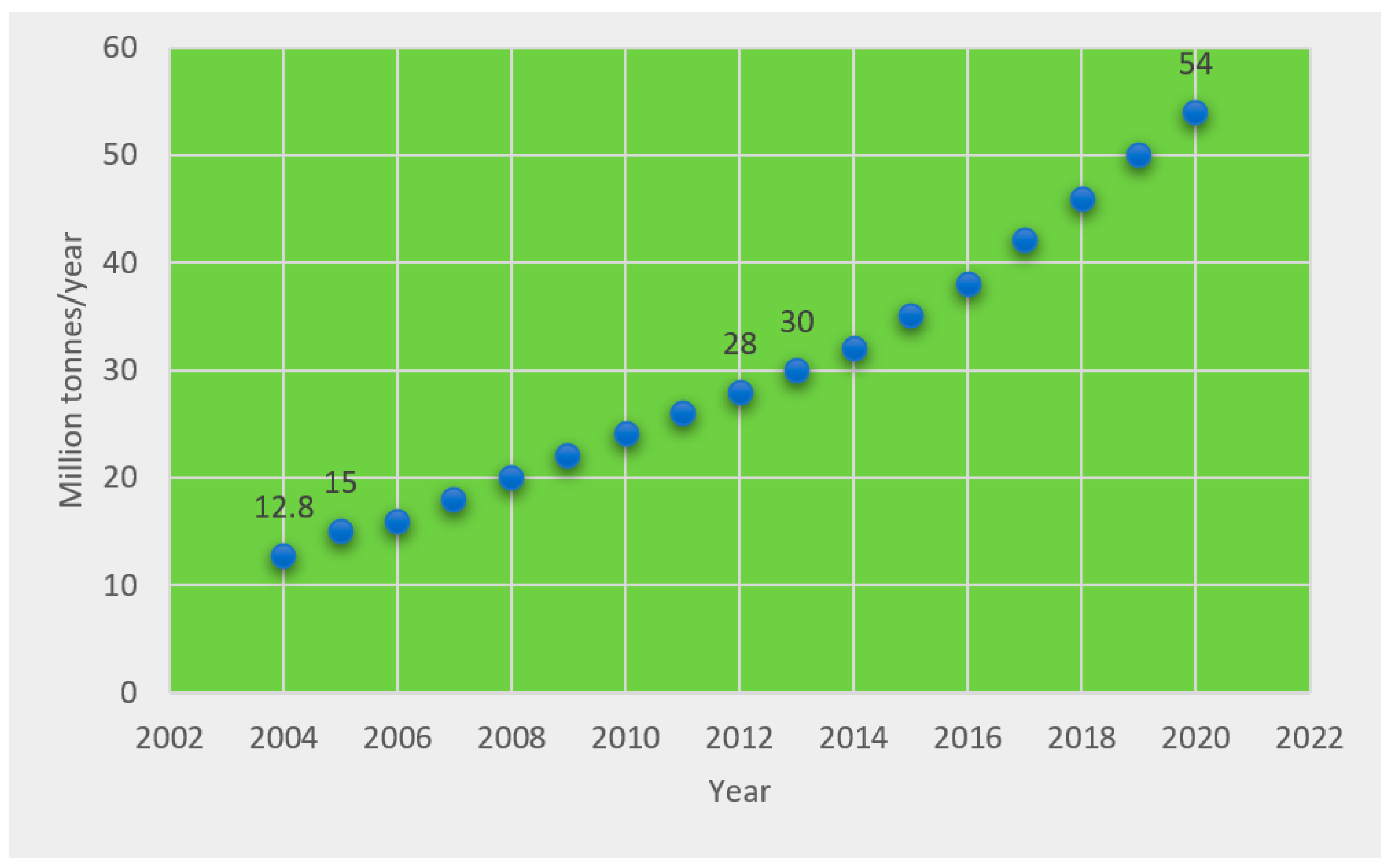
:1. Introduction
- ✓ Combustible substances (plastics, leather, rubber, paper, food, straw, wood, and grass).
- ✓ Non-combustible substances (stone, crockery, porcelain, ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals, and glass).
- ✓ Mixed substances (sand, soil, hair, and pebbles).
2. Literature Review
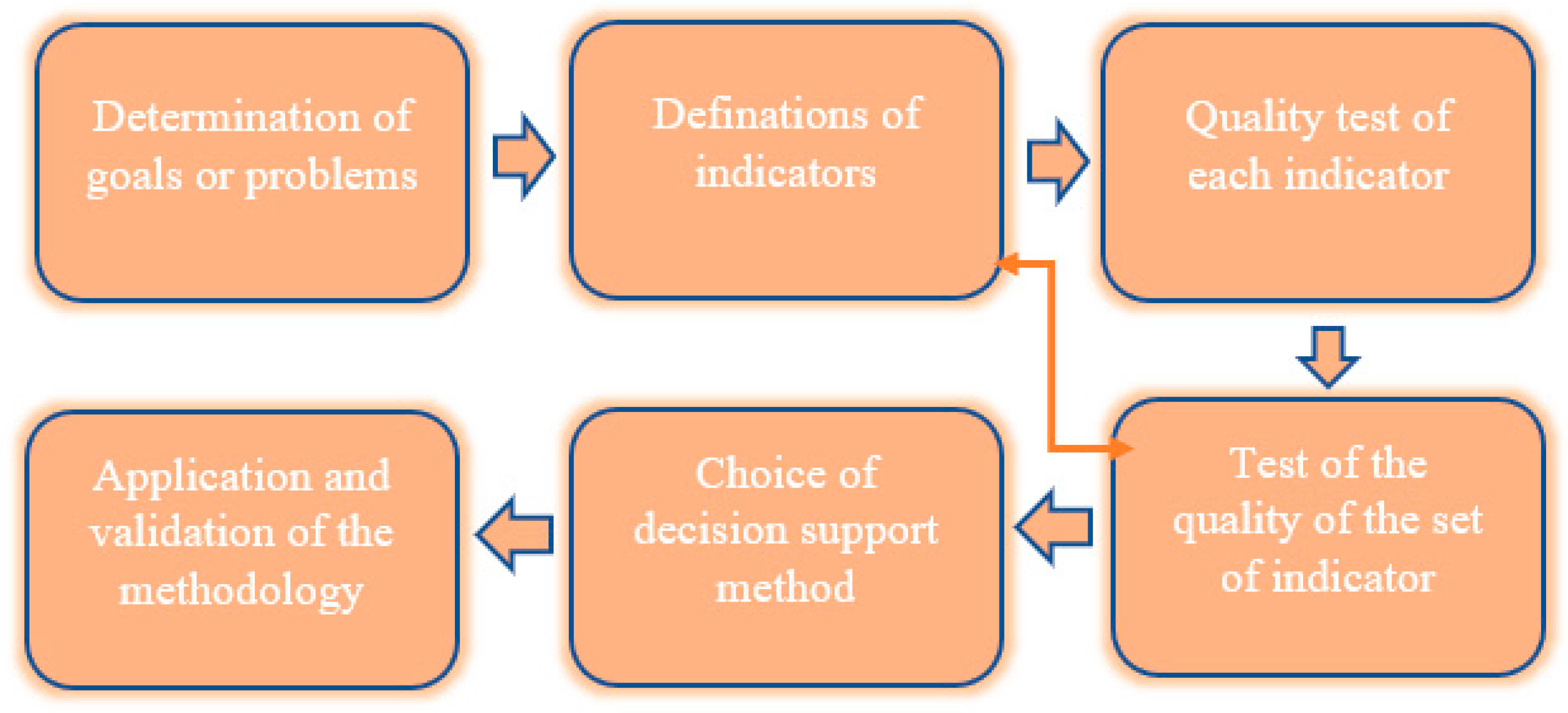
3. Methodology
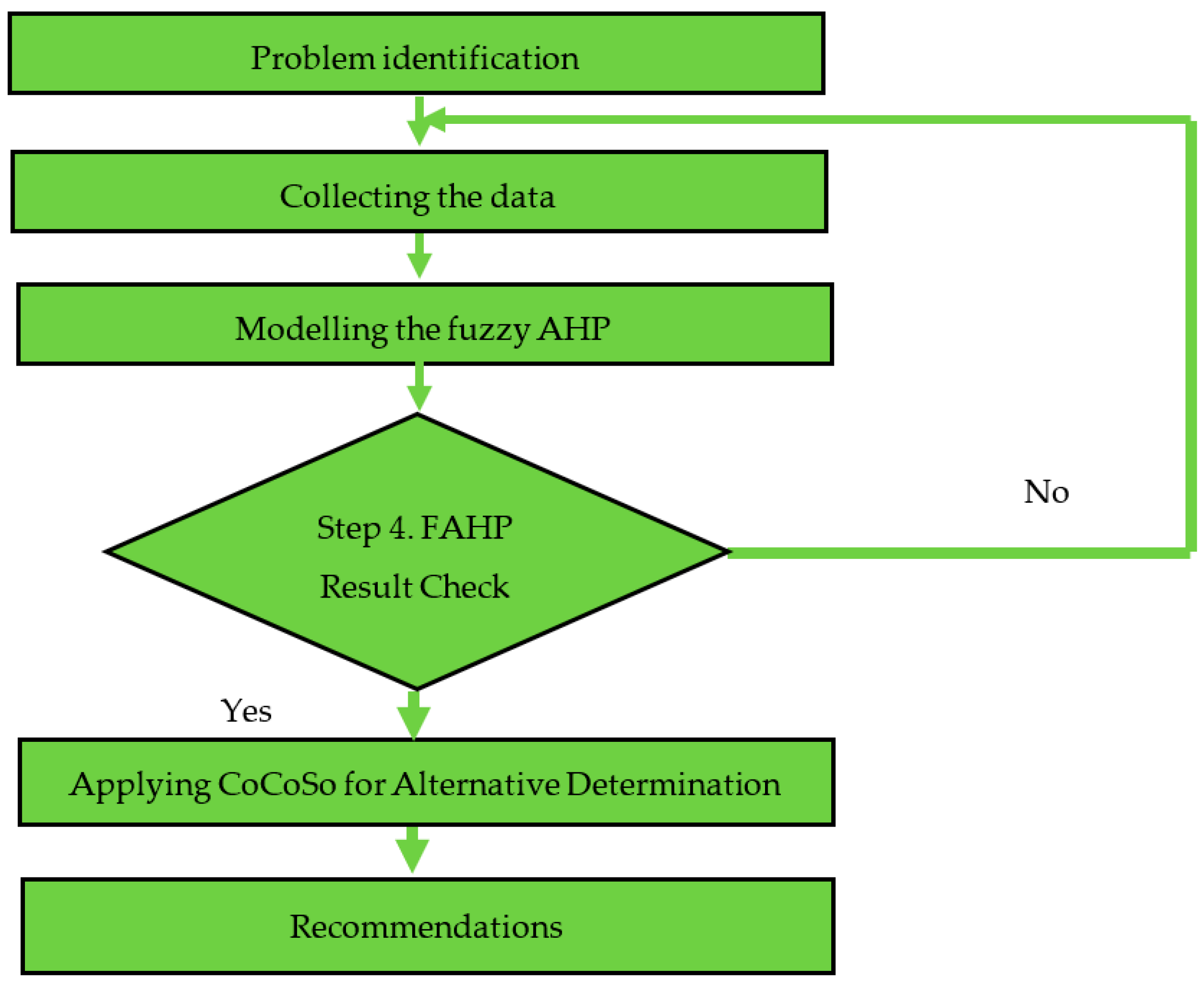
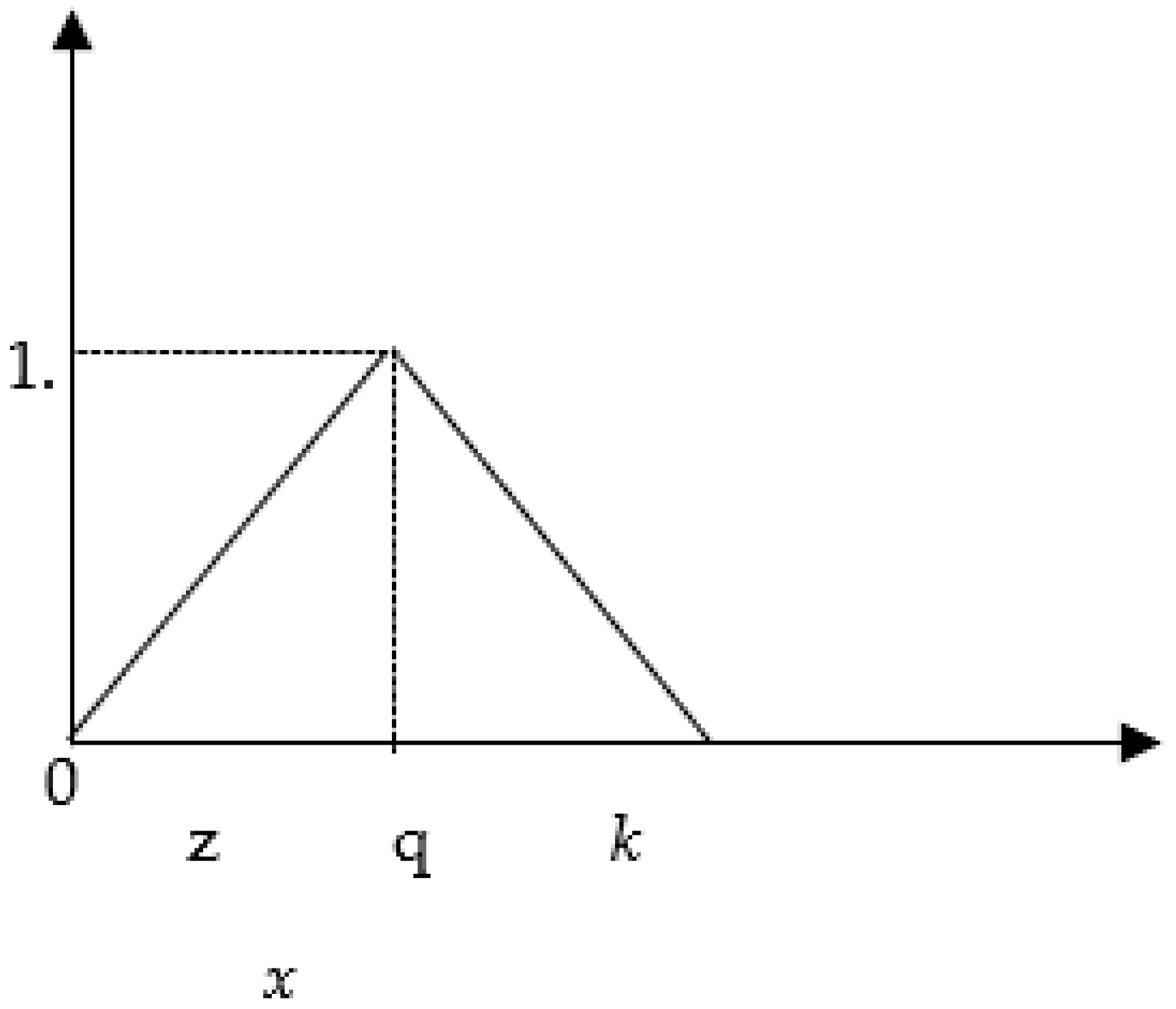
3.1. Definition of a Fuzzy Number
3.2. Fuzzy AHP (FAHP)
- is the geometric mean of the fuzzy comparison value of criterion c to each criteria.
- is the cth criterion’s fuzziness weight.
3.3. Combined Compromise Solution (CoCoSo)
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
- ✓ The suggested model is the first fuzzy MCDM model used to evaluate and select solid-waste-to-energy plant locations in Vietnam, and it is based on expert interviews and literature research.
- ✓ This is the first research to present a case study on the assessment of locations for the renewable energy industry, using a mix of fuzzy theory, the AHP model, and the CoCoSo model.
- ✓ The findings of this study may be used as a beneficial reference to analyze and select the best sites for solid-waste-to-energy projects, as well as for decision makers and investors in other renewable energy initiatives.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tăng Cường Sản Xuất điện Năng Từ chất Thải, Góp Phần Phát Triển Năng Lượng Và Bảo Vệ Môi Trường. Available online: http://daidoanket.vn/tang-cuong-san-xuat-dien-nang-tu-rac-thai-5667575.html (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- CHẤT THẢI RẮN, THÀNH PHẦN PHÂN LOẠI VÀ CÁC QUY TRÌNH XỬ LÝ. Available online: https://moitruonghse.com/chat-thai-ran-thanh-phan-phan-loai-va-cac-quy-trinh-xu-ly (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Một Số Công Nghệ Lò đốt Chất Thải Phát điện. Available online: https://www.most.gov.vn/vn/tin-tuc/20523/mot-so-cong-nghe-lo-dot-chat-thai-phat-dien.aspx (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Wang, C.N.; Nguyen, V.T.; Duong, D.H.; Thai, H.T.N. A hybrid fuzzy analysis network process (FANP) and the technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) approaches for solid waste to energy plant location selection in Vietnam. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benmoussa, N.; Elyamami, A.; Mansouri, K.; Qbadou, M.; Illoussamen, E. A multi-criteria decision making approach for enhancing university accreditation process. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 3726–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, A.; Al-Hanbali, A.; Knutsson, S. Locating solid waste landfills in Mafraq city, Jordan. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Chan, C.W.; Huang, G.H. Using multiple criteria decision analysis for supporting decisions of solid waste management. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2002, 37, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Sharma, L.K.; Nathawat, M.S. Geospatial strategy for sustainable management of municipal solid waste for growing urban environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the environment-review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamorano, M.; Molero, E.; Hurtado, A.; Grindlay, A.; Ramos, A. Evaluation of a municipal landfill site in Southern Spain with GIS-aided methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Kumar, A.; Roy, S.S. Estimating Potential Methane Emission from Municipal Solid Waste and a Site Suitability Analysis of Existing Landfills in Delhi, India. Technologies 2017, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beskese, A.; Demir, H. Landfill site selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS: A case study for Istanbul. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, V.; Memisoglu, T.; Bediroglu, S.; Colak, H.E. Municipal solid waste landfill site selection using multi-criteria decision making and GIS: Case study of Bursa province. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2018, 26, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, S.; Sarkar, S. Identifying potential landfill sites using multicriteria evaluation modeling and GIS techniques for Kharagpur city of West Bengal, India. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Anbari, A.; Thameer, Y.; Al-Ansari, N.; Knutsson, S. Ranking landfill sites in Najaf Governorate, Iraq ssing AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methods. J. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2016, 10, 815–821. [Google Scholar]
- Villacreses, G.; Gaona, G.; Martínez-Gómez, J.; Jijón, D.J. Wind farms suitability location using geographical information system (GIS), based on multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods: The case of continental Ecuador. Renew. Energy 2017, 109, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekçioğlu, M.; Kaya, T.; Kahraman, C. Fuzzy multicriteria disposal method and site selection for municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J. Municipal solid waste landfill site selection based on fuzzy-AHP and geoinformation techniques in Asir region Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichapa, N.; Khokhajaikiat, P. Solving multi-objective facility location problem using the fuzzy analytical hierarchy process and goal programming: A case study on infectious waste disposal centers. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2017, 4, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanine, M.; Boutkhoum, O.; Tikniouine, A.; Agouti, T. Comparison of fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TODIM methods for landfill location selection. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.N.; Tsai, T.T.; Huang, Y.F. A model for optimizing location selection for biomass energy power plants. Processes 2019, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Antucheviciene, J.; Zakarevicius, A. Optimization of weighted aggregated sum product assessment. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2012, 122, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Rani, P. Multi-criteria healthcare waste disposal location selection based on Fermatean fuzzy WASPAS method. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.X.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.Y. Solving solar-wind power station location problem using an extended weighted aggregated sum product assessment (WASPAS) technique with interval neutrosophic sets. Symmetry 2017, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Antucheviciene, J. Applications of WASPAS method as a multi-criteria decision-making tool. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. Res. 2015, 49, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Turskis, Z.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Antucheviciene, J.; Kosareva, N. A hybrid model based on fuzzy AHP and fuzzy WASPAS for construction site selection. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control. 2015, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baušys, R.; Juodagalvienė, B. Garage location selection for residential house by WASPAS-SVNS method. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2017, 23, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagočius, V.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. Multi-person selection of the best wind turbine based on the multi-criteria integrated additive-multiplicative utility function. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2014, 20, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Saraji, M.K.; Mishra, A.R.; Rani, P. A novel extended approach under hesitant fuzzy sets to design a framework for assessing the key challenges of digital health interventions adoption during the COVID-19 outbreak. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlović, J.; Rajković, P.; Petrović, G.; Ćirić, D. The selection of the logistics distribution center location based on MCDM methodology in southern and eastern region in Serbia. Oper. Res. Eng. Sci. Theory Appl. 2019, 2, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, J.J.H.; Yen, L.; Tzeng, G.H. Building an effective safety management system for airlines. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2008, 14, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.W.; Lee, Y.T. Developing global managers’ competencies using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2007, 32, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.Y.; Lu, S.T.; Tzeng, G.H. Fuzzy MCDM approach for planning and design tenders selection in public office buildings. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2004, 22, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, A.T. Evaluation of hazardous waste transportation firms by using a two-step Fuzzy-AHP and TOPSIS methodology. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 4067–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzi, S.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Abedinzadeh, N.; Aalipour, M. Multi-criteria decision analysis FANP based on GIS for siting municipal solid waste incineration power plant in the north of Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Zarate, P.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. A combined compromise solution (CoCoSo) method for multi-criteria decision-making problems. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 2501–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biến Rác Thải Thành điện: Cần có Cơ Chế Thúc đẩy đầu Tư. Available online: https://www.vietnamplus.vn/bien-rac-thai-thanh-dien-can-co-co-che-thuc-day-dau-tu/632126.vnp (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Wu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zeng, B.; Yang, M.; Geng, S. Cloud-based decision framework for waste-to-energy plant site selection–A case study from China. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.; Guo, F.; Huang, X.; Men, H.; Li, M. Site selection decision of waste-To-Energy projects based on an extended cloud-TODIM method from the perspective of low-carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 303, 127036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.; Zsigraiová, Z.; Semiao, V. Multi-criteria GIS-based siting of an incineration plant for municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Waste Management in China: Issues and Recommendation. Urban Development Working Papers East Asia Infrastructure Department World Bank; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]

| No. | Authors | MCDM Models | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yildirim et al. | Geographical information system (GIS); TOPSIS | Combined GIS and TOPSIS models for municipal solid waste landfill site selection |
| 2 | Dolui et al. | AHP, fuzzy AHP, SRS and RSW weightage methods | Identified potential landfill sites |
| 3 | Al-Anbari et al. | AHP, fuzzy TOPSIS | Site capacity criterion was found to be more important than land price and land elevation |
| 4 | Tavares et al. | Geographical information system (GIS); AHP | System effectiveness was provided in ranking potential locations |
| 5 | Ekmekçioğlu et al. | AHP, TOPSIS | Illustrated the importance of weights on various criteria when choosing the optimized location |
| 6 | Mallick’s et al. | GIS-based fuzzy-AHP-MCDA method | Findings can provide an appropriate guideline to assist decision makers in selecting an optimal landfill site |
| 7 | Wichapa et al. | FAHP; goal programming (GP) | The proposed model can lead to selection of optimal locations for infectious waste disposals |
| 8 | Hanine et al. | Fuzzy AHP; fuzzy TODIM | Comparisons of two MCDM methods were made |
| 9 | Wang et al. | FAHP, TOPSIS | The proposed MCDM model can address the complex problems in location selection |
| 10 | Zavadskas | Weighted sum model (WSM); weighted product model (WPM) | The proposed MCDM method increased the ranking accuracy of alternatives |
| 11 | Mishra et al. | WASPAS with Fermatean fuzzy sets | The proposed MCDM model can handle the ambiguity and inaccuracy in decision-making processes |
| 12 | Nie et al. | WASPAS | Solved location selection problem in wind power projects |
| 13 | Chakraborty et al. | WASPAS | Applied WASPAS method as a multi-criteria decision-making tool |
| 14 | Turskis et al. | Fuzzy AHP; fuzzy WASPAS | Applied MCDM model for construction site selection |
| No. | Main Criteria | Sub-Criteria | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literature Review | Experts | |||
| 1 | Economic factor | Construction cost (WE1) | Sadaf Feyzi et al. [36] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X |
| Operation and maintenance cost (WE2) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| Potential demand (WE3) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] | X | ||
| Land use (WE4) | Sadaf Feyzi et al. [36] Tavares et al. [41] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| 2 | Technical factor | Solid waste quantity (WE5) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] | X |
| Distance to the city (WE6) | World bank (2005) [42] | X | ||
| Distance to landfills (WE7) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| Distance from electric grid (WE8) | Sadaf Feyzi et al. [36] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| 3 | Environment factor | Impact on life quality of resident (WE9) | Sadaf Feyzi et al. [36] | X |
| Elevation (WE10) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] | X | ||
| Solid texture (WE11) | World bank (2005) [42] | X | ||
| 4 | Social factor | Growth of GDP (WE12) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] | X |
| Government policy (WE13) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| Public support (WE14) | Jianwei Gao et al. [40] Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| Available employee (WE15) | Yunna Wu et al. [39] | X | ||
| Criteria | Fuzzy Sum of Each Row | Fuzzy Synthetic Extent | Degree of Possibility | Normalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WE 1 | 12.65408 | 17.73456 | 24.11035 | 0.03583 | 0.06835 | 0.12965 | 0.67081 | 0.06695 |
| WE 2 | 12.13408 | 17.32285 | 24.01852 | 0.03436 | 0.06676 | 0.12916 | 0.66183 | 0.06605 |
| WE 3 | 15.52096 | 21.60082 | 28.49693 | 0.04395 | 0.08325 | 0.15324 | 0.86275 | 0.08610 |
| WE 4 | 14.17687 | 20.14792 | 26.85583 | 0.04014 | 0.07765 | 0.14442 | 0.80928 | 0.08077 |
| WE 5 | 18.70575 | 25.73977 | 33.40429 | 0.05297 | 0.09920 | 0.17963 | 1.00000 | 0.09980 |
| WE 6 | 11.38350 | 15.40831 | 20.48769 | 0.03223 | 0.05938 | 0.11017 | 0.57144 | 0.05703 |
| WE 7 | 9.49865 | 13.23950 | 18.79210 | 0.02690 | 0.05103 | 0.10105 | 0.49953 | 0.04985 |
| WE 8 | 13.66866 | 19.27269 | 25.62867 | 0.03870 | 0.07428 | 0.13782 | 0.77295 | 0.07714 |
| WE 9 | 14.15539 | 20.51264 | 28.07008 | 0.04008 | 0.07906 | 0.15095 | 0.82945 | 0.08278 |
| WE 10 | 10.03724 | 13.95303 | 19.88857 | 0.02842 | 0.05378 | 0.10695 | 0.54303 | 0.05420 |
| WE 11 | 9.06600 | 12.49746 | 17.77592 | 0.02567 | 0.04817 | 0.09559 | 0.45508 | 0.04542 |
| WE 12 | 16.26079 | 23.13051 | 31.12386 | 0.04604 | 0.08915 | 0.16737 | 0.91920 | 0.09174 |
| WE 13 | 9.59264 | 13.03898 | 18.30196 | 0.02716 | 0.05025 | 0.09842 | 0.48147 | 0.04805 |
| WE 14 | 8.89311 | 11.98044 | 16.85137 | 0.02518 | 0.04617 | 0.09062 | 0.41520 | 0.04144 |
| WE 15 | 10.21197 | 13.88541 | 19.34778 | 0.02892 | 0.05352 | 0.10404 | 0.52784 | 0.05268 |
| DMUWE 1 | DMUWE 2 | DMUWE 3 | DMUWE 4 | DMUWE 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WE 1 | 0.00000 | 0.03347 | 0.03347 | 0.06695 | 0.03347 |
| WE 2 | 0.00000 | 0.06605 | 0.06605 | 0.00000 | 0.06605 |
| WE 3 | 0.00000 | 0.04305 | 0.08610 | 0.04305 | 0.08610 |
| WE 4 | 0.04038 | 0.00000 | 0.04038 | 0.08077 | 0.04038 |
| WE 5 | 0.09980 | 0.04990 | 0.09980 | 0.00000 | 0.04990 |
| WE 6 | 0.05703 | 0.01901 | 0.00000 | 0.05703 | 0.03802 |
| WE 7 | 0.04985 | 0.00000 | 0.02493 | 0.04985 | 0.00000 |
| WE 8 | 0.03857 | 0.00000 | 0.03857 | 0.07714 | 0.03857 |
| WE 9 | 0.08278 | 0.04139 | 0.04139 | 0.00000 | 0.04139 |
| WE 10 | 0.05420 | 0.05420 | 0.00000 | 0.05420 | 0.05420 |
| WE 11 | 0.02271 | 0.00000 | 0.02271 | 0.04542 | 0.02271 |
| WE 12 | 0.09174 | 0.09174 | 0.04587 | 0.00000 | 0.04587 |
| WE 13 | 0.04805 | 0.02403 | 0.02403 | 0.00000 | 0.04805 |
| WE 14 | 0.02072 | 0.00000 | 0.02072 | 0.04144 | 0.02072 |
| WE 15 | 0.02634 | 0.05268 | 0.00000 | 0.02634 | 0.02634 |
| DMUWE 1 | DMUWE 2 | DMUWE 3 | DMUWE 4 | DMUWE 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WE 1 | 0.0000 | 0.9547 | 0.9547 | 1.0000 | 0.9547 |
| WE 2 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| WE 3 | 0.0000 | 0.9421 | 1.0000 | 0.9421 | 1.0000 |
| WE 4 | 0.9456 | 0.0000 | 0.9456 | 1.0000 | 0.9456 |
| WE 5 | 1.0000 | 0.9332 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9332 |
| WE 6 | 1.0000 | 0.9393 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9771 |
| WE 7 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9660 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 |
| WE 8 | 0.9479 | 0.0000 | 0.9479 | 1.0000 | 0.9479 |
| WE 9 | 1.0000 | 0.9442 | 0.9442 | 0.0000 | 0.9442 |
| WE 10 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| WE 11 | 0.9690 | 0.0000 | 0.9690 | 1.0000 | 0.9690 |
| WE 12 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9384 | 0.0000 | 0.9384 |
| WE 13 | 1.0000 | 0.9672 | 0.9672 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| WE 14 | 0.9717 | 0.0000 | 0.9717 | 1.0000 | 0.9717 |
| WE 15 | 0.9641 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9641 | 0.9641 |
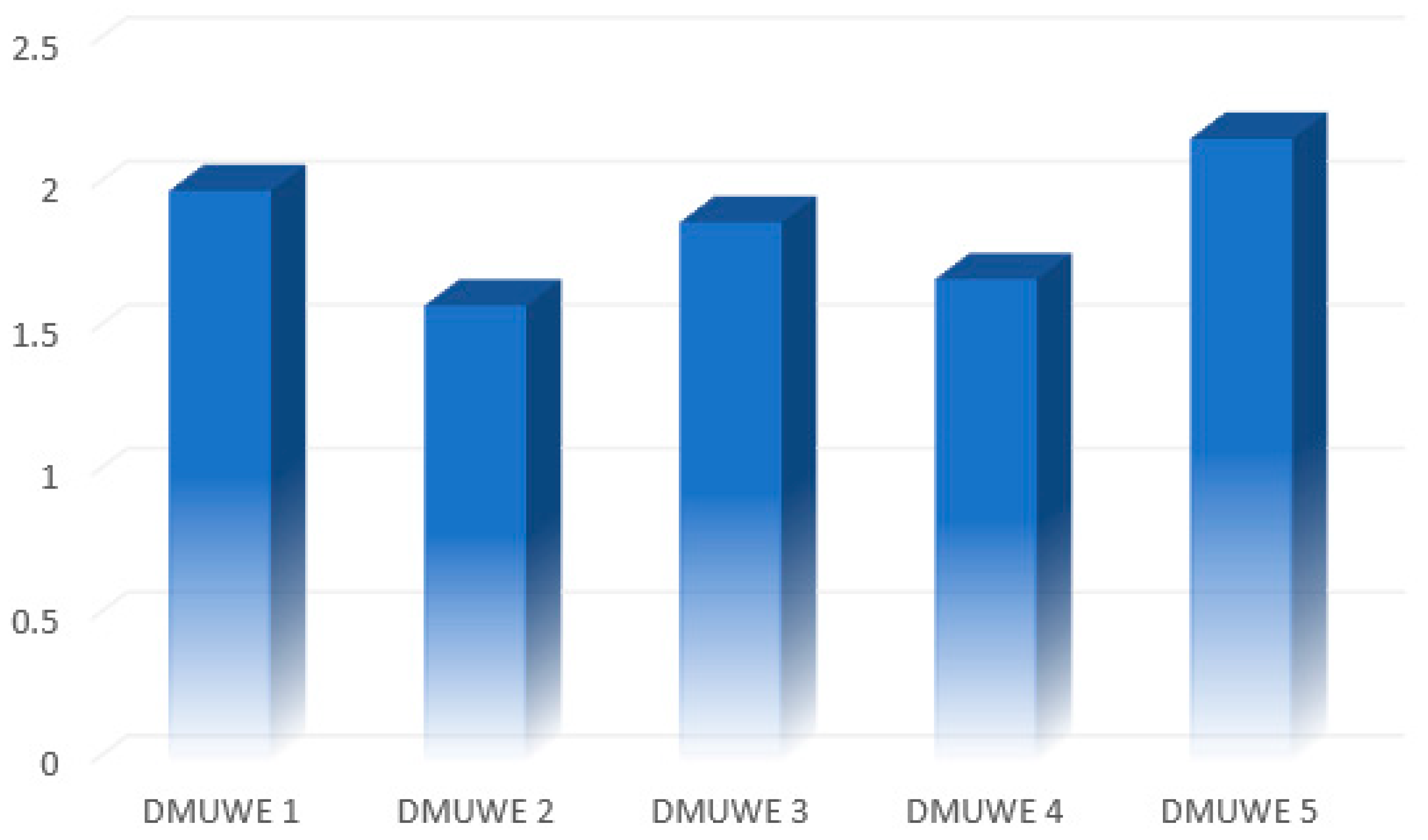
| Alternatives | Ka | Ranking | Kb | Ranking | Kc | Ranking | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMUWE 1 | 0.2095 | 2 | 2.5482 | 2 | 0.8767 | 2 | 1.9879 |
| DMUWE 2 | 0.1711 | 5 | 2.0000 | 5 | 0.7163 | 5 | 1.5884 |
| DMUWE 3 | 0.2047 | 3 | 2.3428 | 3 | 0.8569 | 3 | 1.8783 |
| DMUWE 4 | 0.1761 | 4 | 2.1635 | 4 | 0.7369 | 4 | 1.6803 |
| DMUWE 5 | 0.2386 | 1 | 2.6858 | 1 | 0.9986 | 1 | 2.1694 |
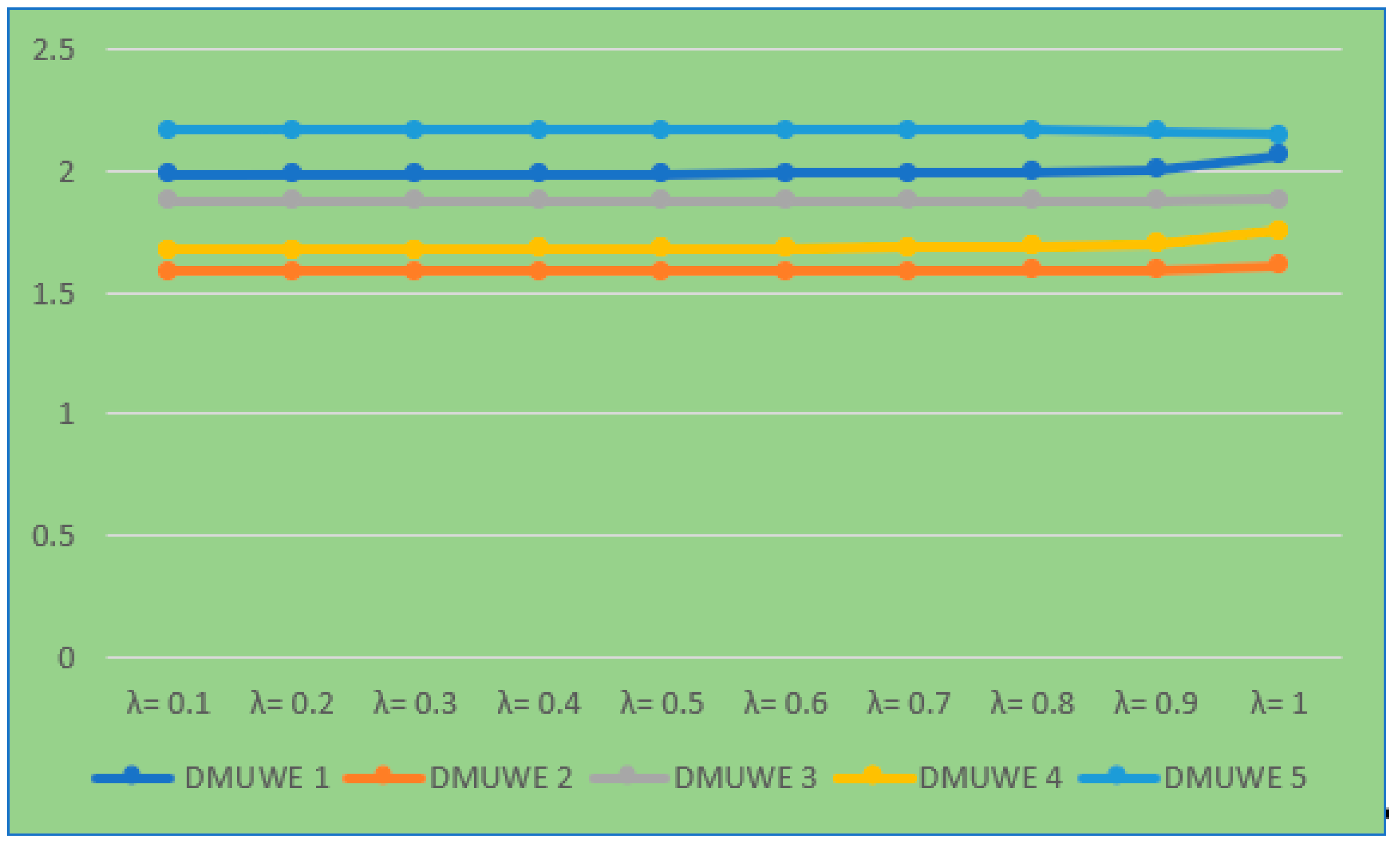
| Alternatives | λ Values | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ = 0.1 | λ = 0.2 | λ = 0.3 | λ = 0.4 | λ = 0.5 | λ = 0.6 | λ = 0.7 | λ = 0.8 | λ = 0.9 | λ = 1 | |
| DMUWE 1 | 1.9847 | 1.9852 | 1.9858 | 1.9867 | 1.9879 | 1.9895 | 1.9922 | 1.9970 | 2.0081 | 2.0637 |
| DMUWE 2 | 1.5875 | 1.5876 | 1.5878 | 1.5881 | 1.5884 | 1.5889 | 1.5896 | 1.5910 | 1.5943 | 1.6106 |
| DMUWE 3 | 1.8782 | 1.8782 | 1.8782 | 1.8783 | 1.8783 | 1.8784 | 1.8784 | 1.8786 | 1.8789 | 1.8806 |
| DMUWE 4 | 1.6771 | 1.6777 | 1.6783 | 1.6791 | 1.6803 | 1.6819 | 1.6845 | 1.6892 | 1.7001 | 1.7545 |
| DMUWE 5 | 2.1702 | 2.1700 | 2.1699 | 2.1697 | 2.1694 | 2.1690 | 2.1683 | 2.1671 | 2.1643 | 2.1501 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Thanh, N. Optimal Waste-to-Energy Strategy Assisted by Fuzzy MCDM Model for Sustainable Solid Waste Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6565. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116565
Van Thanh N. Optimal Waste-to-Energy Strategy Assisted by Fuzzy MCDM Model for Sustainable Solid Waste Management. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6565. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116565
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Thanh, Nguyen. 2022. "Optimal Waste-to-Energy Strategy Assisted by Fuzzy MCDM Model for Sustainable Solid Waste Management" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6565. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116565
APA StyleVan Thanh, N. (2022). Optimal Waste-to-Energy Strategy Assisted by Fuzzy MCDM Model for Sustainable Solid Waste Management. Sustainability, 14(11), 6565. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116565






