Does the Impact of Technology Sustain Students’ Satisfaction, Academic and Functional Performance: An Analysis via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This research examines technology acceptance using learning factors of digital learning.
- This study presents an empirical analysis to observe the relationship of technology between self-regulated and interactive learning.
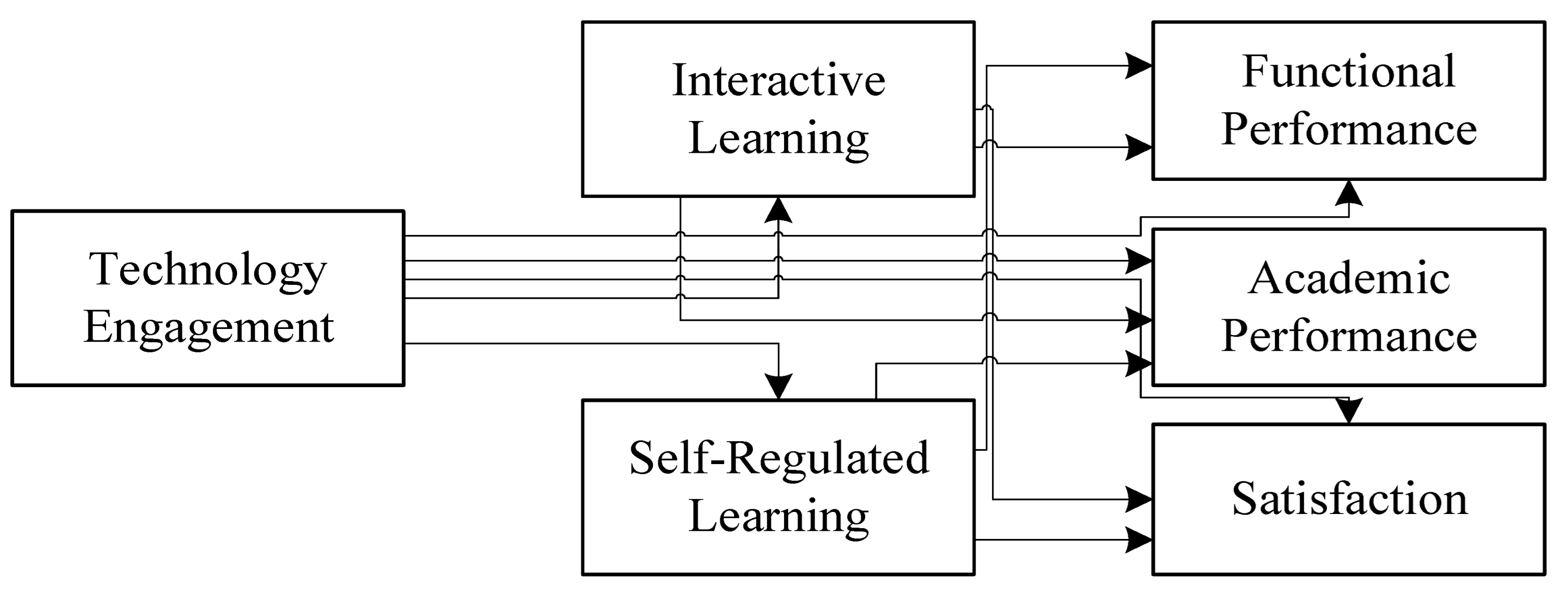
- Students’ engagement with the technology via the mediating role of interactive and self-regulated learning can improve their satisfaction and academic and functional performance.
1.1. Preliminaries
1.2. Learning Factors: Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning
1.3. Students Engaging in Technology via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning
2. Research Model and Methodology
2.1. Sample Selection and Data Analysis
2.2. Measures
2.3. Descriptive Statistics
2.4. Common Method Bias (CMB)
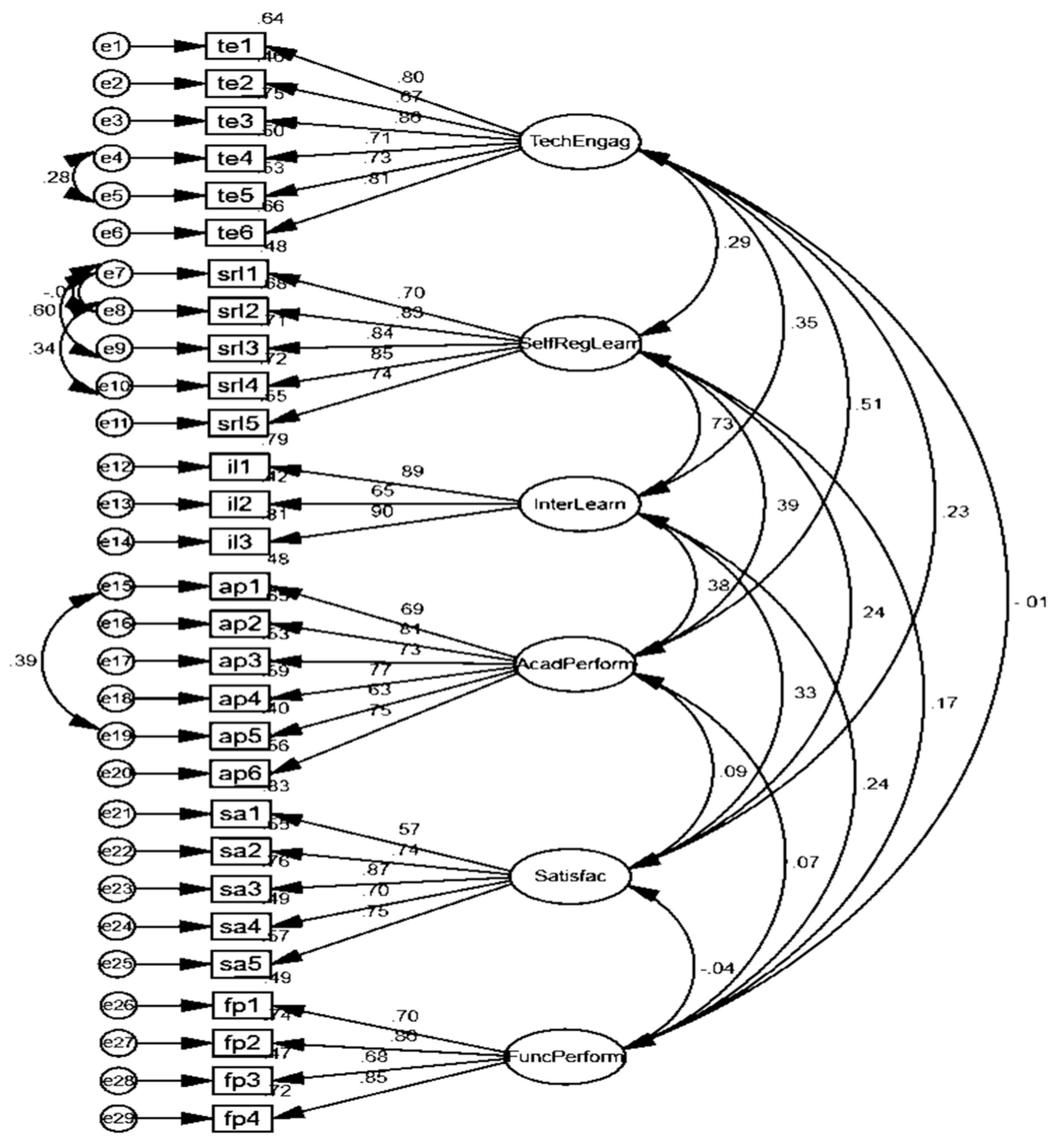
2.5. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
2.6. Model Validity and Reliability
2.7. Correlation
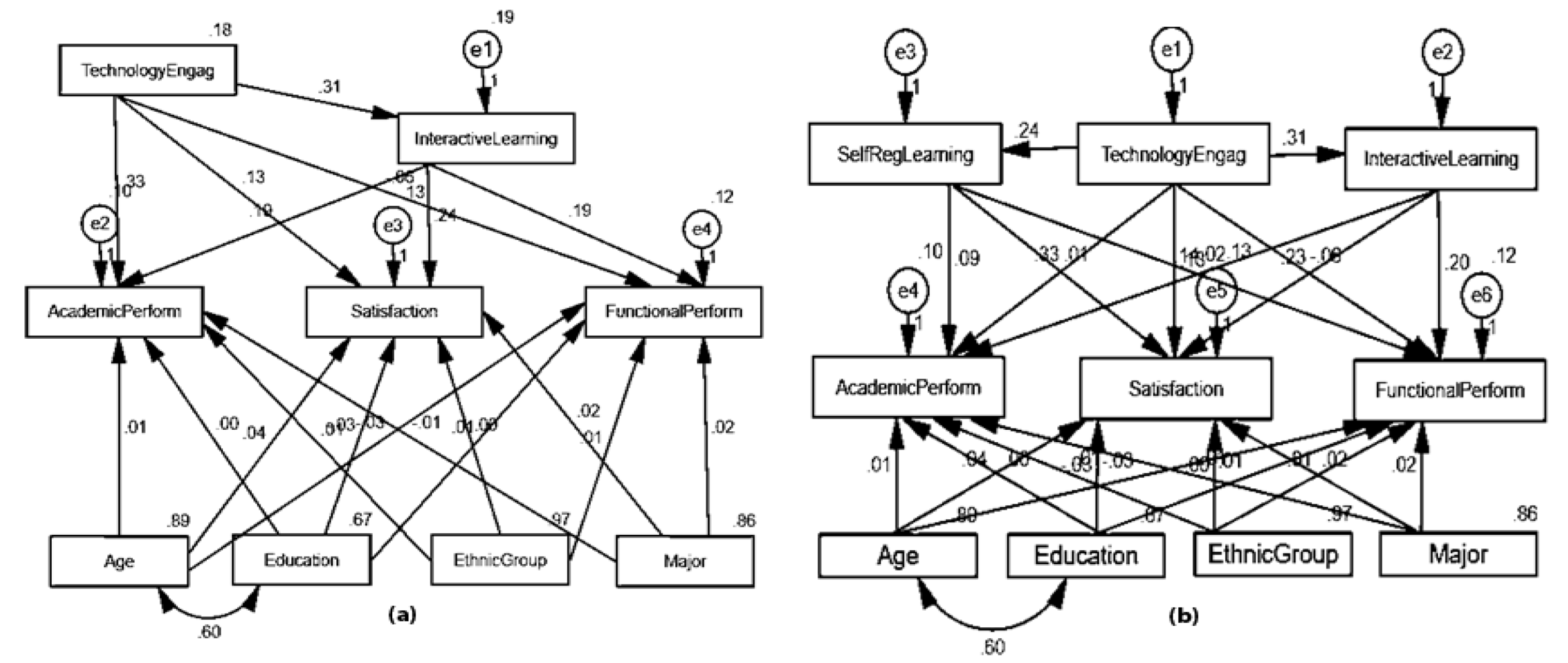
2.8. Structural Models
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Research
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blundell, C.N.; Lee, K.-T.; Nykvist, S. Digital Learning in Schools: Conceptualizing the Challenges and Influences on Teacher s. Practice. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2016, 15, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemmill, L.E.; Peterson, M.J. Technology use among college students: Implications for student affairs professionals. NASPA J. 2006, 43, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chukwuedo, S.O.; Ogbuanya, T.C. Potential pathways for proficiency training in computer maintenance technology among prospective electronic technology education graduates. Educ. Train. 2020, 62, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropley, A. Creativity-focused Technology Education in the Age of Industry 4.0. Creativity Res. J. 2020, 32, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Hassan, M. Science, An Interactive Learning Environment for Information and Communication Theory. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13, 35–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Claire, C.; Wei, C.; Richard, T.; Louise, Y.; Linda, S.; Feng, M. When adaptive learning is effective learning: Comparison of an adaptive learning system to teacher-led instruction. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Martine, B.; Dan, D.; Tim, V.D.Z.; Geert-Jan, H.; Fred, P. Supporting self-regulated learning in online learning environments and MOOCs: A systematic review. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2019, 35, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M. A theory for eLearning. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2003, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrab, M.; Laila, E.; Hamza, A. Mobile learning (m-learning) and educational environments. Int. J. Distrib. Parallel Syst. 2012, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minka, T.; Picard, R. Interactive learning with a “Society of Models”. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J. Do badges increase user activity? A field experiment on the effects of gamification. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 71, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.R. Blended learning systems. In The handbook of Blended Learning: Global Perspectives, Local Designs, 1; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jamei, E.; Mortimer, M.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Investigating the Role of Virtual Reality in Planning for Sustainable Smart Cities. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ejdys, J.; Halicka, K. Sustainable Adaptation of New Technology—The Case of Humanoids Used for the Care of Older Adults. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.F.; Skrbiš, Z. A social inequality of motivation? The relationship between beliefs about academic success and young people’s educational attainment. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2017, 43, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, Y.Y.; Hwang, Y. Predicting the use of web-based information systems: Self-efficacy, enjoyment, learning goal orientation, and the technology acceptance model. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 431–449. [Google Scholar]
- Schneberger, S.; Amoroso, D.L.; Durfee, A. Factors that influence the performance of computer-based assessments: An extension of the technology acceptance model. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2008, 48, 74–90. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, O.; Sanchez-Verdejo, F.J.; Anguita, J.M.; Gonzalez, A.L. Motivation of University Students Towards the Use of Information and Communication Technologies and Their Relation to Learning Styles. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, N.; Kapravelos, E.; Tsiatsos, T. Interaction Analysis for Supporting Students’ Self-Regulation during Blog-based CSCL Activities. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Weidlich, J.; Bastiaens, T.J. Technology Matters—The Impact of Transactional Distance on Satisfaction in Online Distance Learning. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Han, F.; Ellis, R.A. Combining University Student Self-Regulated Learning Indicators and Engagement with Online Learning Events to Predict Academic Performance. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2016, 10, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millsap, R.E.; Kwok, O.-M. Evaluating the Impact of Partial Factorial Invariance on Selection in Two Populations. Psychol. Methods 2004, 9, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, S.; Kishore, R.; Li, P. Within-study measurement invariance of the UTAUT instrument: An assessment with user technology engagement variables. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuegbuzie, A.; Collins, K. A Typology of Mixed Methods Sampling Designs in Social Science Research. Qual. Rep. 2015, 12, 281–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rast, P.; Zimprich, D.; Van Boxtel, M.; Jolles, J. Factor Structure and Measurement Invariance of the Cognitive Failures Questionnaire Across the Adult Life Span. Assessment 2009, 16, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plott, A.R. Web 2.0 in Blackboard learn: Mind the template. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual ACM SIGUCCS Fall Conference: Navigation and discovery, Norfolk, VA, USA, 24–27 October 2010; pp. 285–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yakubu, N.M.; Dasuki, S.I.J. Factors affecting the adoption of e-learning technologies among higher education students in Nigeria: A structural equation modelling approach. Inf. Dev. 2019, 35, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G.D. What We’re Learning About Student Engagement From NSSE: Benchmarks for Effective Educational Practices. Chang. Mag. High. Learn. 2003, 35, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrman, J.W. Keeping Their Attention: Innovative Strategies for Nursing Education. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2011, 42, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, K.M.; Shin, D. Student Satisfaction: An alternative approach to assessing this important concept. J. High. Educ. Policy Manag. 2002, 24, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.H.; Shafiq, M.; Berhanu, G. Factors affecting students’ quality of academic performance: A case of secondary school level. J. Qual. Technol. Manag. 2011, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, S.W.; Effgen, S.K.; Chiarello, L.A.; Jeffries, L.M.; Tezanos, A.V. School-based physical therapy services and student functional performance at school. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.R.; Graham, S. Programmatic Intervention Research: Illustrations from the Evolution of Self-Regulated Strategy Development. Learn. Disabil. Q. 1999, 22, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.A.; Campbell, M. Interactive learning in a multicultural setting. Christ. Educ. J. 2006, 3, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.J. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use and Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seck, A. International technology diffusion and economic growth: Explaining the spillover benefits to developing countries. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2012, 23, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.N.; Perez, C. Technological Revolutions and Financial Capital: The Dynamics of Bubbles and Golden Ages. Foreign Aff. 2003, 82, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, J. Comparing online and blended learner’s self-regulated learning strategies and academic performance. Internet High. Educ. 2017, 33, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, S.N.; Bohner, A.; Stumpp, J.; Limberger, M.F.; Gidion, G. Investigating and fostering self-regulated learning in higher education using interactive ambulatory assessment. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2019, 71, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxton, R.A. The role of interactivity in student satisfaction and persistence in online learning. J. Online Learn. Teach. 2014, 10, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Chavoshi, A.; Hamidi, H. Social, individual, technological and pedagogical factors influencing mobile learning acceptance in higher education: A case from Iran. Telematics Informatics 2019, 38, 133–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, T.; Kennedy, M. Technology Enhanced Learning in higher education; motivations, engagement and academic achievement. Comput. Educ. 2019, 137, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, A.C.; Winslow, A.B.; Bohmer, R.M.J.; Pisano, G.P. Learning How and Learning What: Effects of Tacit and Codified Knowledge on Performance Improvement Following Technology Adoption. Decis. Sci. 2003, 34, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-H.; Chang, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, Y.-S. Determinants of user acceptance of a specific social platform for older adults: An empirical examination of user interface characteristics and behavioral intention. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raman, A.; Thannimalai, R. Importance of Technology Leadership for Technology Integration: Gender and Professional Development Perspective. SAGE Open 2019, 9, 2158244019893707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Walker, A.E.; Schroder, K.E.; Belland, B.R. Interaction, Internet self-efficacy, and self-regulated learning as predictors of student satisfaction in online education courses. Internet High. Educ. 2014, 20, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Takada, J.-I. The Influence of Interactive Learning Materials on Self-Regulated Learning and Learning Satisfaction of Primary School Teachers in Mongolia. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillman, C.D.; Willis, D.J.; Gunawardena, C.N.J. Learner-interface interaction in distance education: An extension of medicontemporary models and strategies for practitioners. Am. J. Distance Educ. 1994, 8, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.; Ashley, M.; Brownell, S.E. Using Expectancy Value Theory as a Framework to Reduce Student Resistance to Active Learning: A Proof of Concept. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doménech-Betoret, F.; Abellán-Roselló, L.; Gómez-Artiga, A. Self-Efficacy, Satisfaction, and Academic Achievement: The Mediator Role of Students’ Expectancy-Value Beliefs. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Study Guide and Reference, 17.0 Update, 10/e; Pearson Education India: Noida, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-Reports in Organizational Research: Problems and Prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, A.; An, Z.Y.; Memon, M.Q. Does financial availability sustain financial, innovative, and environmental performance? Relation via opportunity recognition. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 27, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F.J. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashada, A.; Li, H.; Koshadah, O. Analysis Approach to Identify Factors Influencing Digital Learning Technology Adoption and Utilization in Developing Countries. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2018, 13, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, T.; Pilani, I.B.; Dosaya, D.; Nirban, V.S.; Vavilala, M.P. Factors Extraction of Effective Teaching-Learning in Online and Conventional Classrooms. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2020, 10, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, H.; Jahanshaheefard, M. Essential factors for the application of education information system using mobile learning: A case study of students of the university of technology. Telemat. Inform. 2019, 38, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrie, C.R.; Halverson, L.; Graham, C. Measuring student engagement in technology-mediated learning: A review. Comput. Educ. 2015, 90, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domina, T.; Renzulli, L.; Murray, B.; Garza, A.N.; Perez, L. Remote or Removed: Predicting Successful Engagement with Online Learning during COVID-19. Socius: Sociol. Res. a Dyn. World 2021, 7, 2378023120988200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TechnologyEngag | 302 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.5276 | 0.42375 | 0.188 | −0.198 |
| SelfRegLearning | 302 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.6464 | 0.44792 | −0.134 | −0.182 |
| InteractiveLearning | 302 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.6854 | 0.45305 | 0.057 | 0.125 |
| AcademicPerform | 302 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.1621 | 0.37378 | −0.068 | 1.602 |
| Satisfaction | 302 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 3.1530 | 0.39110 | 0.197 | −1.546 |
| FunctionalPerform | 302 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 3.14 | 0.35291 | −1.325 | 0.199 |
| Variables and Items | Estimates | Sum of Squared Loadings () | AVE | √AVE | CR | Cronbach α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| te1 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.801 *** | 3.534 | 0.589 | 0.767 | 0.895 | 0.899 |
| te2 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.675 *** | |||||
| te3 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.864 *** | |||||
| te4 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.707 *** | |||||
| te5 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.731 *** | |||||
| te6 | <--- | TechEngag | 0.81 *** | |||||
| srl1 | <--- | SelfRegLearn | 0.696 *** | 3.16 | 0.632 | 0.795 | 0.895 | 0.908 |
| srl2 | <--- | SelfRegLearn | 0.827 *** | |||||
| srl3 | <--- | SelfRegLearn | 0.845 *** | |||||
| srl4 | <--- | SelfRegLearn | 0.849 *** | |||||
| srl5 | <--- | SelfRegLearn | 0.745 *** | |||||
| il1 | <--- | InterLearn | 0.89 *** | 2.021 | 0.674 | 0.821 | 0.859 | 0.844 |
| il2 | <--- | InterLearn | 0.65 *** | |||||
| il3 | <--- | InterLearn | 0.898 *** | |||||
| ap1 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.69 *** | 3.208 | 0.534 | 0.731 | 0.873 | 0.877 |
| ap2 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.809 *** | |||||
| ap3 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.725 *** | |||||
| ap4 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.771 *** | |||||
| ap5 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.633 *** | |||||
| ap6 | <--- | AcadPerform | 0.746 *** | |||||
| sa1 | <--- | Satisfac | 0.57 *** | 2.686 | 0.537 | 0.733 | 0.8507 | 0.846 |
| sa2 | <--- | Satisfac | 0.739 *** | |||||
| sa3 | <--- | Satisfac | 0.872 *** | |||||
| sa4 | <--- | Satisfac | 0.698 *** | |||||
| sa5 | <--- | Satisfac | 0.753 *** | |||||
| fp1 | <--- | FuncPerform | 0.702 *** | 2.418 | 0.605 | 0.777 | 0.858 | 0.854 |
| fp2 | <--- | FuncPerform | 0.861 *** | |||||
| fp3 | <--- | FuncPerform | 0.683 *** | |||||
| fp4 | <--- | FuncPerform | 0.847 *** | |||||
| TechnologyEngag | SelfRegLearning | InteractiveLearning | AcademicPerform | Satisfaction | FunctionalPerform | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TechnologyEngag | 1 | |||||
| SelfRegLearning | 0.226 ** | 1 | ||||
| InteractiveLearning | 0.292 ** | 0.659 ** | 1 | |||
| AcademicPerform | 0.451 ** | 0.308 ** | 0.351 ** | 1 | ||
| Satisfaction | 0.217 ** | 0.218 ** | 0.320 ** | 0.091 | 1 | |
| FunctionalPerform | −0.008 | 0.119 * | 0.211 ** | 0.061 | −0.037 | 1 |
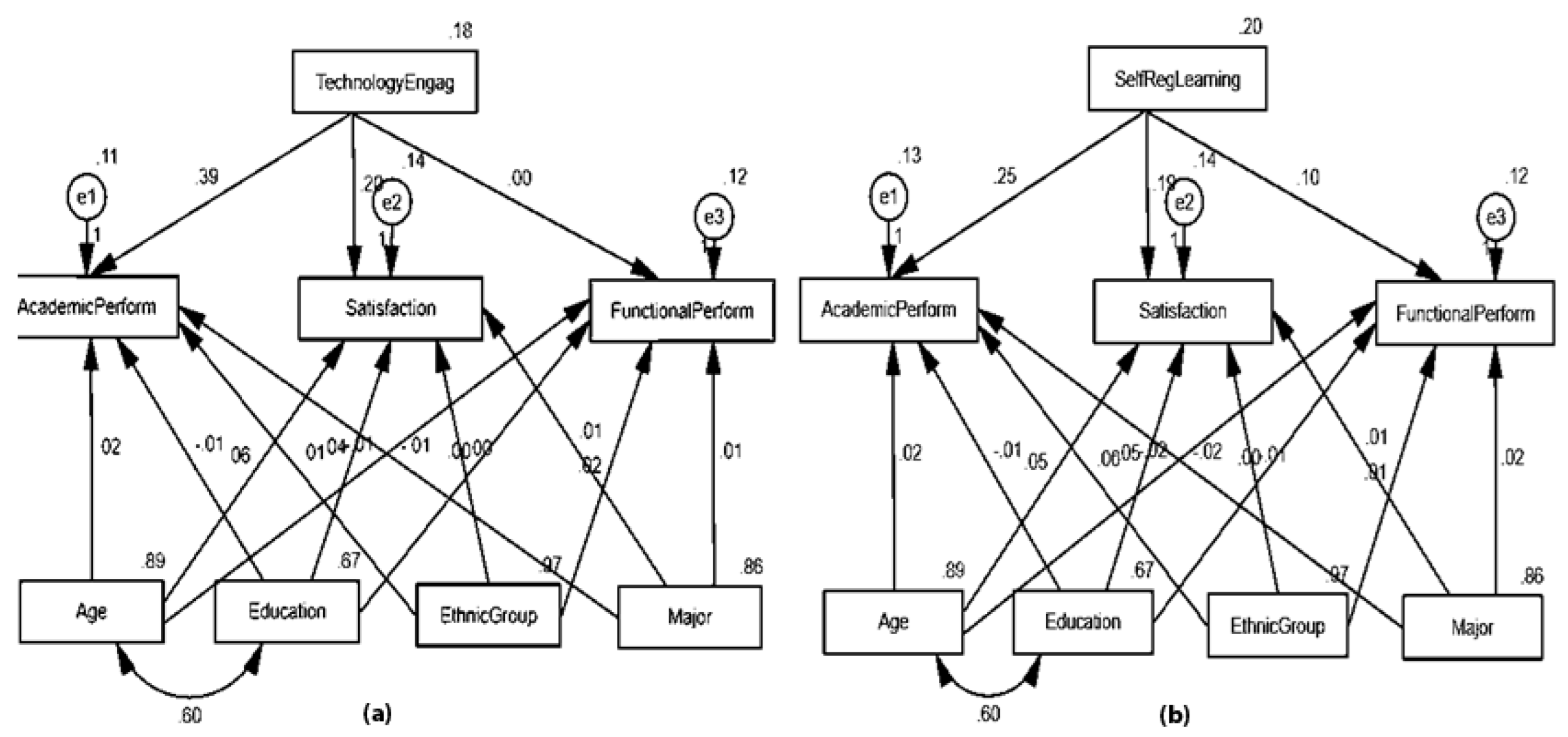
| Structure Model 1 | Estimate | C.R. | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction | <--- | Education | −0.042 | −0.994 | 0.320 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.002 | 0.071 | 0.943 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Education | −0.008 | −0.210 | 0.833 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.011 | 0.544 | 0.586 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Major | −0.011 | −0.554 | 0.580 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Major | 0.014 | 0.626 | 0.532 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.015 | 0.747 | 0.455 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Age | 0.055 | 1.489 | 0.136 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Age | −0.013 | −0.379 | 0.704 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Major | 0.012 | 0.518 | 0.604 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Education | −0.001 | −0.023 | 0.982 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Age | 0.021 | 0.643 | 0.521 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.199 | 3.839 | *** |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.000 | −0.005 | 0.996 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.393 | 8.687 | *** |
| Structure Model 2 | Estimate | C.R. | P | ||
| Satisfaction | <--- | Education | −0.046 | −1.078 | 0.281 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.007 | −0.296 | 0.768 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Education | −0.013 | −0.324 | 0.746 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.004 | −0.192 | 0.848 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Major | −0.015 | −0.694 | 0.488 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Major | 0.018 | 0.841 | 0.400 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.014 | 0.689 | 0.491 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Age | 0.053 | 1.438 | 0.151 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Age | −0.019 | −0.548 | 0.583 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Major | 0.013 | 0.550 | 0.582 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Education | −0.003 | −0.068 | 0.946 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Age | 0.024 | 0.687 | 0.492 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.187 | 3.828 | *** |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.104 | 2.319 | 0.020 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.248 | 5.436 | *** |
| Structure Model 3 | Estimate | C.R. | P | ||
| Satisfaction | <--- | Education | −0.028 | −0.685 | 0.493 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.006 | −0.277 | 0.782 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Education | 0.006 | 0.161 | 0.872 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.003 | −0.132 | 0.895 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Major | −0.019 | −0.872 | 0.383 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Major | 0.018 | 0.848 | 0.396 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.014 | 0.709 | 0.478 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Age | 0.040 | 1.098 | 0.272 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Age | −0.028 | −0.841 | 0.400 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Major | 0.012 | 0.513 | 0.608 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Education | 0.008 | 0.213 | 0.831 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Age | 0.012 | 0.364 | 0.716 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.272 | 5.782 | *** |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.172 | 3.942 | *** |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.283 | 6.367 | *** |
| Structure Model 4 | Estimate | CR | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SelfRegLearning | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.239 | 4.026 | *** |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Education | −0.045 | −1.074 | 0.283 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.001 | −0.063 | 0.950 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Education | −0.011 | −0.301 | 0.764 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.007 | 0.380 | 0.704 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Major | −0.005 | −0.258 | 0.797 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Major | 0.017 | 0.809 | 0.418 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.013 | 0.651 | 0.515 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Age | 0.048 | 1.323 | 0.186 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Age | −0.018 | −0.527 | 0.598 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Major | 0.018 | 0.761 | 0.447 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Education | −0.003 | −0.072 | 0.943 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Age | 0.013 | 0.408 | 0.683 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.165 | 3.147 | 0.002 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | −0.024 | −0.499 | 0.618 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.354 | 7.829 | *** |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.177 | 4.132 | *** |
| Satisfaction | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.154 | 3.118 | 0.002 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | SelfRegLearning | 0.109 | 2.366 | 0.018 |
| Structure Model 5 | Estimate | CR | P | ||
| InteractiveLearning | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.313 | 5.306 | *** |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Education | −0.030 | −0.729 | 0.466 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | EthnicGroup | −0.002 | −0.098 | 0.922 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Education | 0.002 | 0.064 | 0.949 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.008 | 0.403 | 0.687 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Major | −0.009 | −0.434 | 0.664 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Major | 0.016 | 0.768 | 0.442 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | EthnicGroup | 0.012 | 0.623 | 0.533 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Age | 0.037 | 1.044 | 0.296 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Age | −0.027 | −0.812 | 0.417 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | Major | 0.016 | 0.688 | 0.492 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | Education | 0.009 | 0.232 | 0.817 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | Age | 0.006 | 0.200 | 0.842 |
| Satisfaction | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.126 | 2.427 | 0.015 |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | −0.057 | −1.169 | 0.242 |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | TechnologyEngag | 0.334 | 7.300 | *** |
| AcademicPerform | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.194 | 4.522 | *** |
| Satisfaction | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.238 | 4.892 | *** |
| FunctionalPerform | <--- | InteractiveLearning | 0.188 | 4.111 | *** |
| Hypothesis | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction | ← | Technology engagement | 0.137 (0.019) | 0.081(0.000) | 0.218 (0.001) |
| Academic performance | ← | Technology engagement | 0.381 (0.001) | 0.074(0.000) | 0.455 (0.001) |
| Functional performance | ← | Technology engagement | −0.068 (0.247) | 0.069(0.000) | 0.002 (0.991) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Self-regulated learning | 0.006 (0.871) | - | 0.006 (0.871) |
| Academic performance | ← | Self-regulated learning | 0.110 (0.049) | - | 0.110 (0.049) |
| Functional performance | ← | Self-regulated learning | −0.020 (0.773) | - | −0.020 (0.773) |
| Academic performance | ← | Interactive learning | 0.168 (0.022) | - | 0.168 (0.022) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Interactive learning | 0.273 (0.004) | - | 0.273 (0.004) |
| Functional performance | ← | Interactive learning | 0.253 (0.002) | - | 0.253 (0.002) |
| Academic performance | ← | Age | 0.017 (0.883) | - | 0.017 (0.883) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Age | 0.090 (0.424) | - | 0.090 (0.424) |
| Functional performance | ← | Age | −0.072 (0.411) | - | −0.072 (0.411) |
| Academic performance | ← | Education | −0.005 (0.968) | - | −0.005 (0.968) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Education | −0.064 (0.545) | - | −0.064 (0.545) |
| Functional performance | ← | Education | 0.023 (0.771) | - | 0.023 (0.771) |
| Academic performance | ← | Ethnic group | 0.018 (0.740) | - | 0.018 (0.740) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Ethnic group | −0.005 (0.934) | - | −0.005 (0.934) |
| Functional performance | ← | Ethnic group | 0.035 (0.613) | - | 0.035 (0.613) |
| Academic performance | ← | Major | −0.016 (0.739) | - | −0.016 (0.739) |
| Satisfaction | ← | Major | 0.038 (0.440) | - | 0.038 (0.440) |
| Functional performance | ← | Major | 0.042 (0.515) | - | 0.042 (0.515) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Memon, M.Q.; Lu, Y.; Memon, A.R.; Memon, A.; Munshi, P.; Shah, S.F.A. Does the Impact of Technology Sustain Students’ Satisfaction, Academic and Functional Performance: An Analysis via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning? Sustainability 2022, 14, 7226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127226
Memon MQ, Lu Y, Memon AR, Memon A, Munshi P, Shah SFA. Does the Impact of Technology Sustain Students’ Satisfaction, Academic and Functional Performance: An Analysis via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning? Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127226
Chicago/Turabian StyleMemon, Muhammad Qasim, Yu Lu, Abdul Rehman Memon, Aasma Memon, Parveen Munshi, and Syed Farman Ali Shah. 2022. "Does the Impact of Technology Sustain Students’ Satisfaction, Academic and Functional Performance: An Analysis via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning?" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127226
APA StyleMemon, M. Q., Lu, Y., Memon, A. R., Memon, A., Munshi, P., & Shah, S. F. A. (2022). Does the Impact of Technology Sustain Students’ Satisfaction, Academic and Functional Performance: An Analysis via Interactive and Self-Regulated Learning? Sustainability, 14(12), 7226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127226






