Regional Differences, Distribution Dynamics, and Convergence of Air Quality in Urban Agglomerations in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Dagum’s Decomposition of the Gini Coefficient
2.1.2. Kernel Density Estimation
2.1.3. Convergence Model
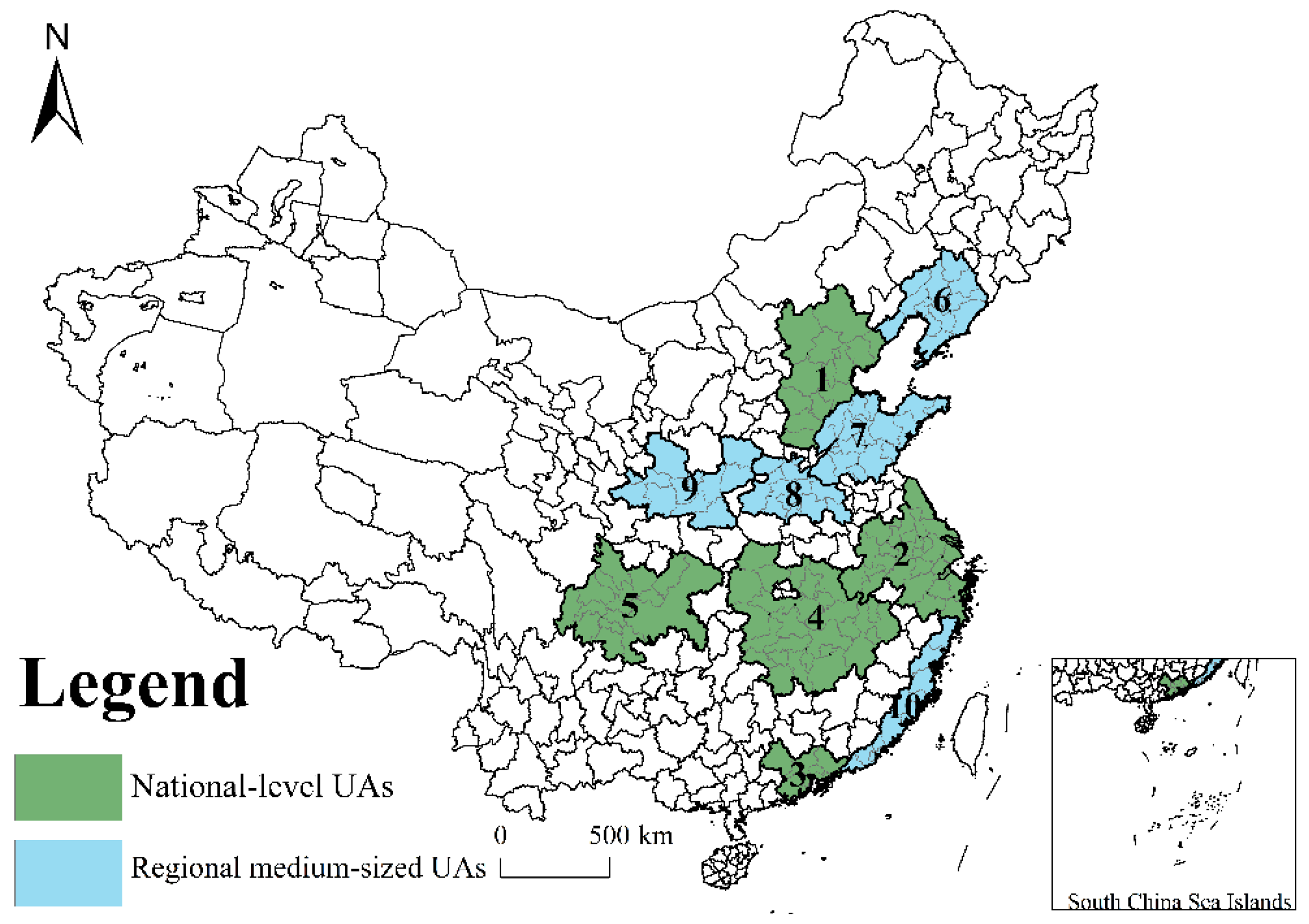
2.2. Data Source
3. Results
3.1. AQI
3.2. Regional Differences and Decomposition of Air Quality
3.2.1. Differences in Air Quality within UAs
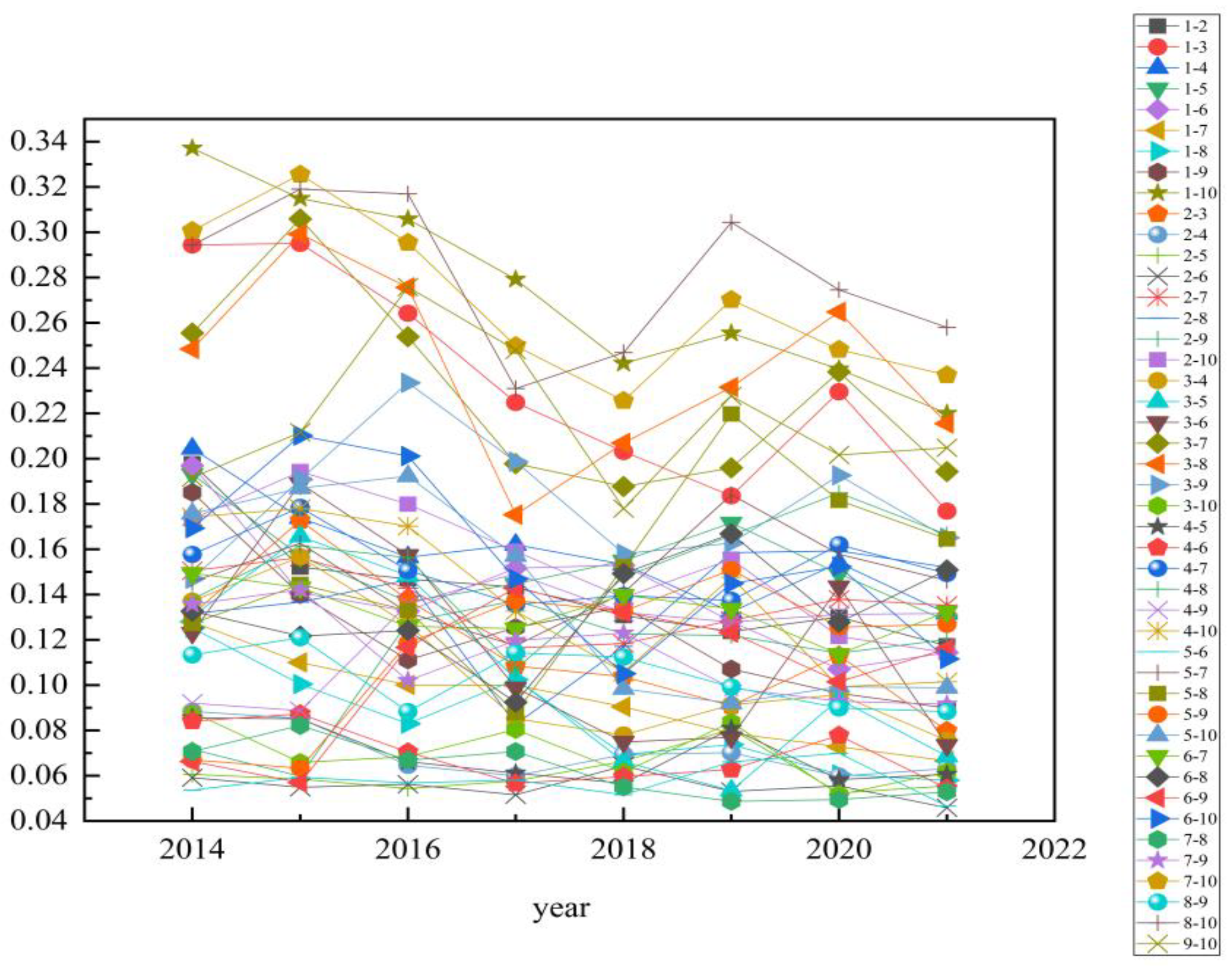
3.2.2. Differences in Air Quality between UAs
3.2.3. Overall Difference and Decomposition of Air Quality
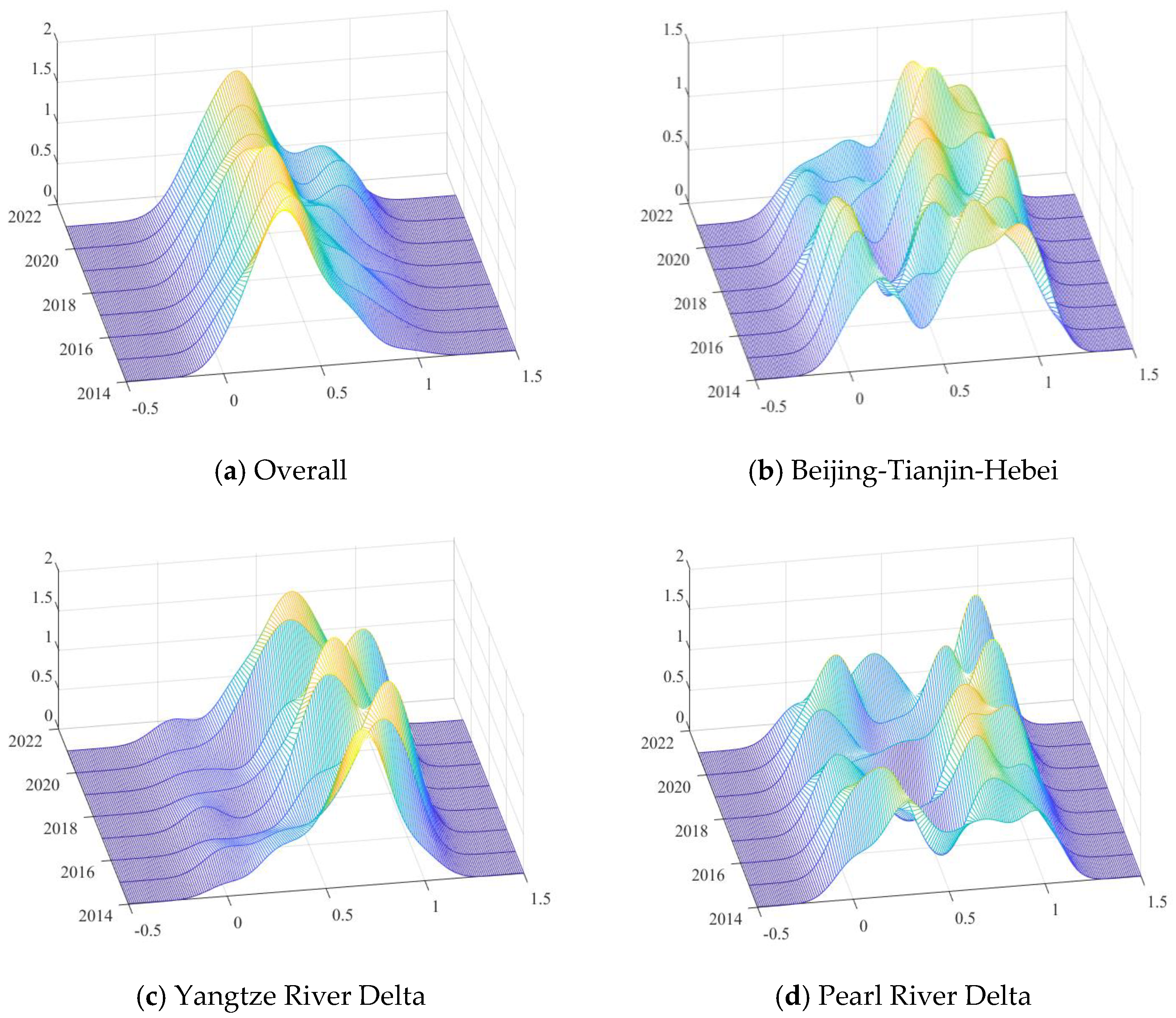
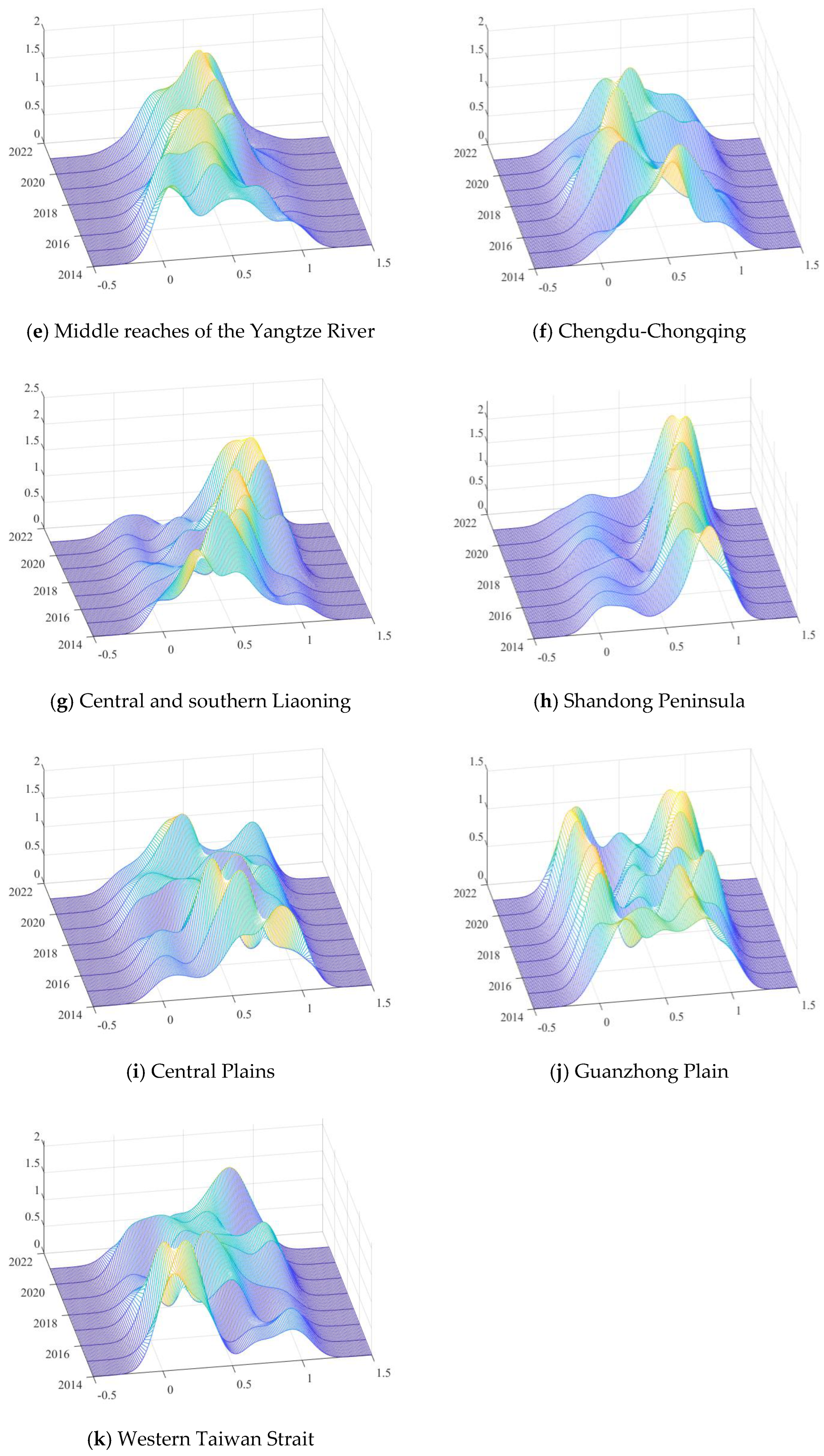
3.3. Distribution Dynamics of Air Quality
3.4. Convergence Analysis of Air Quality
3.4.1. σ-Convergence
3.4.2. β-Convergence
- (1)
- Absolute β-Convergence
- (2)
- Conditional -Convergence
3.4.3. Club Convergence
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, S.Q. Applying the Super-EBM model and spatial Durbin model to examining total-factor ecological efficiency from a multi-dimensional perspective: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2183–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.G.; Hu, T.Y.; Shen, R.J. Evaluating public participation impact on environmental protection and ecological efficiency in China: Evidence from PITI disclosure. China Econ. Rev. 2019, 55, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y. Applying a data envelopment analysis game cross-efficiency model to examining regional ecological efficiency: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.K. Air Pollution, Government regulations and high-quality economic development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Shi, X.Y.; Pan, C.H.; Wang, S.S. Spatial and temporal characteristics of environmental air Quality and its relationship with seasonal climatic conditions in Eastern China during 2015–2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandh, S.A.; Shafi, S.; Peerzada, M.; Rehman, T.; Bashir, S.; Wani, S.A.; Dar, R. Multidimensional analysis of global climate change: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24872–24888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Lin, Z.L.; Liu, L.M.; Liu, L.M.; Qi, J.L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of urban air pollution in 337 Chinese cities and their influencing factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36234–36258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Xu, B.; Shen, N.; He, Q. The adverse impact of air pollution on China’s economic growth. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.L.; Liang, L.T.; Li, M.M. Analysis of temporal and spatial patterns of PM2.5 in Prefecture-Level Cities of China from 1998 to 2016. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.H. Spatio-temporal pattern changes of ambient air PM10 pollution in China from 2002 to 2012. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.J.; Zhou, J.X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, T.M.; Chen, T.T.; Zhong, Q.J.; Yuan, D.; Chen, P.Y.; Ou, C.Q. Spatiotemporal pattern of air quality index and its associated factors in 31 Chinese provincial capital cities. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tui, Y.; Qiu, J.X.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.S. Analysis of spatio-temporal variation characteristics of main air pollutants in Shijiazhuang City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, T.; Morse, S.; Murphy, R. Spatial analysis of air quality assessment in two cities in nigeria: A comparison of perceptions with instrument-based methods. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Q.; Wang, D. Spatio-temporal variations and socio-economic driving forces of air quality in Chinese cities. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Liu, K.; Zhou, L. Spatio-temporal trends and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentrations in urban agglomerations in China between 2000 and 2016. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 10988–11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platikanov, S.; Terrado, M.; Pay, M.T.; Soret, A.; Tauler, R. Understanding temporal and spatial changes of O3 or NO2 concentrations combining multivariate data analysis methods and air quality transport models. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Ganguly, R.; Harbin, P. High resolution spatial and temporal mapping of traffic-related air pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3646–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendez-Espinosa, J.F.; Rojas, N.F.; Vargas, J.; Pachón, J.E.; Belalcazar, L.C.; Ramírez, O. Air quality variations in Northern South America during the COVID-19 lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Fang, C.L.; Huang, J.J.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, Q. The spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D.W.; Sun, F.; Pan, L.B. Spatial-temporal characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing in 2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.Y.; Huang, G.C.; Zhou, H.; Duan, W.S.; Wu, A.A.; Wang, W.J.; Li, T. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and factors of particulate matter concentration in North China. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowosegbe, O.O.; Röösli, M.; Adebayo-Ojo, T.C.; Dalvie, M.A.; Hoogh, K. Spatial and temporal variations in PM10 concentrations between 2010–2017 in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsani, M.H.; Shirmardi, M.; Alavi, N.; Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Babaei, A.; Asgharnia, H.; Marzouni, M.B.; Goudarzi, G. Evaluation of the relationship between PM10 concentrations and heavy metals during normal and dusty days in Ahvaz, Iran. Aeolian Res. 2018, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Y.; Suh, D.H.; Joo, S. Dynamic analysis of air pollution: Implications of economic growth and renewable energy consumption. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Ren, B.H. Spatiotemporal pattern of fine particulate matter and impact of urban socioeconomic factors in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, B.; Ni, Z.Y.; Zhao, L.Y.; Liu, K. Does rural-urban income gap exacerbate or restrain air pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S.; Coondoo, D.; Pal, M. Air quality and economic growth: An empirical study. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 34, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Dong, S.C.; Song, J.F. Modeling economic growth and environmental degradation of Beijing. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xie, R.; Liu, Y. Analysis of driving factors on China’s air pollution emissions from the view of critical supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Mi, K.N. Energy consumption, structural changes and air quality: Empirical test based on inter-provincial panel data. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yu, W.; Wu, S. The impact of the dynamics of agglomeration externalities on air pollution: Evidence from urban panel data in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.M.; Zhang, X. The spatial effect of China’s haze pollution and the impact from economic change and energy structure. China Ind. Econ. 2014, 4, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, D.Q.; Zhong, Z.Q. A study of the influence of regional environmental expenditure on air quality in China: The effectiveness of environmental policy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7454–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Shackman, J.; Liu, X. Impact of income inequality on urban air quality: A game theoretical and empirical study in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Xu, X.D.; Zhang, W. The impacts of urbanization on air quality over the Pearl River Delta in winter: Roles of urban land use and emission distribution. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, J.M.; Coelho, M.C.; Sá, M.E.; Tavares, R.; Borrego, C. Impact of land use on urban mobility patterns, emissions and air quality in a Portuguese medium-sized city. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.W.; Luo, Y.; Yao, X. The effects of transportation infrastructure on air quality: Evidence from empirical analysis in China. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 54, 136–151. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.; Lai, K.K.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.B.; Zhang, W.L. The impact of urban transportation infrastructure on air quality. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.J.; Song, L.; Gao, B.Y.; Jiang, L. Industrial land transfer, industrial selection and urban air quality. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lan, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, J. Haze pollution levels, spatial spillover influence, and impacts of the digital economy: Empirical evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, H.F.; Bai, L. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Impacts of Foreign Direct Investment on Air Pollution: Empirical Evidence from 150 Cities in China Based on AQI. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Ogawa, S. Effects of Meteorological Conditions on PM2.5 Concentrations in Nagasaki, Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9089–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhao, X.W.; Ji, J.H.; Yang, S.Z. Variation of air quality index and its relationship with meteorological elements in Beijing from 2012 to 2015. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, T. Characteristics of air quality index and its relationship with meteorological factors in key cities of Heilongjiang Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Du, H.D.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Zhou, Z.M.; Russo, A.; Xi, H.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhou, C.J. Prediction of the impact of meteorological conditions on air quality during the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiziano, T.; Umberto, R. An analytical air pollution model for complex terrain. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S.; Dou, W. Environmental effects of prohibiting urban fireworks and firecrackers in Jinan, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Shi, Y. Urban spatial structural options for air pollution control in China: Evidence from provincial and municipal levels. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleluia, R.; Drouet, L.; Dingenen, R.; Emmerling, J. Future global air quality indices under different socioeconomic and climate assumptions. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.H.; Tian, P.L.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.J. Effect of urban greening on air quality: Take 27 provincial capitals in China as an example. Bull. Bot. Res. 2019, 39, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irga, P.J.; Burchett, M.D.; Torpy, F.R. Does urban forestry have a quantitative effect on ambient air quality in an urban environment? Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, H.F.; Chen, Z.S. Spatio-temporal characteristics of air quality index and its driving factors in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: An empirical study based on bayesian spatial econometric model. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 2100–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Bash, J.O.; Roselle, S.J.; Shatas, A.; Repinsky, A.; Mathur, R.; Hogrefe, C.; Piziali, J.; Jacobs, T.; Gilliland, A. Unexpected air quality impacts from implementation of green infrastructure in urban environments: A Kansas City case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.X.; Xia, M. Simulation of the impact of urban forest scale on PM2.5 and PM10 based on system dynamics. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagum, C. A new approach to the decomposition of the Gini income inequality ratio. Empir. Econ. 1997, 22, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.H.; Lan, L.Y.; Liang, L.W.; Liu, Y.B.; Xu, X.Y. Spatiotemporal differences and dynamic evolution of PM2.5 pollution in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nan, Z.; Shen, B.G. The over polluted water quality assessment of Weihe River based on Kernel Density Estimation. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.B. Assessing urban atmospheric environmental efficiency and factors influencing it in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, E.; Ren, L.; Sun, H.Y. Evaluation of variations and affecting factors of eco-environmental quality during urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhao, J.; Qi, M.Q.; Chen, F.R. The effect of socioeconomic factors on spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 concentration in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and surrounding areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.H.; Yang, F.; Che, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, D.Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and the influencing factors of PM2.5 in China between 2000 and 2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.F.; Guo, Q.C.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, H. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of air pollution and influencing factors in Hebei province. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.C.; Yuan, Z. China’s Top Ten Urban Agglomerations; Economic Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdani, M.; Baboli, Z.; Maleki, H.; Birgani, Y.T.; Zahiri, M.; Chaharmahal, S.S.H.; Goudarzi, M.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Alam, K.; Sorooshian, A.; et al. Contrasting Iran’s air quality improvement during COVID-19 with other global cities. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Designation | Definition/Unit | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | Population | Resident population/10,000 | 560.3802 | 434.8196 | 3212.43 | 68.93 | 1256 |
| X2 | Technological progress | Science and technology expenditure/CNY 100 million | 23.0596 | 57.56474 | 554.98 | 0.0786 | 1256 |
| X3 | Government financial resources | Financial revenue/CNY 100 million | 411.1661 | 796.1389 | 7771.8 | 20.06 | 1256 |
| X4 | Economic development | GDP per capita/CNY | 65,493.46 | 33,805.19 | 19,1942 | 15,852 | 1256 |
| X5 | Industrial structure | The share of secondary industry in GDP/% | 44.45925 | 8.29326 | 81.13335 | 15.83376 | 1256 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | 128 | 111 | 108 | 109 | 93 | 97 | 88 | 85 | 102 |
| Yangtze River Delta | 89 | 86 | 82 | 85 | 74 | 78 | 69 | 68 | 79 |
| Pearl River Delta | 70 | 61 | 63 | 69 | 62 | 67 | 55 | 60 | 63 |
| The middle reaches of the Yangtze River | 89 | 82 | 81 | 80 | 70 | 77 | 65 | 66 | 76 |
| Chengdu-Chongqing | 90 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 69 | 69 | 66 | 66 | 77 |
| Central and southern Liaoning | 89 | 89 | 86 | 83 | 70 | 77 | 73 | 68 | 79 |
| Shandong Peninsula | 118 | 114 | 105 | 102 | 90 | 100 | 89 | 89 | 101 |
| Central Plains | 116 | 112 | 110 | 98 | 94 | 108 | 95 | 93 | 103 |
| Guanzhong Plain | 93 | 89 | 101 | 102 | 79 | 91 | 81 | 83 | 90 |
| Western Taiwan Strait | 63 | 58 | 57 | 61 | 57 | 57 | 54 | 55 | 58 |
| Year | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | Yangtze River Delta | Pearl River Delta | Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River | Chengdu-Chongqing | Central and Southern Liaoning | Shandong Peninsula | Central Plains | Guanzhong Plain | Western Taiwan Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.1387 | 0.0638 | 0.0809 | 0.1019 | 0.0554 | 0.0495 | 0.0811 | 0.0423 | 0.0716 | 0.0674 |
| 2015 | 0.1193 | 0.0542 | 0.0549 | 0.1010 | 0.0596 | 0.0518 | 0.0944 | 0.0604 | 0.0585 | 0.0654 |
| 2016 | 0.1044 | 0.0504 | 0.0530 | 0.0707 | 0.0531 | 0.0549 | 0.0859 | 0.0387 | 0.1082 | 0.0544 |
| 2017 | 0.1042 | 0.0500 | 0.0643 | 0.0559 | 0.0596 | 0.0495 | 0.0729 | 0.0454 | 0.1354 | 0.0467 |
| 2018 | 0.0938 | 0.0597 | 0.0549 | 0.0636 | 0.0449 | 0.0516 | 0.0783 | 0.0181 | 0.1380 | 0.0365 |
| 2019 | 0.0891 | 0.0584 | 0.0564 | 0.0774 | 0.0453 | 0.0412 | 0.0581 | 0.0241 | 0.1140 | 0.0287 |
| 2020 | 0.0770 | 0.0458 | 0.0595 | 0.0634 | 0.0502 | 0.0440 | 0.0622 | 0.0253 | 0.1007 | 0.0307 |
| 2021 | 0.0627 | 0.0551 | 0.0531 | 0.0672 | 0.0513 | 0.0330 | 0.0630 | 0.0341 | 0.1043 | 0.0381 |
| Mean | 0.0986 | 0.0547 | 0.0596 | 0.0751 | 0.0524 | 0.0469 | 0.0745 | 0.0360 | 0.1038 | 0.0460 |
| Year | Overall | Intra-Regional | Inter-Regional | Intensity of Transvariation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Contribution Rate (%) | Source | Contribution Rate (%) | Source | Contribution Rate (%) | ||
| 2014 | 0.1332 | 0.0091 | 6.8943 | 0.0944 | 71.4669 | 0.0286 | 21.6388 |
| 2015 | 0.1338 | 0.0089 | 6.6828 | 0.0990 | 74.5721 | 0.0249 | 18.7451 |
| 2016 | 0.1251 | 0.0076 | 6.0876 | 0.0953 | 76.5557 | 0.0216 | 17.3567 |
| 2017 | 0.1121 | 0.0072 | 6.4924 | 0.0812 | 72.9369 | 0.0229 | 20.5708 |
| 2018 | 0.1116 | 0.0072 | 6.5502 | 0.0803 | 72.6891 | 0.0229 | 20.7608 |
| 2019 | 0.1189 | 0.0071 | 6.0404 | 0.0932 | 78.9577 | 0.0177 | 15.0020 |
| 2020 | 0.1151 | 0.0063 | 5.5079 | 0.0942 | 82.3444 | 0.0139 | 12.1477 |
| 2021 | 0.1077 | 0.0066 | 6.1811 | 0.0840 | 78.4823 | 0.0164 | 15.3366 |
| Mean | 0.1197 | 0.0075 | 6.3046 | 0.0902 | 76.0006 | 0.0211 | 17.6948 |
| Year | Overall | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | Yangtze River Delta | Pearl River Delta | The Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River | Chengdu-Chongqing | Central and Southern Liaoning | Shandong Peninsula | Central Plains | Guanzhong Plain | Western Taiwan Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.2415 | 0.2562 | 0.1192 | 0.1505 | 0.1825 | 0.1023 | 0.0926 | 0.1585 | 0.0801 | 0.1312 | 0.1327 |
| 2015 | 0.2394 | 0.2196 | 0.1021 | 0.1038 | 0.1803 | 0.1111 | 0.1000 | 0.1769 | 0.1156 | 0.1073 | 0.1314 |
| 2016 | 0.2221 | 0.1926 | 0.0975 | 0.1002 | 0.1292 | 0.0985 | 0.1025 | 0.1669 | 0.0731 | 0.2019 | 0.1049 |
| 2017 | 0.2033 | 0.1936 | 0.0958 | 0.1250 | 0.1037 | 0.1114 | 0.0964 | 0.1471 | 0.0860 | 0.2517 | 0.0884 |
| 2018 | 0.1981 | 0.1739 | 0.1144 | 0.1035 | 0.1148 | 0.0853 | 0.0989 | 0.1522 | 0.0331 | 0.2571 | 0.0677 |
| 2019 | 0.2102 | 0.1644 | 0.1114 | 0.1087 | 0.1403 | 0.0825 | 0.0804 | 0.1165 | 0.0438 | 0.2146 | 0.0533 |
| 2020 | 0.2044 | 0.1444 | 0.0840 | 0.1130 | 0.1185 | 0.0922 | 0.0878 | 0.1281 | 0.0471 | 0.1905 | 0.0571 |
| 2021 | 0.1919 | 0.1158 | 0.1020 | 0.1013 | 0.1212 | 0.0929 | 0.0657 | 0.1220 | 0.0623 | 0.1926 | 0.0727 |
| Area | Overall | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | Yangtze River Delta | Pearl River Delta | The Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River | Chengdu-Chongqing | Central and Southern Liaoning | Shandong Peninsula | Central Plains | Guan-Zhong Plain | Western Taiwan Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Two-way fixed SDM | Two-way fixed OLS | Two-way fixed SAR | Two-way fixed OLS | Two-way fixed SDM | Two-way fixed OLS | Two-way fixed SAR | Two-way fixed OLS | Two-way fixed OLS | Two-way fixed SEM | Two-way fixed SAR |
| −0.6836 *** (−26.29) | −0.3396 *** (−5.31) | −0.6685 *** (−11.49) | −1.0544 *** (−8.83) | −0.7488 *** (−14.22) | −0.2769 *** (−4.48) | −0.8017 *** (−10.15) | −0.4120 *** (−5.90) | −0.6237 *** (−6.31) | −0.5600 *** (−6.25) | −0.6182 *** (−6.56) | |
| 0.3602 *** (8.60) | 0.5511 *** (5.55) | ||||||||||
| or | 0.4251 *** (14.26) | 0.4465 *** (6.67) | 0.4797 *** (6.56) | −0.2383 ** (−2.17) | 0.2631 * (1.87) | −0.2156 ** (−2.28) | |||||
| R2 | 0.2780 | 0.2677 | 0.1432 | 0.5954 | 0.3149 | 0.1742 | 0.1945 | 0.2562 | 0.3408 | 0.3961 | 0.4270 |
| Log-L | 1754.4811 | 365.5720 | 364.5399 | 192.8965 | 115.7514 | 133.9820 | |||||
| Space fixed effect | 257.97 *** | 52.64 *** | 113.70 *** | 45.53 *** | 52.46 *** | 42.52 *** | 117.55 *** | 58.27 *** | 34.40 *** | 33.13 *** | 43.54 *** |
| Time fixed effect | 520.53 *** | 22.63 *** | 99.68 *** | 35.97 *** | 116.56 *** | 45.03 *** | 67.93 *** | 33.85 *** | 21.88 *** | 35.89 *** | 23.65 *** |
| Hausman test | 141.00 *** | 8.72 *** | 119.96 *** | 25.79 *** | 22.66 *** | 5.78 ** | 111.93 *** | 18.88 *** | 9.61 ** | 46.11 *** | 16.45 *** |
| LM (SAR) | 788.946 *** | 52.436 *** | 229.000 *** | 52.867 *** | 197.990 *** | 97.714 *** | 71.577 *** | 109.267 *** | 52.647 *** | 63.4000 *** | 8.386 *** |
| R-LM (SAR) | 0.274 | 2.040 | 0.100 | 13.129 *** | 0.282 | 0.202 | 0.140 | 0.053 | 0.216 | 2.634 | 1.433 |
| LM (SEM) | 825.689 *** | 51.994 *** | 237.974 *** | 40.230 *** | 214.203 *** | 104.723 *** | 77.903 *** | 110.588 *** | 60.323 *** | 60.781 *** | 6.984 *** |
| R-LM (SEM) | 37.016 *** | 1.598 | 9.074 ** | 0.492 | 16.495 *** | 7.212 *** | 6.466 ** | 1.375 | 7.891 *** | 0.015 | 0.031 |
| Area | Overall | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | Yangtze River Delta | Pearl River Delta | The Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River | Chengdu-Chongqing | Central and Southern Liaoning | Shandong Peninsula | Central Plains | Guanzhong Plain | Western Taiwan Strait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.8172 *** (−26.92) | −0.8026 *** (−7.86) | −1.0159 *** (−12.85) | −1.1815 *** (−9.65) | −1.0406 *** (−14.69) | −0.9857 *** (−9.44) | −0.6289 *** (−6.24) | −0.8213 *** (−8.31) | −0.9052 *** (−7.64) | −0.9685 *** (−7.39) | −0.8641 *** (−7.24) | |
| X1 | −0.0691 (−1.06) | 0.0398 * (0.14) | −0.3591 *** (−3.57) | −0.2754 (−0.78) | −0.3830 * (−1.76) | 0.0771 (0.32) | 0.3026 (1.31) | −0.1425 (−0.49) | −0.4329 (−1.22) | 0.0365 (0.12) | 0.3157 (0.80) |
| X2 | 0.0097 (1.28) | −0.0413 (−1.37) | 0.0281 (0.84) | 0.0688 (1.40) | −0.0290 (−1.27) | −0.0397 * (−1.86) | 0.0308 * (−0.92) | 0.0126 (0.52) | 0.0069 (0.18) | −0.0064 (−0.14) | −0.0265 (−1.32) |
| X3 | −0.0344 (−1.44) | −0.1009 (−1.23) | −0.1551 ** (−2.47) | 0.0478 (0.33) | 0.1415 *** (2.69) | −0.0158 (−0.13) | −0.0502 (−0.92) | −0.2694 * (−1.89) | −0.0921 (−0.50) | 0.0324 (0.28) | −0.0979 (−0.96) |
| X4 | −0.2050 *** (−8.32) | −0.1186 (−1.19) | −0.3206 *** (−6.22) | −0.3020 * (−1.79) | −0.3785 *** (−5.81) | −0.3991 *** (−3.49) | −0.0209 (−0.23) | −0.0983 (−1.30) | −0.1807 (−0.99) | −0.3080 ** (−2.26) | −0.0129 (−0.16) |
| X5 | 0.3617 *** (10.88) | 0.3079 *** (3.36) | 0.2050 ** (2.09) | 0.3428 (0.97) | 0.2310 ** (2.13) | 0.2527 (1.55) | 0.2504 *** (2.97) | 0.3874 *** (4.10) | 0.0051 (0.03) | 0.1234 (0.66) | 0.0826 (0.47) |
| R2 | 0.4386 | 0.4852 | 0.5270 | 0.6640 | 0.5802 | 0.5078 | 0.3816 | 0.4631 | 0.4690 | 0.4969 | 0.4950 |
| -Converg | -Converg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | First Layer | Second Layer | First Layer | Second Layer |
| Model | Two-Way Fixed SEM | Two-Way Fixed SEM | Two-Way Fixed SDM | Two-Way Fixed SEM |
| −0.6172 *** (−20.01) | −0.7019 *** (−17.09) | −0.6425 *** (−20.60) | −0.7154 *** (−17.52) | |
| 0.2247 *** (4.10) | ||||
| ρ or λ | 0.5159 *** (14.39) | 0.2463 *** (5.11) | 0.4839 *** (12.84) | 0.2369 *** (4.85) |
| X1 | 0.08830 * (1.76) | 0.0727 (0.89) | ||
| X2 | −0.0139 ** (−2.01) | 0.0056 (0.78) | ||
| X3 | −0.0146 (−0.74) | −0.0204 (−0.70) | ||
| X4 | 0.0444 (1.38) | 0.0861 *** (2.64) | ||
| X5 | 0.0525 (1.44) | −0.0207 (−0.48) | ||
| R2 | 0.2503 | 0.3008 | 0.3135 | 0.2686 |
| Log-L | 1133.4696 | 669.7970 | 1151.7943 | 675.6161 |
| Space fixed effect | 154.00 *** | 147.82 *** | 95.42 *** | 148.18 *** |
| Time fixed effect | 272.98 *** | 224.09 *** | 297.57 *** | 232.87 *** |
| Hausman test | 284.23 *** | 269.66 *** | 60.98 *** | 289.99 *** |
| LM spatial lag | 639.470 *** | 195.079 *** | 642.784 *** | 191.207 *** |
| Robust LM spatial lag | 0.324 | 1.540 | 1.929 | 0.520 |
| LM spatial error | 686.177 *** | 207.926 *** | 677.778 *** | 203.645 *** |
| Robust LM spatial error | 47.031 *** | 14.387 *** | 36.924 *** | 12.958 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Liu, K. Regional Differences, Distribution Dynamics, and Convergence of Air Quality in Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127330
Xue Y, Liu K. Regional Differences, Distribution Dynamics, and Convergence of Air Quality in Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127330
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yuting, and Kai Liu. 2022. "Regional Differences, Distribution Dynamics, and Convergence of Air Quality in Urban Agglomerations in China" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127330
APA StyleXue, Y., & Liu, K. (2022). Regional Differences, Distribution Dynamics, and Convergence of Air Quality in Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability, 14(12), 7330. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127330






