The Nature, Causes and Extent of Land cover Changes in Gamtoos River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: 1991–2017
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Image and Data Compilation
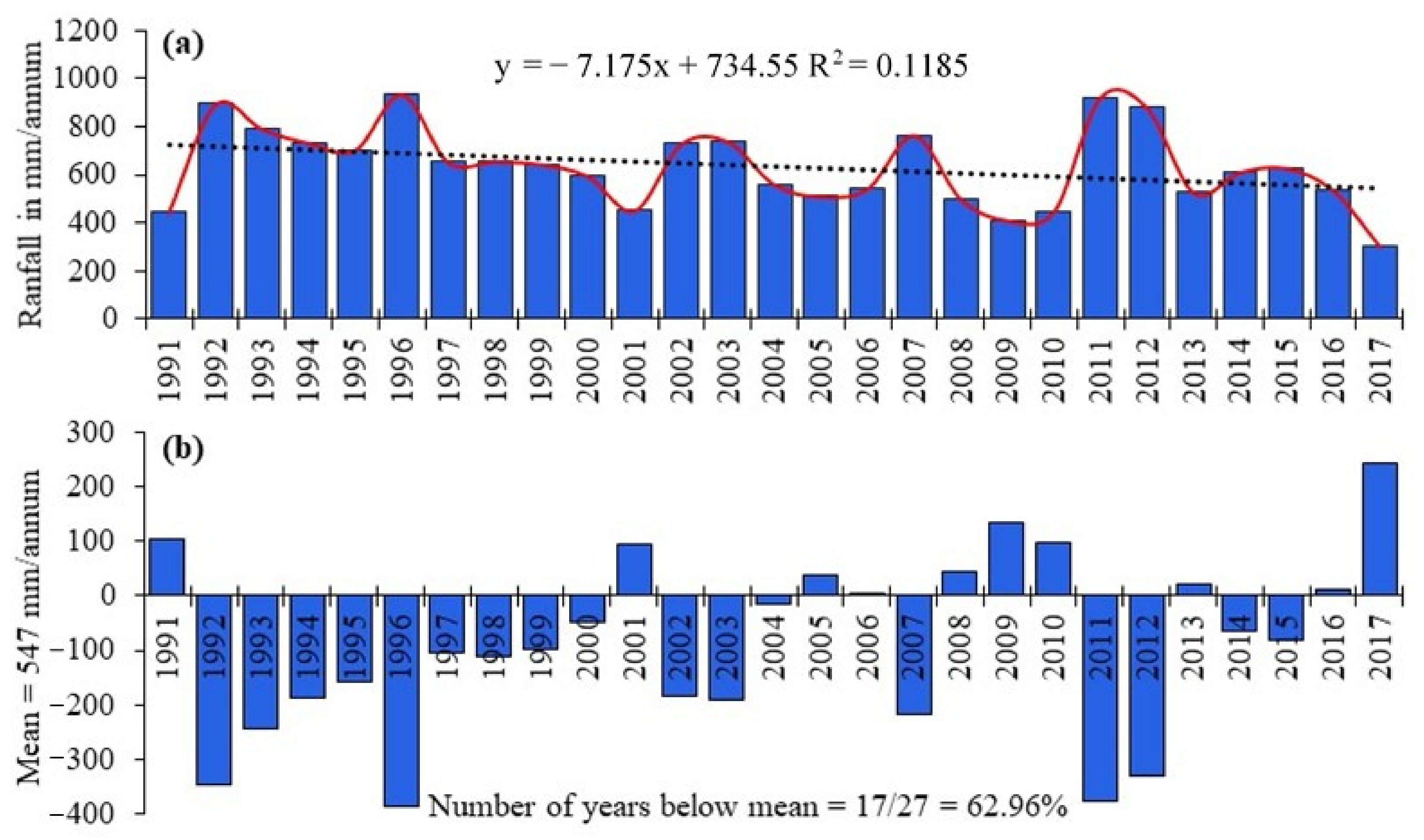
2.3. Rainfall Data
2.4. Field Compilation of Reference Data
2.5. Supervised Classification and Classification Accuracy
3. Results and Statistical Analysis
Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitfield, A.K.; Elliott, M. Ecosystem and biotic classifications of estuaries and coasts. In Treatise on Estuaries and Coasts; Wolanski, E., McLusky, D.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 99–124. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012374711200108X (accessed on 17 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- James, N.C.; Harrison, T.D. A preliminary survey of the estuaries on the southeast coast of South Africa, Cape St Francis–Cape Padrone, with particular reference to the fish fauna. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 2010, 65, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodwell, G.M.; Rich, P.H.; Hall, C.A.S. Carbon in estuaries. In Carbon and the Biosphere; Woodwell, G.M., Peron, E.V., Eds.; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 1973; pp. 221–240. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, C.C.; Crain, C.M.; Beck, M.W. The protective role of coastal marshes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M.J. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, A.J.; Barwell, L.; Taljaard, S. Report on the National Estuaries Workshop: 3–5 May 2000 Port Elizabeth, South Africa. Issue 2 of Marine and Coastal Management Implementation Workshops. Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism. Marine and Coastal Management. MCM, DEA & T and CSIR Environmentek. 2000. Available online: https://books.google.co.za/books?id=2_-XXwAACAAJ&dq=inauthor:%22South+Africa.+Department+of+Environmental+Affairs+and+Tourism.+Marine+and+Coastal+Management%22&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Van Niekerk, L.; Taljaard, S.; Adam, J.B.; Lambert, D.J.; Huizinga, P.; Turpie, J.K.; Wooldridge, T.H. An environmental flow determination method for integrating multiple-scale ecohydrological and complex ecosystem processes in estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, A.; Maze, K.; Lombard, A.T.; Nel, J.; Rouget, M.; Turpie, J.K.; Cowling, R.M.; Desmet, P.; Goodman, P.; Harris, J.; et al. South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004: Summary Report; South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI Publishing): Pretoria, South Africa, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, G.C.; Adams, J.B.; Bate, G.C. Effect of river flow on estuarine microalgal biomass and distribution. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, D.A.; Adams, J.B.; Strydom, N.A. Triggers of phytoplankton bloom dynamics in permanently eutrophic waters of a South African estuary. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 43, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, D.A.; Adams, J.B.; Taljaard, S. Comparative assessment of two agriculturally influenced estuaries: Similar pressure, different response. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, R.A.; Stretch, D.D.; Perissinotto, R. The effects of wastewater discharges on the functioning of a small temporarily open/closed estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.; Blair, A.; Connell, A.; Demetriades, N.T.; Forbes, A.T.; Harrison, T.H.; Lyer, K.; Joubert, M.; Kibirige, I.; Mundree, S.; et al. Contributions to Information Required for the Implementation of Resource Directed Measures for Estuaries (Volume 2). Responses of the Biological Communities to Flow Variation and Mouth State in Two KwaZuluNatal Temporarily Open/closed Estuaries; WRC Report No. 1247/2/04; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, E.; Pearce, M. Freshwater inflow and estuarine variability in the Gamtoos Estuary, South Africa. Estuaries 1997, 20, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinecken, T.J.E.; Bickerton, I.B.; Heydorn, A.E.F. A Summary of Studies of the Pollution Input by Rivers and Estuaries Entering False Bay; CSIR Report T/SEA 8301; Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, E.H.; Pearce, M.W. The Effect of Land Use on Gamtoos Estuary Water Quality. Report to the Water Research Commission by the Department of Geology, University of Port Elizabeth. WRC Report No. 503/1/97. Nd. Available online: http://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/503-1-97.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Pearce, M.W.; Schumann, E.H. The impact of irrigation return flow on aspects of the water quality of the upper Gamtoos Estuary, South Africa. Water SA 2001, 27, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.B.; Van Niekerk, L. Ten principles to determine environmental flow requirements for temporarily closed estuaries. Water 2020, 12, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, L.R.D.; Adams, J.B. Reeds as indicators of nutrient enrichment in a small temporarily open/closed South African estuary. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 36, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, P.; Quinn, N. Influence of man and management of South African estuaries. In Estuaries of South Africa; Allanson, B.R., Baird, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 289–321. [Google Scholar]
- Raw, J.L.; Riddin, T.; Wasserman, J.; Lehman, T.W.K.; Bornman, T.G.; Adams, J.B. Salt marsh elevation and responses to future sea-level rise in the Knysna Estuary, South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornman, T.G.; Schmidt, J.; Adams, J.B.; Mfikili, A.N.; Farre, R.E.; Smit, A.J. Relative sealevel rise and the potential for subsidence of the Swartkops Estuary intertidal salt marshes, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 107, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Lynch, J.C.; Roman, C.T.; Schmit, J.P.; Skidds, D.E. Evaluating the relationship among wetland vertical de-velopment, elevation capital, sea-level rise, and tidal marsh sustainability. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwright, N.M.; Griffith, K.T.; Osland, M.J. Barriers to and opportunities for landward migration of coastal wetlands with sea-level rise. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Walters, D.C.; Reay, W.G.; Carr, J.A. Sea level driven marsh expansion in a coupled model of marsh erosion and migration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4366–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitfield, A.; Bate, G. A Review of Information on Temporarily Open/Closed Estuaries in the Warm and Cool Temperate Biogeographic Regions of South Africa, with Emphasis on the Influence of River Flow on These Systems; WRC Report No. 1581/1/07; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Taljaard, S.; van Niekerk, L.C.A.P.E. Estuaries Programme. Proposed Generic Framework for Estuary Management Plans. Version 1.1; CSIR Report No. CSIR/NRE/CO/ER/2009/0128/A; Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.M.; Perissinotto, R.; Kibirige, I. Phytoplankton biomass and size structure in two South African eutrophic, temporarily open/closed estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 65, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/Nairobi Convention Secretariat. Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis of Land-based Sources and Activities Affecting the Western Indian Ocean Coastal and Marine Environment; UNEP Nairobi: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; Available online: https://nairobiconvention.org/CHM%20Documents/WIOSAP/-Transboundary%20Diagnostic%20Analysis%20of%20Land-based%20Sources%20and%20Activities%20in%20the%20Western%20Indian%20Ocean%20Region.-2009Transboundary%20Diagnostic%20Analysis%20of%20Land-based%20Sources%20and%20Activities-1.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- James, N.C.; van Niekerk, L.; Whitfield, A.K.; Potts, W.M.; Götz, A.; Paterson, A.W. Effects of climate change on South African estuaries and associated fish species. Clim. Res. 2013, 7, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, N.C.; Whitfield, A.K.; Cowley, P.D. Preliminary indications of climate-induced change in a warm-temperate South African estuarine fish community. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynecke, J.O.; Yip Lee, S.; Duke, N.C.; Warnken, J. Effect of rainfall as a component of climate change on estuarine fish production in Queensland, Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.M. Climate change: A looming challenge for fisheries management in southern Africa. Mar. Policy 2006, 2006. 30, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, W. Environmental degradation and the tyranny of small decisions. BioScience 1982, 32, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H. The relationship between land-use change and climate change. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.E.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; George, P.S.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Taljaard, S.; van Niekerk, L.; Lemley, D.A. Nutrient enrichment as a threat to the ecological resilience and health of South African microtidal estuaries. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jezewski, W.A.; Roberts, C.P.R. Estuarine and Lake Freshwater Requirements. Department of Water Affairs; Technical Report No. TR 129; DWAF: Pretoria, South Africa, 1986; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Bate, G.C.; Adams, J.B.; Cowle, P.D.; Froneman, P.W.; Gama, P.T.; Strydom, N.A.; Taljaard, S.; Theron, A.K.; Turpie, J.K.; et al. A review of the ecology and management of temporarily open/closed estuaries in South Africa, with particular emphasis on river flow and mouth state as primary drivers of these systems. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 34, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Kwadwo Gyedu-Ababio, K.T. Pollution status of two river estuaries in the Eastern Cape, South Africa, based on Benthic Meiofauna analyses. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 464–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marais, J.F.K. Fish abundance and distribution in the Gamtoos estuary with notes on the effect of floods. S. Afr. J. Zool. 1983, 18, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupra, V.; Smith, S.V.; Marshall Crossland, J.I.; Crossland, C.J. Land-Ocean Interactions in the Coastal Zone (LOICZ). Estuarine Systems of Sub-Saharan Africa: Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fluxes. LOICZ Reports & Studies 18. 2001. Available online: https://s3-eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/futureearthcoasts/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/30150945/LOICZ-RS18.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Heydorn, A.E.F.; Grindley, J.R. Estuaries of the Cape, Part II. Synopses of Available Information on Individual Systems; Report No.7: Gamtoos. CSIR Res. Rep. 406; National Research Institute for Oceanology Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 1981; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shone, R.W.; Nolte, C.C.; Booth, P.W.K. Pre-Cape rocks of the Gamtoos area—A complex tectonostratigraphic package preserved as a horst block. S. Afr. J. Geol. 1990, 93, 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, W.J.R. August 1971 Gamtoos Valley Floods. 1971. Available online: https://www.baviaans.net/articles/august-1971-gamtoos-valley-floods-03-2019-d1 (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- Gamtoos History & Geology. Available online: https://www.baviaans.net/page/geology_and_history (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Rogers, G. Gamtoos Estuary Closed for the First Time in 70 Years. 2018. Available online: https://www.heraldlive.co.za/news/2018-07-11-gamtoos-estuary-closed-for-first-time-in-70-years/ (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Kopke, D. The climate of the Eastern Cape. In Towards an Environmental Plan for the Eastern Cape; Bruton, M.N., Gess, F.W., Eds.; Rhodes University: Grahamstown, South Africa, 1988; pp. 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Burg, L. Valuing the Benefits of Restoring the Water Regulation Services, in the Subtropical Thicket Biome: A Case Study in the ‘Baviaanskloof Gamtoos watershed’, South-Africa. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. Available online: http://media.dirisa.org/inventory/archive/presence-learning-network/documents/van-der-burg-lennart_2008_benefits-restoring-water-regulation-gamtoos.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Scharler, U.M.; Baird, D. The nutrient status of the agriculturally impacted Gamtoos Estuary, South Africa, with special reference to the river-estuarine interface region (REI). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 13, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEA (Department of Environmental Affairs). Climate Change Adaptation Plans for South African Biomes; Kharika, J.R.M., Mkhize, N.C.S., Munyai, T., Khavhagali, V.P., Davis, C., Dziba, D., Scholes, R., van Garderen, E., von Maltitz, G., Le Maitre, D., et al., Eds.; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2015. Available online: https://www.gov.za/documents/climate-change-adaptation-plans-south-african-biomes-18-jul-2016-0000 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Mucina, L.; Rutherford, M.C. (Eds.) The Vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland. Strelitzia 19; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Enviro-Fish Africa. Gamtoos Estuarine Management Plan Vol. II. 2008. Available online: http://fred.csir.co.za/project/CAPE_Estuaries/documents/Gamtoos%20Draft%20EMP.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Garcia-Rodriguez, F.D.G. The Determination and Distribution of Microbenthic Chlorophyll—A in Selected South Cape Estuaries. Master’s Thesis, University of Port Elizabeth, Port Elizabeth, South Africa, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Scharler, U.M.; Baird, D. The filtering capacity of selected Eastern Cape estuaries, South Africa. Water SA 2006, 31, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consortium for Estuarine Research and Management (CERM). Studies on the River-Estuary Interface Region of Selected Eastern Cape Estuaries. Report No: 756/1/03. 2003. Available online: http://www.fwr.org/wrcsa/756103.htm (accessed on 17 April 2019).
- Watling, R.J.; Watling, H.R. Metal Surveys in South African Estuaries vs. Kromme and Gamtoos Rivers (St Francis Bay). Water SA 1982, 8, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- ATCOR-2/3. Atmospheric/Topographic Correction of Satellite Imagery, ERDAS Imagine ATCOR-2/3 User Guide, Version 9.0.2. 2016. Available online: https://www.rese.ch/pdf/atcor3_manual.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- South Africa National Space Agency (SANSA). Available online: https://www.sansa.org.za/ (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- NGI National Geo-Spatial Information (NGI). Available online: http://www.ngi.gov.za/index.php/contact-ngi (accessed on 16 March 2018).
- Di Gregorio, A. Land Cover Classification System: Classification Concepts and User Manual: LCCS (No. 8); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5232e.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- Thomlinson, J.R.; Bolsta, P.V.; Cohen, W.B. Coordinating methodologies for scaling landcover classifications from site-specific to global: Steps toward validating global map products. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D.A.V. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/@-33.9321432,25.1012905,2194m/data=!3m1!1e3?hl=en-US (accessed on 15 June 2017).
- Peddle, D.R.; Ferguson, D.T. Optimization of multisource data analysis: An example using evidential reasoning for GIS data classification. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.E.; Wulder, M.A. Remote sensing methods in medium spatial resolution satellite data land cover classification of large areas. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2002, 26, 173–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.T.; Tebeje, A.K.; Demissie, S.S.; Belete, M.A.; Jemberrie, M.A.; Teshome, W.M.; Mengistu, D.T.; Teshale, E. Time series land cover mapping and change detection analysis using Geographic Information System and Remote Sensing, Northern Ethiopia. Air Soil Water Res. 2018, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd, H.A.A.; Alnajjar, H.A. Maximum likelihood for land-use/land-cover mapping and change detection using Landsat satellite images: A case study “South of Johor”. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Res. 2013, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.R.; Hardy, E.E.; Roach, J.T.; Witmer, R.E. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data. Geological Survey Professional Paper 671. 1976. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0964/report.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Foody, G.M. Harshness in image classification accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3137–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trodd, N.M. Uncertainly in land cover mapping for modelling land cover change. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 25, 1235–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. A practical look at the sources of confusion in error matrix generation. Photogrametric Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 641–654. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Thontteh, O.; Chen, H. Components of information for multiple resolution comparison between maps that share a real variable. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2008, 15, 111–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V.; Czaplewski, R.L. Design and analysis for thematic map accuracy assessment: Fundamental principles. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Millones, M. Death to Kappa: Birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4407–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1987. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/7037501/;Statistical (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, D.V. Seasonal rainfall trend analysis. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2016, 6, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hamandawana, H.; Atyosi, Y.; Bornman, T.G. Multi-temporal reconstruction of long-term changes in land cover in and around the Swartkops River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandle, D. Vulnerability of Estuaries to Sealevel Rise Stage 1: A Review. 2010. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/291214/scho0310bsac-e-e.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J. Sea-level rise from the late 19th to early 21st century. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jevrejeva, S.; Moore, J.C.; Grinsted, A.; Woodworth, P.L. Recent global sea level acceleration started over 200 years ago? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L08715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CES (Coastal & Environmental Services). Eastern Cape Climate Change Response Strategy. 2011. Available online: https://www.cityenergy.org.za/uploads/resource_182.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Polley, H.W.; Johnson, H.B.; Mayeux, H.S. Carbon dioxide and water fluxes of C3 annuals and C3 and C4 perennials at subambient CO2 concentrations. Funct. Ecol. 1992, 6, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgely, G.F.; Bond, W.J.; Roberts, R.; Wand, S.J.E. Potential Cause of Changes in Savanna Tree Success Due to Rising Atmospheric CO2. Towards Sustainable Management in the Kalahari Region–Some Essential Background Issues; Ringrose, S., Chanda, R., Eds.; University of Botswana: Gaborone, Botswana, 2000; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiter, S.; Higgins, S.I. Impacts of climate change on the vegetation of Africa: An adaptive dynamic vegetation modelling approach. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2224–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamandawana, H.; Chanda, R.; Eckardt, F. Natural and human-induced environmental changes in the distal reaches of Botswana’s Okavango Delta. J. Land Use Sci. 2007, 2, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiza, W.; Hamandawana, H.; Chingombe, W. Monitoring changes in land use and land cover to ascertain the nature, causes and extent of degradation in the Savannas of Raymond Mhlaba Local Municipality, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 79, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, M. Droughts and the ecological future of tropical savanna vegetation. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1531–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Anisfeld, S.C.; Blum, L.K.; Emily, V.; Long, E.V.; Feagin, R.A.; Fernandes, A.; Kearney, W.S.; Williams, K. Sea level rise and the dynamics of the marsh-upland boundary. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slangen, A.B.A.; Katsman, C.A.; Van de Wal, R.S.W.; Vermeersen, L.L.A.; Riva, R.E.M. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change based on IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1191–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idowu, T.E.; Lasisi, K.H. Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of East and Horn of Africa: A review from a regional perspective. Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, e00402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, P.; Simpson, M.J.; Lee, K.-K. Does sea-level rise have an impact on saltwater intrusion? Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation, and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Forestry, Fisheries and Environment. The Garden Route Environmental Management Framework. 2010; pp. 1–168. Available online: https://www.dffe.gov.za/sites/default/files/docs/gardenroute_finalreport.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Daniels, N. Gamtoos River Valley Drought Endangers Citrus Harvest. 2021. Available online: https://www.iol.co.za/capetimes/news/gamtoos-river-valley-drought-endangers-citrus-harvest-d9f4b156-4d2f-405f-a593-96acea8db61c (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Turpie, J.K. Improving the Biodiversity Importance Rating of Estuaries. Water Research Commission Report, Water Research Commission, Pretoria, South Africa. 2004. Available online: http://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/WaterSA_2002_02_1386.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2022).

 denotes Satellite image and
denotes Satellite image and  denotes Geo-located roadside photographs. (A,B)—Selected features in the image targeted for confident identification. (C)—Roadside view of point (A) in satellite image, Nov 2009. 33.924861S; 25.075820E. (D)—Roadside view of point (B) in image, Nov 2009. 33,921407S; 25.077065E. Link to source: [66].
denotes Geo-located roadside photographs. (A,B)—Selected features in the image targeted for confident identification. (C)—Roadside view of point (A) in satellite image, Nov 2009. 33.924861S; 25.075820E. (D)—Roadside view of point (B) in image, Nov 2009. 33,921407S; 25.077065E. Link to source: [66].
 denotes Satellite image and
denotes Satellite image and  denotes Geo-located roadside photographs. (A,B)—Selected features in the image targeted for confident identification. (C)—Roadside view of point (A) in satellite image, Nov 2009. 33.924861S; 25.075820E. (D)—Roadside view of point (B) in image, Nov 2009. 33,921407S; 25.077065E. Link to source: [66].
denotes Geo-located roadside photographs. (A,B)—Selected features in the image targeted for confident identification. (C)—Roadside view of point (A) in satellite image, Nov 2009. 33.924861S; 25.075820E. (D)—Roadside view of point (B) in image, Nov 2009. 33,921407S; 25.077065E. Link to source: [66].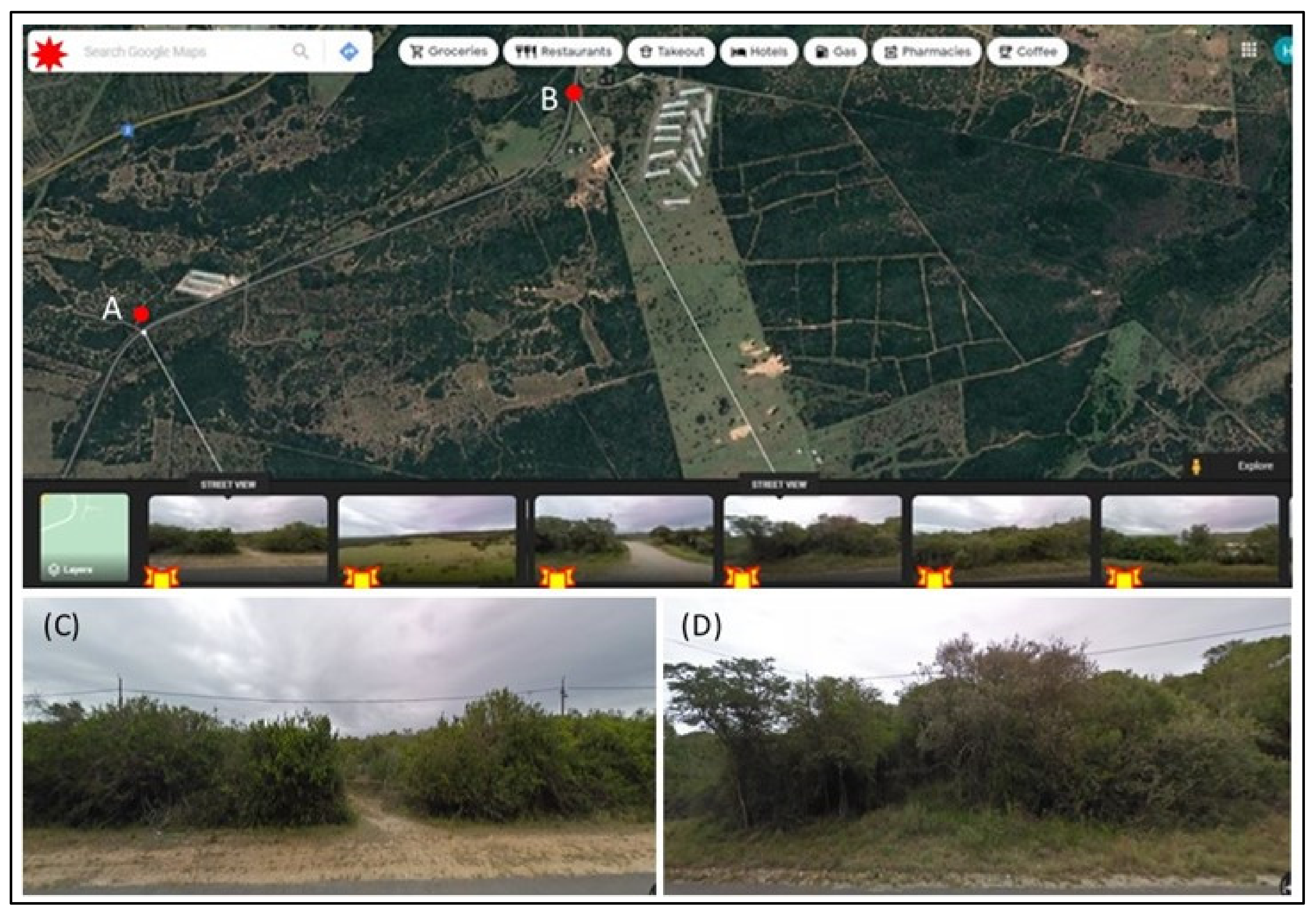

| Satellite Images | Aerial Photographs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Date Acquired | Spectral Bands | Resolution | Cloud Cover | Date Acquired |
| SPOT 2 | 26/07/1991 | B1, B2, B3. | 22.01 m | <5% | 06/05/2013—Tc |
| SPOT 4 | 31/08/2000 | B1, B2, B3. | 21.58 m | 0% | 27/06/2003—Pan |
| SPOT 5 | 11/03/2009 | B1, B2, B3. | 11.91 m | <5% | 05/07/1994—Pan |
| SPOT 7 | 19/07/2017 | B1, B2, B3. | 5.63 m | <5% | 17/05/1980—Pan |
| Year | 1991 | 2000 | 2009 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | 08/1990–07/1991 | 07/1999–08/2000 | 02/2008–03/2009 | 08/2016–07/2017 |
| AAR: mm | 417.9 | 612.5 | 477.4 | 326.8 |
| (a) | Ba | Veg | Sw | Ca | Nc | Total | PA% | UA% | |
| Ba | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 92.86 | 81.25 | |
| Veg | 0 | 21 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 23 | 82.61 | 90.48 | |
| Sw | 0 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 83.33 | 76.92 | |
| Cl | 1 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 1 | 14 | 78.57 | 91.66 | |
| Nc | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 83.33 | 76.92 | |
| Total | 14 | 23 | 11 | 14 | 13 | 75 | |||
| PA = producer accuracy, UA = user accuracy, OA = sum of diagonal entries ÷ total = (65 ÷ 75) = 0.8667 = 86.7% (Ba = bare area, Veg = vegetation, Sw = surface water, Ca = cultivated land, Nc = noncultivated land) | |||||||||
| (b) Matrix produced in calculating the K statistic and explanation of how this was performed | |||||||||
| 196 | 322 | 154 | 196 | 182 | Explanation of calculations | ||||
| 322 | 529 | 253 | 322 | 299 | The first figure in Table (b) (196) is calculated by multiplying the total for bare area in Table (a) (14) with the horizontal row total for bare area in Table (a), i.e., 14 × 14 = 196. The remaining figures are calculated likewise. | ||||
| 168 | 276 | 132 | 168 | 156 | |||||
| 196 | 322 | 154 | 196 | 182 | |||||
| 168 | 276 | 132 | 168 | 156 | |||||
| Total | 1050 | 1725 | 825 | 1050 | 975 | ||||
| Grand total (sum of totals) = 5625 | |||||||||
| Cover Type | Percentage Composition | Percentage Change | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 2000 | 2009 | 2017 | A | B | C | D | |
| Bare area | 12.95 | 21.87 | 9.65 | 16.43 | 8.92 | −12.22 | 6.78 | 3.48 |
| Vegetation | 39.97 | 32.74 | 41.64 | 38.01 | −7.23 | 8.90 | −3.63 | −1.96 |
| Surface water | 7.11 | 12.65 | 7.06 | 7.55 | 5.54 | −5.59 | 0.49 | 0.44 |
| Cultivated land | 14.26 | 23.84 | 20.95 | 20.25 | 9.58 | −2.89 | −0.70 | 5.99 |
| Noncultivated land | 25.71 | 8.90 | 20.69 | 17.77 | −16.81 | 11.79 | −2.92 | −7.94 |
| Total area (ha) | 1736.4 | 1736.4 | 1736.4 | 1736.4 | − | − | − | − |
| Cover Types | Trend Coefficient | R2 | SSE | p (σ 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare area: (Ba) | y = −0.1797x + 15.675 | 0.002 | −0.025 | * 1.0000 |
| Vegetation: (Veg) | y = 0.3029x + 37.334 | 0.010 | 0.009 | ** 1.0000 |
| Surface water: (Sw) | y = −0.4261x + 9.657 (Ɲ) | 0.041 | 0.007 | ** 1.0000 |
| Cultivated land: (Ca) | y = 1.5061x + 16.059 | 0.234 | 0.071 | ** 1.0000 |
| Noncultivated land: (Nca) | y = −1.2032x + 21.275 | 0.049 | −0.292 | * 0.7341 |
| AAR: (1991, 2000, 2009, 2017) | y = −40.84x + 560.75 | 0.194 | −9.258 | * 0.7341 |
| Long-term rainfall: 1991–2017 | y = −7.175x + 734.55 | 0.119 | −11.130 | *** 0.0411 |
| Correlations between AAR and different cover types at σ = 0.05, Critical R = 0.805 | ||||
| * AAR & Ba = 0.453816 | AAR & Sw = ***0.813709 | AAR & Nca = **−0.643962 | ||
| ** AAR & Veg = −0.592468 | AAR & Ca = 0.560341 | *** Significant positive | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndude, M.A.; Gwena, K.R.; Hamandawana, H. The Nature, Causes and Extent of Land cover Changes in Gamtoos River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: 1991–2017. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137859
Ndude MA, Gwena KR, Hamandawana H. The Nature, Causes and Extent of Land cover Changes in Gamtoos River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: 1991–2017. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137859
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdude, Mhlanganisi Africa, Kudzanai Rosebud Gwena, and Hamisai Hamandawana. 2022. "The Nature, Causes and Extent of Land cover Changes in Gamtoos River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: 1991–2017" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137859
APA StyleNdude, M. A., Gwena, K. R., & Hamandawana, H. (2022). The Nature, Causes and Extent of Land cover Changes in Gamtoos River Estuary, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: 1991–2017. Sustainability, 14(13), 7859. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137859







