1. Introduction
Over the last two decades, the average life cycle of electrical and electronic goods has reduced due to the rapid technological progress in line with the ever-escalating consumer demand [
1]. The increasing usage of electronic devices has led to enormous volumes of electronic waste (e-waste) [
2]. In fact, e-waste is one of the world’s fastest emerging waste categories, which records 3–5% on an annual basis [
3]. Based on a study published by the United Nations University’s Global E-waste Monitor 2020, 53.6 million metric tons (Mt) of e-waste were generated in 2019 [
4,
5]. Concurrently, Asian countries generate nearly half of this enormous figure—24.9 Mt. Forti [
6] estimated that 74.7 million Mt of e-waste would be produced by 2030. If significant measures are not taken, this number is expected to rise to 120 Mt by 2050. Unfortunately, only 20% of this tremendous amount of e-waste was recycled in some useful sense [
7,
8,
9]. The remaining 80% were usually disposed of at the landfill, thus causing harm to the environment [
9]. Turning to Malaysia, it yielded 364 kilotons of e-waste or 11.1 kg of e-waste per capita in 2020 [
10]. The Malaysian government statistics, nonetheless, reported that about 25% of e-waste in this country is recycled, while the remaining e-waste improperly recycled was worth about MYR 3 billion [
11].
Yong [
12] highlighted that e-waste generation is now a significant issue across all countries in the world, mainly because the harmful elements and chemical substances can cause adverse effects on both the environment and human health. These hazardous substances (i.e., lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, cathode ray tubes, chromium, and polybrominated biphenyls), if mismanaged, are detrimental to the environment and human health [
4,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. In addition, e-waste releases greenhouse gases and ozone-depleting substances. For instance, both refrigerators and air-conditioners contain chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) (Freon) gases that significantly contribute to global warming and ozone depletion. As ozone depletion increases ultraviolet (UV) radiation to the surface of the Earth, many may succumb to skin cancer [
20]. On the other hand, e-waste is highly valued as secondary raw materials, such as gold, silver, platinum and palladium, iron, copper, aluminum, and plastics, which can be extracted and sold [
21,
22]. According to Widmer [
22], the recovery of these materials from e-waste projects a profitable venture. Since a huge number of precious metals can be found in e-waste, the recovery of e-waste signifies a lucrative economic advantage as it limits spending on costly and scarce resources needed to generate new electronic goods [
3].
Instead of being thrown away, e-waste should be reused, resold, recovered, remanufactured, recycled, or disposed of via a reverse logistics process. Electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) reverse logistics has become the focal point for lawmakers, researchers, and producers [
23]. The rising amount of e-waste in huge volumes, along with poor environment-friendly recycling structures, has been reckoned as a serious issue [
24]. However, the literature on reverse logistics merely concentrates on the recycling theory designed for companies or manufacturers, while omitting the link between reverse logistics system and consumer behavior [
25]. Notably, the reverse logistics process cannot be operated effectively without consumer participation because they are the initial connection in the entire supply chain [
26]. The absence of consumer participation in logistics e-waste recycling can lead to e-waste being disposed of either by incinerating or by throwing it at landfills, which is detrimental to the environment [
25]. Moreover, the literature insufficiently depicts the intention of consumers to sell or recycle, as well as their participation in e-waste management across developing countries [
23]. As such, this study outlined the key determinants of e-waste recycling intentions (ERIs) and e-waste recycling behavior (ERB) due to the scarcity of studies related to reverse logistics and recycling rates in Malaysia.
According to Zhang [
27], large volumes of e-waste have flooded to unauthorized recycling facilities, where the waste is processed with rough refining and non-environment-friendly methods. They added that e-waste collection is hindered due to the unwillingness among consumers to send e-waste to authorized disposal facilities. Haron [
2] claimed that the other obstacles are due to the existence of unauthorized waste collectors, as well as a lack of awareness and knowledge among customers, retailers, and producers. Free Malaysia Today [
28] stated that such activity stems from illegal facilities located near residential areas, which could further lead to pollution that causes significant health issues for the residents living there.
Therefore, this present study bridged the gaps by assessing factors that influence e-waste recycling participation and awareness of e-waste issues through the lens of the theory of planned behavior (TPB). However, the TPB within the recycling context has limitations because it is complicated for the model to predict or determine behavior that is not from personal desire and decision. Recycling behavior involves external resources and expertise [
29]. For example, the key factors for unwillingness to recycle e-waste in developing countries are a shortage of recycling facilities [
30], non-strategic e-waste disposal centers that are located far from residential areas [
31], and a lack of knowledge about the deleterious impacts of e-waste on the environment and human health [
32].
To sum up, everything that has been stated so far, regarding the academic gaps, there are still limited studies investigating the connections between reverse logistics and consumer context in Malaysia because most of the previous literature focused on reverse logistics with companies or manufacturers’ contexts. In addition, there is still insufficient information from the previous research literature about the intention of consumers to sell or recycle as well as the participation of consumers in e-waste management in developing countries, especially in Malaysia. Moreover, in terms of a theoretical gap, even though the TPB model is suitable for predicting recycling behavior, there are still limitations in the TPB model. This is because recycling behavior involves personal desire and decision as well as external resources and expertise, which is out of the individual’s control. Lastly, regarding the practical gaps, there are vast volumes of e-wastes that have flooded to unauthorized recycling facilities which use inappropriate recycling methods and incinerate some valuable parts of e-waste that can be resold. The reason for this circumstance is that prior research discovered that Malaysians have limited knowledge of e-waste and its repercussions [
4,
33]. Thus, Malaysians were reported to be uninformed about proper e-waste disposal.
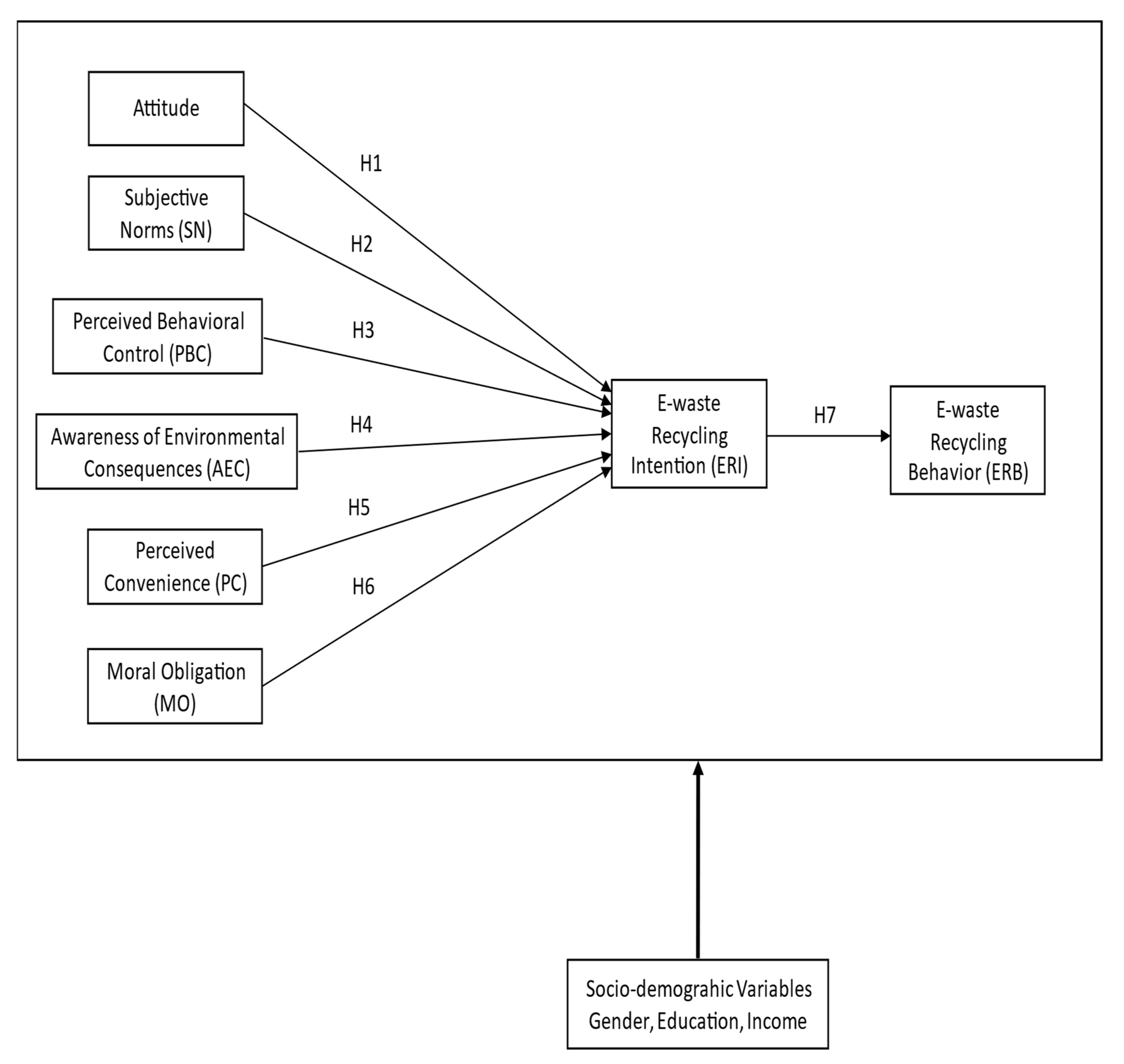
Consequently, to bridge the gaps, there is a need for an extensive understanding of consumers’ behavior concerning e-waste and the aspects that will improve consumer intentions to participate in e-waste recycling. To address these setbacks, an extended TPB model was used in this study to assess recycling intention and behavior among consumers in Malaysia by embedding extra variables: awareness of environmental consequences (AEC), perceived convenience (PC), and moral obligation (MO).
In addition, this paper is the first study that included moral obligation (MO) in the extended TPB to investigate consumers’ e-waste recycling behavior in Malaysia since the importance of MO as a predictor of an individual’s pro-environmental behavior is undervalued. Hence, the impact of moral obligation should be highlighted in behavioral theories such as the TPB since previous studies believed that moral obligation could be more influential than attitude [
34,
35] and subjective norms [
36] in the study of pro-environmental behavior. Evidence of this can be found in Razali’s [
37] study which found that moral obligation is the most significant factor in determining household waste separation behavior in Malaysia. Furthermore, Juliana [
38] and Sulaiman and Chan [
39] also discovered that moral obligations also had a significant effect on recycling behavior in Malaysia. The findings present convincing evidence that moral obligation plays an important role in Malaysian consumers’ behavior. According to Juliana [
38], people in Malaysia were found to have a sense of guilt if they did not engage in recycling behaviors, and failing to recycle would directly contradict their values and principles. Thus, this study wanted to explore the impact of MO on consumers’ recycling behavior, specifically in the e-waste recycling context.
Moreover, no studies exist examining the impact of consumers’ socio-demographic factors in performing e-waste recycling behavior in Malaysia. Thus, this study conducted a multi-group analysis (MGA) in order to investigate the significant disparities that exist across the various groups by employing socio-demographic factors such as gender, education level, and income level in performing e-waste recycling in Malaysia. The implication of the findings is beneficial for the government and all stakeholders, including generators or consumers, non-government agencies, collectors, retailers, and recycling facilities, to promote and encourage e-waste recycling among consumers in Malaysia. Moreover, the study outcomes may be considered when formulating laws and regulations to enhance e-waste recycling efforts that guarantee a sustainable ecosystem in the future.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The continuous production of e-waste has led to a massive threat to the living environment, thus adversely affecting the sustainable economic growth of many countries [
112]. Therefore, an effective regulatory system for the proper disposal of e-waste and an efficient mechanism of a proper take-back system from the public and industries should be implemented. Simply put, recycling by reverse logistics should be promoted to reduce environmental issues, while concurrently generating economic advantages for organizations. Unfortunately, studies that link reverse logistics systems to consumer behavior are in scarcity [
25]. Notably, the reverse logistics process cannot be operated without consumer participation because they are the initial connection in the entire supply chain [
26]. In order to bridge this gap, this present study assessed factors that influence ERI and ERB in Malaysia through the lens of an extended TPB model by adding three variables, namely AEC, PC, and MO.
First, the finding revealed that the relationship between attitude and ERI (H1) is insignificant. The result contradicts that reported in past studies (see [
23,
24,
31,
45,
57,
67,
68,
69]), which depicted that attitude toward e-waste recycling positively determines the intention to perform recycling. According to Greaves [
57], recycling attitudes can be formed by having a favorable assessment of recycling, for instance, a person should assume that waste disposal is responsible, conscientious, and convenient to perform. Moreover, Echegaray and Hansstein [
63] stated that attitude recycling is motivated by the belief that recycling is beneficial for both the environment and human health. Based on the results, the study respondents agreed that recycling e-waste is responsible, pleasant, beneficial, and sensible. However, this attitude factor did not encourage them to actually perform the recycling behavior. This happened because Malaysians still have limited knowledge of e-waste and its consequences on environmental and human health. Previous studies have explained that some people refuse to make fair use of their positive attitude toward recycling intentions and behavior [
113]. In Malaysia, consumers do not perform recycling activities because they believe recycling is a voluntary activity with no benefit or incentive [
114]. That is why Chan and Bishop [
35] introduced a new TPB framework by replacing attitude elements with moral norms to study recycling intention and behavior because previous researchers [
35,
71,
74] have identified that internalized norms such as moral obligation can be predictors of intention, attitude, or a replacement for attitude in the research of general conservation behavior that includes components about recycling.
Next, the association between SN and ERI (H2) was insignificantly negative in this study. Prior studies (see [
72,
76,
115]) are in line with this outcome, mainly because SN is a statistically insignificant predictor of recycling intention. This insignificant result of the SN–ERI link in this study denotes that Malaysians, especially the young generation, do not feel pressure from individuals that they consider important to them (e.g., friends, colleagues, mass media, and society) to perform recycling activities [
76,
115]. One possible explanation for the insignificant effect of SN is that the society in Malaysia barely performs any waste segregation or recycling activities [
116]. Moving on, Hypothesis 3 (H3) indicates an insignificant PBC–ERI relationship. The finding contradicts that of past studies, which reported a positive impact of PBC on one’s recycling intention (see [
24,
64,
68,
72,
92]). This insignificant result is ascribed to appropriate recycling channels which are rather difficult to find in Malaysia. Moreover, the study respondents did not perform e-waste recycling because they were unsure which e-waste items could be recycled. Nonetheless, this finding is in line with that found by Echegaray and Hansstein [
63]; the PBC emerged as the most negligible influential factor when compared to other factors. This notion is attributed to the inadequate supply of solid garbage collection facilities, as well as inadequate information and resources about e-waste recycling. Hence, it is rather difficult for them to decide if recycling is practical to perform as part of their ordinary activities [
23].
Next, the result shows that the relationship between AEC and ERI (H4) is not supported in this study. On the contrary, Echegaray and Hansstein [
63] reported that awareness of environmental issues and consideration for the state of the environment forecast a positive disposition toward recycling behavior. Nonetheless, consumers become unaware of the consequences of not recycling e-waste because it is not seen as a lucrative or environment-friendly practice [
23]. Afroz [
77] revealed that although most Malaysian consumers were aware of the adverse effect of electronic goods on environmental and human health, only 2–3% of them were interested in recycling those goods. Even though most consumers believe that e-waste recycling is vital, they are still unsure if e-waste is a serious threat to the environment [
45]. The insignificant result retrieved for the AEC–ERI link in this study is ascribed to the awareness and concern for the environment and recycling not being nurtured from an early age in Malaysia. Hence, the education system at both primary and secondary levels in Malaysia should foster and encourage recycling behavior [
114].
Next, this study recorded a significantly positive link between PC and ERI (H5). This result is in agreement with prior studies (see [
2,
27,
79,
117]) that PC is a significant factor in motivating consumers’ intention to recycle. This signifies that most Malaysian consumers feel that convenience, particularly time, space, and distance, will motivate them to recycle their e-waste. Notably, e-waste recycling may be increased with adequate time to organize e-waste, effort to clear personal information on electronic goods, and sufficient storage space. The respondents agreed that recycling e-waste does not take much time and room. The respondents agreed that implementing more recycling bins at strategic points can make recycling more convenient, as well as improve their participation in recycling activity [
118].
Apparently, MO emerged as the strongest predictor of ERI (H6) in this study. Similarly, Razali [
37] and Saphores [
79] reported that MO is the most influential determinant of their extended TPB models. Turning to this present study, internal motivation (i.e., MO) can increase consumers’ ERI. This result justifies the role of psychological variables, such as intrinsic motivation, in specific behavior, including pro-environmental behavior [
37]. Tonglet [
70] claimed that someone who perceives it is necessary to recycle or vice versa is likely to include personal norms in the decision-making process. This is because the encouragement to perform recycling behavior may be low if there is no incentive, and e-waste return may be costly if customers need to go to the disposal center to deposit their e-waste. This return action concentrates on morals instead of rationale, stemming from MO [
31]. Chan and Bishop [
35] initiated a new TPB framework by replacing the attitude element with moral norm to assess recycling intention and behavior. This is because past studies (see [
35,
81,
119]) have identified that internalized norms, such as MO, may serve as predictors of intention and attitude or as a replacement for attitude in studies related to general conservation behavior that includes recycling components. This finding proves that intrinsic motivation is more influential in motivating consumers to recycle their e-waste than receiving extrinsic incentives.
A significantly positive relationship was observed between ERI and ERB (H7) in this study, which is in agreement with previous studies (see [
35,
64,
68,
84,
88]). In a similar vein, Shaharudin [
76] showed that Malaysians intending to discard their e-waste would inevitably affect their execution of ERB, especially when their electronic goods are damaged and have outdated features or models. Malaysians, especially the young generation, prefer adopting the appropriate method to manage their e-waste so that they too can conserve and preserve the environment [
76]. Ho [
86] and Echegaray and Hansstein [
63] claimed that intentions have strong connections with behavior. Hence, ERB can be increased when the respondents have the intention to recycle e-waste, drop off their e-waste at an authorized facility, or return their e-waste to the retailer or manufacturer [
45].
Lastly, this study investigated the effects of socio-demographic variables as moderating factors on recycling behavior under varying socio-demographic backgrounds (gender, education, and income) by employing the MGA-PLS method. First, the MGA for gender was divided into female and male. Similar to that reported by do Valle [
94] and Botetzagias et al. [
72], gender had no statistically significant relationship with ERI. The result proves that there are no significant differences between males and females in recycling behaviors in Malaysia. Second, the MGA-PLS was executed to determine the effect of the high education (postgraduate level) and low/middle education (undergraduate or diploma level) groups. As a result, only PC and ERI passed the significance test. The lower/middle education group displayed a more significant effect on ERI or ERB than the higher education group. The results suggest that people with a lower/middle level of education concurred that convenience, particularly in terms of time, space, and distance, will encourage them to recycle their electronic waste. Finally, the findings show the multi-group effect regarding the low-income group (MYR 2000 and below) and the high-income group (MYR 6000 and above). Apparently, income level had no impact on ERI and ERB. Similarly, Botetzagias [
72], Nguyen [
67], and Wang [
92] found that income level was insignificant when determining the intention of consumers to recycle e-waste. This proved that the low or poor performance of Malaysian consumers in recycling e-waste is not primarily caused by their level of income. Overall, socio-demographic variables were discovered to be statistically non-significant predictors of ERI and ERB, except for education.
5.1. Implications
This study provides practical and theoretical implications that may benefit academicians, the government, and industrial players. From the practical stance, the study outcomes are crucial because they offer several practical implications for the government and the industry or manufacturers, especially in Malaysia, in terms of implementing effective e-waste recycling initiatives to promote social sustainability. Notably, MO emerged as the most significant factor in influencing ERI and ERB among consumers. Hence, the government should be able to strengthen the regulations and implementations of e-waste recycling activities that place more focus on consumers’ intrinsic motivation, while concurrently devising an effective method to foster ERB as MO among consumers in Malaysia. The government can promote e-waste recycling campaigns or programs that illustrate the significance of ERB and how it is viewed as a necessary behavior among consumers. Consumers should be advised about how ERB can be practiced on a daily basis and view it as their part of MO. According to Razali [
37], extrinsic motivation may serve as the pressure that triggers the behavior, whereas intrinsic motivation encourages people to continue and maintain practicing and performing the behavior in the future. Thus, intrinsic motivation should be enhanced and strengthened instead of concentrating on the provision of extrinsic incentives.
The results reveal that PC displayed a positive influence on ERI. Therefore, undeniably, making recycling more convenient enhances recycling intentions among consumers, thus increasing the recycling rate. This study proved that the impact of the logistic structure of waste disposal, including the proximity of recycling bins and the allocation of curbside collection, is vital to achieve greater public involvement in recycling. The involvement of all stakeholders is integral, including consumers, non-government agencies, collectors, retailers, and recycling facilities. Manufacturers and retailers must collaborate with third-party logistics companies to reduce the volume of e-waste via reverse logistics to effectively manage discarded and outdated electronic goods. Effective recycling driven by take-back and collection initiatives generates the reverse logistics strategy of businesses [
45].
Additionally, the implementation of an efficient e-waste management method should be strengthened and enhanced by deploying relevant legislation and regulations. In Malaysia, e-waste is listed as scheduled waste under the Environmental Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005. It specifies that no individual shall be permitted to dispose of any e-waste in a landfill, e-waste should be recycled and recovered at authorized recovery facilities, and the disposal process should take place only at licensed recycling facilities in an environment-friendly manner. The DOE has drafted a new regulation, known as the Environmental Quality (Household Scheduled Waste) Regulation, which is under review by the Attorney General’s Chambers of Malaysia (AGC Malaysia). Specifically, the government shoulders the responsibility to develop rules and regulations, monitor the operation of recovery facilities, and impose a penalty on unauthorized recovery facilities. Simultaneously, consumers have the responsibility to gather and dispose of their e-waste at authorized recycling facilities.
The government should also implement more educational campaigns regarding e-waste recycling. Such campaigns can increase awareness and attitude among Malaysians about the importance of recycling to converse our natural resources, as well as minimize the use of landfills and greenhouse gas emissions. When consumers realize how beneficial it is to recycle their e-waste, it will encourage them to recycle their e-waste in the future and promote e-waste recycling practices to others. In light of the insignificant link between SN and ERI, social media and marketing strategies in Malaysia should play a significant role and be better planned in order to motivate more individuals to participate in recycling activities. As for the low PBC score, educational and engagement actions should be taken to educate Malaysians on the appropriate methods to recycle and reuse their e-waste, as well as the types of e-waste elements that can be recycled. Another effective method that may convince consumers to engage in formal e-waste recycling activity is providing adequate resources for recycling e-waste. In fact, the insignificant PBC–ERI link observed in this study revealed that recycling behavior can be disrupted by the inconvenience of recycling. Hence, the necessity to ensure the availability and accessibility of e-waste disposal facilities should be of top concern.
From the theoretical perspective, this study contributes to the body of knowledge by extending the TPB framework in terms of ERB among consumers in Malaysia. The TPB model was extended by embedding attitude, SN, and PBC. However, some setbacks were noted when this model was applied in the context of pro-environmental behavior in past studies. For instance, pro-environmental behavior that involved skills, resources, accessibility, and control was poorly predicted by the TPB model. Therefore, the extended TPB model was proposed in this study to fill the gap through the inclusion of AEC, PC, and MO. With that, new findings were reported in this study pertaining to attitude, SN, PBC, AEC, PC, and MO with ERI, as well as ERI with ERB, among consumers in Malaysia.
In this study, MO emerged as the most influential factor in enhancing the intrinsic motivation of consumers to participate in ERI and ERB. This proves that intrinsic motivation is essential when adopting specific behavior, such as recycling e-waste among Malaysian consumers. Consumers display a greater sense of MO because they will feel right or wrong about what they should perform or should not. For instance, ERI increases if they feel guilty when they could not perform e-waste recycling activity and it is against their principles not to recycle e-waste. This study revealed how more compelling intrinsic motivation is than extrinsic rewards. MO is identified as positive behavior that should be fostered and embraced by all consumers in Malaysia.
The second highest score denotes the relationship between ERI and ERB. This proves that intentions to recycle have strong correlations with recycling behavior. The respondents agreed that if they have the intention to drop off or return their e-waste at a nearby recycling station or retailer, they would probably perform the intended recycling behavior in the future.
Next, PC displayed a significantly positive link to ERI. This means convenience can influence ERI among consumers in Malaysia. Apparently, the respondents agreed that when recycling is more convenient, their recycling intentions will be enhanced, and this can effectively increase the recycling rate. This study discovered that the conditions of the logistics chain of waste disposal, such as the physical closeness of bins or the availability of curbside waste, can affect the participation of the public in recycling activities. Performing e-waste recycling is eased when they have adequate space to store recycled e-waste at home and have sufficient time to recycle their e-waste. These should intensify their recycling intentions.
Notably, the relationships of ERI with attitude, SN, PBC, and AEC were insignificant in the context of Malaysian consumers. This calls for further investigations, mainly because past studies (see [
17,
30,
37,
87,
120]) found that attitude, SN, PBC, and AEC had a positive impact on behavioral intention.
5.2. Future Research Endeavor and Limitations
This study had several limitations. As the concepts of e-waste and e-waste recycling are still at their early stages in Malaysia, most of the consumers are still unfamiliar with e-waste. Moreover, this study used a limited sample size, and the results show that the relationship of ERI with attitude, SN, PBC, and AEC emerged as insignificant in the study, although in previous studies, the independent variables were strong predictors of recycling behavioral intention. For instance, Wan [
52] and Tonglet [
70] reported that attitude is the most significant determinant of recycling intention. Therefore, it is recommended that future empirical studies introduce and construct attitude from a different conceptual view, such as conceptualizing attitude as the willingness [
121] and attitude of eagerness [
122] toward pro-environmental studies such as e-waste recycling behavior. Meanwhile, other studies (see [
23,
30,
123,
124]) highlighted that SN is a crucial influencer of waste recycling intention. In addition, Pakpour [
64] indicated that PBC does not just predict behavioral intention, but it can also predict behavior and intention. On top of that, many studies have proven that AEC can positively predict recycling intentions (see [
32,
45,
52,
63]). Thus, future researchers may expand their sample size to test the extended TPB model.
Although the sample size (
n = 159) deployed in this study meets the required minimum sample size of G*Power (
n = 138), it failed to represent the whole population in Malaysia aged 18 years and above with the purchasing power of electrical and electronic products, as well as with the intention to recycle electrical and electronic goods. Therefore, in order to explore the changing behavior of consumers, future studies should focus on a specific group. For example, the specific group can be low-income consumers, high-income consumers, youth consumers, or even university consumers. These specific groups could establish a more comprehensive explanation of why consumers refuse to participate in ERB. Past studies (see [
25,
45,
125]) have assessed university students as their target respondents to study recycling intention and behavior. Meanwhile, Shaharudin [
52] studied youth and Kumar looked into young adults to determine ERI and ERB.
Next, the survey questionnaire method was executed online using Google Forms in this study. This survey method led to some shortcomings in this study. Despite being a free online tool that allows researchers to create surveys within a short time and gather data easily, Google Forms involves a number of disadvantages including respondents facing poor Internet connection to access Google Forms. Hence, future researchers should distribute the questionnaire forms manually to the target respondents. In addition, researchers may also provide an explanation to the respondents to ensure that the respondents completely understand the questions before providing responses.
In this study, ERB on ERI implementation scored an R2 value of 0.231 (rather weak), implying that the variable displayed poor fit in this model. Hence, future researchers may use or add additional variables as the extended determinants in the TPB to enhance the predictive accuracy of the model.