Biochemical Analysis and Toxicity Assessment of Utilization of Argon Oxygen Decarbonization Slag as a Mineral Fertilizer for Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb) Planting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AOD Slag
2.2. Batch Leaching Test
2.3. Pot Experiments
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Minerals and Morphology of AOD Slag
3.2. Leaching Behavior of AOD Slag and Soil
3.3. Effects of AOD Slag Fertilization on Growth of Tall Fescue Seedling
3.4. Effects of AOD Slag on Chlorophyll Content
3.5. Cr Accumulation in Tall Fescue Seedling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adegoloye, G.; Beaucour, A.L.; Ortola, S.; Noumowé, A. Concretes made of EAF slag and AOD slag aggregates from stainless steel process: Mechanical properties and durability. Constr. Build Mater. 2016, 115, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; Marroccoli, M.; Nobili, M.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L. The use of oil well-derived drilling waste and electric arc furnace slag as alternative raw materials in clinker production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, P.E.; Papadimitriou, G.D.; Tsivilis, S.; Koroneos, C. Utilization of steel slag for portland cement clinker production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Xue, Y.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Y. Utilization of steel slag as aggregates for stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixtures. Build Environ. 2007, 42, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslehuddin, M.; Sharif, A.M.; Shameem, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Barry, M.S. Comparison of properties of steel slag and crushed limestone aggregate concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Kalbasi, M.; Shariatmadari, H. Effect of steel converter sludge as iron fertilizer and soil amendment in some calcareous soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 27, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Tu, C.; Yu, Z. Environmental risks for application of iron and steel slags in soils in China: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, L.R.; Rodrigues, S.L.; Ramos, S.J.; Pereira, H.S.; Amaral, D.C.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Beneficial use of a by-product from the phosphate fertilizer industry in tropical soils: Effects on soil properties and maize and soybean growth. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 112, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, F.H.A.; Nunes, G.H.D.S.; Preston, W.; Souza, E.B.D.; Mariano, R.D.L.R.; Datnoff, L.E.; Araújo Do Nascimento, C.W. Slag-based silicon fertilizer improves the resistance to bacterial fruit blotch and fruit quality of melon grown under field conditions. Crop Prot. 2021, 147, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Fan, Y.; Hua, L.; Cheng, F.Q.; Xue, Z.J.; Ling, L.Y. Effects of magnesium slag based Si-K fertilizer on salty soil fertility and growth of Brassica campestris L. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2015, 42, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, I.M.; Prado, R.M.; Nogueira, T.A.R. Macronutrients in marandu palisade grass as influenced by lime, slag, and nitrogen fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2011, 42, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Forssberg, E.; Nordström, U. Physicochemical and mineralogical properties of stainless steel slags oriented to metal recovery. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2004, 40, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Georgiadou, E.C.; Zissimos, A.M.; Christoforou, I.C.; Fotopoulos, V. Uptake of hexavalent chromium by Lactuca sativa and Triticum aestivum plants and mediated effects on their performance, linked with associated public health risks. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Kiran, S.; Shah, F.; Wajid, N. Alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize by Fe fortification and chromium tolerant ACC deaminase production plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2019, 185, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Adhikari, S.; Ghosh, S.; Azahar, I.; Hossain, Z. Imbalance of redox homeostasis and antioxidant defense status in maize under chromium (VI) stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 169, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kapoor, D.; Wang, J.F.; Shahzad, B.; Kumar, V.; Bali, A.S.; Jasrotia, S.; Zheng, B.S.; Yuan, H.; Yan, D.L. Chromium bioaccumulation and its impacts on plants: An overreview. Plants 2020, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, D.; Tiwari, M.; Dutta, P.; Singh, P.; Chawda, K.; Kumari, M.; Chakrabarty. Chromium stress in plants: Toxicity, tolerence and phytoremediation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, A.; Xu, M.; Gan, Y. Chromium-induced reactive oxygen species accumulation by altering the enzymatic antioxidant system and associated cytotoxic, genotoxic, ultrastructural, and photosynthetic changes in palnts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Li, Y.; Long, S.; Wen, S.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Guo, H.; Xu, Y. Hydrogen sulfide improves tall fescue photosynthesis response to low-light stress by regulating chlorophyll and carotenoid metabolisms. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2022, 170, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Ren, Q.Q.; Zeng, Y.N.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.J. Toxicity assessment of the utilization of AOD slag as a mineral fertilizer for pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) planting. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 328, 129617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L. Determination of Chlorophyll a and b Contents, Experimental Guidance for Plant Physiology; High Education Press Beijing: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Chen, L.; Fan, J.; Fu, J. Alleviation of heat damage to photosystem II by nitric oxide in tall fescue. Photosynth. Res. 2013, 116, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A.C. Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 2, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, E.J.; Choi, Y.C. Development of carbon-capture binder using stainless steel argon oxygen decarburization slag activated by carbonation. J. Cleaner Prod. 2018, 180, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Renman, G.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Klysubun, W. Phosphorus removal by slag depends on its mineralogical composition: A comparative study of AOD and EAF slags. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 25, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, K.; Blottnitz, H.; Petersen, J. Ageing of chromium(III)-bearing slag and its relation to the atmospheric oxidation of solid chromium(III)-oxide in the presence of calcium oxide. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qu, Z.M. Physicochemical property and chromium leaching behavior in different environments of glass ceramics prepared from AOD stainless steel slag. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 805, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samada, Y.; Miki, T.; Hino, M. Prevention of chromium elution from stainless steel slag into seawater. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Tu, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, T. Recovery of chromium from chromium-bearing slags produced in the stainless-steel smelting: A review. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 296, 126467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Shen, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y. Mechanisms involved in the roasting of pellets composed of stainless steel slag and sodium hydroxide to extract chromium. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Calvo-Polanco, M.; Chen, Z.C.; Zwiazek, J.J. Growth and physicological responses of trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides), white spruce (Picea glauca) and tamarack (Larix laricina) seedlings to root zone pH. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, F.; Zwiazek, J.J. Response of jack pine (Pinus banksiana) seedlings to root zone pH and calcium. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 111, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Das, H.; Meena, V.D. Assessment of chromium efficacy on germination, root elongation, and coleoptile growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at different growth periods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, J.; Zhang, G. Experimental investigation on optimization of vegetation performance of porous sea sand concrete mixtures by pH adjustment. Constr. Build Mater. 2020, 249, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahoonia, T.S.; Care, D.; Nielsen, N.E. Root hairs and phosphorus acquisition of wheat and barley cultivars. Plant Soil 1997, 191, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zwiazek, J.J. Responses of Reclamation Plants to High Root Zone pH: Effects of Phosphorus and Calcium Availability. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalcorso, G.; Manara, A.; Piasentin, S.; Furini, A. Nutrient metal elements in plants. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1770–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Sinam, G.; Kumar Mishra, R.; Sinha, S. Interactive effects of Cr and Fe treatments on plants growth, nutrition and oxidative status in Zea mays L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Windt, L.; Chaurand, P.; Rose, J. Kinetics of steel slag leaching: Batch tests and modeling. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medda, S.; Mondal, N.K. Chromium toxicity and ultrastructural deformation of Cicer arietinum with special reference of root elongation and coleoptile growth. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, M.F.; Ma, L. Effect of chromium on seed germination, early seedling growth and chromium accumulation in tomato genotypes. Acta. Physiol. Plant 2021, 43, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambulska, U.Y.; Bayliak, M.M.; Lushchak, V.I. Chromium(VI) Toxicity in Legume Plants: Modulation Effects of Rhizobial Symbiosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8031213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, N. Effect of chromium on seed germination and seedling growth of green garm (Phaseols aureus L.) and chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Int. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2017, 6, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Meng, Z.W.; Chen, Y.P. Toxicity assessment of molybdenum slag as a mineral fertilizer: A case study with pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Chemosphere 2019, 217, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, M.; Chen, X.; Deng, T.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Morel, J.L.; Qiu, R.; Wang, S. Chromium biogeochemical behaviour in soil-plant systems and remediation strategies: A critical review. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 424, 127233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.P.; Mahajan, P.; Kaur, S.; Batish, D.R.; Kohli, R.K. Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Iqbal, M.; Aslam Bharwana, S.; Siddiqi, Z.; Farid, M.; Ali, Q.; Saeed, R.; Rizwan, M. Mannitol alleviates chromium toxicity in wheat plants in relation to growth, yield, stimulation of anti-oxidative enzymes, oxidative stress and Cr uptake in sand and soil media. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
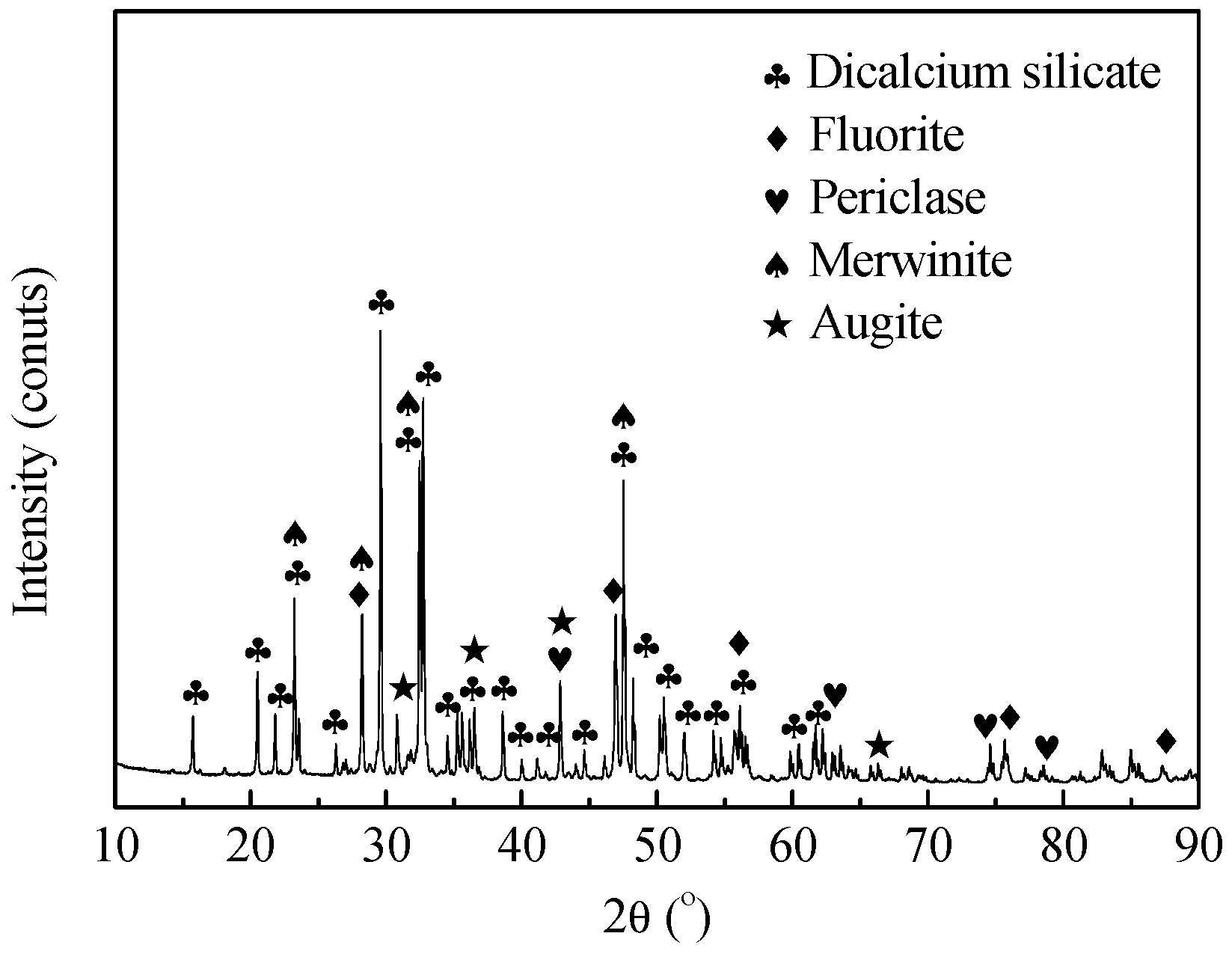

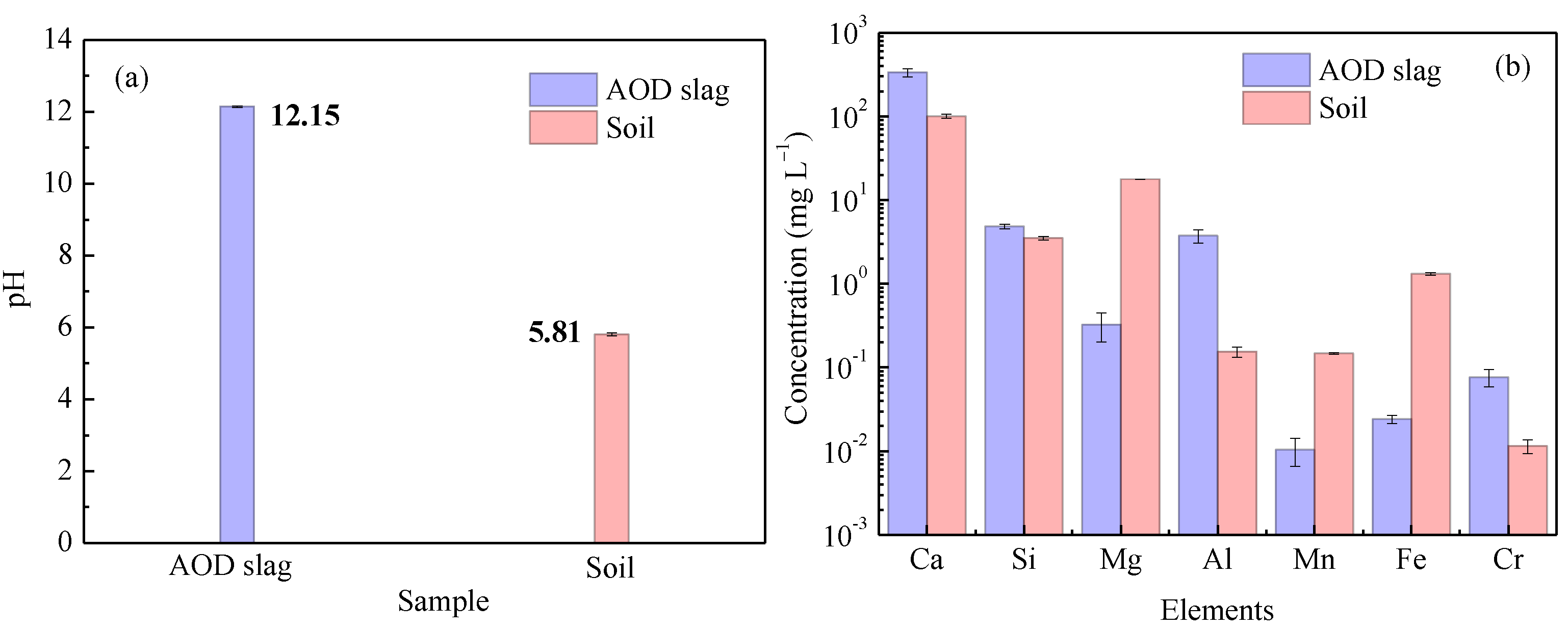
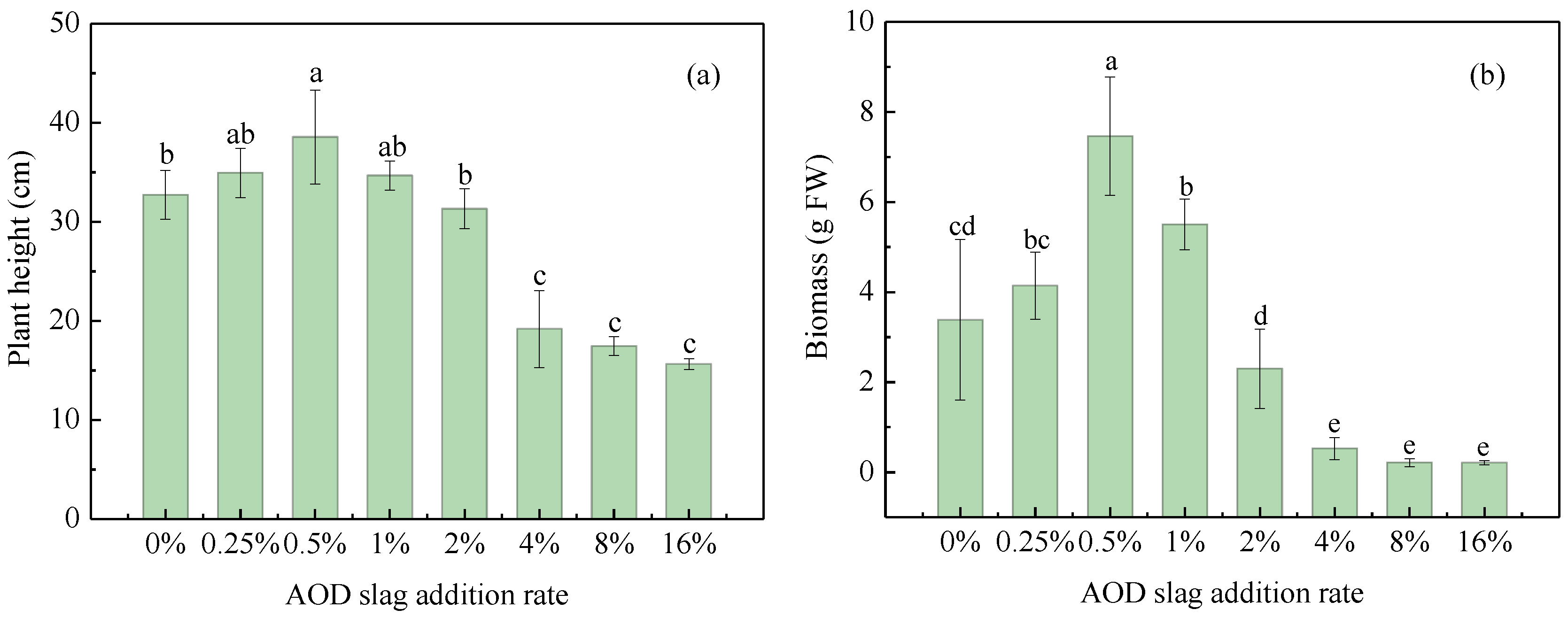

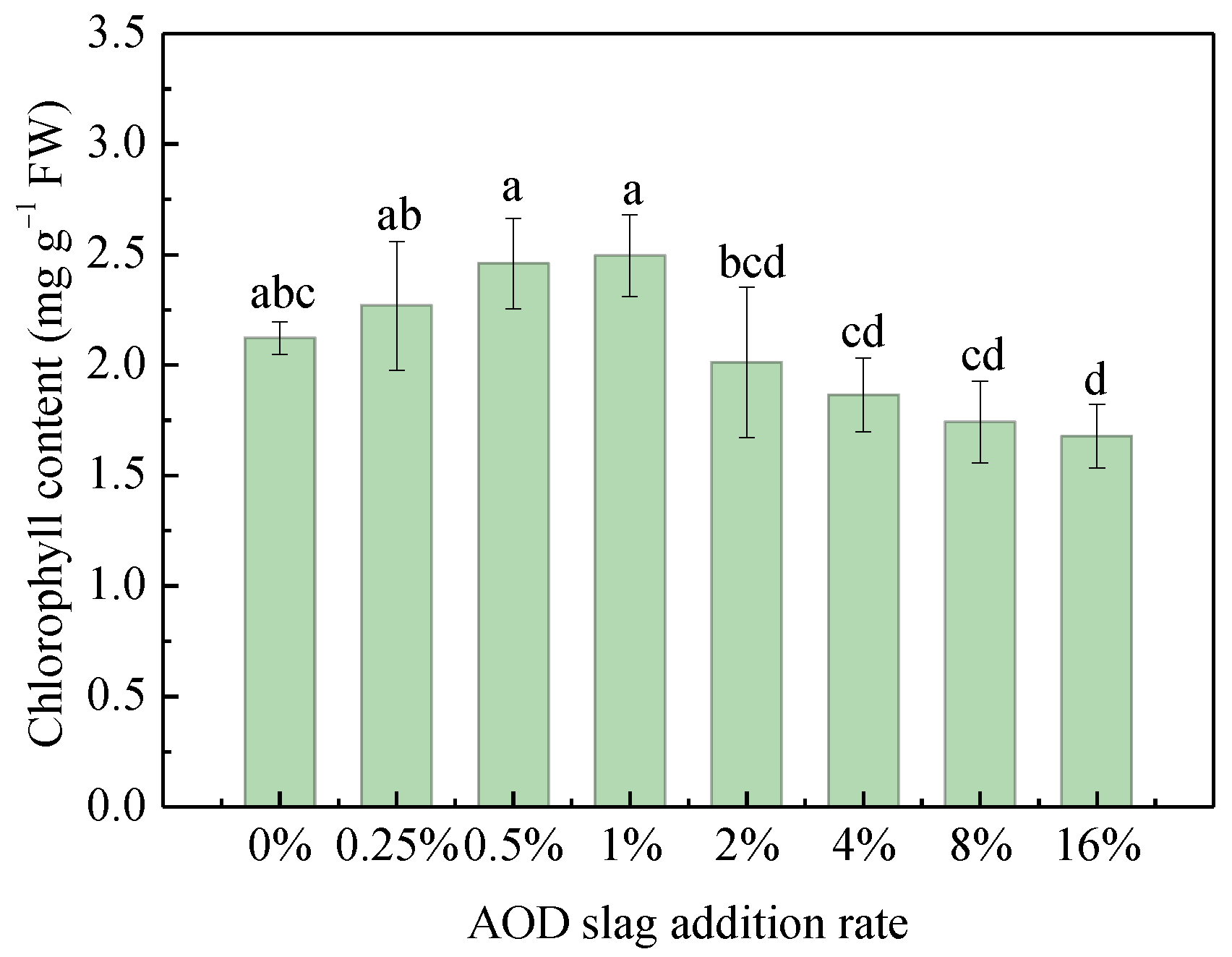


| Oxide | Content (wt.%) | Oxide | Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 62.076 | MnO | 0.171 |
| SiO2 | 26.213 | SrO | 0.024 |
| MgO | 4.863 | ZrO2 | 0.012 |
| Al2O3 | 1.722 | Nb2O5 | 0.007 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.358 | SO3 | 0.594 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.378 | P2O5 | 0.006 |
| TiO2 | 0.212 | F | 3.363 |
| Type | Value | Element | Content (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.13 ± 0.06 | Ca | 11,843.19 ± 493.69 |
| EC (mS cm−1) | 0.50 ± 0.04 | Si | 1335.44 ± 39.38 |
| OM (g kg−1) | 601.17 ± 14.51 | Mg | 1236.86 ± 156.10 |
| Total N (g kg−1) | 7.06 ± 0.73 | Al | 376.05 ± 9.36 |
| Total P (g kg−1) | 0.72 ± 0.09 | Fe | 695.05 ± 19.69 |
| Total K (g kg−1) | 1.01 ± 0.12 | Mn | 56.28 ± 10.09 |
| Available N (mg kg−1) | 337.54 ± 6.22 | Ti | 10.29 ± 0.77 |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 80.44 ± 2.09 | Cr | 3.52 ± 0.26 |
| Available K (mg kg−1) | 589.00 ± 9.35 | Cu | 0.57 ± 0.08 |
| - | - | Zn | 18.02 ± 1.94 |
| - | - | Ni | 5.21 ± 0.70 |
| - | - | Cd | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| - | - | Hg | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| - | - | Pb | 3.86 ± 0.48 |
| Addition Rate | Tall Fescue | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRL (cm) | RSA (cm2) | RT | RH | |
| 0% | 104.69 ± 8.11 c | 13.54 ± 1.89 bc | 298 ± 12 c | 733 ± 51 cd |
| 0.25% | 120.86 ± 12.03 b | 14.48 ± 1.39 b | 344 ± 28 b | 831 ± 69 c |
| 0.5% | 147.11 ± 11.21 a | 17.11 ± 1.96 a | 483 ± 31 a | 1387 ± 102 a |
| 1% | 106.10 ± 9.66 bc | 13.20 ± 0.58 bc | 271 ± 36 cd | 989 ± 77 b |
| 2% | 89.33 ± 3.12 d | 12.20 ± 0.78 bc | 246 ± 29 d | 698 ± 49 d |
| 4% | 73.12 ± 5.02 e | 11.36 ± 1.21 c | 198 ± 19 e | 517 ± 41 e |
| 8% | 55.44 ± 4.91 f | 8.27 ± 0.61 d | 159 ± 14 f | 344 ± 28 f |
| 16% | 36.22 ± 3.24 g | 5.53 ± 0.28 e | 137 ± 20 f | 244 ± 16 f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Biochemical Analysis and Toxicity Assessment of Utilization of Argon Oxygen Decarbonization Slag as a Mineral Fertilizer for Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb) Planting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159286
Cai S, Liu B, Li J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Wang Y, Liu T. Biochemical Analysis and Toxicity Assessment of Utilization of Argon Oxygen Decarbonization Slag as a Mineral Fertilizer for Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb) Planting. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159286
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Shuang, Bao Liu, Junguo Li, Yuzhu Zhang, Yanan Zeng, Yajun Wang, and Tianji Liu. 2022. "Biochemical Analysis and Toxicity Assessment of Utilization of Argon Oxygen Decarbonization Slag as a Mineral Fertilizer for Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb) Planting" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159286
APA StyleCai, S., Liu, B., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Zeng, Y., Wang, Y., & Liu, T. (2022). Biochemical Analysis and Toxicity Assessment of Utilization of Argon Oxygen Decarbonization Slag as a Mineral Fertilizer for Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb) Planting. Sustainability, 14(15), 9286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159286





