A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Latin American Universities
2.2. Smart Campus
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. IPA Analysis
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Vaujany, F.X.; Walsh, I.; Mitev, N. An Historically Grounded Critical Analysis of Research Articles in IS. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2011, 20, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melé, D. Re-thinking Capitalism: What We can Learn from Scholasticism? J. Bus. Ethic 2014, 133, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrais, C.A.; Corcioli, G.; Medina, G.D.S. The Role Played by Public Universities in Mitigating the Coronavirus Catastrophe in Brazil: Solidarity, Research and Support to Local Governments Facing the Health Crisis. Front. Sociol. 2021, 6, 610297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsakova, R.; Kuzmina, N.; Kochkina, D. Smart Technology Integration in the System of Bachelors’ Language Training. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tikhonova, E.P. Possibilities OF Digital Culture in Searching of Educational New Technologies and Academia Formation. Vestnik Tomsk. Gos. Univ. Kul’turologiya i Iskusstv. 2019, 30, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Bautista, D.; Medina-Cárdenas, Y.; Coronel-Rojas, L.A.; Cuesta-Quintero, F.; Barrientos-Avendaño, E.; León, R.A.G.; Maestre-Góngora, G.P. Smart university: Strategic map since the adoption of technology. RISTI Rev. Iber. De Sist. E Tecnol. De Inf. 2020, E27, 711–724. [Google Scholar]
- UN (United Nations). Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; A/RES/70/1; UN (United Nations): New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 16301. [Google Scholar]
- Makieła, Z.J.; Stuss, M.M.; Mucha-Kuś, K.; Kinelski, G.; Budziński, M.; Michałek, J. Smart City 4.0: Sustainable Urban Development in the Metropolis GZM. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-Y. How Should the Structure of Smart Cities Change to Predict and Overcome a Pandemic? Sustainability 2022, 14, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawviang, A.; Kiattisin, S. Sustainable Development: Smart Co-Operative Management Framework. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Arias-Navarrete, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Proposal of an Architecture for the Integration of a Chatbot with Artificial Intelligence in a Smart Campus for the Improvement of Learning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min-Allah, N.; Alrashed, S. Smart campus—A sketch. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, R.W. Transdisciplinarity: Science for and with society in light of the university’s roles and functions. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, A.J. Reformed Confessions and Scholasticism. Diversity and Harmony. Perichoresis 2016, 14, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kintzinger, M. Historiography of the University. A New Field for an Old Topic in German Historical Scholarship = Historiograf? A sobre la Universidad. Un nuevo campo para un viejo tema en la Historia de la Universidad alemana. CIAN-Rev. Hist. Univ. 2017, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velde, D.T. The Relevance of Reformed Scholasticism for Contemporary Systematic Theology. Perichoresis 2016, 14, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arocena, R.; Sutz, J. Latin American Universities: From an Original Revolution to an Uncertain Transition. High. Educ. 2005, 50, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.-G.; Serra, M.A.; Vieira, M.-J. Social Engagement in Latin American Universities. High. Educ. Policy 2017, 31, 513–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnove, R.F. A Survey of Literature and Research on Latin American Universities. Lat. Am. Res. Rev. 1967, 3, 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, B.V.; Vasen, F.; Soto, J.C.V. Interdisciplinary Centers in Latin American Universities: The Challenges of Institutionalization. High. Educ. Policy 2018, 32, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nez, E. Antecedentes Históricos da Universidade no Brasil e no mundo: Do predomínio da Igreja ao início da democratização do acesso. Humanid. Inovação 2018, 5, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Montoya, M.S. Transformación Digital e Innovación Educativa En Latinoamérica En El Marco Del COVID-19. Campus Virtuales Rev. Científica Iberoam. Tecnol. Educ. 2020, 9, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Coccoli, M.; Maresca, P.; Stanganelli, L. The role of big data and cognitive computing in the learning process. J. Vis. Lang. Comput. 2017, 38, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.W.; Eisenberg, L. Agile sustainable communities: On-site renewable energy generation. Util. Policy 2008, 16, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Sánchez, A.; Álvarez-García, J.; Del Río-Rama, M.C.; Sarango-Lalangui, P.O. Analysis of the Scientific Literature Published on Smart Learning. Espacios 2018, 39, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, A.; Sugino, N.; Suzuki, T.; Ishijima, S. Step towards the Smart Campus: A Venture Project Based on Distance Learning by a Hybrid Video Conferencing System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–11 October 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Prandi, C.; Monti, L.; Ceccarini, C.; Salomoni, P. Smart Campus: Fostering the Community Awareness Through an Intelligent Environment. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2019, 25, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.-S.; Chang, J.-W.; Lee, M.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, D.-S. Enabling Intelligent Environment by the Design of Emotionally Aware Virtual Assistant: A Case of Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62032–62041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, W.; Kurniawan, N.B.; Suhardi, S.; Yazid, S. Smart Campus Features, Technologies, and Applications: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation, Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2017; Volume 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, E.; Tamminen, S.; Yasmin, R.; Ristimella, E.; Peltonen, E.; Harju, M.; Lovén, L.; Riekki, J.; Pirttikangas, S. Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. Data Acquisition and Analysis of Smart Campus Based on Wireless Sensor. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 102, 2897–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; An, L.; Su, S.; Yin, X.; Yin, L.; Cui, X. A Real-Time Correlation of Host-Level Events in Cyber Range Service for Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35355–35364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-J. Teaching Performance Evaluation in Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 77754–77766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, D.; Sun, M.; Yang, S.; Yu, S.-J.; Manogaran, G.; Mastorakis, G.; Mavromoustakis, C.X. Research on Key Technologies of Smart Campus Teaching Platform Based on 5G Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 20664–20675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Bautista, D.; Maestre-Góngora, G.P.; Guerrero, C.D. Smart University: Characterization of the Current Situation of Intelligent Technologies, Based on Two Case Studies Caracterización de La Situación Actual de Las Tecnologías Inteligentes Para Una Universidad Inteligente En Colombia/Latinoamérica. RISTI Rev. Iber. Sist. Tecnol. Inf. 2020, 2020, 484–501. [Google Scholar]
- Celdran, A.H.; Clemente, F.J.G.; Saenz, J.; De La Torre, L.; Salzmann, C.; Gillet, D. Self-Organized Laboratories for Smart Campus. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2019, 13, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.Q.; Donsión, M.P. Contribution to the knowledge of a microgrid. Smart Campus. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2016, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yange, C.; Xiaopin, Y.; Zhili, Z.; Liang, Z. Study and Design of SDN Intelligent Campus Architecture based on IPv6. Int. J. Future Gener. Commun. Netw. 2016, 9, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, T.; Yang, X.; Ren, M. The Design and Implementation of Smart Campus System. J. Comput. 2017, 12, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Torres, B.; Alberto Rodriguez-Rodriguez, J.; Willmer Rico-Bautista, D.; Guerrero, C.D. Smart Campus: Trends in Cybersecurity and Future Development. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Pedagog. Tecnol. Colomb. 2018, 27, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards Next Generation Teaching, Learning, and Context-Aware Applications for Higher Education: A Review on Blockchain, IoT, Fog and Edge Computing Enabled Smart Campuses and Universities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nan, F.; Suo, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y.; Shan, S. Real-Time Monitoring of Smart Campus and Construction of Weibo Public Opinion Platform. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76502–76515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G. Design and Implementation of Smart Campus Automatic Settlement PLC Control System for Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62601–62611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.M.; Li, S.-S.; Ren, C.-H.; Liu, H.-X.; Han, Y.; Liu, L. Situational Awareness System in the Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 63976–63986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, J.; Kefalakis, N.; Serrano, M.; Hauswirth, M. Design principles for utility-driven services and cloud-based computing modelling for the Internet of Things. Int. J. Web Grid Serv. 2014, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Muñoz, A.; Soto, J.; Botía, J.A. Resource assignment in intelligent environments based on similarity, trust and reputation. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2014, 6, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Kalasek, R.; Pichler-Milanovic, N.; Meijers, E. Smart Cities Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities. Cent. Reg. Sci. 2007, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragliu, A.; Del Bo, C.; Nijkamp, P. Smart Cities in Europe. J. Urban Technol. 2011, 18, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, A.F.C.; Da Nóbrega, P.I.S. Decision making based on citizens standpoint: An Importance-Performance Analysis of Smart City Indicators. Int. J. Manag. Decis. Mak. 2021, 20, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.R.; Prasetiyowati, M.I. Gamifying Student Routines to Improve Campus Experience through Mobile Application in Indonesia. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, X.; Duan, S. Articulatory-Acoustic Analyses of Mandarin Words in Emotional Context Speech for Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48418–48427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, S.; Santoyo-Ramón, J.A.; Palacios, D.; Baena, E.; Mora-García, R.; Medina, M.; Mora, P.; Barco, R. The Campus as a Smart City: University of Málaga Environmental, Learning, and Research Approaches. Sensors 2019, 19, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Campana, M.; López, G.; Vázquez, E.; Villagrá, V.A.; Berrocal, J. Smart CEI Moncloa: An IoT-based Platform for People Flow and Environmental Monitoring on a Smart University Campus. Sensors 2017, 17, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagol, P.; Ramos, F.; Trilles, S.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Perales, F.J. New Trends in Using Augmented Reality Apps for Smart City Contexts. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasileva, R.; Rodrigues, L.; Hughes, N.; Greenhalgh, C.; Goulden, M.; Tennison, J. What Smart Campuses Can Teach Us about Smart Cities: User Experiences and Open Data. Information 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martilla, J.A.; James, J.C. Importance-Performance Analysis. J. Mark. 1977, 41, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, I. Importance-performance analysis: A valid management tool? Tour. Manag. 2015, 48, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boley, B.B.; McGehee, N.G.; Hammett, A.T. Importance-performance analysis (IPA) of sustainable tourism initiatives: The resident perspective. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Weiler, B.; Young, M.; Lee, Y.L. Conceptualizing and Measuring Service Quality: Towards Consistency and Clarity in its Application to Travel Agencies in China. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2016, 17, 516–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLeay, F.; Robson, A.; Yusoff, M. New applications for importance-performance analysis (IPA) in higher education. J. Manag. Dev. 2017, 36, 780–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal University of Campina Grande UFCG Em Números. Available online: https://portal.ufcg.edu.br/ (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Federal University of Campina Grande Portal UOL Destaca a UFCG Como a Maior Inventora Do País. Available online: https://portal.ufcg.edu.br/ultimas-noticias/3096-portal-uol-destaca-a-ufcg-como-a-maior-inventora-do-pais.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Madeiro, C. Como Universidade No Agreste Paraibano Virou Maior Inventora Do Brasil. Available online: https://www.uol.com.br/tilt/noticias/redacao/2021/11/15/universidade-publica-no-agreste-paraibano-virou-a-maior-inventora-do-brasil.htm (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Bi, J.-W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.-P.; Zhang, J. Wisdom of crowds: Conducting importance-performance analysis (IPA) through online reviews. Tour. Manag. 2018, 70, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.K.W.; Hitchcock, M. Importance–performance analysis in tourism: A framework for researchers. Tour. Manag. 2015, 48, 242–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, K.; Kniss, J.; Riesenfeld, R.; Johnson, C. Visualizing Summary Statistics and Uncertainty. Comput. Graph. Forum 2010, 29, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukey, J.W. Exploratory Data Analysis; Pearson: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, K.M.; Iglewicz, B. Bivariate Extensions of the Boxplot. Technometrics 1992, 34, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Vandervieren, E. An adjusted boxplot for skewed distributions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 5186–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S. Service Encapsulation-Based Model for Smart Campus. J. Electron. Commer. Organ. 2012, 10, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, V.; Abu Alnaaj, K.; Saboor, S. An Investigation into Stakeholders’ Perception of Smart Campus Criteria: The American University of Sharjah as a Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderström, O. The three modes of existence of the pandemic smart city. Urban Geogr. 2020, 42, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offenhuber, D. The platform and the bricoleur—Improvisation and smart city initiatives in Indonesia. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1565–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, Y.; Mathew, S.S.; Lakas, A. Building a smart campus to support ubiquitous learning. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2014, 6, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccoli, M.; Guercio, A.; Maresca, P.; Stanganelli, L. Smarter universities: A vision for the fast changing digital era. J. Vis. Lang. Comput. 2014, 25, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; García-Valverde, T.; Pereñíguez, F.; Botía, J.A. Activity recommendation in intelligent campus environments based on the Eduroam federation. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2016, 8, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segredo, E.; Miranda, G.; Leon, C. Towards the Education of the Future: Computational Thinking as a Generative Learning Mechanism. Educ. Knowl. Soc. 2017, 18, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
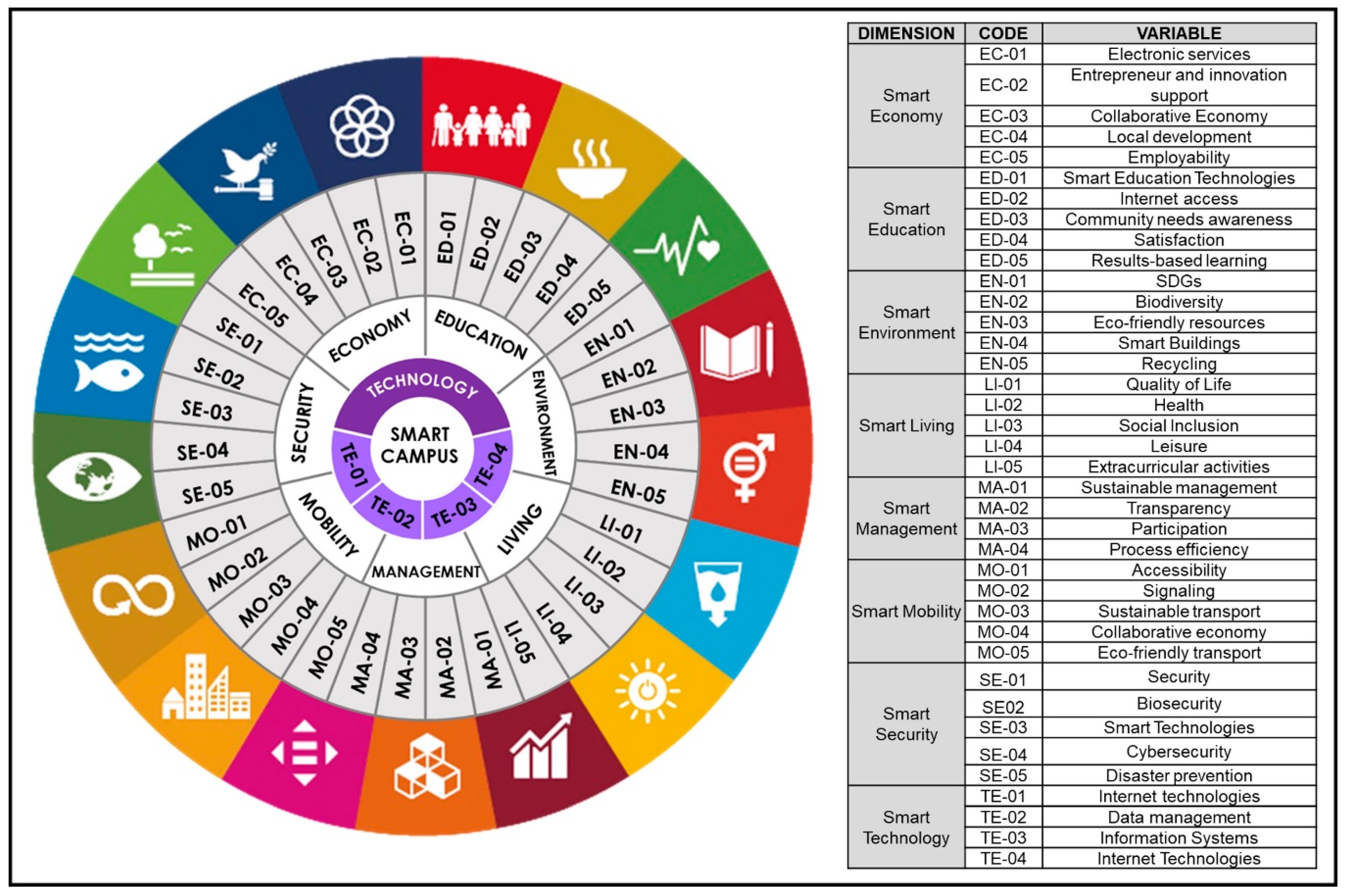




| Dimension | Indicators | Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Economy (EC) | On my campus, it is possible to perform electronic transactions, such as paying university fees or making payments in stores. | Electronic services |
| My campus supports business ideas through entrepreneurship centers, innovation centers, entrepreneur incubators, specialized centers, etc. | Entrepreneur and innovation support | |
| My campus has collaborative economy networks or actions of shared economy. | Collaborative economy | |
| My campus supports local economic development with projects and actions toward the community. | Local development | |
| My campus has a department or sector to support employability. | Employability | |
| Smart Education (ED) | My campus uses smart technologies for teaching, for example, cloud computing, IoT, IA, big data, etc. | Smart education technologies |
| My campus has open and available internet bandwidth for all. | Internet access | |
| My campus consults the community about its educational needs (e.g., course availability). | Community needs awareness | |
| My campus monitors the satisfaction level of students and staff. | Satisfaction | |
| On my campus, the teaching methodology is results-based learning. | Results-based learning | |
| Smart Environment (EN) | My campus develops actions toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). | SDGs |
| On my campus, there are actions to protect the local biodiversity. | Biodiversity | |
| My campus uses bioenergy and smart technologies to manage energy and water resources, such as automatic lighting. | Eco-friendly resources | |
| My campus has smart buildings, e.g., buildings with automated management of resources. | Smart buildings | |
| My campus recycles residues. | Recycling | |
| Smart Living (LI) | On my campus, there is quality-of-life and well-being monitoring. | Quality of life |
| My campus implements occupational health and wellness programs. | Health | |
| My campus measures the level of social inclusion among students. | Social inclusion | |
| My campus has adequate leisure spaces. | Leisure | |
| On my campus, there are extracurricular activities for the community. | Extracurricular activities | |
| Smart Management (MA) | My campus has a management focused on the sustainable use of resources. | Sustainable management |
| My campus publishes the accountability annually. | Transparency | |
| My campus performs participatory strategic planning. | Participation | |
| My campus has an online process management platform. | Process efficiency | |
| Smart Mobility (MO) | There is adequate public transport to access my campus. | Accessibility |
| There is traffic signaling on campus. | Signaling | |
| My campus encourages or uses low-carbon transport. | Sustainable transport | |
| My campus encourages collaborative transport, such as rides. | Collaborative economy | |
| My campus has support facilities for bikes. | Eco-friendly transport | |
| Smart Security (SE) | My campus ensures physical and material security. | Security |
| My campus has biosafety protocols. | Biosecurity | |
| My campus has technological systems to support security (e.g., facial recognition system). | Smart technologies | |
| My campus has protection from cyber attacks. | Cybersecurity | |
| My campus has protocols for the prevention and management of risks and disasters. | Disaster prevention | |
| Smart Technology (TE) | My campus uses internet technologies, such as the Internet of Things. | Internet technologies |
| My campus has systems for data management and interconnection. | Data management | |
| My campus has technological control systems, such as sensors. | Information systems | |
| My campus has systems (e.g., webpage) to offer and manage services to its stakeholders. | Internet technologies |
| Characteristic | Number of Respondents | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 213 | 56.2 |
| Male | 166 | 43.8 |
| Age | ||
| Less than 18 years old | 2 | 0.5 |
| Between 18 and 30 years old | 315 | 83.1 |
| Between 31 and 40 years old | 40 | 10.6 |
| Between 41 and 50 years old | 15 | 4.0 |
| Between 51 and 60 years old | 5 | 1.3 |
| More than 61 years old | 2 | 0.5 |
| Course type | ||
| Undergraduate | 304 | 80.2 |
| Graduate and Postgraduate | 75 | 19.8 |
| Campus | ||
| Campina Grande city | 291 | 76.8 |
| Cajazeiras city | 10 | 2.6 |
| Cuite city | 16 | 4.2 |
| Patos city | 13 | 3.4 |
| Pombal city | 10 | 2.6 |
| Sousa city | 29 | 7.7 |
| Sume city | 10 | 2.6 |
| Ranking | Importance | Performance | GAP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Mean | SD | Alpha | Dimension | Mean | SD | Alpha | Dimension | I–P | |
| 1 | LI | 4.713 | 0.024 | 0.911 | MA | 2.898 | 0.578 | 0.737 | MA | 1.779 |
| 2 | TE | 4.710 | 0.082 | 0.845 | TE | 2.783 | 0.657 | 0.754 | EC | 1.878 |
| 3 | SE | 4.707 | 0.077 | 0.916 | EC | 2.562 | 0.289 | 0.775 | TE | 1.927 |
| 4 | MA | 4.677 | 0.042 | 0.907 | ED | 2.527 | 0.234 | 0.779 | ED | 2.122 |
| 5 | EN | 4.672 | 0.086 | 0.924 | EN | 2.495 | 0.484 | 0.815 | EN | 2.177 |
| 6 | ED | 4.649 | 0.040 | 0.887 | LI | 2.473 | 0.129 | 0.839 | MO | 2.221 |
| 7 | MO | 4.633 | 0.135 | 0.898 | MO | 2.412 | 0.726 | 0.745 | LI | 2.240 |
| 8 | EC | 4.440 | 0.107 | 0.893 | SE | 2.382 | 0.463 | 0.818 | SE | 2.325 |
| - | TOTAL | 4.650 | 0.074 | 0.976 | TOTAL | 2.566 | 0.445 | 0.950 | TOTAL | 2.08 |
| Variables | Importance | Performance | Gap | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Mean | SD | Rank | Mean | SD | Rank | I–P | Rank | |
| Electronic services | EC-01 | 4.30 | 0.92 | 38 | 2.78 | 1.31 | 13 | 1.52 | 3 |
| Entrepreneur and innovation support | EC-02 | 4.49 | 0.83 | 36 | 2.64 | 1.18 | 16 | 1.85 | 11 |
| Collaborative economy | EC-03 | 4.35 | 0.90 | 37 | 2.28 | 1.19 | 26 | 2.07 | 17 |
| Local development | EC-04 | 4.53 | 0.77 | 32 | 2.87 | 1.24 | 9 | 1.66 | 6 |
| Employability | EC-05 | 4.52 | 0.86 | 34 | 2.23 | 1.11 | 28 | 2.29 | 26 |
| Smart education technologies | ED-01 | 4.64 | 0.68 | 25 | 2.72 | 1.16 | 15 | 1.92 | 15 |
| Internet access | ED-02 | 4.70 | 0.70 | 13 | 2.21 | 1.19 | 30 | 2.49 | 30 |
| Community needs awareness | ED-03 | 4.61 | 0.74 | 27 | 2.46 | 1.12 | 21 | 2.16 | 20 |
| Satisfaction | ED-04 | 4.68 | 0.64 | 19 | 2.45 | 1.21 | 23 | 2.23 | 24 |
| Results-based learning | ED-05 | 4.61 | 0.69 | 28 | 2.80 | 1.17 | 12 | 1.81 | 9 |
| SDGs | EN-01 | 4.75 | 0.61 | 5 | 2.93 | 1.10 | 7 | 1.81 | 10 |
| Biodiversity | EN-02 | 4.72 | 0.61 | 10 | 2.85 | 1.29 | 10 | 1.86 | 12 |
| Eco-friendly resources | EN-03 | 4.65 | 0.70 | 22 | 2.12 | 1.15 | 32 | 2.53 | 32 |
| Smart buildings | EN-04 | 4.53 | 0.81 | 33 | 1.84 | 1.01 | 37 | 2.69 | 37 |
| Recycling | EN-05 | 4.71 | 0.67 | 11 | 2.72 | 1.21 | 14 | 1.99 | 16 |
| Quality of life | LI-01 | 4.69 | 0.65 | 18 | 2.27 | 1.18 | 27 | 2.41 | 28 |
| Health | LI-02 | 4.70 | 0.65 | 12 | 2.43 | 1.15 | 24 | 2.28 | 25 |
| Social inclusion | LI-03 | 4.70 | 0.65 | 14 | 2.50 | 1.23 | 20 | 2.20 | 23 |
| Leisure | LI-04 | 4.75 | 0.59 | 6 | 2.57 | 1.27 | 18 | 2.18 | 21 |
| Extracurricular activities | LI-05 | 4.73 | 0.62 | 8 | 2.59 | 1.23 | 17 | 2.13 | 18 |
| Sustainable management | MA-01 | 4.65 | 0.72 | 24 | 2.45 | 1.16 | 22 | 2.20 | 22 |
| Transparency | MA-02 | 4.67 | 0.68 | 21 | 2.91 | 1.29 | 8 | 1.75 | 8 |
| Participation | MA-03 | 4.65 | 0.70 | 23 | 2.52 | 1.21 | 19 | 2.13 | 19 |
| Process efficiency | MA-04 | 4.74 | 0.63 | 7 | 3.71 | 1.24 | 1 | 1.03 | 1 |
| Accessibility | MO-01 | 4.84 | 0.51 | 1 | 3.22 | 1.34 | 3 | 1.62 | 5 |
| Signaling | MO-02 | 4.70 | 0.68 | 15 | 3.17 | 1.35 | 4 | 1.53 | 4 |
| Sustainable transport | MO-03 | 4.55 | 0.87 | 31 | 1.68 | 0.97 | 38 | 2.87 | 38 |
| Collaborative economy | MO-04 | 4.51 | 0.87 | 35 | 1.98 | 1.20 | 35 | 2.53 | 33 |
| Eco-friendly transport | MO-05 | 4.57 | 0.83 | 30 | 2.01 | 1.15 | 34 | 2.56 | 34 |
| Security | SE-01 | 4.83 | 0.48 | 2 | 2.95 | 1.28 | 6 | 1.88 | 13 |
| Biosecurity | SE-02 | 4.72 | 0.67 | 9 | 2.81 | 1.28 | 11 | 1.91 | 14 |
| Smart technologies | SE-03 | 4.63 | 0.72 | 26 | 1.96 | 1.18 | 36 | 2.67 | 36 |
| Cybersecurity | SE-04 | 4.67 | 0.76 | 20 | 2.17 | 1.16 | 31 | 2.51 | 31 |
| Disaster prevention | SE-05 | 4.69 | 0.73 | 16 | 2.03 | 1.10 | 33 | 2.66 | 35 |
| Internet technologies | TE-01 | 4.76 | 0.60 | 4 | 2.30 | 1.19 | 25 | 2.47 | 29 |
| Data management | TE-02 | 4.69 | 0.64 | 17 | 2.98 | 1.24 | 5 | 1.71 | 7 |
| Information systems | TE-03 | 4.60 | 0.74 | 29 | 2.23 | 1.20 | 29 | 2.37 | 27 |
| Internet technologies | TE-04 | 4.79 | 0.52 | 3 | 3.63 | 1.29 | 2 | 1.16 | 2 |
| AVERAGE | - | 4.65 | 0.70 | - | 2.55 | 1.20 | - | 2.10 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva-da-Nóbrega, P.I.; Chim-Miki, A.F.; Castillo-Palacio, M. A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159640
Silva-da-Nóbrega PI, Chim-Miki AF, Castillo-Palacio M. A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159640
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva-da-Nóbrega, Pedro Ivo, Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki, and Marysol Castillo-Palacio. 2022. "A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159640
APA StyleSilva-da-Nóbrega, P. I., Chim-Miki, A. F., & Castillo-Palacio, M. (2022). A Smart Campus Framework: Challenges and Opportunities for Education Based on the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability, 14(15), 9640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159640







