Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Photovoltaic/Thermal Systems: Parameter Analysis and Determination of Optimum Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Establishment and Numerical Simulation
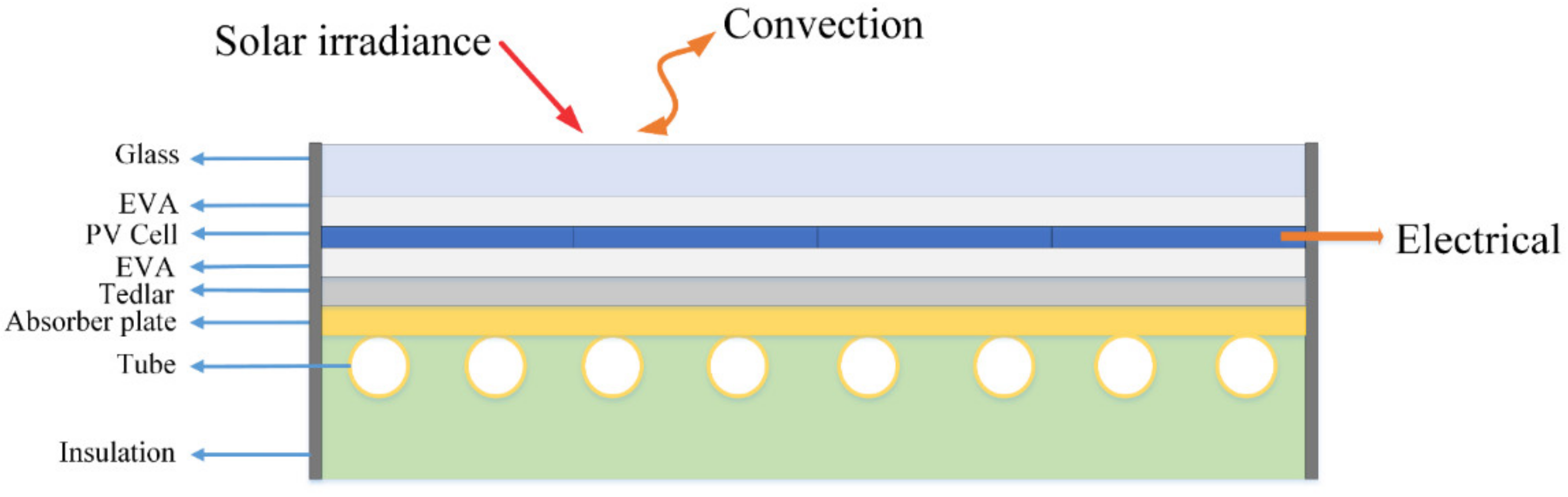
2.1. PV/T Collector Model
2.2. Thermodynamic Analysis and Efficiency Assessment
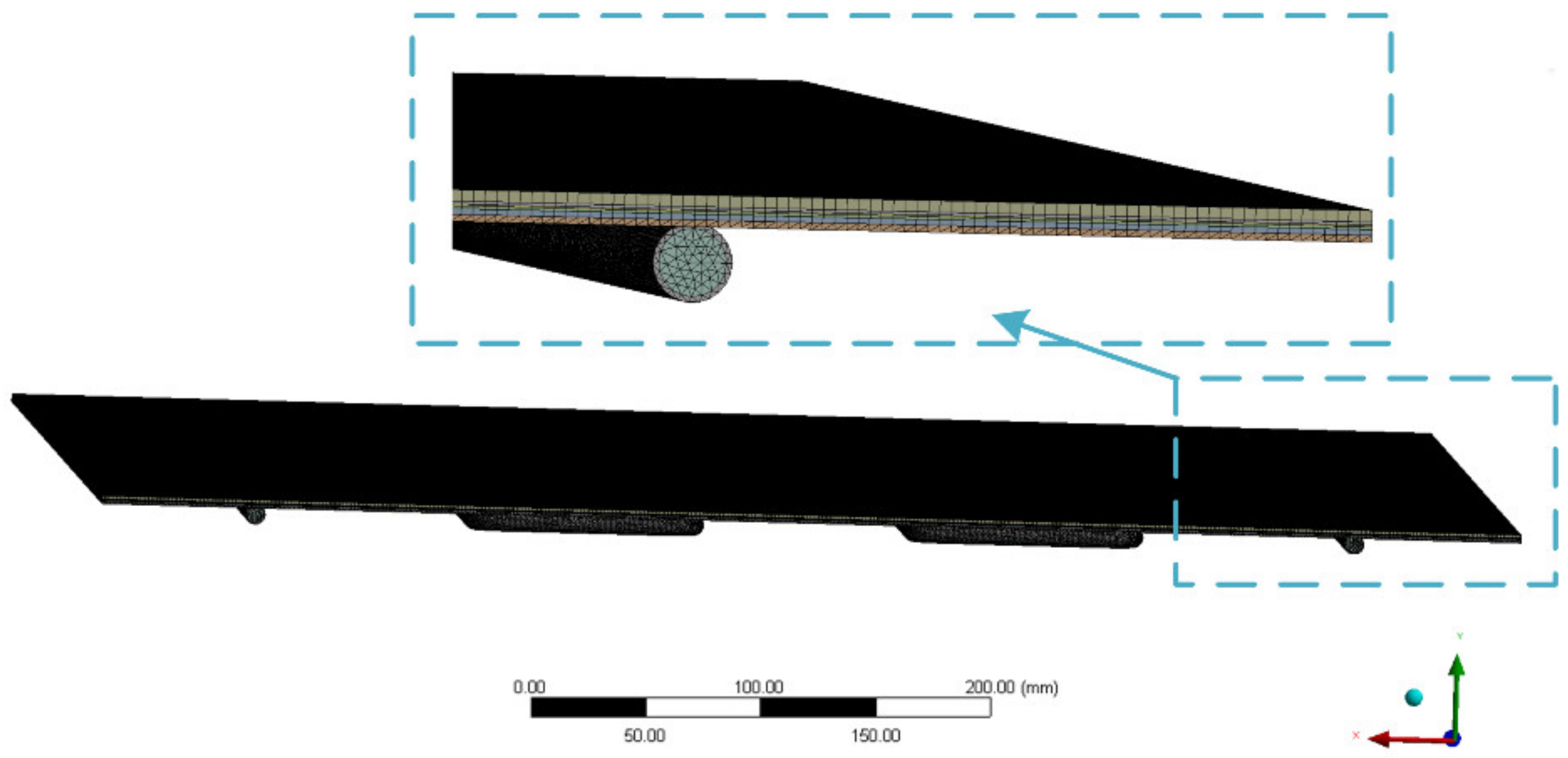
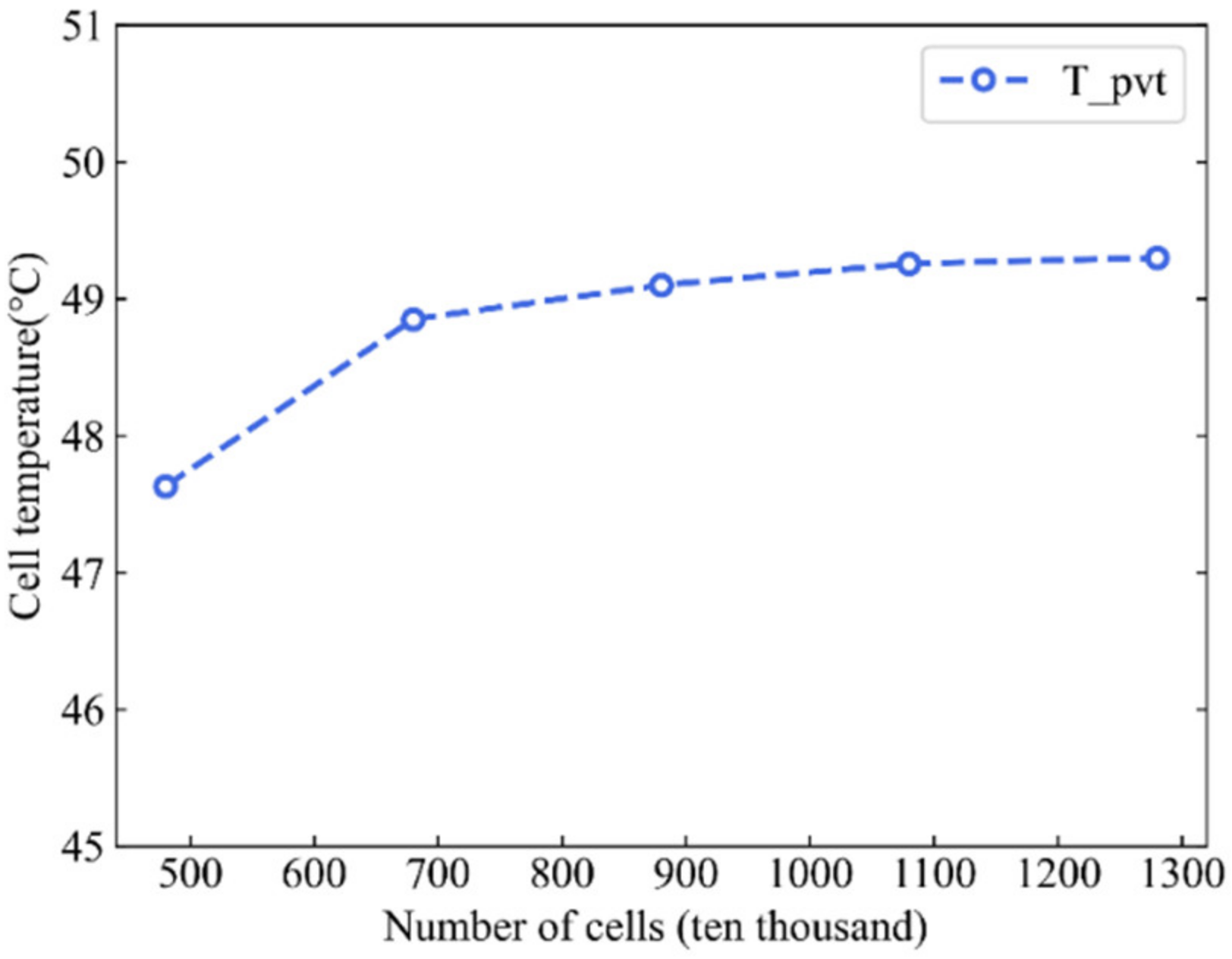
2.3. Mesh Research
2.4. Simulation Association and Boundary Conditions
- (1)
- Assuming that each layer of PV/T is perfectly contacted, and the contact thermal resistance between each layer is ignored [24];
- (2)
- On the surface, dust and shadows will not affect solar absorption;
- (3)
- The fluid in the tube is non-compressed fluid, the flow in the pipeline is turbulent, and the fluid is evenly distributed in the tube [25];
- (4)
- The thermal physical properties of different PV/T components under different conditions are considered constant.
- (1)
- The inlet boundary is set as the mass flow inlet;
- (2)
- Export boundaries are considered fully developed;
- (3)
- Convection and radiation exist on the surface of the glass cover plate. The formulas for calculating sky temperature and convective heat transfer coefficient of wind under black body radiation are shown in Equations (12) and (13);
- (4)
- The bottom of the PV/T collector and pipe, and the side walls of the module are considered as adiabatic walls.
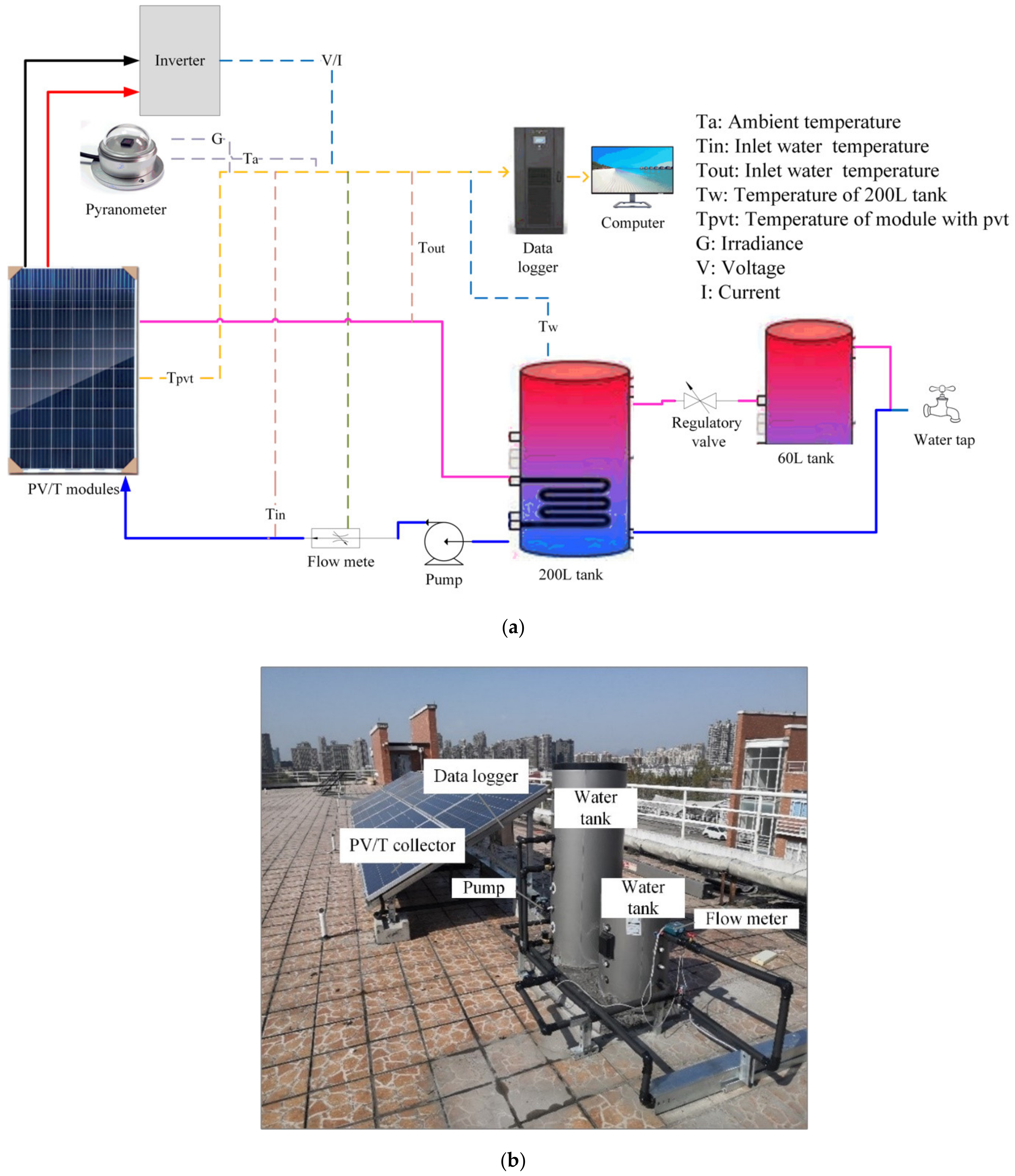
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussions
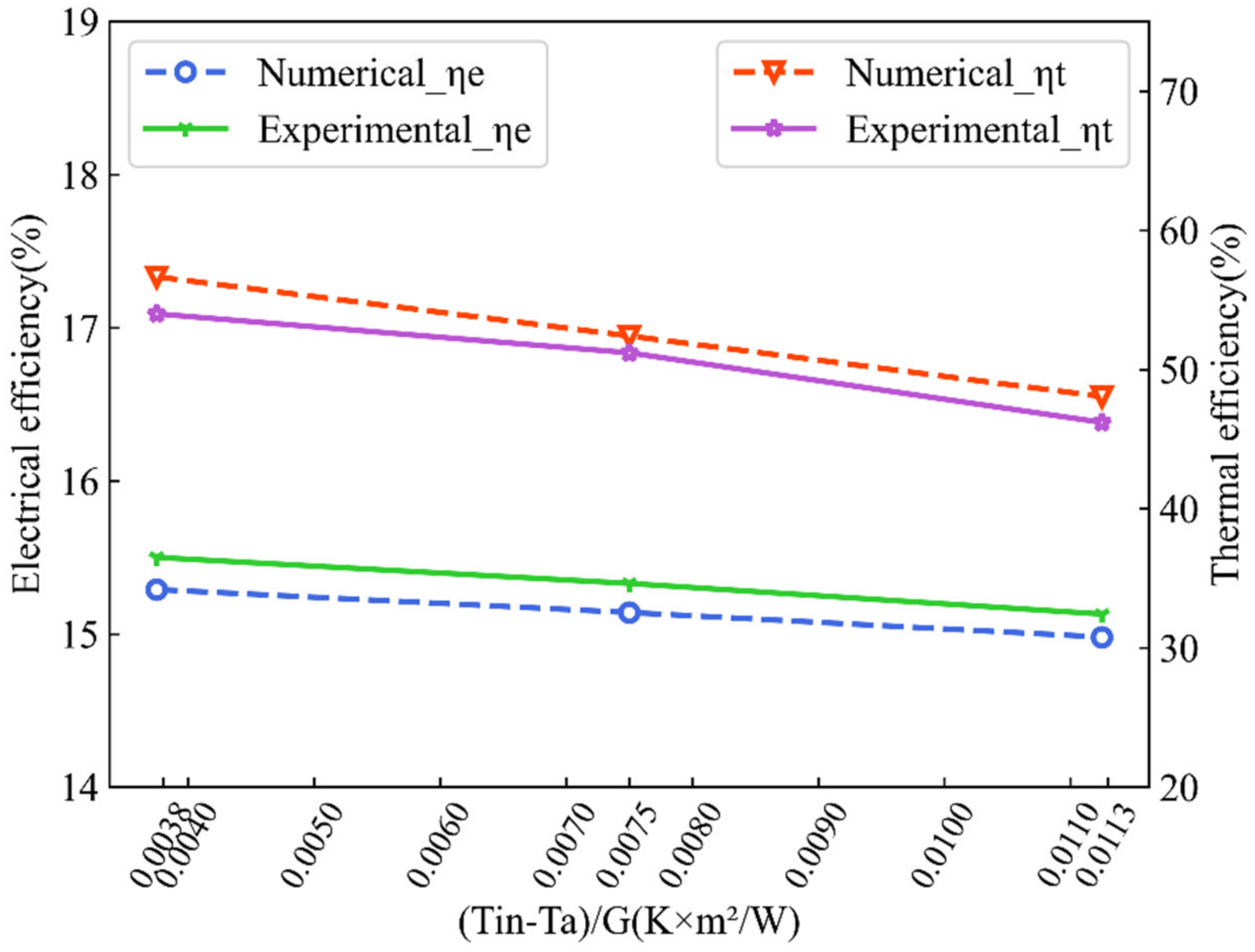
4.1. Model Validation
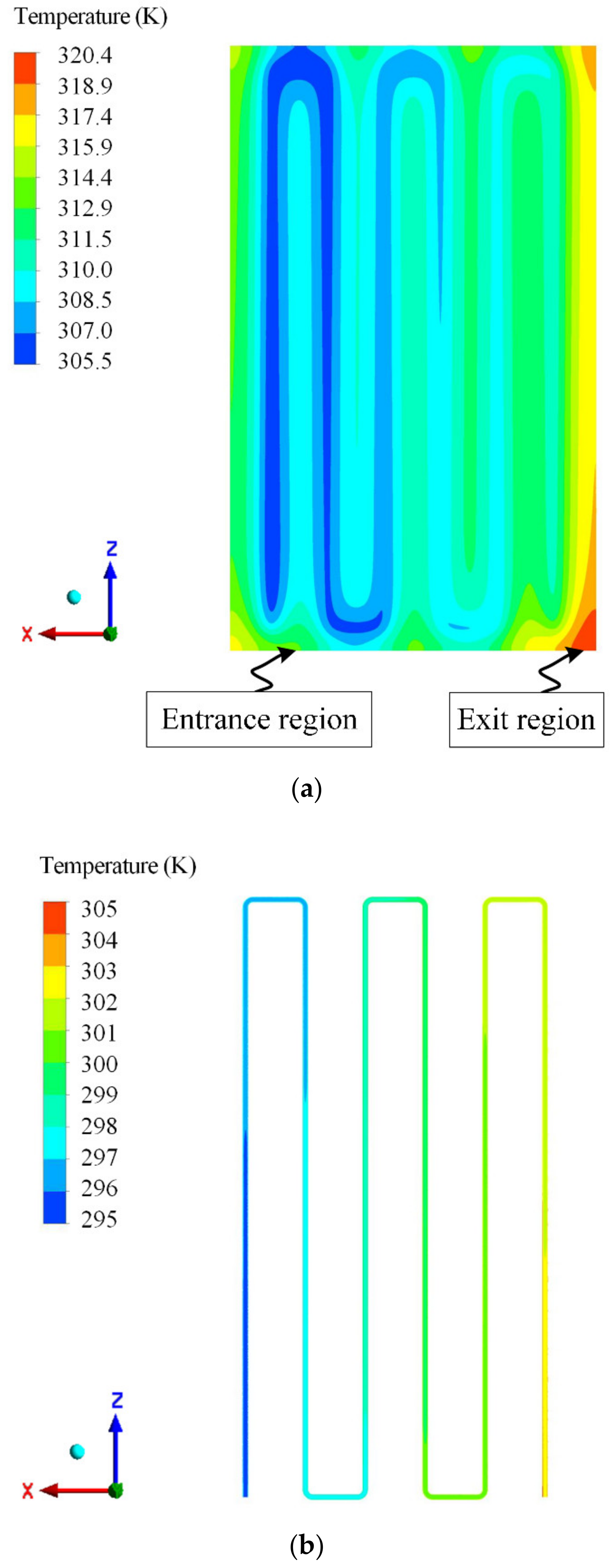
4.2. PV/T Temperature Distribution Characteristics
4.3. Parameter Analysis
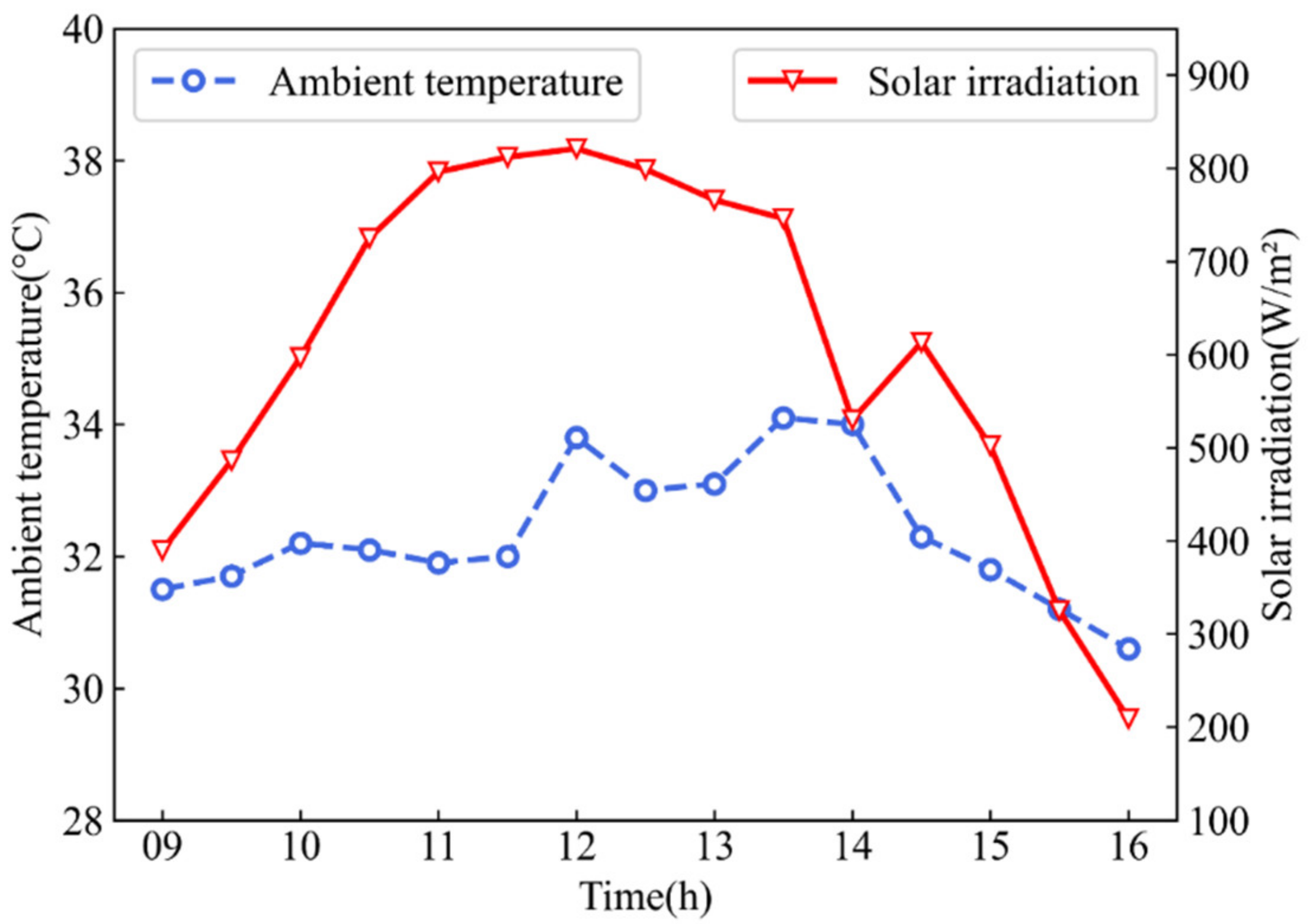
4.3.1. Analysis of Solar Radiation
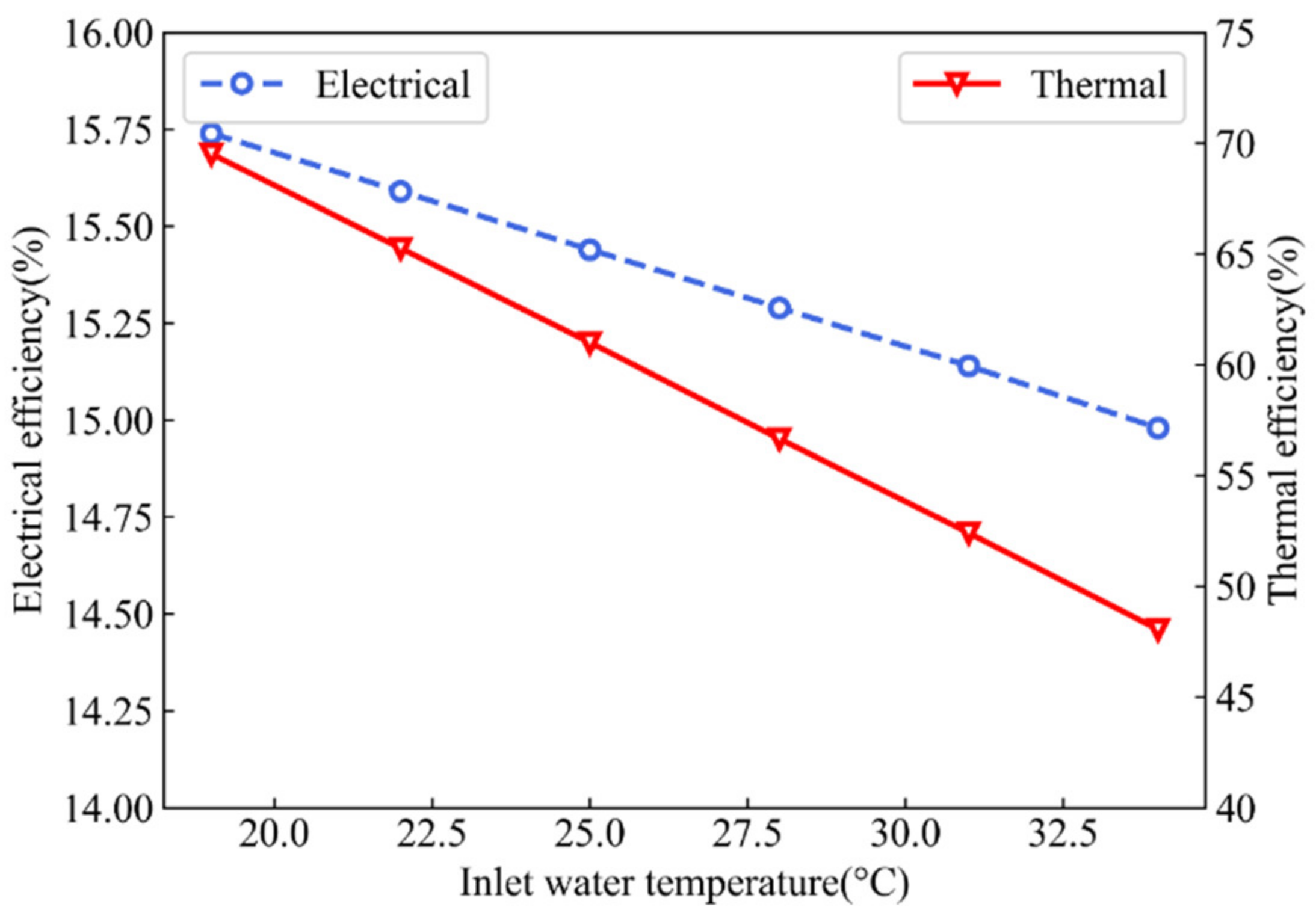
4.3.2. Analysis of Inlet Temperature
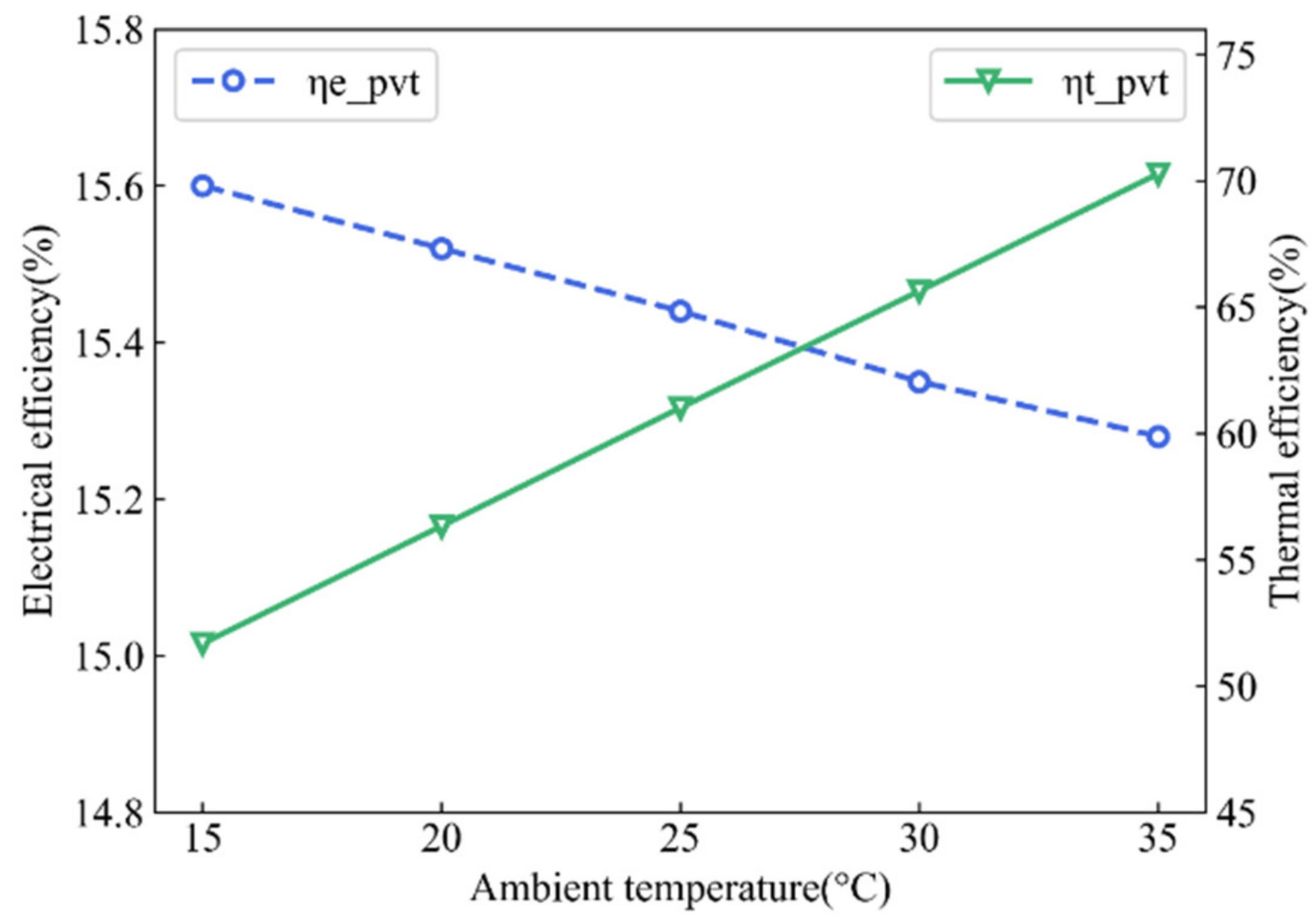
4.3.3. Analysis of Ambient Temperature
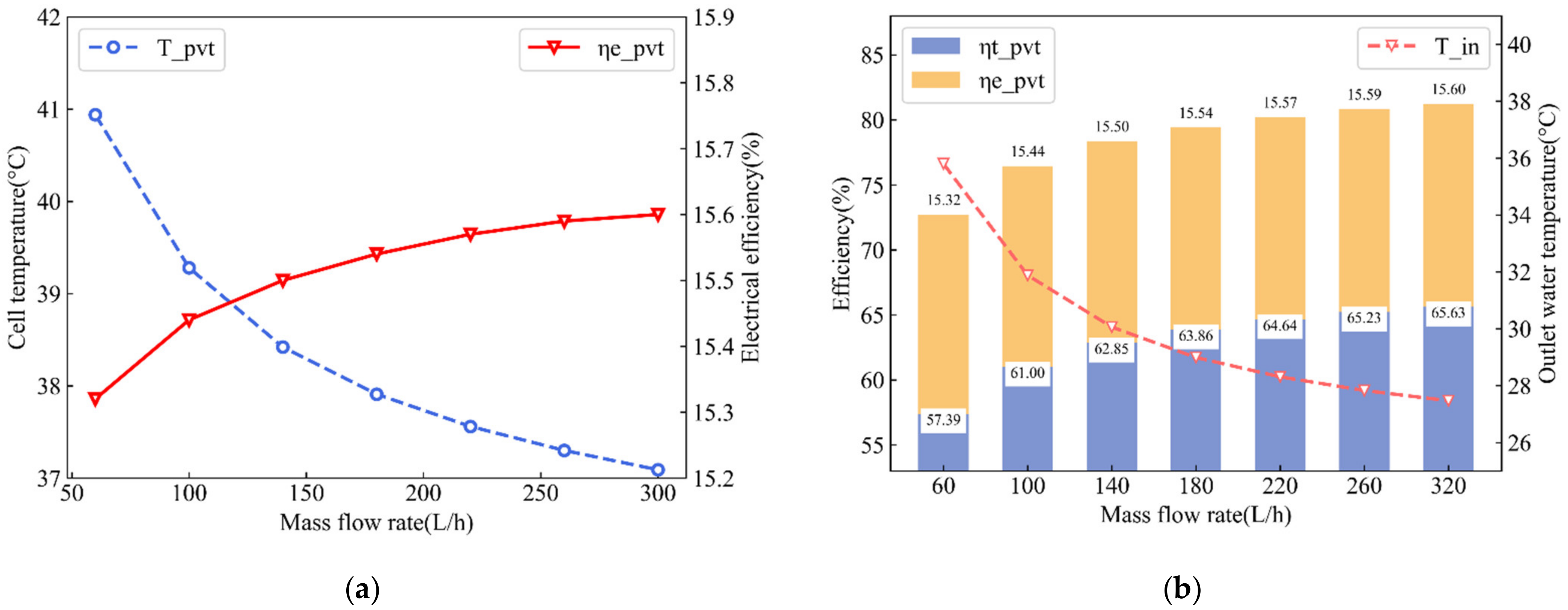
4.3.4. Analysis of Mass Flow Rate
4.4. Experimental Design Based on Orthogonal Table
4.5. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
4.6. Regression Analysis
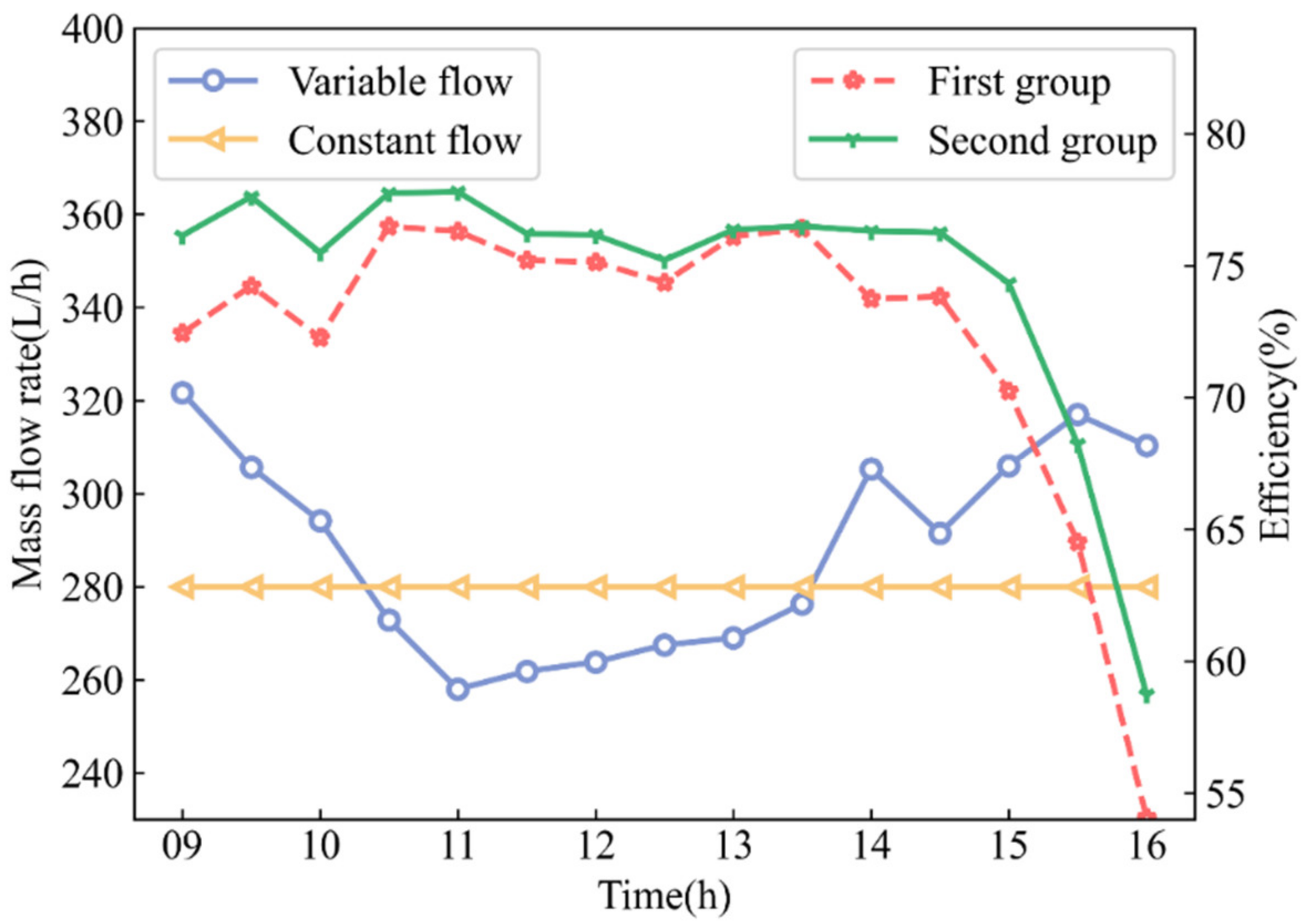
4.7. Influence Experiment of Variable Flow on the System
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- For every 200 W/m2 increase in solar radiation, the inlet temperature increases by 1.86 °C on average. When solar radiation increases from 800 to 1000 W/m2, the thermal efficiency increase rate gradually becomes slower. When the inlet temperature increases from 19 to 34 °C, the overall energy efficiency decreases by 22.22%. The mass flow rate increases from 60 to 320 L/h, and the thermal efficiency increases by 8.24%. For each 40 L/h increase in mass flow rate, the electrical efficiency increases by 0.047%. Although the overall efficiency can be enhanced by improving the mass flow, when it is too great, the rate of increase of electrical and thermal efficiency is gradually reduced.
- (2)
- Sixteen orthogonal experimental designs were designed for the operating parameters of the PV/T system, and the influence of various operating parameters and parameter combinations on the system were subjected to ANOVA. The combination of inlet temperature and solar radiation, and the combination of the inlet temperature and mass flow have a greater impact on the overall efficiency.
- (3)
- A mathematical model was established for the overall efficiency of the PV/T system, and a flow control formula proposed for improving the overall efficiency. The experimental results show that the overall energy gain is increased by 2.5% by flow control compared with the optimal constant mass flow.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez-Camacho, C.E.; Ruggeri, B. Energy Sustainability Analysis (ESA) of Energy-Producing Processes: A Case Study on Distributed H2 Production. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, M.; Shahsavar, A.; Khanmohammadi, S. Scenario-Based Multi-Objective Optimization of an Air-Based Building-Integrated Photovoltaic/Thermal System. J. Sol. Energy Eng. Trans.-ASME 2018, 140, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirn, B.; Topic, M. Diffuse and direct light solar spectra modeling in PV module performance rating. Sol. Energy 2017, 150, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.A.; Sopian, K.; Jaaz, A.H.; Al-Shamani, A.N. Experimental investigation of jet array nanofluids impingement in photovoltaic/thermal collector. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Use of TRNSYS for modelling and simulation of a hybrid pv–thermal solar system for Cyprus. Renew. Energy 2001, 23, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Selvaraj, J.; Abd Rahim, N.; Rivai, A.; Tyagi, V.V. Thermal performance analysis of parallel serpentine flow based photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) system under composite climate of Malaysia. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 153, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudholi, A.; Sopian, K.; Yazdi, M.H.; Ruslan, M.H.; Ibrahim, A.; Kazem, H.A. Performance analysis of photovoltaic thermal (PVT) water collectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Cui, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.W.; Zhang, L.R.; Yan, H. Experimental effect of high mass flow rate and volume cooling on performance of a water-type PV/T collector. Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrek, M.; Al-Alili, A. Experimental Investigation of a Flat Plate Photovoltaic/Thermal Collector. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 12th International Conference on Energy Sustainability collocated with the ASME 2018 Power Conference and the ASME 2018 Nuclear Forum, Lake Buena Vista, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.H.; Romagnoli, A.; Yang, R.; Xie, D.M.; Liu, C.P.; Ding, Y.L.; Li, Y.L. Numerical study on energy and exergy performances of a microencapsulated phase change material slurry based photovoltaic/thermal module. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 183, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, I.; Menlik, T. Numerical study of a photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) system using mono and hybrid nanofluid. Sol. Energy 2021, 224, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanifard, F.; Ebrahimnia-Bajestan, E.; Ameri, M. Investigating the performance of a water-based photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) collector in laminar and turbulent flow regime. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Salari, A.; Sardarabadi, M.; Passandideh-Fard, M. Optimization and parametric analysis of a nanofluid based photovoltaic thermal system: 3D numerical model with experimental validation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 160, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.M.; Liu, H. Modeling In-Vehicle VOCs Distribution from Cabin Interior Surfaces under Solar Radiation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.R.; Al-Dhaifallah, M.; Alahmer, A.; Rezk, H. Design, Modeling, and Experimental Investigation of Active Water Cooling Concentrating Photovoltaic System. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarabadi, M.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Heris, S.Z. Experimental investigation of the effects of silica/water nanofluid on PV/T (photovoltaic thermal units). Energy 2014, 66, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, G.; Fung, A.S. Optimum Tilt Angle and Orientation of Photovoltaic Thermal System for Application in Greater Toronto Area, Canada. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarabadi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Kazemian, A.; Passandideh-Fard, M. Experimental investigation of the effects of using metal-oxides/water nanofluids on a photovoltaic thermal system (PVT) from energy and exergy viewpoints. Energy 2017, 138, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanifard, F.; Ameri, M.; Ebrahimnia-Bajestan, E. Performance of nanofluid-based photovoltaic/thermal systems: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2017, 76, 323–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewchoothong, N.; Sukato, T.; Narato, P.; Nuntadusit, C. Flow and heat transfer characteristics on thermal performance inside the parallel flow channel with alternative ribs based on photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 185, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waeli, A.H.A.; Chaichan, M.T.; Sopian, K.; Kazem, H.A.; Mahood, H.B.; Khadom, A.A. Modeling and experimental validation of a PVT system using nanofluid coolant and nano-PCM. Sol. Energy 2019, 177, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadi, S.R.; Sabzali, H.; Kolahan, A.; Wood, D. Improving the performance of PV/T systems by using conical-leaf inserts in the coolant tubes. Sol. Energy 2020, 212, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadi, S.R.; Kolahan, A.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Sardarabadi, M.; Moloudi, R. Characterization of PVT systems equipped with nanofluids-based collector from entropy generation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjari, Y.; Pourfayaz, F.; Kasaeian, A.B. Numerical investigation on using of nanofluid in a water-cooled photovoltaic thermal system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 122, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preet, S.; Bhushan, B.; Mahajan, T. Experimental investigation of water based photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) system with and without phase change material (PCM). Sol. Energy 2017, 155, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Sodha, M.S. Performance evaluation of solar PV/T system: An experimental validation. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, R.; Oladipo, A.A.; Sharifpur, M.; Taher, R.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Issakhov, A. Efficiency Enhancement in Double-Pass Perforated Glazed Solar Air Heaters with Porous Beds: Taguchi-Artificial Neural Network Optimization and Cost-Benefit Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasakthivel, T.; Murugesan, K.; Thomas, H.R. Optimization of operating parameters of ground source heat pump system for space heating and cooling by Taguchi method and utility concept. Appl. Energy 2014, 116, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; de Dear, R. Application of Taguchi method in optimising thermal comfort and cognitive performance during direct load control events. Build. Environ. 2017, 111, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Component | Density (kg m−3) | Specific Heat Capacity (W m−1 K−1) | Thermal Conductivity (J kg−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 2450 | 500 | 2 |
| EVA | 960 | 2090 | 0.35 |
| PV cell | 2330 | 700 | 148 |
| Tedlar | 1200 | 1250 | 0.2 |
| Aluminum | 2719 | 871 | 202 |
| Component | Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|
| Glass cover | 1640 × 992 × 2 |
| EVA | 1640 × 992 × 0.5 |
| PV cell | 1640 × 992 × 0.3 |
| Tedlar | 1640 × 992 × 1 |
| Aluminum absorber plate | 1640 × 992 × 1.5 |
| Water pipe inner diameter | 11 |
| Water pipe outer diameter | 9 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Mono-crystalline silicon |
| Maximum power (W) | 270 |
| Number of solar cells | 60 (6 × 10) |
| Open-circuit voltage (V) | 37.99 |
| Short-circuit current (A) | 9.15 |
| Electrical efficiency (%) | 16.4 |
| Dimension (mm) | 1640 × 992 |
| Parameter | Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Mass flow rate(L/h) | 60 | 100 | 140 | 180 |
| Inlet temperature (°C) | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 |
| Solar irradiation (W/m2) | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| Ambient temperature (°C) | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 |
| Exp | Mass Flow Rate (L/h) | Inlet Temperature (°C) | Solar Irradiation (W/m²) | Ambient Temperature (°C) | Electrical Efficiency (%) | Thermal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 25 | 400 | 20 | 16.05 | 43.81 |
| 2 | 60 | 28 | 600 | 25 | 15.496 | 50.567 |
| 3 | 60 | 31 | 800 | 30 | 14.949 | 53.585 |
| 4 | 60 | 34 | 1000 | 35 | 14.409 | 55.196 |
| 5 | 100 | 28 | 800 | 35 | 15.134 | 65.776 |
| 6 | 100 | 25 | 1000 | 30 | 15.08 | 65.35 |
| 7 | 100 | 34 | 400 | 25 | 15.567 | 30.462 |
| 8 | 100 | 31 | 600 | 20 | 15.509 | 41.809 |
| 9 | 140 | 31 | 1000 | 25 | 14.933 | 56.527 |
| 10 | 140 | 34 | 800 | 20 | 15.121 | 44.808 |
| 11 | 140 | 25 | 600 | 35 | 15.622 | 73.745 |
| 12 | 140 | 28 | 400 | 30 | 16.103 | 58.458 |
| 13 | 180 | 34 | 600 | 30 | 15.261 | 50.742 |
| 14 | 180 | 31 | 400 | 35 | 15.602 | 60.354 |
| 15 | 180 | 28 | 1000 | 20 | 15.203 | 57.263 |
| 16 | 180 | 25 | 800 | 25 | 15.544 | 63.719 |
| Factor | DOF | Adjacent SS | Adjacent MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass flow rate | 1 | 466.096163 | 466.096163 | 3015.301718 | 6.584611 × 10−7 |
| Inlet temperature | 1 | 574.788079 | 574.788079 | 3718.459020 | 4.331587 × 10−7 |
| Ambient temperature | 1 | 666.070378 | 666.070378 | 4308.988820 | 3.226479 × 10−7 |
| Solar irradiation | 1 | 173.712401 | 173.712401 | 1123.792351 | 4.722882 × 10−6 |
| Mass flow rate × Mass flow rate | 1 | 11.860753 | 11.860753 | 76.730407 | 9.362557 × 10−4 |
| Inlet temperature × Inlet temperature | 1 | 18.967772 | 18.967772 | 122.707629 | 3.777234 × 10−4 |
| Ambient temperature × Ambient temperature | 1 | 11.066675 | 11.066675 | 71.593302 | 1.069080 × 10−3 |
| Solar irradiation × Solar irradiation | 1 | 17.514703 | 17.514703 | 113.307337 | 4.410675 × 10−4 |
| Mass flow rate × Inlet temperature | 1 | 29.430910 | 29.430910 | 190.396487 | 1.598740 × 10−4 |
| Mass flow rate × Ambient temperature | 1 | 0.379681 | 0.379681 | 2.456256 | 1.921257 × 10−1 |
| Mass flow rate × Solar irradiation | 1 | 6.966391 | 6.966391 | 45.067459 | 2.563096 × 10−3 |
| Inlet temperature × Ambient temperature | 1 | 0.368991 | 0.368991 | 2.387103 | 1.972290 × 10−1 |
| Inlet temperature × Solar irradiation | 1 | 41.967494 | 41.967494 | 271.499034 | 7.943742 × 10−5 |
| Solar irradiation × Ambient temperature | 1 | 6.862096 | 6.862096 | 44.392752 | 2.636133 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, B.; Wu, Q.; Chi, X.; Wu, C.; Luo, P.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, P. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Photovoltaic/Thermal Systems: Parameter Analysis and Determination of Optimum Flow. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610156
Yan B, Wu Q, Chi X, Wu C, Luo P, Luo Y, Zeng P. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Photovoltaic/Thermal Systems: Parameter Analysis and Determination of Optimum Flow. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610156
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Bin, Qiuxuan Wu, Xiaoni Chi, Chenxi Wu, Ping Luo, Yanbin Luo, and Pingliang Zeng. 2022. "Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Photovoltaic/Thermal Systems: Parameter Analysis and Determination of Optimum Flow" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610156
APA StyleYan, B., Wu, Q., Chi, X., Wu, C., Luo, P., Luo, Y., & Zeng, P. (2022). Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Photovoltaic/Thermal Systems: Parameter Analysis and Determination of Optimum Flow. Sustainability, 14(16), 10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610156






