Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum-Agricultural Waste Composites for Developing Eco-Friendly False Ceiling Tiles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Gypsum
2.2. Wheat Straw
2.3. Rice Husk
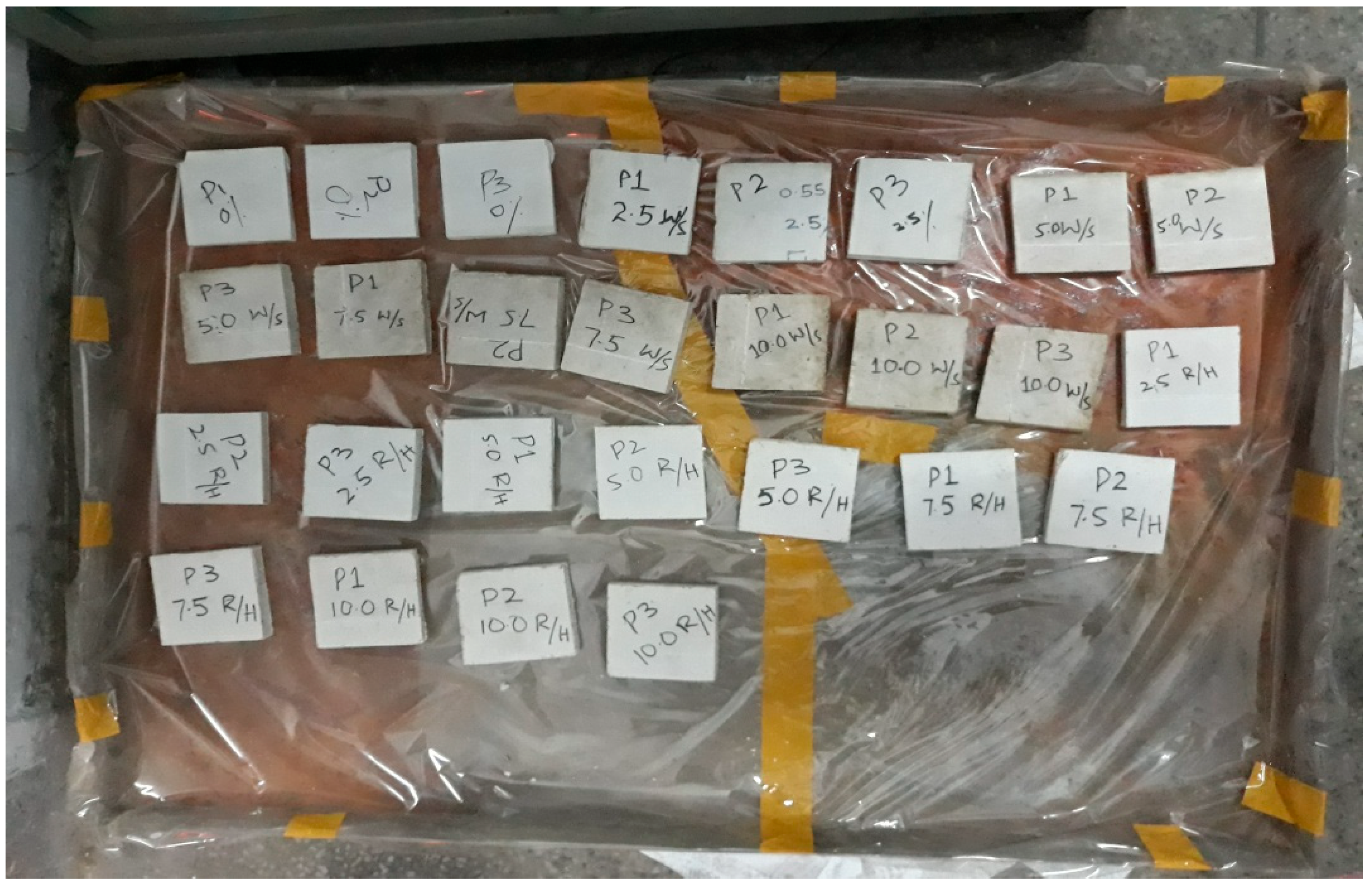
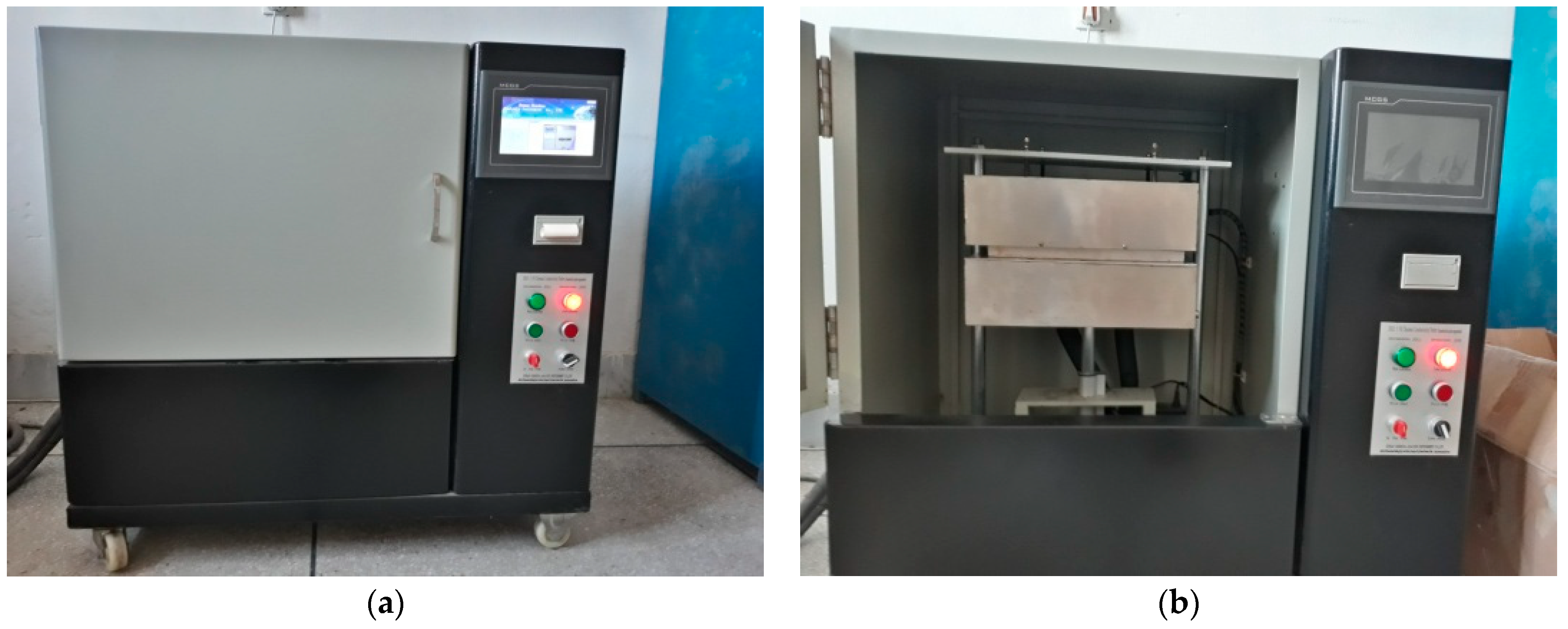
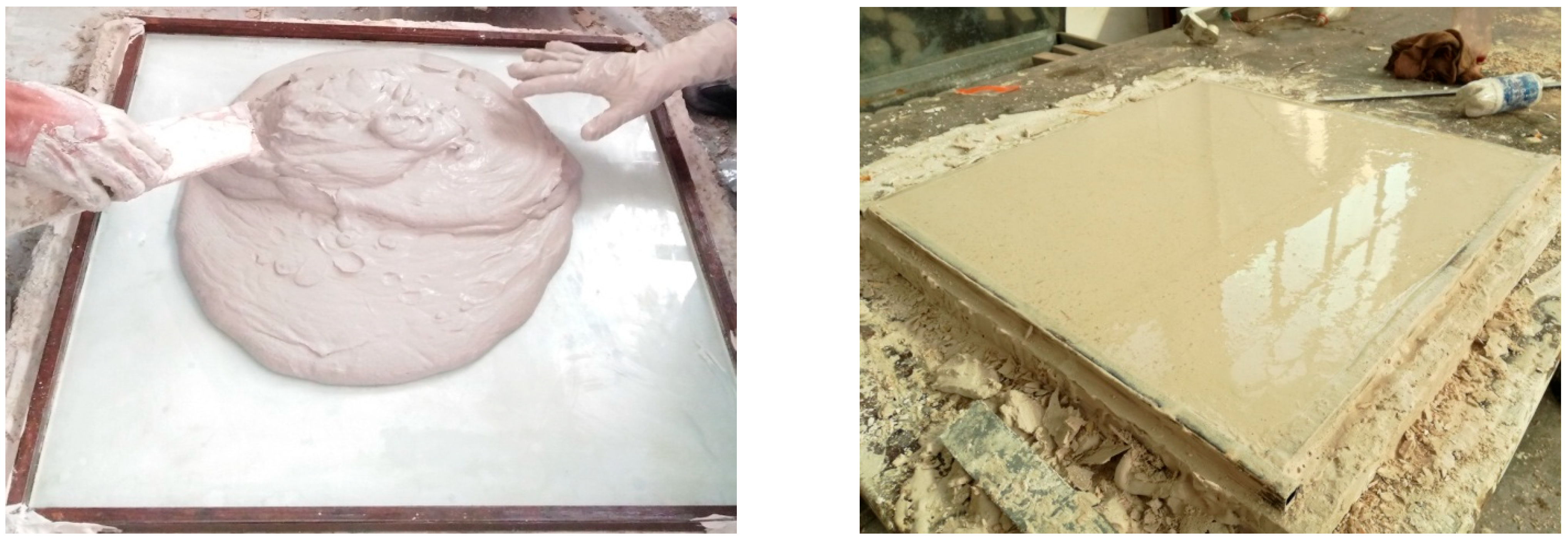
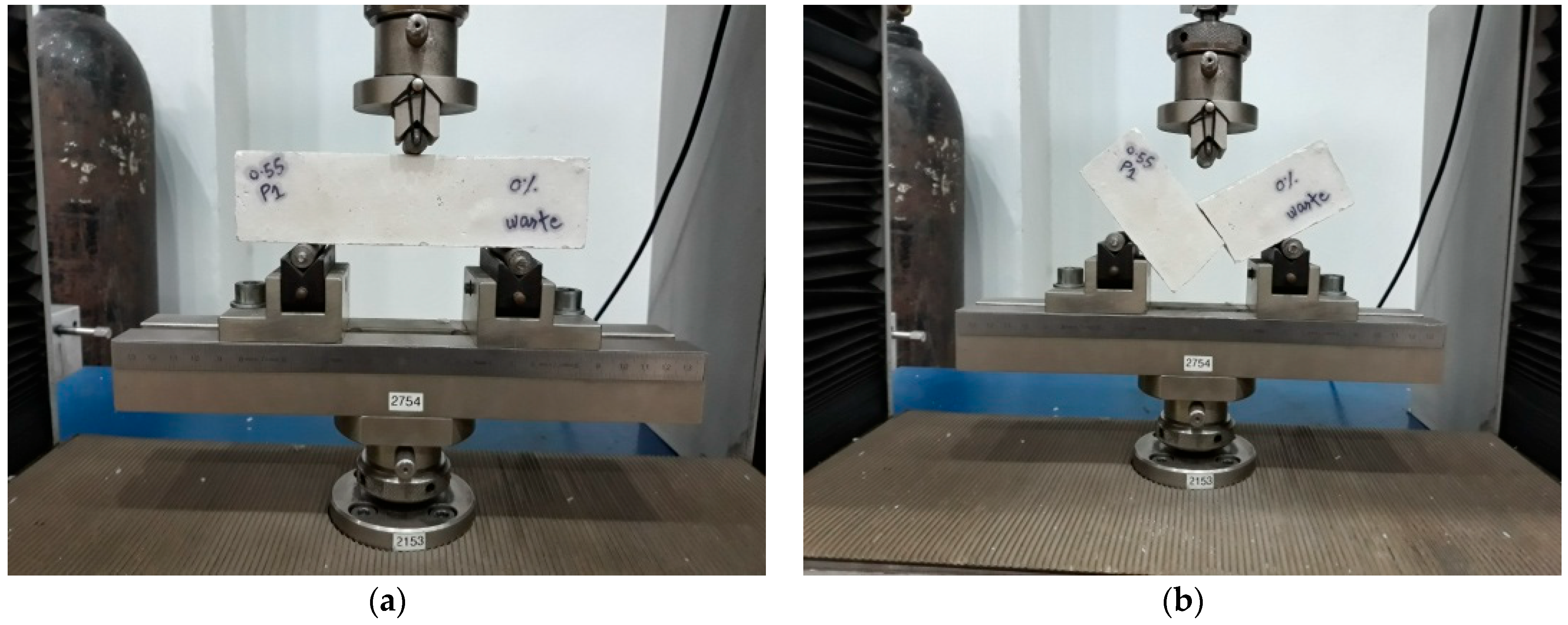
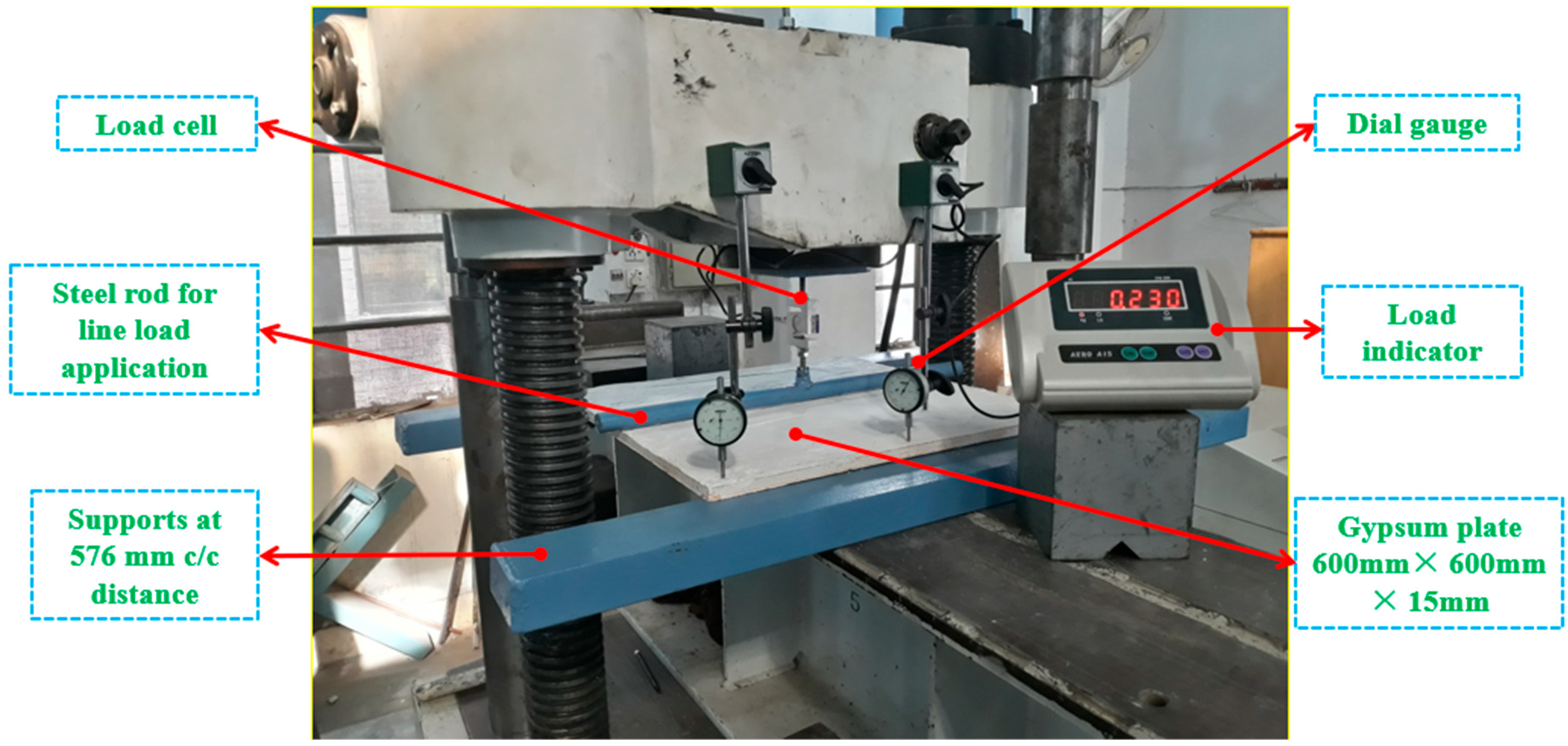
3. Experimental Program
Test Specimens and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
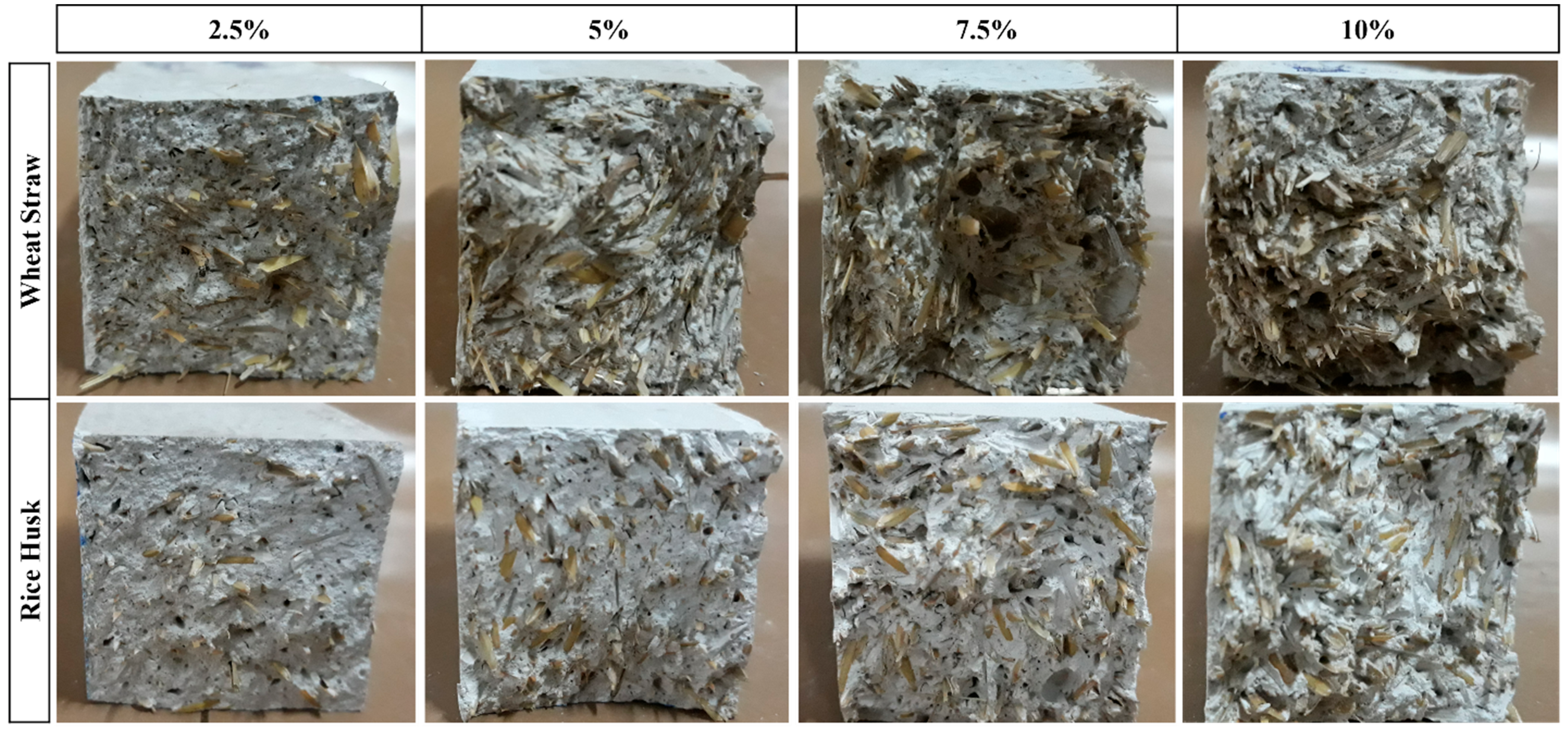
4.1. Tests on Gypsum Composites
4.1.1. Density
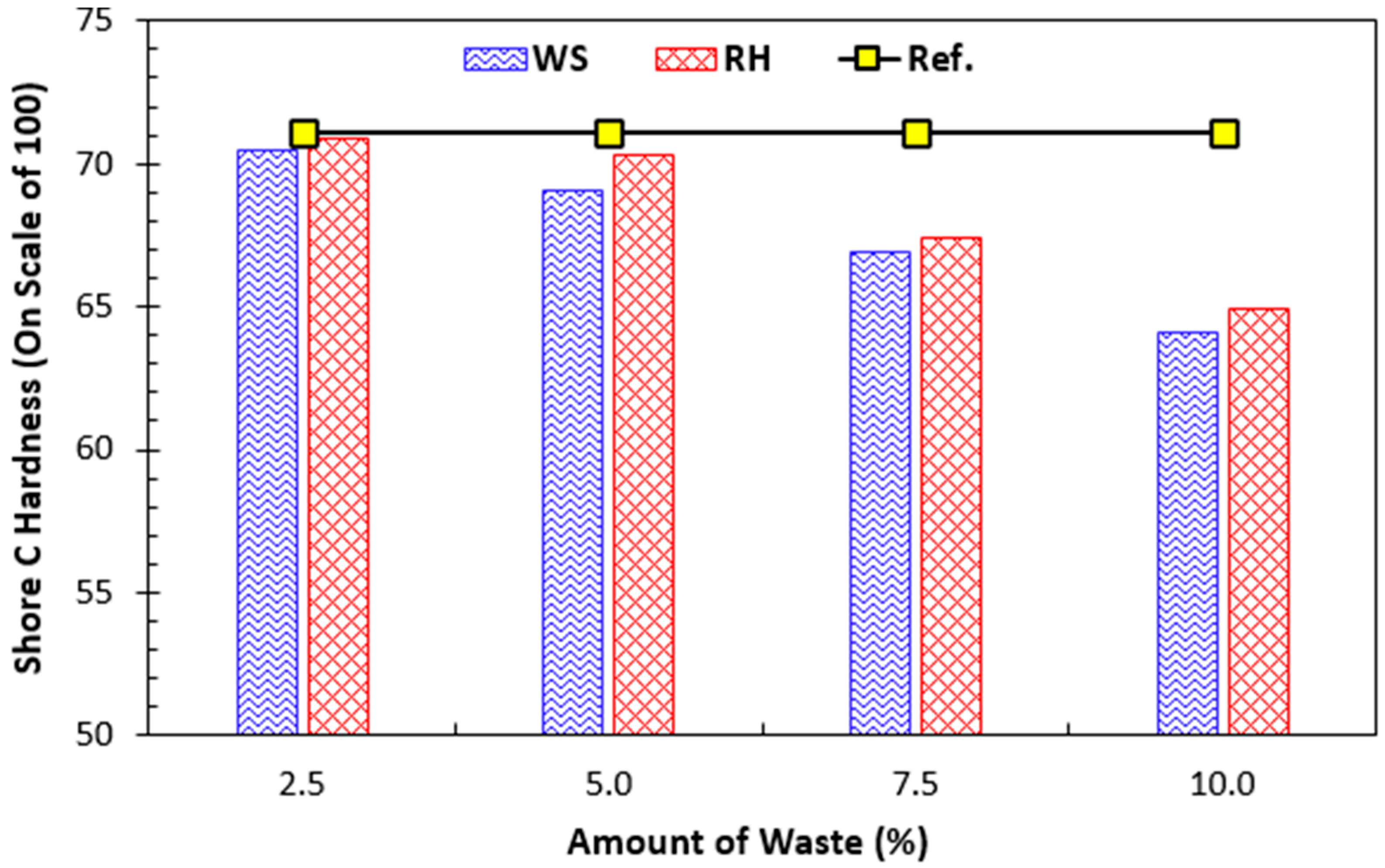
4.1.2. Shore C Hardness
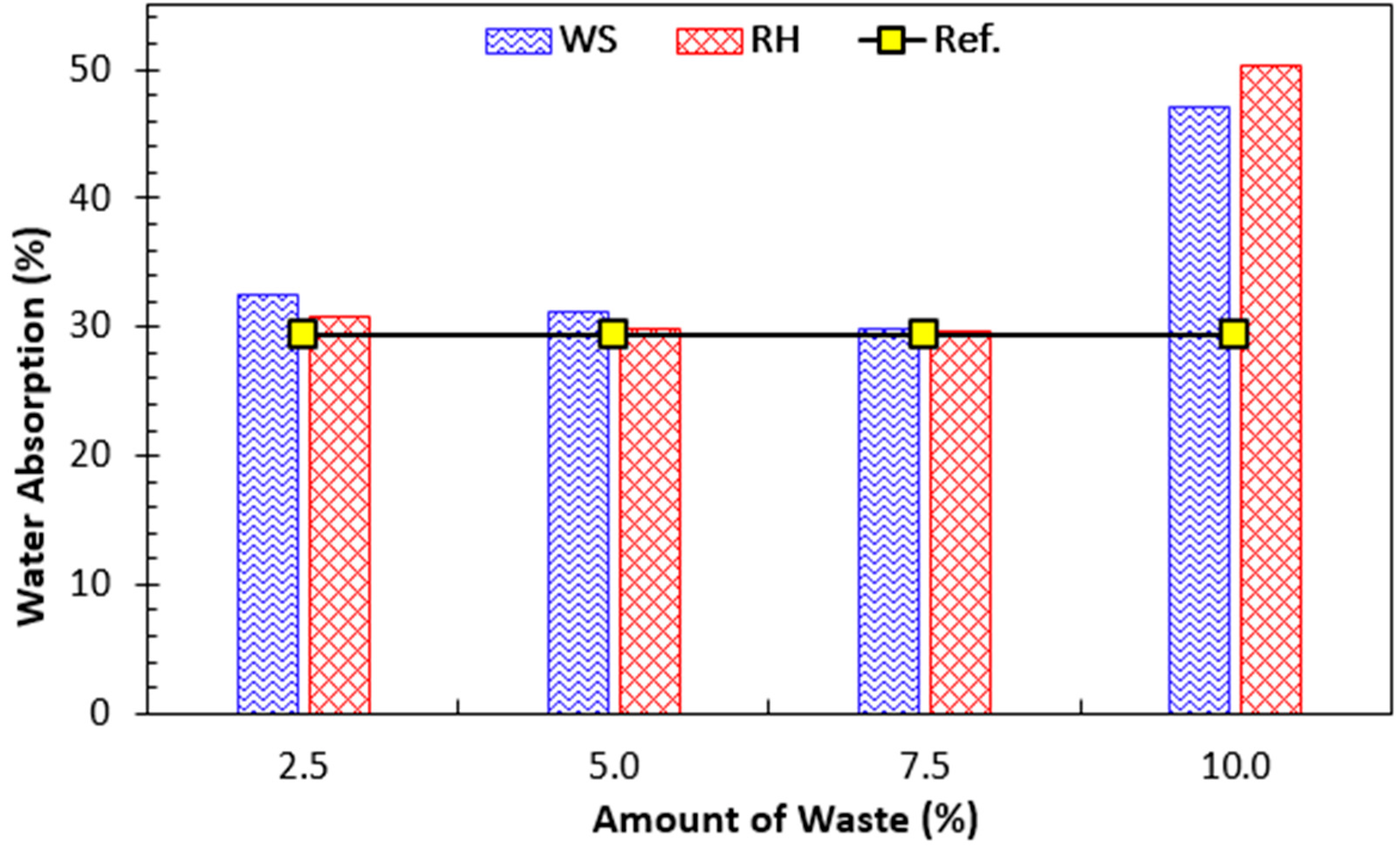
4.1.3. Water Absorption
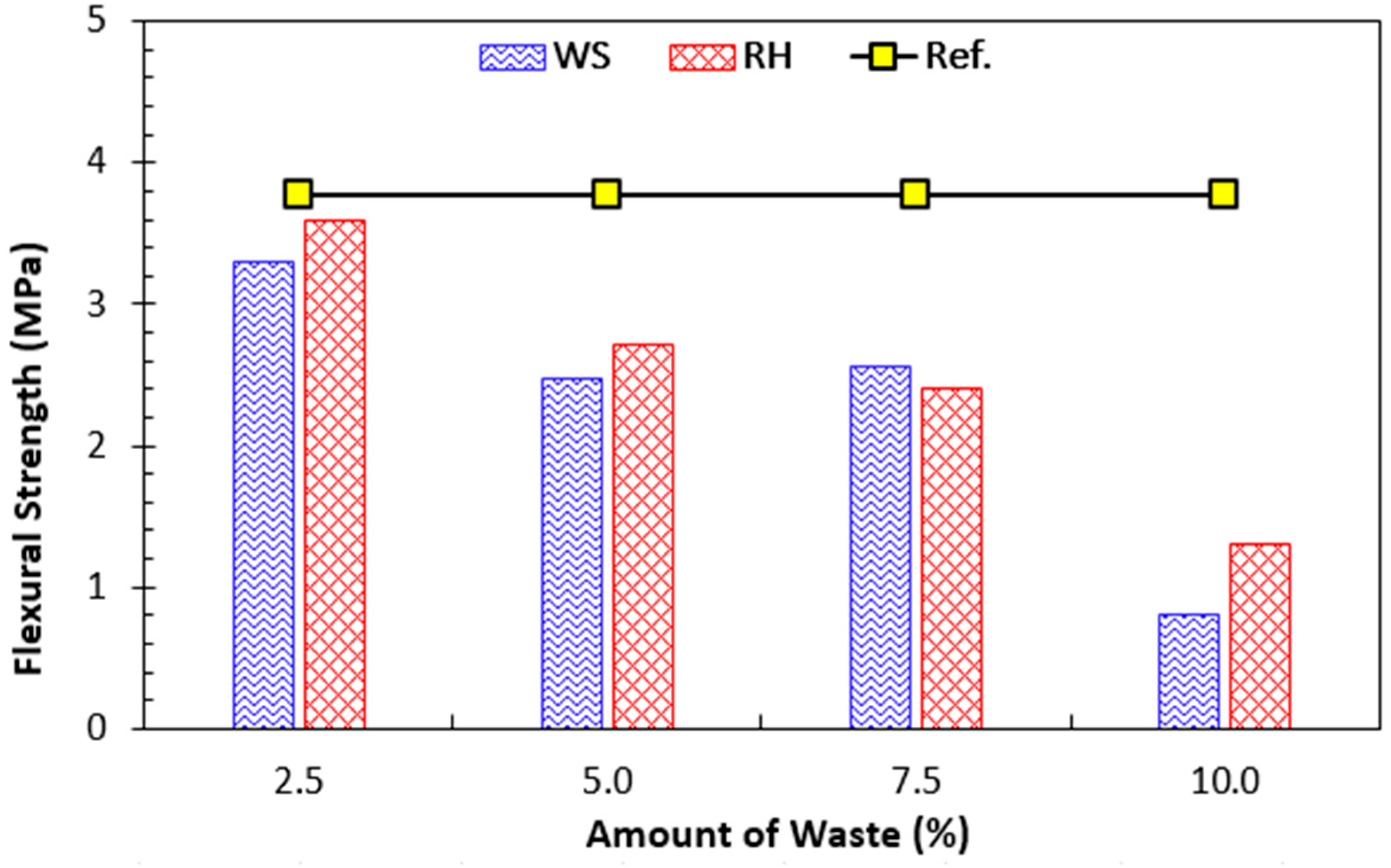
4.1.4. Flexure Strength
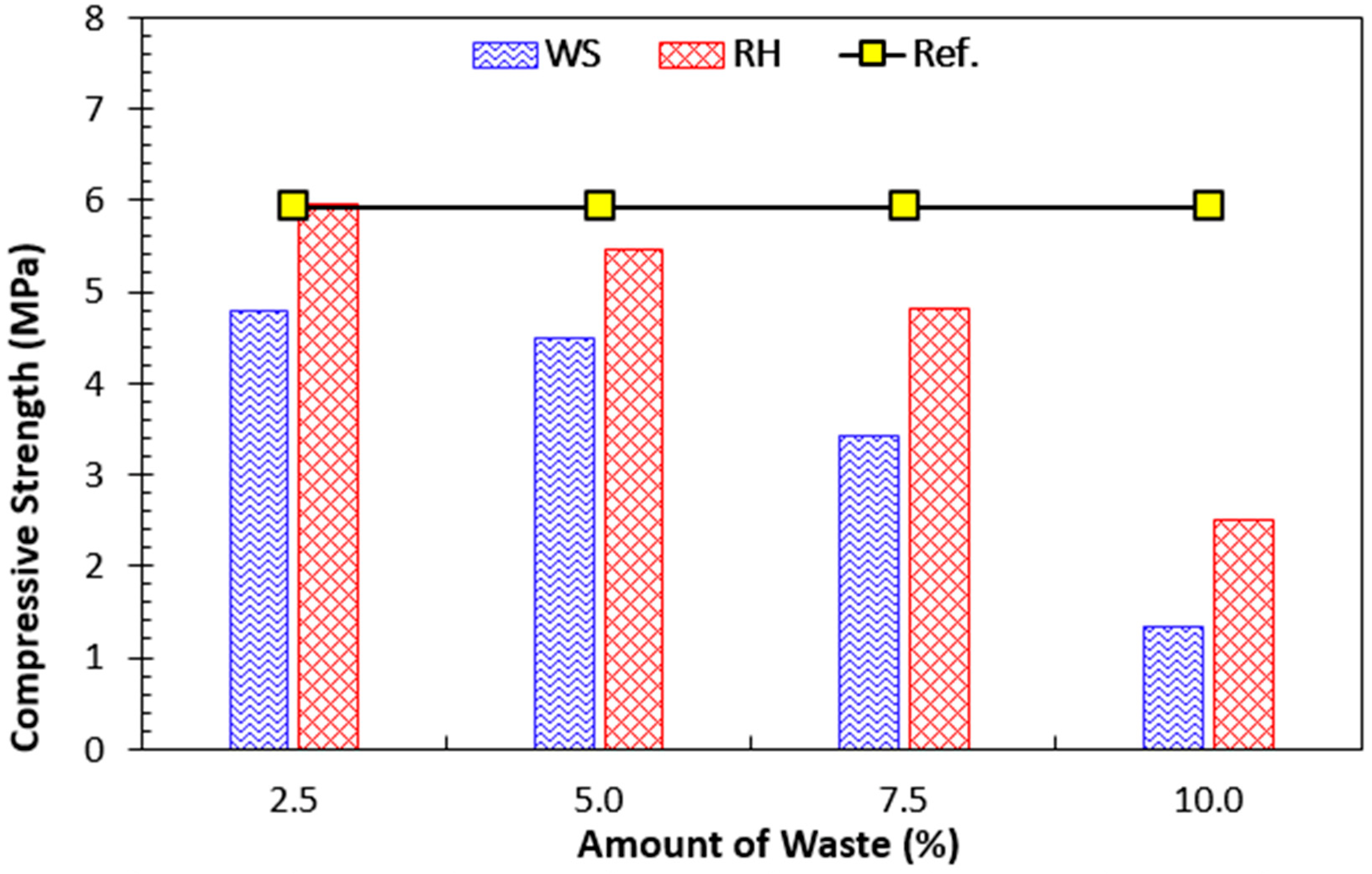
4.1.5. Compressive Strength
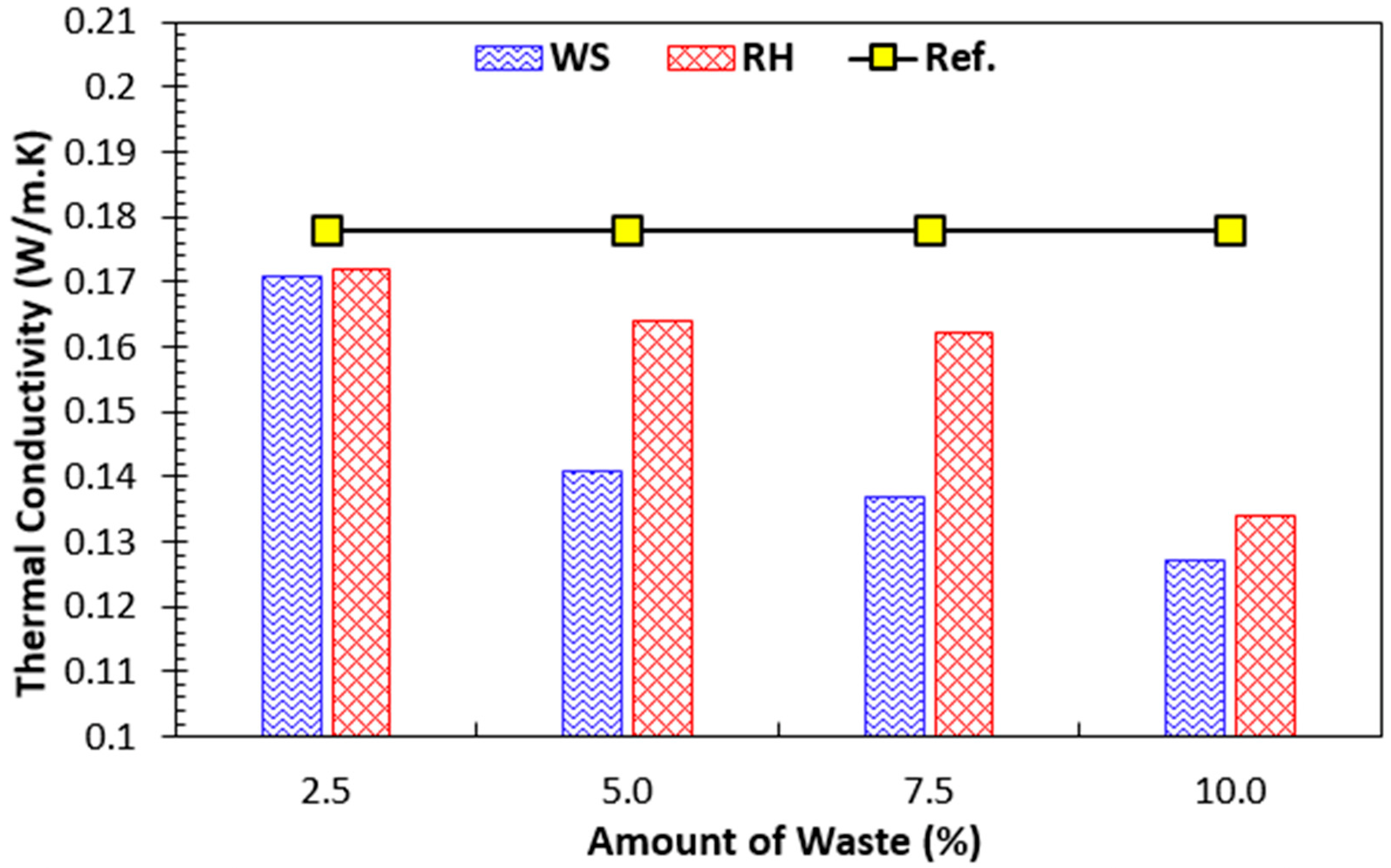
4.1.6. Thermal Behavior
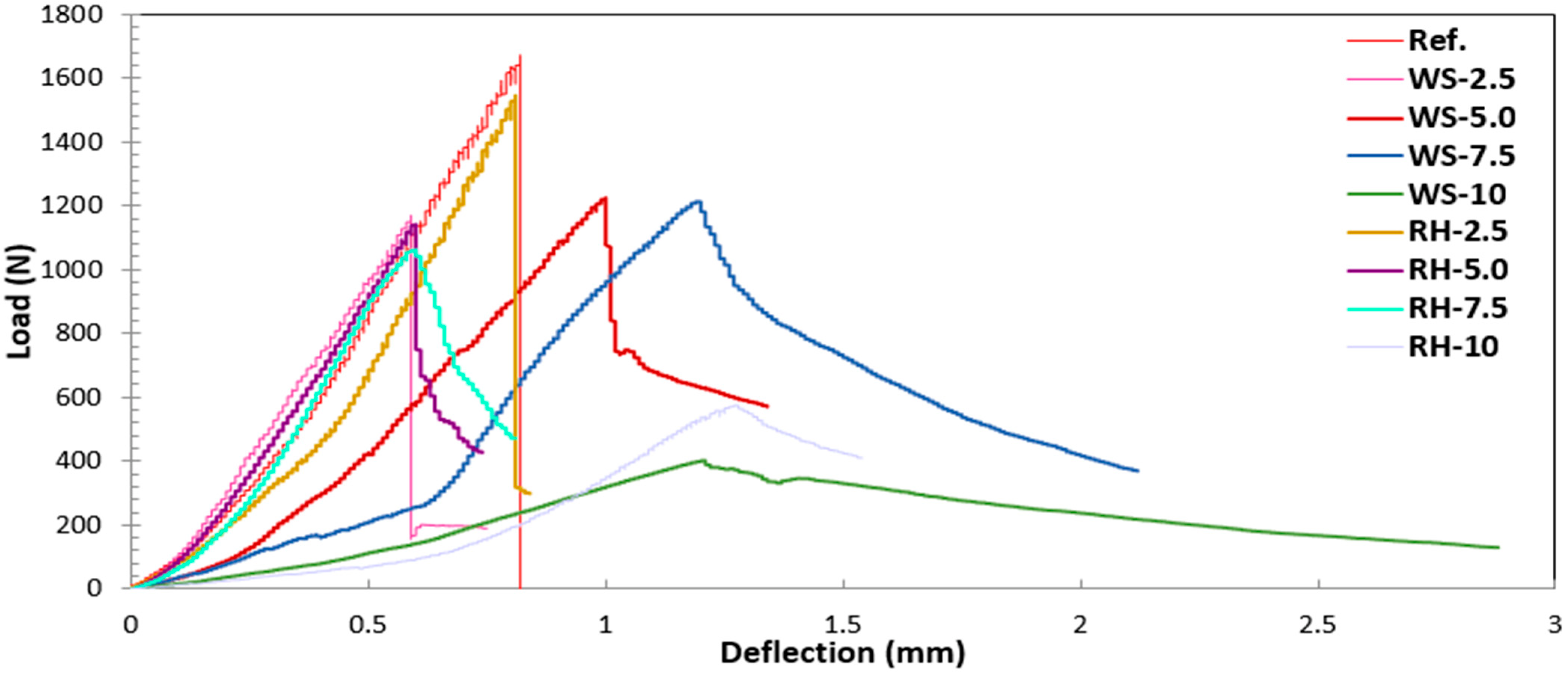
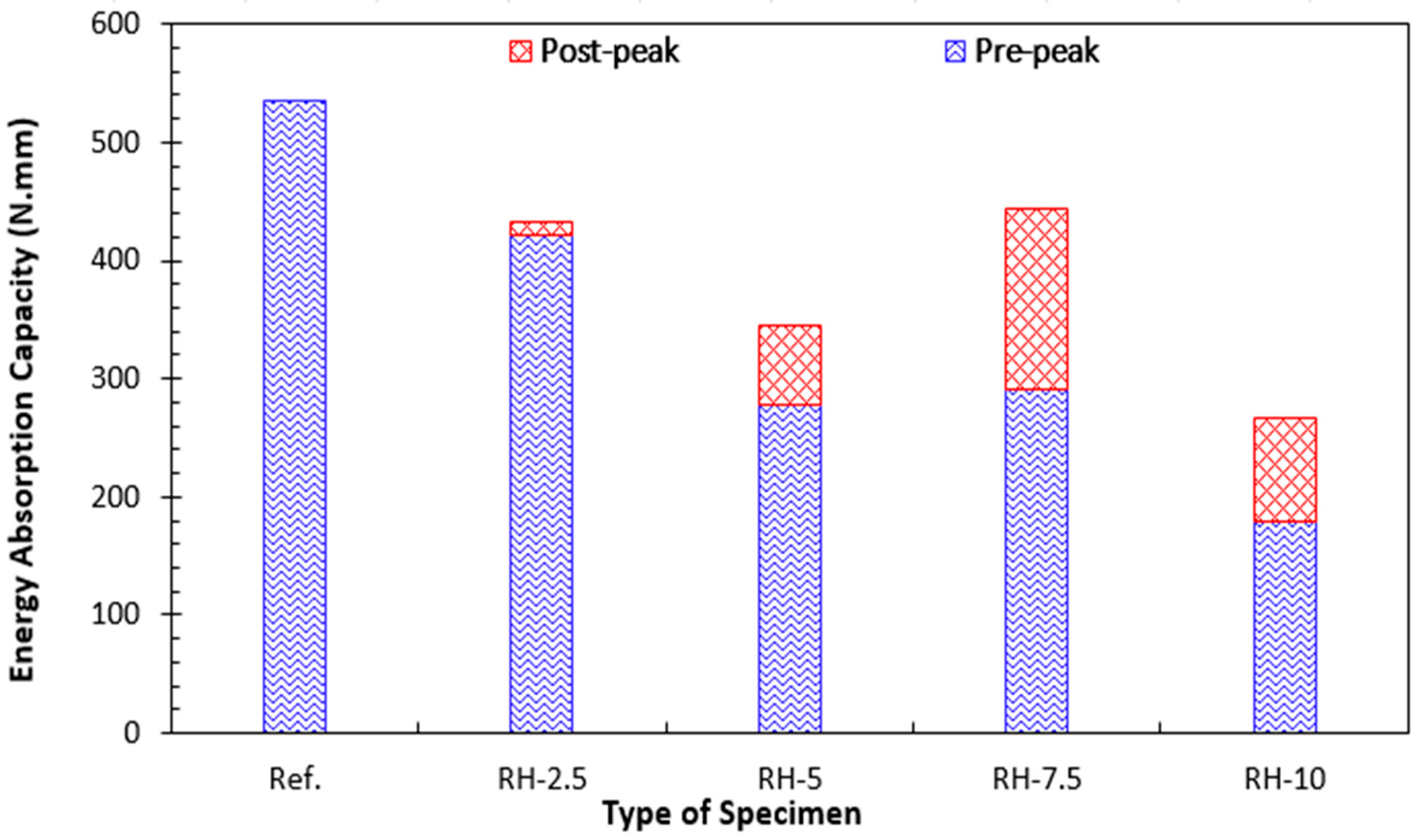
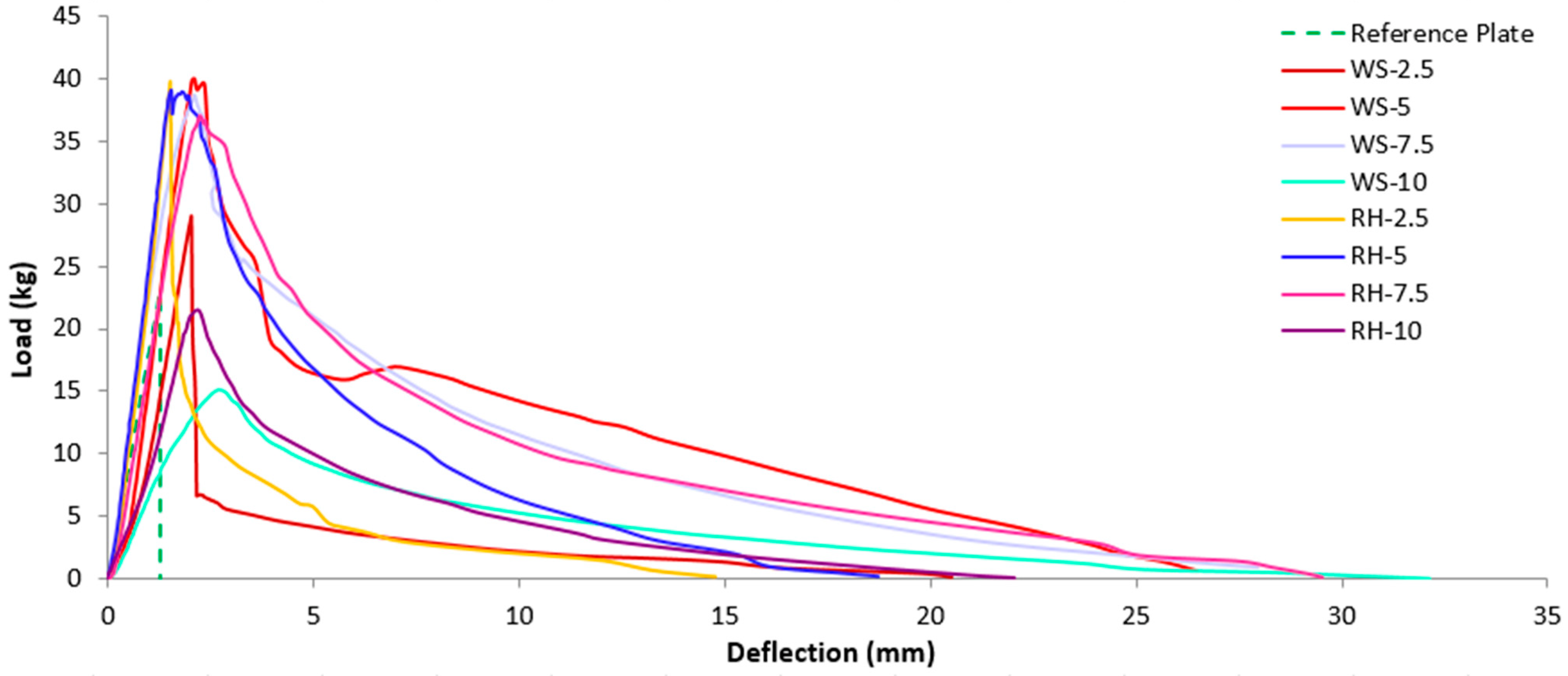
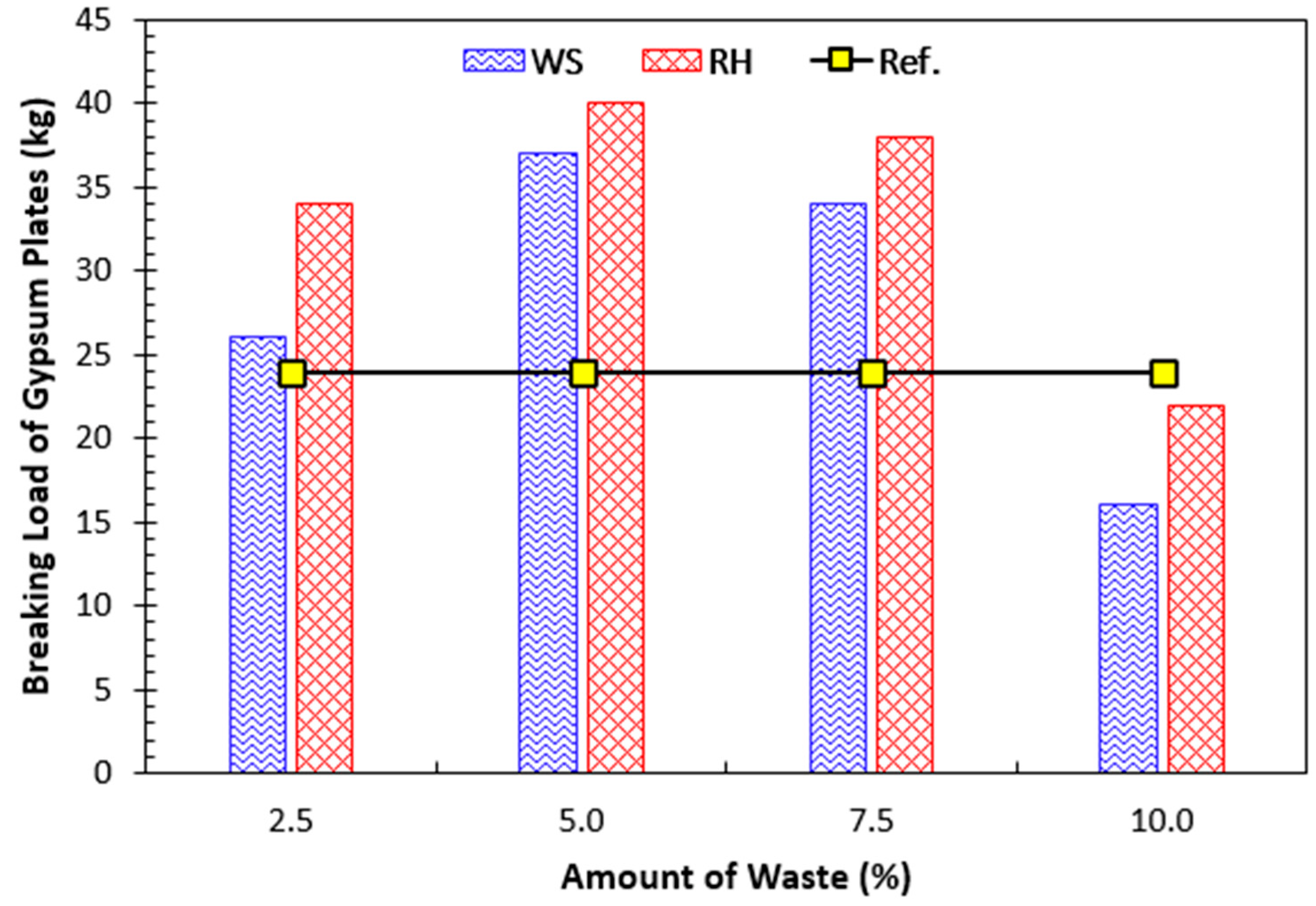
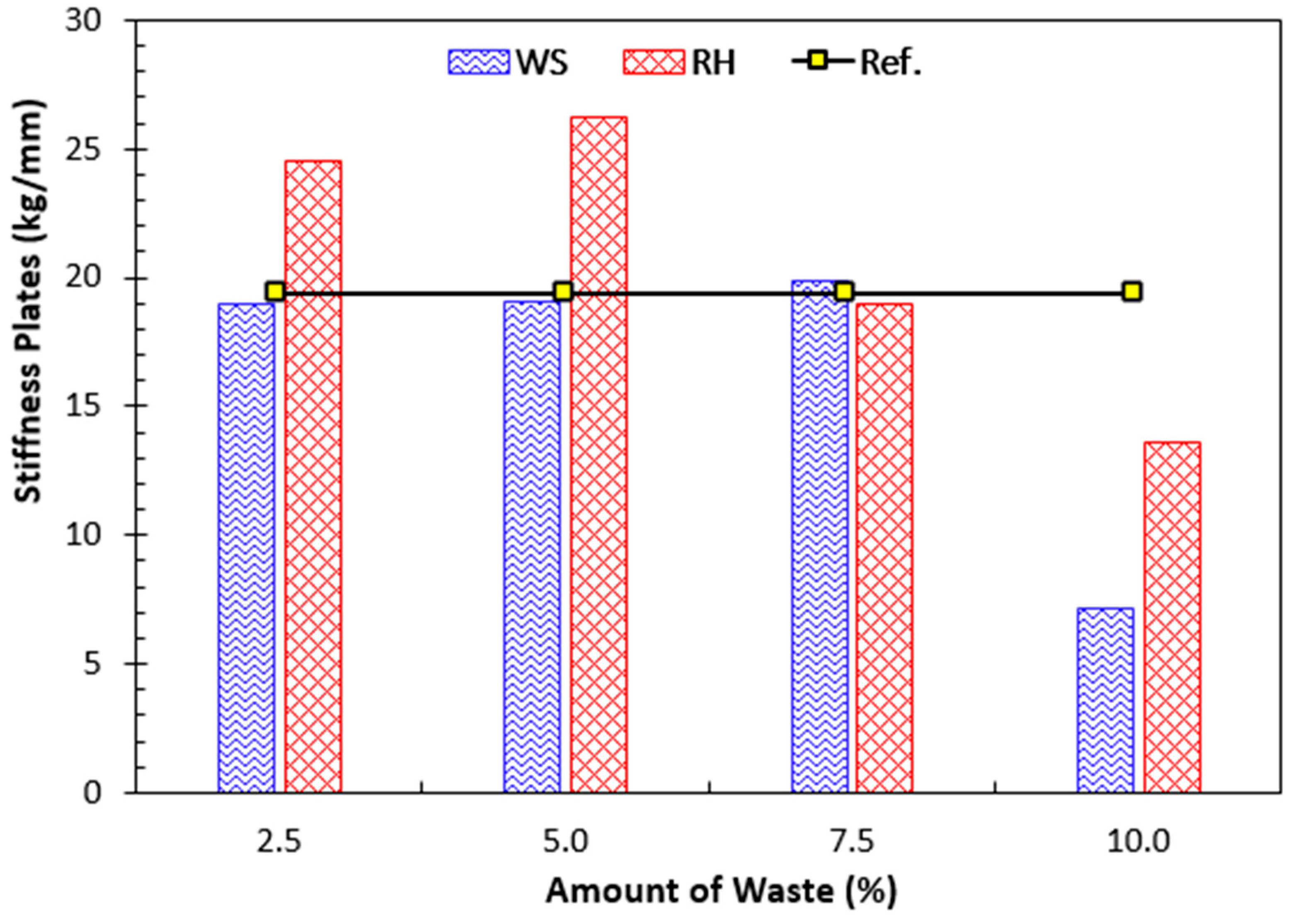
4.2. Tests on False Ceiling Plates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Happho. Why Is False Ceiling Design Important in a House? Available online: https://happho.com/why-is-false-ceiling-design-important-in-a-house/ (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Gharpedia. Things to Know about False Ceiling for Your Interior! Available online: https://gharpedia.com/blog/things-to-know-about-false-ceiling-for-your-interior/ (accessed on 28 November 2017).
- Space, T.A. False Ceilings—Types, Advantages and Its Materials. Available online: https://thearchspace.com/false-ceilings-and-its-materials/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Farooqui, Y.N. Trade Development Authority of Pakistan Report on Analysis of Minerals and Metals Sector of Pakistan; The Case of Gypsum: Karachi, Pakistan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- SAARC Energy Center Report. In Possible Uses of Crop Residue for Energy Generation Instead of Open Burning; SAARC Energy Centre: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2019.
- Saeed, M.A.; Irshad, A.; Sattar, H.; Andrews, G.E.; Phylaktou, H.N.; Gibbs, B.M. Agricultural waste biomass energy potential in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the International Bioenergy Exhibition and Asian Bioenergy Conference, Shanghai, China, 21–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, H.U.; Mahmood, A.; Ullah, A.; Gheewala, S.H. Life Cycle Environmental and Economic Performance Analysis of Bagasse-Based Electricity in Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Nasim, S.; Shahab, A. Charting Pakistan’s Air Quality Policy Landscape; International Growth Centre: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, W.; Saeed, S.; Saulat, H.; Gul, H.; Sarfraz, M.; Sonne, C.; Sohn, Z.-H.; Brown, R.J.C.; Kim, K.H. A review on the deteriorating situation of smog and its preventive measures in Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, R.; Horgnies, M.; Junco, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Calderón, V. Lightweight structural eco-mortars made with polyurethane wastes and non-Ionic surfactants. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boquera, L.; Olacia, E.; Fabiani, C.; Pisello, A.L.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F.; Cabeza, L.F. Thermo-acoustic and mechanical characterization of novel bio-based plasters: The valorisation of lignin as by-product from biomass extraction for green building applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezelova, M.; Krejsova, J.; Scheinherrova, L.; Vimmrova, A. Comparison of structure and properties of gypsum mortars with different types of aggregates. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, International Conference Building Materials, Products and Technologies (ICBMPT 2020), Telč, Czech Republic, 2–4 June 2022; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK; Volume 1039, p. 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrández, D.; Álvarez, M.; Saiz, P.; Zaragoza, A. Experimental Study with Plaster Mortars Made with Recycled Aggregate and Thermal Insulation Residues for Application in Building. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guna, V.; Yadav, C.; Maithri, B.R.; Ilangovan, M.; Touchaleaume, F.; Saulnier, B.; Grohens, Y.; Reddy, N. Wool and coir fiber reinforced gypsum ceiling tiles with enhanced stability and acoustic and thermal resistance. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreno-Rojas, M.; Flores-Colen, I.; De Brito, J.; Rodríguez-Linán, C. Influence of the heating process on the use of gypsum wastes in plasters: Mechanical, thermal and environmental analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras Amores, C.; Santa Cruz Astorqui, J.; Del Río Merino, M.; Villoria Sáez, P.; Viñas Arrebola, C. Thermal behavior of traditional lightweight gypsum with construction and demolition waste materials. DYNA 2019, 94, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santa-Cruz-Astorqui, J.; Del-Río Merino, M.; Villoria-Sáez, P.; Porras-Amores, C. Analysis of the viability of prefabricated elements for partitions manufactured with plaster and EPS from waste recycling. DYNA 2019, 94, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Villoria Sáez, P.; del Río Merino, M.; Sorrentino, M.; Porras Amores, C.; Santa Cruz Astorqui, J.; Viñas Arrebola, C. Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum Composites Containing Inert and Insulation Materials from Construction and Demolition Waste and Further Application as A Gypsum Block. Materials 2020, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yedra, E.; Ferrández, D.; Morón, C.; Saiz, P. New test methods to determine water absorption by capillarity. Experimental study in masonry mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 125988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreño-Rojas, M.; Morales-Conde, M.; Pérez-Gálvez, F.; Rodríguez-Liñán, C. Eco-efficient acoustic and thermal conditioning using false ceiling plates made from plaster and wood waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Conde, M.; Rodríguez-Liñán, C.; Pedreño-Rojas, M. Physical and mechanical properties of wood-gypsum composites from demolition material in rehabilitation works. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTMC62-01; Standard Specification for Building Brick (Solid Masonry Units Made From Clay or Shale). ASTM International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001.
- Dai, D.; Fan, M. Preparation of bio-composite from wood sawdust and gypsum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreño-Rojas, M.A.; Morales-Conde, M.J.; Pérez-Gálvez, F.; Rubio-de-Hita, P. Reuse of CD and DVD Wastes as Reinforcement in Gypsum Plaster Plates. Materials 2020, 13, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Segura, M.; Porras-Amores, C.; Villoria-Sáez, P.; Caballol-Bartolomé, D. Characterization of Gypsum Composites Containing Cigarette Butt Waste for Building Applications. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantilli, A.P.; Jóźwiak-Niedźwiedzka, D.; Denis, P. Bio-Fibres as a Reinforcement of Gypsum Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidales-Barriguete, A.; Santa-Cruz-Astorqui, J.; Piña-Ramírez, C.; Kosior-Kazberuk, M.; Kalinowska-Wichrowska, K.; Atanes-Sánchez, E. Study of the Mechanical and Physical Behavior of Gypsum Boards with Plastic Cable Waste Aggregates and Their Application to Construction Panels. Materials 2021, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakrafli, H.; Tahiri, S.; Albizane, A.; El Otmani, M. Effect of wet blue chrome shaving and buffing dust of leather industry on the thermal conductivity of cement and plaster based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, A.J.; de Guzmán Báez, A.; Navarro, J.G. New composite gypsum plaster–ground waste rubber coming from pipe foam insulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 55, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, S.; Mayor, P.; Hernández-Olivares, F. Influence of proportion and particle size gradation of rubber from end-of-life tires on mechanical, thermal and acoustic properties of plaster–rubber mortars. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serna, Á.; del Río, M.; Palomo, J.G.; González, M. Improvement of gypsum plaster strain capacity by the addition of rubber particles from recycled tyres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Zaldívar, O.; Lozano-Díez, R.; del Cura, S.H.; Mayor-Lobo, P.; Hernández-Olivares, F. Effects of water absorption on the microstructure of plaster with end-of-life tire rubber mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V.; Donnini, J.; Nardinocchi, A. Lightweight plasters containing plastic waste for sustainable and energy-efficient building. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, M.Y. Experimental research on gypsum-based mixtures containing recycled roofing tile powder at ambient and high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Romero, L.A.; Calderón, V.; Rodríguez, Á.; Gutiérrez-González, S. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) between standard gypsum ceiling tile and polyurethane gypsum ceiling tile. Energy Build. 2022, 259, 111867. [Google Scholar]
- EN 13279-2; Gypsum Binders and Gypsum Plasters-Part. 2: Test. Methods. British Standards: London, UK, 2014.
- Wang, Y.; Ji, X.-X.; Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Si, C.; Wang, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, D. Effects of two different enzyme treatments on the microstructure of outer surface of wheat straw. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shivkumar, S. Microstructure and tensile properties of various varieties of rice husk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14246; Gypsum Elements for Suspended Ceilings—Definitions, Requirements and test Methods. British Standards: London, UK, 2006.
- EN 102042; Plasters and Construction Plasters Other Test Methods. British Standards: London, UK, 2013.
- Kim, S. Incombustibility, physico-mechanical properties and TVOC emission behavior of the gypsum–rice husk boards for wall and ceiling materials for construction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12667:2001; Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Products. Determination of Thermal Resistance by Means of Guarded Hot Plate and Heat Flow Meter Methods. Products of High and Medium Thermal Resistance. British Standards: London, UK, 2001.
- EN 13279-1; Gypsum Binders and Gypsum Plasters: Part 1: Definitions and Requirements. European Committee for Standardization: Brüssels, Belgium, 2006.











| Property | Gypsum (%) | Wheat Straw (%) | Rice Husk (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 39.24 | 12.51 | Traces |
| MgO | 1.04 | 2.38 | 0.530 |
| SiO2 | 2.17 | 62.44 | 91.10 |
| SO3 | 47.29 | 1.34 | 0.408 |
| Al2O3 | 1.59 | 4.29 | 0.576 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.083 | 0.96 | 0.417 |
| L.O.I | 8.01 | 7.06 | 6.47 |
| Cl | 0.007 | 0.0021 | 0.032 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 877 | 95 | 76.72 |
| pH | 7.5 | 10.4 | 9.9 |
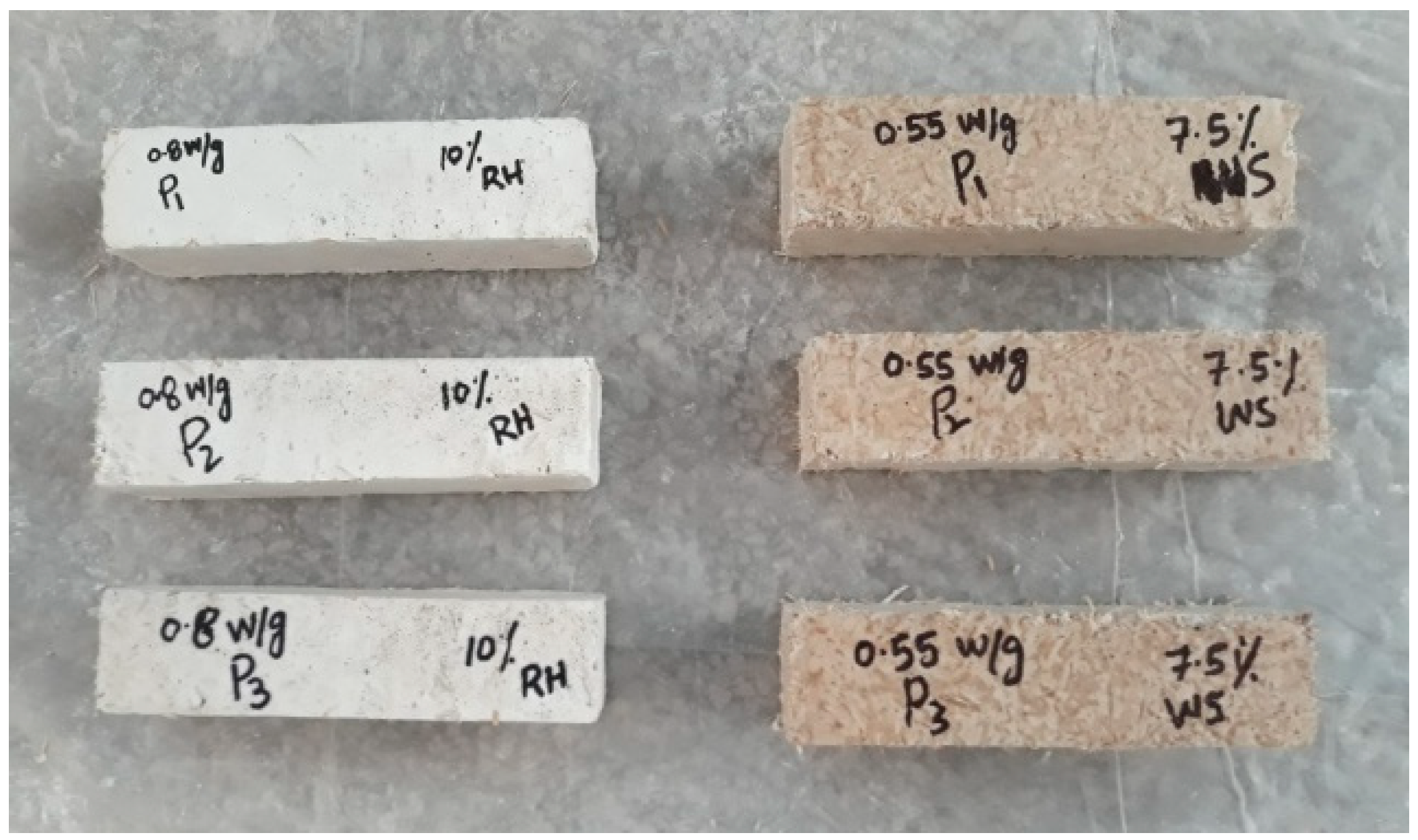
| Material | Acronyms | Gypsum (g) | Water (g) | W/G* Ratio | Wheat Straw (g) (%) | Rice Husk (g) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gypsum | Ref. | 1000 | 550 | 0.55 | - | - |
| Gypsum | WS-2.5 | 975 | 536.25 | 0.55 | 25 (2.5%) | - |
| + | WS-5 | 950 | 522.5 | 0.55 | 50 (5%) | - |
| Wheat | WS-7.5 | 925 | 508.75 | 0.55 | 75 (7.5%) | - |
| Straw | WS-10 | 900 | 720 | 0.8 | 100 (10%) | - |
| Gypsum | RH-2.5 | 975 | 536.25 | 0.55 | - | 25 (2.5%) |
| + | RH-5 | 950 | 522.5 | 0.55 | - | 50 (5%) |
| Rice | RH-7.5 | 925 | 508.75 | 0.55 | - | 75 (7.5%) |
| Husk | RH-10 | 900 | 720 | 0.8 | - | 100 (10%) |
| Test | Dimensions of Test Specimens (mm) | Number of Specimens for Each Mix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density, Hardness, Flexural Strength | 160 × 40 × 40 | 3 | EN 102042:2013 [40] EN 13279-2:2014 [36] |
| Water absorption | 100 × 100 × 15 | 3 | Sumin Kim [41] |
| Thermal conductivity | 300 × 300 × 15 | 3 | EN 12667:2001 [42] |
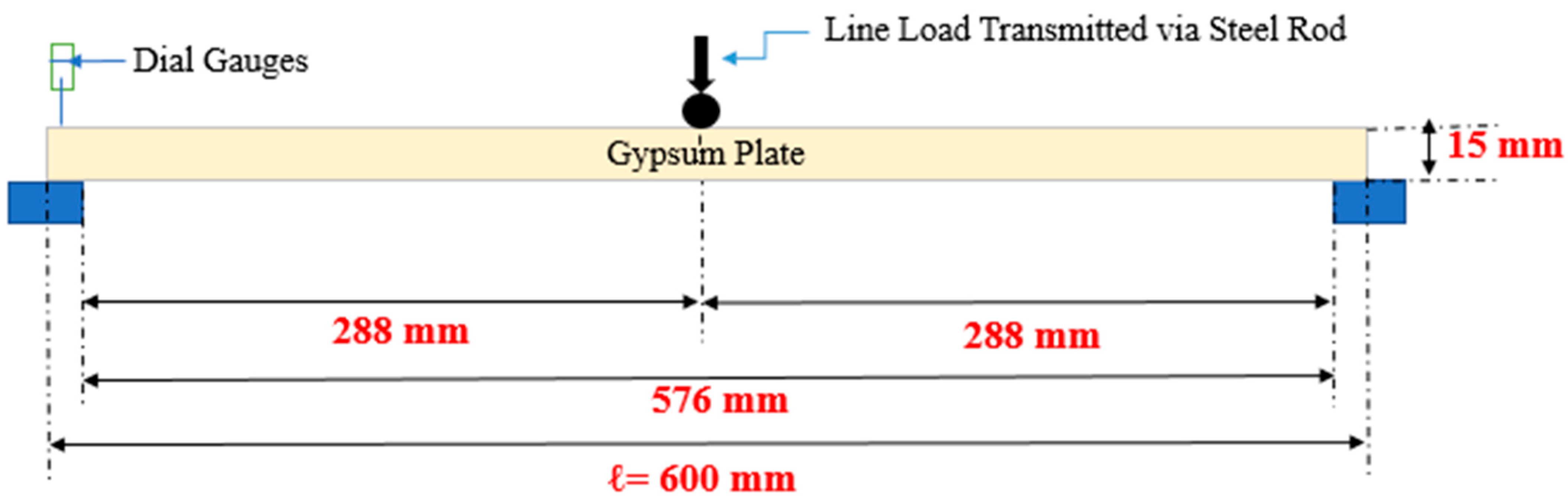
| Bending test of plates | 600 × 600 × 15 | 3 | EN 14246:2006 [39] |
| Requirements | Requirements according to EN 14246:2006 |
|---|---|
| Dimension (Type A) | Length: 600–1200 mm; Width: 600 mm; Thickness: 15 mm |
| Spacing of Supports | 576 mm spacing between supports for a plate with exposed gird |
| Flexure Strength | Can support a 6 kg centered linear load for 30 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ejaz, M.F.; Riaz, M.R.; Azam, R.; Hameed, R.; Fatima, A.; Deifalla, A.F.; Mohamed, A.M. Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum-Agricultural Waste Composites for Developing Eco-Friendly False Ceiling Tiles. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169797
Ejaz MF, Riaz MR, Azam R, Hameed R, Fatima A, Deifalla AF, Mohamed AM. Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum-Agricultural Waste Composites for Developing Eco-Friendly False Ceiling Tiles. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169797
Chicago/Turabian StyleEjaz, Muhammad Fahad, Muhammad Rizwan Riaz, Rizwan Azam, Rashid Hameed, Anam Fatima, Ahmed Farouk Deifalla, and Abdeliazim Mustafa Mohamed. 2022. "Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum-Agricultural Waste Composites for Developing Eco-Friendly False Ceiling Tiles" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169797
APA StyleEjaz, M. F., Riaz, M. R., Azam, R., Hameed, R., Fatima, A., Deifalla, A. F., & Mohamed, A. M. (2022). Physico-Mechanical Characterization of Gypsum-Agricultural Waste Composites for Developing Eco-Friendly False Ceiling Tiles. Sustainability, 14(16), 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169797









