Emerging Associates of the Circular Economy: Analysing Interactions and Trends by a Mixed Methods Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- ▪
- SDG 6: the Goal on Clean Water and Sanitation,
- ▪
- SDG 7: the Goal on Affordable and Clean Energy,
- ▪
- SDG 8: the Goal on Decent Work and Economic Growth,
- ▪
- SDG 12: the Goal on Responsible Consumption and Production, and
- ▪
- SDG 15: the Goal on Life on Land
2. Material and Research Methodology
- ▪
- RQ 1: Which keywords are manifested from one-decade literature on CE and over a hundred definitions of CE?
- ▪
- RQ 2: Which keywords are ontologically allied with CE and meet the definition of an associate?
- ▪
- RQ 3: Which associates are significant as per one decade of CE literature?
- ▪
- RQ 4: What can be the holistic CE framework with emerged associates demonstrating individuation of the concept of CE?
- To explore and map common keywords from literature and CE definitions.
- To explore the ontological connection of emerged keywords with CE and generate a list of associates.
- To examine associates with respect to CE and rank them to understand their current state.
- To develop a holistic framework with associates of CE and demonstrate the ontological connections.
2.1. Article Screening Process for Literature Review
- (a)
- English journal articles published between 2010 and 2019, a decade, because a decent amount of published research in the field emerged from 2010.
- (b)
- The journal article’s concept and subject area, as demonstrated in the flowchart. The final step of screening was based on its title, abstract, keywords, and citation score.
- (c)
- the conceptual nature of the paper,
- high citation score,
- at least published in quartiles 1 or 2 journals,
- non-repetitive or no duplicate contents, and
- in the English language
2.2. Applications Rationale and Methods
- ▪
- Text Analysis,Semantic Analysis and Relation Mapping (TROPES V8.4): Tropes V8.4 processes texts to extract relevant information for stylistic, syntactic (syntactic analysis may depend on the types of words, but not their meaning), and semantic equivalents analysis, covering several themes in various graphs, reports, or specific data structures [38]. The application indexes the articles, using a preloaded dictionary, in the citations network, either as citation sources or cited articles. It captures features and precise traits of the scientific discourse. The selection is based on the initial results from text conversion and citations identification [39].
- ▪
- Bibliometric Analysis (VOSviewer): Bibliometric analysis is often represented as a network visualization, which ranges from entirely graphical user interface-based software such as VOSviewer. It explores the bibliometric networks structured from data mining and keyword selection [40]. Maps are created from keywords co-occurrence and their frequency, finally assigned to clusters, producing set of items and links.
- ▪
- Content Analysis and WAPR (MS Excel): It is an interpretive technique which is both observational and narrative in nature. It is used to determine, quantify and analyse the presence, meanings, and relationships of keywords or themes in the text. The text is coded into categories to summarise data by generating binary values to create an occurrences or frequency map.
- ▪
- Association Rules Data Mining (WEKA): The Apriori algorithm is an algorithm in machine learning that discovers plausible associations and creates association rules. It finds out the minimum support and confidence threshold while computing these rules. Apriori works with binary attributes or nominal data. The tool Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis (WEKA) allows one to perform frequent pattern mining by implementing Apriori for finding features which occur together or are correlated.
- ▪
- K-Means Clustering (SPSS): The unsupervised learning algorithm is used to cluster the unlabelled dataset based on a centroid by minimizing the sum of distances between data points and their corresponding clusters having similar properties following an iterative process.
3. Systematic Qualitative Literature Review: Content and Semantic Analysis
3.1. Circular Economy: Epistemology and Origin
3.2. Circular Economy: Definitions, Principles, Strategies
4. Statistical Analysis and Results
4.1. Text Analysis, Bibliometric Analysis, Relation Mapping from Syntactic Analysis of Keywords and Associate Mapping
4.2. Semantic Analysis of 76 Articles and 122 Definitions
- ▪
- Occurrence and frequency mapping of 76 articles
- ▪
- Occurrence and frequency mapping of 122 definitions
4.3. Weighted Average Priority Ranking (WAPR) on ARTICLES and Definitions
4.4. Association Rule Mining and K-Means Clustering
4.5. Development of an Integrated CE System
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Name of Journal | Abbreviation | Name of Journal |
| BSE | Business Strategy and the Environment | JoIE | Journal of Industrial Ecology |
| CJoMScT | CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology | JoIPE | Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering |
| ED | Environmental Development | JoMCWM | Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management |
| EE | Ecological Economics | LE | Local Economy |
| EIST | Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions | OmUK | Omega (United Kingdom) |
| EMS | Environmental Modelling & Software | Pa | Particuology |
| Eng | Energy | PHG | Progress in Human Geography |
| Fut | Futures | PToTRSMPESc | Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences |
| IJoPE | International Journal of Production Economics | ReCR | Resources Conservation and Recycling |
| IJPoR | International Journal of Production Research | Re | Resources |
| IJoSDWE | International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology | RSER | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews |
| JoBE | Journal of Business Ethics | SS | Sustainability (Switzerland) |
| JoCP | Journal of Cleaner Production | TFSC | Technological Forecasting & Social Change |
| JoEM | Journal of Environmental Management | WM | Waste Management |
Appendix A



| List of Keywords | The Word, Other Allied and Associated Words | |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability Pillar | Sustainable | Sustainable, Sustainability, Sustainable Development Goal, SDG |
| Society | Society, Social, Societal, Culture, Access, Community, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Tradition, Job, Employment, Recruitment, Wellbeing, Equality, People | |
| Economy | Profit, Growth, Development, Consumption, Production, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP), National Income | |
| Environment | Environment, Environmental, Climate, Weather, Planet, Carbon, Footprint, Ecology, Eco, Ecosystem, Global Warming, Emission, Organic, Biodegradable, Biology, Pollution, Natural, Nature, Conserve, Green House Gas (GHG), Preserve, Anaerobic | |
| List of Keywords | Allied and Similar Words | |
| Other Similar Keywords (Part of Business Model Canvas, Other R-imperative, Influencers, and Regulation and Standardization) | Barrier | Barrier, Challenge, Difficult, Hinder, Negative |
| Behaviour | Behaviour, Habit, Customer Behaviour, Leader, Nudge, Steward, Decision | |
| Business | Business, Business Management, Circular Business Model, Lease, Rent, Share, Business Model Canvas, Start-up, Value Chain, Value Proposition, Enterprise, Company, Corporate, Fund, Producer, Consumer, Cost, Investment, Market, Gain, Loss, Solution, Competition, Resale, Similar Words | |
| Collaborate | Collaborate, Partnership, Joint | |
| Countries | Country, America, Brazil, China, Japan, Europe, Korea, Switzerland, Germany, India | |
| Design | Design, Cradle, Process Design, Product Design, Cradle to Cradle | |
| Driver | Driver, Enabler, Positive, Scope, Hope, Opportunity, Positive | |
| Energy | Energy, Renewable, Biomass, Solar, Hydro | |
| Government | Government, Govern, Governance, Governmental | |
| Implementation | Implementation, Meso, Micro, Macro, Local, Global | |
| Industry | Industrial, Symbiosis, Agriculture, Chemical, Construction, Education, Electrical, Electronics, Fashion, Food, Water, Glass, Rubber, Plastic, Package, Wood, Transport, Tourism, Operation, Health, Similar Words | |
| Infrastructure | Infrastructure, Infrastructural, Private and Public Infrastructure | |
| Innovation | Innovation, Disruptive Innovation, Frugal Innovation, Job to Be Done Theory, Nudge Theory, Radical | |
| Institute | Institute, Bank, Educational Institute, Institution, Organization | |
| Life Cycle | Lifecycle | |
| Measurement | Measure, Assess, Indicator, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Material Flow Analysis (MFA), Efficiency, Impact, Perform, Rate, Ratio, Allied Words | |
| Policy | Policy, Act, Law, Legal, Regulation | |
| Principle | Principle, Fundamental | |
| Product | Product, Durable, Longevity, Goods, Product Service System, Maintenance, Price, Other Allied Words | |
| Raw Material | Raw Material | |
| Refill | Refill, Refillable | |
| Replace | Replace, Replacing, and Replacement | |
| Resource | Resource, Resources | |
| Return | Return, Returning | |
| Risk | Risk, Uncertain, Uncertainty, Shock, and Insurance | |
| Supply Chain | Supply Chain, SC, Reverse Logistic | |
| System | System, Systematic | |
| Technology | Technology, Tech, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Automation, Big Data | |
| Waste | Waste, Garbage, Waste Management, Collection, Disposal, E-Waste, Segregation, Landfill | |
| List of Keywords | The Word, Other Allied and Similar Words | |
| 10 R Framework (R-imperatives) | Recycle | Recycle, Recycled, Recyclability, Recycling |
| Refuse | Refuse, Refusal, Deny | |
| Rethink | Rethink, Rethinking | |
| Reduce | Reduce, Reduction, Reduced | |
| Reuse | Reuse, Reused | |
| Repair | Repair, Repaired, Repairing | |
| Refurbish | Refurbish, Refurbished, Refurbishment | |
| Remanufacture | Remanufacture, Remanufacturing | |
| Repurpose | Repurpose, Repurposing | |
| Recover | Recover, Recovery | |
| List of Keywords | The Word, Other Allied and Similar Words | |
| ReSOLVE Framework | Regenerate | Regenerate, Regeneration, Regenerative |
| Share | Share, Sharing | |
| Optimize | Optimize, Optimization, Optimal | |
| Loop | Loop, Close, Slow, Narrow, Dematerialize, Intensify | |
| Virtualize | Virtualize, Internet, Online, Virtual | |
| Exchange | Exchange, Exchanged |
| Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance | PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| CBM | Circular Business Model | SC | Supply Chain |
| CE | Circular Economy | SCI | Sustainable Circular Index |
| CSCM | Circular Supply Chain Management | SD | Sustainable Development |
| EMF | Ellen MacArthur Foundation | SDG | Sustainable Development Goals |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product | SLR | Systematic Literature Review |
| GRI | Global Reporting Initiative | SQLR | Systematic Quantitative Literature Review |
| LCA | Life Cycle assessment | TBL | Triple Bottom Line |
| MFA | Material Flow Analysis | WAPR | Weighted Average Priority Ranking |
| NDF | Normalize Definition Frequency | WoS | Web of Science |
| NDO | Normalize Definition Occurrence | UN | United Nation |
References
- Lacy, P.; Keeble, J.; McNamara, R.; Rutqvist, J.; Haglund, T.; Cui, M.; Buddemeier, P. Circular Advantage: Innovative Business Models and Technologies to Create Value in a World without Limits to Growth. 2014. Available online: https://sharingcitiesalliance.knowledgeowl.com/help/circular-advantage-innovative-business-models-and-technologies-to-create-value-in-a-world-without-limits-to-growth (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A new sustainability paradigm. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. Growth within: A Circular Economy Vision for a Competitive Europe. 2015. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/publications/EllenMacArthurFoundation_Growth-Within_July15.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Kirchherr, J.; Piscicelli, L.; Bour, R.; Kostense-Smit, E.; Muller, J.; Huibrechtse-Truijens, A.; Hekkert, M. Barriers to the Circular Economy: Evidence from the European Union (EU). Ecol. Econ. 2018, 150, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, M.P.P.; McAloone, T.C.; Pigosso, D.C.A. Business model innovation for circular economy and sustainability: A review of approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J. 3 challenges facing the UN’ s Sustainable Development Goals. World Economic Forum. 2015. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/authors/james-patterson (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Newman, C. Achieving Sustainable Development. 2020. Available online: https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/achieving-sustainable-development/0/steps/35495 (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Schroeder, P.; Anggraeni, K.; Weber, U. The Relevance of Circular Economy Practices to the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, B.; Shen, L.; Reike, D.; Carreón, J.R.; Worrell, E. Towards sustainable development through the circular economy—A review and critical assessment on current circularity metrics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winans, K.; Kendall, A.; Deng, H. The history and current applications of the circular economy concept. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Sadagopan, M.; Rosado, L. Circular economy—From review of theories and practices to development of implementation tools. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ramakrishna, S. (Eds.) An Introduction to Circular Economy; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöggl, J.P.; Stumpf, L.; Baumgartner, R.J. The narrative of sustainability and circular economy—A longitudinal review of two decades of research. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.M.; Elrehail, H.; Alatailat, M.A.; Elçi, A. Knowledge management, decision-making style and organizational performance. J. Innov. Knowl. 2019, 4, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelnik, R. What is the Value of Circular Economy Without Sustainability? 2019. Available online: https://medium.com/@razgo/what-is-the-value-of-circular-economy-without-sustainability-67e663867ff9 (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Padilla-Rivera, A.; Russo-Garrido, S.; Merveille, N. Addressing the social aspects of a circular economy: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, V.; Gnoni, M.G.; Tornese, F. Measuring circular economy strategies through index methods: A critical analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homrich, A.S.; Galvão, G.; Abadia, L.G.; Carvalho, M.M. The circular economy umbrella: Trends and gaps on integrating pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friant, M.C.; Vermeulen, W.J.V.; Salomone, R. A typology of circular economy discourses: Navigating the diverse visions of a contested paradigm. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Nuur, C.; Feldmann, A.; Birkie, S.E. Circular economy as an essentially contested concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 544552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, M.; Yannou, B.; Leroy, Y.; Cluzel, F.; Kendall, A. A taxonomy of circular economy indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clube, R.K.M.; Tennant, M. The Circular Economy and human needs satisfaction: Promising the radical, delivering the familiar. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 177, 106772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomsma, F. Collective ‘action recipes’ in a circular economy—On waste and resource management frameworks and their role in collective change. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Sandoval, V.; Jaca, C.; Ormazabal, M. Towards a consensus on the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Eiroa, B.; Fernández, E.; Méndez-Martínez, G.; Soto-Oñate, D. Operational principles of circular economy for sustainable development: Linking theory and practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. The benefits of publishing systematic quantitative literature reviews for PhD candidates and other early-career researchers. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2014, 33, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebb, A.T.; Parrigon, S.; Woo, S.E. Exploratory data analysis as a foundation of inductive research. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2017, 27, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, S. Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Data in Mixed Methods Research—Challenges and Benefits. J. Educ. Learn. 2016, 5, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 349, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Real, J.L.; Uribe-Toril, J.; Valenciano, J.D.P.; Gázquez-Abad, J.C. Worldwide Research on Circular Economy and Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. Citation Indexes for Science a New Dimension in Documentation through Association of Ideas. Science 1955, 122, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, R.M.; Savietto, J.P.; Battistelle, R.A.G.; Ometto, A.R. Trends in publications on the circular economy. Rev. Espac. 2017, 38, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Tur, A.; Guijarro, M.; Carrilero, A. The influence of the circular economy: Exploring the knowledge base. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moed, H.F. Citation Analysis in Research Evaluation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 49, p. 6221. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R.K.; Gaston, J. The Sociology of Science: An Episodic Memoir; Southern Illinois University Press: Carbondale, IL, USA, 1977; pp. 1–141. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2068816 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Molette, P.; Landre, A. Software Tropes, Version 8. 2010. Available online: http://www.forhe.ro/docs/tropes_manual_de_referinta.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Velter, V.; Dumitrache, I.; Avram, S.; Dumitrache, I. Semantic Analysis Applications in Computational Bibliometrics. 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261607093 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Pattnaik, D. Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research: A bibliometric analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, P.; Griffith, T.L. Creating and Disseminating Knowledge Among Organizational Scholars: The Role of Special Issues. Organ. Sci. 2004, 15, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, Y.; Ghuman, K.; Dhir, A. Sustainable manufacturing. Bibliometrics and content analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.W. A conceptual framework for quantitative text analysis: On joining probabilities and substantive inferences about texts. Qual. Quant. 2000, 34, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, C.; Markoff, G. Text Analysis for the Social Science: Methods for Drawing Statistical Inferences from Text and Transcripts; Routledge: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, E.B.; Holsti, O.R. Content Analysis for the Social Sciences and Humanities; American Sociological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, W.; Tarnai, C. Content analysis in empirical social research. Int. J. Educ. Res. 1999, 31, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Kasén, A.; Eriksson, K. Semantic analysis according to Peep Koort—A substance-oriented research methodology. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2010, 24, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newing, H.; Eagle, C.M.; Puri, R.K.; Watson, C.W. Conducting Research in Conservation: Social Science Methods and Practice; Oxfordshire: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, J.; Clifton, C. Privacy preserving association rule mining in vertically partitioned data. In Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 23–26 July 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, E.; Shao, J. A taxonomy of circular economy implementation strategies for manufacturing firms: Analysis of 391 cradle-to-cradle products. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Manzardo, A.; Toniolo, S.; Scipioni, A. Sustainability of hydrogen supply chain. Part I: Identification of critical criteria and cause-effect analysis for enhancing the sustainability using DEMATEL. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 14159–14171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, R.; Preziosi, M.; Acampora, A. How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, M. Sustainability and sustainable development: Historical and conceptual review. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 1988, 18, 493–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisellini, P.; Cialani, C.; Ulgiati, S. A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Skene, K.; Haynes, K. The Circular Economy: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Concept and Application in a Global Context. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 140, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.S. An introductory note on the environmental economics of the circular economy. Sustain. Sci. 2007, 2, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Heshmati, A.; Geng, Y.; Yu, X. A review of the circular economy in China: Moving from rhetoric to implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 42, 15–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomsma, F.; Brennan, G. The Emergence of Circular Economy: A New Framing Around Prolonging Resource Productivity. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 21, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bertalanffy, L. An outline of general system theory. Br. J. Philos. Sci. 1950, 1, 134–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wautelet, T.; Impakt, P. The Concept of Circular Economy: Its Origins and Its Evolution. 2018. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322555840_The_Concept_of_Circular_Economy_its_Origins_and_its_Evolution (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Sorensen, P.B. The Basic Environmental Economics of the Circular Economy. SSRN Electron. J. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneese, A.V.; Ayres, R.U.; D’arge, R.C. Economics and the Environment: A Materials Balance Approach; Routledge: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, W.R.; Reday, G. The Potential for Substituting Manpower for Energy; Battelle, Geneva Research Centre: Geneva, Switzerland, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Frosch, R.A. Industrial ecology: A philosophical introduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfang, G. Consuming Values and Contested Cultures: A Critical Analysis of the UK Strategy for Sustainable Consumption and Production. Rev. Soc. Econ. 2004, 62, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, F. Circular business models: Business approach as driver or obstructer of sustainability transitions? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commoner, B. The Environmental ‘Crisis’ and ‘The Ecosphere’ in The Closing Circle: Nature, Man and Technology; Routledge: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, J.T. Regenerative Design for Sustainable Development; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-471-17843-9. [Google Scholar]
- Benyus, J.M. Biomimicry: Innovation Inspired by Nature. Am. Biol. Teach. 1998, 60, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, W.; Braungart, M. Remaking the Way We Make Things: Creating a New Definition of Quality with Cradle-to-Cradle Design in the International Handbook on Environmental Technology Management; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allenby, B.R. Industrial Ecology and Sustainable Engineering in Encyclopedia of Sustainability in Higher Education; Pearson: Cham, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 23–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, W.R. The Performance Economy; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, G. The Blue Economy Book; Xlibris: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, N.; McLaughlin, E.; Börger, T. The Circular Economy: Swings and Roundabouts? Ecol. Econ. 2019, 158, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Bi, J.; Moriguichi, Y. The Circular Economy: A New Development Strategy in China. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 10, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocken, N.M.P.; de Pauw, I.; Bakker, C.; van der Grinten, B. Product design and business model strategies for a circular economy. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2016, 33, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, N.; Kumar, V.; Pongsakornrungsilp, S.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Gupta, B.; Pongsakornrungsilp, P. Understanding circular economy awareness and practices in manufacturing firms. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2019, 32, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reike, D.; Vermeulen, W.J.V.; Witjes, S. The circular economy: New or Refurbished as CE 3.0? —Exploring Controversies in the Conceptualization of the Circular Economy through a Focus on History and Resource Value Retention Options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Shimamura, K.; Aizawa, H. 3R strategies for the establishment of an international sound material-cycle society. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2007, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, K. A 3R Implementation Framework to Enable Circular Consumption in Community. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allenby, B.R.; Cοmrie, P.R. Matrix approaches to abridged life cycle assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 134A–139A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayies, R.U.; Ayres, L.W.; Klöpffer, W. Industrial ecology: Towards closing the material cycle. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 1997, 2, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buren, N.; Demmers, M.; van der Heijden, R.; Witlox, F. Towards a circular economy: The role of Dutch logistics industries and governments. Sustainability 2016, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; Dekker, R.; van der Laan, E.; van Nunen, J.A.E.E.; van Wassenhove, L.N. Quantitative models for reverse logistics: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 103, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.L.; Scorpio, D.E.; Kibert, C.J. Strategies for successful construction and demolition waste recycling operations. Constr. Manag. Econ. 1997, 15, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvonen, S.; Ritola, T. Conceptualizing ReX for aggregating end-of-life strategies in product development. Procedia Cirp 2015, 29, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, M.P.; Dekker, R. A Framework for Reverse Logistics in Reverse Logistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, M.; Salomon, M.; van Nunen, J.; van Wassenhove, L. Strategic Issues in Product Recovery Management. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1995, 37, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.L.; Renó, G.W.S.; Sevegnani, G.; Sevegnani, T.B.; Truzzi, O.M.S. Comparison of disposable and returnable packaging: A case study of reverse logistics in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, J.M.; Ashby, M.F.; Gutowski, T.G.; Worrell, E. Material efficiency: A white paper. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, J.; Hekkert, M.; Worrell, E.; Hanemaaijer, A. Circular Economy: Measuring Innovation in the Product Chain—Policy Report; PBL Netherlands Environ Assessment Agency: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Lieder, M.; Rashid, A. Towards circular economy implementation: A comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, M. Designing the business models for circular economy-towards the conceptual framework. Sustainability 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.; Williander, M. Circular Business Model Innovation: Inherent Uncertainties. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2017, 26, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdeke-Freund, F.; Gold, S.; Bocken, N.M.P. A Review and Typology of Circular Economy Business Model Patterns. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 36–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planing, P. Business Model Innovation in a Circular Economy Reasons for Non-Acceptance of Circular Business Models. Open J. Bus. Model Innov. 2014, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, K.; Hasanagic, M. A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: A supply chain perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 278–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressanelli, G.; Perona, M.; Saccani, N. Challenges in supply chain redesign for the Circular Economy: A literature review and a multiple case study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 7395–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Morioka, S.N.; de Carvalho, M.M.; Evans, S. Business models and supply chains for the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; de los Rios, C.; Rowe, Z.; Charnley, F. A conceptual framework for circular design. Sustainability 2016, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antikainen, M.; Valkokari, K. A Framework for Sustainable Circular Business Model Innovation. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2016, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.; Sarasini, S.; van Loon, P. A Metric for Quantifying Product-Level Circularity. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 21, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, F.; Rem, P.C. A Robust Indicator for Promoting Circular Economy through Recycling. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga, G.; Huysveld, S.; Mathieux, F.; Blengini, G.A.; Alaerts, L.; Van Acker, K.; De Meester, S.; Dewulf, J. Circular economy indicators: What do they measure? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, N.; Lafhaj, Z.; Yehya, M.; Payet, J. Global Resource Indicator for life cycle impact assessment: Applied in wind turbine case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, B.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y. A novel Dempster-Shafer theory-based approach with weighted average for failure mode and effects analysis under uncertainty. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 65, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, P.; Ghodasara, Y. Using Apriori with WEKA for Frequent. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2014, 12, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbade, M.J. Understanding K-means Clustering in Machine Learning How the K-means algorithm works K-means algorithm example problem. 2018, pp. 1–7. Available online: https://blog.educationecosystem.com/understanding-k-means-clustering-in-machine-learning/ (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Zhu, Q.; Geng, Y.; Lai, K. Circular economy practices among Chinese manufacturers varying in environmental-oriented supply chain cooperation and the performance implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Geng, Y.; Lai, K. Environmental Supply Chain Cooperation and Its Effect on the Circular Economy Practice-Performance Relationship Among Chinese Manufacturers. J. Ind. Ecol. 2011, 15, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Sarkis, J.; Filho, M.G. Unlocking the circular economy through new business models based on large-scale data: An integrative framework and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 114, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, K.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

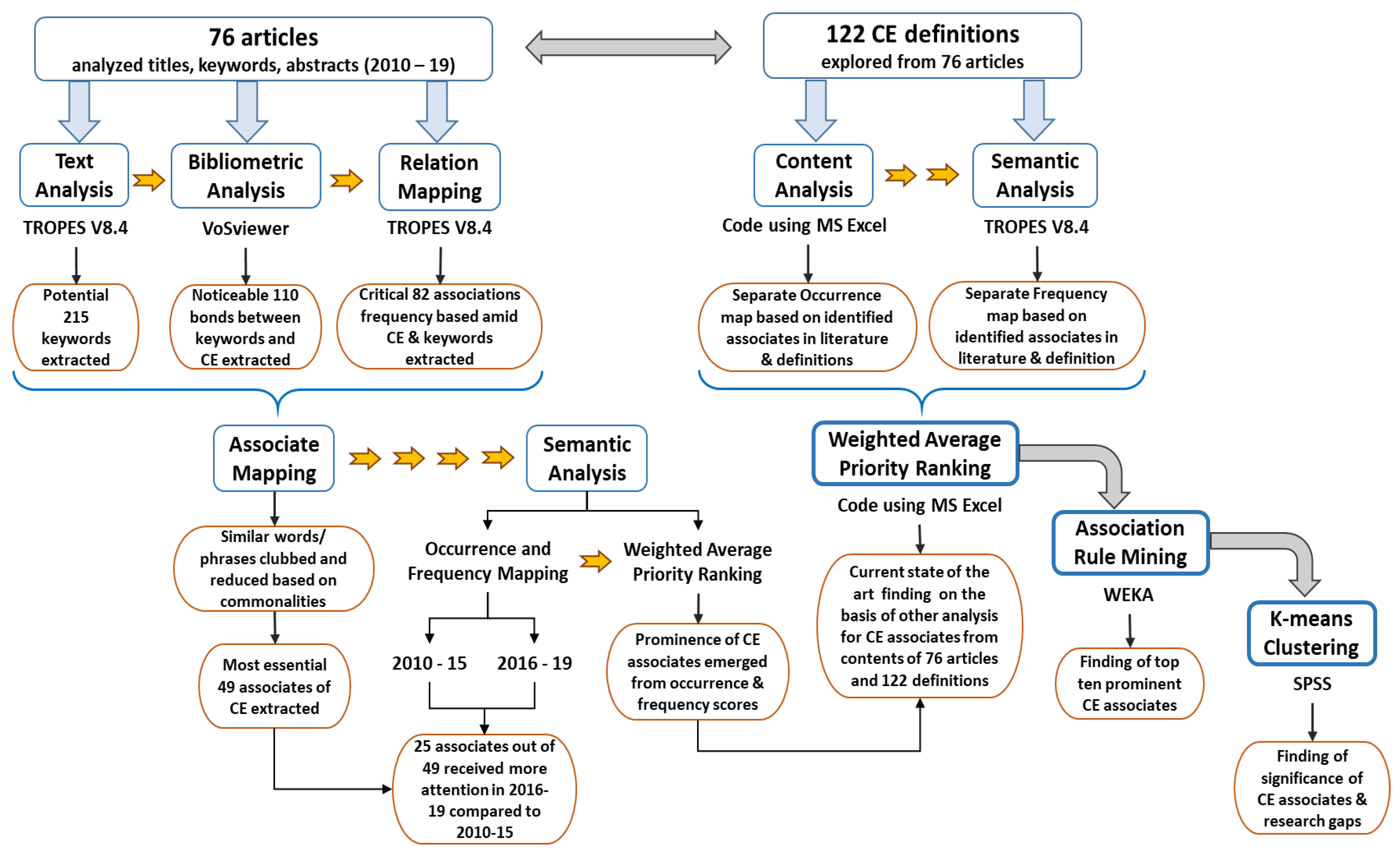










| Statistical Tools | Software | Rationale | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bibliometric analysis | VoSviewer | A popular research method that enables scholars to examine the past and future growth of scientific work [41,42] | Extensive qualitative analysis of CE articles emerged, quantitative metrics extracting critical keywords in CE literature. It also helped to derive the interactions of critical keywords with CE sequentially. |
| Text Analysis | TROPES V8.4 | Assists in drawing statistical inferences from texts and transcripts [43,44] | |
| Relation Mapping | TROPES V8.4 | Relation graph/exercise gives the number of relations (co-occurrence frequency) existing between various equivalent classes | |
| Content Analysis | VOSviewer and Microsoft Excel Coding | Makes inferences by objectively and systematically identifying specified characteristics of messages [45,46] | CE’s multifaceted associates’ stance to promote CE as a facilitator was observed. Generated a frequency map to explore the prominence and significance of extracted CE associates. |
| Sematic Analysis | TROPES V8.4 | Ontological conceptual understanding is revealed from Semantic analysis [47] | |
| Weighted Average Priority Ranking | Microsoft Excel | Provides an order of preference and indicates relative magnitude [48] | Findings showed a lack of consensus on CE terminologies and definitions, so advanced methods are used. Generated a priority rank for CE’s associates and identified the most and least significant CE’s associates for the future research agenda. Validation of findings of WAPR, Association mapping and Cluster analysis was followed, to describe the character of CE and its associates. |
| Association Rules Data Mining | WEKA | Identify associations in which transactions are distributed across multiple sources [49] | |
| K-Means Clustering | SPSS | Non-hierarchical clustering and iterative partitioning method that divides observations into a predetermined number of clusters. [50] |
| R Framework | Strategies | Studies |
|---|---|---|
| 3R | Reduce, Reuse, Recycle | [80,81] |
| 4R | 3R + Recover | [82,83,84] |
| 5R | 3R + Refurbish + Repair | [85] |
| 6R | 5R + Remanufacture | [86,87] |
| 7R | 6R + Refuse | [88] |
| 8R | 7R + Repurpose | [89] |
| 9R | 8R + Rethink | [90] |
| 10R | 9R + Recover | [13,91,92] |
| Sl | Title | Authors | WoS | SoP | Year | Journal | Type | Method | Contribution | DOI | Major Associates | Country | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A circular economy model of economic growth | George, Donald A. R.; Lin, Brian Chi-ang; Chen, Yunmin | 41 | 54 | 2015 | Environmental Modelling & Software | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Identified CE model with two types of economic resource, i.e., polluting input and recyclable input. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.06.014 | Recycle and Economy | China | Review |
| 2 | A conceptual framework for circular design | Moreno M., De los Rios C., Rowe Z., Charnley F. | 98 | 2016 | Sustainability (Switzerland) | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Conceptual framework for circular economy design strategy incorporation. | doi:10.3390/su8090937 | Design and Innovation | United Kingdom | Review | |
| 3 | A Review and Typology of Circular Economy Business Model Patterns | Lüdeke-Freund F., Gold S., Bocken N.M.P. | 41 | 53 | 2019 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Proposed six major CE Business Model patterns with potential to support closing of resource flows. | 10.1111/jiec.12763 | Business and Resource | Germany | Review |
| 4 | A review of the circular economy in China: Moving from rhetoric to implementation | Su, Biwei; Heshmati, Almas; Geng, Yong; Yu, Xiaoman | 280 | 333 | 2013 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Current development of CE and policy recommendations. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.11.020 | Implementation and Policy | China | Review |
| 5 | A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems | Ghisellini P., Cialani C., Ulgiati S. | 692 | 856 | 2016 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Demonstrated CE’s reliability as a solution to environmental issues emerging of current businesses. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007 | Environment and Business | China | Review |
| 6 | A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective | Govindan K., Hasanagic M. | 57 | 83 | 2018 | International Journal of Production Research | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Consolidated and described the factors influencing CE adoption in organizations. | doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1402141 | Driver, and Barrier | Denmark | Review |
| 7 | A taxonomy of circular economy indicators | Saidani M., Yannou B., Leroy Y., Cluzel F., Kendall A. | 47 | 2019 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illustrated multiple dimensions of C-indicators and comprehended their application in Industry. | 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.014 | Measurement and Implementation | France | Review | |
| 8 | Circular economy as an essentially contested concept | Korhonen J., Nuur C., Feldmann A., Birkie S.E. | 90 | 117 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illustrated methodological models on conducting researches on CE. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.111 | Policy and Product | Swede | Review |
| 9 | Circular economy in China-The environmental dimension of the harmonious society | Naustdalslid J. | 40 | 52 | 2014 | International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Comprehended Chinese version of CE, and its implementation. | 10.1080/13504509.2014.914599 | Implementation and Society | China | Review |
| 10 | An exploration of firms’ awareness and behavior of developing circular economy: An empirical research in China | Liu Y., Bai Y. | 67 | 73 | 2014 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Identified contextual, and cultural factors creating gaps in awareness generation and actual behaviour | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2014.04.002 | Environment and Behaviour | China | Case Study |
| 11 | Business models and supply chains for the circular economy | Geissdoerfer M., Morioka S.N., de Carvalho M.M., Evans S. | 70 | 92 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Developed a framework to integrate circular business models and circular supply chain management for Sustainable Development. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.159 | Business and Supply Chain | India | Case Study |
| 12 | Circular Business Model Innovation: Inherent Uncertainties | Linder M., Williander M. | 112 | 140 | 2017 | Business Strategy and the Environment | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Identified the characteristics and challenges of circular business models (CBMs). | 10.1002/bse.1906 | Remanufacture and Reuse | Sweden | Review |
| 13 | Business model innovation to create and capture resource value in future circular material chains | Roos G. | 44 | 2014 | Resources | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Compiled the process of business model development for ensuring innovative circular value chain | 10.3390/resources3010248 | Business and Industry | Australia | Case Study | |
| 14 | Circular economy practices among Chinese manufacturers varying in environmental-oriented supply chain cooperation and the performance implications | Zhu, Qinghua; Geng, Yong; Lai, Kee-hung | 136 | 165 | 2010 | Journal of Environmental Management | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Identified and exhibited causal relation between environmental-oriented supply chain cooperation practices and CE | 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.02.013 | Environment and Supply Chain | China | Review |
| 15 | Circular Economy Rebound | Zink, Trevor; Geyer, Roland | 91 | 117 | 2017 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Compiled the potential environmental rebound of the circular economy. | 10.1111/jiec.12545 | Reuse, Refurbish, and Recycle | USA | Review |
| 16 | Development pattern and enhancing system of automotive components remanufacturing industry in China | Zhang, Tongzhu; Chu, Jiangwei; Wang, Xueping; Liu, Xianghai; Cui, Pengfei | 111 | 126 | 2011 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light three barriers of remanufacturing sector. | 10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.09.015 | Remanufacture and Technology | China | Case Study |
| 17 | Circular economy-From review of theories and practices to development of implementation tools | Kalmykova Y., Sadagopan M., Rosado L. | 120 | 148 | 2018 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated two sets of data-driven tools for implementing CE. | doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.034 | Raw Material and Measurement | Sweden | Review |
| 18 | Circular Integration of processes, industries, and economies | Walmsley T.G., Ong B.H.Y., Klemeš J.J., Tan R.R., Varbanov P.S. | 22 | 25 | 2019 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light a unified framework of Circular Integration (CI) to stimulate large transdisciplinary research. | doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.039 | Business and Industry | Czech Republic | Case Study |
| 19 | Do circular economy business models capture intended environmental value propositions? | Manninen K., Koskela S., Antikainen R., Bocken N., Dahlbo H., Aminoff A. | 63 | 77 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated a framework for evaluating the environmental value propositions for CE-driven business models, | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.003 | Business and Environment | Finland | Case Study |
| 20 | Product/Service-Systems for a Circular Economy: The Route to Decoupling Economic Growth from Resource Consumption? | Kjaer L.L., Pigosso D.C.A., Niero M., Bech N.M., McAloone T.C. | 34 | 2019 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | A two-step framework to support analyses of Product/Service-System and their potential to lead to absolute resource decoupling. | 10.1111/jiec.12747 | Product and Business | Denmark | Review | |
| 21 | Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions | Kirchherr, Julian; Reike, Denise; Hekkert, Marko | 356 | 452 | 2017 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Fundamental, Empirical, Analytical | Quantitative and Qualitative | Compiled much conceptual information around the Circular Economy to bring coherence. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.005 | System and Business | Netherland | Review |
| 22 | Closed-loop production systems-A sustainable supply chain approach | Winkler H. | 88 | 2011 | CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light the importance of integrating environmental goals into the production system, with sustainable supply chain networks (SSCN). | 10.1016/j.cirpj.2011.05.001 | Economy and Environment | Austria | Review | |
| 23 | Closing the loop or squaring the circle? Locating generative spaces for the circular economy | Kersty Hobson | 72 | 2016 | Progress in Human Geography | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Revealed scope and purpose of conducting critical analysis on socio-political and economic mechanisms with respect to Circular Economy. | 10.1177/0309132514566342 | Product and Society | United Kingdom | Review | |
| 24 | Constructivism scenario evolutionary analysis of zero emission regional planning: A case of Qaidam Circular Economy Pilot Area in China | Liu D., Li H., Wang W., Dong Y. | 27 | 2012 | International Journal of Production Economics | Analytical, Empirical, Conceptual, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Revealed important policy implications on China’s regional development plan due to evolutionary constructivism. | 10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.04.008 | Sustainable and Industry | China | Case Study | |
| 25 | Towards a national circular economy indicator system in China: An evaluation and critical analysis | Geng Y., Fu J., Sarkis J., Xue B. | 235 | 277 | 2012 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light a national level sustainability indicator system for developing countries. | 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.07.005 | Government and Policy | China | Case Study |
| 26 | Who is in charge? A review and a research agenda on the ‘human side’ of the circular economy | Chiappetta Jabbour C.J., Sarkis J., Lopes de Sousa Jabbour A.B., Scott Renwick D.W., Singh S.K., Grebinevych O., Kruglianskas I., Filho M.G. | 36 | 2019 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Supplemented conceptual foundations on CE business models by integrating green human resource management theory and practices. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.038 | Business and Resource | France | Review | |
| 27 | Process engineering in circular economy | Reh, Lothar | 41 | 48 | 2013 | Particuology | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Compiled progress and challenges of recycling industry. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2012.11.001 | Energy and Recycle | China | Case Study |
| 28 | Product design and business model strategies for a circular economy | Bocken N.M.P., de Pauw I., Bakker C., van der Grinten B. | 357 | 2016 | Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated insights on the current product design and business model strategies suited embracing circular economy. | dx.doi.org/10.1080/21681015.2016.1172124 | Product and Design | Netherlands | Review | |
| 29 | Business model innovation for circular economy and sustainability: A review of approaches | Pieroni, Marina P. P.; McAloone, Tim C.; Pigosso, Daniela C. A. | 38 | 52 | 2019 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Compiled and presented different approaches on circular or sustainable business model innovation process. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.036 | Innovation and Business | Denmark | Review |
| 30 | Diversifying and de-growing the circular economy: Radical social transformation in a resource-scarce world | Hobson K., Lynch N. | 69 | 2016 | Futures | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Described the social and political implications of CE-driven transformations in a system. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.futures.2016.05.012 | ReSOLVE and Technology | United Kingdom | Review | |
| 31 | Methodological Aspects of Applying Life Cycle Assessment to Industrial Symbioses | Mattila T., Lehtoranta S., Sokka L., Melanen M., Nissinen A. | 63 | 72 | 2012 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Comprehended the methodological issues encountered while applying life cycle assessment, besides historical development and current status of industrial symbiosis (IS) | 10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00443.x | Life Cycle Assessment and Industry | Finland | Review |
| 32 | Effectiveness of the policy of circular economy in China: A DEA-based analysis for the period of 11th five-year-plan | Wu H.-Q., Shi Y., Xia Q., Zhu W.-D. | 88 | 102 | 2014 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Described data envelopment analysis to measure efficiency of CE development in China. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.10.003 | Policy and Implementation | China | Case Study |
| 33 | Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues | D’Amato, D.; Droste, N.; Allen, B.; Kettunen, M.; Laehtinen, K.; Korhonen, J.; Leskinen, P.; Matthies, B. D.; Toppinen, A. | 104 | 117 | 2017 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Elaborated the conceptual differences between Circular Economy and Bio-economy and Green Economy. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.053 | Economy and Environment | Finland | Review |
| 34 | Lost in Transition? Drivers and Barriers in the Eco-innovation Road to the Circular Economy | de Jesus A., Mendonça S. | 65 | 83 | 2018 | Ecological Economics | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light the insights of soft and hard factors in generating eco-innovation (EI) during transition to circular economy (CE) | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.08.001 | Driver and Barrier | Portugal | Review |
| 35 | The Emergence of Circular Economy A New Framing Around Prolonging Resource Productivity | Blomsma, Fenna; Brennan, Geraldine | 125 | 165 | 2017 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Described the potentially catalytic function the CE performs in waste and resource management | doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12603 | Waste and Resource | United Kingdom | Review |
| 36 | The Relevance of Circular Economy Practices to the Sustainable Development Goals | Schroeder, Patrick; Anggraeni, Kartika; Weber, Uwe | 36 | 47 | 2019 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented the relationship of CE practices and the SDGs, as well as highlighting CE practices that can help to achieve the SDG targets. | 10.1111/jiec.12732 | Sustainable and Business | United Kingdom | Review |
| 37 | Strategies on implementation of waste-to-energy (WTE) supply chain for circular economy system: a review | Pan, Shu-Yuan; Du, Michael Alex; Huang, I-Te; Liu, I-Hung; Chang, E-E; Chiang, Pen-Chi | 140 | 171 | 2015 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented several cases in the waste-to-energy supply chain to assess the level of circularity. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.124 | Waste and Energy | China | Case Study |
| 38 | The Circular Economy A new sustainability paradigm? | Geissdoerfer, Martin; Savaget, Paulo; Bocken, Nancy M. P.; Hultink, Erik Jan | 544 | 654 | 2017 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Illustrated conceptual trends of CE using bibliometric analysis and semi-structured snowballing technique. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.048 | Sustainable and Economy | United Kingdom | Review |
| 39 | Towards a new taxonomy of circular economy business models | Andrea Urbinati, Davide Chiaroni, Vittorio Chiesa | 84 | 112 | 2017 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented the strengths and weakness of the classification framework to assess the method besides the agenda. | doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.045 | Life Cycle, and Recycle | Belgium | Review |
| 40 | Products that go round: Exploring product life extension through design | Bakker C., Wang F., Huisman J., Den Hollander M. | 172 | 188 | 2014 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Brought to light the number of product life extension strategies besides showing the requirement for tailored approaches. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.01.028 | Design and Product | Dutch | Case Study |
| 41 | Progress Toward a Circular Economy in China The Drivers (and Inhibitors) of Eco-industrial Initiative | Mathews, John A.; Tan, Hao | 164 | 178 | 2011 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Demonstrated common themes across case studies on eco-industrial aspects. | 10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00332.x | Driver and Industry | China | Case Study |
| 42 | Circular economy indicators: What do they measure? | Moraga G., Huysveld S., Mathieux F., Blengini G.A., Alaerts L., Van Acker K., de Meester S., Dewulf J. | 29 | 2019 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated a classification framework for CE indicators and used it to evaluate quantitative indicators to measure CE and its process. | doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.045 | Measurement and Implementation | Belgium | Review | |
| 43 | Energy conservation and circular economy in China’s process industries | Li, Huiquan; Bao, Weijun; Xiu, Caihong; Zhang, Yi; Xu, Hongbin | 87 | 104 | 2010 | Energy | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Described the energy conservation method of China’s process industry for the learning of other nations. | doi:10.1016/j.energy.2009.04.021 | Waste and Energy | China | Case Study |
| 44 | The circular economy, design thinking and education for sustainability | Andrews D. | 54 | 2015 | Local Economy | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illustrated the necessity for inclusion of design thinking and practice in education curricula. | 10.1177/0269094215578226 | Design and Product | United Kingdom | Review | |
| 45 | Operational principles of circular economy for sustainable development: Linking theory and practice | Suárez-Eiroa B., Fernández E., Méndez-Martínez G., Soto-Oñate D. | 26 | 2019 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Identified seven operational principles to emphasize the role of design and education as transversal elements, besides introducing a new definition of CE. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.271 | Sustainable and System | Spain | Review | |
| 46 | Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy-a review | Tukker, Arnold | 443 | 542 | 2015 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Elaborated the process of implementation of Product Service Systems (PSS), besides identification of factors enabling implementation seeking attention. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.11.049 | Product and System | Netherlands | Review |
| 47 | Unlocking the circular economy through new business models based on large-scale data: An integrative framework and research agenda | Jabbour C.J.C., Jabbour A.B.L.D.S., Sarkis J., Filho M.G. | 46 | 2019 | Technological Forecasting & Social Change | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated an integrative framework for illustrating the nexus between CE and large-scale data (LD). | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.010 | ReSOLVE and Society | France | Review | |
| 48 | Consumer product knowledge and intention to purchase remanufactured products | Wang Y., Hazen B.T. | 73 | 88 | 2016 | International Journal of Production Economics | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Comprehended remanufacturing and closed-loop supply chain managing policies besides marketing strategies. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.08.031 | Remanufacture and Supply chain | China | Case Study |
| 49 | Creating integrated business and environmental value within the context of China’s circular economy and ecological modernization | Park, Jacob; Sarkis, Joseph; Wu, Zhaohui | 122 | 144 | 2010 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental, and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illustrated emerging integration of business value and environmental returns in the context of CE in China applying the theoretical lens. | 10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.06.001 | Environment and Economy | China | Case Study |
| 50 | Green chemistry and green engineering in China: Drivers, policies and barriers to innovation | Matus K.J.M., Xiao X., Zimmerman J.B. | 58 | 2012 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Described the crucial barriers to and enablers of green chemistry and engineering innovations in China. | 10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.03.033 | Innovation and Policy | China | Case Study | |
| 51 | How Circular is the Global Economy?: An Assessment of Material Flows, Waste Production, and Recycling in the European Union and the World in 2005 | Haas, Willi; Krausmann, Fridolin; Wiedenhofer, Dominik; Heinz, Markus | 198 | 237 | 2015 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Fundamental, Empirical, Analytical | Quantitative and Qualitative | Revealed the necessity for review, new definition, and measurement of circularity. | 10.1111/jiec.12244 | Production, and Recycle | United Kingdom | Case Study |
| 52 | How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review | Merli R., Preziosi M., Acampora A. | 90 | 112 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light the best practices and solutions from several schools of thoughts to execute CE. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112 | Innovation and Environment | Italy | Review |
| 53 | Implementation of circular economy business models by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): Barriers and enablers | Rizos V., Behrens A., van der Gaast W., Hofman E., Ioannou A., Kafyeke T., Flamos A., Rinaldi R., Papadelis S., Hirschnitz-Garbers M., Topi C. | 84 | 99 | 2016 | Sustainability (Switzerland) | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented the understanding around requirement of sufficient knowledge and technical knowhow to execute circular economy in small and medium-sized enterprises | 10.3390/su8111212 | Barrier and Risk | United Kingdom | Case Study |
| 54 | The Circular Economy: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Concept and Application in a Global Context | Murray A., Skene K., Haynes K. | 357 | 2017 | Journal of Business Ethics | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Demonstrated CE’s relation with sustainable business and applications, besides policy implications. | 10.1007/s10551-015-2693-2 | Business and policy | United Kingdom | Review | |
| 55 | The circular economy: New or Refurbished as CE 3.0?—Exploring Controversies in the Conceptualization of the Circular Economy through a Focus on History and Resource Value Retention Options | Reike D., Vermeulen W.J.V., Witjes S. | 66 | 90 | 2018 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Quantitative and Qualitative | Illustrated numerous R-imperatives and their attributes for conceptualizing the key CE principle. | doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.08.027 | R-imperatives | Netherlands | Review |
| 56 | Towards a consensus on the circular economy | Prieto-Sandoval V., Jaca C., Ormazabal M. | 87 | 107 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Revealed the three eco-innovation determinants after their application in CE was regulated and policy was framed for the supply side and demand side. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.224 | Innovation and Environment | Spain | Review |
| 57 | Reutilisation-extended material flows and circular economy in China | Li N., Zhang T., Liang S. | 21 | 2013 | Waste Management | Analytical, Empirical, Conceptual, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Introduced readers to reutilisation-related laws and regulations with respect to CE. | 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.01.029 | Measurement and Raw Material | China | Review | |
| 58 | Introduction of the circular economy within developing regions: A comparative analysis of advantages and opportunities for waste valorization | Ferronato N., Rada E.C., Gorritty Portillo M.A., Cioca L.I., Ragazzi M., Torretta V. | 24 | 27 | 2019 | Journal of Environmental Management | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented the main opportunities for improving the current state of solid waste management in upcoming big cities. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.095 | Recycle and Raw Material | Romania & Bolivia | Case Study |
| 59 | Measuring circular economy strategies through index methods: A critical analysis | Valerio EliaMaria, GraziaGnoni, FabianaTornese | 84 | 101 | 2017 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Proposed and demonstrated a four-level framework to support the assessment during monitoring of multiple stages of CE. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.196 | Measurement and Implementation | Italy | Review |
| 60 | Food packaging in the circular economy: Overview of chemical safety aspects for commonly used materials | Birgit Geueke, Ksenia Groh, Jane Muncke | 35 | 41 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Brought to light the important properties of food packaging materials affecting their recyclability and safety aspects. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.005 | Recycle, Reduce and Reuse | Switzerland | Case Study |
| 61 | Environmental Supply Chain Cooperation and Its Effect on the Circular Economy Practice-Performance Relationship Among Chinese Manufacturers | Zhu, Qinghua; Geng, Yong; Lai, Kee-hung | 61 | 66 | 2011 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Brought to notice the facts on leading manufacturers with higher levels of implementation of Environmental Supply Chain Cooperation practices. | doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00329.x | Environment and Supply chain | China | Case Study |
| 62 | The Impact of Scale, Recycling Boundary, and Type of Waste on Symbiosis and Recycling | Chen, Xudong; Fujita, Tsuyoshi; Ohnishi, Satoshi; Fujii, Minoru; Geng, Yong | 42 | 46 | 2012 | Journal of Industrial Ecology | Analytical, Empirical, Conceptual, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Revealed the relationships between recycling boundary, project scale, and performance of each eco-town besides the recycling facility in eco-towns with regard to the types of waste treated. | 10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00422.x | Waste and Recycle | Japan | Case Study |
| 63 | The Circular Economy: Swings and Roundabouts? | Millar N., McLaughlin E., Börger T. | 28 | 2019 | Ecological Economics | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Presented literature once and Sustainable Development to demonstrate their potential for economic growth. | doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2018.12.012 | Development and Economy | Ireland | Review | |
| 64 | Designing the business models for circular economy-towards the conceptual framework | Lewandowski M. | 211 | 227 | 2016 | Sustainability (Switzerland) | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illuminated the researchers of CE with classifications, characteristic, and integration processes for circular business models. | doi:10.3390/su8010043 | Business and Principle | Poland | Review |
| 65 | Developing country experience with eco-industrial parks: a case study of the Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area in China | Shi, Han; Chertow, Marian; Song, Yuyan | 180 | 196 | 2010 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Elucidated the process Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area adopted to form a complex industrial symbiosis network in a mixed industrial park besides examining the features and patterns of existing and discontinued IS exchanges. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.10.002 | Industry and Economy | China | Case Study |
| 66 | Environmental sciences, sustainable development and circular economy: Alternative concepts for trans-disciplinary research | Sauvé S., Bernard S., Sloan P. | 152 | 182 | 2016 | Environmental Development | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Elucidated three alternative concepts on transdisciplinary research, and showcased the opportunities besides associated challenges. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2015.09.002 | Environment and Sustainable | Canada | Review |
| 67 | The history and current applications of the circular economy concept | Winans, K.; Kendall, A.; Deng, H. | 132 | 154 | 2017 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Illustrated assessment of ongoing CE initiatives and highlighted barriers to sustained circularity due to material flows that exceeded or did not meet demand, and transport and infrastructure. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.123 | Policy and Infrastructure | Denmark | Review |
| 68 | New business models for a radical change in resource efficiency | Schulte U.G. | 43 | 2013 | Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Highlighted new businesses which cropped up with the notion of serving as an intermediary, because they own the material content of products and sell back the materials to the producer at the end of the life cycle. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eist.2013.09.006 | Business and Resource | Netherland | Case Study | |
| 69 | Challenges in supply chain redesign for the Circular Economy: a literature review and a multiple case study | Bressanelli G., Perona M., Saccani N. | 25 | 2019 | International Journal of Production Research | Conceptual, Emperical, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Identified and classified challenges about CE supply chain redesign based on analysis of previous literature. | doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1542176 | Supply chain and Design | Italy | Review & Case Study | |
| 70 | Survey of officials’ awareness on circular economy development in China: Based on municipal and county level | Xue, Bing; Chen, Xing-peng; Geng, Yong; Guo, Xiao-jia; Lu, Cheng-peng; Zhang, Zi-long; Lu, Chen-yu | 62 | 81 | 2010 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Revealed facts on awareness of the concept of CE in government and the public. | doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.05.010 | Policy and Government | China | Case Study |
| 71 | The circular economy umbrella: Trends and gaps on integrating pathways | Homrich A.S., Galvão G., Abadia L.G., Carvalho M.M. | 67 | 84 | 2018 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Presented definition of CE, besides highlighting the main trends, research gaps. | doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.064 | Economy and Business | Brazil | Review |
| 72 | Towards a more Circular Economy: Proposing a framework linking sustainable public procurement and sustainable business models | Witjes S., Lozano R. | 160 | 136 | 2016 | Resources, Conservation and Recycling | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Generated a framework with socio-cultural specifications besides physical and social proximity between the stakeholders to include technical and non-technical aspects of product/service combinations to improve resource usage efficiency through recovery. | doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.04.015 | Collaborate and Business | Netherlands | Review |
| 73 | Sustainable supply chain management and the transition towards a circular economy: Evidence and some applications | Genovese, Andrea; Acquaye, Adolf A.; Figueroa, Alejandro; Koh, S. C. Lenny | 198 | 229 | 2017 | Omega (United Kingdom) | Analytical, Empirical, and Applied | Quantitative | Elucidated the environmental implications related to implementation of circular production systems, comparing performances of traditional and circular production systems across a range of indicators. | dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.05.015 | Environment and Supply Chain | United Kingdom | Case Study |
| 74 | Circular Economy: The Concept and its Limitations | Korhonen J., Honkasalo A., Seppälä J. | 224 | 281 | 2018 | Ecological Economics | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Demonstrated the scientific basis for the CE concept and assessed the CE concept critically to describe high value and high quality material cycles and show the possibilities of the sharing economy besides sustainable production for a more sustainable production and consumption. | 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.06.041 | Environment and Sustainable | Finland | Review |
| 75 | Policy for material efficiency-Sustainable taxation as a departure from the throwaway society | Stahel W.R. | 57 | 2013 | Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences | Conceptual, Fundamental and Descriptive | Qualitative | Highlighted the finding that taxing materials and energies may promote low-carbon and low-resource solutions and may stimulate a move towards a ‘circular’ regional economy. | dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0567 | Society and Policy | United Kingdom | Case Study | |
| 76 | International comparative study of 3R and waste management policy developments | Shin-ichi Sakai, Hideto Yoshida, Yasuhiro Hirai, Misuzu Asari, Hidetaka Takigami, Shin Takahashi, Keijirou Tomoda, Maria Victoria Peeler, Jakub Wejchert, Thomas Schmid-Unterseh, Aldo Ravazzi Douvan, Roy Hathaway, Lars D. Hylander, Christian Fischer, Gil Jong Oh, Li Jinhui & Ngo Kim Chi | 70 | 83 | 2011 | Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management volume | Analytical, Empirical, Conceptual, and Applied | Quantitative and Qualitative | Described the current situation, historical background, and effectiveness of 3R policies within one specific region. | 10.1007/s10163-011-0009-x | R-imperatives and Countries | USA, Korea, Japan, China, and Vietnam | Case Study |
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definitions | 8, 9, 11, 12, 15, 16, 18, 22, 27, 43, 46, 51, 52, 66, 75, 77, 86, 108, 114 | 2, 4, 14, 17, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 31, 33, 37, 42, 45, 70, 71, 72, 74, 85, 98, 103, 111, 115, 116, 121 | 5, 68, 105 | 6, 13, 30, 35, 36, 47, 62, 63, 79, 81, 99, 113 | 3, 7, 10, 41, 48, 49, 53, 54, 59, 60, 76, 84, 88, 95, 97, 106, 107, 110 | 1, 19, 20, 21, 29, 32, 39, 40, 50, 56, 57, 58, 61, 64, 65, 67, 78, 80, 82, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 96, 101, 109, 117, 118, 119, 120, 122 | 34, 38, 44, 55, 73, 83, 87, 100, 102, 112 | 69, 104 |
| Number | 19 | 25 | 3 | 12 | 18 | 33 | 10 | 2 |
| Highly Significant (Sig. < 0.05) | Moderately Significant (0.05 < Sig. ≤ 0.10) | Insignificant (Sig. > 0.10 or No Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Waste, Policy, Industry, Energy, Risk, Raw Material, Product, Design, Technology, Business, Driver, Barrier, Environmental, Social, Measurement, Sustainable, Country, Infrastructure, Rethink, Replace, Reuse, Recycle, Reduce, Return, Regenerate, Resource, Optimize, Economy, System, Principle, Loop | Institute | Behaviour, Implementation, Innovation, Life Cycle, Refuse, Refurbish, Refill, Recover, Repair, Remanufacture, Share, Exchange, Government, Collaborate, Supply Chain, Repurpose, Virtualize |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, A.; Bhola, P.; Sivarajah, U. Emerging Associates of the Circular Economy: Analysing Interactions and Trends by a Mixed Methods Systematic Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169998
Ghosh A, Bhola P, Sivarajah U. Emerging Associates of the Circular Economy: Analysing Interactions and Trends by a Mixed Methods Systematic Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169998
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Animesh, Prabha Bhola, and Uthayasankar Sivarajah. 2022. "Emerging Associates of the Circular Economy: Analysing Interactions and Trends by a Mixed Methods Systematic Review" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169998
APA StyleGhosh, A., Bhola, P., & Sivarajah, U. (2022). Emerging Associates of the Circular Economy: Analysing Interactions and Trends by a Mixed Methods Systematic Review. Sustainability, 14(16), 9998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169998





_Sivarajah.jpg)

