A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework to Assess the Sustainable Development of Schools within a University: Application to a Chinese University
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Comprehensive Evaluation Framework
2.1. Model Preparation
2.1.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.1.2. Weight Decision
2.2. Model Building
2.3. Expanding Model Interpretability
2.4. Stability Analysis
3. An Application Example
3.1. Indicator Selection and Refinement
3.2. Comprehensive Evaluation Results & Discussion
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trow, M. Reflections on the transition from elite to mass to universal access: Forms and phases of higher education in modern societies since WWII. In International Handbook of Higher Education; Forest, J.J.F., Altbach, P.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 18, pp. 243–280. [Google Scholar]
- Cortese, A.D. The critical role of higher education in creating a sustainable future. Plan. High. Educ. 2003, 31, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). Education for People and Planet: Creating Sustainable Futures for All; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2016; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000245752 (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). Sustainable Development Begins with Education: How Education Can Contribute to the Proposed Pose-2015 Goals; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2014; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/publications/2275sdbeginswitheducation.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Al-Youbi, A.O.; Zahed, A.H.M.; Nahas, M.N.; Hegazy, A.A. The Leading World’s Most Innovative Universities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- German Committee Future Earth. The Contribution of Science in Implementing the Sustainable Development Goals; German Committee Future Earth: Stuttgart/Kiel, Germany, 2016; Available online: https://irp-cdn.multiscreensite.com/be6d1d56/files/uploaded/2016_report_contribution_science_sdgs.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Stuart, D.L. Reputational Rankings: Background and Development. New Dir. Inst. Res. 1995, 88, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, M.M.; Balas, E.A.; Momani, S. Are university rankings useful to improve research? A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, T. The rank boost by inconsistency in university rankings: Evidence from 14 rankings of Chinese universities. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nature Portfolio. A Brief Guide to the Nature Index. Available online: https://www.nature.com/nature-index/brief-guide (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Çakır, M.P.; Acartürk, C.; Alaşehir, O.; Çilingir, C. A comparative analysis of global and national university ranking systems. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 813–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L.; Liu, L.; Huo, M. A Comprehensive Post Evaluation of the Implementation of Water-Saving Measures in Xiangtan, Hunan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xia, S.; Cao, H.; Geng, X.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, H.; Jia, M.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J. Evaluation and Optimization of Sustainable Development Level of Construction Industrialization: Case Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zheng, S.; Feng, J. A Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Method for Sustainable Ferry Operator Selection: A Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Dun, Z.; Cheng, J.; Li, H.; Dun, Z. Resilience evaluation of high-speed railway subgrade construction systems in goaf sites. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qi, N.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q. Reliability Assessment of Highway Bridges Based on Combined Empowerment–TOPSIS Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, K.M.A.S. Application of the AHP in project management. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2001, 19, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; Huelgas, A.P.; Promentilla, M.A.B. Fuzzy AHP approach to selection problems in process engineering involving quantitative and qualitative aspects. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; De Paola, P. Rethinking design and urban planning for the cities of the future. Buildings 2017, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.S.K.; Gupta, H.; Bandyopadhayay, A. Selection of a sustainability awareness project in an academic institution using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Int. J. Technol. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 14, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Özdemir, M.S.; Shang, J.S. The rationality of punishment—measuring the severity of crimes: An AHP-based orders-of-magnitude approach. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2015, 14, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarte, M.M.; Ravi, B. Casting product–process–producer compatibility evaluation and improvement. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 4917–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Kaa, G.; van Heck, E.; de Vries, H.J.; van den Ende, J.; Rezaei, J. Supporting decision making in technology standards battles based on a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2013, 61, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Ma, X. The state-of-the-art integrations and applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.J.; Liu, T.Y.; Hwang, C.L. Topsis for MODM. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1994, 76, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xi, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, D. Combined approach for government E-tendering using GA and TOPSIS with intuitionistic fuzzy information. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130767. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.W. GRA method for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information in intuitionistic fuzzy setting. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2010, 23, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xie, N. A summary on the research of GRA models. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2013, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges Jr, C.C. Hierarchical cluster analysis. Psychol. Rep. 1966, 18, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagelj, V. Generalized Ward and Related Clustering Problems. In Classification and Related Methods of Data Analysis; Bock, H.H., Ed.; NorthHolland: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1988; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hervada-Sala, C.; Jarauta-Bragulat, E. A program to perform Ward’s clustering method on several regionalized variables. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikryukov, A.; Mazurov, M. The task of improving the university ranking based on the statistical analysis methods. In International Conference of Artificial Intelligence, Medical Engineering, Education; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R.; Chatterjee, P.; Chakraborty, S. Evaluating performance of engineering departments in an Indian University using DEMATEL and compromise ranking methods. Opsearch 2015, 52, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Chen, J.K.; Chen, I.S.; Zhuo, H.H. Ranking universities based on performance evaluation by a hybrid MCDM model. Measurement 2012, 45, 856–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
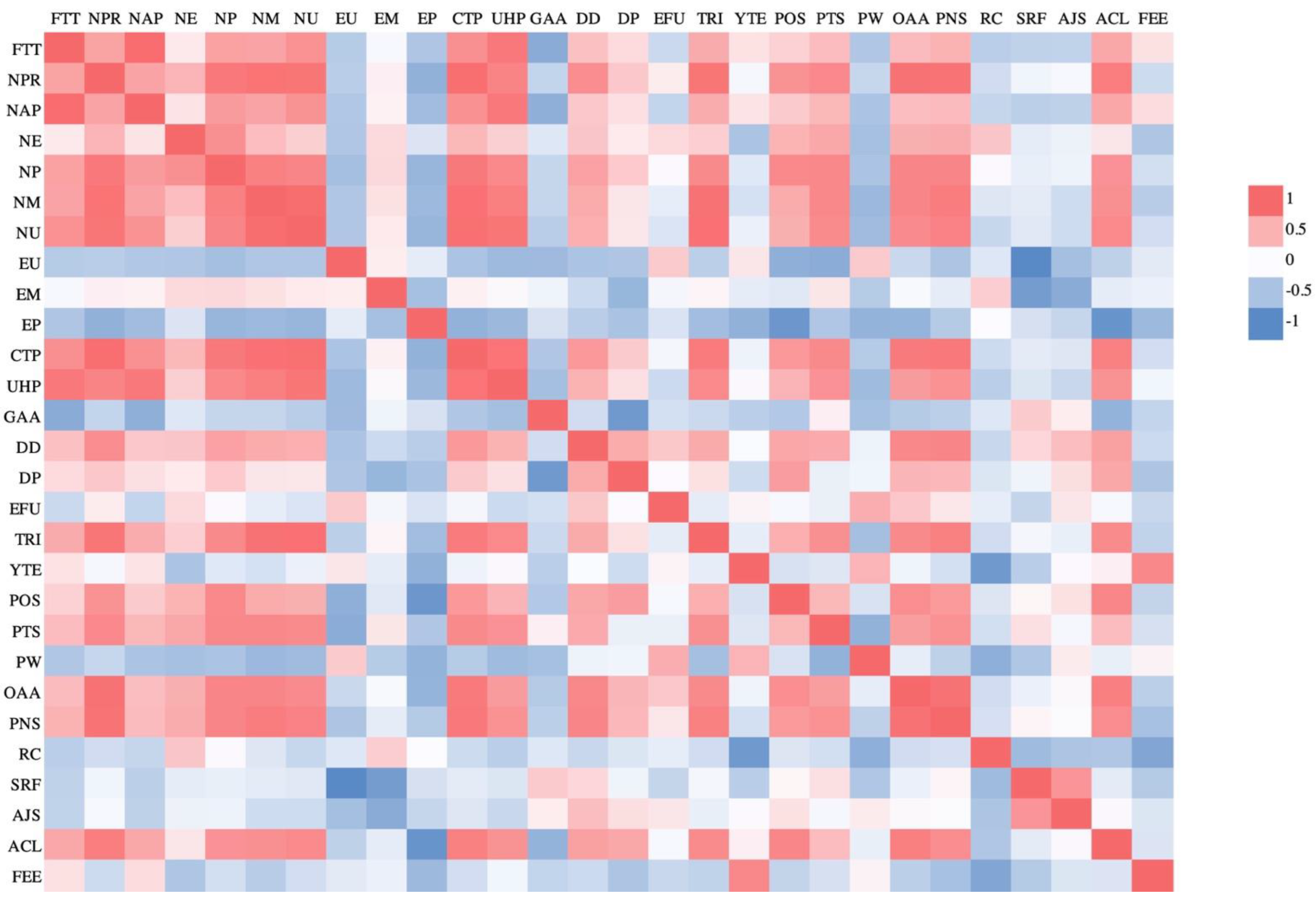

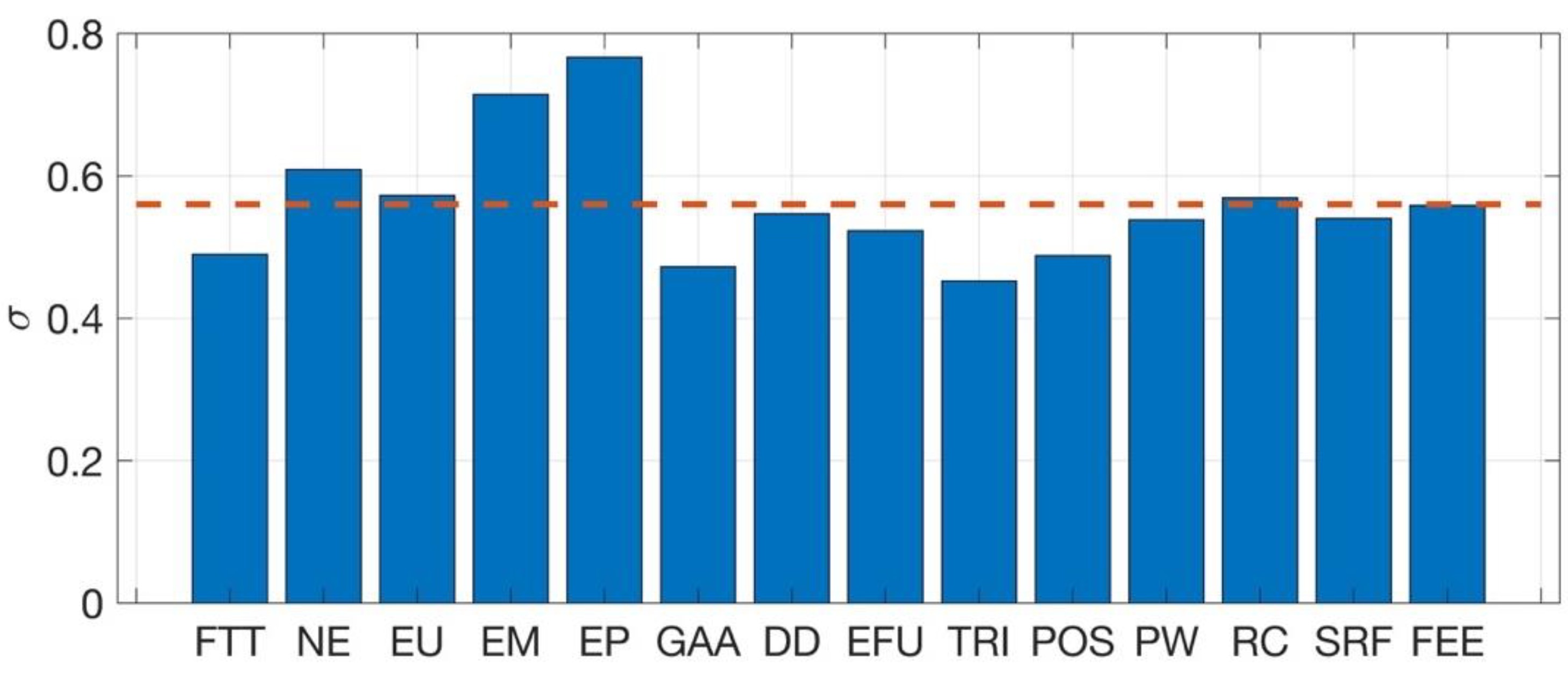
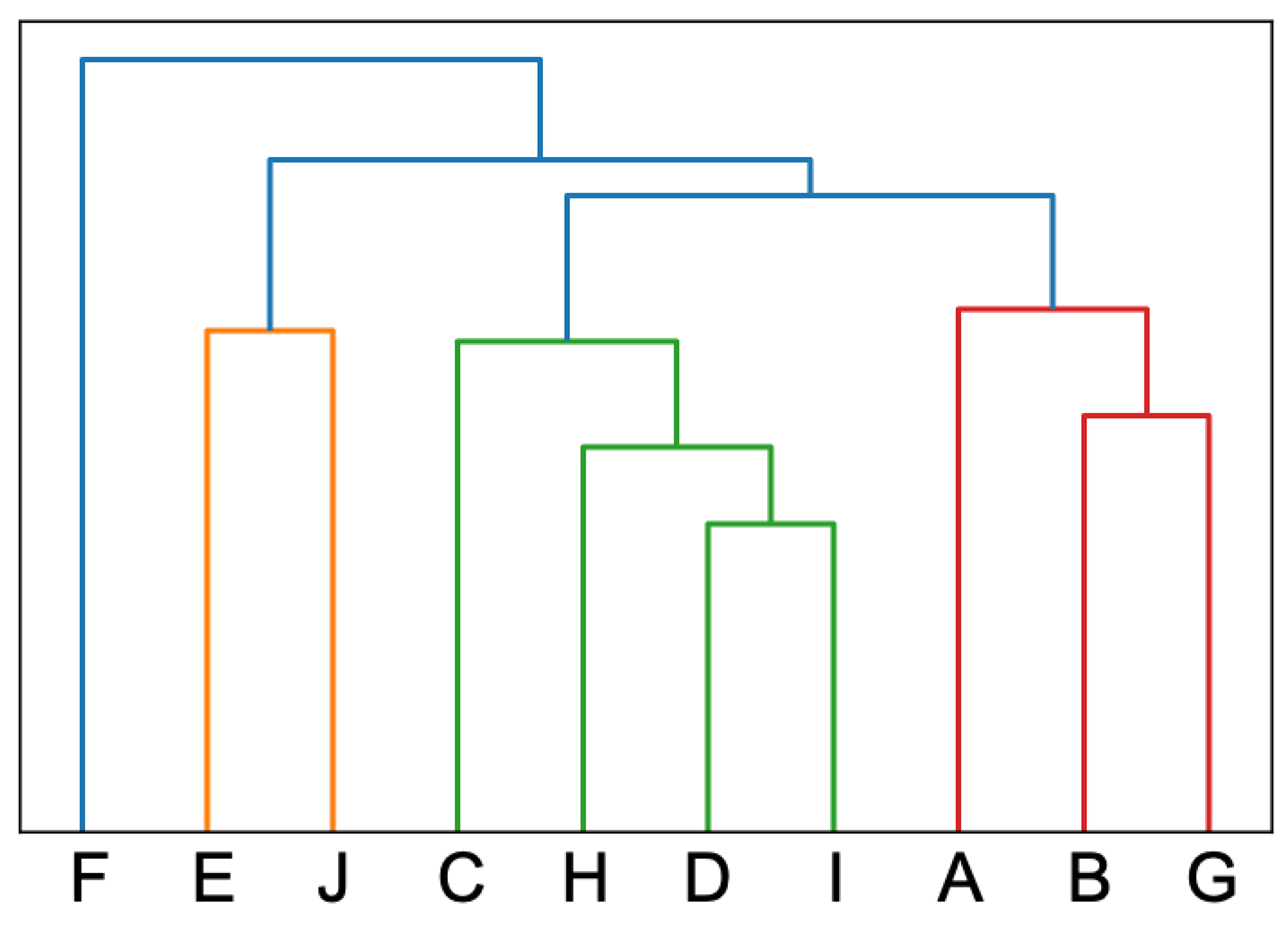

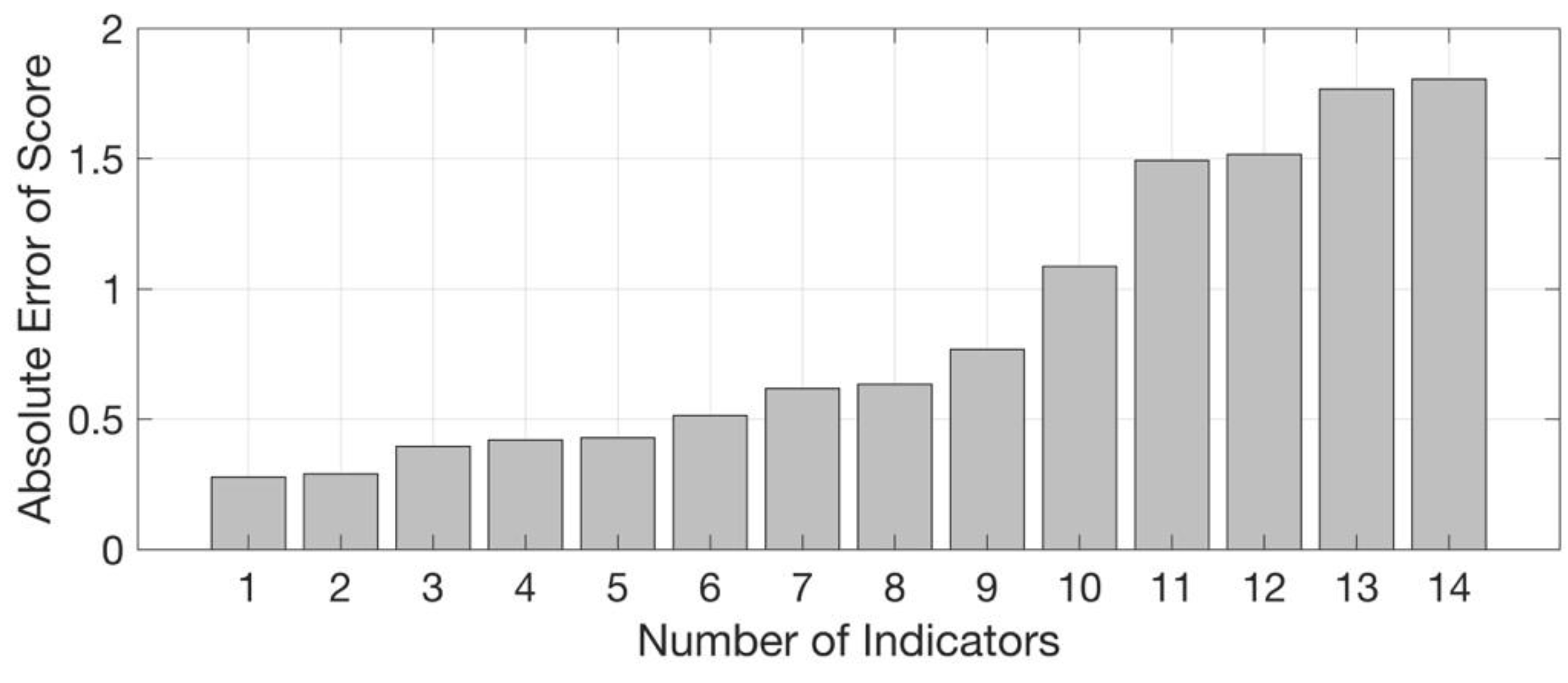
| Primary Index | Indicators | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Faculty Strength | Number of full-time teachers | FTT |
| Number of professors | NPR | |
| Number of associate professors | NAP | |
| Number of nationally and internationally recognized experts | NE | |
| Education Outcome | Number of PhD degree graduates | NP |
| Number of Master’s degree graduates | NM | |
| Number of Bachelor’s (Undergraduate) degree graduates | NU | |
| Employment rate of Bachelor’s (Undergraduate) degree graduates | EU | |
| Employment rate of Master’s degree graduates | EM | |
| Employment rate of PhD degree graduates | EP | |
| Number of approved “college student innovation and entrepreneurship training” projects | CTP | |
| Number of undergraduate students receiving honors above the provincial level | UHP | |
| Number of graduate students receiving academic innovation awards | GAA | |
| Discipline Development | Number of “double first-class” disciplines and nationally designated key disciplines | DD |
| Number of provincially designated key disciplines | DP | |
| Number of “national excellence” courses and “first-class” undergraduate courses | EFU | |
| Number of teaching and research equipment and instruments | TRI | |
| Talent Attraction | Number of “young talent” from the country and abroad | YTE |
| Number of postdoctoral fellows | POS | |
| Achievement in Research | Number of papers included in the top three citation index systems | PTS |
| Number of published works | PW | |
| Number of outstanding achievement awards received from the Ministry of Education, the province, or the city | OAA | |
| Number of projects approved by the National Social Science Foundation or the Humanities and Social Sciences Research Division of the Ministry of Education | PNS | |
| Number of nationally or provincially commissioned research centers and think tanks | RC | |
| Sum of research funds | SRF | |
| Number of academic journals sponsored | AJS | |
| Academic Exchange | Number of academic conferences and lectures | ACL |
| Number of long-term foreign experts employed | FEE |
| Indicator | Weight |
|---|---|
| FTT | 0.1118 |
| NE | 0.0373 |
| EU | 0.0373 |
| EM | 0.0373 |
| EP | 0.0373 |
| GAA | 0.0745 |
| DD | 0.1118 |
| EFU | 0.1491 |
| TRI | 0.1118 |
| POS | 0.0123 |
| PW | 0.0745 |
| RC | 0.0373 |
| SRF | 0.1491 |
| FEE | 0.0186 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Chen, Z. A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework to Assess the Sustainable Development of Schools within a University: Application to a Chinese University. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10671. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710671
Li H, Chen Z. A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework to Assess the Sustainable Development of Schools within a University: Application to a Chinese University. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10671. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710671
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hong, and Zilin Chen. 2022. "A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework to Assess the Sustainable Development of Schools within a University: Application to a Chinese University" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10671. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710671
APA StyleLi, H., & Chen, Z. (2022). A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework to Assess the Sustainable Development of Schools within a University: Application to a Chinese University. Sustainability, 14(17), 10671. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710671







