Sustainable Food Waste Recycling for the Circular Economy in Developing Countries, with Special Reference to Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. An Overview of FW and the Current Scenario in Developing Countries
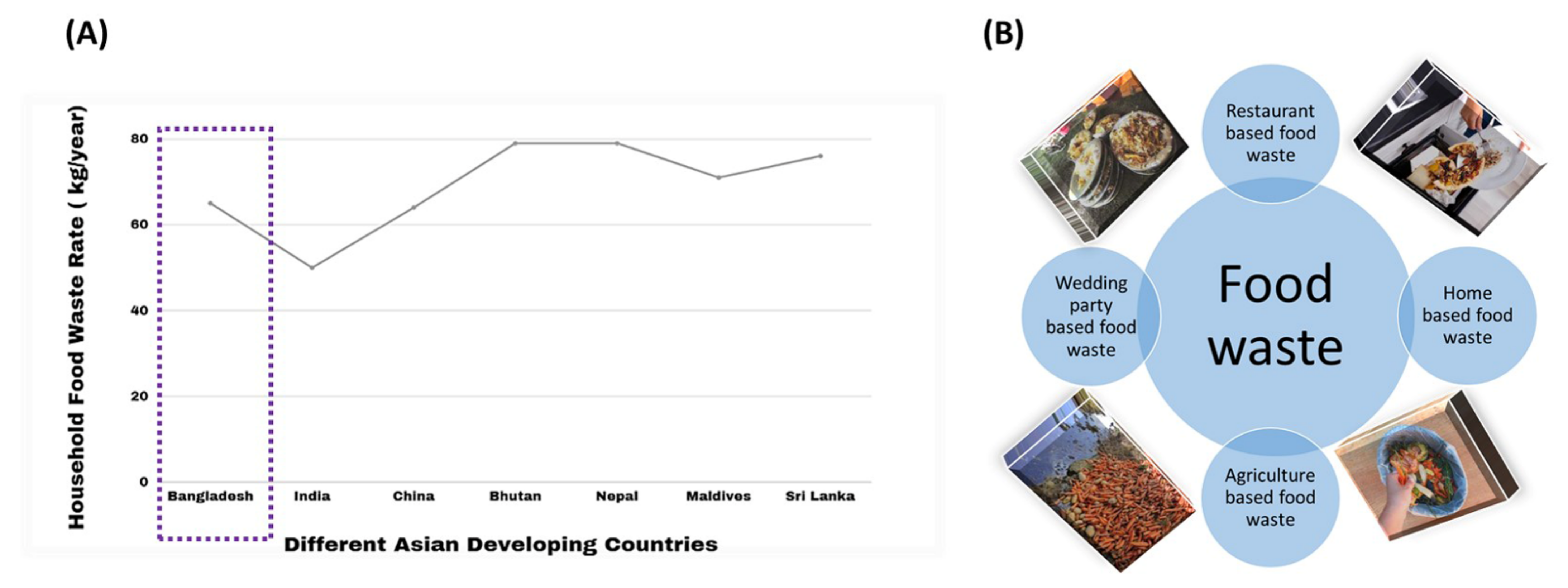
2.1. FW in Developing Asian Countries
2.2. FW: A Hidden Sink of Nutrients, and Bioactive Molecules
3. Current Status of FW and Its Management in Bangladesh
3.1. FW Status in Bangladesh
3.2. Management of FW in Bangladesh
3.3. Existing Strategies of FW Management in Bangladesh
4. Food Loss and FW: A Global Debate
4.1. Debate between Consumer and Agribusiness Stakeholders
4.2. Misconception and Negligence about Good Policy for FW Recycling in Bangladesh
5. FW Valorization and Circular Economy
5.1. Prospects of Advanced FW Valorization Strategies in Bangladesh
5.2. Sustainable FW Valorization to Enhance the Circular Economy
5.3. Prospects of Circular Economy through Waste to Energy Approach
5.4. Knowledge Gap concerning Circular Economy
6. Research Gap and Opportunities of FW Valorization in Bangladesh
7. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ong, K.L.; Kaur, G.; Pensupa, N.; Uisan, K.; Lin, C.S.K. Trends in food waste valorization for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels: Case study South and Southeast Asia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananno, A.A.; Masud, M.H.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Dabnichki, P.; Ahmed, N.; Arefin, A.M.E. Sustainable food waste management model for Bangladesh. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, A.W.; Haque, M.M.; Islam, K.S.; Hasan, K.A. A Proposal for Integrated Market Waste Management in Bangladesh. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Technol. 2012, 1, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Baul, T.K.; Sarker, A.; Nath, T.K. Restaurants’ waste in Chittagong city, Bangladesh: Current management, awareness on environmental hazard and perception towards potential uses. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Sahu, J.N.; Rahman, S.M.S.; Ahsan, A. Sustainable waste management policy in Bangladesh for reduction of greenhouse gases. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 33, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahan, M.; Laila, I. Restaurant Waste Management in Dhaka City: Current measures and the way forward. J. Asia Entrepren. Sustain. 2020, 16, 65–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, S.; Kumar, A.N.; Shanthi, S.J.; Chatterjee, S.; Sarkar, O.; Mohan, S.V. Food waste biorefinery: Sustainable strategy for circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Sustainable bioconversion of food waste into high-value products by immobilized enzymes to meet bio-economy challenges and opportunities—A review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbitt, C.W. The role of clean technology research in creating sustainable urban food waste solutions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gaur, V.K.; Sirohi, R.; Varjani, S.; Hyoun, K.S.; Wong, J.W.C. Sustainable processing of food waste for production of bio-based products for circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Andrew Lin, K.Y.; Hong, E.; Kwon, E.E.; Lee, J. The valorization of food waste via pyrolysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannah, Y.R.; Merrylin, J.; Devi, P.T.; Kavitha, S.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Kumar, G.; Banu, R.J. Food waste valorization: Biofuels and value added product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 11, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, F.O.; Thomas, C.L.P.; Afolabi, O.O.D. Integrated conversion technologies for sustainable agri-food waste valorization: A critical review. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 156, 106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujauddin, M.; Huda, S.M.S.; Hoque, A.T.M.R. Household solid waste characteristics and management in Chittagong, Bangladesh. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.M.N. Greenhouse gas footprint and the carbon flow associated with different solid waste management strategy for urban metabolism in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Alamgir, M.; El-Sergany, M.M.; Shams, S.; Rowshon, M.K.; Daud, N.N. Assessment of municipal solid waste management system in a developing country. Chin. J. Eng. 2014, 11, 561935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, O.; Qiao, X. An in-depth review on municipal solid waste management, treatment and disposal in Bangladesh. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, Q.H.; Hassan, M.K.; Haque, E.M. Solid waste recycling in Rajshahi city of Bangladesh. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, A.; Ahsan, M.; Marbach, M.; Zurbrügg, C. Impacts of policy and market incentives for solid waste recycling in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Waste Manag. 2015, 39, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.M.; Rahman, S.A.H.M.; Kabir, A.S.; Hasan, F.M.M.; Ahmed, S. Systematic assessment of the availability and utilization potential of biomass in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.S.M.M.; Ammenberg, J. Biogas potential from municipal and agricultural residual biomass for power generation in Hazaribagh, Bangladesh—A strategy to improve the energy system. Renew. Energy Focus 2019, 29, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.M.N.; Jashimuddin, M. Reliability and economic analysis of moving towards wastes to energy recovery based waste less sustainable society in Bangladesh: The case of commercial capital city Chittagong. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.M.N. Municipal solid waste to energy generation: An approach for enhancing climate co-benefits in the urban areas of Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2472–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I. Waste to biogas through anaerobic digestion: Hydrogen production potential in the developing world—A case of Bangladesh. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 15951–15962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Penarubia, O.R. Seafood waste management status in bangladesh and potential for silage production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, N.B.D.; Kumar, G.; Lin, C.Y. An overview of food waste management in developing countries: Current status and future perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otles, S.; Kartal, C. Food Waste Valorization, Sustainable Food Systems from Agriculture to Industry. In Food Waste Recovery; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Pyrolyzed waste stream and biochar performance evaluation in food waste anaerobic digestion. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Loss and Food Waste. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/food-loss-and-food-waste/flw-data (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Sahakian, M.; Shenoy, M.; Soma, T.; Watabe, A.; Yagasa, R.; Premakumara, D.G.J.; Liu, C.; Favis, A.M.; Saloma, C. Apprehending food waste in Asia: Policies, practices and promising trends. In Routledge Handbook of Food Waste; Routledge: Abington, UK, 2020; pp. 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, P.; Trethewie, S. Tackling Urban and Rural Food Wastage in Southeast Asia: Issues and Interventions. S. Rajaratnam Sch. Int. Stud. (JSTOR). 2012. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep17171 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- NPR. Even Poor Countries End Up Wasting Tons of Food: Goats and Soda: NPR. 2022. Available online: https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2015/09/28/444188475/even-poor-countries-end-up-wasting-tons-of-food (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- UNEP. Food Waste Index Report (FWIR). 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/unep-food-waste-index-report-2021 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Bangladesh Statistical Year Book BSYB. Statistical Year Book Bangladesh, 2018. Available online: http://bbs.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/bbs.portal.gov.bd/page/b2db8758_8497_412c_a9ec_6bb299f8b3ab/SYB-2018.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Joardder, M.U.; Masud, M.H. Food Preservation in Developing Countries: Challenges and Solutions; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, A.M.M.; Campos, M.R.S. Bioactive Compounds as Therapeutic Alternatives. In Bioactive Compounds: Health Benefits and Potential Applications; Campos, M.R.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganas, A.; Giamouri, E.; Pappas, A.C.; Papadomichelakis, G.; Galliou, F.; Manios, T.; Tsiplakou, E.; Fegeros, K.; Zervas, G. Bioactive compounds in food waste: A review on the transformation of food waste to animal feed. Foods 2020, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Gangopadhyay, N.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Ultrasonic extraction of steroidal alkaloids from potato peel waste. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socaci, S.A.; Farcas, A.C.; Vodnar, D.C.; Tofana, M. Food Wastes as Valuable Sources of Bioactive Molecules. In Superfood and Functional Food—The Development of Superfoods and Their Roles as Medicine; Shiomi, N., Waisundara, V., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martillanes, S.; Rocha-Pimienta, J.; Delgado-Adámez, J. Agrifood By-Products as a Source of Phytochemical Compounds. In Descriptive Food Science; Díaz, A.V., García-Gimeno, R.M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; García-Sancho, C.; Maireles-Torres, P.J.; Luque, R. Industrial Food Waste Valorization: A General Overview. In Biorefinery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Corral, M.; Otero, P.; Echave, J.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Jarboui, A.; Nuñez-Estevez, B.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. By-products of agri-food industry as tannin-rich sources: A review of tannins’ biological activities and their potential for valorization. Foods 2021, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, C.; Tränkler, J.; Kuruparan, P.; Basnayake, B.F.A.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Kurian, J.; Gonming, Z. Asian regional research programme on sustainable solid waste landfill management in Asia. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Italy, 3–7 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bigdeloo, M.; Teymourian, T.; Kowsari, E.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ehsani, A. Sustainability and circular economy of food wastes: Waste reduction strategies, higher recycling methods, and improved valorization. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2021, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Sarker, A.; Yadav, A.; Miftah, A.O.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Integrated biorefinery approach to valorize citrus waste: A sustainable solution for resource recovery and environmental management. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.T.; Dhar, R.B. A multi-perspective review on microbial electrochemical technologies for food waste valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture. In Moving forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, C.M. Food Waste Recovery: Prospects and Opportunities, Sustainable Food Systems from Agriculture to Industry; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagroudy, S.; Warith, M.A.; El Zayat, M. Municipal Solid Waste Management and Green Economy; Global Young Academy: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gulisano, G.; Strano, A.; De Luca, A.I.; Falcone, G.; Iofrida, N.; Stillitano, T. Evaluating the Environmental, Economic, and Social Sustainability of Agro-Food Systems Through Life Cycle Approaches. In Sustainable Food Systems from Agriculture to Industry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, L.; Benavente-Ferraces, I.; Plaza, C.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Centeno, T.A. Hydrothermal carbonization as a sustainable strategy for integral valorisation of apple waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.K.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Mubofu, E.B.; Abderrahim, S.; Clark, J.H.; Koutinas, A.; Kopsahelis, N.; Stamatelatou, K.; Dickson, F.; et al. Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 426–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; Jamil, F.; Rafiq, S. Valorization of solid waste biomass by inoculation for the enhanced yield of biogas. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Hou, P. Ethanol production from waste pizza by enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 156, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, J.; Cederberg, C.; Sonesson, U.; Van Otterdijk, R.; Meybeck, A. Global Food Losses and Food Waste; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kibler, K.M.; Reinhart, D.; Hawkins, C.; Motlagh, A.M.; Wright, J. Food waste and the food-energy-water nexus: A review of food waste management alternatives. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banožić, M.; Banjari, I.; Jakovljević, M.; Šubarić, D.; Tomas, S.; Babić, J.; Jokić, S. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of some bioactive compounds from tobacco waste. Molecules 2019, 24, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, O.H.; Tiwari, K.K. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Indian orange peel oil and hydro distillation comparison on their compositions. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.P.; Janardhan, A.; Viswanath, B.; Monika, K.; Jung, J.Y.; Narasimha, G. Evaluation of orange peel for biosurfactant production by Bacillus licheniformis and their ability to degrade naphthalene and crude oil. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Gope, P.C.; Chauhan, S.; Bisht, D.S. Mechanical behavior of banana fiber based hybrid biocomposites. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarangsi, P.; Tippayawong, N.; Moran, J.C.; Rerkkriangkrai, P. Overview of livestock biogas technology development and implementation in Thailand. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2013, 17, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaiam, G.; Sokrai, P.; Makul, N. Novel ternary blends of Type 1 Portland cement, residual rice husk ash, and limestone powder to improve the properties of self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueksakorn, K.; Gheewala, S.H.; Sagisaka, M.; Kudoh, Y. Sugarcane biorefinery complex in Thailand and a proposed method to cope with apportioning its environmental burdens to co-products. J. Sustain. Energy Environ. 2014, 5, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, K.L.; Tan, B.W.; Liew, S.L. Pineapple cannery waste as a potential substrate for microbial biotranformation to produce vanillic acid and vanillin. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Pyar, H.; Liong, M.T.; Peh, K.K. Potentials of pineapple waste as growth medium for Lactobacillus species. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Aruldass, C.A.; Rubiyatno Venil, C.K.; Ahmad, W.A. Violet pigment production from liquid pineapple waste by Chromobacterium violaceum UTM5 and evaluation of its bioactivity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51524–51536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M. Conversion of waste seed oil of Citrus aurantium into methyl ester via green and recyclable nanoparticles of zirconium oxide in the context of circular bioeconomy approach. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 310–320. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, F.; Bhandari, R.; Gäth, S.A. Life cycle assessment on the treatment of organic waste streams by anaerobic digestion, hydrothermal carbonization and incineration. Waste Manag. 2021, 130, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-González, J.; Martinez-Sanchez, V.; Puig-Ventosa, I. Tools for a circular economy: Assessing waste taxation in a CGE multi-pollutant framework. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Selva, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Luque, R. Waste-to-wealth: Biowaste valorization into valuable bio (nano) materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4791–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidelis, M.; de Moura, C.; Kabbas Junior, T.; Pap, N.; Mattila, P.; Mäkinen, S.; Putnik, P.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Tian, Y.; Yang, B.; et al. Fruit seeds as sources of bioactive compounds: Sustainable production of high value-added ingredients from by-products within circular economy. Molecules 2019, 24, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Caneghem, J.; Van Acker, K.; De Greef, J. Waste-to-energy is compatible and complementary with recycling in the circular economy. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talan, A.; Tiwari, B.; Yadav, B.; Tyagi, R.D.; Wong, J.W.C.; Drogui, P. Food waste valorization: Energy production using novel integrated systems. Bioresourc. Technol. 2021, 322, 124538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Mathimani, T.; Varjani, S.; Rene, E.R.; Kumar, G.; Kim, S.H.; Ponnusamy, V.; Yoon, J.J. Biobutanol: A promising liquid fuel for the future- recent updates and perspectives. Fuel 2019, 253, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vea, E.B.; Romeo, D.; Thomsen, M. Biowaste Valorisation in a Future Circular Bioeconomy. Procedia CIRP 2018, 69, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.M.W.; Xiong, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yu, I.K.M.; Poon, C.S. Sustainable food waste management towards circular bioeconomy: Policy review, limitations and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, S.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Koutinas, A. A roadmap towards a circular and sustainable bioeconomy through waste valorization. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2017, 8, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulya, K.; Jukuri, S.; Venkata Mohan, S. Sustainable multistage process for enhanced productivity of bioplastics from waste remediation through aerobic dynamic feeding strategy: Process integration for up-scaling. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 188, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paritosh, K.; Kushwaha, S.K.; Yadav, M.; Pareek, N.; Chawade, A.; Vivekanand, V. Food Waste to Energy: An Overview of Sustainable Approaches for Food Waste Management and Nutrient Recycling. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2370927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuly, K.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Muldoon, O.T.; Kuehr, R. Behavioral change for the circular economy: A review with focus on electronic waste management in the EU. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 6, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, P.; Imbert, E. Food waste and social acceptance of a circular bioeconomy: The role of stakeholders. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 23, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Varjani, S. Valorization of agro-industrial wastes for biorefinery process and circular bioeconomy: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.S.; Sridhar, A.; Vishali, S. Utilization of fruit and vegetable waste to produce value-added products: Conventional utilization and emerging opportunities-A review. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.; Ahmed, S.; Kumar, A. Anaerobic digestion (AD) of fruit and vegetable market waste (FVMW): Potential of FVMW, bioreactor performance, co-substrates, and pre-treatment techniques. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 12, 3573–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathioudakis, D.; Karageorgis, P.; Papadopoulou, K.; Thomas Fruergaard Astrup, T.F.; Lyberato, G. Environmental and Economic Assessment of Alternative Food Waste Management Scenarios. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizeau, K.; von Massow, M.; Martin, R. Household-level dynamics of food waste production and related beliefs, attitudes, and behaviours in Guelph, Ontario. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelradi, F. Food waste behaviour at the household level: A conceptual framework. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, L.V.; Herpen, E.V.; Trijp, H.V. Household Food waste—How to avoid it? An integrative review. In Food Waste Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.E.; Speight, R.E.; Blinco, J.L.; O’Hara, I.M. Biorefining within food loss and waste frameworks: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 154, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Dai, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Z.; Yu, B. Environmental and Economic Life-Cycle Assessments of Household Food Waste Management Systems: A Comparative Review of Methodology and Research Progress. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Islam, T.; Rahman, S.; Nandi, R.; Kim, J.E. Uncertainty of pesticides in foodstuffs, associated environmental and health risks to humans—A critical case of Bangladesh with respect to global food policy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54448–54465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, A.; Kim, J.E.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Bilal, M.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Nandi, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, T. Heavy metals contamination and associated health risks in food webs—A review focuses on food safety and environmental sustainability in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3230–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debora Puglia, D.; Daniela Pezzolla, D.; Giovanni Gigliotti, G.; Torre, L.; Bartucca, M.L.; Buono, D.D. The Opportunity of Valorizing Agricultural Waste, Through Its Conversion into Biostimulants, Biofertilizers, and Biopolymers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Study Region | Food Waste Source/Materials | Employed Methods or Techniques | Valorization Approach | Experiment Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America and Europe | 280–300 kg of food waste | Peel and seeds of fruits and vegetables | Supercritical extraction, and Bioconversion | Pilot-phase study | [55] |
| USA | Wastewater | 2400 m3 per capita | Agriculture production and energy resources (16% consumption) | Footprint | [56] |
| Tobacco-waste | Scrap, dust, midrib | Extraction of bioactive compounds (phenolic compounds and solanesol from leaves) | Industrial processing | [57] | |
| UAE | Orange peel waste | Presence of methyl esters | Water-soluble pectinic acid | Jam, jelly, nutritional product | [58] |
| Orange peel | Orange peel residues, enzymatic hydrolysis | Supercritical carbon dioxide method, bioconversion | Flavor and pharmaceutical industries | [58] | |
| India | Mango peel | Enzymatic extraction | 40% higher lactic acid concentration, biosurfactant production | Fermentation | [59] |
| Banana fibers & stem wastes | Pseudo stem biomass | Hybrid biocomposites | Fillers or composites | [60] | |
| Rice and sugarcane waste (cereal wastage) | Decomposition | 3.4 kg CO2 equivalents/kg (carbon) | Large scale | [47] | |
| Organic waste (slaughterhouse, fresh market waste) | Anaerobic digester, biodigester, or a bioreactor | Biogas production | Large scale | [61] | |
| Thailand and Southeast Asia | Rice husk | Decomposition | 20,000 kW/year of electricity | Leading state-owned power utility | [62] |
| Thailand | Sugarcane waste (bagasse and molasses) | Biochemical production, use of substrate in bioethanol production | Feedstock (microbial growth and bio-based products production), electricity, and steam generation | Large scale, industrially | [63] |
| Pineapple cannery waste | Biotransformation | Vanillic acid and vanillin | Large scale | [64] | |
| Pineapple cannery waste | Bacterial growth | Commercial media (Mann, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS)) | Fermentation | [65] | |
| Indonesia | Liquid pineapple waste | Chromobacterium violaceum UTM5, tryptophan supplementation | 16.256 ± 0.44 g/L violacein (violet pigment production), bioethanol | Large scale | [66] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarker, A.; Ghosh, M.K.; Islam, T.; Bilal, M.; Nandi, R.; Raihan, M.L.; Hossain, M.N.; Rana, J.; Barman, S.K.; Kim, J.-E. Sustainable Food Waste Recycling for the Circular Economy in Developing Countries, with Special Reference to Bangladesh. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912035
Sarker A, Ghosh MK, Islam T, Bilal M, Nandi R, Raihan ML, Hossain MN, Rana J, Barman SK, Kim J-E. Sustainable Food Waste Recycling for the Circular Economy in Developing Countries, with Special Reference to Bangladesh. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarker, Aniruddha, Mithun Kumar Ghosh, Tofazzal Islam, Muhammad Bilal, Rakhi Nandi, Md Lamiur Raihan, Mohammad Nabil Hossain, Juwel Rana, Subrato Kumar Barman, and Jang-Eok Kim. 2022. "Sustainable Food Waste Recycling for the Circular Economy in Developing Countries, with Special Reference to Bangladesh" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912035
APA StyleSarker, A., Ghosh, M. K., Islam, T., Bilal, M., Nandi, R., Raihan, M. L., Hossain, M. N., Rana, J., Barman, S. K., & Kim, J.-E. (2022). Sustainable Food Waste Recycling for the Circular Economy in Developing Countries, with Special Reference to Bangladesh. Sustainability, 14(19), 12035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912035












