Potential Role of Combined Microbial Inoculants and Plant of Limnocharis flava on Eliminating Cadmium from Artificial Contaminated Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pot Experiments
2.3. Analysis of Cd Content in L. flava Plants after Harvest

2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Removal of Cd from the Soil
3.2. The Accumulation of Cd in Microbial and Fungal Biomass
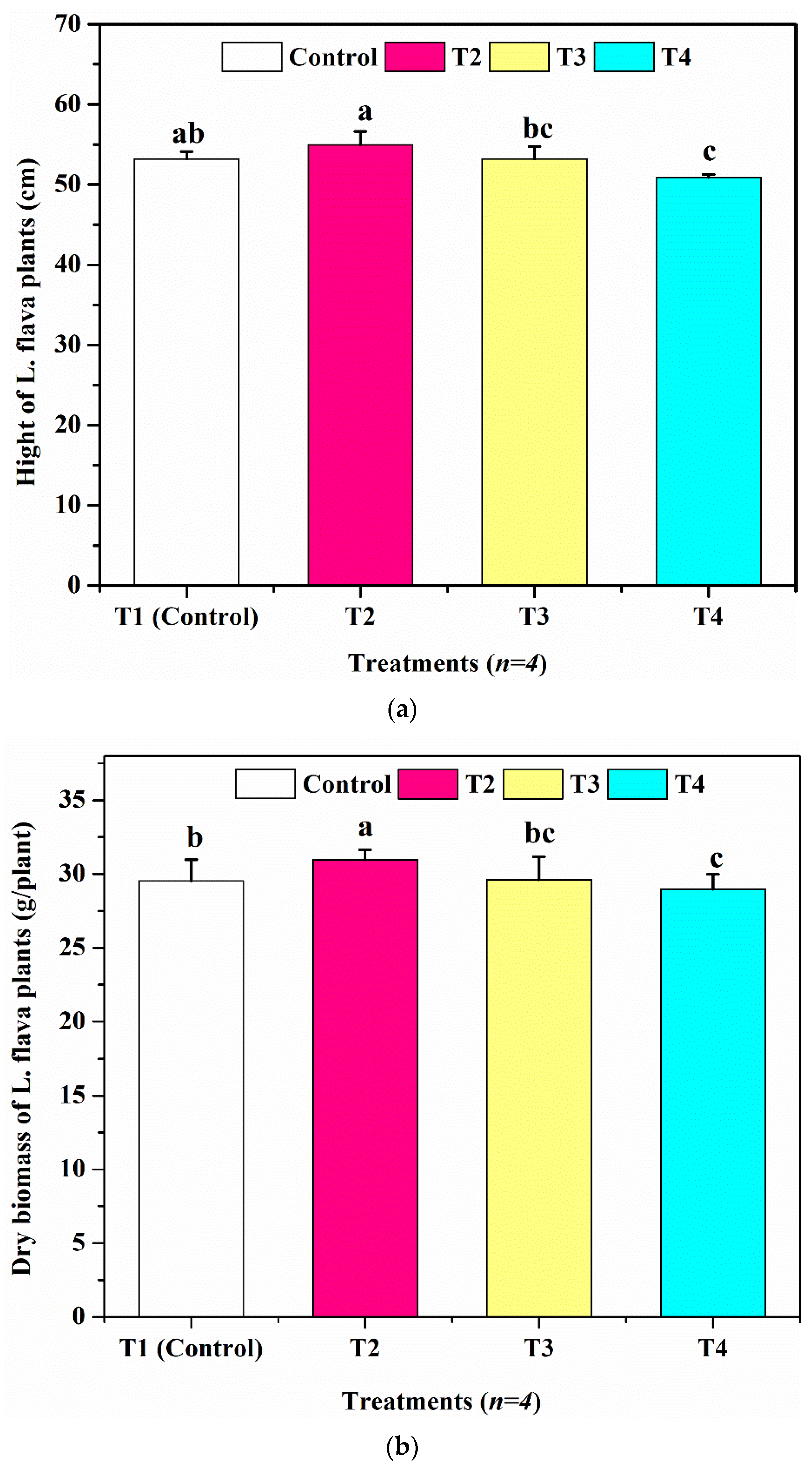
3.3. The Growth of L. flava Plants under High Heavy Metal Concentrations
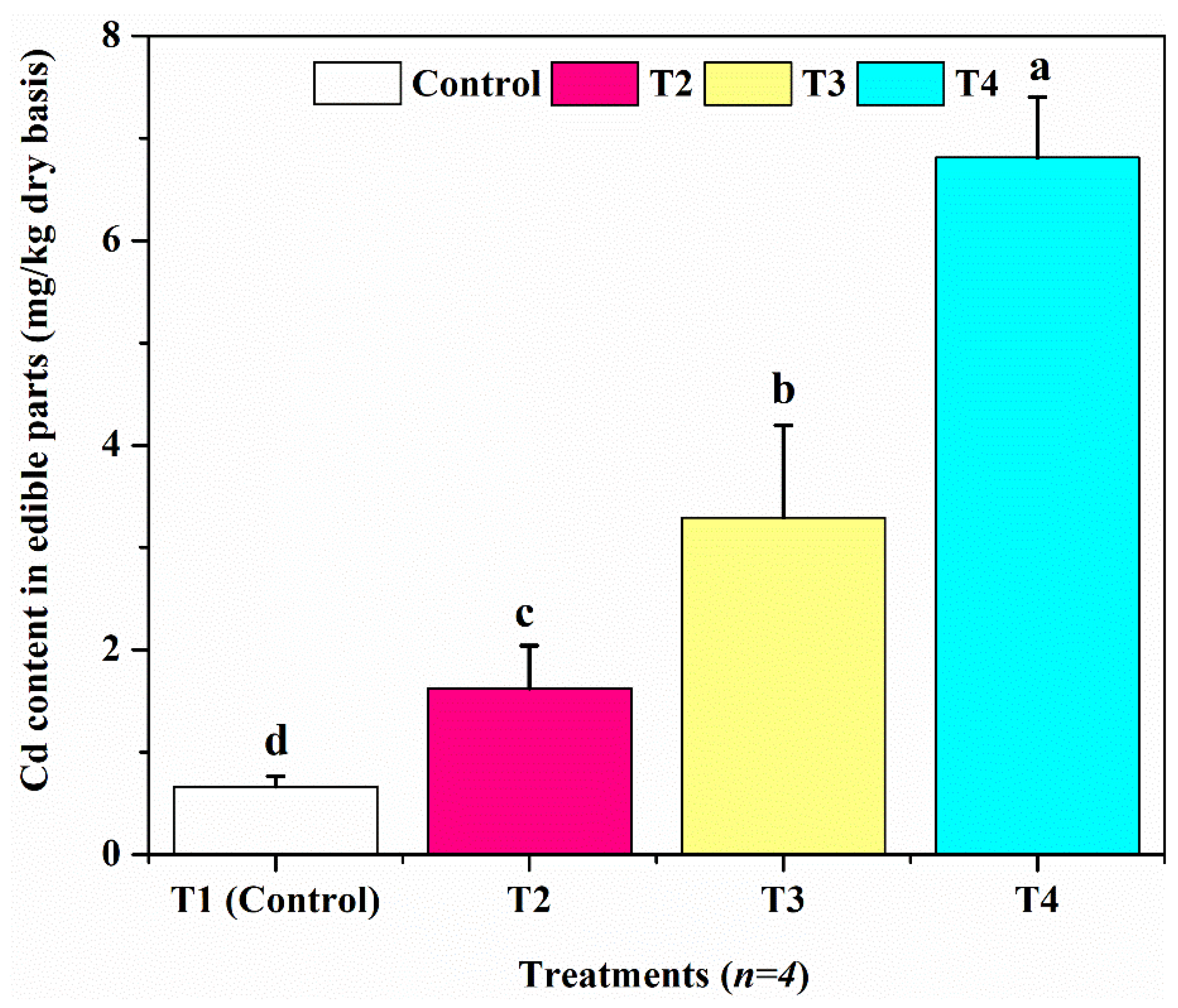
3.4. The Accumulation Capacity of Cd by L. flava Plants
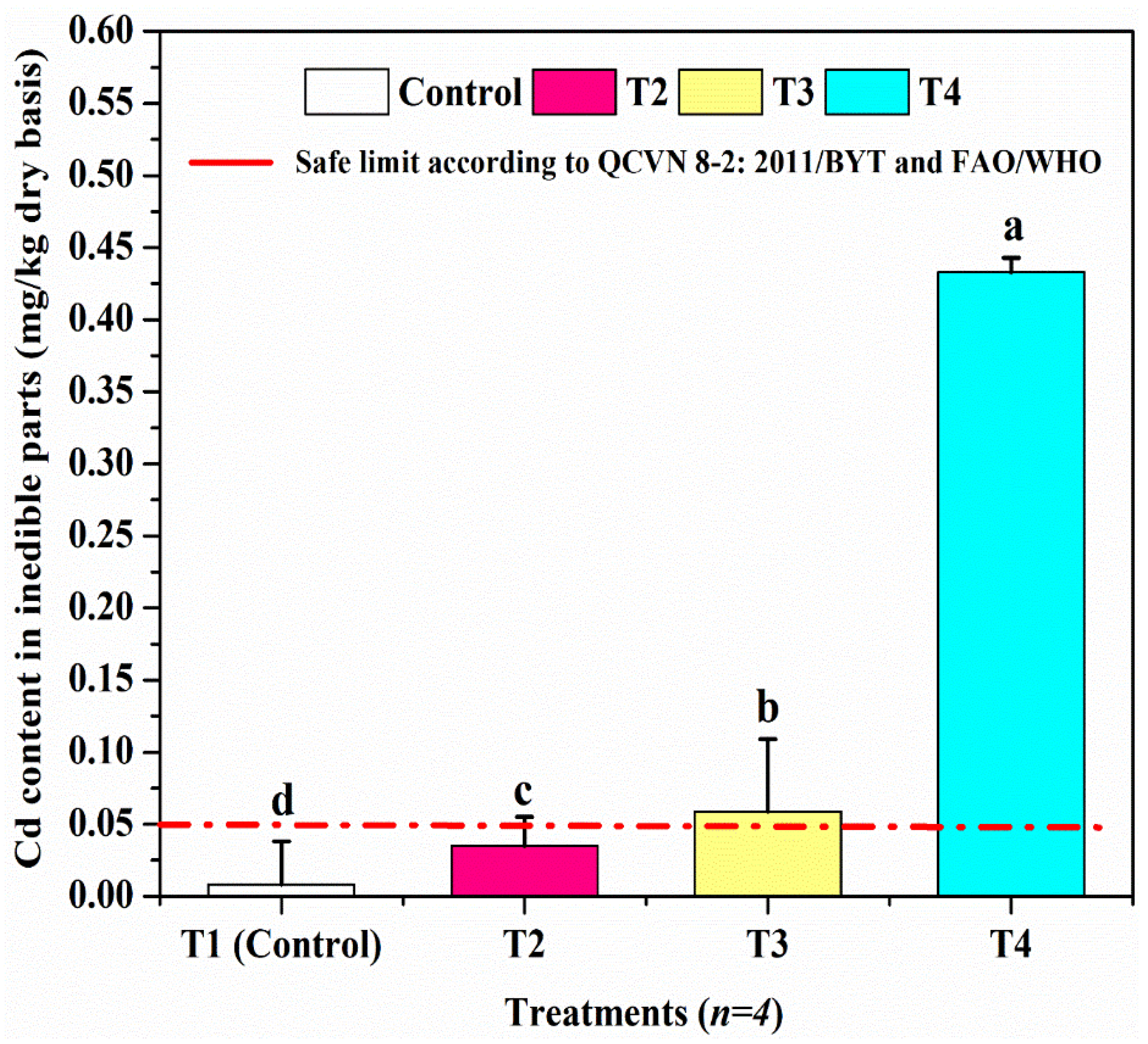
3.5. Assessment of Cd Accumulation in the Edible Parts of L. flava
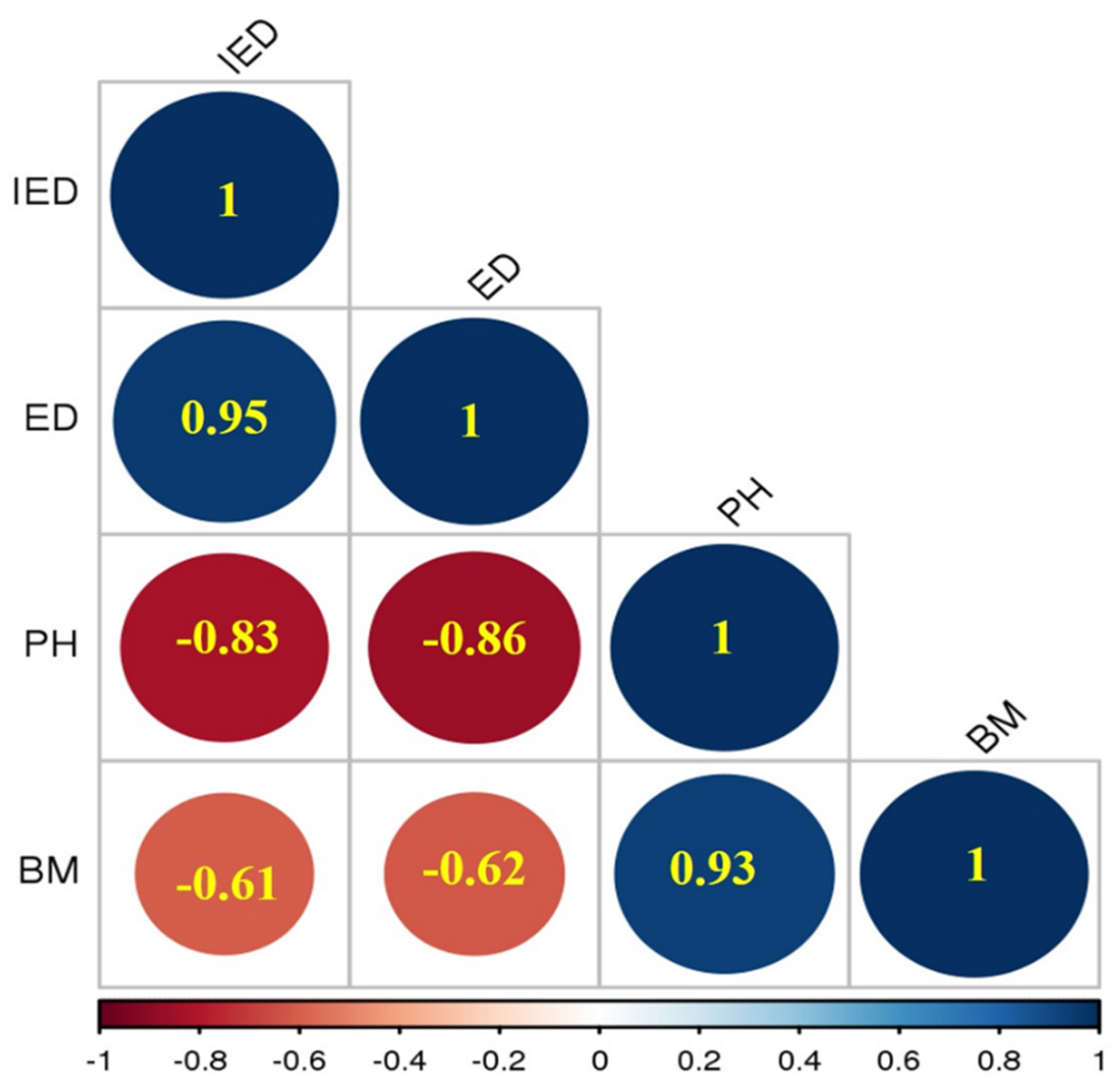
3.6. Correlation Matrix
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; You, S.; Zheng, J. Review in Strengthening Technology for Phytoremediation of Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 242, 052003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Han, Z.; Son, Y.; Khim, J. Evaluation of stabilizing materials for immobilization of toxic heavy metals in contaminated agricultural soils in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, E.S.; Dias, Y.N.; Da Costa, H.S.C.; Pinto, D.A.; Oliveira, D.M.; Souz, N.P.; Teixeira, F.A.; Fernandes, A.R. Organic residues and biochar to immobilize potentially toxic elements in soil from a gold mine in the Amazon. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Kumar, C. Biotechnological advances in bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystems: An overview with special reference to phytoremediation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 843–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Moreno, A.; Zhang, C.; Freitas, H. Serpentine endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas azotoformans ASS1 accelerates phytoremediation of soil metals under drought stress. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z. Biochemical mechanism of phytoremediation process of lead and cadmium pollution with Mucor circinelloides and Trichoderma asperellum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xu, M.; Wei, Q.; Tang, M.; Guan, L.; Lou, L.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; et al. Promotion of growth and phytoextraction of cadmium and lead in Solanum nigrum L. mediated by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Zeng, P.; Wang, X. Co-application of indole-3-acetic acid/gibberellin and oxalic acid for phytoextraction of cadmium and lead with Sedum alfredii Hance from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gitau, M.; Han, S.; Fu, J.; Xie, Y. Effects of cadmium-resistant fungi Aspergillus aculeatus on metabolic profiles of bermudagrass (Cynodondactylon (L.) Pers.) under Cd stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, H.; Marques, A.P.G.C.; Franco, A.R.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Castro, P.M.L. Phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils using maize (Zea mays L.) assisted by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9742–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangthong, C.; Setkit, K.; Prapagdee, B. Improvement of cadmium phytoremediation after soil inoculation with a cadmium-resistant Micrococcus sp. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Stéphane, D. The effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi inoculantion on Pb removel of Fern (Pteris vittata L.) from populltion soil Vietnam. J. Agri. Sci. 2016, 14, 1510–15107. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Pramanik, K.; Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, P.K.; Soren, T.; Maiti, T.K. Bioaccumulation of cadmium by Enterobacter sp. and enhancement of rice seedling growth under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.; Park, K.; Han, T.; Park, C.; Ahn, Y.S. Inoculation with Bacillus licheniformis MH48 promotes nutrient uptake in seedlings of the ornamental plant Camellia japonica grown in Korean reclaimed coastal lands. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.V.; Tran, D.X.; Myint, S.W.; Huang, C.; Pham, H.V.; Luu, T.H.; Vo, T.M.T. Examining spatiotemporal salinity dynamics in the Mekong River Delta using Landsat time series imagery and a spatial regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Marschner, P.; Cao, W.; Zuo, C.; Qin, W. Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int. Soil. Water. Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.M.; Kang, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Kien, C.N.; Noi, N.V.; Son, L.T. Levels and Chemical Forms of Heavy Metals in Soils from Red River Delta, Vietnam. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 207, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.L.; Ohtsubo, M.; Li, L.; Higashi, T.; Kanayama, M. Heavy-Metal Contamination of Soil and Vegetables in Wastewater-Irrigated Agricultural Soil in a Suburban Area of Hanoi, Vietnam. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2010, 41, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudzaman, A.N.; Aziz, R.A.; Jalil, M.F. Removal of heavy metals from landfill leachate using horizontal and vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland planted with Limnocharis flava. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2011, 11, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, A.L. Potential of Penicillium species in the bioremediation field. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 1393–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.S. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 266–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, P.C.; Pandey, V.C.; Srivastava, P.; Rakesh, P.S.; Chandran, S.; Singh, N.; Thomas, A.P. Phytofiltration of cadmium from water by Limnocharis flava (L.) Buchenau grown in free-floating culture system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.H.; Chai, L.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Tang, C.; Tong, H.; Yuan, P. Bioleaching of heavy metals from a contaminated soil using indigenous Penicillium chrysogenum strain F1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xia, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W. Role of Penicillium chrysogenum XJ-1 in the detoxification and bioremediation of cadmium. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, F.M.; Duz, Z.M. Removal of cadmium (II) in the aqueous solutions by biosorption of Bacillus licheniformis isolated from soil in the area of Tigris River. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, B.V.; Koli, S.H.; Narkhede, C.P.; Patil, S.N.; Patil, S.V. Prospective of microbial exopolysaccharide for heavy metal exclusion. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, M.T.; Bui, H.A.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, M.H. Heavy metals in agricultural soil and using plants to clean up contaminated soils (phytoremediation) in Vietnam. In Proceedings of the MARCO-FFTC Joint International Seminar on Management and Remediation Technologies of Rural Soils Contaminated by. Heavy Metals and Radioactive Materials, Taichung, Taiwan, 23–24 September 2014; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Shah, A.H.; Hussain, A.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.A.; Hamayun, M.; Hassan, Y.; Jan, S.A. Identification and characterization of Penicillium chrysogenum T8 as potent plant growth promoting endophytic fungi. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 4896–4902. [Google Scholar]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.J.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Hashem, A. Phytohormones and beneficial microbes: Essential components for plants to balance stress and fitness. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, M.; Ae, N.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Freitas, H. Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H. Optimization of plant-bacteria complex for phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Int. J. Bot. 2008, 4, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xia, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W. Biosorption of cadmium by a metal-resistant filamentous fungus isolated from chicken manure compost. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, R.H. Study of characteristics on metabolism of Penicillium chrysogenum F1 during bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.C.; Lai, H.Y. Subcellular distribution of cadmium in two paddy rice varieties with different cooking methods. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 7, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Shang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R. Cadmium accumulation and its effects on nutrient uptake and photosynthetic performance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2017, 100, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadur, D.S.; Ahmed, S.R.; Lahori, A.H.; Hussain, T.; Alvi, S.K.; Shafique, S.; Fatima, S.; Vambol, V.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Hinduja, P.; et al. Novel Fuller Earth, Rock Phosphate, and Biochar for Phytomanagement of Toxic Metals in Polluted Soils. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
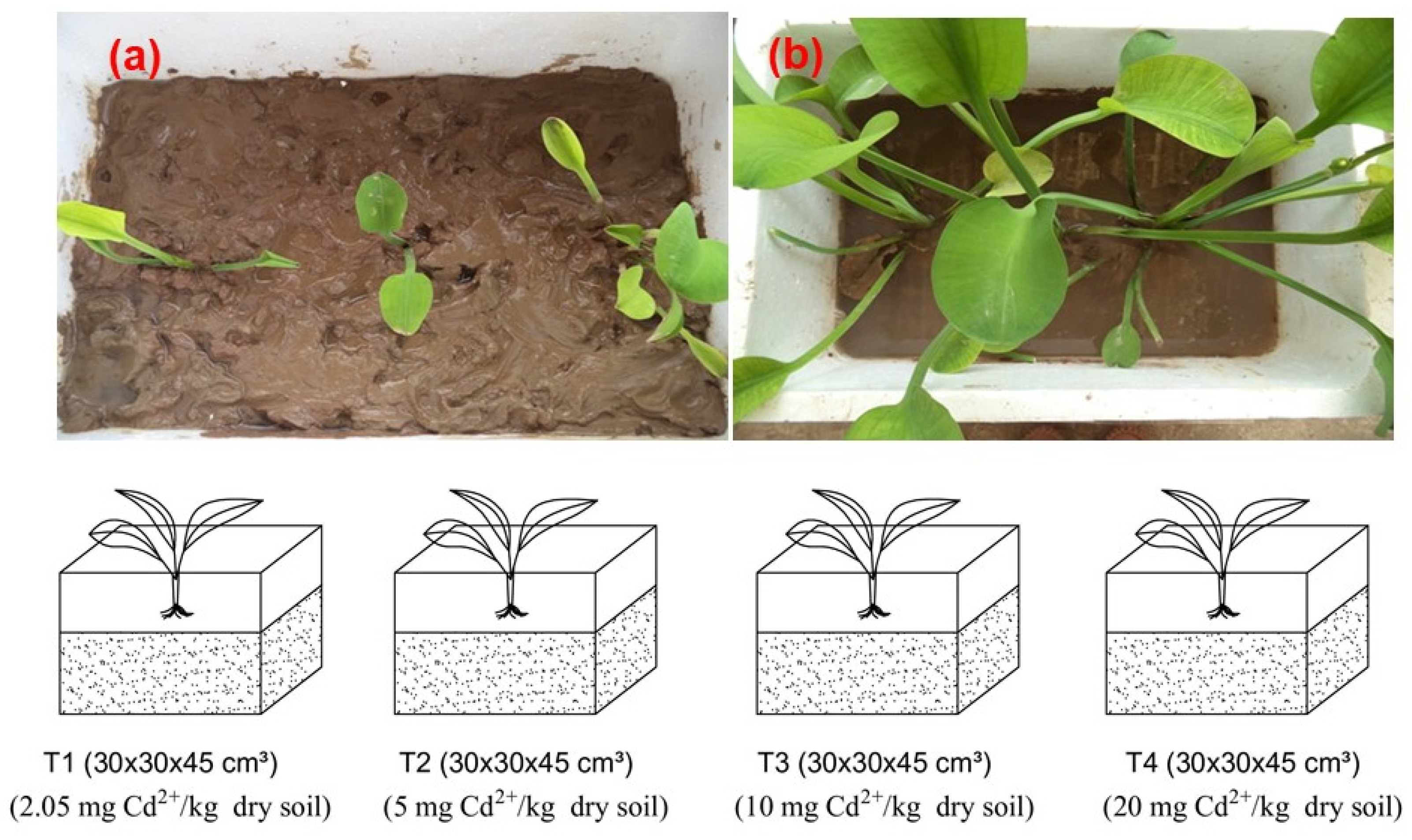
| Treatments (T) | Total Cd and Flexible Cd in the Soils (mg/kg Dry Soil) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cd | Reduction Rate(%) | Flexible Cd | Reduction Rate(%) | |||
| Before Treatment | After Treatment | Before Treatment | After Treatment | |||
| T1 | 2.05 ± 0.187 | 2.0 ± 0.021 | 2.44 | 0.4 ± 0.178 | 0.35 ± 0.029 | 12.50 |
| T2 | 5 ± 0.095 | 4.86 ± 0.022 | 2.8 | 1.15 ± 0.069 | 1.0 ± 0.034 | 13.04 |
| T3 | 10 ± 0.09 | 9.56 ± 0.225 | 4.4 | 3.3 ± 0.026 | 2.86 ± 0.043 | 13.33 |
| T4 | 20 ± 0.167 | 18.44 ± 0.215 | 7.8 | 11.2 ± 0.022 | 9.64 ± 0.029 | 13.93 |
| Microbial Strains | Cd2+ Accumulation in Microbial Biomass in Different Concentrations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 mg/L | 5 mg/L | 10 mg/L | 20 mg/L | |
| Bacillus licheniformis | 1.05 ± 0.04 | 2.85 ± 0.05 | 5.91 ± 0.13 | 34.70 ± 1.32 |
| Penicillium chrysogenum strain | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 7.87 ± 0.04 | 16.71 ± 0.09 | 33.43 ± 1.87 |
| Treatments | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry biomass (g/plant) | 30.41 ± 0.7846 | 31.22 ± 0.3648 | 30.02 ± 0.4163 | 29.57 ± 0.5041 |
| Height of plants (cm) | 52.76 ± 0.5452 | 54.24 ± 1.0124 | 51.82 ± 1.421 | 49.95 ± 0.7816 |
| Treatments | T1 (mg) | T2 (mg) | T3 (mg) | T4 (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inedible part | 0.634 ± 0.02186 | 1.643 ± 0.02093 | 3.32325 ± 0.02750 | 3.32325 ± 0.01435 |
| Edible part | 0.01 ± 0.00216 | 0.031 ± 0.00365 | 0.05 ± 0.00258 | 0.4305 ± 0.00265 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lam, N.T.; Song, S.; Dung, B.T.N.; Binh, T.N.; Maleki, A.; Godini, K.; Tang, V.T. Potential Role of Combined Microbial Inoculants and Plant of Limnocharis flava on Eliminating Cadmium from Artificial Contaminated Soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912209
Lam NT, Song S, Dung BTN, Binh TN, Maleki A, Godini K, Tang VT. Potential Role of Combined Microbial Inoculants and Plant of Limnocharis flava on Eliminating Cadmium from Artificial Contaminated Soil. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912209
Chicago/Turabian StyleLam, Nguyen Thi, Shaoxian Song, Bui Thi Ngoc Dung, Tran Ngoc Binh, Afshin Maleki, Kazem Godini, and Van Tai Tang. 2022. "Potential Role of Combined Microbial Inoculants and Plant of Limnocharis flava on Eliminating Cadmium from Artificial Contaminated Soil" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912209
APA StyleLam, N. T., Song, S., Dung, B. T. N., Binh, T. N., Maleki, A., Godini, K., & Tang, V. T. (2022). Potential Role of Combined Microbial Inoculants and Plant of Limnocharis flava on Eliminating Cadmium from Artificial Contaminated Soil. Sustainability, 14(19), 12209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912209









